Quercetin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Polymyxin E Against MCR-1-Positive Bacteria by Inhibiting the Biological Functions of the Cell Membrane
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Animals
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
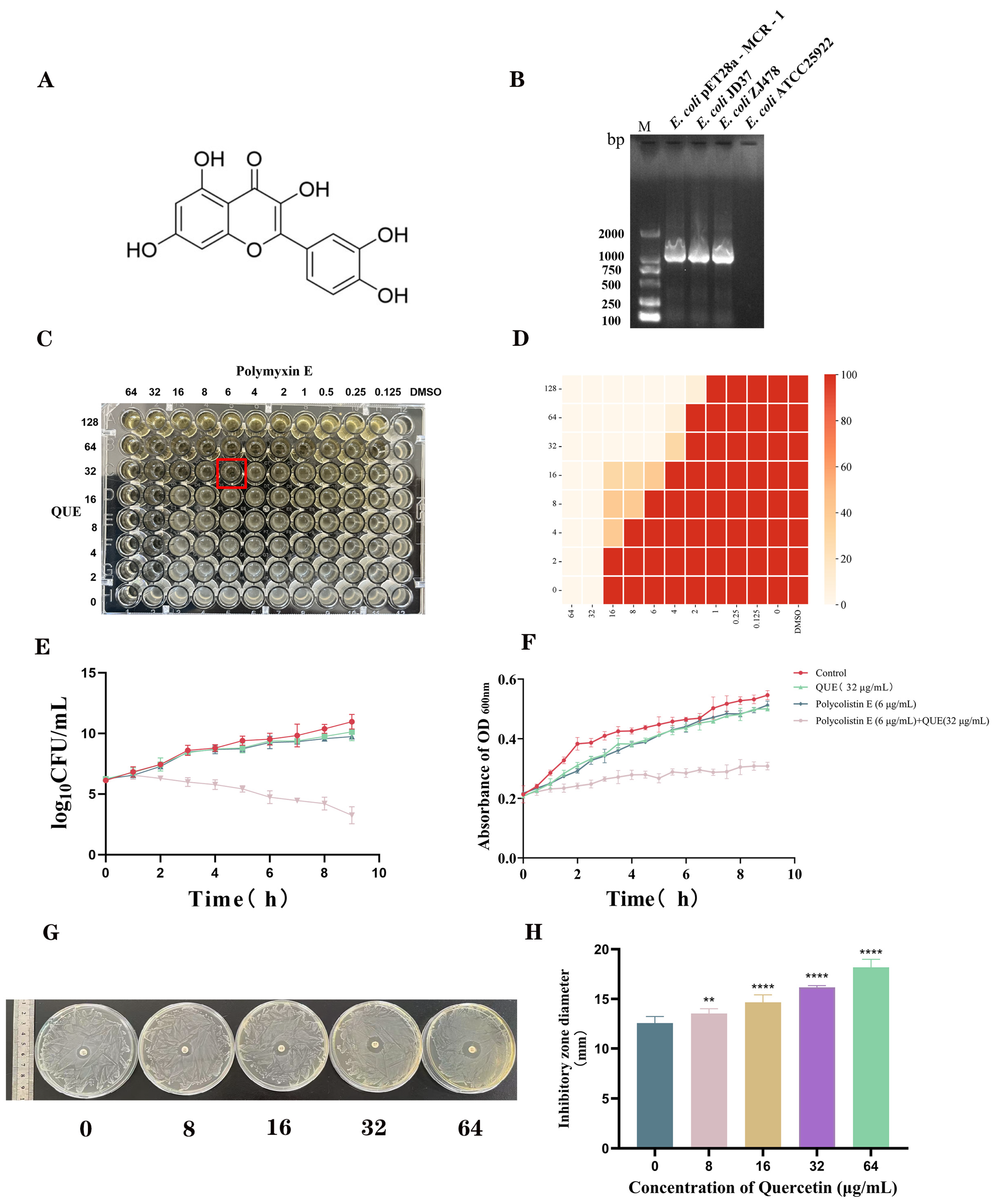
2.3. Combined Drug Sensitivity Test
2.4. Time-Kill Curves
2.5. Growth Curves
2.6. Agar Diffusion Test
2.7. Membrane Permeability Detection
2.7.1. The Determination of LPS-Related Regulatory Genes and LPS Content Involved Co-Incubating a Bacterial Suspension
2.7.2. Cell Membrane Staining
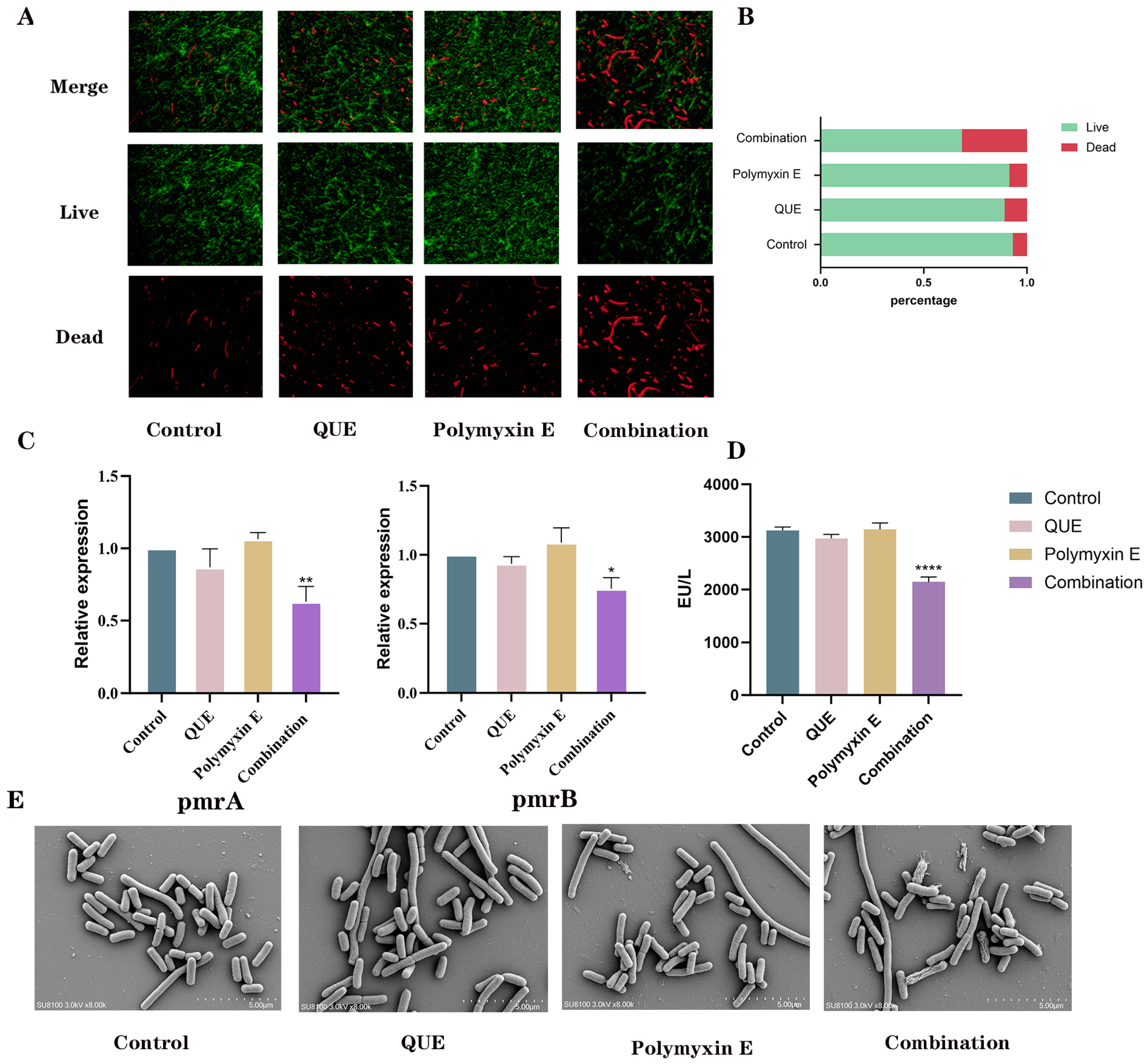
2.7.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.8. Measurement of Membrane Fluidity
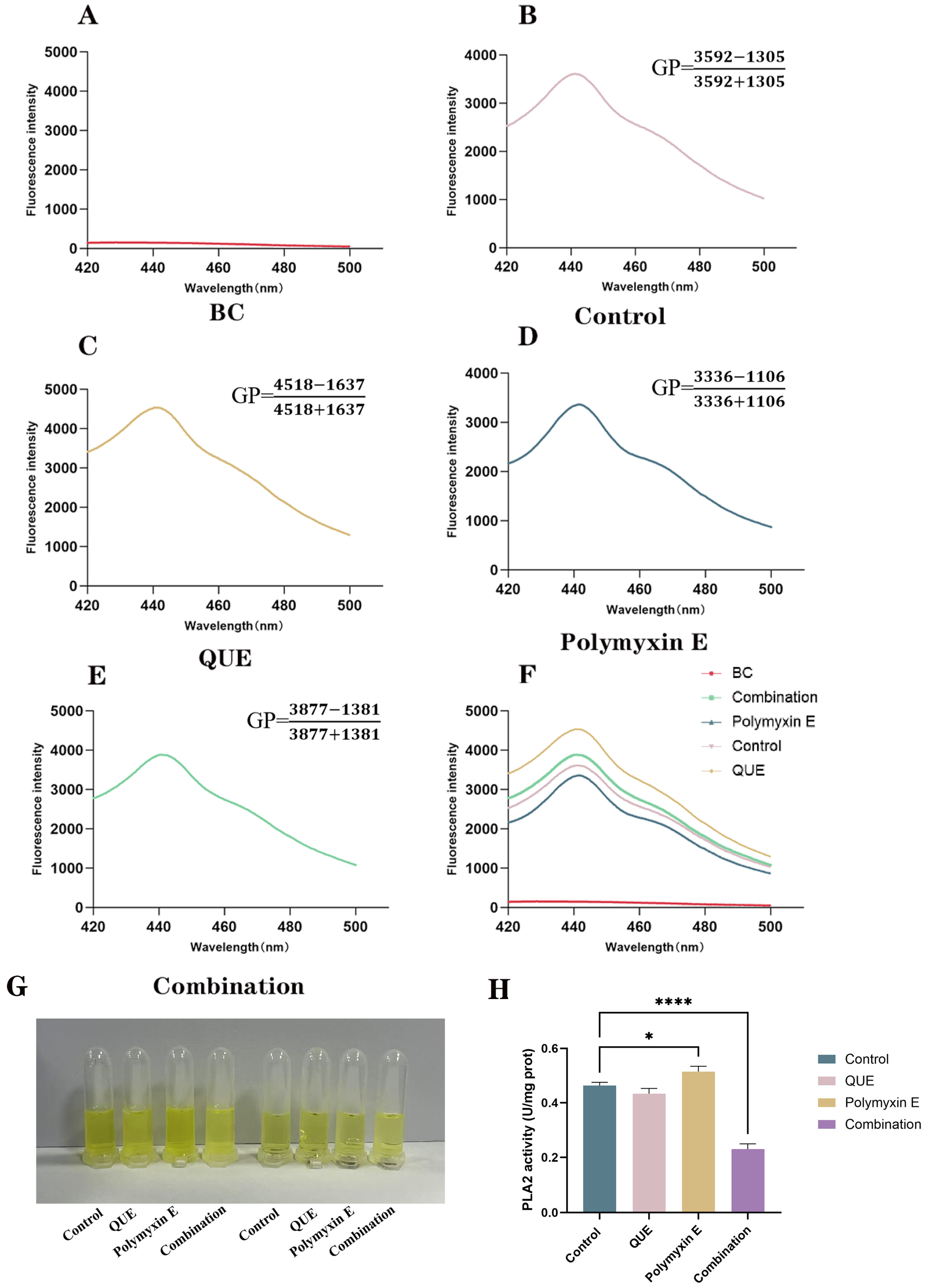
2.9. Determination of Phospholipase A2 Activity
2.10. Measurement of Membrane Potential
2.11. Detection of AcrAB-TolC Efflux Pump
2.12. Molecular Docking
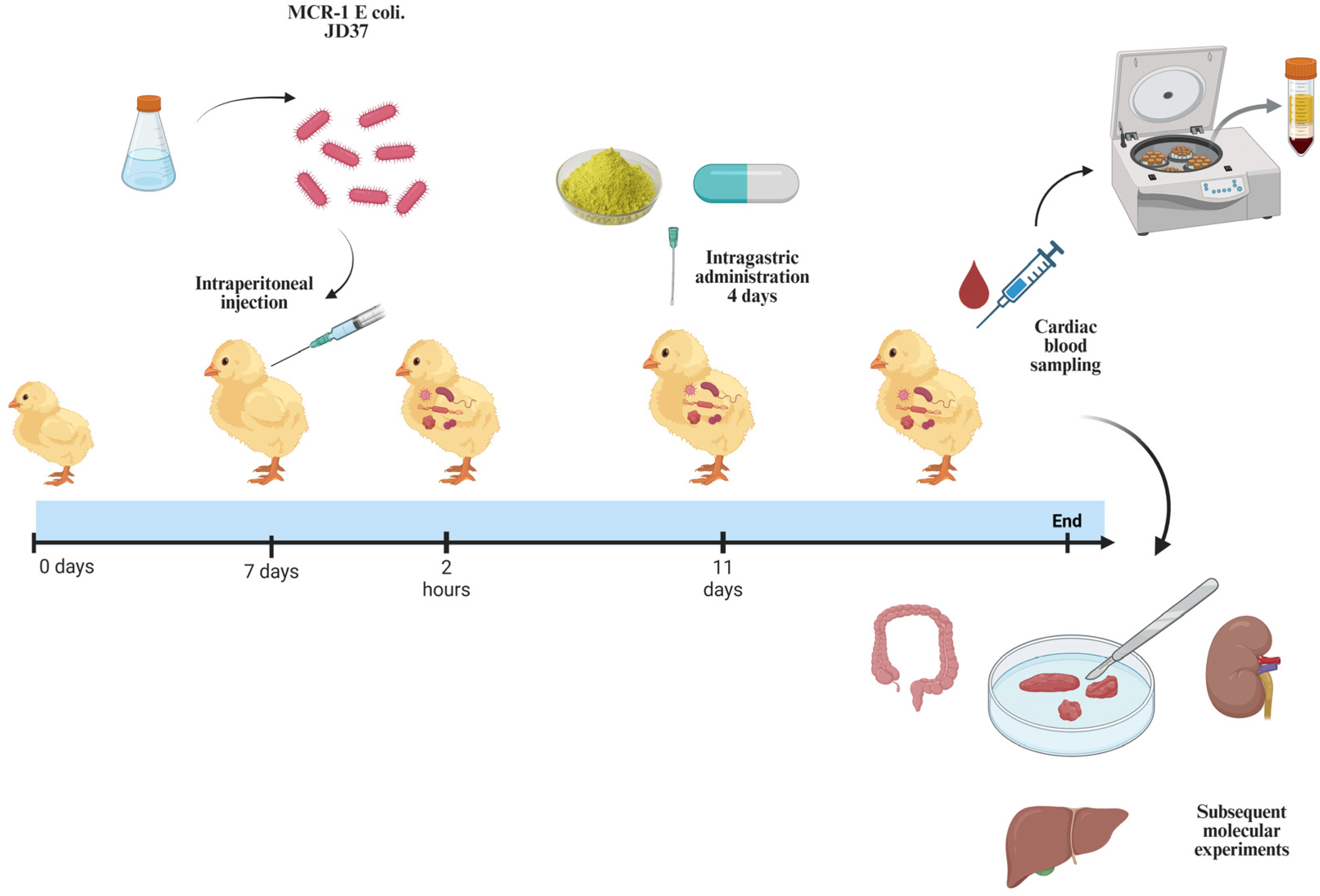
2.13. Animal Experiments
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. QUE Restored the Sensitivity of E. coli JD37 to Polymyxin E
3.2. QUE Enhances the Permeability of the Bacterial Cell Membrane
3.3. QUE Changes the Fluidity of the Bacterial Cell Membrane
3.4. QUE Changed the Membrane Potential of Bacteria
3.5. QUE Suppresses the Expression of Genes Associated with the AcrAB-TolC Efflux Pump System in Bacteria
3.6. The Binding Site of QUE on MCR-1
3.7. QUE in Combination with Polymyxin E Demonstrates Protective Efficacy in Chickens Infected with E. coli JD37
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QUE | Quercetin |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| HIS | histidine |
| ASP | Linear dichroism |
| THR | Threonine |
| GLU | Glutamate |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| IL-1β | iinterleukin-1 beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| GP | generalized polarization |
| PDR | pandrug resistance |
| MDR | multidrug resistance |
References
- Lutful Kabir, S.M. Avian colibacillosis and salmonellosis: A closer look at epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, control and public health concerns. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.; van Hout, J.; Wiegel, J.; Iatridou, D.; Chantziaras, I.; De Briyne, N. Colistin Use in European Livestock: Veterinary Field Data on Trends and Perspectives for Further Reduction. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, I.; Jouy, E.; Chauvin, C. Colistin use and colistin resistance in bacteria from animals. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballı, F.N.; Ekinci, P.B.; Kurtaran, M.; Kara, E.; Dizman, G.T.; Sönmezer, M.Ç.; Hayran, M.; Demirkan, K.; Metan, G. Battle of polymyxin induced nephrotoxicity: Polymyxin B versus colistin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabalizadeh, R.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Renoprotective effects of crocin against colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in a rat model. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Siu, L.K.; Chang, F.Y.; Tsai, Y.K.; Huang, L.Y.; Lin, J.C. Influence of PhoPQ and PmrAB two component system alternations on colistin resistance from non-mcr colistin resistant clinical E. Coli strains. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J.Y.; Tresco, B.I.C.; Ramkissoon, A.; Aleksandrova, E.V.; Syroegin, E.A.; See, D.N.Y.; Liow, P.; Dittemore, G.A.; Yu, M.; Testolin, G.; et al. An antibiotic preorganized for ribosomal binding overcomes antimicrobial resistance. Science 2024, 383, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muetter, M.; Angst, D.C.; Regoes, R.R.; Bonhoeffer, S. The impact of treatment strategies on the epidemiological dynamics of plasmid-conferred antibiotic resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2406818121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathdee, S.A.; Hatfull, G.F.; Mutalik, V.K.; Schooley, R.T. Phage therapy: From biological mechanisms to future directions. Cell 2023, 186, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlongo, J.T.; Waddad, A.Y.; Albericio, F.; de la Torre, B.G. Antimicrobial Peptide Synergies for Fighting Infectious Diseases. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Du, F.; Long, M.; Li, P. Limitations of Phage Therapy and Corresponding Optimization Strategies: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.S.; Prodhan, Z.H.; Biswas, S.K.; Le, C.F.; Sekaran, S.D. Antimicrobial peptides from different plant sources: Isolation, characterisation, and purification. Phytochemistry 2018, 154, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyhoegen, C.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Uecker, H. The many dimensions of combination therapy: How to combine antibiotics to limit resistance evolution. Evol. Appl. 2024, 17, e13764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabes, J.M.; Stewart, L.; Shaikh, F.; Robben, P.M.; Petfield, J.L.; Ganesan, A.; Campbell, W.R.; Tribble, D.R.; Blyth, D.M. Risk of Acute Kidney Injury in Combat-Injured Patients Associated With Concomitant Vancomycin and Extended-Spectrum β-Lactam Antibiotic Use. J. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 36, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Qiu, Y.; Hua, X.; Ye, B.; Luo, H.; Liu, D.; Qu, P.; Qiu, Z. Novel Opportunity to Reverse Antibiotic Resistance: To Explore Traditional Chinese Medicine with Potential Activity Against Antibiotics-Resistance Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 610070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, S.; Ji, Q.; Jia, J.; Huo, M.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Revealing active constituents within traditional Chinese Medicine used for treating bacterial pneumonia, with emphasis on the mechanism of baicalein against multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 321, 117488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, X.; Qiao, F.; Guo, J.; Deng, S. Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine and its Active Ingredients on Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.D.; Zhang, J.K.; Sun, Y.W.; Yan, F.B.; Zhao, J.F.; He, D.D.; Pan, Y.S.; Yuan, L.; Zhai, Y.J.; Hu, G.Z. Synergistic antibacterial activity of baicalin and EDTA in combination with colistin against colistin-resistant Salmonella. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Niu, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X. Discovery of a potential MCR-1 inhibitor that reverses polymyxin activity against clinical mcr-1-positive Enterobacteriaceae. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Efferth, T.; Liu, S.; Hua, X. Cajanin stilbene acid: A direct inhibitor of colistin resistance protein MCR-1 that restores the efficacy of polymyxin B against resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 114, 154803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Sheng, Q.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Qiu, J.; Cui, M.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L. Enhancing the effectiveness of Polymyxin E with a Fisetin Nanoemulsion against a Colistin-resistant Salmonella typhimurium infection. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 130, 155768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X. Pterostilbene, a Potential MCR-1 Inhibitor That Enhances the Efficacy of Polymyxin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, 10.1128/aac.02146-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, K.; Liu, S.; Liu, P.; Luo, X.; Zhao, J.; Yan, F.