Effect of Noise on Bornean Orangutans’ Glucocorticoid Metabolite (GCM) Levels
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
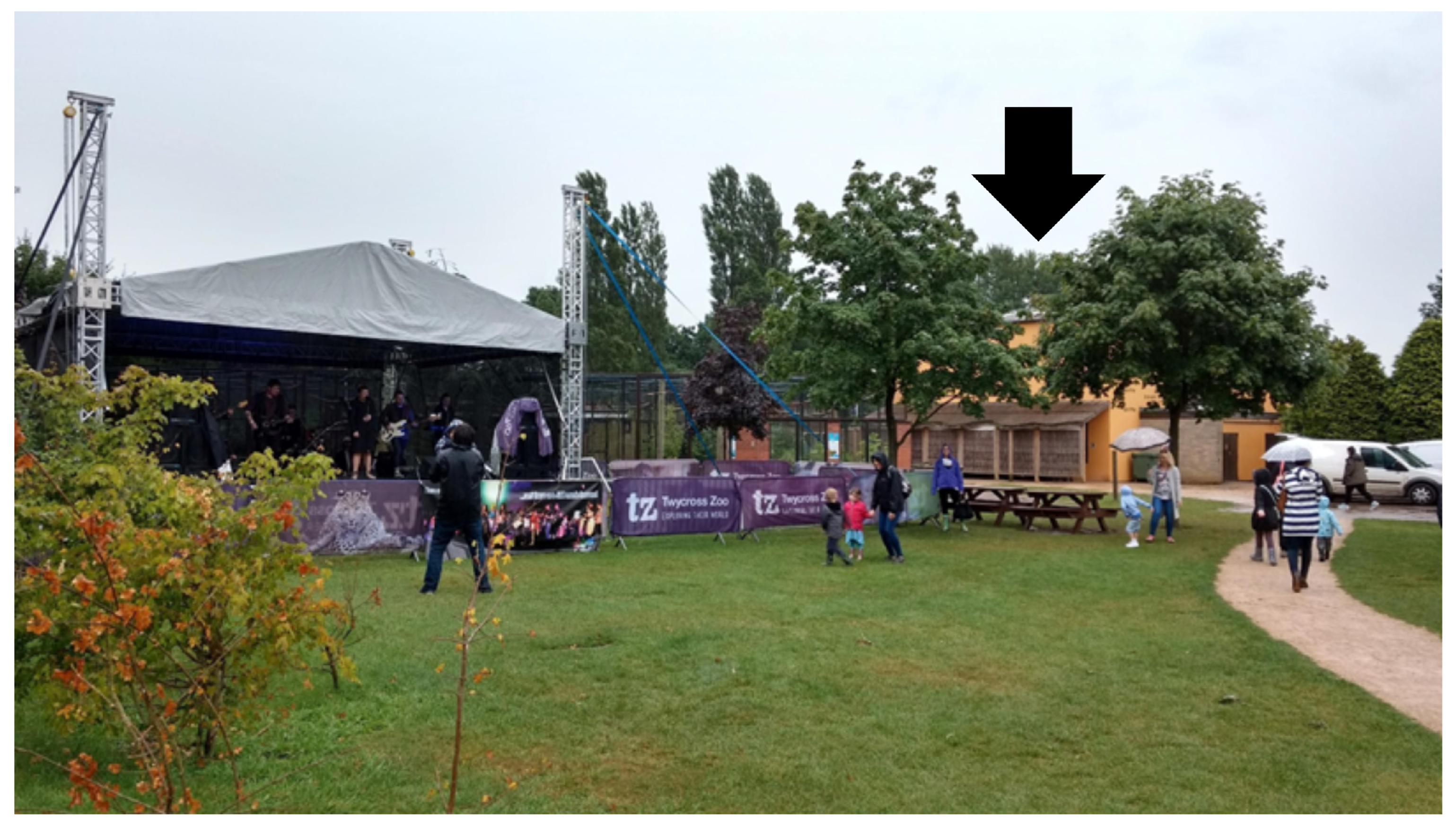
2.1. Study Site and Subjects
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Analysis of FGCMs
2.4. Acoustic Metrics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
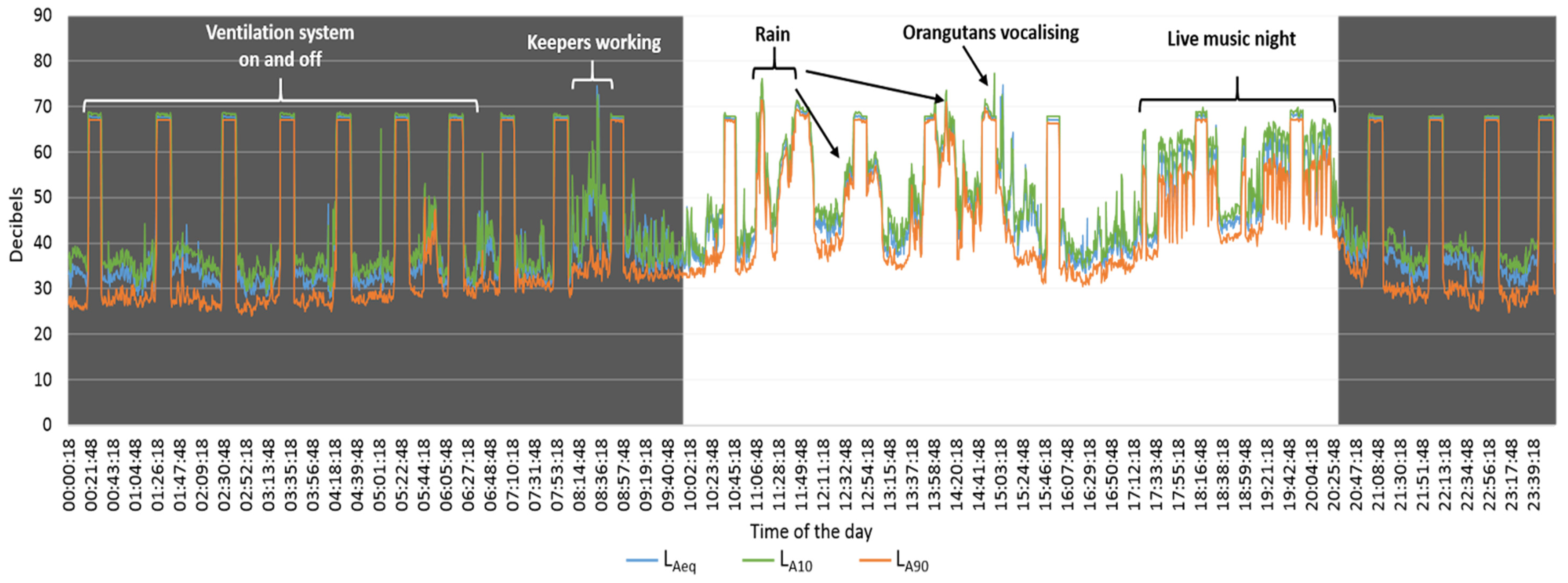
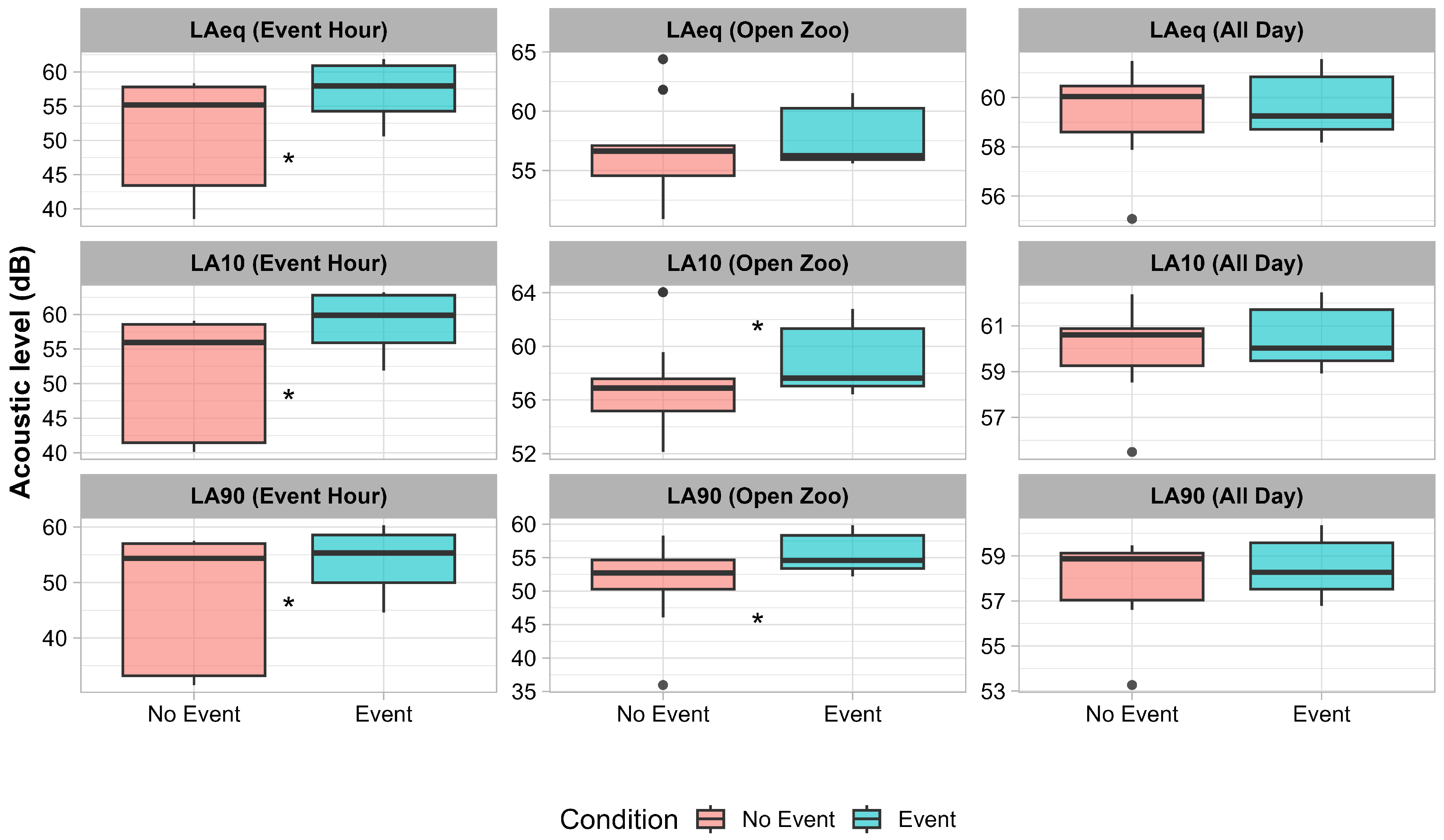
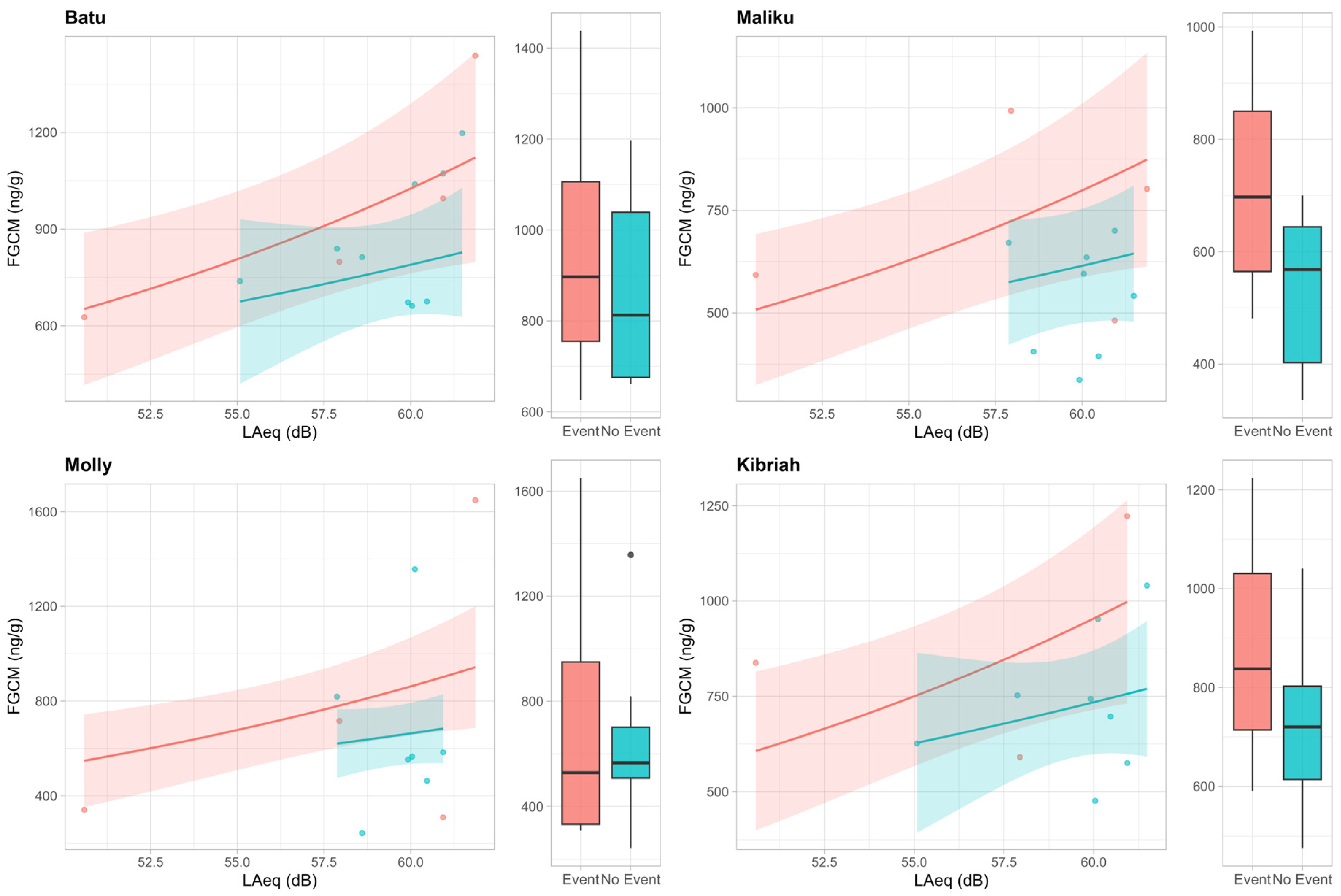
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FGCMs | Faecal glucocorticoid metabolites |
| SPL | Sound pressure level |
| dB | Decibel |
| SLM | Sound level metre |
| DOB | Date of birth |
| Leq | Equivalent continuous sound level |
| EIA | Enzyme immunoassay |
References
- Grantina, E.; Budanceva, J. Incorporating art events into marketing activities—Good practice by European zoos. Econ. Cult. 2023, 20, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, J.J.; Rowden, L.J.; Clifforde, L.M.; Power, A.; Stanley, C.R. Preliminary investigation of the effects of a concert on the behaviour of zoo animals. Zoo Biol. 2022, 41, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Fulwell, T.; Walsh, N.D.; Harley, J.J.; Johnson, B. The Impacts of Evening Events in Zoos: A Christmas Event at Knowsley Safari. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2023, 4, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.J.; Azevedo, C.S.; Cipreste, C.F. Environmental Enrichment. In Zoo Animal Learning and Training; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Weladji, R.B.; Lazure, L.; Paré, P. Zoo soundscape: Daily variation of low-to-high-frequency sounds. Zoo Biol. 2020, 39, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadros, S.; Goulart, V.D.L.; Passos, L.; Vecci, M.A.M.; Young, R.J. Zoo visitor effect on mammal behaviour: Does noise matter? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2014, 156, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.B.; Young, R.J. The Different Physical and Behavioural Characteristics of Zoo Mammals That Influence Their Response to Visitors. Animals 2018, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, F.E.; Dunn, J.C. From Soundwave to Soundscape: A Guide to Acoustic Research in Captive Animal Environments. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 889117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandoli, F.; Mace, J.; Knight, A. The Integrated Effect of Environmental Conditions and Human Presence on the Behaviour of a Pair of Zoo-Housed Asian Small-Clawed Otters. Animals 2023, 13, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.; Brereton, J.E.; Croft, D.P. Measuring welfare in captive flamingos: Activity patterns and exhibit usage in zoo-housed birds. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 205, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, C.; Romano, M.; Knapp, C.R. The effects of anthropogenic noise on frogs housed on exhibit at a public aquarium. Zoo Biol. 2024, 43, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, L.; Larsen, H.; Taylor, P.S. A preliminary study investigating the impact of musical concerts on the behaviour of captive Fiordland penguins (Eudyptes pachyrhynchus) and collared peccaries (Pecari tajacu). Animals 2020, 10, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orban, D.A.; Soltis, J.; Perkins, L.; Mellen, J.D. Sound at the zoo: Using animal monitoring, sound measurement, and noise reduction in zoo animal management. Zoo Biol. 2017, 36, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.L.; Oswald, M.; Tufano, S.; Baird, M.; Mulsow, J.; Ridgway, S.H. A System for Monitoring Acoustics to Supplement an Animal Welfare Plan for Bottlenose Dolphins. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2021, 2, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.; Rice, T. Stakeholder Perspectives on Zoo Sound Environments and Associated Impacts on Captive Animal Behaviour, Management and Welfare. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2025, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcloughlin, M.P.; Stewart, R.; McElligott, A.G. Automated bioacoustics: Methods in ecology and conservation and their potential for animal welfare monitoring. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, M.; Villain, A.S.; Briefer, E.F. A scoping review of the use of bioacoustics to assess various components of farm animal welfare. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2024, 275, 106286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.N.; Williams, L.J. Hullabaloo at the zoo: Aligning acoustic research with the goals of the conservation zoo. Bioacoustics 2025, 34, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dratva, J.; Phuleria, H.C.; Foraster, M.; Gaspoz, J.M.; Keidel, D.; Kunzli, N.; Liu, L.J.S.; Pons, M.; Zemp, E.; Gerbase, M.W.; et al. Transportation Noise and Blood Pressure in a Population-Based Sample of Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganswindt, A.; Brown, J.L.; Freeman, E.W.; Kouba, A.J.; Penfold, L.M.; Santymire, R.M.; Vick, M.M.; Wielebnowski, N.; Willis, E.L.; Milnes, M.R. International Society for Wildlife Endocrinology: The future of endocrine measures for reproductive science, animal welfare and conservation biology. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touma, C.; Palme, R. Measuring faecal glucocorticoid metabolites in mammals and birds: The importance of validation. In Bird Hormones and Bird Migrations: Analysing Hormones in Droppings and Egg Yolks and Assessing Adaptations in Long-Distance Migration; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1046, pp. 54–74. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzenberger, F. The many uses of non-invasive faecal steroid monitoring in zoo and wildlife species. Int. Zoo Yearb. 2007, 41, 52–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwen, S.L.; Hemsworth, P.H. The Visitor Effect on Zoo Animals: Implications and Opportunities for Zoo Animal Welfare. Animals 2019, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.N.; Williams, L.J.; de Kort, S.R.; Gilman, R.T. Assessing the effect of zoo closure on the soundscape using multiple acoustic indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancrenaz, M.; Gumal, M.; Marshall, A.J.; Meijaard, E.; Wich, S.A.; Husson, S. Pongo pygmaeus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T17975A17966347. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/17975/123809220 (accessed on 16 April 2018).
- Species360 Zoological Information Management System, Version 1.7; Species360: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2014.
- Association of Zoos and Aquariums [AZA]. Orangutan Species Survival Plan (SSP). In Orangutan Species Survival Plan: Program Update, January 2024; Association of Zoos and Aquariums: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- European Association of Zoos and Aquaria [EAZA]. Best Practice Guidelines for Orangutans (Pongo spp.); EAZA Executive Office: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Buwalda, B.; van Reenen, K. Individual variation in coping with stress: A multidimensional approach of ultimate and proximate mechanisms. Brain Behav. Evol. 2007, 70, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santicchia, F.; Dantzer, B.; van Kesteren, F.; Palme, R.; Martinoli, A.; Wauters, L.A. Relationships between personality traits and the physiological stress response in a wild mammal. Curr. Zool. 2020, 66, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery Thompson, M.; Fox, S.A.; Berghänel, A.; Sabbi, K.H.; Phillips-Garcia, S.; Enigk, D.K.; Otali, E.; Machanda, Z.P.; Wrangham, R.W.; Muller, M.N. Wild chimpanzees exhibit humanlike aging of glucocorticoid regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8424–8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.B.C.; Galvão, A.C.M.; Sales, C.J.R.; Castro, D.C.; Galvão-Coelho, N.L. Endocrine and cognitive adaptations to cope with stress in immature common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus): Sex and age matter. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, N.O.; Sonnweber, R.; Schülke, O.; Moscovice, L.R.; Deschner, T.; Hohmann, G. Bonobo mothers have elevated urinary cortisol levels during early but not mid or late lactation. Primates 2023, 64, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, N.H.; Brown, J.L.; Jolly, C.J.; Phillips-Conroy, J.E.; Rogers, J.; Bernstein, R.M. Sources of variation in hair cortisol in wild and captive non-human primates. Zoology 2016, 119, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twycross Zoo. Twycross Zoo Conservation Strategy 2023–2030; Twycross Zoo: Atherstone, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Weingrill, T.; Willems, E.P.; Zimmermann, N.; Steinmetz, H.; Heistermann, M. Species-specific patterns in faecal glucocorticoid and androgen levels in zoo-living orangutans (Pongo spp.). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, G.; Margulis, S.W.; Santymire, R. The Effectiveness of Indigestible Markers for Identifying Individual Animal Faeces and Their Prevalence of Use in North American Zoos. Zoo Biol. 2011, 30, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palme, R.; Touma, C.; Arias, N.; Dominchin, M.F.; Lepschy, M. Steroid extraction: Get the best out of faecal samples. Wien. Tierärztl. Monatsschr. 2013, 100, 238–246. [Google Scholar]
- Frigerio, D.; Dittami, J.; Möstl, E.; Kotrschal, K. Excreted corticosterone metabolites co-vary with air temperature and air pressure in male Greylag geese (Anser anser). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 137, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, T.P.; Heistermann, M.; Agil, M.; Purwantara, B.; Supriatna, I.; Gholib, G.; van Schaik, C.P.; Weingrill, T. Validation of a field-friendly extraction and storage method to monitor fecal steroid metabolites in wild orangutans. Primates 2017, 58, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 1996-1:2016; Acoustics—Description, Measurement and Assessment of Environmental Noise—Part 1: Basic Quantities and Assessment Procedures. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Masali, M.; Tarli, S.B.; Maffei, M. Auditory Ossicles and the Evolution of the Primate Ear: A Biomechanical Approach. In Language Origin: A Multidisciplinary Approach; Wind, J., Chiarelli, B., Bichakjian, B., Nocentini, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Spoor, F.; Zonneveld, F. Comparative Review of the Human Bony Labyrinth. Yearb. Phys. Anthropol. 1998, 41, 211–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S. Comparison of auditory functions in the chimpanzee and human. Folia Primatol. 