Oleic Acid Increases Lipid Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes by Promoting Apolipoprotein A1 Expression
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Duck Primary Hepatocyte Isolation and Culture
2.2. Oleic Acid-Induced Steatosis Model Establishment
2.3. Cytotoxicity and Triglyceride Quantification
2.4. Oil Red O Staining
2.5. Transcriptome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.6. Overexpression and Knockdown of APOA1 Gene in Duck Primary Hepatocytes
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
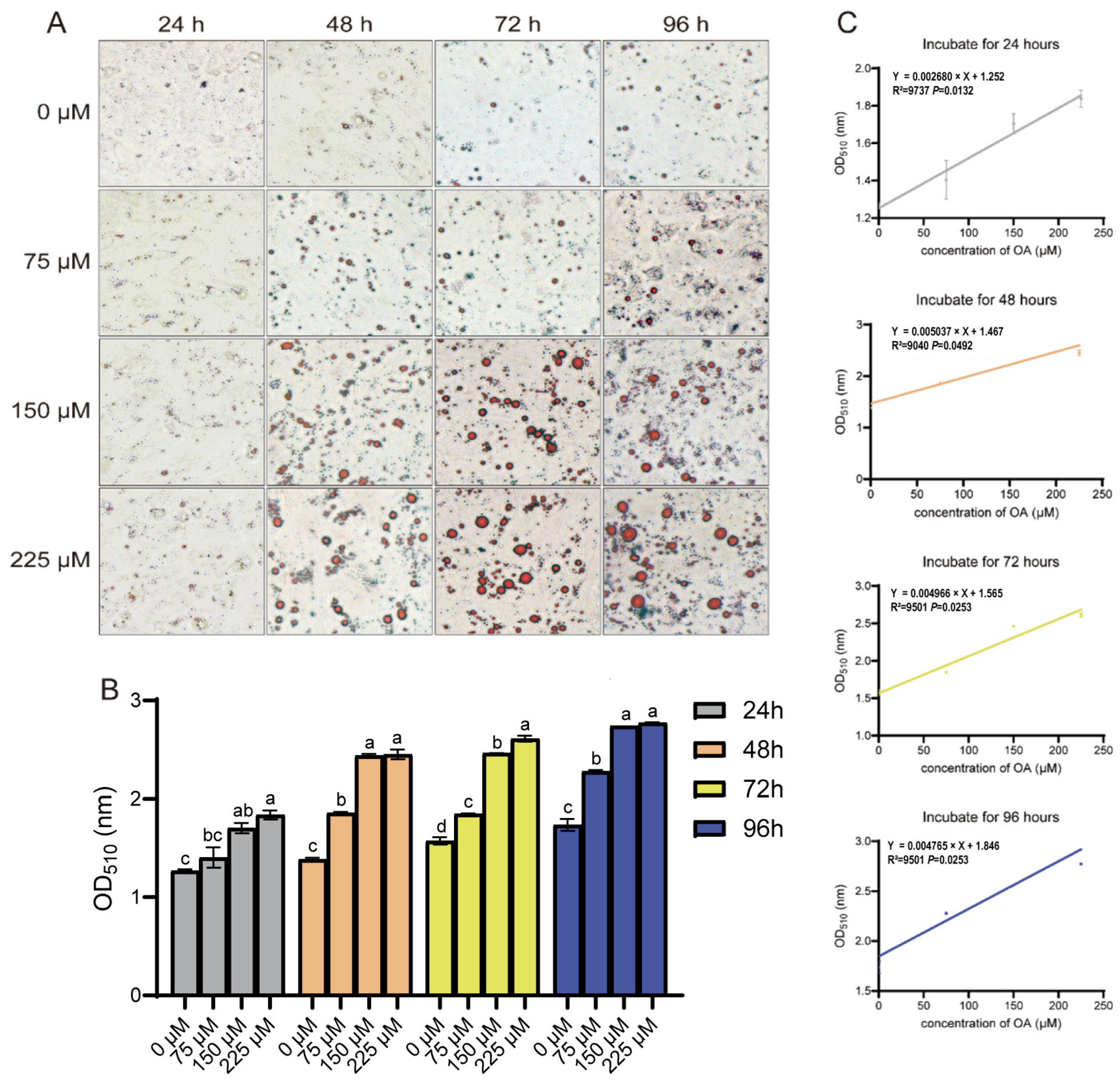
3.1. Oleic Acid Induces Lipid Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes
3.2. Oleic Acid Promotes Lipid Droplet Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes
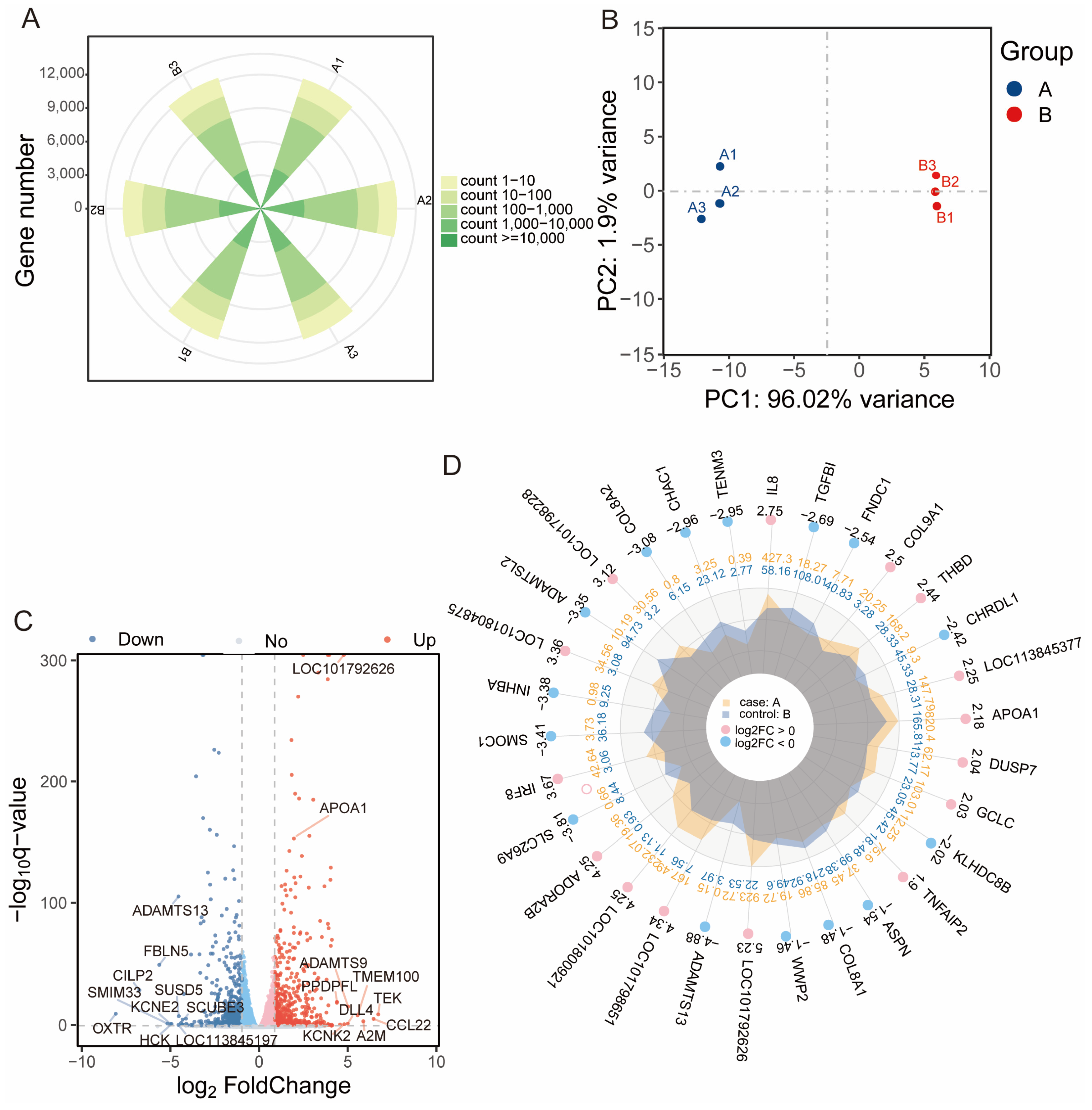
3.3. Clustering Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
3.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
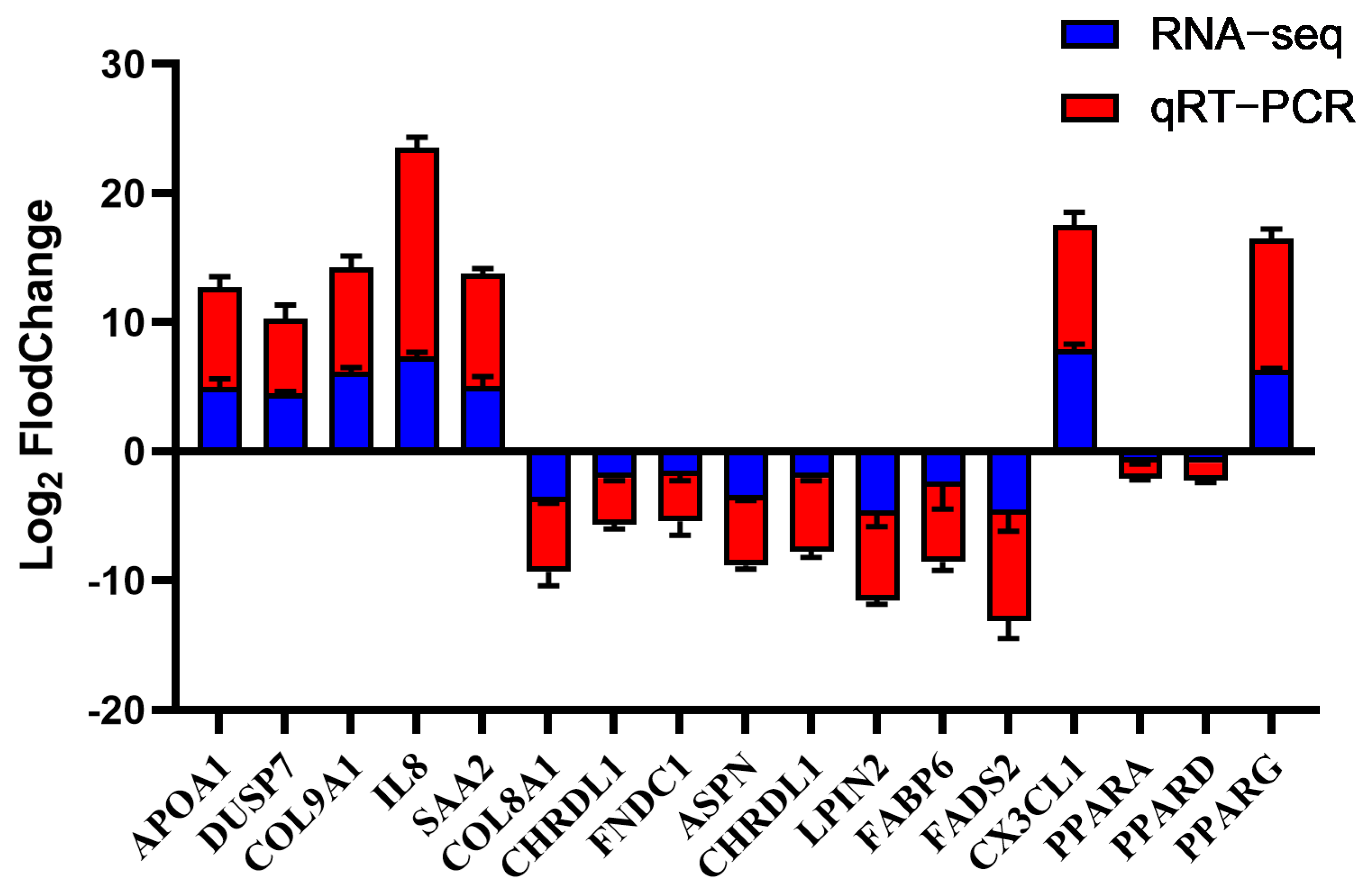
3.5. Candidate Gene Validation and Selection
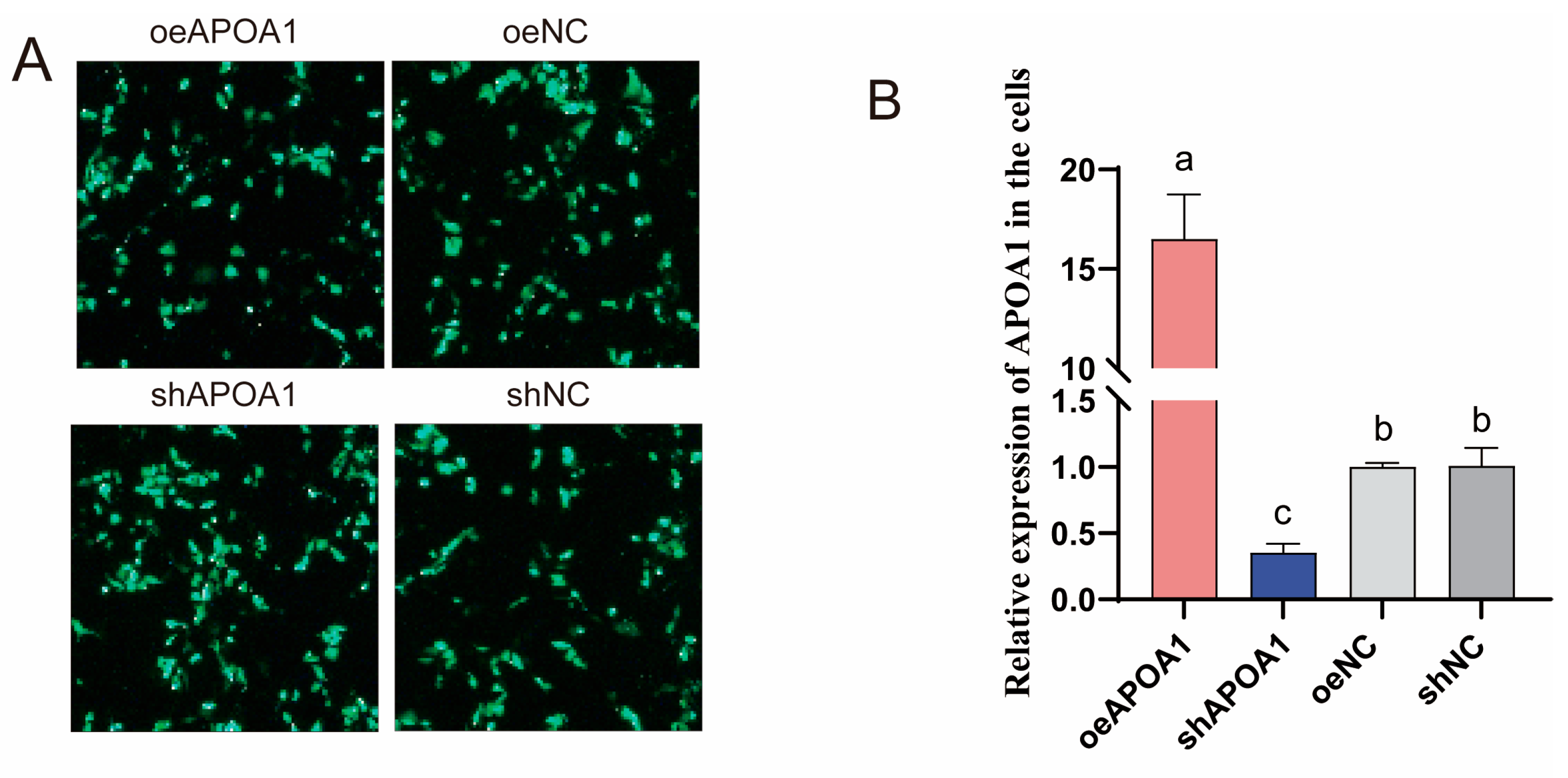
3.6. Functional Role of APOA1 in Regulating Triglyceride Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermier, D.; Guy, G.; Guillaumin, S.; Davail, S.; André, J.-M.; Hoo-Paris, R. Differential Channelling of Liver Lipids in Relation to Susceptibility to Hepatic Steatosis in Two Species of Ducks. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 135, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, B.; Marty-Gasset, N.; Manse, H.; Bannelier, C.; Bravo, C.; Domitile, R.; Rémignon, H. Cellular Markers of Mule Duck Livers after Force-Feeding. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3567–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shini, S.; Shini, A.; Bryden, W.L. Unravelling Fatty Liver Haemorrhagic Syndrome: 1. Oestrogen and Inflammation. Avian Pathol. 