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, Y.; Hu, G. Synergistic antibacterial activity of tetrandrine combined with colistin against MCR-mediated colistin-resistant Salmonella. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, L.; Gu, F.; Bao, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Wu, Z.; Li, J. Quercetin restores respiratory mucosal barrier dysfunction in Mycoplasma gallisepticum-infected chicks by enhancing Th2 immune response. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 133, 155953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, M.; Noei, M.; Chegini, Z.; Shariati, A. Natural compounds in the fight against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: A review of antibiofilm strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1491363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.C.; Tsai, T.Y.; Wang, C.J. The Potential Benefits of Quercetin for Brain Health: A Review of Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, N.; Yousefi, Z.; Golabi, M.; Khalilian, P.; Ghezelbash, B.; Montazeri, M.; Shams, M.H.; Baghbadorani, P.Z.; Eskandari, N. The potential anti-cancer effects of quercetin on blood, prostate and lung cancers: An update. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1077531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, P.; Patton, E.; VanderVeen, B.N.; Unger, C.; Aladhami, A.; Enos, R.T.; Madero, S.; Chatzistamou, I.; Fan, D.; Murphy, E.A.; et al. Sub-chronic oral toxicity screening of quercetin in mice. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.F.S.; Tintino, S.R.; da Silva, A.R.P.; dos S. Barbosa, C.R.; Scherf, J.R.; de S. Silveira, Z.; de Freitas, T.S.; de Lacerda Neto, L.J.; Barros, L.M.; de A. Menezes, I.R.; et al. Enhancement of the antibiotic activity by quercetin against Staphylococcus aureus efflux pumps. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2021, 53, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabaş Köse, E.; Koyuncu Özyurt, Ö.; Bilmen, S.; Er, H.; Kilit, C.; Aydemir, E. Quercetin: Synergistic Interaction with Antibiotics against Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ye, D.; Chen, L.; Huang, N.; Zeng, W.; Liao, W.; Zhan, Y.; Zhou, T.; et al. Quercetin Rejuvenates Sensitization of Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Isolates to Colistin. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 795150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Hussain, E.A.; Shujaat, S.; Khan, M.U.; Ali, Q.; Malook, S.U.; Ali, D. Antibacterial potential of Propolis: Molecular docking, simulation and toxicity analysis. AMB Express 2024, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.F.; Li, H.Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.F.; Tan, J.; Zeng, Y.B.; Wei, Q.P.; Huang, J.N.; Wu, C.C.; Li, N.; et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of bacterial pathogens isolated from poultry in Jiangxi Province, China from 2020 to 2022. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaisinghani, R.N. Antibacterial properties of quercetin. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 8, 6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.X.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Y.J.; Wei, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Long, T.F.; He, Q.; Li, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.F.; Yu, Y.; et al. Natural flavonoids disrupt bacterial iron homeostasis to potentiate colistin efficacy. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaojun, T.; Jingyu, Z.; Nuo, S.; Xiang-Ming, W.; Qi, W.; Yu, Z.; Ren, H.; Yingying, P.; Huanqin, D.; Biao, R.; et al. Berberine reverses multidrug resistance in Candida albicans by hijacking the drug efflux pump Mdr1p. Sci. Bull. 2020, 66, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Tripathi, A. Quercetin inhibits carbapenemase and efflux pump activities among carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2020, 128, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenazy, R. Drug Efflux Pump Inhibitors: A Promising Approach to Counter Multidrug Resistance in Gram-Negative Pathogens by Targeting AcrB Protein from AcrAB-TolC Multidrug Efflux Pump from Escherichia coli. Biology 2022, 11, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarralde-Guerrero, M.; Taraveau, F. Role of AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump in drug-resistance acquisition by plasmid transfer. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 945–947. [Google Scholar]
- Chetri, S.; Bhowmik, D.; Paul, D.; Pandey, P.; Chanda, D.D.; Chakravarty, A.; Bora, D.; Bhattacharjee, A. AcrAB-TolC efflux pump system plays a role in carbapenem non-susceptibility in Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Levy, S.B. Many chromosomal genes modulate MarA-mediated multidrug resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang, Z.; James, N.R.; Voss, J.E.; Klimont, E.; Ohene-Agyei, T.; Venter, H.; Chiu, W.; Luisi, B.F. Structure