Epidemiological Investigation on Pathogenic Bacteria of Buffalo Subclinical Mastitis and Their Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Characteristics in Guangxi, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
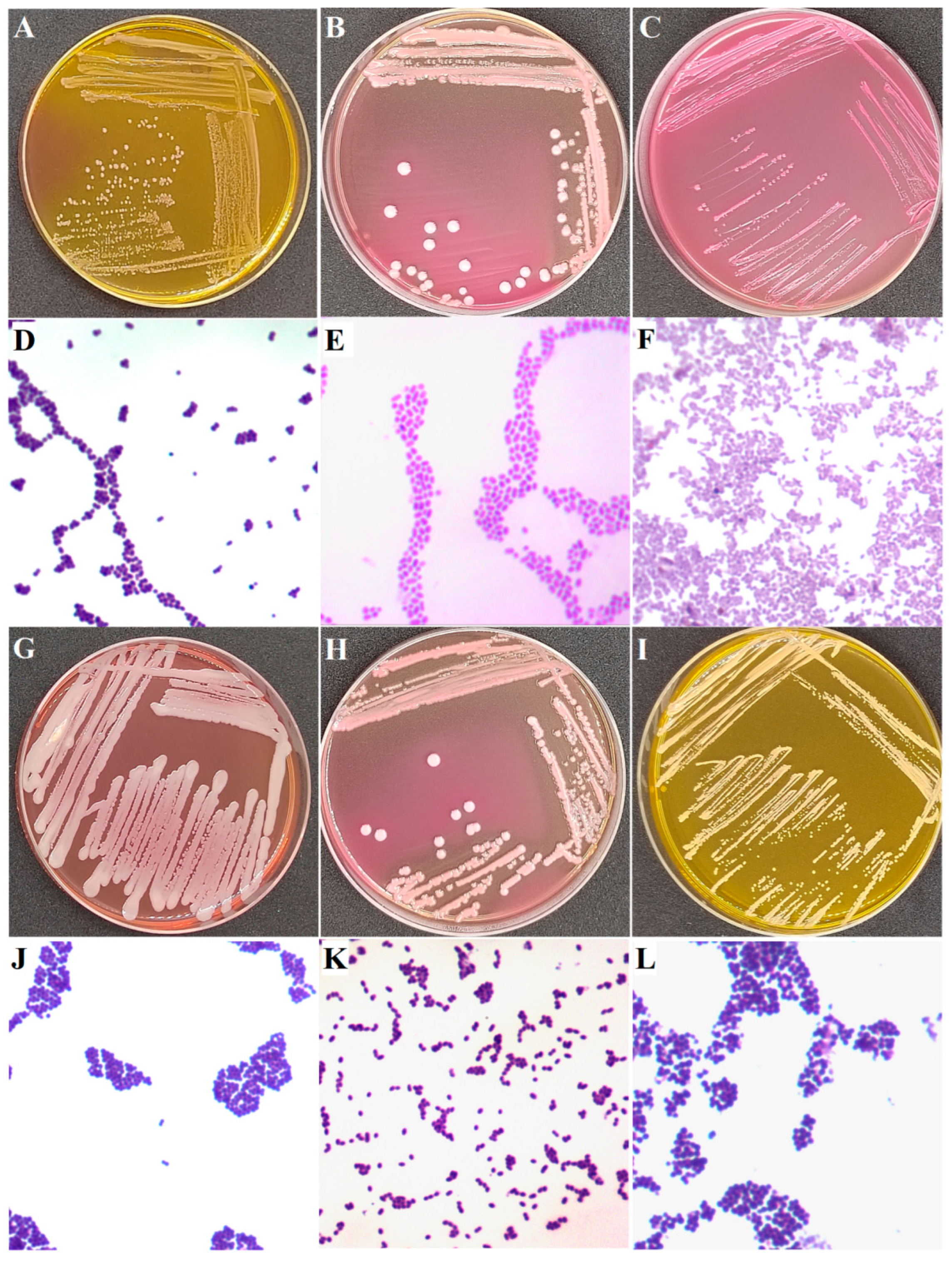
2.2. Isolation of Bacteria
- (a)
- Direct spread: 0.1 mL of milk samples was directly spread on chromogenic S. aureus agar, mannitol salt agar, Baird Parker agar, blood agar, and MacConkey agar. Then, plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h to 48 h.