2020, 49, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Ma, N.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Zhao, X. Untargeted and Targeted Metabolomics Profiling Reveals the Underlying Pathogenesis and Abnormal Arachidonic Acid Metabolism in Laying Hens with Fatty Liver Hemorrhagic Syndrome. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, R.; Zhang, J.; Sun, P.; Xing, X.; Wang, L.; Sairijima, T.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; et al. Oleic Acid-Induced Steatosis Model Establishment in LMH Cells and Its Effect on Lipid Metabolism. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M. Recent Insights into Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Werneburg, N.W.; Canbay, A.; Guicciardi, M.E.; Bronk, S.F.; Rydzewski, R.; Burgart, L.J.; Gores, G.J. Free Fatty Acids Promote Hepatic Lipotoxicity by Stimulating TNF-Alpha Expression via a Lysosomal Pathway. Hepatology 2004, 40, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Sullivan, S.; Klein, S. Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Biochemical, Metabolic, and Clinical Implications. Hepatology 2010, 51, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérault, F.; Duby, C.; Baéza, E.; Diot, C. Adipogenic Genes Expression in Relation to Hepatic Steatosis in the Liver of Two Duck Species. Animal 2018, 12, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Xu, M.; Liu, F.; Dong, X.; Zou, X.; Zeng, T.; Lu, L. Sodium Butyrate Attenuates Lipid Metabolism Disorder via Improving Mitochondrial Function and Activating Autophagy in LMH Cells. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartrin, P.; Bernadet, M.-D.; Guy, G.; Mourot, J.; Hocquette, J.