Risk Factors Associated with Azotemia in Dogs Presented to the Chiang Mai University Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Thailand: A Retrospective Study (2017–2021)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
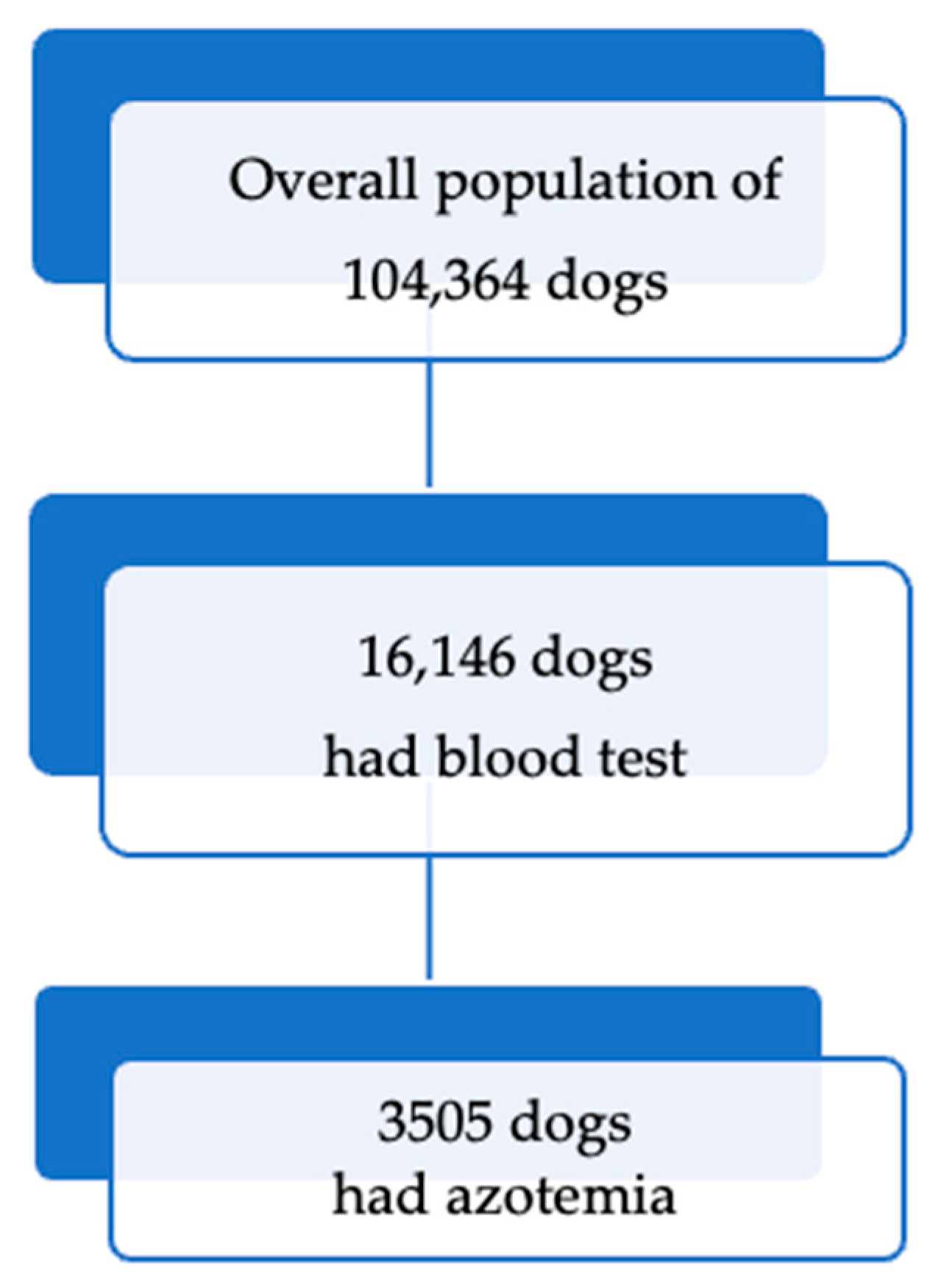
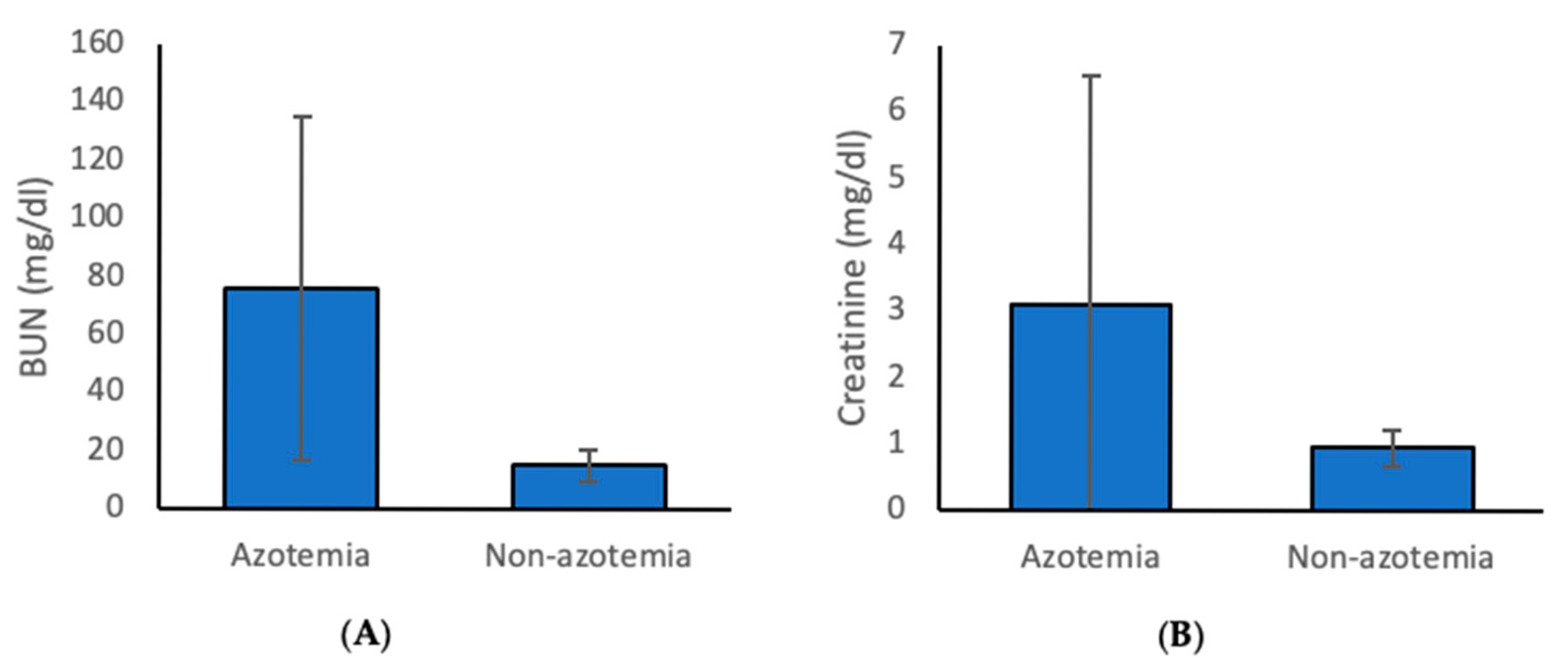
3.1. Prevalence and Classification of Azotemia
3.2. Risk Associated with Azotemia in Dogs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CVS | Cardiovascular disease |
| IRIS | International Renal Interest Society |
| NGAL | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
| OR | Odds ratios |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SCr | Serum creatinine |
| SDMA | Symmetric dimethylarginine |
| UK | United Kingdom |
| USA | United States of America |
References
- Polzin, D.J. Chronic kidney disease in small animals. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiBartola, S.; Westropp, J. Chapter 41: Clinical Manifestations of Urinary Disorders. In Small Animal Internal Medicine, 5th ed.; Couto, C.G., Nelson, R.W., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Riverport Lane, MO, USA, 2014; pp. 629–637. [Google Scholar]
- Yerramilli, M.; Farace, G.; Quinn, J.; Yerramilli, M. Kidney disease and the nexus of chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury: The role of novel biomarkers as early and accurate diagnostics. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 46, 961–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartges, J.W. Chronic kidney disease in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 42, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, L. Acute kidney injury in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, C.; Eatroff, A. Acute kidney injury. August’s Consult. Feline Intern. Med. 2016, 7, 483. [Google Scholar]
- Lees, G.E.; Brown, S.A.; Elliott, J.; Grauer, G.E.; Vaden, S.L. Assessment and management of proteinuria in dogs and cats: 2004 ACVIM Forum Consensus Statement (small animal). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2005, 19, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunaevich, A.; Chen, H.; Musseri, D.; Kuzi, S.; Mazaki-Tovi, M.; Aroch, I.; Segev, G. Acute on chronic kidney disease in dogs: Etiology, clinical and clinicopathologic findings, prognostic markers, and survival. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlem, D.; Neiger, R.; Schweighauser, A.; Francey, T.; Yerramilli, M.; Obare, E.; Steinbach, S. Plasma symmetric dimethylarginine concentration in dogs with acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, D.; Elliott, J.; Church, D.; McGreevy, P.; Thomson, P.; Brodbelt, D. Chronic kidney disease in dogs in UK veterinary practices: Prevalence, risk factors, and survival. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legatti, S.A.M.; El Dib, R.; Legatti, E.; Botan, A.G.; Camargo, S.E.A.; Agarwal, A.; Barretti, P.; Paes, A.C. Acute kidney injury in cats and dogs: A proportional meta-analysis of case series studies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altheimer, K.; Jongwattanapisan, P.; Luengyosluechakul, S.; Pusoonthornthum, R.; Prapasarakul, N.; Kurilung, A.; Broens, E.M.