- (b)
- Enrichment before spread: 5 mL of milk samples was added to 45 mL of brain heart infusion, azide dextrose broth, and Luria broth, respectively, and cultured at 37 °C for 18 h to 24 h. One milliliter of cultures was added into a sterile test tube having 9 mL of sterile water. After mixing, the culture was serially diluted up to 1: 105. Then, 0.1 mL of each dilution was spread to corresponding agar plates (Figure 1) and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h to 48 h. The culture enriched by brain heart infusion was spread on chromogenic S. aureus agar, mannitol salt agar, Baird Parker agar, and blood agar. The culture enriched by azide dextrose broth was spread on Baird Parker agar and blood agar. The culture enriched by Luria broth was spread on Baird Parker agar, blood agar, and MacConkey agar.
2.3. Identification of Pathogenic Bacteria of Subclinical Mastitis
2.4. Screening Principles for Strains Used in Antibiotic Resistance and Galleria mellonella Larvae Infection Tests
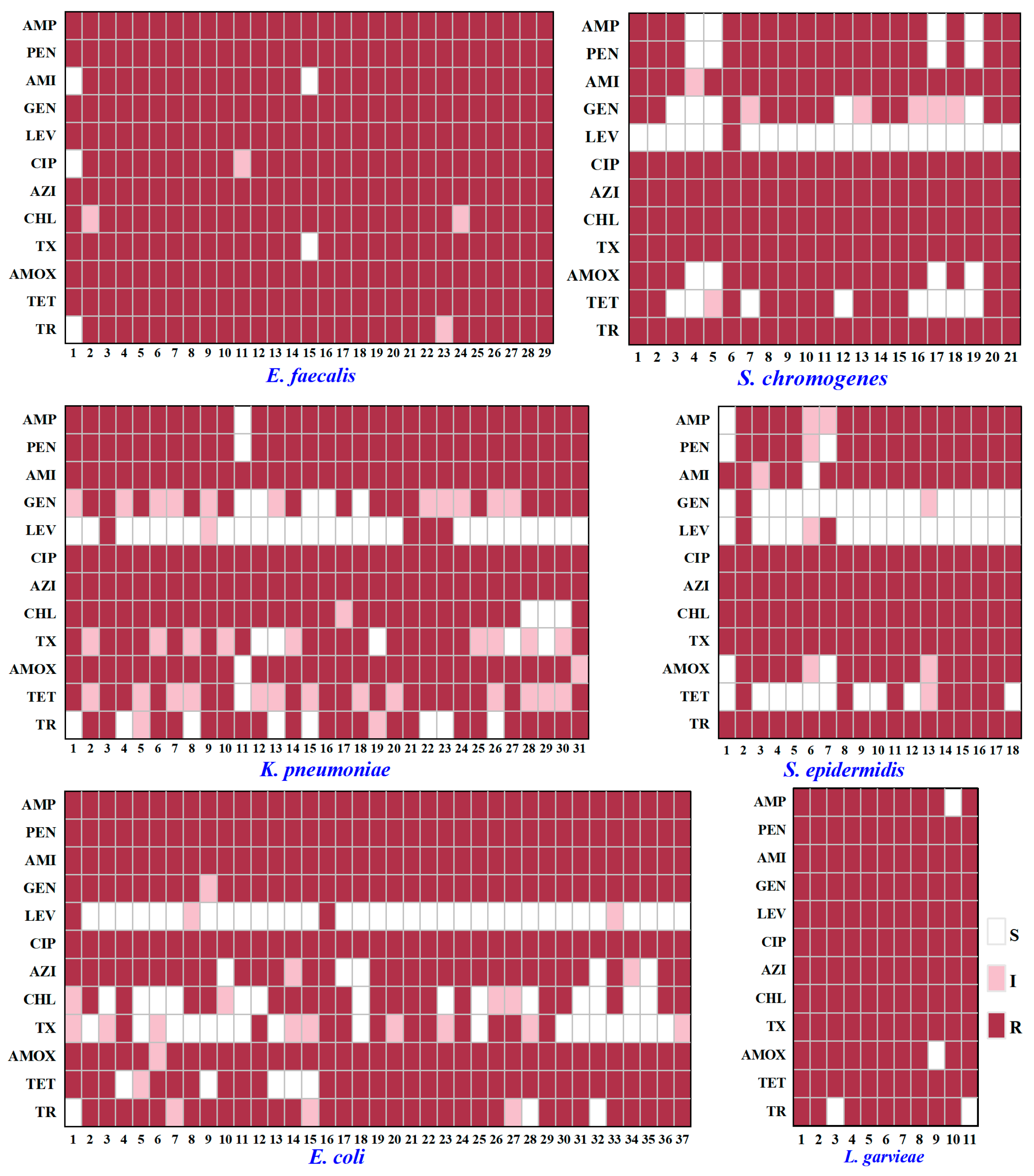
2.5. Analysis on Antibiotic Resistance of Typical PSM
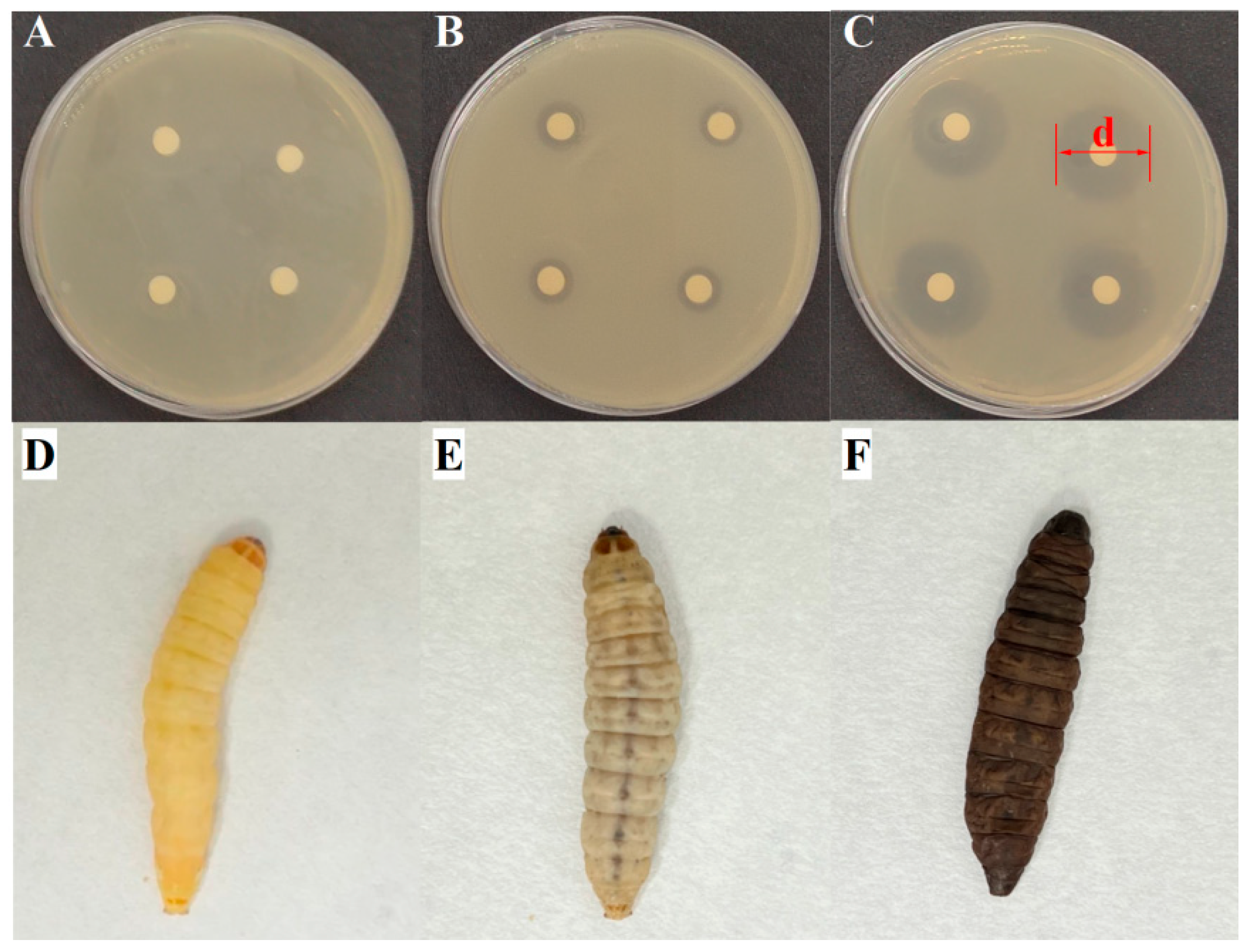
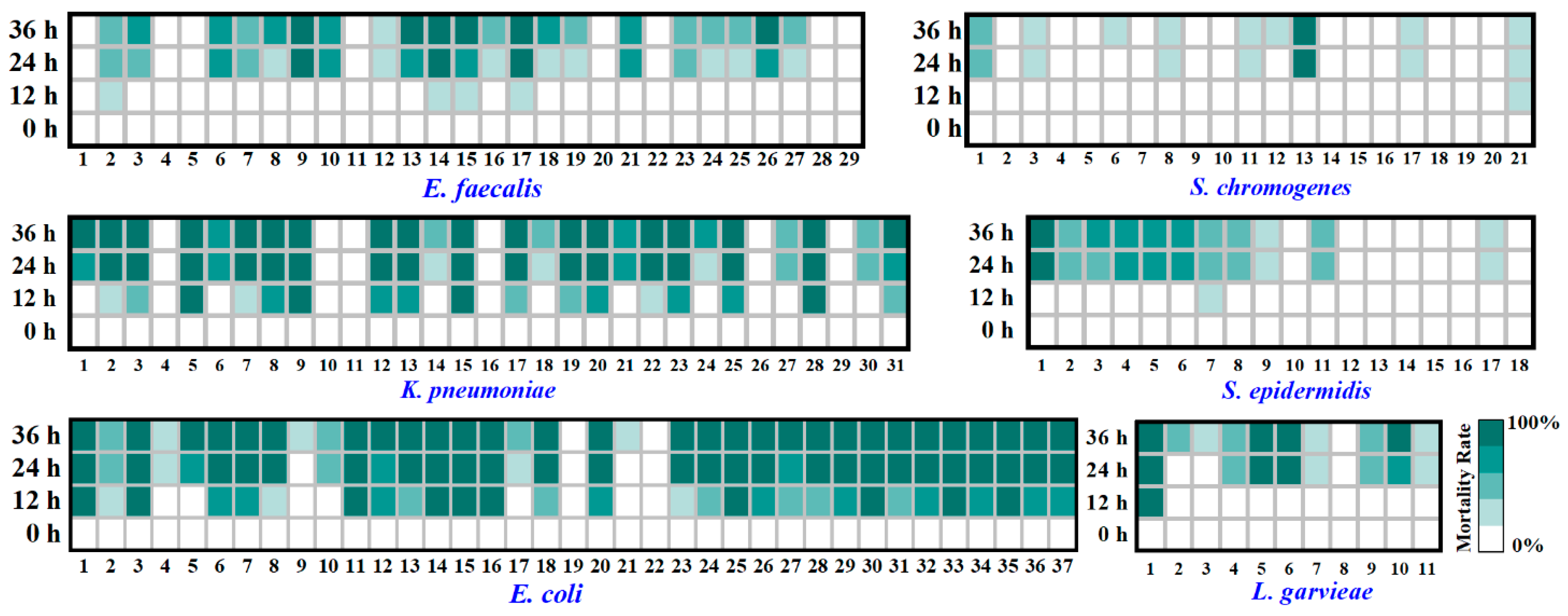
2.6. Analysis on Virulence of Typical PSM
2.7. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence and Isolation of Buffalo PSM in Different Farms
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance of Typical PSM
3.3. Virulence of Typical PSM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCM | Subclinical mastitis |
| PSM | Pathogenic bacteria of subclinical mastitis |
| CoNS | Coagulase-negative Staphylococci |
| SCC | Somatic cell count |
| 16S rRNA | 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| S | Sensitive |
| I | Intermediate |
| R | Resistant |
| AMP | Ampicillin |
| PEN | Penicillin |
| AMI | Amikacin |
| GEN | Gentamicin |
| LEV | Levofloxacin |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
| AZI | Azithromycin |
| CHL | Chloramphenicol |
| TX | Ceftriaxone |
| AMOX | Amoxicillin |
| TET | Tetracycline |
| TR | Trimethoprim |
References
- De Paula, I.L.; Scaldini Teixeira, E.B.; Francisquini, J.D.A.; Stephani, R.; Perrone, Í.T.; Fernandes De Carvalho, A.; Cappa De Oliveira, L.F. Buffalo powder dairy products with and without lactose hydrolysis: Physical-chemical and technical-functional characterizations. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Pan, B.; Ahmad, M.J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Yao, Z.; Lv, H.; Wei, K.; Yang, L. Summer Buffalo Milk Produced in China: A Desirable Diet Enriched in Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Amino Acids. Foods 2022, 11, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Neglia, G.; Campanile, G.; De Marchi, M. Milk somatic cell count and its relationship with milk yield and quality traits in Italian water buffaloes. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 5485–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kamran; Raziq, A.; Wazir, I.; Ullah, R.; Shah, P.; Ali, M.I.; Han, B.; Liu, G. Prevalence of Mastitis Pathogens and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Isolates from Cattle and Buffaloes in Northwest of Pakistan. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 746755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chu, M.; Kang, X.; Liu, G. A deep learning approach combining DeepLabV3+ and improved YOLOv5 to detect dairy cow mastitis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 216, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rearte, R.; Corva, S.G.; de la Sota, R.L.; Lacau-Mengido, I.M.; Giuliodori, M.J. Associations of somatic cell count with milk yield and reproductive performance in grazing dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 6251–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Richoux, R.; Boutinaud, M.; Martin, P.; Gagnaire, V. Role of somatic cells on dairy processes and products: A review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 94, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, M.; Dai, B.; Miao, J.; Yin, Y. Variant innate immune responses of mammary epithelial cells to challenge by Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and the regulating effect of taurine on these bioprocesses. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 96, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztachańska, M.; Barański, W.; Janowski, T.; Pogorzelska, J.; Zduńczyk, S. Prevalence and etiological agents of subclinical mastitis at the end of lactation in nine dairy herds in North-East Poland. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizauro, L.J.L.; de Almeida, C.C.; Silva, S.R.; MacInnes, J.I.; Kropinski, A.M.; Zafalon, L.F.; de Avila, F.A.; de Mello Varani, A. Genomic comparisons and phylogenetic analysis of mastitis-related staphylococci with a focus on adhesion, biofilm, and related regulatory genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Deng, Z.; Cai, L.; Shan, R.; Zhang, S.; Zou, J.; Kastelic, J.P.; et al. Incidence of clinical mastitis and distribution of pathogens on large Chinese dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4797–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, R.; Shukla, V.; Agrawal, Y. Nanoparticles in Managing Bovine Mastitis Pathogens-Isolation, Identification, and Therapeutic Strategies. BioNanoScience 2024, 14, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pan, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, F.; Dong, J.; Wang, T.; Li, L. Prevalence, Virulence, and Antibiotics Gene Profiles in Lactococcus garvieae Isolated from Cows with Clinical Mastitis in China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhaeghen, W.; Piepers, S.; Leroy, F.; Van Coillie, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Vliegher, S. Identification, typing, ecology and epidemiology of coagulase negative Staphylococci associated with ruminants. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Ahmad, M.; Anjum, A. Prevalence of sub clinical mastitis in dairy buffaloes of punjab, pakistan. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2011, 3, 477–480. Available online: https://digitalcommons.memphis.edu/facpubs/14117 (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Han, B.; Meng, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Ren, F.; Zeng, Q.; Robert Nout, M.J. A survey on the microbiological and chemical composition of buffalo milk in China. Food Control 2007, 18, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.R.; Hossain, H.; Rahman, M.N.; Rahman, A.; Ghosh, P.K.; Uddin, M.B.; Nazmul Hoque, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Rahman, M.M. Emergence of highly virulent multidrug and extensively drug resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in buffalo subclinical mastitis cases. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ubaldo, A.L.; Rivero-Perez, N.; Valladares-Carranza, B.; Velázquez-Ordoñez, V.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, L.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A. Bovine mastitis, a worldwide impact disease: Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and viable alternative approaches. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2023, 21, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Y.; Keddie, B.A. The Galleria mellonella-Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Model System: Characterization of Pathogen Virulence and Insect Immune Responses. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insua, J.L.; Llobet, E.; Moranta, D.