-F.; Rideau, N.; Duclos, M.J.; Baéza, E. Does Overfeeding Enhance Genotype Effects on Liver Ability for Lipogenesis and Lipid Secretion in Ducks? Comp. Biochem. Physiology Part Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2006, 145, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérault, F.; Houée-Bigot, M.; Baéza, E.; Bouchez, O.; Esquerré, D.; Klopp, C.; Diot, C. RNA-Seq Analysis of Hepatic Gene Expression of Common Pekin, Muscovy, Mule and Hinny Ducks Fed Ad Libitum or Overfed. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hérault, F.; Diot, C.; Corre, E. Development of a Relevant Strategy Using de Novo Transcriptome Assembly Method for Transcriptome Comparisons between Muscovy and Common Duck Species and Their Reciprocal Inter-Specific Mule and Hinny Hybrids Fed Ad Libitum and Overfed. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, J.; Lan, F.; Wen, C.; Li, J.; Yang, N.; Sun, C. Hepatic Steatosis Is Associated with Dysregulated Cholesterol Metabolism and Altered Protein Acetylation Dynamics in Chickens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Molecular Mechanism of Hepatic Fat Metabolism Disorder Caused by Muscovy Duck Reovirus Infection. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ramie, J.J.; Barber, J.L.; Sarzynski, M.A. Effects of Exercise on HDL Functionality. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2019, 30, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, B.J.; Ong, K.-L.; Manandhar, B.; Rye, K.-A. APOA1: A Protein with Multiple Therapeutic Functions. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhale, A.S.; Venkataraman, K. Leveraging Knowledge of HDLs Major Protein ApoA1: Structure, Function, Mutations, and Potential Therapeutics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Tu, M.; Chen, H.J. Triglycerides to Apolipoprotein A1 Ratio: An Effective Insulin Resistance-Associated Index in Identifying Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1384059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Jia, W.