Multi-Omics Insights into the Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and Abdominal Fat Deposition in Meat Ducks
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Extraction of Genomic DNA
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Data Processing and Analysis
2.5. Metagenomic Library Construction and Sequencing
2.6. Metagenomic Sequencing Data Processing and Analysis
2.7. Diversity Analysis
2.8. Combined Metagenomic and Whole Transcriptome Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
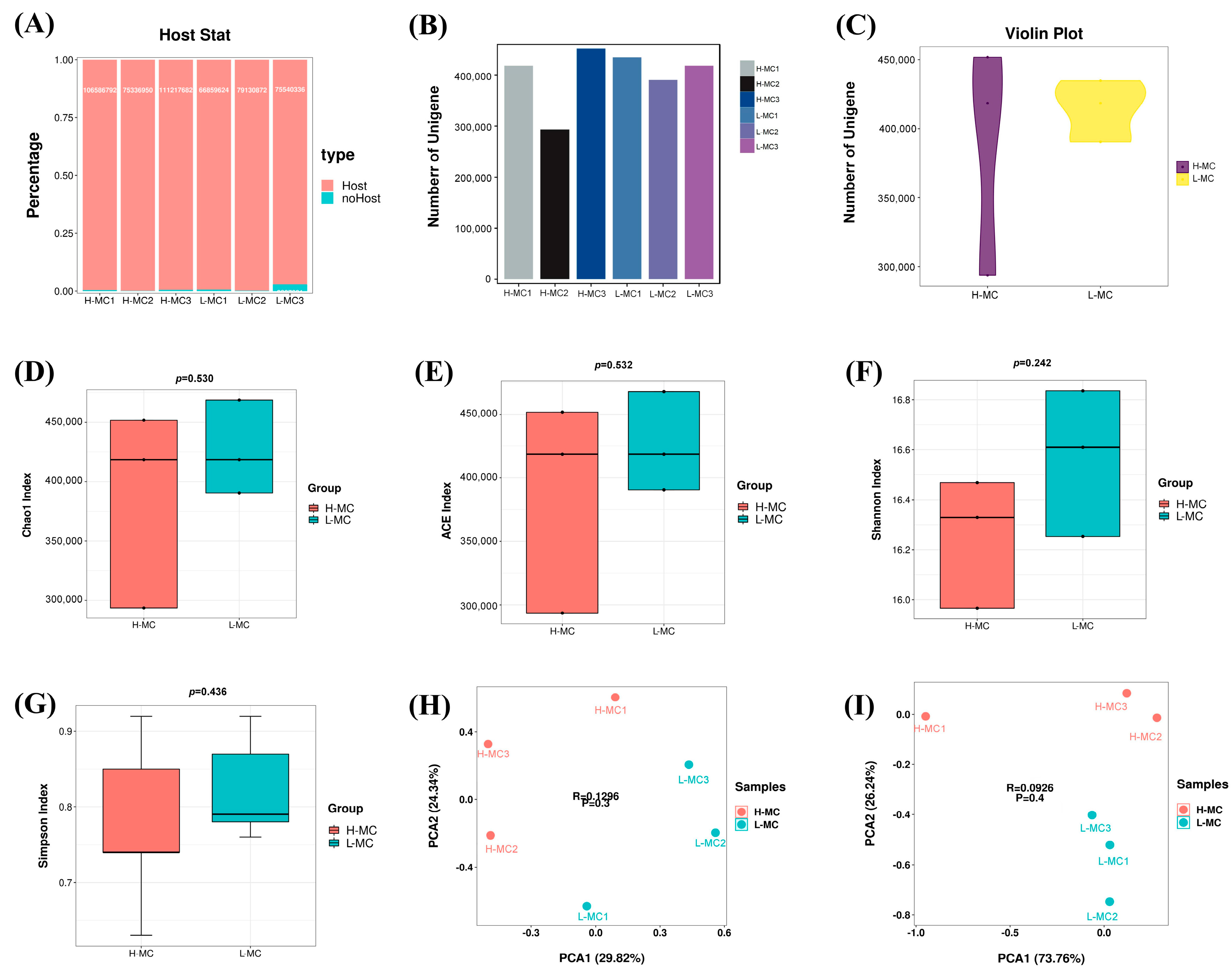
3.1. Statistical and Diversity Analysis of OTUs
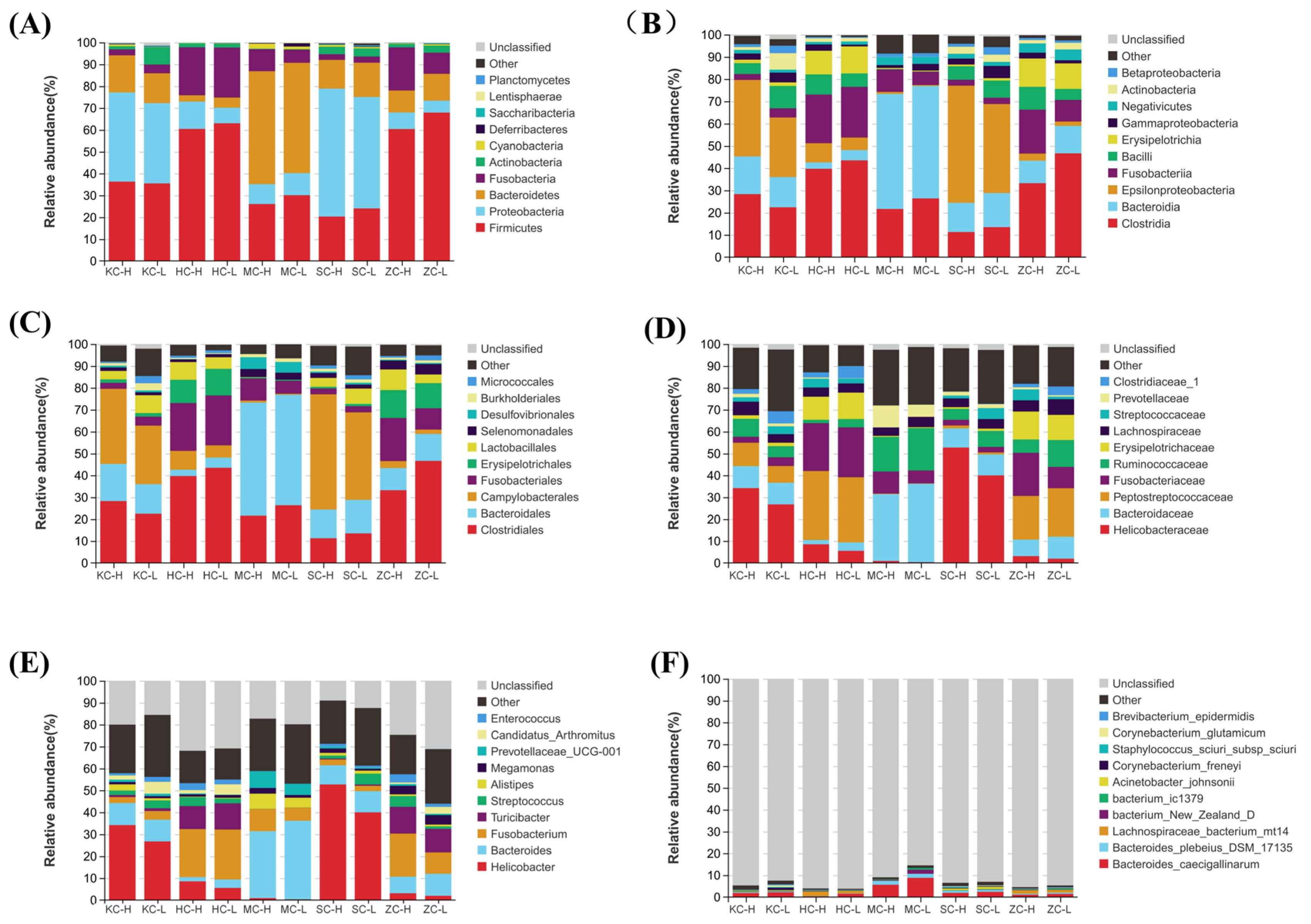
3.2. Dominant Intestinal Flora
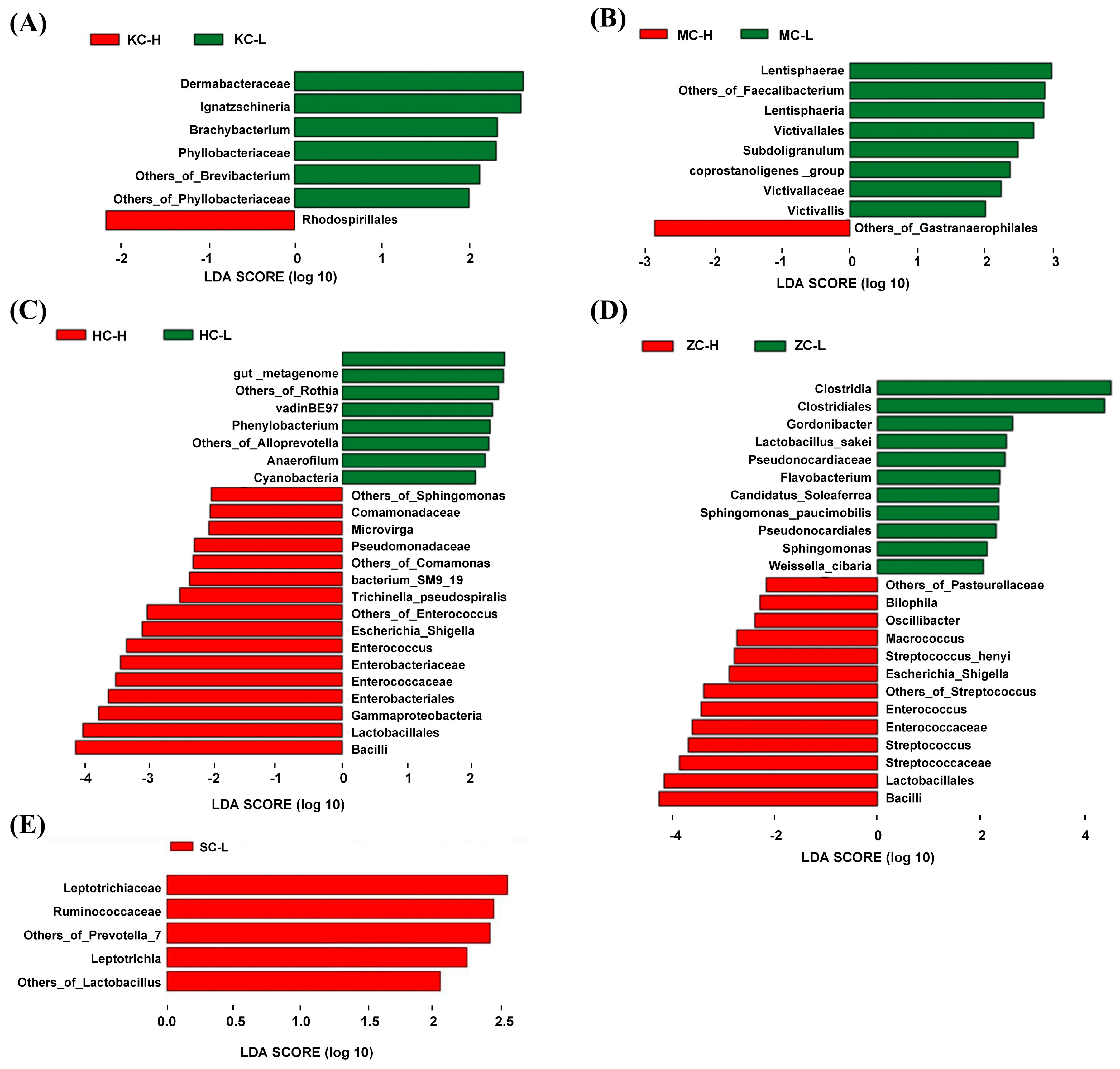
3.3. Significantly Differential Microflora
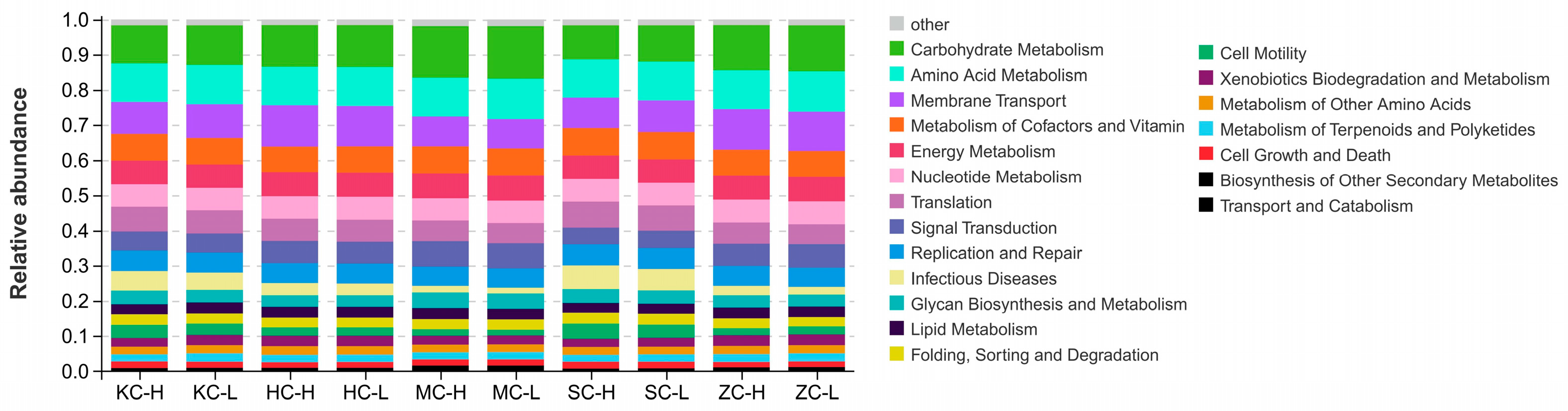
3.4. Community Function Prediction
3.5. Cecal Microbial Diversity Analysis
3.6. Cecal Microbial Indicator Species Analysis
3.7. Cecal Microbial Function Between the High and Low Abdominal Fat Rate Groups
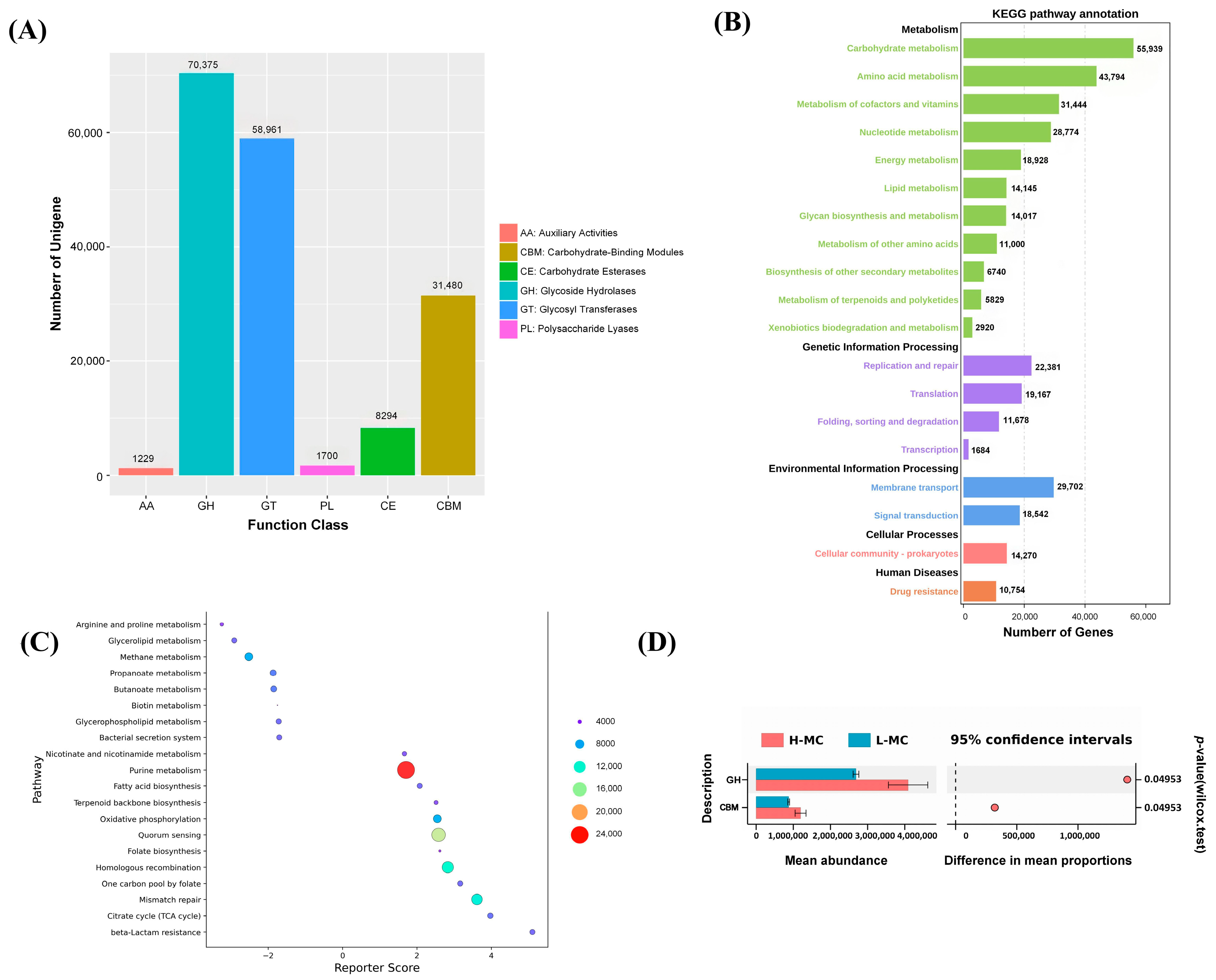
3.8. Combined Metagenomic and Whole Transcriptome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.S.; Chang, W.H.; Liu, G.H.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, A.J.; Li, Y.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Cai, H.Y. Effects of flavones of sea buckthorn fruits on growth performance, carcass quality, fat deposition and lipometabolism for broilers. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeure, O.; Duclos, M.J.; Bacciu, N.; Le Mignon, G.; Filangi, O.; Pitel, F.; Boland, A.; Boland, S.; Lagarrigue, L.A.; Cogburn, J.; et al. Genome-wide interval mapping using SNPs identifies new QTL for growth, body composition and several physiological variables in an F2 intercross between fat and lean chicken lines. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2013, 45, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiah, S.K.; Meng, G.Y.; Wei, T.S.; Keong, Y.S.; Ebrahimi, M. Dietary Conjugated Linoleic Acid Supplementation Leads to Downregulation of PPAR Transcription in Broiler Chickens and Reduction of Adipocyte Cellularity. PPAR Res. 2014, 2014, 137652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, K.; Ye, P.; Yang, L.; Kuang, J.; Chen, X.; Geng, Z. Comparison of slaughter performance, meat traits, serum lipid parameters and fat tissue between Chaohu ducks with high-and low-intramuscular fat content. Anim. Biotechnol. 2020, 31, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Watkins, P.; Ball, A.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Piyasiri, U.; Sewell, J.; Ortuño, J.; Stark, J.; Warner, R. Impact of Brassica and Lucerne Finishing Feeds and Intramuscular Fat on Lamb Eating Quality and Flavor. A Cross-Cultural Study Using Chinese and Non-Chinese Australian Consumers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6856–6868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Song, Q.; Dong, B.; Bi, Y.; Bai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, G.; Chen, G. Transcriptome Sequencing to Identify Important Genes and lncRNAs Regulating Abdominal Fat Deposition in Ducks. Animals 2022, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Garach, A.; Diaz-Perdigones, C.; Tinahones, F.J. Gut microbiota and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Org, E.; Lusis, A.J. Using the natural variation of mouse populations to understand host-gut microbiome interactions. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2018, 28, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussar, S.; Fujisaka, S.; Kahn, C.R. Interactions between host genetics and gut microbiome in diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Sears, C.L.; Maruthur, N. Gut microbiome and its role in obesity and insulin resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1461, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Midtvedt, T.; Gordon, J.I. How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science. 