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C.; Tomás, A.; Garmendia, J.; Bengoechea, J.A. Modeling Klebsiella pneumoniae Pathogenesis by Infection of the Wax Moth Galleria mellonella. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3552–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivaria, F.M.; Noordhuizen, J.P.T.M.; Nielen, M. Interpretation of California mastitis test scores using Staphylococcus aureus culture results for screening of subclinical mastitis in low yielding smallholder dairy cows in the Dar es Salaam region of Tanzania. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 78, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, R.M.S.B.; Deshapriya, R.M.C.; Abeygunawardana, D.I.; Rahularaj, R.; Dematawewa, C.M.B. Subclinical mastitis in dairy cows in major milk-producing areas of Sri Lanka: Prevalence, associated risk factors, and effects on reproduction. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 12900–12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widodo, A.; Lamid, M.; Effendi, M.H.; Khailrullah, A.R.; Kurniawan, S.C.; Silaen, O.S.M.; Riwu, K.H.P.; Yustinasari, L.R.; Afnani, D.A.; Dameanti, F.N.A.E.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance characteristics of multidrug resistance and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli from several dairy farms in Probolinggo, Indonesia. Biodivers. J. Biol. Divers. 2023, 24, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, N.; Alemu, T.; Jirata Birri, D.; Dessalegn, A. Isolation, identification, and determination of antibiogram characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus in cow milk and milk products (yoghurt and cheese) in West Showa Zone, Ethiopia. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 137, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahaman, M.; Arafat, K.Y.; Haider, M.G.; Aminoor Rahman, A.N.M.; Talukder, A.K.; Das, Z.C.; Hoque, M.N. Genomic characterization of Pseudomonas asiatica as an emerging mastitis pathogen in dairy cows with resistance and virulence implications. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2025, 44, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emon, A.A.; Hossain, H.; Chowdhury, M.S.R.; Rahman, M.A.; Tanni, F.Y.; Asha, M.N.; Akter, H.; Hossain, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.M. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility profiles and resistant gene identification of bovine subclinical mastitis pathogens in Bangladesh. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Su, C.; He, Z. Isolation, characterization, and fermentation potential of coagulase-negative Staphylococci with taste-enhancing properties from Chinese traditional bacon. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyavathy, K.; Madhusudhan, B.K. Isolation, Identification, Speciation and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Klebsiella Species among Various Clinical Samples at Tertiary Care Hospital. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2021, 33, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, R.; Peters, R.; Gierveld, S.; Schuurman, T.; Kooistra-Smid, M.; Savelkoul, P. Improved detection of microbial DNA after bead-beating before DNA isolation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCFC Standard. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Approved Standard-Third Edition. 2008. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/14654009/vet01s#references (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Casadevall, A.; Pirofski, L.A. Host-Pathogen Interactions: The Attributes of Virulence. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guembe, M.; Hafian, R.; Díaz-Navarro, M.; Visedo, A.; De Maio, F.; Pimpinelli, F.; Cavallo, I.; Truglio, M.; Sivori, F.; Di Domenico, E.G. Virulence profile of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains by an in vivo model of Galleria mellonella. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e221524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.; Wu, A.; Li, R.; Cai, D.; Tong, H.; Wang, N.; Tan, J. Identification of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae based on biomarkers and Galleria mellonella infection model. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Loh, J.M.S.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella infection models for the study of bacterial diseases and for antimicrobial drug testing. Virulence 2016, 7, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuko, S.; Raivio, T.L. Mutations That Impact the Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Cpx Envelope Stress Response Attenuate Virulence in Galleria mellonella. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Gizdavic-Nikolaidis, M.; Swift, S. Investigation of Polyaniline and a Functionalised Derivative as Antimicrobial Additives to Create Contamination Resistant Surfaces. Materials 2018, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaca, A.O.; Abranches, J.; Kajfasz, J.K.; Lemos, J.A. Global transcriptional analysis of the stringent response in Enterococcus faecalis. Microbiology 2012, 158, 1994–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, F.; Guan, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, K.; Wu, C. The prevalence of pathogens causing bovine mastitis and their associated risk factors in 15 large dairy farms in China: An observational study. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 247, 108757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.J.; Pandit, R.J.; Bhatt, V.D.; Kunjadia, P.D.; Nauriyal, D.S.; Koringa, P.G.; Joshi, C.G.; Kunjadia, A.P. Metagenomic approach to study the bacterial community in clinical and subclinical mastitis in buffalo. Meta Gene 2017, 12, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaas, I.C.; Zadoks, R.N. An update on environmental mastitis: Challenging perceptions. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Xia, P.; Tian, R.; Li, R.; Xia, L. Molecular epidemiology, phenotypic and genomic characterization of antibiotic-resistant enterococcal isolates from diverse farm animals in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różańska, H.; Lewtak-Piłat, A.; Kubajka, M.; Weiner, M. Occurrence of enterococci in mastitic cow’s milk and their antimicrobial resistance. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysanek, D.; Zouharova, M.; Babak, V. Monitoring major mastitis pathogens at the population level based on examination of bulk tank milk samples. J. Dairy Res. 2009, 76, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.P.; Aragão, B.B.; de Melo, R.P.B.; Da Silva, D.M.S.; de Carvalho, R.G.; Juliano, M.A.; Farias, M.P.O.; de Lira, N.S.C.; Mota, R.A. Bovine mastitis in northeastern Brazil: Occurrence of emergent bacteria and their phenotypic and genotypic profile of antimicrobial resistance. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 85, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Shang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Li, H.; Li, J. Short communication: Antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes of Enterococcus faecalis isolated from subclinical bovine mastitis cases in China. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Loong, S.; Khoo, J.; Lim, F.; Chai, L.; Suntharalingam, C.; Sivalingam, J.; AbuBakar, S. Impact of Hygiene Intervention Practices on Microbial Load in Raw Milk. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. Int. Res. J. Microbiol. 