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xu, M.; Bai, H.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; et al. Threonine Deficiency Increases Triglyceride Deposition in Primary Duck Hepatocytes by Reducing STAT3 Phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Li, G.; Du, G.; Zhang, C.; Jin, S.; Geng, Z. A Novel in Duck Myoblasts: The Transcription Factor Retinoid X Receptor Alpha (RXRA) Inhibits Lipid Accumulation by Promoting CD36 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hong, W.; Yao, K.-N.; Zhu, X.-H.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Ye, L. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Ameliorates Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in LO2 Cells by Regulating the AKT/mTOR/SREBP-1 Signaling Pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervois, P.; Torra, I.P.; Fruchart, J.C.; Staels, B. Regulation of Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism by PPAR Activators. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaigne, D.; Butruille, L.; Staels, B. PPAR Control of Metabolism and Cardiovascular Functions. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, K.C.; Ryan, M.C.; Wilson, A.M. The Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated with Increased Cardiovascular Risk in a Large Cohort of Non-Obese Asian Subjects. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, G.-S.; Chen, Y. Apolipoprotein A-I Possesses an Anti-Obesity Effect Associated with Increase of Energy Expenditure and up-Regulation of UCP1 in Brown Fat. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Mao, Y.; Liu, A.; Du, J. Role of Apolipoprotein A1 in PPAR Signaling Pathway for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PPAR Res. 2022, 2022, 4709300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Ding, H. APOA1/C3/A4/A5 Gene Cluster at 11q23.3 and Lipid Metabolism Disorders: From Epigenetic Mechanisms to Clinical Practices. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pavanello, C.; Hutchins, P.M.; Tang, C.; Pourmousa, M.; Vaisar, T.; Song, H.D.; Pastor, R.W.; Remaley, A.T.; Goldberg, I.J.; et al. Flipped C-Terminal Ends of APOA1 Promote ABCA1-Dependent Cholesterol Efflux by Small HDLs. Circulation 2024, 149, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Morris, J.; You, Y.; Sexmith, H.; Street, S.E.; Thibert, S.M.; Attah, I.K.; Hutchinson Bunch, C.M.; Novikova, I.V.; Evans, J.E.; et al. APOA2 Increases Cholesterol Efflux Capacity to Plasma HDL by Displacing the C-Terminus of Resident APOA1. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhu, W.; Huang, L.; Miao, Y. Liver X Receptor α Promotes Milk Fat Synthesis in Buffalo Mammary Epithelial Cells by Regulating the Expression of FASN. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 12980–12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Li, M.; Peng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, N. ACACA Reduces Lipid Accumulation through Dual Regulation of Lipid Metabolism and Mitochondrial Function via AMPK- PPARα- CPT1A Axis. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.W.; Wang, X.; Zecchin, A.; Thienpont, B.; Cornelissen, I.; Kalucka, J.; García-Caballero, M.; Missiaen, R.; Huang, H.; Brüning, U.; et al. The Role of Fatty Acid β-Oxidation in Lymphangiogenesis. Nature 2017, 542, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Chen, X.; Tan, M.; Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, X.; Dean, J.M.; Razani, B.; Lodhi, I.J. Acetyl-CoA Derived from Hepatic Peroxisomal β-Oxidation Inhibits Autophagy and Promotes Steatosis via mTORC1 Activation. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 30–42e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borén, J.; Packard, C.J.; Binder, C.J. Apolipoprotein B-Containing Lipoproteins in Atherogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2025, 22, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Yu, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Apolipoprotein A1-Encoding Recombinant Adenovirus Remodels Cholesterol Metabolism in Tumors and the Tumor Microenvironment to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2025, 275, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Geng, Z. Oleic Acid Increases Lipid Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes by Promoting Apolipoprotein A1 Expression. Animals 2025, 15, 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243603
Pan Z, Li X, Wu D, Xie L, Chen X, Geng Z. Oleic Acid Increases Lipid Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes by Promoting Apolipoprotein A1 Expression. Animals. 2025; 15(24):3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243603
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Ziyi, Xuewen Li, Dongsheng Wu, Longfei Xie, Xingyong Chen, and Zhaoyu Geng. 2025. "Oleic Acid Increases Lipid Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes by Promoting Apolipoprotein A1 Expression" Animals 15, no. 24: 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243603
APA StylePan, Z., Li, X., Wu, D., Xie, L., Chen, X., & Geng, Z. (2025). Oleic Acid Increases Lipid Accumulation in Duck Hepatocytes by Promoting Apolipoprotein A1 Expression. Animals, 15(24), 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15243603




