Overview of Donkey Welfare and Husbandry Practices in Asia
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology for Literature Search
3. Demographics and Population Distribution of Donkeys in Asia
4. Donkey Welfare Management in Asia
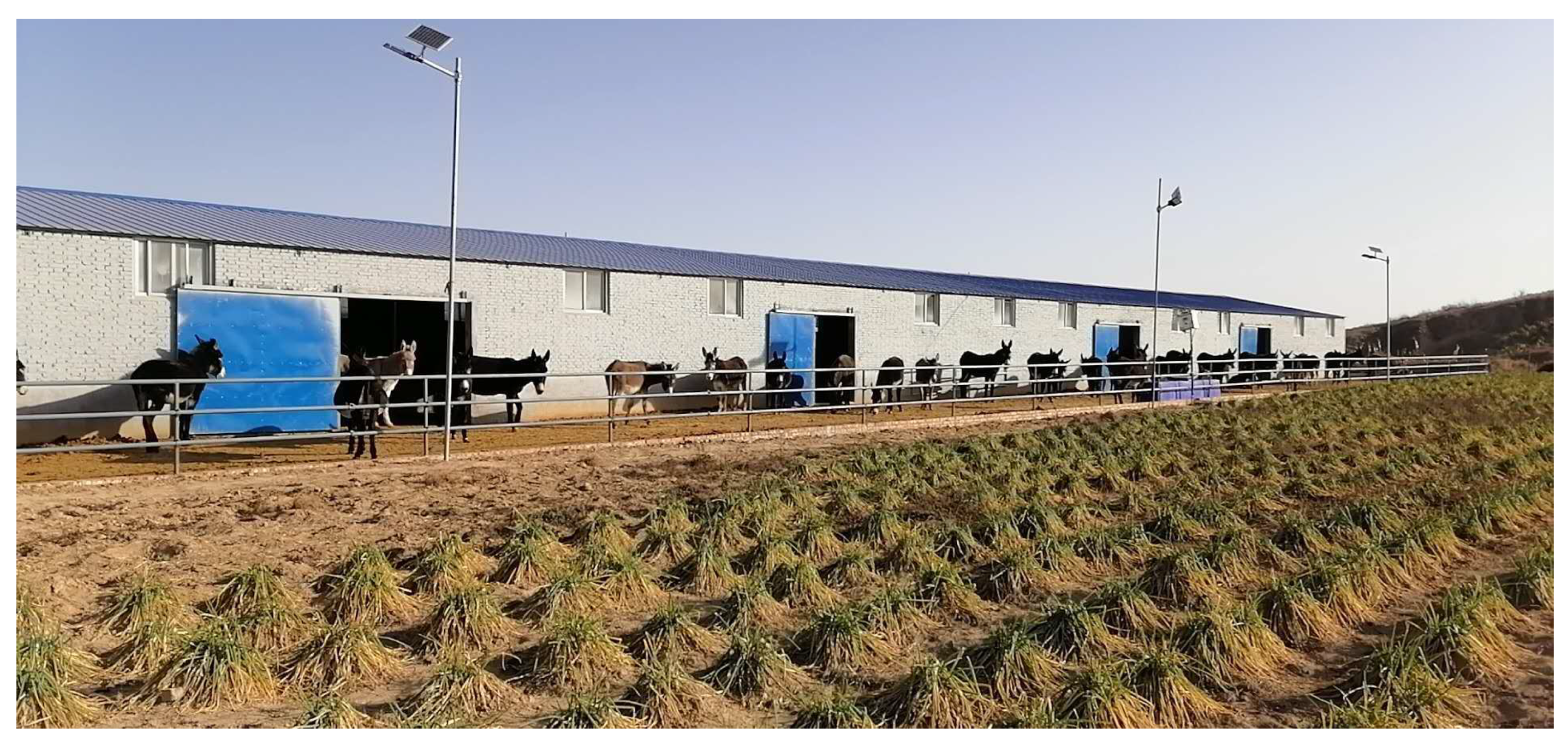
4.1. Shelter and Feeding Management of Donkeys in Asia
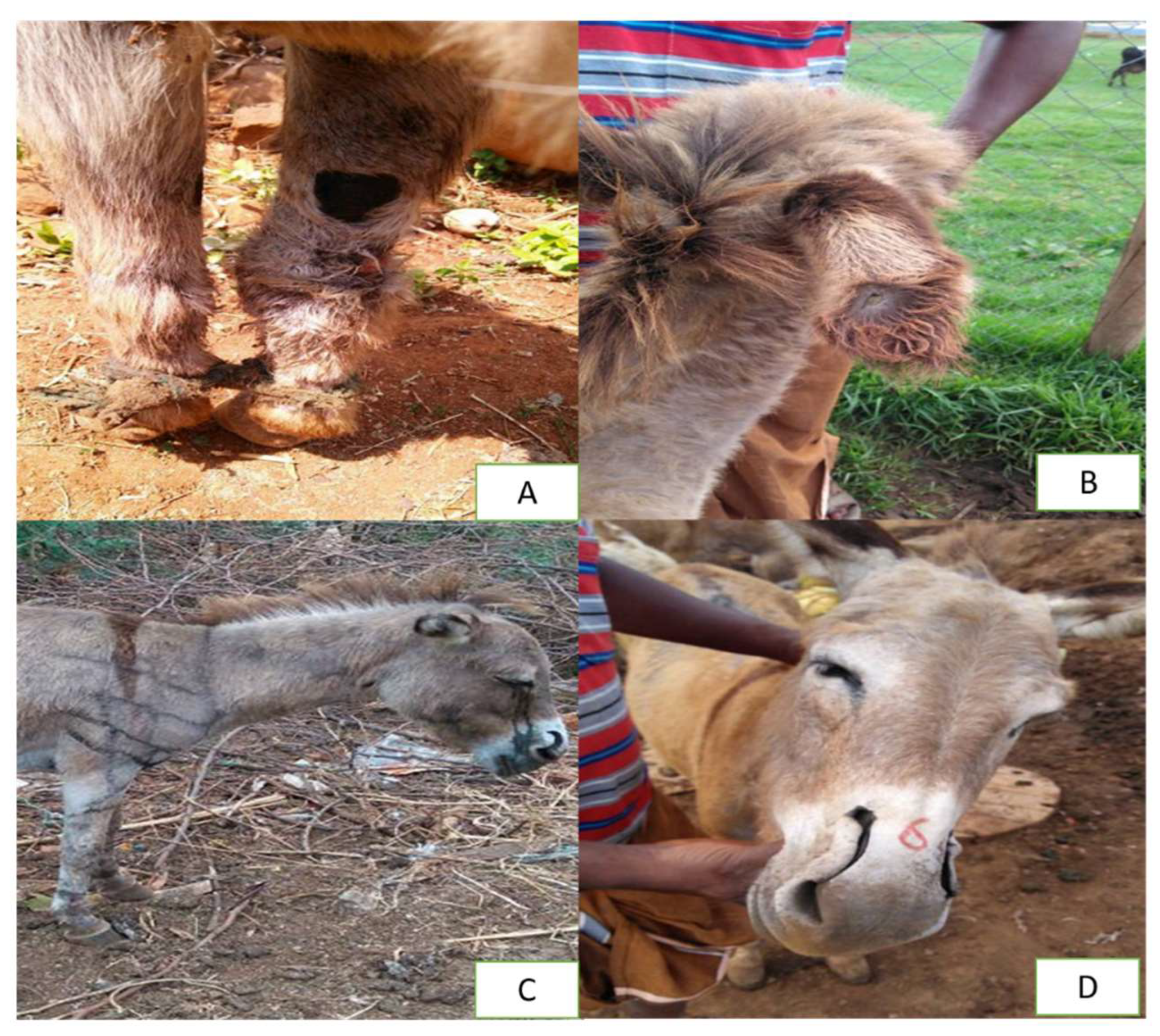
4.2. Health and Disease Management of Donkeys in Asia
| Region/Country | Welfare Improvement Challenges | Preventive Healthcare Practices | Welfare Improvement Measures | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pakistan | Poor shelter, inadequate nutrition, lack of veterinary care, overloading, wounds, hoof problems | Low vaccination and deworming rates; minimal preventive care awareness | Owner education, shelter improvements, farriery training, veterinary access | [26,79] |
| India | Overworking in brick kilns, poor shelter, irregular feeding, lack of veterinary services | Limited vaccination (tetanus, influenza); poor access to vets | Improved feeding, water access, shelter, community training programs | [7,20,38] |
| Afghanistan | Basic shelters, poor feed quality, parasitic infections, limited vet outreach | Minimal vaccination; absence of national programs | Awareness campaigns, improved feed and shelter, training for farmers | [40] |
| China | Housing deficiencies, limited vaccination, parasitic and viral infections, inconsistent feeding standards | Low vaccination (none in surveyed farms); 37.9% no deworming | Structured welfare programs, improved housing, adoption of total mixed ration feeding, biosecurity reinforcement | [54,80,114,115] |
| Iran | Parasitic infections (Giardia, helminths), reproductive losses (Neospora caninum), and limited welfare research | General livestock vaccination applies to equids; limited equine-specific programs | Enhanced hygiene, targeted Parasite control, better reproductive monitoring | [87,88] |
| Central Asia (Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan) | Small populations, limited management systems, and minimal welfare documentation | Not well documented; presumed minimal preventive care | Regional welfare documentation and management program development | [116,117] |
4.3. Vaccination Strategies
5. Reproduction and Breeding Practices
6. Donkey Overwork and Ethical Considerations in Asia
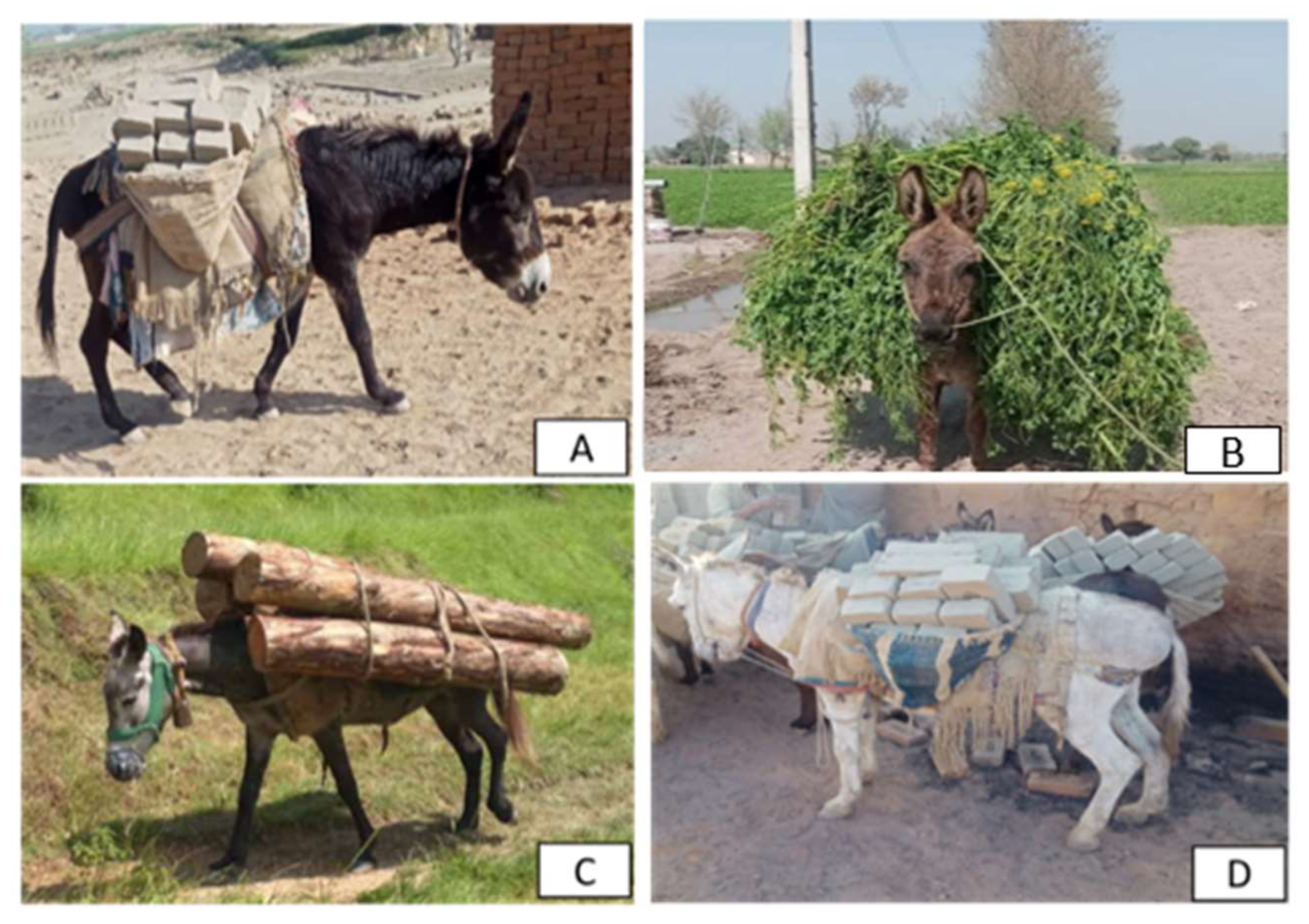

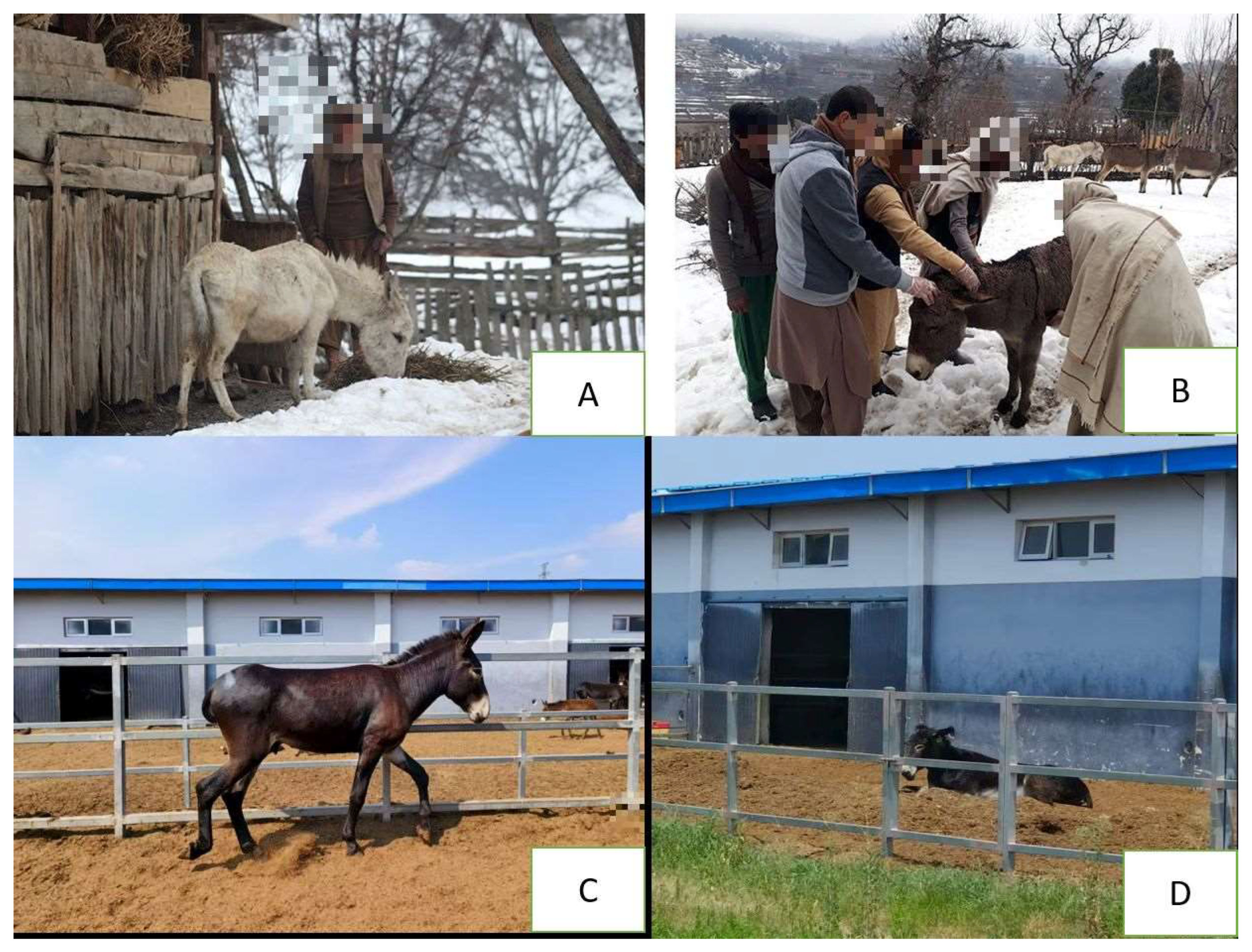
7. Donkey Conservation Efforts in Asia
8. Recommendations for Improving Donkey Welfare in Asia
| Region/Country | Reproduction and Breeding Practices | Overwork and Ethical Concerns | Conservation Status and Key Drivers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pakistan | Natural service is predominant; AI is rarely used due to financial and technical constraints. Hormonal induction (GnRH, hCG, PG) is effective but not applied widely. Low genetic selection and unstructured breeding programs. | Severe overloading, poor farriery, and inadequate access to veterinary care. Welfare affected by poverty; owners show partial awareness of donkey pain and emotions | No formal conservation programs; population threatened by neglect, disease, and mechanization. Conservation is mainly achieved indirectly through welfare improvement. | [7,14,61,79,84,85] |
| India | Traditional, utility-driven breeding. Little use of selective breeding or reproductive technologies. Weak record-keeping. | Brick-kiln donkeys exposed to harsh conditions, punishment, poor nutrition, and extreme workloads. Ethical concerns tied to marginalized socioeconomic groups. | Fragmented conservation efforts; limited documentation. Mechanization and social marginalization contribute to population decline. | [20,38,62] |
| Afghanistan | Entirely traditional and unregulated mating. No structured breeding programs; minimal veterinary involvement; low foal survival rates. | Heavy dependence on donkeys due to poverty; widespread neglect, overloading, and lack of healthcare. | Very limited conservation documentation; population vulnerable due to poverty and conflict. | [40] |
| China | Highly modernized breeding sector. AI widely used in large farms (70–92% conception rates). Genomic tools, hormonal protocols, and structured breeding centers established. Strong government subsidy support. | Ethical issues linked to the ejiao industry and transport/slaughter conditions. Nutritional mismanagement may lead to metabolic disorders (laminitis, hyperlipemia). | Strong national conservation framework: 24 indigenous breeds preserved; multi-tier breeding centers; formal welfare standard (SN/T 5485-2022) implemented. Mechanization reduces traditional use. | [41,43,54,125,141,142] |
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aroua, M.; Ben Said, S.; Mahouachi, M. Donkeys: Unsung Heroes of Agriculture, Health, and Sustainability in a Changing World. SSAR J. Arts Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2025, 2, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hua, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, C. Origin, evolution, and research development of donkeys. Genes 2022, 13, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.T.; Tonasso-Calvière, L.; Chauvey, L.; Schiavinato, S.; Fages, A.; Seguin-Orlando, A.; Clavel, P.; Khan, N.; Pérez Pardal, L.; Patterson Rosa, L. The genomic history and global expansion of domestic donkeys. Science 2022, 377, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyiti, S.; Kelimu, A. Donkey industry in China: Current aspects, suggestions and future challenges. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 102, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marincheva, V. European perspectives in donkey husbandry and breeding with insights from Bulgaria. Bulg. J. Anim. Husb. 2025, 62, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-S.; Yang, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-B.; Zhang, C.-M.; Qin, F.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Lan, X.-Y.; Chen, H.; Lei, C.-Z. Cytochrome b genetic diversity and maternal origin of Chinese domestic donkey. Biochem. Genet. 2010, 48, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmy, K.; Ravichandran, T.; Rahman, H.; Perumal, R.K. Policy dialogues for donkeys and their owning communities in India. In Donkey & Non-Bovine Milk; ILRI-NRCC Publication: Bikaner, India, 2024; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Z.; Chen, W.; Li, M.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Ullah, Q.; Wei, L.; Wang, T.; Khan, A. Is there sufficient evidence to support the health benefits of including donkey milk in the diet? Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1404998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, L.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, W.; Man, L.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C. Characterization and discrimination of donkey milk lipids and volatiles across lactation stages. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Liang, H.; Zahoor Khan, M.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Xing, S.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, C. Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis unveils the interplay of mRNA and LncRNA expression in shaping collagen organization and skin development in Dezhou donkeys. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1335591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Akhtar, F.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Shi, X.; Ren, W. Polymorphism detection of PRKG2 gene and its association with the number of thoracolumbar vertebrae and carcass traits in Dezhou donkey. BMC Genom. Data 2023, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Wei, L.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, W. A review of genetic resources and trends of omics applications in donkey research: Focus on China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1366128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Ma, Q.; Wang, C. Advances in Donkey Disease Surveillance and Microbiome Characterization in China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.S.; Rosanowski, S.M.; McElligott, A.G.; Parkes, R.S. Welfare concerns for mounted load carrying by working donkeys in Pakistan. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 886020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Y.; Mohamed, S.; Mohamud, A.; Mohamud, A.; Jimale, K.; Ibrahim, S.A. Assessment of welfare and health conditions on working donkeys in Benadir region, Somalia. Vet. Sci. Res. Rev. 2021, 7, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClaughlin, E.; Clancy, C.; Cooke, F. Donkey discourse: Corpus linguistics and charity communications for improved animal welfare. Appl. Corpus Linguist. 2022, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, Z.; Nóvoa, M.; Leiva, B.; Andrade, D.; Quaresma, M. Donkey welfare assessment in north-east Portugal. Anim. Welf. 2021, 30, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, M.; Hockenhull, J.; Buller, H.; Kedir, M.J.; Engida, G.T.; Getachew, M.; Burden, F.; Whay, H. Comparison of the socio-economic value and welfare of working donkeys in rural and urban Ethiopia. Anim. Welf. 2021, 30, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, T.; Perumal, R.K.; Kennady, V.; Baltenweck, I.; Wright, I.A.; Burden, F.; Rahman, H. Mapping the Indian Donkey and Mule Population and Potential Intervention Strategies and Partners; International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI): Nairobi, Kenya, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, T.L.; Kubasiewicz, L.M.; Chamberlain, N.; Nye, C.; Raw, Z.; Burden, F.A. Cultural “blind spots,” social influence and the welfare of working donkeys in brick kilns in northern India. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, T.; Kubasiewicz, L.M.; Nye, C.; Thapa, S.; Chamberlain, N.; Burden, F.A. The welfare and access to veterinary health services of mules working the mountain trails in the Gorkha region, Nepal. Austral J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 55, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z. Silent Workers of Somalia: Health, Welfare and the Epidemiological Implications of Donkey Use. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. Diagn. 2025, 6, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Raspa, F.; Cavallarin, L.; McLean, A.K.; Bergero, D.; Valle, E. A review of the appropriate nutrition welfare criteria of dairy donkeys: Nutritional requirements, farm management requirements and animal-based indicators. Animals 2019, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G.; Burden, F.A. Practical donkey and mule nutrition. Equine Appl. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 1, 304–316. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, M. A Survey on Major Health and Management Problems of Donkeys under Traditional Husbandry System at Selected Sites in Central Highland of Ethiopia. Int. J. Sci. Basic Appl. Res. 2017, 31, 28–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kamran, K.; Akbar, A.; Naseem, M.; Samad, A.; Samiullah; Achakzai, J.K.; Rehman, Z.U.; Sohail Sajid, M.; Ali, A. Participatory appraisal for healthcare and welfare management strategies of donkeys (Equus ascinus) in Balochistan, Pakistan. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1005079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrandeguy, M.E.; Carossino, M. Infectious diseases in donkeys and mules: An overview and update. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, J.; Gerber, V.; Hungerbühler, V.; Schaefler, S.; Unger, L. Management, health, and veterinary care of donkeys in Switzerland: A cross-sectional study. Schweiz. Arch. Für Tierheilkd 2024, 166, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perzyna, M.; Grzędzicka, J.; Milczek-Haduch, D.; Dąbrowska, I.; Trela, M.; Pawliński, B.; Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O. Immunological Responses to Tetanus and Influenza Vaccination in Donkeys. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2025, 39, e70137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.B.; De Blas Giral, I.; Thiemann, A.K.; Vázquez Bringas, F. Demography, preventative healthcare and reason for relinquishment of donkeys to an equine charity in the UK (2013–2015). Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onono, J.O.; Kithuka, J. Assessment of provision of extension services and advocacy on donkey health and welfare in Kenya. Asian J. Agric. Ext. Econ. Sociol. 2020, 38, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguma, B.E.; Price, S.J.; Blakeway, S. Improving donkey welfare in Ethiopia: Using a sustainable scalable integrated community-based approach. CABI One Health 2025, 4, 0009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsi, M.; Anderson, N.E.; Carder, G. The socioeconomic impact of diseases of working equids in low and middle-income countries: A critical review. Animals 2023, 13, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raw, Z.; Collins, J.A.; Burden, F.A. What is a working equid? analysis of current terminology and a suggested definition. Animals 2024, 14, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masebo, N.T.; Benedetti, B.; Angeloni, M.G.; Lee, L.; Bigi, D.; Padalino, B. Systematic Literature Review on Donkeys (Equus asinus): Husbandry and Welfare in Europe. Animals 2025, 15, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.; Ayesha, A.; Rahman, H.U.; Murtaza, I.; Manzoor, H.; Aqdas, A.; Dawoud, T.M.; Mehmood, R.; Shahzadi, W.; Ullah, S. Molecular detection and genetic diversity of blood borne pathogens infecting domestic donkeys (Equus asinus). Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2025, 57, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, A.; Verma, A.; Odedra, M.; Sabapara, G.; Padodara, R.; Mane, D. Dwindling population of indian working equines: A worrying trend. Indian J. Vet. Anim. Sci. Res. 2024, 53, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasiewicz, L.M.; Watson, T.; Nye, C.; Chamberlain, N.; Perumal, R.K.; Saroja, R.; Norris, S.L.; Raw, Z.; Burden, F.A. Bonded labour and donkey ownership in the brick kilns of India: A need for reform of policy and practice. Anim. Welf. 2023, 32, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Review, W.P.; Donkey Population by Country. World Population Review. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/donkey-population-by-country (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Ahmadzai, M.R.; Ismail, M.H.; Hassan Zaki, P.; Magiman, M.M.; Bawon, P.; Rahmawaty Ullah, H. Transforming livestock production: Unraveling the impact of socioeconomic dynamics and land use changes in Khost Province. J. Land Use Sci. 2025, 20, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. A survey report on the donkey original breeding farms in China: Current aspects and future prospective. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1126138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Ren, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Chai, W. An investigation of genetic diversity in three Dezhou donkey original breeding farms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wei, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Wei, J.; Zhu, M.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Nutritional Composition and Biological Activities of Donkey Milk: A Narrative Review. Foods 2025, 14, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T.; Zhao, Z.-Z. History of the Chinese medicinal gelatin. Chin. Med. Cult. 2022, 5, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.; Pfuderer, S. The potential for new donkey farming systems to supply the growing demand for hides. Animals 2020, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wong, S.K.; Wang, T.; Chin, K.-Y. A Comprehensive Review of Traditional Chinese Medicine Ejiao (Colla Corii Asini): Chemical Composition, Quality Control, and Pharmacological Actions. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2025, 20, 1934578X251335424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Dong, J.; Cao, Y.; Sun, Y. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and indels identified from whole-genome re-sequencing of four Chinese donkey breeds. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusugli, E.J. Development of transportation types and their usage on caravan roads in middle ages. Int. J. Integr. Educ. J. 2020, 3, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Crossley, P. The Influence of Central Asia on Horse Use. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Asian History; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Clancy, C.L.; Kubasiewicz, L.M.; Raw, Z.; Cooke, F. Science and knowledge of free-roaming donkeys—A critical review. J. Wildl. Manag. 2021, 85, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Khamesipour, F.; Taktaz-Hafshejani, T.; Tebit, K.E.; Razavi, S.M.; Hosseini, S.R. Prevalence of endo-and ecto-parasites of equines in Iran: A systematic review. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abood, D.A.; Dawood, M.S.; Mohammed, L.E.; Karim, A.J. Histological and histochemical characteristics of the esophagus in local breed donkey (Equus asinus). J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2023, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Meshgi, B.; ESLAMI, A.; Bokaei, S.; Sobhani, M.; Agha, E.S.R. Prevalence and biodiversity of helminth parasites in donkeys (Equus asinus) in Iran. Int. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Shi, S.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Han, Y.; Xie, P. A survey of smallholder farms regarding demographics, health care, and management factors of donkeys in northeastern China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 626622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/ (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Rodrigues, J.B.; Raw, Z.; Santurtun, E.; Cooke, F.; Clancy, C. Donkeys in transition: Changing use in a changing world. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2021, 58, e174325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Live Animals (Data). Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/ (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- FAOSTAT. Crop and Livestock Statistics. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Haddy, E.; Burden, F.; Prado-Ortiz, O.; Zappi, H.; Raw, Z.; Proops, L. Comparison of working equid welfare across three regions of Mexico. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.; Burden, F.; Proudman, C.; Trawford, A.; Pinchbeck, G. Demographics, management and health of donkeys in the UK. Vet. Rec. 2010, 166, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.Z.U.; Rosanowski, S.M.; Saleem, W.; Parkes, R.S.V. Cross-sectional questionnaire of donkey owners and farriers regarding farriery practices in the Faisalabad region of Pakistan. Animals 2022, 12, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasiewicz, L.; Watson, T.; Norris, S.; Chamberlain, N.; Nye, C.; Perumal, R.; Saroja, R.; Raw, Z.; Burden, F. One welfare: Linking poverty, equid ownership and equid welfare in the brick kilns of India. Anim. Welf. 2022, 31, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, S.F.; McLean, A.K.; Mahmoud, H.F. Welfare assessment and identification of the associated risk factors compromising the welfare of working donkeys (Equus asinus) in egyptian brick kilns. Animals 2020, 10, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y.; Khan, M.Z.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Kou, X.; Wang, L. Elucidating the role of transcriptomic networks and DNA methylation in collagen deposition of Dezhou donkey skin. Animals 2024, 14, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Luo, X.; Yue, X. Characterization and nutrition assessment of amino acids in different domains between donkey colostrum and mature milk. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Effects of donkey milk on oxidative stress and inflammatory response. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, F.; Du, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Analysis of the differentially expressed proteins in donkey milk in different lactation stages. Foods 2023, 12, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Sun, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y. Effects of roughage on the lipid and volatile-organic-compound profiles of donkey Milk. Foods 2023, 12, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Ning, J.; Bai, X.; Cao, X.; Yue, X.; Yang, M. Identification and analysis of miRNAs expression profiles in human, bovine, and donkey milk exosomes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, L.; Du, X.; Ren, W.; Man, L.; Chai, W.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Characterization of lipids and volatile compounds in boiled donkey meat by lipidomics and volatilomics. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, M.; Gong, Y.; Wang, C. Identification and functional prediction of lncRNAs associated with intramuscular lipid deposition in Guangling donkeys. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1410109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, Q.; Khan, M.Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Chai, W. Data-independent acquisition method for in-depth proteomic screening of donkey meat. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.; Qu, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yao, H.; Li, Z. RNA-seq analysis identifies differentially expressed gene in different types of donkey skeletal muscles. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, N.; Wei, Z.; Liu, G. Study on the Extracting Technology for Antioxidant Oligopeptides from Donkey Meat by Two-Step Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Pak. J. Zool. 2022, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Gao, N.; Waller, A.S.; Cook, F.; Fan, S.; Yuan, D.; Du, Y.; Li, F.; Norimine, J.; Zhu, W. An outbreak of strangles associated with a novel genotype of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi in donkeys in China during 2018. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterková, H. The Role of the Donkey in the Development of Rural Communities and its Potential within Animal-Assisted Interventions. Bachelor’s Thesis, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Tropical AgriSciences, Prague, Czechia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Molla, B.; Dembela, S.; Megersa, B.; Mekuria, W. The welfare, watering, housing, feeding and working management of working donkeys in and around Hawassa City, Southern Ethiopia. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Husb. 2017, 2, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Union, A. Awin Welfare Assessment Protocol for Donkeys. Available online: https://air.unimi.it/retrieve/handle/2434/269100/384805/AWINProtocolDonkeys.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Bukhari, S.S.; Rosanowski, S.M.; McElligott, A.G.; Parkes, R.S. Welfare concerns with mounted load carrying by working donkeys. In Proceedings of the 55th Congress of the International Society of Applied Ethology (ISAE 2022), Ohrid, North Macedonia, 4–8 September 2022; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2019; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Shi, L.; Guo, W.; Xu, Y.; Jin, X.; Yan, S.; Shi, B. Effects of housing and management systems on the growth, immunity, antioxidation, and related physiological and biochemical indicators of donkeys in cold weather. Animals 2022, 12, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Xie, L.; Xing, J.; Lu, T.; Qi, X.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Akhtar, M.F.; Jin, Y.; Liu, G. Effects of concentrate feeding sequence on VFA production, and cecal microbiota of Dezhou donkeys by metagenomic technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1401980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Khan, M.Z.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H.; Kou, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Yeast polysaccharide supplementation: Impact on lactation, growth, immunity, and gut microbiota in Dezhou donkeys. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1289371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.Z.U.; Rosanowski, S.M.; Parkes, R.S.V. Hoof morphometry in a population of lame and nonlame working donkeys in Pakistan. Equine Vet. J. 2023, 55, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.Z.A.; Nawaz, Z.; Nawaz, S.; Carder, G.; Ali, M.; Soomro, N.; Compston, P.C. The role and welfare of cart donkeys used in waste management in Karachi, Pakistan. Animals 2019, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, E.L.; Airikkala-Otter, I.; Susheelan, A.; Mellanby, R.J.; Meunier, N.V.; Gibson, A.; Gamble, L. Prevalence of mutilations and other skin wounds in working donkeys in Tamil Nadu, India. Vet. Rec. 2018, 183, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, A.; Yousefi, A.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Badali, R.; Shamsi, L.; Köseoğlu, A.E.; Abbaszadeh, A.; Shams, M.; Mohammadi-Ghalehbin, B. Comparative molecular epidemiology, subtype distribution, and zoonotic potential of Blastocystis sp. in Equus animals (horses, donkeys, and mules) in northwestern Iran. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 106, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazmand, A.; Bahari, A.; Papi, S.; Otranto, D. Parasitic diseases of equids in Iran (1931–2020): A literature review. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.S.; Malekifard, F.; Tavassoli, M. Neospora caninum, a cause of abortion in donkeys (Equus asinus) in Iran. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, A.A.; Derakhshanfar, A.; Mohammadpour, O.; Hadadipour Zarandi, M. First Report of Idiopathic Advanced Follicular Atrophy of the Thyroid Gland in Three Miniature Donkeys. Vet. Comp. Biomed. Res. 2025, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W. Detection of equine herpesvirus antibodies in large-scale donkey farms in Liaocheng area. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e70016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, S.; Ma, H.; Akhtar, M.F.; Tan, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C. An overview of infectious and non-infectious causes of pregnancy losses in equine. Animals 2024, 14, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tuo, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, F.; Chuai, L.; Qi, M.; Jing, B. Occurrence and genetic characteristics of Giardia duodenalis in donkeys in Xinjiang, China. Parasite 2023, 30, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Sun, Y.; Cui, L.; Meng, X.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, F.; Li, J. Abortion in donkeys associated with Salmonella abortus equi infection. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xi, C.; Geng, Y.; Tian, W.; Li, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, J. Pathogenicity and host cytokines response of EqHV-8 infection in C57BL/6J mice. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 186, 106506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, T.; Ren, H.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Characterizing the pathogenesis and immune response of equine herpesvirus 8 infection in lung of mice. Animals 2022, 12, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Geng, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Heme oxygenase-1 is an equid alphaherpesvirus 8 replication restriction host protein and suppresses viral replication via the PKCβ/ERK1/ERK2 and NO/cGMP/PKG pathway. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03220–e03223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Xu, M. Rutin prevents EqHV-8 induced infection and oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1386462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cui, X.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C. Blebbistatin as a novel antiviral agent targeting equid herpesvirus type 8. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1390304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hu, L.; Li, R.; Ren, H.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Hyperoside inhibits EHV-8 infection via alleviating oxidative stress and IFN production through activating JNK/Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e00159-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shen, F.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. Cobalt Protoporphyrin blocks EqHV-8 infection via IFN-α/β production. Animals 2023, 13, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, P.; Zhao, F.; Yan, S.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Hao, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, H.; Tang, M.; Hui, W. Detection of hepatitis E virus genotypes 3 and 4 in donkeys in northern China. Equine Vet. J. 2020, 52, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.-J.; Li, J.; Tu, Q.-H.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.-L.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.-H.; Xiao, Y.-Q. Identification of a novel astrovirus from intestinal tissue of a donkey foal with severe diarrhea in China. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.-W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.-H.; Xiao, H.-D.; Su, N.; Tao, M.-F.; Wu, Z.-X.; Zhang, Z.-D.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Xie, S.-C. Prevalence and multilocus genotyping of Giardia duodenalis in donkeys in Shanxi Province, North China. Animals 2023, 13, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Cao, M.; Yu, F.; Zhao, A.; Tao, D.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, M. Molecular detection of piroplasms in domestic donkeys in Xinjiang, China. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.-M.; Ma, J.-G.; Li, F.-C.; Hou, J.-L.; Zheng, W.-B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.-X.; Zhu, X.-Q. Occurrence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in donkeys (Equus asinus) in China: A public health concern. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-D.; Xiao, H.-D.; Wang, D.-Y.; Su, N.; Liu, X.-Z.; Wang, Z.-R.; Xie, S.-C.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.-W. Molecular prevalence and associated risk factors of Entamoeba spp. in donkeys in Shanxi Province, North China. Parasites Vectors 2025, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Fan, W.; Yi, C.; Liu, H.-X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Su, X.; Liu, Y. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in donkeys of Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Acta Parasitol. 2025, 70, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, N.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, M.; Jin, W.; Meng, Y.; Jia, L. Molecular occurrence and risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection in equids in Jilin, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Meng, Q.-F. Detection of specific IgG-antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in the serum and milk of domestic donkeys during lactation in China: A potential public health concern. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 760400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.-F.; Gao, X.-Y.; Ji, J.-K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Cheng, K.-H.; Cui, N.; Zhu, M.-L.; Hu, T.; Dong, X. Identification of a recombinant equine coronavirus in donkey, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.; Marinho, C.; Gonçalves, A.; Sousa, M.; Nóvoa, M.; Quaresma, M.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Vaginal bacterial microbiota of an endangered donkey breed: A comparison between Miranda donkey breed (Equus asinus) jennies with and without reproductive problems. J. Integr. OMICS 2016, 6, 193. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mi, J.; Yi, Z.; Holyoak, G.R.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, S. Comparative proteome analysis of serum uncovers differential expression of proteins in donkeys (Equus asinus) with endometritis caused by Escherichia coli. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2023, 122, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.C.; Sullivan, R.J.; Rickards, K. Emergency management for donkeys and mules. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2021, 37, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C. Survival rate of donkey foals: Status quo and improvement methods. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchekina, A.; Karimova, T.Y.; Neronov, V. The Current State of Kulan Populations (Equus hemionus Pallas, 1775) in Central Asia Countries. Arid Ecosyst. 2024, 14, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholnazarovna, O.Z. Etymology of Zoophraseologisms in the Uzbekistan Language. ACUMEN Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 1, 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadnejad, M.; Jalilzadeh-Amin, G. Investigating the Gasterophilus infections in donkeys around Urmia using the equine endoscopic method. J. Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 6, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W. Epidemiological Investigation of Equine Herpesvirus in Large-Scale Donkey Farms in Liaocheng Area and Its Effect on Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3420287/v1 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Mendoza, F.J.; Toribio, R.E. An Overview of Donkey Neonatology. Animals 2025, 15, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Chen, W.; Shi, L.; Wang, M.; Geng, M.; Na, J.; Akhtar, M.F.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C. Challenges and Enhancing Strategies of Equine Semen Preservation: Nutritional and Genetic Perspectives. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Qu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Reproductive disorders in donkeys: Current evidence and update. Animals 2024, 14, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.F.; Umar, M.; Ahmad, E.; Li, L.; Yin, H.; Wang, C. Investigating Biotechnological Advances and Reproductive Biology in Donkeys: A Prospective Review. 2024. Available online: https://www.authorea.com/doi/full/10.22541/au.173081346.60552651 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Rehan, A.; Tunio, M.T.; Badar, S.T.; Mahmood, K. Factors Affecting the Reproductive Efficiency of American Mammoth Jackstock Donkey Mares (Equus asinus) Under Subtropical Conditions of Pakistan. 2025. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/394146187_Factors_Affecting_the_Reproductive_Efficiency_of_American_Mammoth_Jackstock_Donkey_Mares_Equus_asinus_under_Subtropical_Conditions_of_Pakistan (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Hancock, T.; Wang, X. China Bets on Donkey Breeding to Curb Africa Imports. Financ. Times Online 2018, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, W.; Nie, L.-B.; Qin, S.-Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Qian, A.-D.; Meng, Q.-F. Prevalence of Neospora spp. in donkeys in China. Parasite 2018, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Status of Chinese donkey industry. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Donkey Science, Jinan, China, 14–17 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.-F.; Li, D.; Yao, G.-Z.; Zou, Y.; Cong, W.; Shan, X.-F. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection and variables associated with seropositivity in donkeys in eastern China. Parasite 2018, 25, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shi, S.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Liao, Q.; Xie, P. A cross-sectional survey of foaling-related parameters of jennies (Equus asinus) under smallholder farm conditions in Northeast China. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 87, 102928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miragaya, M.H.; Neild, D.M.; Alonso, A.E. A review of reproductive biology and biotechnologies in donkeys. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.F.; Umar, M.; Chai, W.; Li, L.; Ahmad, E.; Wang, C. Effect of Inhibin Immunization on Reproductive Hormones and Testicular Morphology of Dezhou Donkeys During the Non-Breeding Season. Animals 2025, 15, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Song, Y.; Zhang, R. The Management System of Beef Cattle Breeding based on the Data Record of Whole Industry Chain. Proc. Sci. 2018, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-L.; Zhou, X.-L.; Yang, H.-J.; Chen, R. Effect of dietary forage/concentrate ratio on nutrient digestion and energy and protein metabolism in adult donkeys. Animals 2020, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, M.B.P.; Quet, M. Feral pharmaceuticalization—Biomedical uses of animal life in light of the global donkey hide trade. BioSocieties 2023, 18, 679–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.S.; Li, C.M.; Kenéz, Á.; Steagall, P.V.; McElligott, A.G.; Parkes, R.S. Donkey hair cortisol concentrations are associated with carrying heavy load and being beaten at work. BMC Vet. Res. 2025, 21, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.S.; McElligott, A.G.; Rosanowski, S.M.; Parkes, R.S. Recognition of emotion and pain by owners benefits the welfare of donkeys in a challenging working environment. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Khan, M.Z.; Chai, W.; Ullah, Q.; Wang, C. Exploring genetic markers: Mitochondrial DNA and genomic screening for biodiversity and production traits in donkeys. Animals 2023, 13, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Pal, Y. Socio-Economic Contribution of Donkey and Mule Rearing in Haryana (India)—A Review. Asian J. Agric. Ext. Econ. Sociol. 2021, 39, 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Li, L.; Tong, M.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Guo, Y.; Shi, B.; Yan, S. Effect of varying dietary crude protein level on milk production, nutrient digestibility, and serum metabolites by lactating donkeys. Animals 2022, 12, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, M.; Wei, P.; Hou, Y.; Marshall, F.B. From pack animals to polo: Donkeys from the ninth-century Tang tomb of an elite lady in Xi’an, China. Antiquity 2020, 94, 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Camillo, F.; Rota, A.; Biagini, L.; Tesi, M.; Fanelli, D.; Panzani, D. The current situation and trend of donkey industry in Europe. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- SN/T 5485-2022; Protocol of Animal Welfare for Donkey During Breeding, Transport and Slaughter. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/SNT5485-2022 (accessed on 10 November 2024).