2017, 11, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, A.; Gaio, V.; Lopes, N.; Melo, L.D.R. Virulence Factors in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Pathogens 2021, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Visscher, A.; Piepers, S.; Supré, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Vliegher, S. Short communication: Species group-specific predictors at the cow and quarter level for intramammary infection with coagulase-negative Staphylococci in dairy cattle throughout lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5448–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazal, M.A.; Rana, E.A.; Akter, S.; Alim, M.A.; Barua, H.; Ahad, A. Molecular identification, antimicrobial resistance and virulence gene profiling of Staphylococcus spp. associated with bovine sub-clinical mastitis in Bangladesh. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2023, 21, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Nobrega, D.B.; Cobo, E.R.; Han, B.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Barkema, H.W.; Gao, J. Molecular epidemiology and distribution of antimicrobial resistance genes of Staphylococcus species isolated from Chinese dairy cows with clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1571–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janštová, B.; Dračková, M.; Dlesková, K.; Cupáková, Š.; Necidová, L.; Navrátilová, P.; Vorlová, L. Quality of raw milk from a farm with automatic milking system in the Czech Republic. Acta Vet. Brno 2011, 80, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 33, D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drugea, R.I.; Siteavu, M.I.; Pitoiu, E.; Delcaru, C.; Sârbu, E.M.; Postolache, C.; Bărăităreanu, S. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from Raw Cow’s Milk. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouamba, A.J.K.; Gagnon, M.; LaPointe, G.; Chouinard, P.Y.; Roy, D. Graduate Student Literature Review: Farm management practices: Potential microbial sources that determine the microbiota of raw bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7276–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Gao, J.; Ali, T.; Yu, D.; Zhang, S.; Khan, S.U.; Fanning, S.; Han, B. Characteristics of Aerococcus viridans isolated from bovine subclinical mastitis and its effect on milk SCC, yield, and composition. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; You, J.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, H. Association with Elevated Somatic Cell Counts and Characterization of Aerococcus viridans Isolates from Bovine Mastitis Milk in South Korea. Curr. Microbiol. 2025, 82, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, G.; Arzu, F.; Nilgün, G.; Serhat, A.S.; Alper, Ç.; Ece, K.; Serhat, A.; Murat, F. Investigation on the Etiology of Subclinical Mastitis in Jersey And Hybrid Jersey Dairy Cows. Acta Vet. 2015, 65, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Corral, Y.; Santos, Y. Predicting antimicrobial resistance of Lactococcus garvieae: PCR detection of resistance genes versus MALDI-TOF protein profiling. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawneh, J.I.; Vezina, B.; Ramay, H.R.; Al-Harbi, H.; James, A.S.; Soust, M.; Moore, R.J.; Olchowy, T.W.J. Survey and Sequence Characterization of Bovine Mastitis-Associated Escherichia coli in Dairy Herds. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 582297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, S.; Jung, D.; Ronholm, J.; George, S. Prevalence and mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from mastitic dairy cattle in Canada. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartor, Y.H.; Abd El-Aziz, N.K.; Gharieb, R.M.A.; El Damaty, H.M.; Enany, S.; Soliman, E.A.; Abdellatif, S.S.; Attia, A.S.A.; Bahnass, M.M.; El-Shazly, Y.A.