Effects of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on the Rumen Microbiota of Leizhou Goats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Ethics Statement
2.2. Design and Housing
2.3. Preparation of R. palustris
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
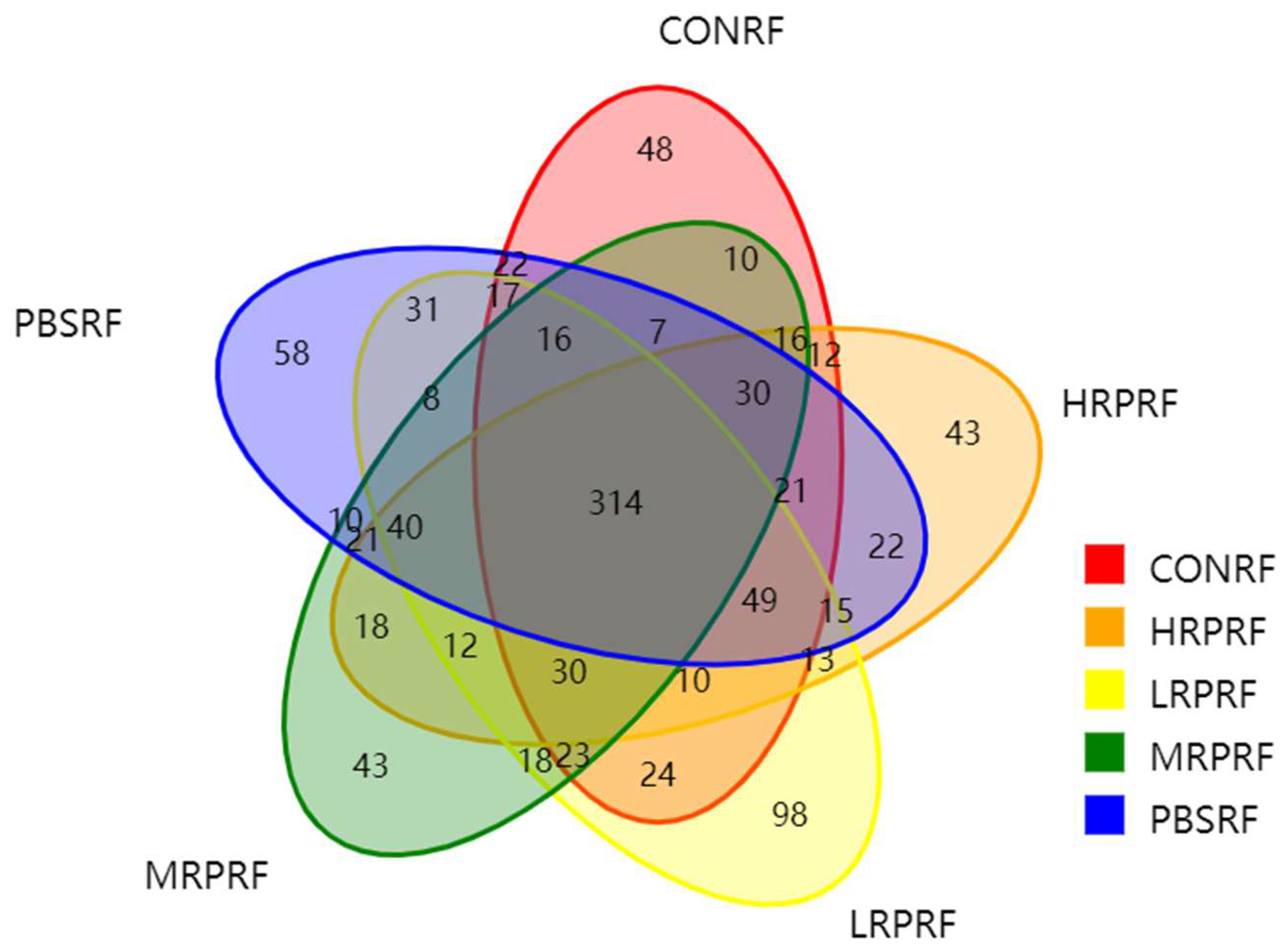
3.1. Analysis of Microbial OTUs in Goat Rumen
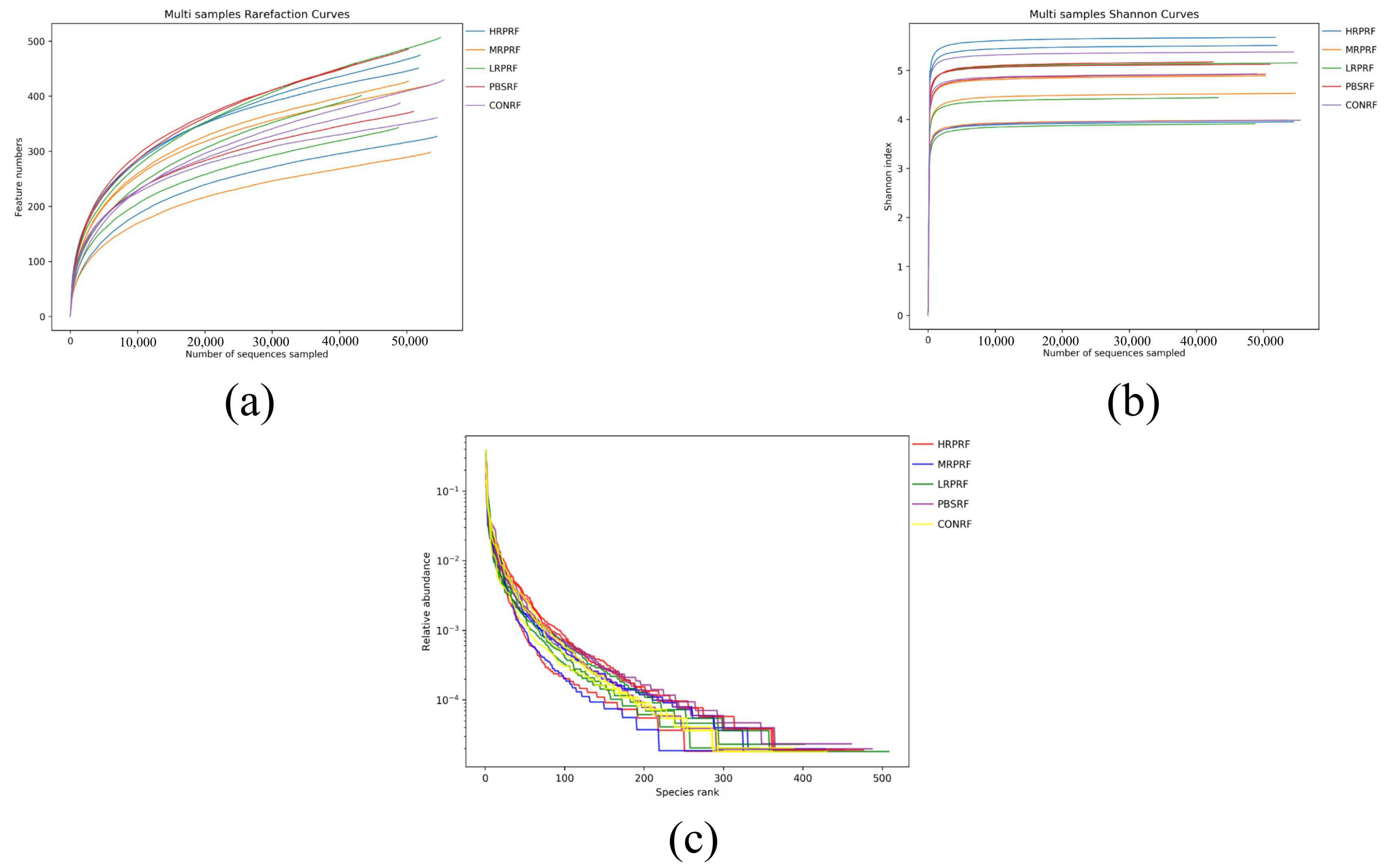
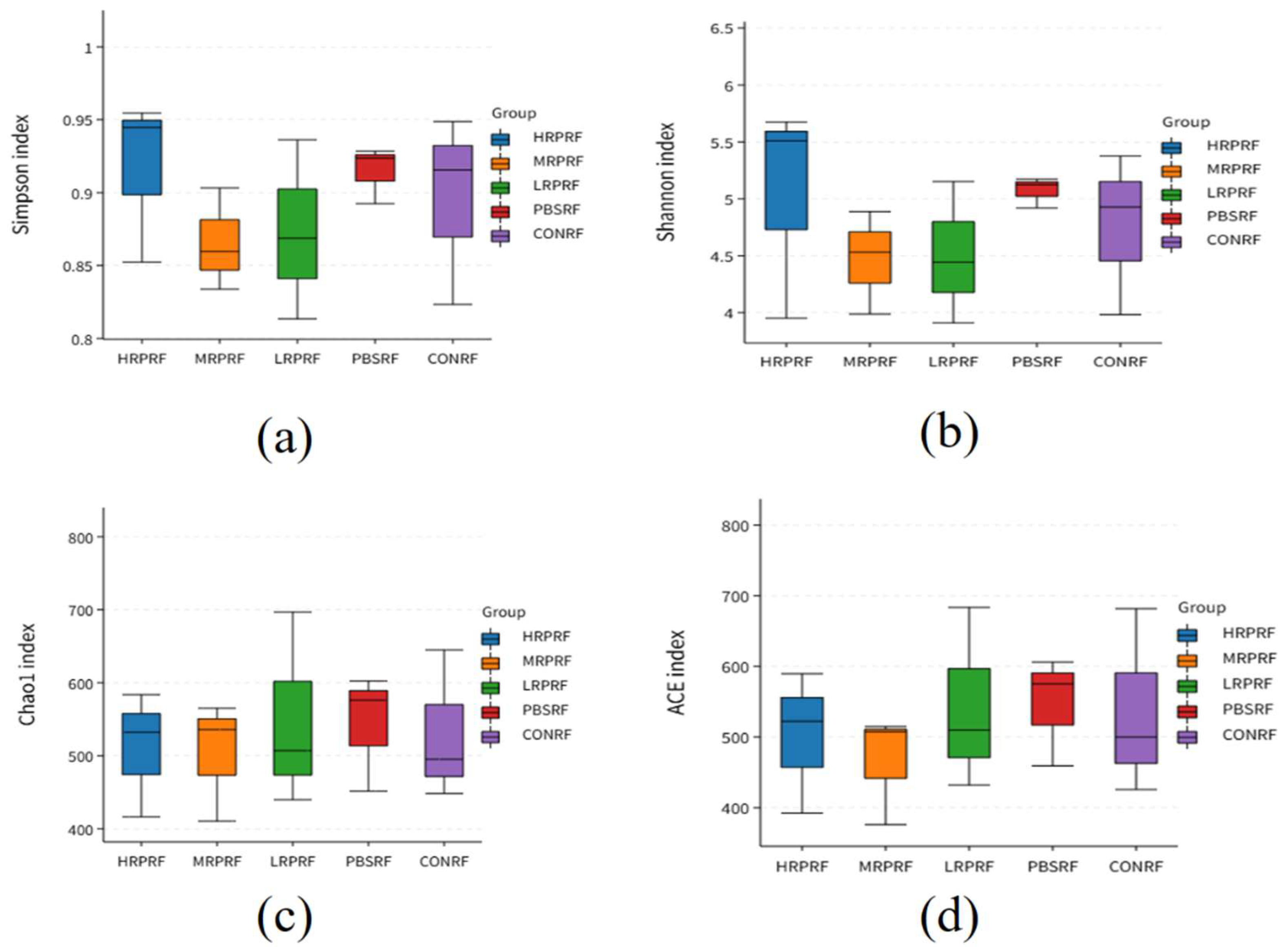
3.2. Effect of R. palustris on the Alpha Diversity of Microorganisms in the Gastric Rumen of Goats
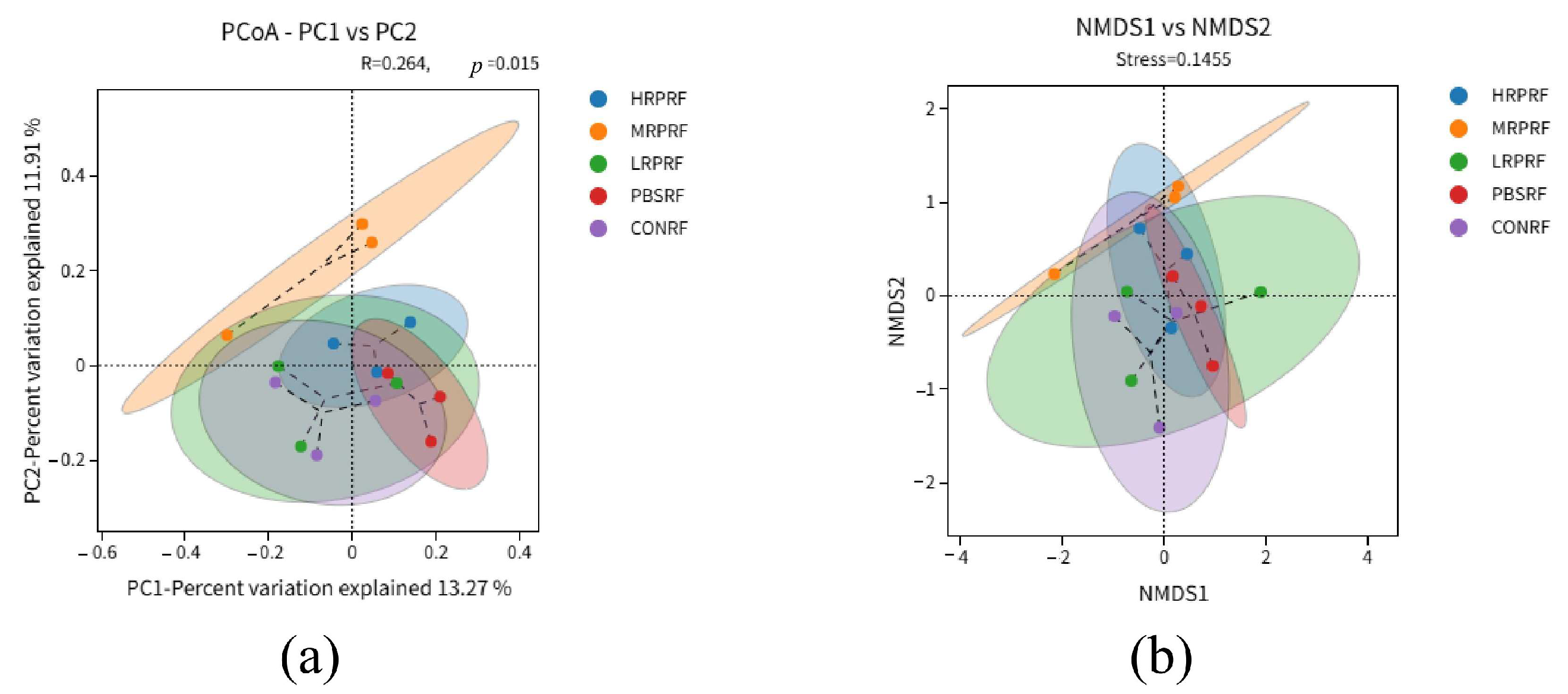
3.3. Effect of R. palustris on the Diversity of Microorganisms in the Gastric Rumen of Goats
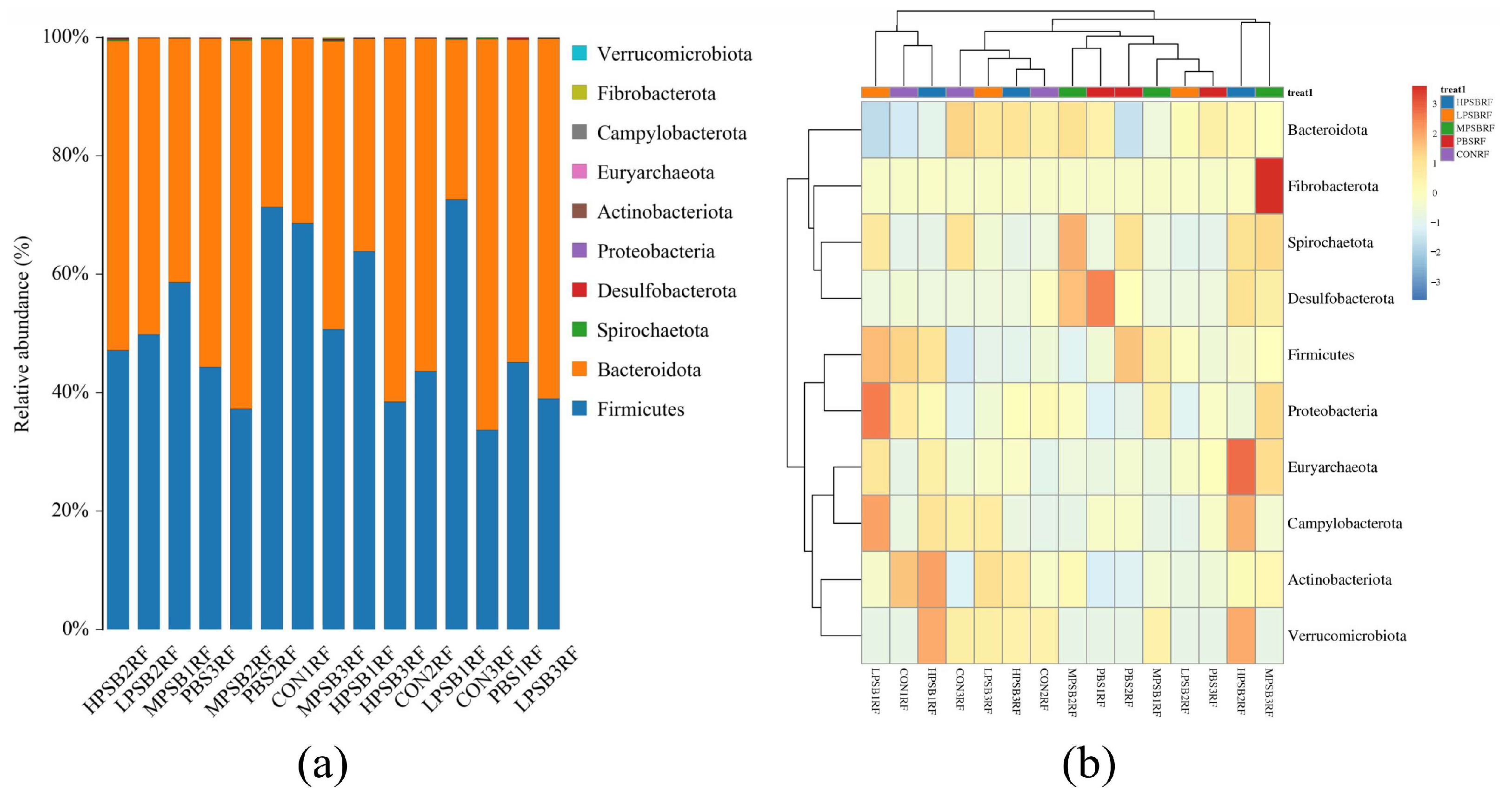
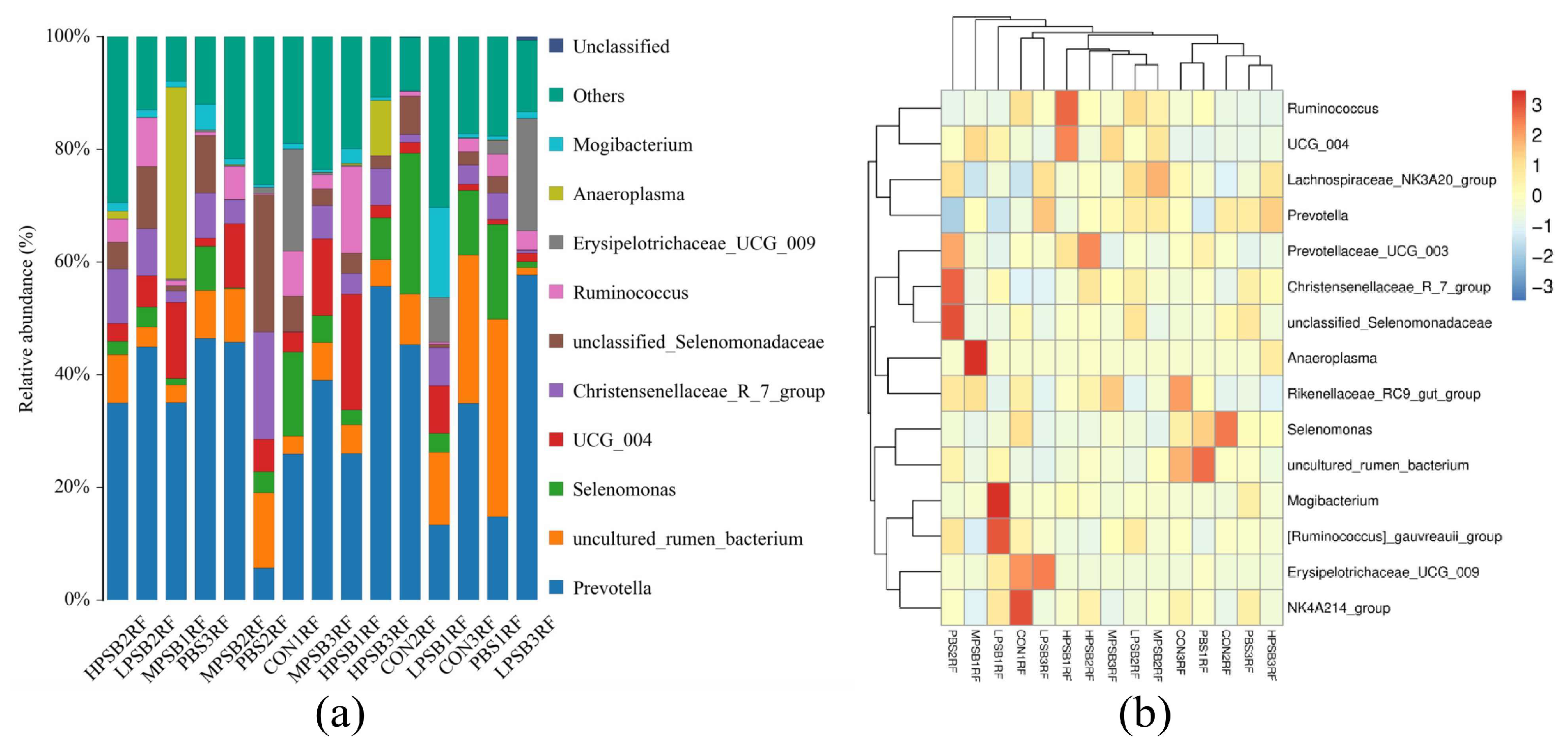
3.4. Effects of R. palustris on the Composition and Community Structure of Rumen Flora in Leizhou Goats
3.5. LEfSe Species Difference Analysis
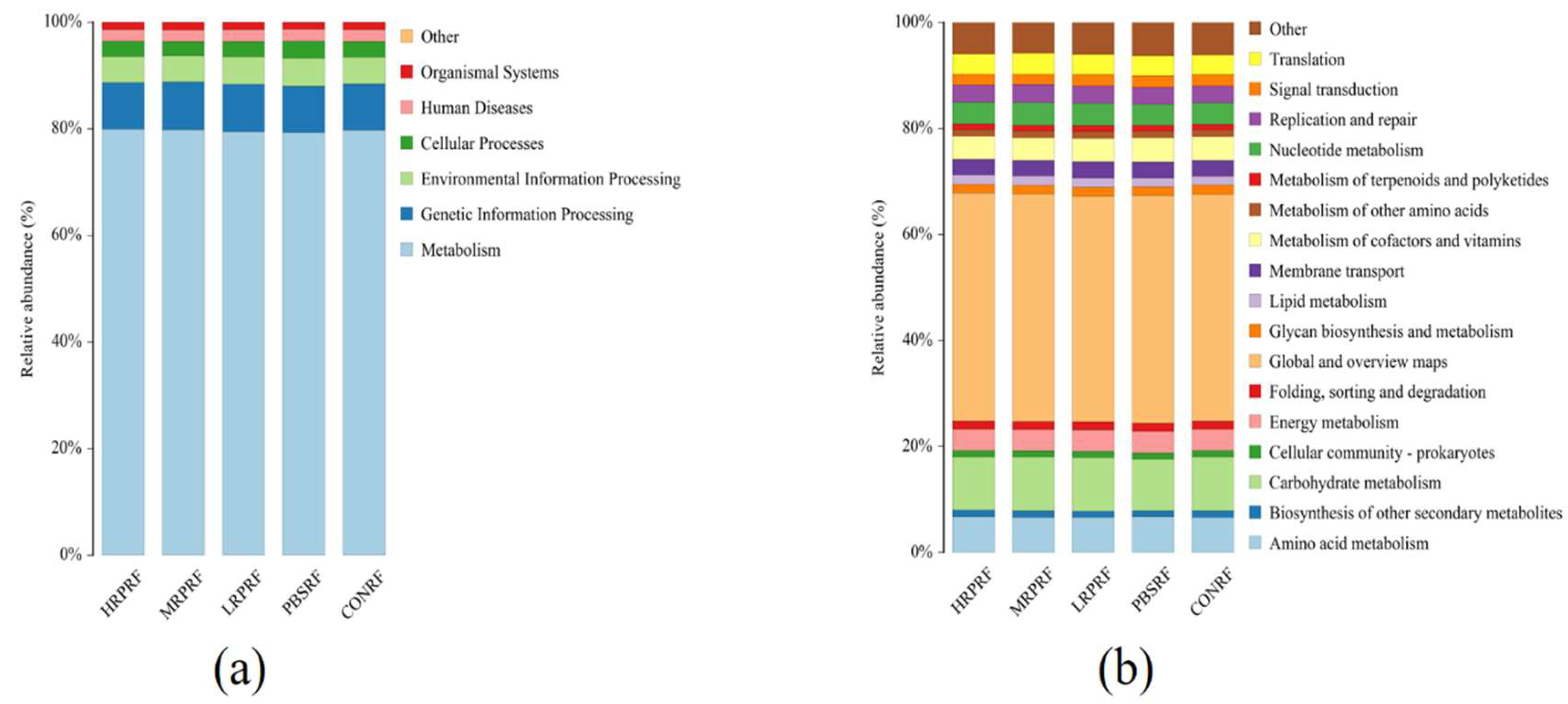
3.6. Predictive Analysis of Colony Function (Picrust2)
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of R. palustris on Rumen Microbial Diversity
4.2. Influence of R. palustris on the Structure of Rumen Microbial Communities
4.3. Influence of R. palustris on Rumen Differential Flora
4.4. Changes in the Environment of the Rumen
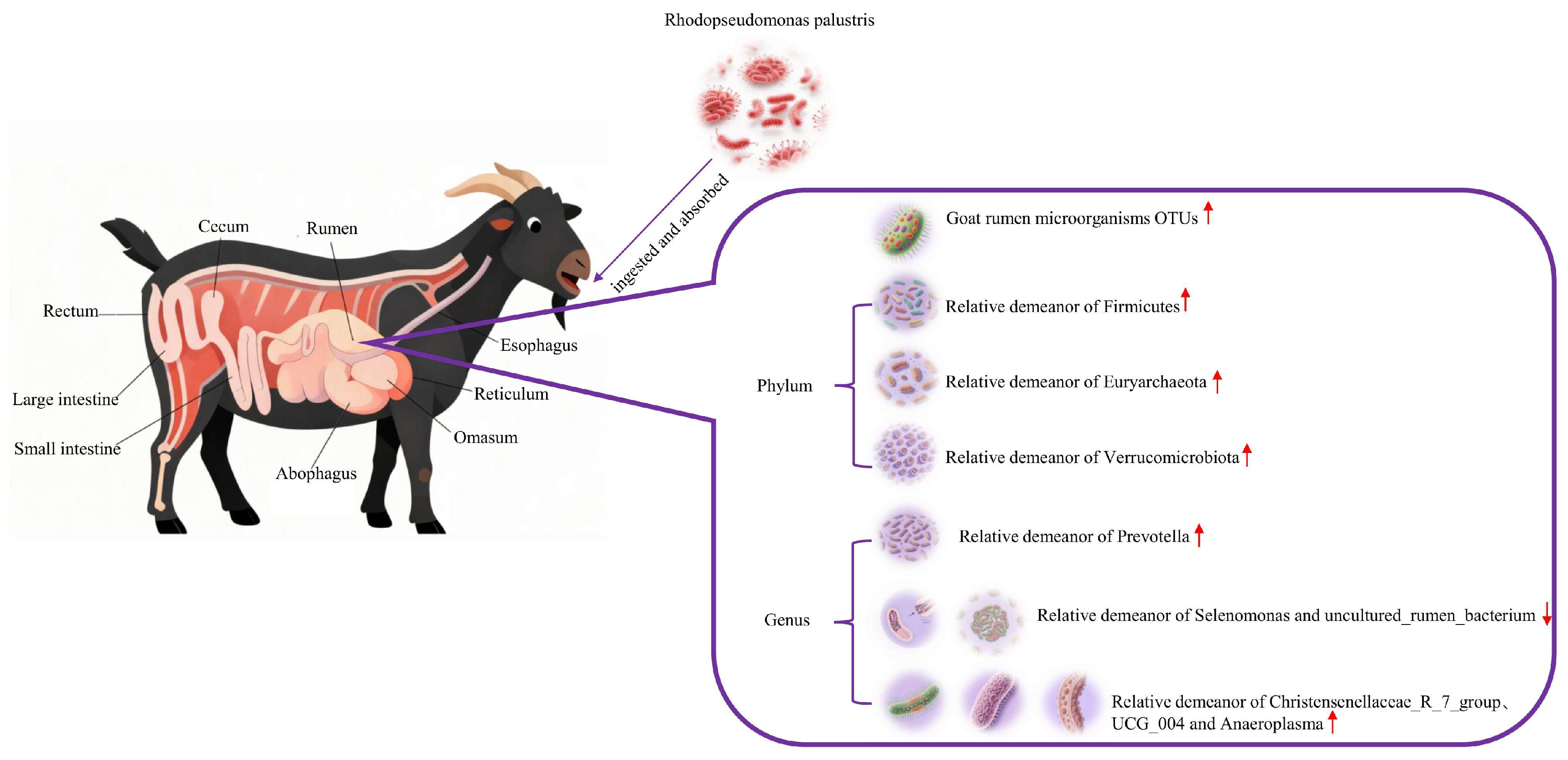
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krause, D.O.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Wright, A.D.G.; Callaway, T.R. Board-invited review: Rumen microbiology: Leading the way in microbial ecology1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.B.; Hespell, R.B. Microbial Rumen Fermentation. J. Dairy Sci. 1981, 64, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newbold, C.J.; Ramos-Morales, E. Review: Ruminal microbiome and microbial metabolome: Effects of diet and ruminant host. Animal 2020, 14, s78–s86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béra-Maillet, C.; Devillard, E.; Cezette, M.; Jouany, J.P.; Forano, E. Xylanases and carboxymethylcellulases of the rumen protozoa Polyplastron multivesiculatum Eudiplodinium maggii and Entodinium sp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, D.E.; Borneman, W.S. Role of Rumen Fungi in Fiber Degradation. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.B.; Rychlik, J.L. Factors That Alter Rumen Microbial Ecology. Science 2001, 292, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ke, S.; Chen, X.; Kenéz, Á.; Xu, W.; Cao, Y. Yak rumen microbiome elevates fiber degradation ability and alters rumen fermentation pattern to increase feed efficiency. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnigan, T.; Mach, K.; Edlin, A. Mycoprotein: A healthy new protein with a low environmental impact. In Sustainable Protein Sources; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 539–566. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Jiao, J.; He, Z.; Tan, Z.; Han, X. Rumen-protected glucose supplementation in transition dairy cows shifts fermentation patterns and enhances mucosal immunity. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. Dynamic changes in rumen fermentation and bacterial community following rumen fluid transplantation in a sheep model of rumen acidosis: Implications for rumen health in ruminants. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8453–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisi, E.; Riva, F.; Filipe, J.F.S.; Massara, M.; Minuti, A.; Bani, P.; Amadori, M. Innate immune responses to metabolic stress can be detected in rumen fluids. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 117, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F. Taxonomy and Physiology of Phototrophic Purple Bacteria and Green Sulfur Bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.H.; Shen, M.W.; Chen, J.C.; Lur, H.S.; Liu, C.T. The Photosynthetic Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris Strain PS3 Exerts Plant Growth-Promoting Effects by Stimulating Nitrogen Uptake and Elevating Auxin Levels in Expanding Leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 573634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Zhang, F. Growth-Promoting Ability of Rhodopseudomonas palustris G5 and Its Effect on Induced Resistance in Cucumber Against Salt Stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, K.; Zahra, T.F.; Rehman, Y. Arsenic-Redox Transformation and Plant Growth Promotion by Purple Nonsulfur Bacteria Rhodopseudomonas palustris CS2 and Rhodopseudomonas faecalis SS5. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 1, 6250327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shu, M.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, W.; Deng, B.; Shen, W. Effect of photosynthetic bacteria on water quality and microbiota in grass carp culture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, B.; Du, X.; Zeng, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, C. Effects of water supplemented with Bacillus subtilis and photosynthetic bacteria on egg production, egg quality, serum immunoglobulins and digestive enzyme activity of ducks. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, B.K. Mass production of Rhodopseudomonas palustris as diet for aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 23, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirong, Z.; Wei, L. Use of fluidized bed biofilter and immobilized Rhodopseudomonas palustris for ammonia removal and fish health maintenance in a recirculation aquaculture system. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.; Cryan, J.F.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P.; Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C. Gut microbiota, the pharmabiotics they produce and host health. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, P. Rhodopseudomonas palustris in effluent enhances the disease resistance, TOR and NF-κB signalling pathway, intestinal microbiota and aquaculture water quality of Pelteobagrus vachelli. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 3959–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Q.; Yan, H.; Liu, X.L.; Lv, L.; Yin, C.H.; Wang, P. Growth performance and meat quality of broiler chickens supplemented with Rhodopseudomonas palustris in drinking water. Br. Poult. Sci. 2014, 55, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Effect of treatment with probiotics as water additives on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth performance and immune response. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, W.K.; Zhang, Z.W.; Si, X.M.; Cao, Z.J.; Yang, H.J. Beneficial effect of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on in vitro rumen digestion and fermentation. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xu, M.; Han, X.; Liu, H.; Han, J.; Sun, W.; Zhou, H. Transcriptome analysis of muscle atrophy in Leizhou black goats: Identification of key genes and insights into limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Mao, H.; Wang, W.; Peng, W.; Mao, K.; Sun, W.; Zhou, H. Comparison of average daily gain, apparent digestibility, rumen fermentation parameters and bacterial communities, and serum antioxidant indices in Leizhou goats fed with or without rumen-protected fat. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1518826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NY/T 816-2021; Feeding Standard of Meat-Producing Sheep and Goats. Agricultural Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Krause, D.O.; Denman, S.E.; Mackie, R.I.; Morrison, M.; Rae, A.L.; Attwood, G.T.; Mcsweeney, C.S. Opportunities to improve fiber degradation in the rumen: Microbiology, ecology, and genomics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 663–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A.; Rincon, M.T.; Lamed, R.; White, B.A. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: Potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehority, B.A.; Grubb, J.A. Characterization of the predominant bacteria occurring in the rumen of goats (Capra hircus). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 33, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Worlds within worlds: Evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.M.; Ahir, V.B.; Tripathi, A.K.; Ramani, U.V.; Sajnani, M.; Koringa, P.G.; Joshi, C.G. Metagenomic analysis of Surti buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) rumen: A preliminary study. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 4841–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Chen, H.; Luo, X.; Guan, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, X. Microbial diversity in the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum of yak on a rapid fattening regime in an agro-pastoral transition zone. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Van Niekerk, J.K.; Zhou, M.; Steele, M.A.; Guan, L.L. Longitudinal assessment revealed the shifts in rumen and colon mucosal-attached microbiota of dairy calves during weaning transition. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 5948–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.A.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Kalwar, Q.; Liang, Z.; Li, C.; Ding, X. Effects of Dietary Energy Levels on Rumen Fermentation, Microbial Diversity, and Feed Efficiency of Yaks (Bos grunniens). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharechahi, J.; Vahidi, M.F.; Sharifi, G.; Atriaeenejad, S.; Ding, X.Z.; Han, J.L.; Salekdeh, G.H. Lignocellulose degradation by rumen bacterial communities: New insights from metagenome analyses. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.R.; Gurung, N.; Shange, R.; Solaiman, S. Potential role of rumen microbiota in altering average daily gain and feed efficiency in meat goats fed simple and mixed pastures using bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 3523–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Indugu, N.; Vecchiarelli, B.; Pitta, D. Associative patterns among anaerobic fungi, methanogenic archaea, and bacterial communities in response to changes in diet and age in the rumen of dairy cows. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Elekwachi, C.O.; Jiao, J.; Wang, M.; Tang, S.; Zhou, C.; Forster, R.J. Investigation and manipulation of metabolically active methanogen community composition during rumen development in black goats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, K.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Cui, K.; Wang, F. Association between body weight and distal gut microbes in Hainan black goats at weaning age. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 951473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolin, R.C.; Vargas, A.R.; Gasparotto, J.; Chaves, P.R.; Schnorr, C.E.; Da, B.; Marinello, K. A new animal diet based on human Western diet is a robust diet-induced obesity model: Comparison to high-fat and cafeteria diets in term of metabolic and gut microbiota disruption. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, V.; Tiago, I.; Aires, A.; Coelho, C.; Nunes, J.; Matiins, L.O.; Verissimo, A. The gastrointestinal microbiome of browsing goats (Capra hircus). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Goldfarb, K.C.; Karaoz, U.; Leal, S.; Garcia-Amado, M.A.; Hugenholtz, P.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G. Comparative analyses of foregut and hindgut bacterial communities in hoatzins and cows. ISME J. 2012, 6, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.; Brazel, D.M.; Swan, B.K.; Kai, Z.; Jacques, R. Capturing Single Cell Genomes of Active Polysaccharide Degraders: An Unexpected Contribution of Verrucomicrobia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, R.R. Evolutionary steps of ecophysiological adaptation and diversification of ruminants: A comparative view of their digestive system. Oecologia 1989, 78, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharechahi, J.; Sarikhan, S.; Han, J.L.; Ding, X.Z.; Salekdeh, G.H. Functional and phylogenetic analyses of camel rumen microbiota associated with different lignocellulosic substrates. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamola, V.D.; Ghosh, A.; Kapardar, R.K.; Lal, B.; Cheema, S.; Sarma, P.; Chaudhry, R. Gut microbial diversity in health and disease: Experience of healthy Indian subjects, and colon carcinoma and inflammatory bowel disease patients. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2017, 28, 1322447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickdam, E.; Khiaosa-Ard, R.