Gut Metagenome Reveals the Microbiome Signatures in Tibetan and Black Pigs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Management and Sample Collection
2.2. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Processing, Assembly, and Quality Assessment in Metagenomics
2.4. Gene Taxonomy and Functional Annotation
2.5. Alpha and Beta Diversity
3. Results
3.1. Metagenomic Sequencing Results Statistics
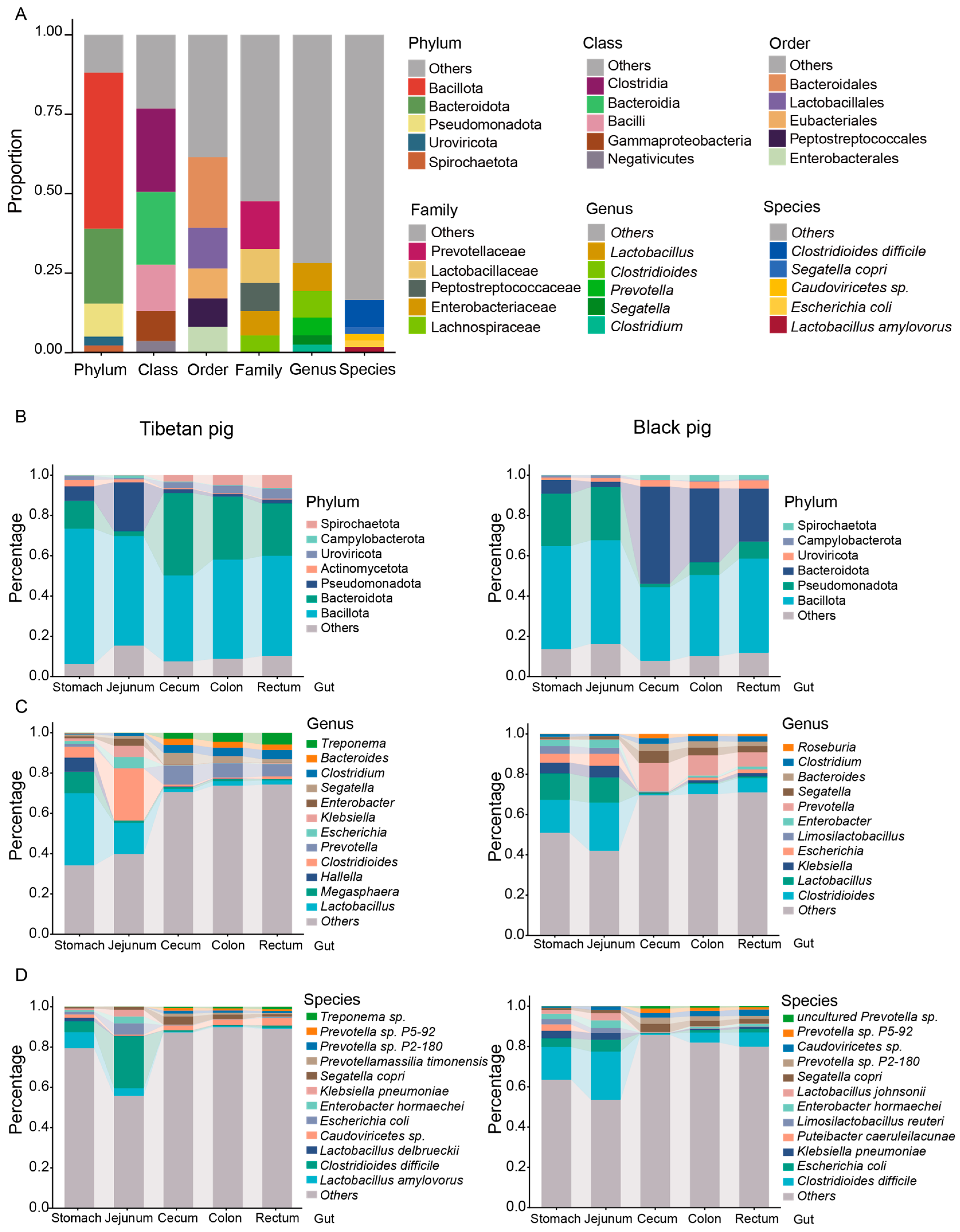
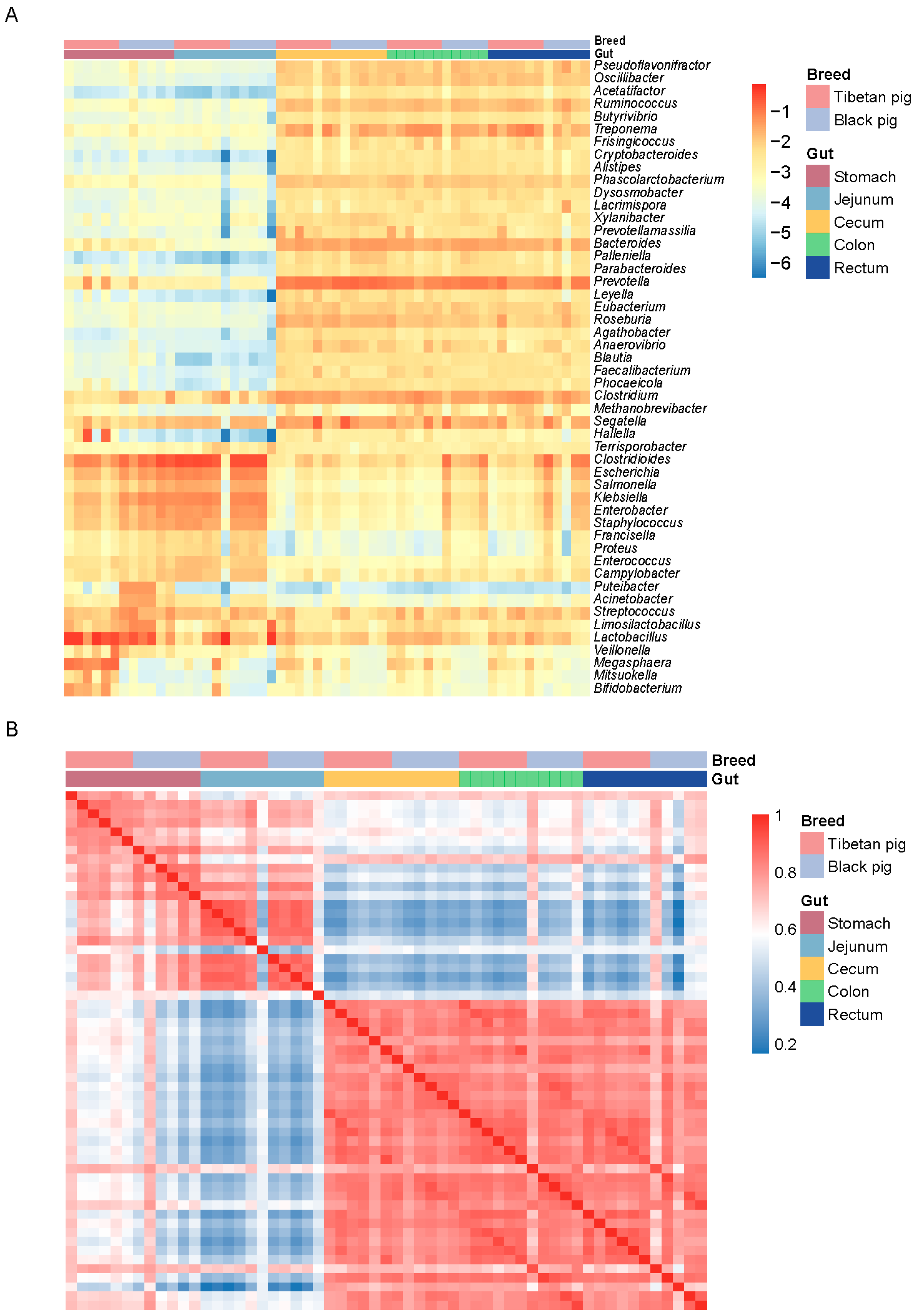
3.2. Composition Characteristics of GI Flora in Tibetan Pigs and Black Pigs
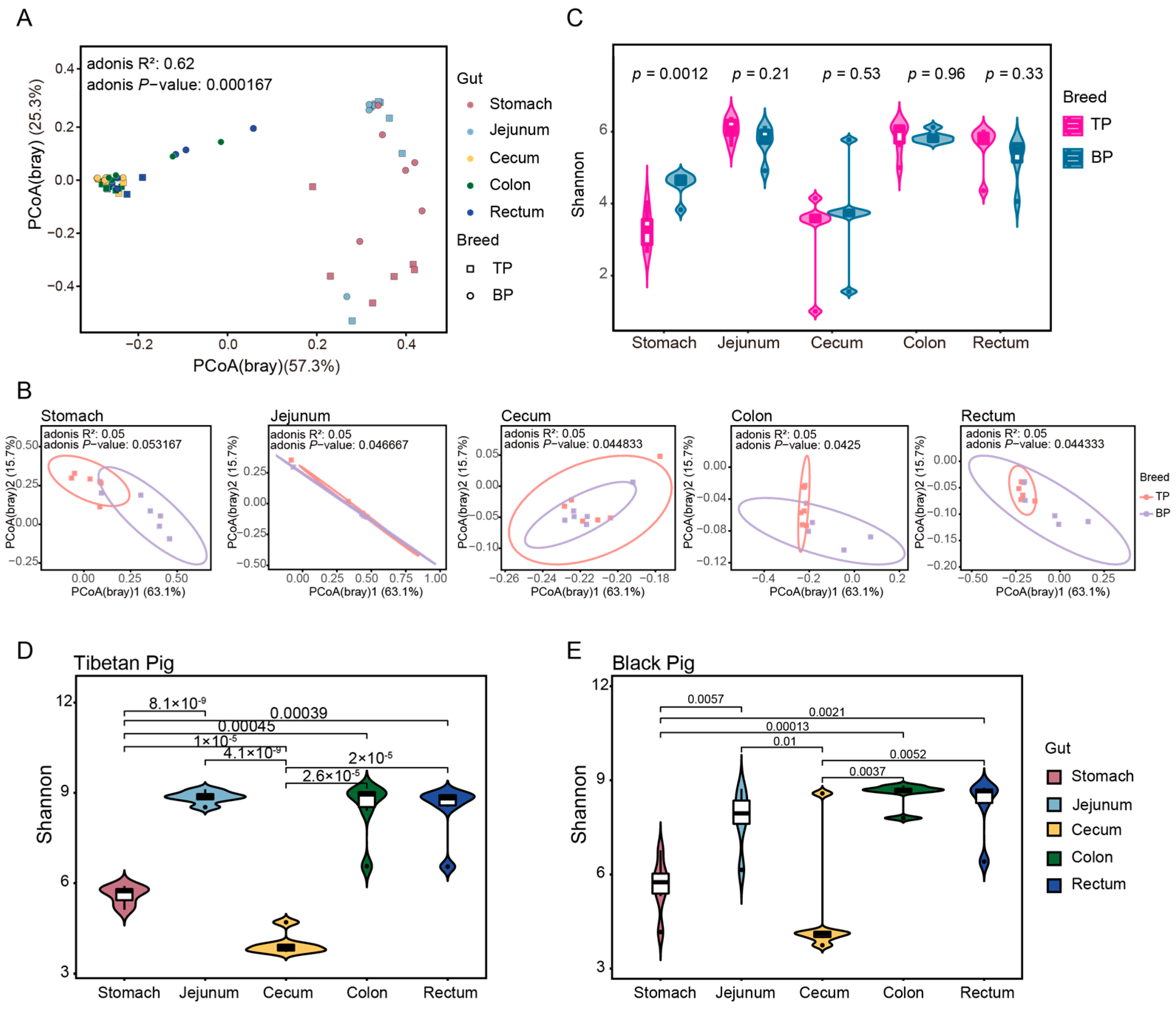
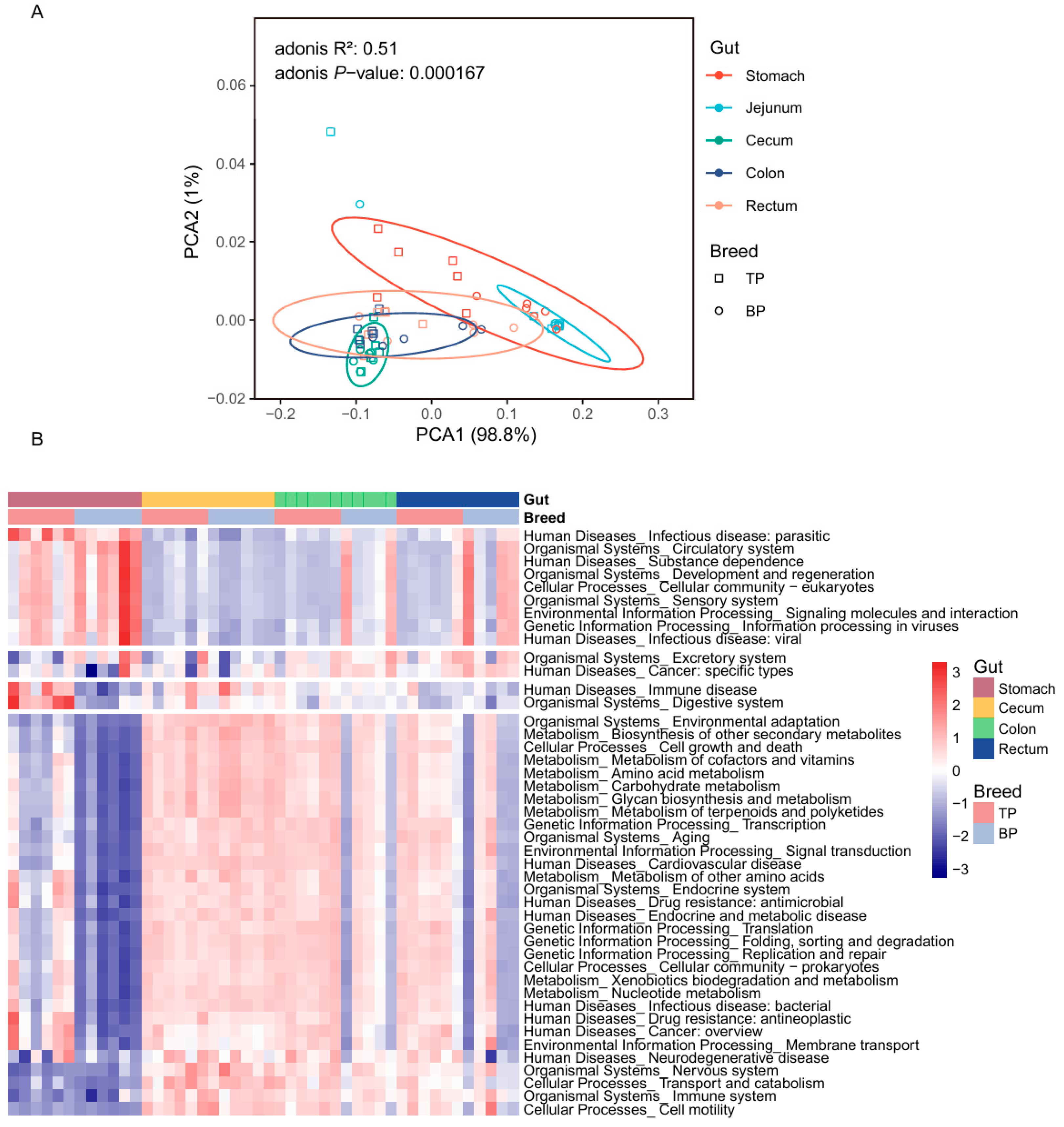
3.3. Diversity of GIl Flora of Tibetan Pigs and Black Pigs
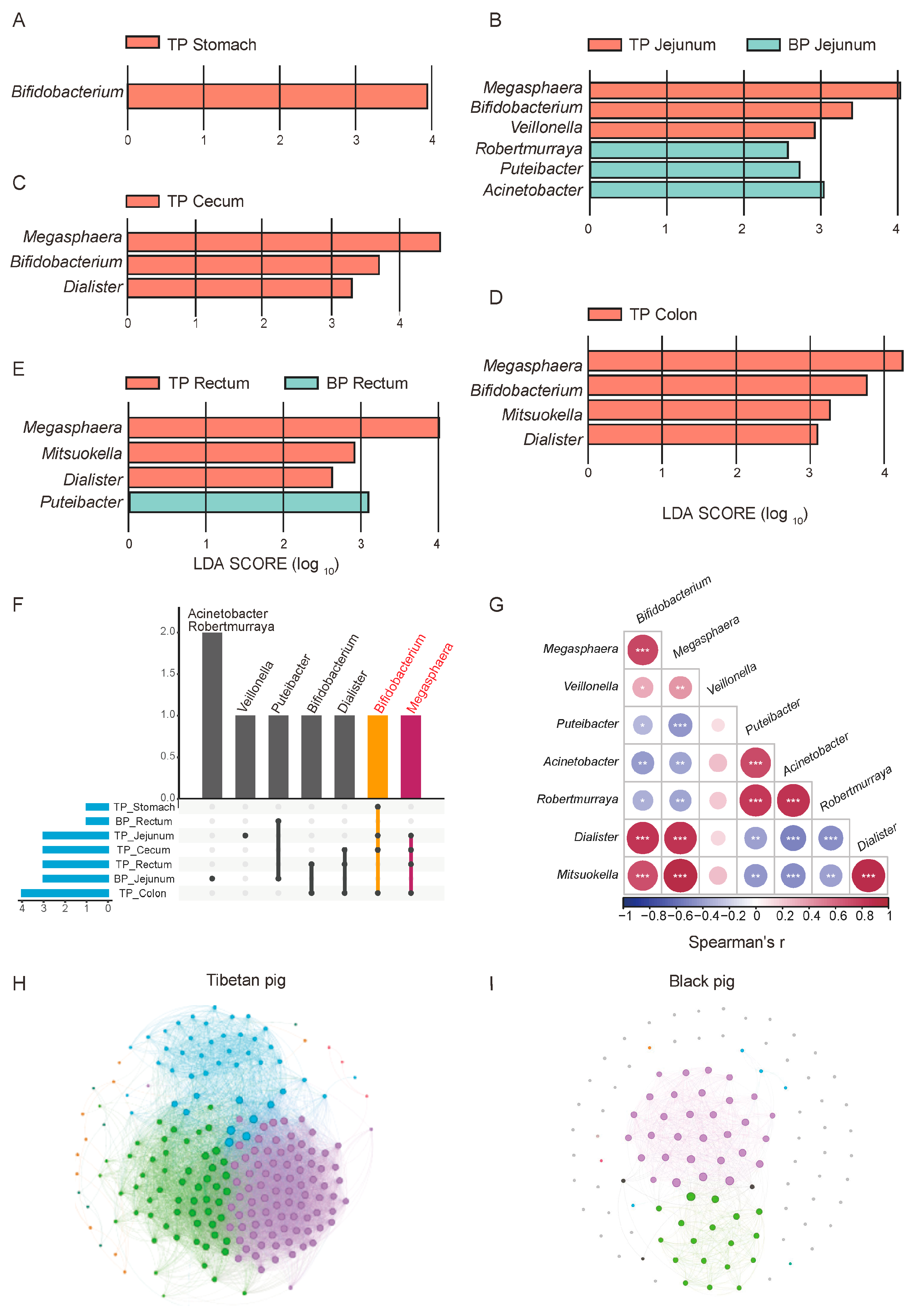
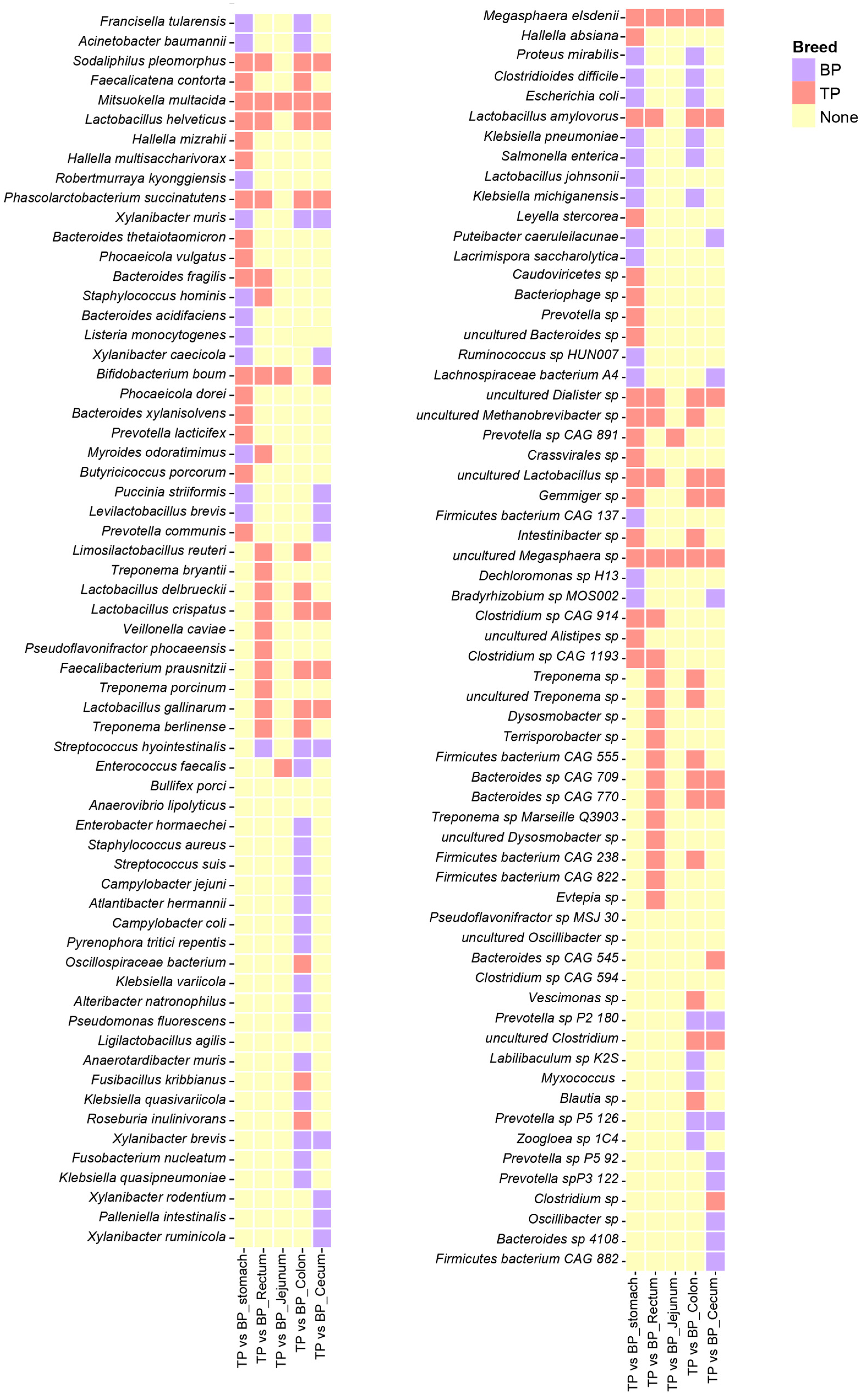
3.4. Differences in GI Flora Between Tibetan Pigs and Black Pigs
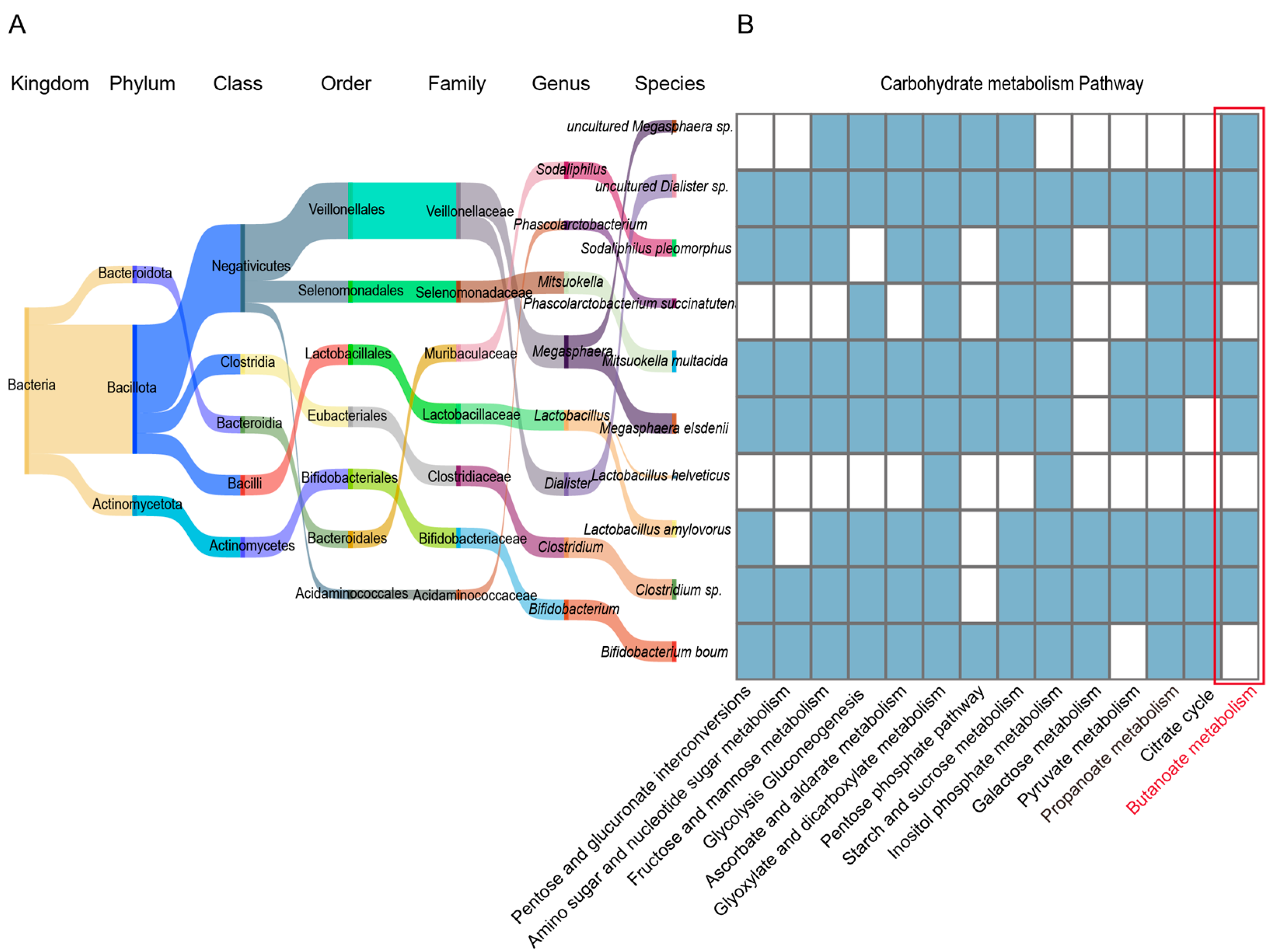
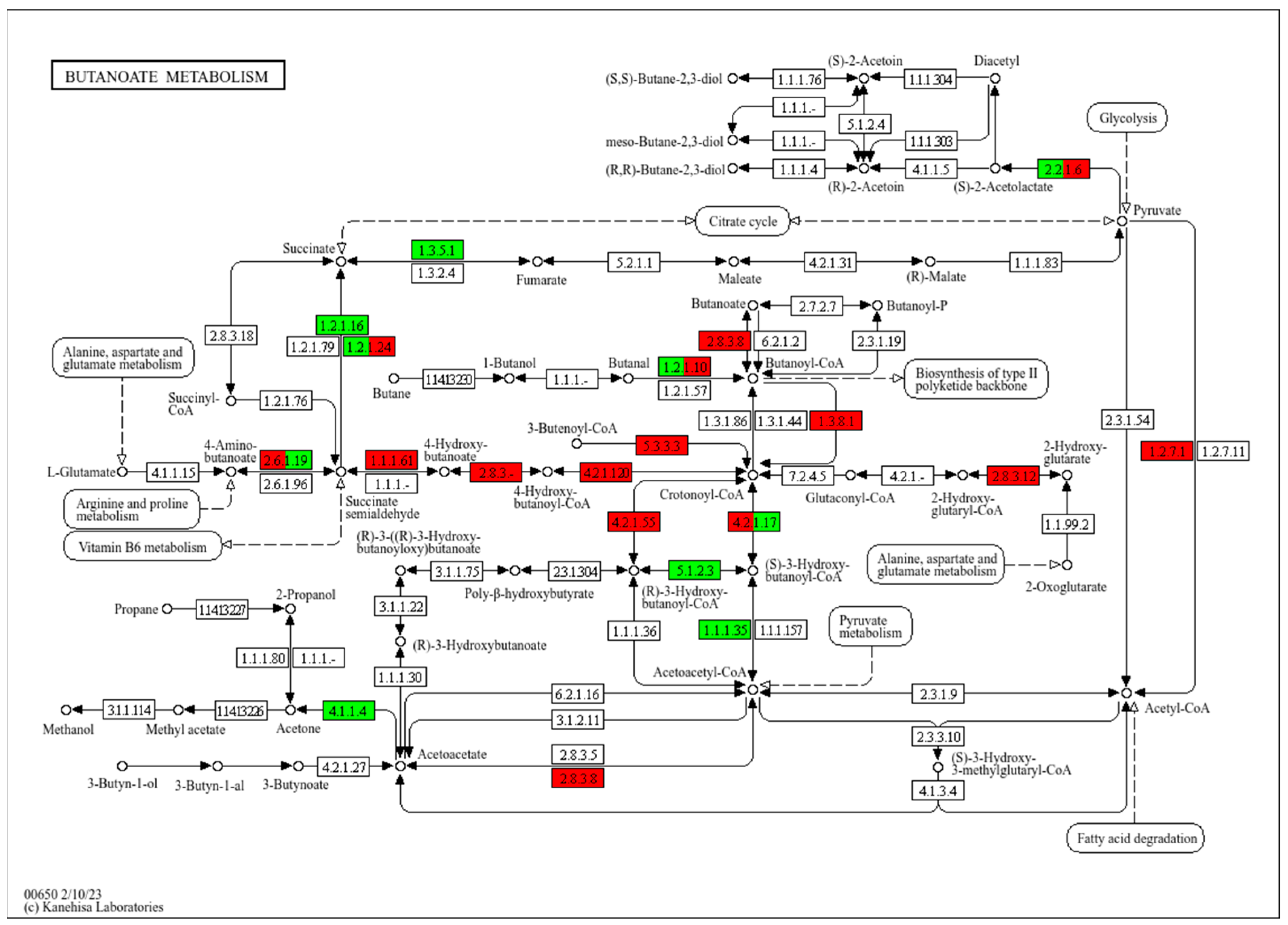
3.5. KEGG Functional Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, H.; Yan, D.; Lu, S.; Lian, L.; Zhao, G.; Yan, Y.; Deng, W.; Shi, X.; et al. The local origin of the Tibetan pig and additional insights into the origin of Asian pigs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jin, Z.-B.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.-F.; Li, X.-M.; Liang, Y.-B.; Mao, J.-Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Z.; Bakshi, A.; et al. Genetic signatures of high-altitude adaptation in Tibetans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4189–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yao, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L. Genetic Adaptations of the Tibetan Pig to High-Altitude Hypoxia on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zhong, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, T.; Gu, Y.; Li, M.; Miao, X.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Xu, W.; et al. Metagenomic profiling uncovers microbiota and antibiotic resistance patterns across human, chicken, pig fecal, and soil environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shi, L.; Ge, Y.; Leng, D.; Zeng, B.; Wang, T.; Jie, H.; Li, D. Dynamic Changes in the Gut Microbial Community and Function during Broiler Growth. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, D.; Zhu, W.; Wang, T.; Mishra, S.K.; Wei, R.; Xu, Z.; He, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. Association of female reproductive tract microbiota with egg production in layer chickens. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunney, J.K.; Van Goor, A.; Walker, K.E.; Hailstock, T.; Franklin, J.; Dai, C. Importance of the pig as a human biomedical model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, P.T.; Carr, A. Gastric acid and digestive physiology. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 91, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, I.; Araújo, J.R.; Rolhion, N.; Demignot, S. Jejunum: The understudied meeting place of dietary lipids and the microbiota. Biochimie 2020, 178, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, A.; Neu, J.; Riezzo, G.; Raimondi, F.; Martinelli, D.; Francavilla, R.; Indrio, F. Gastrointestinal function development and microbiota. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2013, 39, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbuckle, W.E.; Tennant, B.C. Chapter 15—Gastrointestinal Function. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Kaneko, J.J., Harvey, J.W., Bruss, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Qu, F.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Ren, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Ge, S.; Wu, C.; et al. SCFAs alleviated steatosis and inflammation in mice with NASH induced by MCD. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 245, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengler, F.; Kraetzig, A.; Gäbel, G. Butyrate Protects Porcine Colon Epithelium from Hypoxia-Induced Damage on a Functional Level. Nutrients 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. The role of the gut microbiota