of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump. Nature 2014, 509, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridou, V.; King, M.S.; Bazzone, A.; Springett, R.; Kunji, E.R.S. Membrane potential stimulates ADP import and ATP export by the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier due to its positively charged binding site. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadp7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damper, P.D.; Epstein, W. Role of the membrane potential in bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 20, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.-H.P.J. Spatially structured exchange of metabolites enhances bacterial survival and resilience in biofilms. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, M.; Gudmundsdottir Jonina, S.; Nilsson, T.; König, F.; Warsi, O.; Rajer, F.; Ädelroth, P.; Andersson Dan, I. De Novo Emergence of Peptides That Confer Antibiotic Resistance. mBio 2019, 10, 10.1128/mbio.00837-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, S.-F.; Xiang, J.; Zeng, Y.-Y.; Peng, X.-X.; Li, H. Elevated Membrane Potential as a Tetracycline Resistance Mechanism in Escherichia coli. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 2196–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Fu, R.; Buhe, A.; Xu, B. Quercetin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic inflammation by modulating autophagy and necroptosis. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, F.A.; Maccagni, E.A.; Puccio, S.; Peano, C.; De Castro, C.; Palmigiano, A.; Garozzo, D.; Martorana, A.M.; Polissi, A.; Dehò, G.; et al. Mutation and Suppressor Analysis of the Essential Lipopolysaccharide Transport Protein LptA Reveals Strategies to Overcome Severe Outer Membrane Permeability Defects in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, 10.1128/jb.00487-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberta, T.M. Identification of Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in pmrC-, pmrA-, and pmrB-Deficient Acinetobacter Baumannii. Master’s Thesis, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-dependent effects of polystyrene microplastics on cytotoxicity and efflux pump inhibition in human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, K.; Prasad, T.; Saini, P.; Pucadyil Thomas, J.