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xiang, Y.; Robinson, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, Y. Gut Microbiota Is a Major Contributor to Adiposity in Pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yan, W.; Sun, C.; Ji, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, J.; Yang, N. The gut microbiota is largely independent of host genetics in regulating fat deposition in chickens. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1422–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Dai, B.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y. Cecal Microbiota Modulates Fat Deposition in Muscovy Ducks. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 609348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, Y.; Hu, S.; Hu, X.; Ma, J.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.; He, H.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Comparative analysis of amino acid content and protein synthesis-related genes expression levels in breast muscle among different duck breeds/strains. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, A.; Bai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, G.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. Comparative analysis of duck meat quality in different breeds and age. Food Chem. X. 2025, 29, 102651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanes, C.G.; Witt, J.; Ebeling, M.; Schaller, S.; Baier, V.; Bone, A.J.; Preuss, T.G.; Heckmann, D. Quantitative Morphometric, Physiological, and Metabolic Characteristics of Chickens and Mallards for Physiologically Based Kinetic Model Development. Front Physiol. 2022, 13, 858283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Tang, H.; Zheng, S.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, R.; et al. Breed-specific gut microbiota and enterotype divergence in Chinese indigenous ducks. Front Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1602641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Akhtar, M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liang, Y.; Shi, D.; Cheng, R.; Cui, L.; Hu, Y.; Nafady, A.A.; et al. Chicken jejunal microbiota improves growth performance by mitigating intestinal inflammation. Microbiom 2022, 10, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods. 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Nagarajan, N.; Pop, M. Statistical methods for detecting differentially abundant features in clinical metagenomic samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Method. 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.H.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.M.; Niu, B.F.; Zhu, Z.W.; Wu, S.T.; Li, W.Z. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Mitra, S.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Weber, N.; Schuster, S.C. Integrative analysis of environmental sequences using MEGAN4. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ji, Y.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, H.; Kang, J.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, H.; Hyun, C.K.; Kim, K.T.; Holzapfel, W.H. Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 regulates gut microbiota and adipose tissue accumulation in a diet-induced obesity murine model. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Zamorano, N.; Fabbiano, S.; Chevalier, C.; Stojanović, O.; Colin, D.J.; Stevanović, A.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Tarallo, V.; Rigo, D.; Germain, S.; et al. Microbiota depletion promotes browning of white adipose tissue and reduces obesity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A.; Rincon, M.T.; Lamed, R.; White, B.A. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: Potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 121–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Monson, M.; Wang, P.; Mu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Na, W.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Leng, L.; et al. Multi-Omics Association Reveals the Effects of Intestinal Microbiome-Host Interactions on Fat Deposition in Broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 815538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Tang, D.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; et al. The chicken gut metagenome and the modulatory effects of plant-derived benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Microbiome 2018, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz Carrasco, J.M.; Casanova, N.A.; Fernández Miyakawa, M.E. Microbiota, Gut Health and Chicken Productivity: What Is the Connection? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Yin, M.; Pan, C.; Huang, L.; Kong, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, S.; et al. Dysbiosis Signatures of Gut Microbiota Along the Sequence from Healthy, Young Patients to Those with Overweight and Obesity. Obesity 2018, 26, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechrkong, T.; Incharoen, T.; Hwanhlem, N.; Kaewkong, W.; Subsoontorn, P.; Tartrakoon, W.; Numthuam, S.; Jiménez, G.; Charoensook, R. Effect of Bacillus toyonensis BCT-7112T supplementation on growth performance, intestinal morphology, immune-related gene expression, and gut microbiome in Barbary ducks. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Gan, J.K.; Zeng, D.S.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Zhao, H.Q.; Yang, Y.; Tan, S.W.; Li, G.; Luo, C.W.; et al. Specific Microbial Taxa and Functional Capacity Contribute to Chicken Abdominal Fat Deposition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouter, K.E.; van Raalte, D.H.; Groen, A.K.; Nieuwdorp, M. Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Pathogenesis of Obesity and Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjalbert, F.; Combes, S.; Zened, A.; Meynadier, A. Rumen microbiota and dietary fat: A mutual shaping. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Louca, P.; Zhang, X.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Falchi, M.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. Circulating Levels of the Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate Mediate the Effect of the Gut Microbiome on Visceral Fat. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 711359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.M.; de Souza, R.; Kendall, C.W.; Emam, A.; Jenkins, D.J. Colonic health: Fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Han, H.; Chen, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Wu, X.; Deng, J.; Yu, Q.; Huang, X. Melatonin reprogramming of gut microbiota improves lipid dysmetabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Pineal. Res. 2018, 65, e12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, S.; Tappu, R.M.; Damms-Machado, A.; Huson, D.H.; Bischoff, S.C. Characterization of the Gut Microbial Community of Obese Patients Following a Weight-Loss Intervention Using Whole Metagenome Shotgun Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Huang, F.J.; Zhao, A.H.; Lei, S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xie, G.X.; Chen, T.L.; Qu, C.; Rajani, C.; Dong, B.; et al. Bile acid is a significant host factor shaping the gut microbiome of diet-induced obese mice. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ingredients (%) | 0–22 d | 23–42 d | Nutrient Composition | 0–22 d | 23–42 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 10.56 | 46.75 | Metabolizable energy b (MJ/kg) | 12.21 | 12.45 |
| Wheat middlings | 15.31 | 8.56 | Crude protein a (g·kg−1) | 18.8 | 17.3 |