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Klevenhusen, F.; Chizzola, R.; Zebeli, Q. Rumen microbial abundance and fermentation profile during severe subacute ruminal acidosis and its modulation by plant derived alkaloids in vitro. Anaerobe 2016, 39, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Restrepo, C.A.; Tan, C.; López-Villalobos, N.; Padmanabha, J.; Wang, J.; Mcsweeney, C.S. Methane production, fermentation characteristics, and microbial profiles in the rumen of tropical cattle fed tea seed saponin supplementation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 216, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, A.Z.; Koike, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Genetic diversity and diet specificity of ruminal Prevotella revealed by 16S rRNA gene-based analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 305, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myer, P.R.; Wells, J.E.; Smith, T.P.L.; Kuehn, L.A.; Freetly, H.C. Cecum microbial communities from steers differing in feed efficiency1,2,3. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 5327–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuskin, F.; Lowe, E.C.; Temple, M.J.; Zhu, Y.; Cameron, E.A.; Pudlo, N.A.; Gilbert, H.J. Human gut Bacteroidetes can utilize yeast mannan through a selfish mechanism. Nature 2015, 517, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur-Murillo, C.L.; Aguilar-Marín, S.B.; Jovel, J. Prevotella: A Key Player in Ruminal Metabolism. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cidrini, I.A.; Ferreira, I.M.; Oliveira, K.; Granja-Salcedo, Y.; Lage, J.F.; Siqueira, G.; Resende, F. PSX-B-9 Effect of trace mineral sources in the supplement for grazing cattle on ruminal bacteria diversity. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Yin, Y.Y.; Jin, W.; Mao, S.Y.; Liu, J.H. Response of rumen microbiota, and metabolic profiles of rumen fluid, liver and serum of goats to high-grain diets. Animal 2019, 13, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, D.B.; Wagschal, K. Properties and applications of microbial β-D-xylosidases featuring the catalytically efficient enzyme from Selenomonas ruminantium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyonyo, T.; Shinkai, T.; Mitsumori, M. Improved culturability of cellulolytic rumen bacteria and phylogenetic diversity of culturable cellulolytic and xylanolytic bacteria newly isolated from the bovine rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, S.; Yoshitani, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tanaka, K. Phylogenetic analysis of fiber-associated rumen bacterial community and PCR detection of uncultured bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 229, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Fibrolytic Rumen Bacteria: Their Ecology and Functions. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joblin, K.N.; Naylor, G.E. The Ruminal Mycoplasmas: A Review. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2002, 21, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetze, V.V. Direct Induction of TGF-β Signaling by the Gut Commensal Anaeroplasma; Technische Universitaet: Berlin, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Beller, A.; Kruglov, A.; Durek, P.; Goetze, V.V.; Hoffmann, U.; Maier, R.; Chang, H.D. P104 Anaeroplasma, a potential anti-inflammatory probiotic for the treatment of chronic intestinal inflammationP104. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, A45–A46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricke, S.C.; Martin, S.A.; Nisbet, D.J. Ecology, metabolism, and genetics of ruminal selenomonads. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1996, 22, 27–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawanon, S.; Koike, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Evidence for the possible involvement of Selenomonas ruminantium in rumen fiber digestion. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 325, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schingoethe, D.J. A 100-Year Review: Total mixed ration feeding of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10143–10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Yadav, H.; Sinha, P.R. Stimulation of Innate Immunity by Oral Administration of Dahi Containing Probiotic Lactobacillus casei in Mice. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranto, M.P.; Medici, M.; Perdigon, G.; Holgado, A.R.; Valdez, G.F.L. Evidence for Hypocholesterolemic Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri in Hypercholesterolemic Mice. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdigon, G.; De Macias, M.E.N.; Alvarez, S.; De Ruiz Holgado, A.A.P.; Oliver, G. Prevention of gastrointestinal infection using immunobiological methods with milk fermented with Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus acidophilus. J. Dairy Res. 1990, 57, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commane, D.; Hughes, R.; Shortt, C.; Rowland, I. The potential mechanisms involved in the anti-carcinogenic action of probiotics. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2005, 591, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiofalo, V.; Liotta, L.; Chiofalo, B. Effects of the administration of Lactobacilli on body growth and on the metabolic profile in growing Maltese goat kids. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2004, 44, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salva, S.; Villena, J.; Alvarez, S. Immunomodulatory activity of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains isolated from goat milk: Impact on intestinal and respiratory infections. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foksowicz-Flaczyk, J.; Wójtowski, J.A.; Danków, R.; Mikołajczak, P.; Pikul, J.; Gryszczyńska, A.; Stanisławski, D. The Effect of Herbal Feed Additives in the Diet of Dairy Goats on Intestinal Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) Count. Animals 2022, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Mehmood, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Probiotic Potential of Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides and Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Yaks. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, X. Oral Probiotics Ameliorate the Behavioral Deficits Induced by Chronic Mild Stress in Mice via the Gut Microbiota-Inflammation Axis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, T.S.; Gibson, G.R. Microbial-gut interactions in health and disease. Prebiotics Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 18, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Exploring the cecal microbial community associated with fat deposition in sheep and its possible pathways of action. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e01488-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, T.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. High-grain feeding alters caecal bacterial microbiota composition and fermentation and results in caecal mucosal injury in goats. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Content % |
|---|---|
| Pennisetum × sinese | 56.00 |
| Corn | 22.00 |
| Soybean meal | 11.00 |
| Bran (Triticum aestivum L.) | 4.50 |
| Cottonseed meal | 4.50 |
| Limestone powder | 0.30 |
| Calcium hydrogen phosphate | 0.20 |
| Salt | 0.30 |
| Compound premix 1 | 1.20 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| Nutritional level | Content |
| ME MJ/kg 2 | 9.80 |
| DM (%) | 56.06 |
| CP (%) | 16.20 |
| NDF (%) | 45.50 |
| ADF (%) | 30.20 |
| Ca (%) | 0.92 |
| P (%) | 0.51 |
| Items | CONRF Group | PBMRF Group | LRPRF Group | MRPRF Group | HRPRF Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace index | 533.78 ± 131.49 | 546.80 ± 77.32 | 541.84 ± 128.52 | 466.23 ± 77.89 | 501.44 ± 100.24 | 0.863 |
| Chao1 index | 529.46 ± 102.62 | 510.66 ± 85.66 | 503.98 ± 133.19 | 547.92 ± 133.19 | 543.30 ± 80.62 | 0.974 |
| Simpson index | 0.89 ± 0.06 | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 0.86 ± 0.03 | 0.87 ± 0.06 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 0.637 |
| Shannon index | 4.76 ± 0.71 | 5.04 ± 0.95 | 4.46 ± 0.45 | 4.50 ± 0.62 | 5.07 ± 0.13 | 0.665 |
| PD whole tree | 20.31 ± 2.89 | 21.86 ± 3.19 | 21.19 ± 2.35 | 22.40 ± 2.79 | 22.27 ± 2.89 | 0.886 |
| Coverage % | 99.800 | 99.823 | 99.823 | 99.766 | 99.776 | 0.474 |
| Items | CONRF Group % | PBMRF Group % | LRPRF Group % | MRPRF Group % | HRPRF Group % | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firmicutes | 48.65 ± 17.99 | 53.61 ± 15.40 | 53.80 ± 17.21 | 48.91 ± 10.82 | 49.82 ± 12.89 | 0.98 |
| Bacteroidota | 51.17 ± 17.96 | 46.15 ± 15.44 | 46.00 ± 17.32 | 50.67 ± 10.66 | 49.89 ± 12.89 | 0.98 |
| Spirochaetota | 0.65 ± 0.79 | 0.68 ± 0.85 | 0.63 ± 0.69 | 1.45 ± 1.04 | 0.66 ± 0.87 | 0.72 |
| Desulfobacterota | 0.22 ± 0.19 | 1.08 ± 1.35 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.99 ± 0.95 | 0.47 ± 0.82 | 0.48 |
| Proteobacteria | 0.37 ± 0.20 | 0.21 ± 0.11 | 0.28 ± 0.00 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.08 | 0.16 |
| Actinobacteriota | 0.31 ± 0.24 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.31 ± 0.17 | 0.31 ± 0.06 | 0.47 ± 0.17 | 0.23 |
| Euryarchaeota | 0.04 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.07 | 0.21 ± 0.12 | 0.17 ± 0.21 | 0.38 ± 0.29 | 0.26 |