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Bovine Mastitis and Raw Milk: The First Emergence of Colistin mcr-10 and Fosfomycin fosA5 Resistance Genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae in Middle East. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 770813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegewi, U.A.; Esemu, S.N.; Ndip, R.N.; Ndip, L.M. Prevalence and risk factors of coliform-associated mastitis and antibiotic resistance of coliforms from lactating dairy cows in North West Cameroon. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e268247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, Y.; Qin, A.; Yang, Z.; et al. Isolation and characterization of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from raw cow milk in Jiangsu and Shandong provinces, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson Waller, K.; Myrenås, M.; Börjesson, S.; Kim, H.; Widerström, M.; Monsen, T.; Sigurðarson Sandholt, A.K.; Östlund, E.; Cha, W. Genotypic characterization of Staphylococcus chromogenes and Staphylococcus simulans from Swedish cases of bovine subclinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 7991–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmdel, S.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Torriani, S.; Gatto, V.; Pashangeh, S. Safety hazards in bacteriocinogenic Staphylococcus strains isolated from goat and sheep milk. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowoyo, P.T.; Ogunbanwo, S.T. Antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-negative Staphylococci from Nigerian traditional fermented foods. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, D.S.; Fish, D.N.; Redington, J.J. Levofloxacin, a second-generation fluoroquinolone. Pharmacotherapy 1998, 18, 915–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitovs, A.; Sartini, I.; Giorgi, M. Levofloxacin in veterinary medicine: A literature review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzin, T.; Nazir, K.; Zahan, M.; Parvej, M.; Zesmin, K.; Rahman, M. Antibiotic resistance profile of bacteria isolated from raw milk samples of cattle and buffaloes. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2016, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, S.M.; Sahito, J.K.; Soomro, A.A.; Mirani, A.H.; Memon, M.A.; Kalhoro, N.H. Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase genes among Escherichia coli isolates of buffalo mastitis milk. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2024, 33, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.S.; Zussman, J.; Donegan, N.P.; Ramos, R.I.; Garcia, N.C.; Uslan, D.Z.; Iwakura, Y.; Simon, S.I.; Cheung, A.L.; Modlin, R.L.; et al. Noninvasive In Vivo Imaging to Evaluate Immune Responses and Antimicrobial Therapy against Staphylococcus aureus and USA300 MRSA Skin Infections. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedos, J.P.; Rieux, V.; Bauchet, J.; Muffat-joly, M.; Carbon, C.; Azoulay-dupuis, E. Efficacy of trovafloxacin against penicillin-susceptible and multiresistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a mouse pneumonia model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaatout, N. An overview on mastitis-associated Escherichia coli: Pathogenicity, host immunity and the use of alternative therapies. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 256, 126960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuenzalida, M.J.; Ruegg, P.L. Negatively controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate intramammary treatment of nonsevere, gram-negative clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5438–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, R.N.; Griffiths, H.M.; Munoz, M.A.; Ahlstrom, C.; Bennett, G.J.; Thomas, E.; Schukken, Y.H. Sources of Klebsiella and Raoultella species on dairy farms: Be careful where you walk. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhaeghen, W.; Piepers, S.; Leroy, F.; Van Coillie, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Vliegher, S. Invited review: Effect, persistence, and virulence of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species associated with ruminant udder health. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5275–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Bacteria | No. of Total Strains Isolated | No. of Total Samples Containing the Bacteria | Isolation Ratio of Samples (%) 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Samples n = 132 | Herd A n = 115 | Herd B n = 8 | Herd C n = 9 | |||
| Enterococcus faecalis 1 | 386 | 68 | 51.52 | 52.17 | - | 88.89 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae 1 | 85 | 37 | 28.03 | 32.17 | - | - |
| Escherichia coli 1 | 75 | 42 | 31.82 | 24.35 | 75.00 | 88.89 |
| Staphylococcus chromogenes 1,2 | 59 | 25 | 18.94 | 13.04 | 25.00 | 88.89 |
| Macrococcus caseolyticus 1 | 59 | 17 | 12.88 | 13.91 | - | 11.11 |
| Lactococcus garvieae 1 | 58 | 31 | 23.48 | 26.09 | - | 11.11 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 42 | 22 | 16.67 | 19.13 | - | - |
| Enterococcus gallinarum | 40 | 23 | 17.42 | 19.13 | - | 11.11 |
| Enterobacter cloacae 1 | 33 | 24 | 18.18 | 20.00 | - | 11.11 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis 1,2 | 31 | 15 | 11.36 | 8.70 | - | 55.56 |
| Mammaliicoccus sciuri 1 | 29 | 18 | 13.64 | 12.17 | 12.50 | 33.33 |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus 1,2 | 28 | 17 | 12.88 | 6.96 | 50.00 | 55.56 |
| Streptococcus macedonicus | 25 | 12 | 9.09 | 10.43 | - | - |
| Kurthia gibsonii | 25 | 11 | 8.33 | 9.57 | - | - |
| Staphylococcus borealis 1,2 | 24 | 14 | 10.61 | 6.96 | - | 66.67 |
| Aerococcus viridans 1 | 20 | 9 | 6.82 | 1.74 | 62.50 | 22.22 |
| Staphylococcus cohnii 2 | 20 | 10 | 7.58 | 8.70 | - | - |
| CoNS | 257 | 73 | 55.30 | 49.57 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| PSM | 1058 | 126 | 95.45 | 94.78 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total | 1659 | 132 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, R.; Dan, X.; Li, J.; Hau, E.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ding, J.; et al. Epidemiological Investigation on Pathogenic Bacteria of Buffalo Subclinical Mastitis and Their Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Characteristics in Guangxi, China. Animals 2025, 15, 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223321
Li L, Zhang J, Wei X, Wang R, Dan X, Li J, Hau E, Zeng Q, Liu Q, Ding J, et al. Epidemiological Investigation on Pathogenic Bacteria of Buffalo Subclinical Mastitis and Their Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Characteristics in Guangxi, China. Animals. 2025; 15(22):3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223321
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ling, Jiaping Zhang, Xingqi Wei, Ruimin Wang, Xia Dan, Jianfeng Li, Enghuan Hau, Qingkun Zeng, Qingyou Liu, Jiafeng Ding, and et al. 2025. "Epidemiological Investigation on Pathogenic Bacteria of Buffalo Subclinical Mastitis and Their Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Characteristics in Guangxi, China" Animals 15, no. 22: 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223321
APA StyleLi, L., Zhang, J., Wei, X., Wang, R., Dan, X., Li, J., Hau, E., Zeng, Q., Liu, Q., Ding, J., & Cui, K. (2025). Epidemiological Investigation on Pathogenic Bacteria of Buffalo Subclinical Mastitis and Their Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Characteristics in Guangxi, China. Animals, 15(22), 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223321