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Prasad, R. Membrane Sphingolipid-Ergosterol Interactions Are Important Determinants of Multidrug Resistance in Candida albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1778–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, L.J.; Ferreira, M.; Gameiro, P. Evaluation of membrane fluidity of multidrug-resistant isolates of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in presence and absence of antibiotics. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 181, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.C.; Rastogi, P.; Beckett, C.S.; McHowat, J. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çomaklı, S.; Küçükler, S.; Değirmençay, Ş.; Bolat, İ.; Özdemir, S. Quinacrine, a PLA2 inhibitor, alleviates LPS-induced acute kidney injury in rats: Involvement of TLR4/NF-κB/TNF α-mediated signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 126, 111264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sheng, W.; He, Y.; Cui, J.; Haidekker, M.A.; Sun, G.Y.; Lee, J.C. Secretory phospholipase A2 type III enhances alpha-secretase-dependent amyloid precursor protein processing through alterations in membrane fluidity. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabadie, H.; Motta, C.; Peuchant, E.; LeRuyet, P.; Mendy, F. Variations in daily intakes of myristic and alpha-linolenic acids in sn-2 position modify lipid profile and red blood cell membrane fluidity. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 96, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ramirez, D.L.; Carmona-Salazar, L.; Morales-Cedillo, F.; Ramírez-Salcedo, J.; Cahoon, E.B.; Gavilanes-Ruíz, M. Plasma Membrane Fluidity: An Environment Thermal Detector in Plants. Cells 2021, 10, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berraquero, M.; Tallada, V.A.; Jimenez, J. Ltc1 localization by EMC regulates cell membrane fluidity to facilitate membrane protein biogenesis. iScience 2025, 28, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-B.; Ye, B.-C. High-level iron mitigates fusaricidin-induced membrane damage and reduces membrane fluidity leading to enhanced drug resistance in Bacillus subtilis. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinthia, A.; Ihosvany, C. Molecular Docking in Drug Discovery: Techniques, Applications, and Advancements. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025, 32, 5924–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Gu, F.; Guo, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; et al. Exploiting an evolutionary constraint: Targeting TatD nuclease with chrysosplenol D disrupts Mycoplasma gallisepticum infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 321, 146394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanpaibool, C.; Ounjai, P.; Yotphan, S.; Mulholland, A.J.; Spencer, J.; Ngamwongsatit, N.; Rungrotmongkol, T. Enhancement by pyrazolones of colistin efficacy against mcr-1-expressing E. coli: An in silico and in vitro investigation. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2023, 37, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
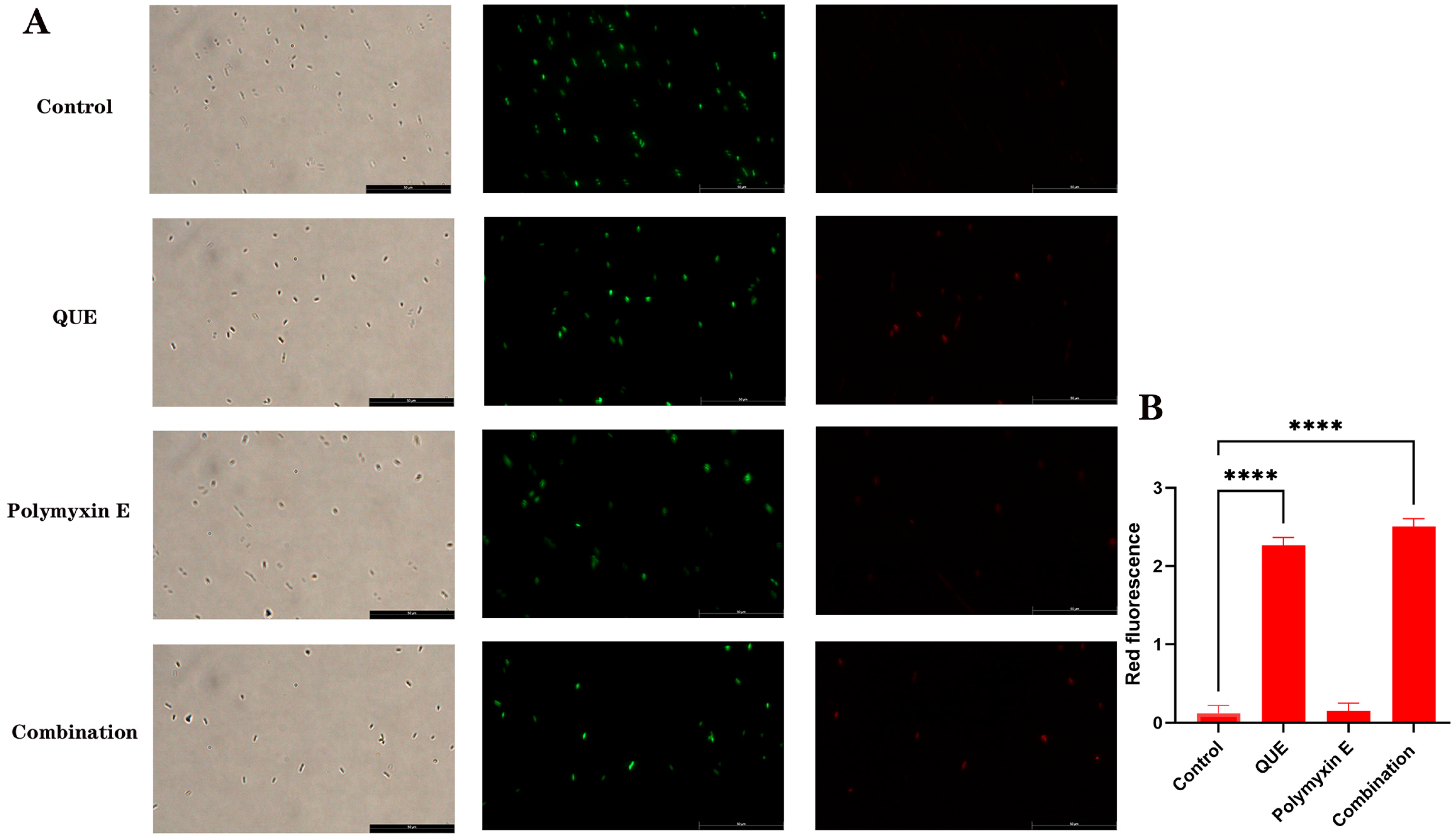
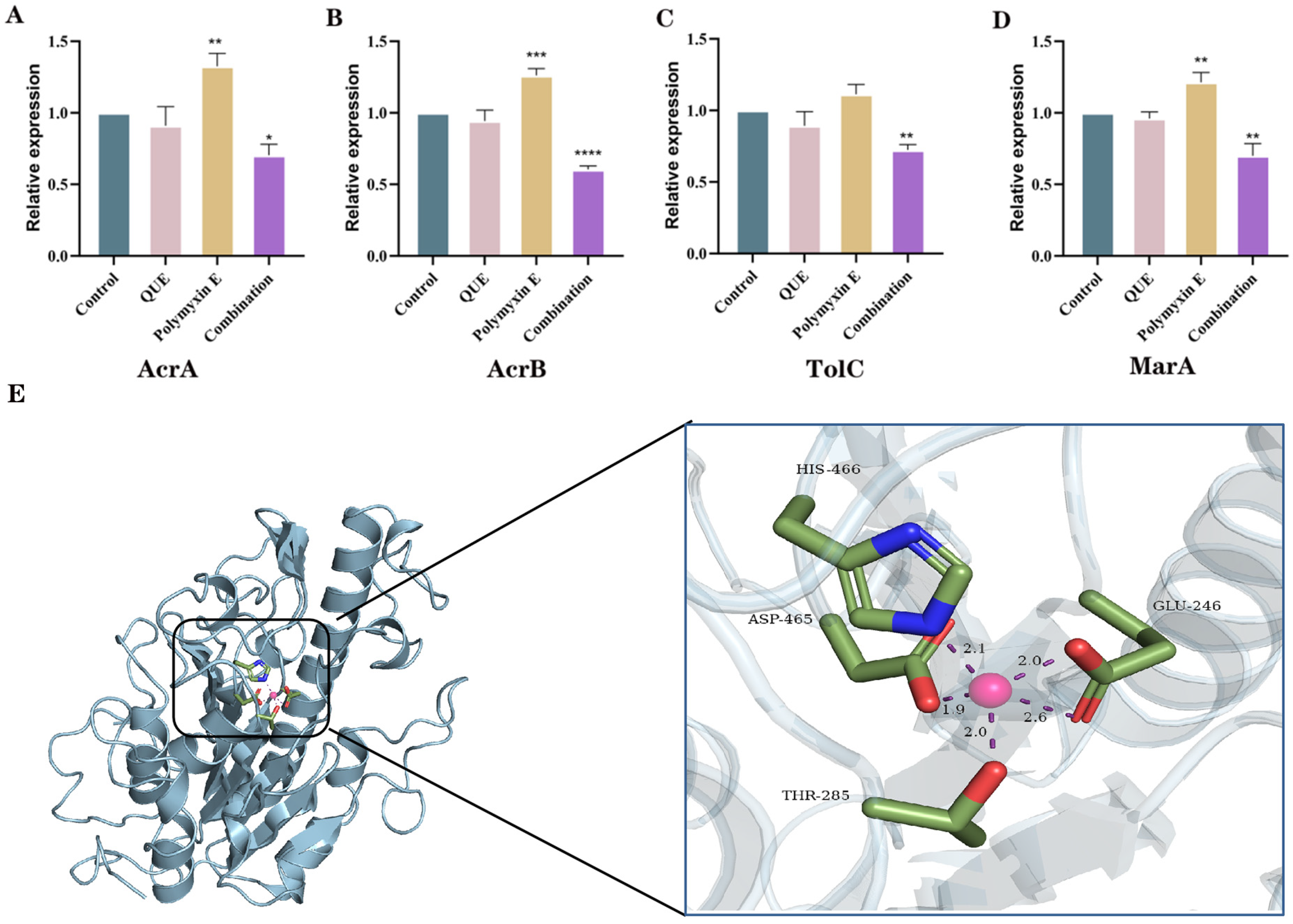
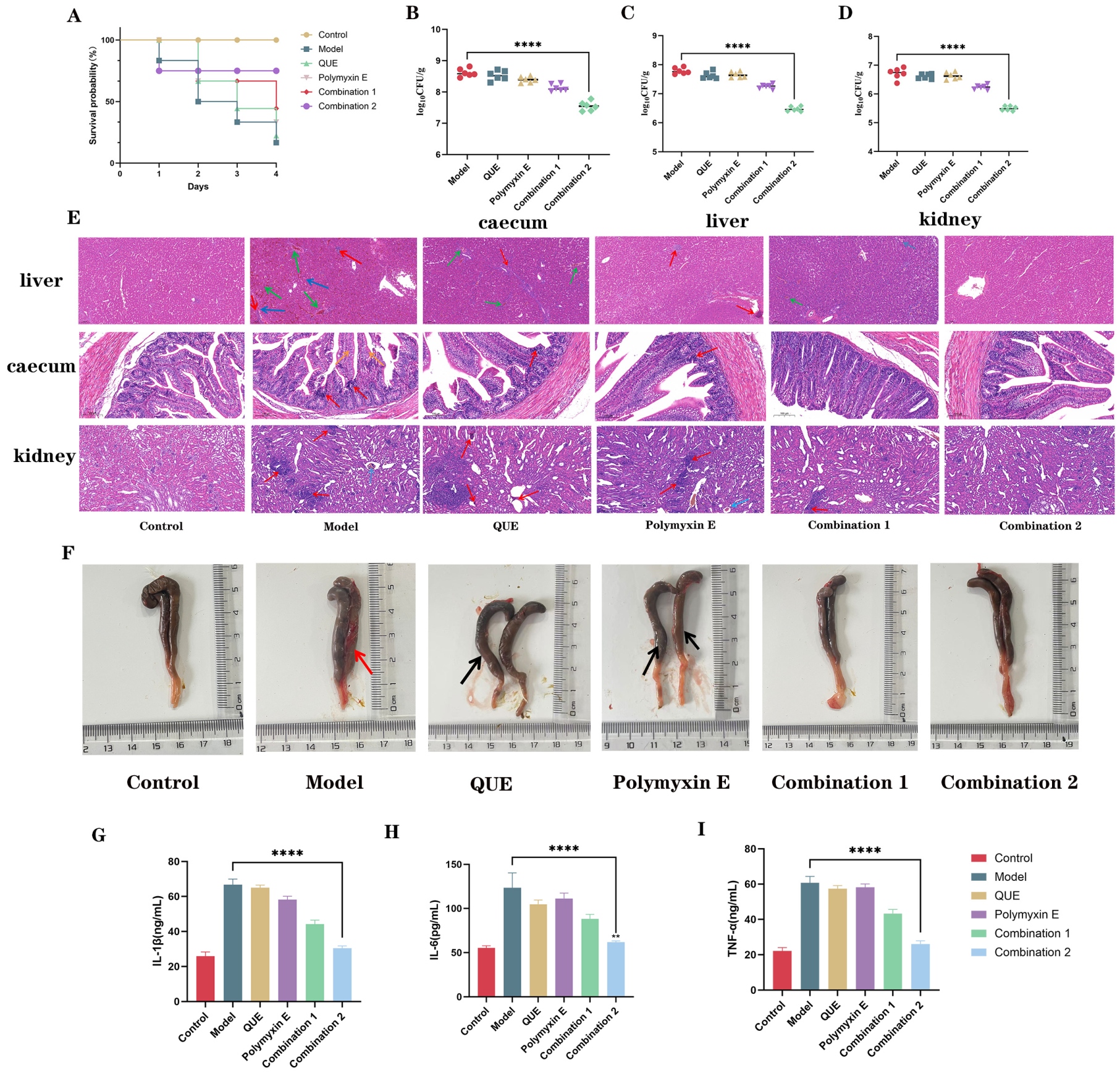
| Primer Name | Oligonucleotide (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| acrA | F:CTTAGCCCTAACAGGATGTG R:TTGAAATTACGCTTCAGGAT |
| acrB | F:GAGAAGAGCACGCACCACTACAC R:GGCAGACGCACGAACAGATAGG |
| TolC | F:GGTACGTTGAACGAGCAGGATC R:CCATCAGCAATAGCATTCTGTTCC |
| PmrA | F:CCTTTTGCGCTGGAAGAGT R:TCTTTGGGCGTCAGAATCAAC |
| PmrB | F:CTGCAAGAAGATGACGGAGC R:CTGTGTAATGCGGCTGACCA |
| 16sRNA | F:CTCTTGCCATCAGATGTGCC R:TTCTTCATACACGCGGCATG |
| MCR-1 | F:ATGATGCAGCATACTTCTGTGTG R:TCAGCGGATGAATGCGGTGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Li, R.; Li, J.; Chen, C. Quercetin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Polymyxin E Against MCR-1-Positive Bacteria by Inhibiting the Biological Functions of the Cell Membrane. Animals 2025, 15, 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233491
Zhang Y, Guo L, Wang S, Zhang J, Ren X, Li R, Li J, Chen C. Quercetin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Polymyxin E Against MCR-1-Positive Bacteria by Inhibiting the Biological Functions of the Cell Membrane. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233491
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yongjie, Liyang Guo, Shun Wang, Jie Zhang, Xinlei Ren, Rui Li, Jichang Li, and Chunli Chen. 2025. "Quercetin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Polymyxin E Against MCR-1-Positive Bacteria by Inhibiting the Biological Functions of the Cell Membrane" Animals 15, no. 23: 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233491
APA StyleZhang, Y., Guo, L., Wang, S., Zhang, J., Ren, X., Li, R., Li, J., & Chen, C. (2025). Quercetin Enhances the Antibacterial Activity of Polymyxin E Against MCR-1-Positive Bacteria by Inhibiting the Biological Functions of the Cell Membrane. Animals, 15(23), 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233491