in energy metabolism and metabolic disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Pamp, S.J.; Hill, J.A.; Surana, N.K.; Edelman, S.M.; Troy, E.B.; Reading, N.C.; Villablanca, E.J.; Wang, S.; Mora, J.R.; et al. Gut immune maturation depends on colonization with a host-specific microbiota. Cell 2012, 149, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Ge, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, D. The digestive and reproductive tract microbiotas and their association with body weight in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Peng, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, J.; Fu, X.; Nie, Y. Host Genetic and Environmental Factors Shape the Composition and Function of Gut Microbiota in Populations Living at High Altitude. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1482109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Sun, G.; Duan, J.; Han, H.; Zhong, R.; Chen, L.; Wangdui, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Effects of high-altitude hypoxic environment on colonic inflammation, intestinal barrier and gut microbiota in three-way crossbred commercial pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 968521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Xia, T.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. Comparative Analyses of Fecal Microbiota in European Mouflon (Ovis orientalis musimon) and Blue Sheep (Pseudois nayaur) Living at Low or High Altitudes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, P.; Wei, M.; Duan, M.; Yan, F.; Chamba, Y. Healthy Gut Microbiome Composition Enhances Disease Resistance and Fat Deposition in Tibetan Pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 965292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, P.; Bai, X.; Tian, S.; Yang, M.; Leng, D.; Kui, H.; Zhang, S.; Yan, X.