Genomic Mosaicism in Fowl Adenovirus 3 Strains
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Strains
2.2. Genome Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Analysis
2.4. Data Reposition
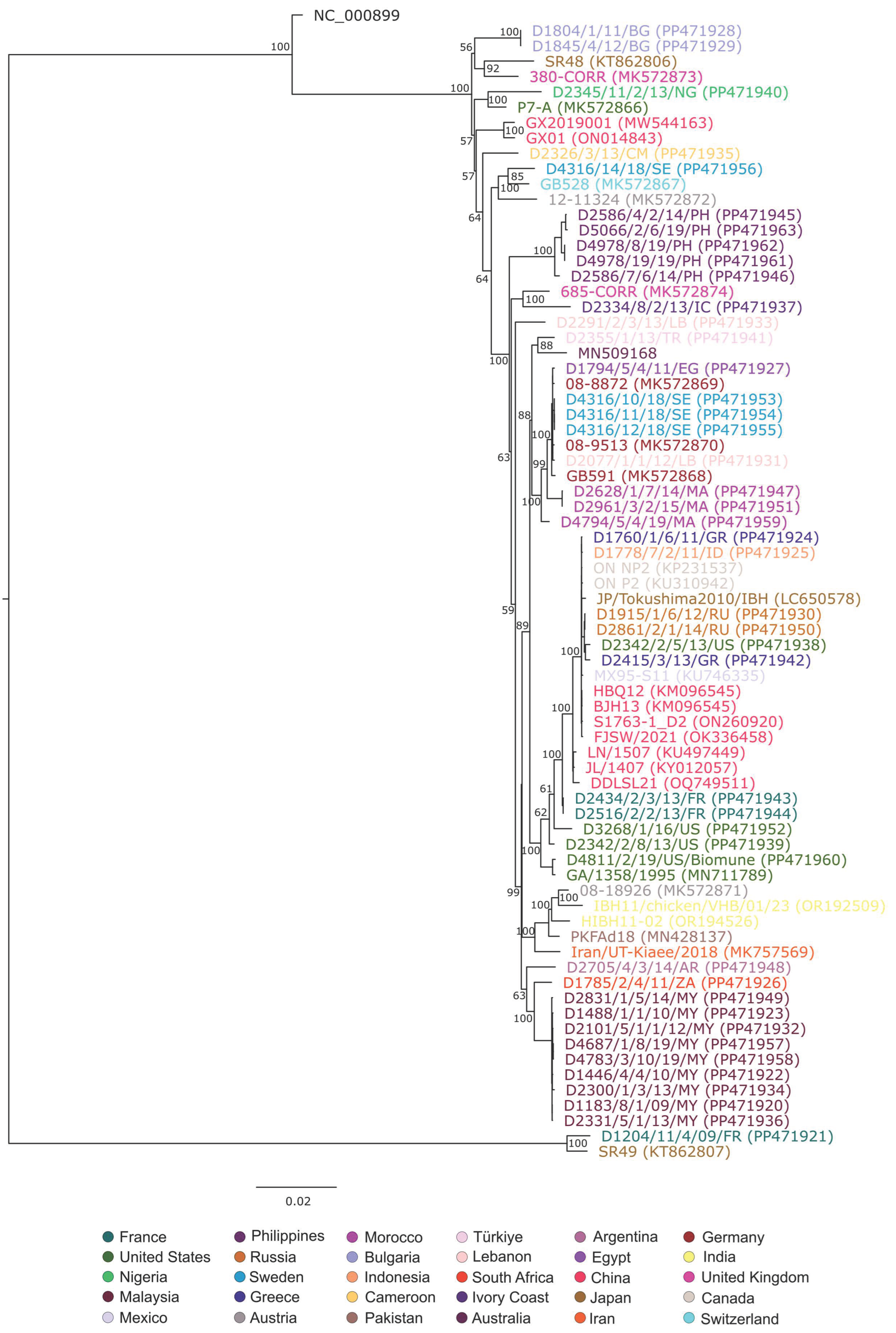
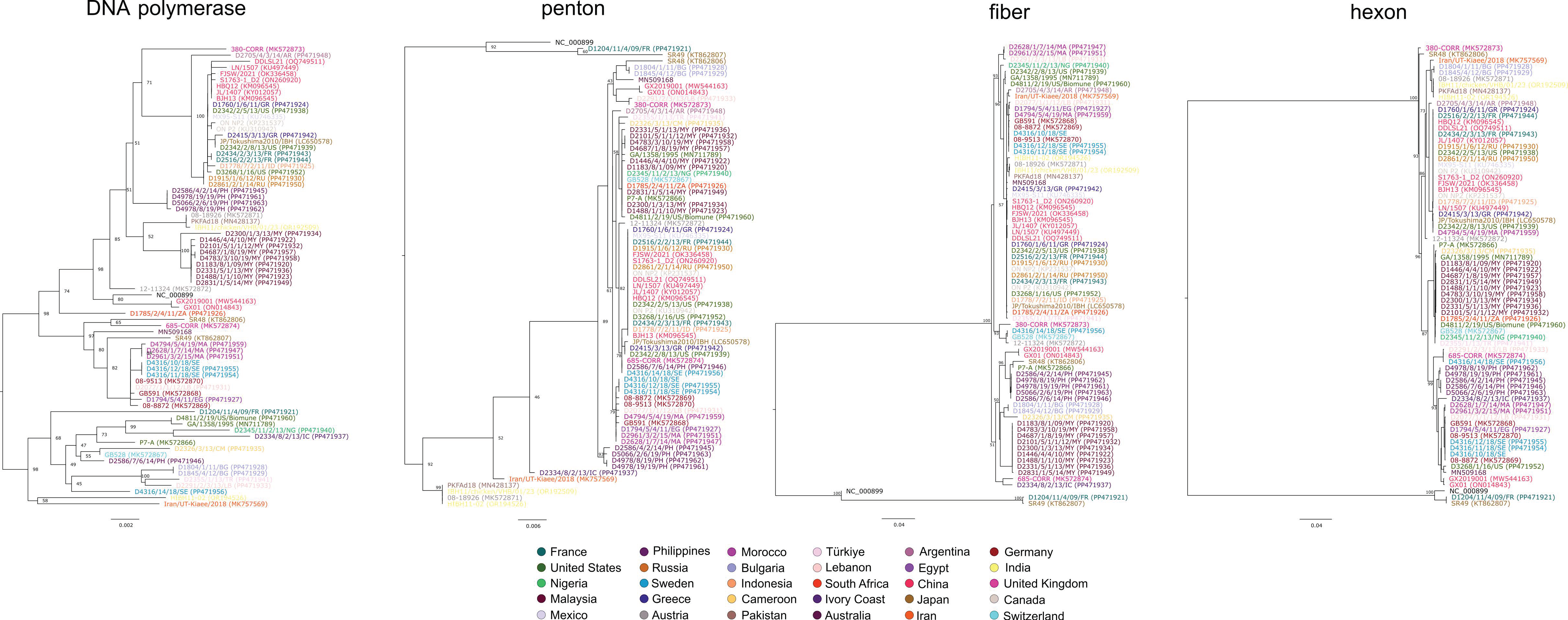
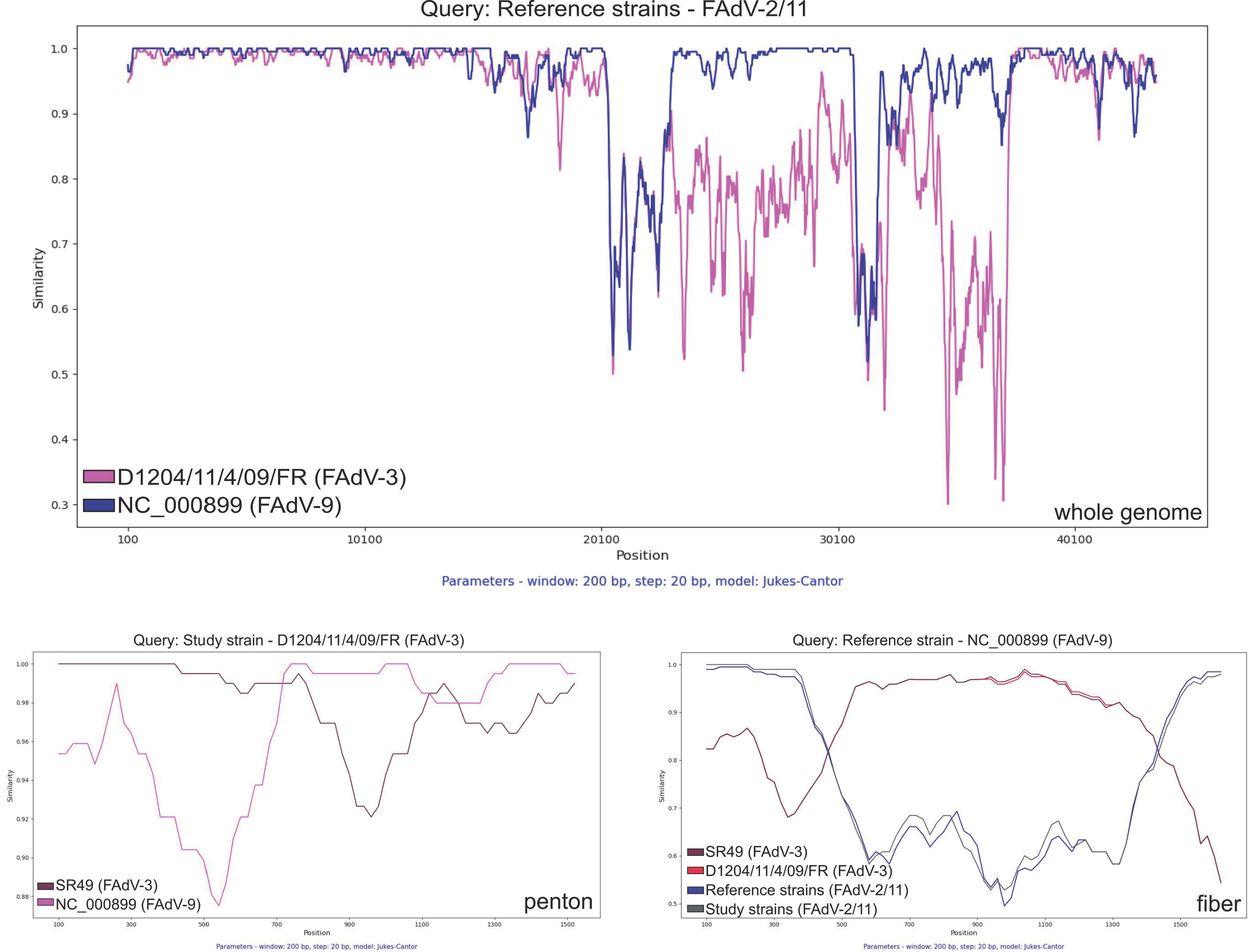
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benkő, M.; Aoki, K.; Arnberg, N.; Davison, A.J.; Echavarría, M.; Hess, M.; Jones, M.S.; Kaján, G.L.; Kajon, A.E.; Mittal, S.K.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Adenoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shall, N.A.; El-Hamid, H.S.A.; Elkady, M.F.; Ellakany, H.F.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Gado, A.R.; Geneedy, A.M.; Hasan, M.E.; Jaremko, M.; Selim, S.; et al. Epidemiology, pathology, prevention, and control strategies of inclusion body hepatitis and hepatitis-hydropericardium syndrome in poultry: A comprehensive review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 963199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, I.; Homonnay, Z.G.; Mató, T.; Bányai, K.; Palya, V. Research note: An overview on distribution of fowl adenoviruses. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaján, G.L.; Kecskeméti, S.; Harrach, B.; Benkő, M. Molecular typing of fowl adenoviruses, isolated in Hungary recently, reveals high diversity. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Mase, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takizawa, K.; Kabeya, M.; Wakuda, T.; Matsuda, M.; Chikuba, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ohyama, T.; et al. Inclusion body hepatitis caused by fowl adenovirus in broiler chickens in Japan, 2009–2010. Avian Dis. 2011, 55, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.S.; Kye, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeon, W.J.; Lee, E.K.; Park, K.Y.; Sung, H.W. Epidemiological investigation of outbreaks of fowl adenovirus infection in commercial chickens in Korea. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2502–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steer, P.A.; Kirkpatrick, N.C.; O’Rourke, D.; Noormohammadi, A.H. Classification of fowl adenovirus serotypes by use of high-resolution melting-curve analysis of the hexon gene region. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maartens, L.H.; Joubert, H.W.; Aitchison, H.; Venter, E.H. Inclusion body hepatitis associated with an outbreak of fowl adenovirus type 2 and type 8b in broiler flocks in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2014, 85, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzuto, M.S.; De Battisti, C.; Marciano, S.; Capua, I.; Cattoli, G. Pyrosequencing analysis for a rapid classification of fowl adenovirus species. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, E.B.; Kunert Filho, H.C.; Withoeft, J.A.; de Oliveira Cunha, A.L.; Fonseca, A.; Casagrande, R.A. Fowl aviadenovirus (FAdV-11) as the causative agent of a vertical outbreak of inclusion body hepatitis in commercial broiler breeders in Brazil. Microbe 2024, 3, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Q.; Wu, M.; Ma, J.; Wei, Y.; Pang, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; et al. Phylogenetic and pathogenic characterization of current fowl adenoviruses in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 105, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Feng, J.; Duan, B.; Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Epidemiological survey of avian adenovirus in China from 2015 to 2021 and the genetic variability of highly pathogenic Fadv-4 isolates. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 101, 105277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niczyporuk, J.S.; Kozdruń, W.; Czekaj, H.; Styś-Fijoł, N.; Piekarska, K. Detection of fowl adenovirus D strains in wild birds in Poland by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olasz, F.; Mészáros, I.; Marton, S.; Kaján, G.L.; Tamás, V.; Locsmándi, G.; Magyar, T.; Bálint, Á.; Bányai, K.; Zádori, Z. A simple method for sample preparation to facilitate efficient whole-genome sequencing of African swine fever virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, K.; Bálint, Á.; Farsang, A.; Marton, S.; Nagy, B.; Kaszab, E.; Belák, S.; Palya, V.; Bányai, K. Recombination events shape the genomic evolution of infectious bronchitis virus in Europe. Viruses 2021, 13, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, S.; Lord, É.; Makarenkov, V. SimPlot++: A Python application for representing sequence similarity and detecting recombination. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 3118–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachner, A.; Gonzalez, G.; Endler, L.; Ito, K.; Hess, M. Fowl adenovirus (FAdV) recombination with intertypic crossovers in genomes of FAdV-D and FAdV-E, displaying hybrid serological phenotypes. Viruses 2019, 11, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Teng, X.; Jiang, T.; Tang, W.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Genome analysis of a novel avian atadenovirus reveals a possible horizontal gene transfer. Virology 2024, 593, 109999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homonnay, Z.; Jakab, S.; Bali, K.; Kaszab, E.; Mató, T.; Kiss, I.; Palya, V.; Bányai, K. Genome sequencing of a novel variant of fowl adenovirus B reveals mosaicism in the pattern of homologous recombination events. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, A.; Kaján, G.L.; Kosiol, C.; Benkő, M.; Schachner, A.; Hess, M. Genetic diversity of species Fowl aviadenovirus D and Fowl aviadenovirus E. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strain ID | Year of Isolation | Country of Origin | Isolated from Sample | Production Type/Age | Sero-/Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1183/8/1/09/MY | 2009 | Malaysia | bursa | broiler/D45 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1204/11/4/09/FR | 2009 | France | liver | slow-grown broiler/D56 | FAdV-3 |
| D1446/4/4/10/MY | 2010 | Malaysia | cecal tonsil | broiler/D34 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1488/1/1/10/MY | 2010 | Malaysia | liver | broiler/D20 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1760/1/6/11/GR | 2011 | Greece | liver | broiler | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1778/7/2/11/ID | 2011 | Indonesia | proventriculus | broiler/D20 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1785/2/4/11/ZA | 2011 | South Africa | liver | broiler embryo | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1794/5/4/11/EG | 2011 | Egypt | cecal tonsil | broiler/D39 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1804/1/11/BG | 2011 | Bulgaria | liver | broiler/D10 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1845/4/12/BG | 2012 | Bulgaria | liver | broiler/D10 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D1915/1/6/12/RU | 2012 | Russia | liver | broiler/D19 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2101/5/1/1/12/MY | 2012 | Malaysia | cecal tonsil | broiler/D42 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2291/2/3/13/LB | 2013 | Lebanon | cecal tonsil | broiler/D42 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2300/1/3/13/MY | 2013 | Malaysia | cecal tonsil | broiler/D36 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2326/3/13/CM | 2013 | Cameroon | intestine | broiler/D42 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2331/5/1/13/MY | 2013 | Malaysia | liver | broiler/D35 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2334/8/2/13/IC | 2013 | Ivory Coast | cecal tonsil | broiler/D42 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2342/2/5/13/US | 2013 | United States | liver | broiler | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2342/2/8/13/US | 2013 | United States | liver | broiler | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2345/11/2/13/NG | 2013 | Nigeria | cecal tonsil | broiler/D32 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2355/1/13/TR | 2013 | Türkiye | cecal tonsil | broiler/D40 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2434/2/3/13/FR | 2013 | France | cecal tonsil | broiler/D29 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2516/2/2/13/FR | 2013 | France | liver | broiler/D26 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2586/4/2/14/PH | 2014 | Philippines | cecal tonsil | broiler/D35 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2586/7/6/14/PH | 2014 | Philippines | cecal tonsil | broiler/D29 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2628/1/7/14/MA | 2014 | Morocco | cecal tonsil | broiler/D36 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2705/4/3/14/AR | 2014 | Argentina | proventriculus | broiler/D38 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2831/1/5/14/MY | 2014 | Malaysia | cecal tonsil | broiler/D38 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2861/2/1/14/RU | 2014 | Russia | gizzard | broiler/D20 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2961/3/2/15/MA | 2015 | Morocco | kidney | broiler/D36 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D3268/1/16/US | 2016 | United States | liver | broiler/D7 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4316/10/18/SE | 2018 | Sweden | cecal tonsil | n. a. | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4316/11/18/SE | 2018 | Sweden | liver | n. a. | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4316/12/18/SE | 2018 | Sweden | liver | n. a. | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4316/14/18/SE | 2018 | Sweden | liver | n. a. | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4687/1/8/19/MY | 2019 | Malaysia | cecal tonsil | broiler/D38 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4783/3/10/19/MY | 2019 | Malaysia | cecal tonsil | broiler/D37 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4794/5/4/19/MA | 2019 | Morocco | liver | broiler/D40 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2077/1/1/12/LB | 2012 | Lebanon | cecal tonsil | broiler/D39 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D2415/3/13/GR | 2013 | Greece | cecal tonsil | broiler/D45 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4811/2/19/US | 2019 | United States | liver | n. a. | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4978/19/19/PH | 2019 | Philippines | liver | broiler/D32 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D4978/8/19/PH | 2019 | Philippines | liver | broiler/D32 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
| D5066/2/6/19/PH | 2019 | Philippines | bursa | broiler/D21 | FAdV-2/FAdV-11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Homonnay, Z.; Jakab, S.; Marton, S.; Domán, M.; Bali, K.; Kaszab, E.; Kemenesi, G.; Mató, T.; Kiss, I.; Palya, V.; et al. Genomic Mosaicism in Fowl Adenovirus 3 Strains. Animals 2025, 15, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040508
Homonnay Z, Jakab S, Marton S, Domán M, Bali K, Kaszab E, Kemenesi G, Mató T, Kiss I, Palya V, et al. Genomic Mosaicism in Fowl Adenovirus 3 Strains. Animals. 2025; 15(4):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040508
Chicago/Turabian StyleHomonnay, Zalán, Szilvia Jakab, Szilvia Marton, Marianna Domán, Krisztina Bali, Eszter Kaszab, Gábor Kemenesi, Tamás Mató, István Kiss, Vilmos Palya, and et al. 2025. "Genomic Mosaicism in Fowl Adenovirus 3 Strains" Animals 15, no. 4: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040508
APA StyleHomonnay, Z., Jakab, S., Marton, S., Domán, M., Bali, K., Kaszab, E., Kemenesi, G., Mató, T., Kiss, I., Palya, V., & Bányai, K. (2025). Genomic Mosaicism in Fowl Adenovirus 3 Strains. Animals, 15(4), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15040508