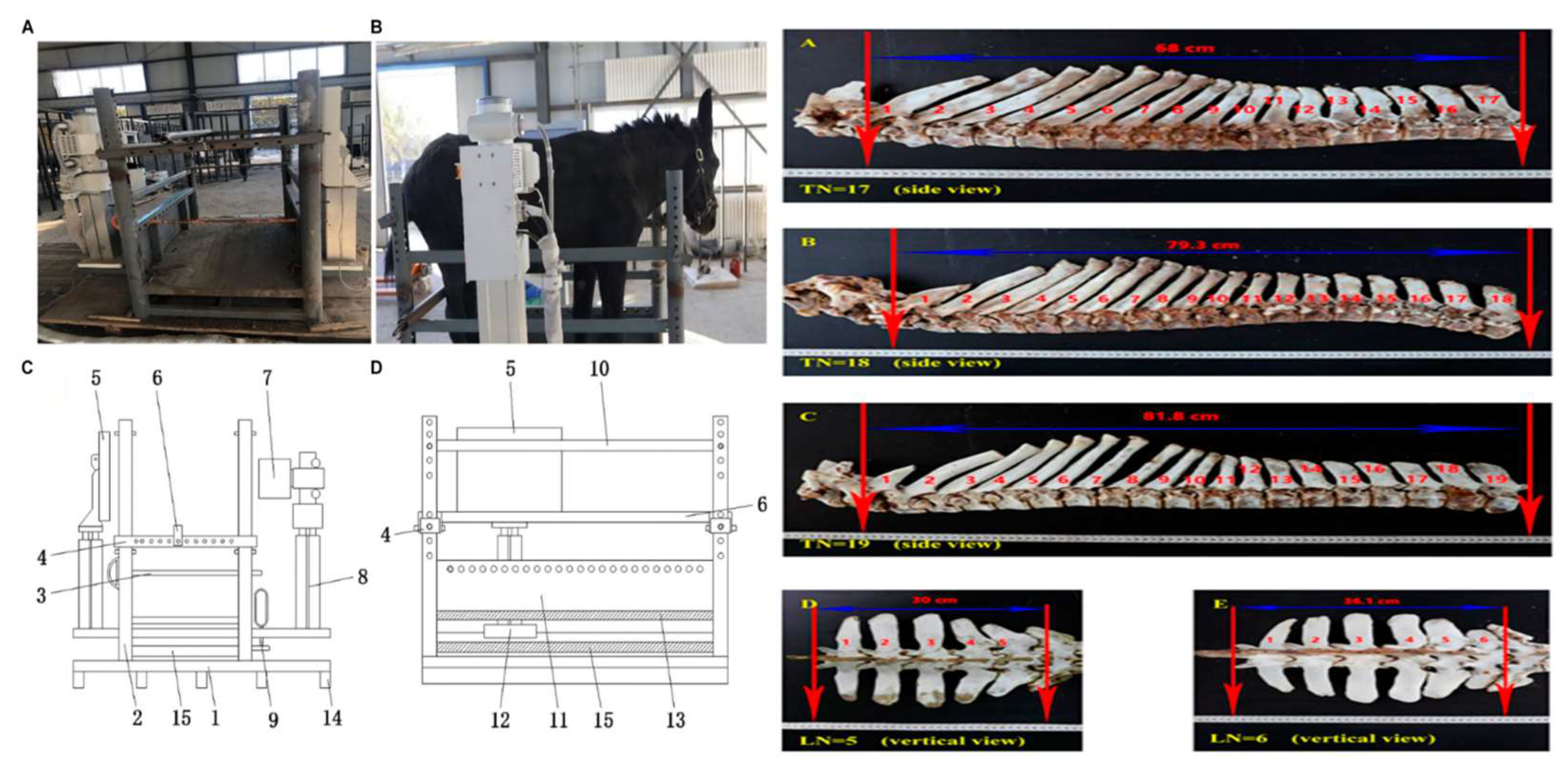
- Liu, Z.; Gao, Q.; Wang, T.; Chai, W.; Zhan, Y.; Akhtar, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, C. Multi-thoracolumbar variations and NR6A1 gene polymorphisms potentially associated with body size and carcass traits of Dezhou donkey. Animals 2022, 12, 1349. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Wang, C. Identification of LTBP2 gene polymorphisms and their association with thoracolumbar vertebrae number, body size, and carcass traits in Dezhou donkeys. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 969959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Liang, H.; Wang, C.; Chai, W. Genotypes and haplotype combination of DCAF7 gene sequence variants are associated with number of thoracolumbar vertebrae and carcass traits in Dezhou donkey. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2023, 51, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liang, H.; Kou, X.; Chen, Y. Association of HOXC8 genetic polymorphisms with multi-vertebral number and carcass weight in Dezhou Donkey. Genes 2022, 13, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S. Donkey genomes provide new insights into domestication and selection for coat color. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chai, W.; Wang, C. Advancements in genetic marker exploration for livestock vertebral traits with a focus on China. Animals 2024, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Teng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Ning, C.; et al. Genome-wide association study for numbers of vertebrae in Dezhou donkey population reveals new candidate genes. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holderegger, R.; Balkenhol, N.; Bolliger, J.; Engler, J.O.; Gugerli, F.; Hochkirch, A.; Nowak, C.; Segelbacher, G.; Widmer, A.; Zachos, F.E. Conservation genetics: Linking science with practice. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 3848–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Su, J.; Yang, Q.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Jafari, H.; Lei, C.; Sun, Y.; Dang, R. Genome-wide analyses based on a novel donkey 40K liquid chip reveal the gene responsible for coat color diversity in Chinese Dezhou donkey. Anim. Genet. 2024, 55, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitshweditse, B.; Tsvakirai, C.; Mabuza, M.; Tshehla, M. Towards the expansion of the functional dairy market: Determining donkey milk value propositions and identifying possible consumers. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zahoor Khan, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Ren, W.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, C. Utilizing mobile digital radiography for detection of thoracolumbar vertebrae traits in live donkeys. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1322921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, X.; Li, Y.; Lv, Y. Research on the development opportunities and countermeasures of donkey ndustry in Dezhou city under the new situation. China Livest. Poult. Seed Ind. 2023, 19, 121–124. [Google Scholar]




| Region | Country/Area | Estimated Donkey Population | Year of Estimation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | Worldwide | Approximately 50 million | 2023 | [2,5] |
| Africa | Continental share | Approximately 30.5 million (≈61% of the globe’s donkey population) | 2023 | [2,4,5] |
| Asia (Total) | Continental share | Approximately 13 million (≈26% of the globe’s donkey population) | 2023 | [2,4,5] |
| South Asia | Pakistan | 5.9 million | 2023–2024 | [36] |
| India | 1.2 million | 2019 | [37] | |
| Afghanistan | 1.52 million | 2023 | [39,40] | |
| East Asia | China | 2.68 million | 2020 | [54,55] |
| Central Asia | Kazakhstan | 0.030 | 2023 | [39] |
| Uzbekistan | 0.088 | 2023 | [39] | |
| Western Asia | Iran | 1.53 | 2023 | [39,53] |
| Americas | Continental share | Approximately 6.5–6.6 | 2018–2023 | [4,56,57] |
| The European continent and Oceania | Combined share | Approximately 0.13 million | 2023 | [4,57,58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C. Overview of Donkey Welfare and Husbandry Practices in Asia. Animals 2025, 15, 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233464
Ullah A, Khan MZ, Wang C. Overview of Donkey Welfare and Husbandry Practices in Asia. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233464
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Abd, Muhammad Zahoor Khan, and Changfa Wang. 2025. "Overview of Donkey Welfare and Husbandry Practices in Asia" Animals 15, no. 23: 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233464
APA StyleUllah, A., Khan, M. Z., & Wang, C. (2025). Overview of Donkey Welfare and Husbandry Practices in Asia. Animals, 15(23), 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233464