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Vaginal microbiota are associated with in vitro fertilization during female infertility. Imeta 2024, 3, e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X.; Qin, Y.; Sun, N.; Xin, J.; Zeng, Y.; Jing, B.; Fang, J.; Pan, K.; et al. Lactobacillus johnsonii YH1136 plays a protective role against endogenous pathogenic bacteria induced intestinal dysfunction by reconstructing gut microbiota in mice exposed at high altitude. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1007737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Kong, F.; Yu, X.; Wang, P.; Yang, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, M.; Ni, Q.; et al. Gut microbiota of Tibetans and Tibetan pigs varies between high and low altitude environments. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 235, 126447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Pan, H.; Zeng, X.; Qiao, S. Exploration of the Potential for Efficient Fiber Degradation by Intestinal Microorganisms in Diqing Tibetan Pigs. Fermentation 2021, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Feng, X.Z.; Shi, C.W.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H.L.; Huang, H.B.; Jiang, Y.L.; Wang, J.Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; et al. Gut Bacterial Composition and Functional Potential of Tibetan Pigs Under Semi-Grazing. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 850687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Mueller, O.; Stocker, S.; Salowsky, R.; Leiber, M.; Gassmann, M.; Lightfoot, S.; Menzel, W.; Granzow, M.; Ragg, T. The RIN: An RNA integrity number for assigning integrity values to RNA measurements. BMC Mol. Biol. 2006, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, W.; Schink, M.; Zopf, Y. Microbiota in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropini, C.; Earle, K.A.; Huang, K.C.; Sonnenburg, J.L. The Gut Microbiome: Connecting Spatial Organization to Function. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutsch, A.; Kantsjö, J.B.; Ronchi, F. The gut-brain axis: How microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 604179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.A.; Stewart, F.J.; Eppley, J.M.; DeLong, E.F. Microbial community phylogenetic and trait diversity declines with depth in a marine oxygen minimum zone. Ecology 2012, 93, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yang, M.; Shi, X.; Tian, S.; Li, Y.; Xie, W.; Zou, Z.; Leng, D.