| Wheat bran | - | 18.56 | Crude fat b (g·kg−1) | 2.8 | 3.6 |
| Rice flour | 35.02 | - | Crude fiber b (g·kg−1) | 6.0 | 7.0 |
| Rice bran | 15.52 | 3.23 | Crude ash b (g·kg−1) | 9.0 | 10.0 |
| Peanut meal | - | 3.12 | Calcium b (g·kg−1) | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Corn gluten meal | - | 4.98 | Phosphorus b (g·kg−1) | 0.52 | 0.52 |
| Soybean meal | 12.62 | 6.01 | Methionine b (g·kg−1) | 0.42 | 0.31 |
| Nucleotide-rich yeast | 2.45 | - | Lysine b (g·kg−1) | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| Limestone powder | 1.46 | 1.78 | |||
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.06 | 1.01 | |||
| Compound premix | 6 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Song, Q.; Bai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, G.; Chen, G. Multi-Omics Insights into the Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and Abdominal Fat Deposition in Meat Ducks. Animals 2025, 15, 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233393
Wang Z, Yang C, Li Y, Dong B, Song Q, Bai H, Jiang Y, Chang G, Chen G. Multi-Omics Insights into the Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and Abdominal Fat Deposition in Meat Ducks. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233393
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhixiu, Chunyan Yang, Yan Li, Bingqiang Dong, Qianqian Song, Hao Bai, Yong Jiang, Guobin Chang, and Guohong Chen. 2025. "Multi-Omics Insights into the Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and Abdominal Fat Deposition in Meat Ducks" Animals 15, no. 23: 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233393
APA StyleWang, Z., Yang, C., Li, Y., Dong, B., Song, Q., Bai, H., Jiang, Y., Chang, G., & Chen, G. (2025). Multi-Omics Insights into the Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and Abdominal Fat Deposition in Meat Ducks. Animals, 15(23), 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233393