| Campylobacterota | 0.10 ± 0.14 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.27 ± 0.27 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.29 ± 0.23 | 0.36 |
| Fibrobacterota | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.64 ± 0.11 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.47 |
| Verrucomicrobiota | 0.01 ± 0.01 a | <0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.02 |
| Items | CONRF Group % | PBMRF Group % | LRPRF Group % | MRPRF Group % | HRPRF Group % | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevotella | 35.40 ± 9.74 | 22.33 ± 21.41 | 38.68 ± 22.84 | 39.97 ± 5.42 | 38.93 ± 15.24 | 0.67 |
| uncultured_rumen_bacterium | 12.83 ± 12.02 | 18.95 ± 14.13 | 5.91 ± 6.12 | 6.40 ± 3.15 | 6.11 ± 3.15 | 0.34 |
| Selenomonas | 17.11 ± 7.02 b | 9.47 ± 3.87 b | 2.63 ± 1.19 a | 2.04 ± 2.40 a | 4.12 ± 2.82 a | 0.01 |
| UCG_004 | 2.20 ± 1.22 | 2.67 ± 2.67 | 5.16 ± 3.48 | 12.28 ± 1.28 | 8.67 ± 10.29 | 0.12 |
| Christensenellaceae_R_7_group | 1.63 ± 1.67 | 10.59 ± 7.52 | 5.19 ± 4.17 | 4.08 ± 1.94 | 6.59 ± 2.99 | 0.19 |
| unclassified_Selenomonadaceae | 5.14 ± 2.44 | 12.53 ± 10.88 | 3.89 ± 6.19 | 1.34 ± 1.46 | 3.54 ± 1.96 | 0.23 |
| Ruminococcus | 3.72 ± 3.80 | 1.56 ± 2.08 | 4.15 ± 4.22 | 3.06 ± 2.52 | 6.53 ± 7.91 | 0.76 |
| Erysipelotrichaceae_UCG_009 | 6.13 ± 10.38 | 1.33 ± 1.02 | 9.32 ± 10.00 | 0.30 ± 0.08 | 0.10 ± 0.14 | 0.36 |
| Anaeroplasma | 0.01 ± 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 11.40 ± 19.56 | 3.81 ± 5.18 | 0.50 |
| Mogibacterium | 0.58 ± 0.41 | 1.92 ± 0.22 | 6.16 ± 0.85 | 0.85 ± 0.30 | 1.58 ± 0.98 | 0.46 |
| Prevotellaceae_UCG_003 | 1.92 ± 0.14 | 3.12 ± 2.68 | 1.25 ± 0.67 | 0.89 ± 0.44 | 3.83 ± 2.84 | 0.28 |
| Lachnospiraceae_NK3A20_group | 0.75 ± 1.00 | 1.75 ± 0.96 | 2.29 ± 1.09 | 1.63 ± 1.86 | 1.79 ± 0.73 | 0.63 |
| [Ruminococcus]_gauvreauii_group | 1.47 ± 0.38 | 1.33 ± 0.93 | 2.56 ± 1.77 | 0.85 ± 0.65 | 0.75 ± 0.23 | 0.23 |
| NK4A214_group | 1.98 ± 1.90 | 1.24 ± 0.40 | 1.05 ± 0.76 | 0.43 ± 0.41 | 1.04 ± 0.48 | 0.46 |
| Others | 4.68 ± 1.03 | 6.51 ± 1.79 | 4.60 ± 2.73 | 5.82 ± 4.13 | 4.46 ± 1.66 | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Kang, D.; He, X.; Yin, F.; Gan, S.; Zhou, G. Effects of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on the Rumen Microbiota of Leizhou Goats. Animals 2025, 15, 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233390
Zheng L, Kang D, He X, Yin F, Gan S, Zhou G. Effects of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on the Rumen Microbiota of Leizhou Goats. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233390
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Longqing, Danju Kang, Xuanhui He, Fuquan Yin, Shangquan Gan, and Guangxian Zhou. 2025. "Effects of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on the Rumen Microbiota of Leizhou Goats" Animals 15, no. 23: 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233390
APA StyleZheng, L., Kang, D., He, X., Yin, F., Gan, S., & Zhou, G. (2025). Effects of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on the Rumen Microbiota of Leizhou Goats. Animals, 15(23), 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233390