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, C.; et al. Multiomics analysis provides insights into musk secretion in muskrat and musk deer. Gigascience 2025, 14, giaf006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, D.; He, M.; Kui, H.; Bai, J.; Chen, Z.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; et al. Building Haplotype-Resolved 3D Genome Maps of Chicken Skeletal Muscle. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2305706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, J.P.; Berryman, C.E.; Young, A.J.; Radcliffe, P.N.; Branck, T.A.; Pantoja-Feliciano, I.G.; Rood, J.C.; Pasiakos, S.M. Associations between the gut microbiota and host responses to high altitude. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G1003–G1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, Z.J.; Gorini Pereira, F.; Gillum, T.L.; Amorim, F.T.; Deyhle, M.R.; Mermier, C.M. High-altitude exposures and intestinal barrier dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 322, R192–R203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, S.; Chang, L.; Wang, H.; Ga, Q.; Ma, L.; Bai, Z.; Shen, Y.; Ge, R.L. Gut microbiota adaptation to high altitude in indigenous animals. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Gillingham, T.; Guo, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhu, W.; Walker, W.A.; Ganguli, K. Secretions of Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus acidophilus Protect Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewaschuk, J.B.; Diaz, H.; Meddings, L.; Diederichs, B.; Dmytrash, A.; Backer, J.; Looijer-van Langen, M.; Madsen, K.L. Secreted bioactive factors from Bifidobacterium infantis enhance epithelial cell barrier function. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G1025–G1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, L.D.S.; Weimer, P.J. Megasphaera elsdenii: Its Role in Ruminant Nutrition and Its Potential Industrial Application for Organic Acid Biosynthesis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, J.J.; Looft, T. Megasphaera stantonii sp. nov., a butyrate-producing bacterium isolated from the cecum of a healthy chicken. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3409–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Yin, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhong, B.; Qiu, H.; Li, J. Multi-omics analysis reveals interactions between host and microbes in Bama miniature pigs during weaning. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1482925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiura, T.; Matsutani, M.; Tseng, H.C.; Fujimoto, N.; Ohnishi, A. Succinate-mediated symbiosis between Dialister hominis and an uncharacterized Segatella-like pectinophile. Anaerobe 2024, 89, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, H. Fecal Microbiota and Its Correlation With Fatty Acids and Free Amino Acids Metabolism in Piglets After a Lactobacillus Strain Oral Administration. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W. Dietary citrus pectin drives more ileal microbial protein metabolism and stronger fecal carbohydrate fermentation over fructo-oligosaccharide in growing pigs. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Rao, L.; Yan, X.; Gao, R.; Shen, T.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, C.; Zhou, L. Probiotic Cocktail Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation Through Improving Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Colitis Mice. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 886061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, H.M.; Jonkers, D.; Venema, K.; Vanhoutvin, S.; Troost, F.; Brummer, R.J. The role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plöger, S.; Stumpff, F.; Penner, G.B.; Schulzke, J.D.; Gäbel, G.; Martens, H.; Shen, Z.; Günzel, D.; Aschenbach, J.R. Microbial butyrate and its role for barrier function in the gastrointestinal tract. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1258, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, C.; Mou, H.; Kong, Q. Nondigestible carbohydrates, butyrate, and butyrate-producing bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, S130–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach Knudsen, K.E.; Lærke, H.N.; Hedemann, M.S.; Nielsen, T.S.; Ingerslev, A.K.; Gundelund Nielsen, D.S.; Theil, P.K.; Purup, S.; Hald, S.; Schioldan, A.G. Impact of diet-modulated butyrate production on intestinal barrier function and inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, P.S.; Cowles, R.A. Butyrate and the Intestinal Epithelium: Modulation of Proliferation and Inflammation in Homeostasis and Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Magee, K.L.; Colon-Perez, L.M.; Larkin, R.; Liao, Y.S.; Balazic, E.; Cowart, J.R.; Arocha, R.; Redler, T.; Febo, M. Impaired butyrate absorption in the proximal colon, low serum butyrate and diminished central effects of butyrate on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Physiol. 2019, 226, e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, M.P.; Mattace Raso, G.; Cavaliere, G.; Trinchese, G.; De Filippo, C.; Aceto, S.; Prisco, M.; Pirozzi, C.; Di Guida, F.; Lama, A. Butyrate regulates liver mitochondrial function, efficiency, and dynamics in insulin-resistant obese mice. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Krishnan, S.; Ramakrishna, B.; Mathan, M.; Pulimood, A.; Murthy, S. Butyrate and glucose metabolism by colonocytes in experimental colitis in mice. Gut 2000, 46, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Pan, Q.; Xin, F.-Z.; Zhang, R.-N.; He, C.-X.; Chen, G.-Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Fan, J.-G. Sodium butyrate attenuates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice by improving gut microbiota and gastrointestinal barrier. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, K.E.B.; Serena, A.; Canibe, N.; Juntunen, K.S. New insight into butyrate metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, U.; Cengiz, Ö.; Raza, I.; Kuter, E.; Chacher, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Umar, S.; Çakir, S. Sodium butyrate in chicken nutrition: The dynamics of performance, gut microbiota, gut morphology, and immunity. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2016, 72, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloteau, P.; Martin, L.; Eeckhaut, V.; Ducatelle, R.; Zabielski, R.; Van Immerseel, F. From the gut to the peripheral tissues: The multiple effects of butyrate. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 366–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Du, R.; Yao, W.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.; Teligun; Li, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, S.; et al. Host-microbe interaction-mediated resistance to DSS-induced inflammatory enteritis in sheep. Microbiome 2024, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canani, R.B.; Costanzo, M.D.; Leone, L.; Pedata, M.; Meli, R.; Calignano, A. Potential beneficial effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, X.; Gu, Y.; Li, D.; Li, M. Gut Metagenome Reveals the Microbiome Signatures in Tibetan and Black Pigs. Animals 2025, 15, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050753
Bai X, Gu Y, Li D, Li M. Gut Metagenome Reveals the Microbiome Signatures in Tibetan and Black Pigs. Animals. 2025; 15(5):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050753
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Xue, Yiren Gu, Diyan Li, and Mingzhou Li. 2025. "Gut Metagenome Reveals the Microbiome Signatures in Tibetan and Black Pigs" Animals 15, no. 5: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050753
APA StyleBai, X., Gu, Y., Li, D., & Li, M. (2025). Gut Metagenome Reveals the Microbiome Signatures in Tibetan and Black Pigs. Animals, 15(5), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15050753