1990, 55, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.M. Welfare, stress and the evolution of feelings. Adv. Stud. Behav. 1998, 27, 371–403. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, T. patchwork: The Composer of Plots, R Package Version 1.1.2. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=patchwork (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Field, A.; Miles, J.; Field, Z. Discovering Statistics Using R; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, F. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models, R Package Version 0.5.6.0. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=DHARMa (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Lenth, R.V.; Singmann, H.; Love, J.; Buerkner, P.; Hervé, M. emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least Squares Means, R package version 1.11.0. 2025. Available online: https://rvlenth.github.io/emmeans/ (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Kumar, V.; Reddy, V.P.; Kokkiligadda, A.; Shivaji, S.; Umapathy, G. Non-invasive assessment of reproductive status and stress in captive Asian elephants in three south Indian zoos. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 201, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott, J.M. Frequency and intensity discrimination in humans and monkeys. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babb, J.A.; Masini, C.V.; Day, H.E.W.; Campeau, S. Habituation of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical axis hormones to repeated homotypic stress and subsequent heterotypic stressor exposure in male and female rats. Stress 2014, 17, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferland, C.L.; Harris, E.P.; Lam, M.; Schrader, L.A. Facilitation of the HPA Axis to a Novel Acute Stress Following Chronic Stress Exposure Modulates Histone Acetylation and the ERK/MAPK Pathway in the Dentate Gyrus of Male Rats. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2942–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kight, C.R.; Swaddle, J.P. How and why environmental noise impacts animals: An integrative, mechanistic review. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.M.; Narins, P.M. Effects of Anthropogenic Noise on Amphibians and Reptiles. In Effects of Anthropogenic Noise on Animals, Springer Handbook of Auditory Research 66; Slabbekoorn, H., Dooling, R.J., Popper, A.N., Fay, R.R., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, Part of Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 179–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ortega, B.; Hendry, A.P. A meta-analysis of human disturbance effects on glucocorticoid hormones in free-ranging wild vertebrates. Biol. Rev. 2023, 98, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, M.M.; Stottlemyre, H.J.; Gabor, C.R. Traffic Noise Impacts Glucocorticoid Response, Activity, and Growth in Two Species of Tadpoles. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2024, 64, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.S.; Young, R.J.; Davies, W.J.; Waddington, D.; Wood, M.D. A Systematic Review of Anthropogenic Noise Impact on Avian Species. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024, 10, 684–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, K.; Forland, T.N.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Rieucau, G.; Slabbekoorn, H.; Sivle, L.D. Predicting the effects of anthropogenic noise on fish reproduction. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2020, 30, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, L.; Kearns, R. Performing encounters (and encountering performance) at Auckland Zoo. N. Z. Geog. 2022, 78, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, H.R.; Gordon, T.A.C.; Eastcott, E.; Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N. Causes and consequences of intraspecific variation in animal responses to anthropogenic noise. Behav. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Jiménez, L.; Iglesias-Merchan, C.; Martínez-Salazar, A.I.; Barja, I. Effect of intensity and duration of anthropic noises on European mink locomotor activity and fecal cortisol metabolite levels. Curr. Zool. 2022, 68, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.M.; Carlstead, K.; Tarou, L.R.; Brown, J.L.; Monfort, S.L. Effects of construction noise on behavior and cortisol levels in a pair of captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Zoo Biol. 2006, 25, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.A.; Swaisgood, R.R.; Czekala, N.M.; Steinman, K.; Lindburg, D.G. Monitoring stress in captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca): Behavioral and hormonal responses to ambient noise. Zoo Biol. 2004, 23, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, F.E.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Hartley, A.; King, A.J.; Lee, T.; Routh, A.; Walker, S.L.; George, K. Relationship between behavior, adrenal activity, and environment in zoo-housed western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla). Zoo Biol. 2012, 31, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, K.A.; Bethell, E.J.; Jacobson, S.L.; Egelkamp, C.; Hopper, L.M.; Ross, S.R. Evaluating Mood Changes in Response to Anthropogenic Noise with a Response-Slowing Task in Three Species of Zoo-housed Primates. Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2018, 5, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, A.; Otsuki, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Murakami, M.; Kotera, Y.; Ozaki, A.; Akutsu, T. Individual Differences in Sensitivity to Everyday Sounds: Developmental, Environmental, and Personality Predictors of Auditory Processing. Cureus 2025, 17, e88141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiVincenti, L., Jr.; McDowell, A.; Herrelko, E.S. Integrating Individual Animal and Population Welfare in Zoos and Aquariums. Animals 2023, 13, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, R. Non-invasive measurement of glucocorticoids: Advances and problems. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 199, 229–243559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, R.; Rettenbacher, S.; Touma, C.; El-Bahr, S.M.; Mostl, E. Stress hormones in mammals and birds—Comparative aspects regarding metabolism, excretion, and noninvasive measurement in fecal samples. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1040, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstead, K.; Brown, J.L.; Seidensticker, J. Behavioral and Adrenocortical Responses to Environmental-Changes in Leopard Cats (Felis bengalensis). Zoo Biol. 1993, 12, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Estimate | Std. Error | z Value | Pr(>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 3.924 | 1.131 | 3.470 | 0.001 |
| Laeq | 0.048 | 0.020 | 2.461 | 0.014 |
| Event | 0.721 | 2.503 | 0.288 | 0.773 |
| Laeq/Event | −0.016 | 0.042 | −0.388 | 0.698 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Queiroz, M.B.d.; Passos, L.F.; Azevedo, C.S.d.; Schork, I.; Palme, R.; Davies, W.J.; Young, R.J. Effect of Noise on Bornean Orangutans’ Glucocorticoid Metabolite (GCM) Levels. Animals 2025, 15, 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233384
Queiroz MBd, Passos LF, Azevedo CSd, Schork I, Palme R, Davies WJ, Young RJ. Effect of Noise on Bornean Orangutans’ Glucocorticoid Metabolite (GCM) Levels. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233384
Chicago/Turabian StyleQueiroz, Marina Bonde de, Luiza Figueiredo Passos, Cristiano Schetini de Azevedo, Ivana Schork, Rupert Palme, William J. Davies, and Robert John Young. 2025. "Effect of Noise on Bornean Orangutans’ Glucocorticoid Metabolite (GCM) Levels" Animals 15, no. 23: 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233384
APA StyleQueiroz, M. B. d., Passos, L. F., Azevedo, C. S. d., Schork, I., Palme, R., Davies, W. J., & Young, R. J. (2025). Effect of Noise on Bornean Orangutans’ Glucocorticoid Metabolite (GCM) Levels. Animals, 15(23), 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233384