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Goris, M.G.; Ahmed, A.A. Leptospira infection and shedding in dogs in Thailand. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissi, D.R.; Brown, C.A. Diagnostic features in 10 naturally occurring cases of acute fatal canine leptospirosis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2014, 26, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, E.; Lippi, I.; Guidi, G.; Perondi, F.; Pierini, A.; Marchetti, V. Acute pancreatitis and acute kidney injury in dogs. Vet. J. 2019, 245, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiene, R.; Kristiansen, V.; Teige, J.; Jansen, J.H. Renal histomorphology in dogs with pyometra and control dogs, and long term clinical outcome with respect to signs of kidney disease. Acta Vet. Scand. 2007, 49, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Lane, I.; Stokes, J. Acute postrenal azotemia: Etiology, clinicopathology, and pathophysiology. Compendium 2009, 31, 520–530, 533; quiz 530. [Google Scholar]
- IRIS. IRIS Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Dogs and Cats (Modified 2023). Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/666b9ecb4064a156963b4162/t/66a6dbc90ca6986e1b5c06bd/1722211273243/2_IRIS_Staging_of_CKD_2023.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Cowgill, L. IRIS Guideline Recommendations for Grading of AKI in Dogs and Cats. 2016. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/666b9ecb4064a156963b4162/t/67cb04e9e54f3e17317349f9/1741358315504/4_ldc-revised-grading-of-acute-kidney-injury.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Latimer, K.S. Duncan and Prasse’s Veterinary Laboratory Medicine: Clinical Pathology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkinos, Y.; Morrison, J.; Bradley, R.; Panagiotakos, T.; Ogeer, J.; Chew, D.; O’Flynn, C.; De Meyer, G.; Watson, P.; Tagkopoulos, I. An early prediction model for canine chronic kidney disease based on routine clinical laboratory tests. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.; Taylor, D.; Lowe, M.; Barlow, S.; Jackson, J. Replicating the real-world evidence methods available in human health to assess burden and outcomes for dogs with chronic kidney disease, their owners, and the veterinary healthcare system in the United States of America. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1502933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emejuo, N.T.; Omeke, J.N.; Iheodioha, J.I.; Shoyinka, S.V.O. Occurrence and correlates of azotaemia in dogs presented for veterinary care in a tertiary veterinary hospital in Nigeria. Rev. Med. Vet. 2023, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, E.J.; Cortellini, S.; Cole, L.P. Prevalence of Acute Kidney Injury and Its Association with Severity and Outcome in Small Animal Trauma Patients: 387 Cases (2017–2021). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2025, 35, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweighauser, A.; Henke, D.; Oevermann, A.; Gurtner, C.; Francey, T. Toxicosis with grapes or raisins causing acute kidney injury and neurological signs in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, G.; Benedicenti, L.; Mathews, K. Retrospective cohort study on the incidence of acute kidney injury and death following hydroxyethyl starch (HES 10% 250/0.5/5:1) administration in dogs (2007–2010). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2016, 26, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoen, M.E.; Kerl, M.E. Characterization of acute kidney injury in hospitalized dogs and evaluation of a veterinary acute kidney injury staging system. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2011, 21, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, I.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury in severe sepsis: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2015, 25, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghneim, G.; Viers, J.; Chomel, B.; Kass, P.; Descollonges, D.; Johnson, M. Use of a case-control study and geographic information systems to determine environmental and demographic risk factors for canine leptospirosis. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyn, C.M.; Libera, K.C.; Weese, J.S.; Jardine, C.M.; Berke, O.; Grant, L.E. Social and environmental risk factors for canine leptospirosis: A scoping review. Vet. Rec. 2024, 195, e4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.P. Seasonality of canine leptospirosis in the United States and Canada and its association with rainfall. Prev. Vet. Med. 2002, 56, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.; Hartmann, K.; Lunn, K.; Moore, G.; Stoddard, R.; Goldstein, R. 2010 ACVIM small animal consensus statement on leptospirosis: Diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment, and prevention. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lv, C.; Guo, W.; Li, Z. Temperature and humidity as drivers for the transmission of zoonotic diseases. Anim. Res. One Health 2024, 2, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Aeddula, N.R. Azotemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vaden, S.L.; Levine, J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. A retrospective case-control of acute renal failure in 99 dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1997, 11, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preyß-Jägeler, C.; Hartmann, K.; Dorsch, R. Changes in renal parameters and their association with subclinical vector-borne infections in Bernese Mountain dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugford, A.; Li, R.; Humm, K. Acute kidney injury in dogs and cats 1. Pathogenesis and diagnosis. InPractice 2013, 35, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, I.; Perondi, F.; Lubas, G.; Gori, E.; Pierini, A.; D’Addetta, A.; Marchetti, V. Erythrogram patterns in dogs with chronic kidney disease. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segev, G.; Kass, P.; Francey, T.; Cowgill, L. A novel clinical scoring system for outcome prediction in dogs with acute kidney injury managed by hemodialysis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008, 22, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, I.; Perondi, F.; Gori, E.; Pierini, A.; Bernicchi, L.; Marchetti, V. Serum bicarbonate deficiency in dogs with acute and chronic kidney disease. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segev, G.; Cortellini, S.; Foster, J.D.; Francey, T.; Langston, C.; Londoño, L.; Schweighauser, A.; Jepson, R.E. International Renal Interest Society best practice consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in cats and dogs. Vet. J. 2024, 305, 106068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defauw, P.; Daminet, S.; Leisewitz, A.L.; Goddard, A.; Paepe, D.; Duchateau, L.; Schoeman, J.P. Renal azotemia and associated clinical and laboratory findings in dogs with Babesia rossi infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 260, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Manzanilla, C.A.; Cárdenas-Marrufo, M.F.; Gutiérrez-Blanco, E.; Jiménez-Coello, M.; Pech-Sosa, N.R.; Ortega-Pacheco, A. Clinical features of chronic kidney disease in dogs with the serological presence of Leptospira spp., Ehrlichia canis, and Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Anim. Dis. 2023, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthélemy, A.; Magnin, M.; Pouzot-Nevoret, C.; Bonnet-Garin, J.M.; Hugonnard, M.; Goy-Thollot, I. Hemorrhagic, hemostatic, and thromboelastometric disorders in 35 dogs with a clinical diagnosis of leptospirosis: A prospective study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, A.; Schweighauser, A.; Francey, T. Increasing incidence of canine leptospirosis in Switzerland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 7242–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeyam, T.; Tablerk, P.; Petchanok, B.; Pichpol, D.; Padungtod, P. Seroprevalence and risk factors associated with leptospirosis in dogs. Southeast. Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2006, 37, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Niwetpathomwat, A.; Assarasakorn, S. Preliminary investigation of canine leptospirosis in a rural area of Thailand. Med. Weter. 2007, 63, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Boonciew, P.; Saisongkorh, W.; Brameld, S.; Thongpin, M.; Kurilung, A.; Krangvichian, P.; Niyomtham, W.; Patarakul, K.; Phichitraslip, T.; Hampson, D.J. Improved Antibody Detection for Canine Leptospirosis: ELISAs Modified Using Local Leptospiral Serovar Isolates from Asymptomatic Dogs. Animals 2024, 14, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, S.; Weis, J.; Schweighauser, A.; Francey, T.; Neiger, R. Plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase–associated Lipocalin (NGAL) in dogs with acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defauw, P.; Schoeman, J.P.; Leisewitz, A.L.; Goddard, A.; Duchateau, L.; Aresu, L.; Meyer, E.; Daminet, S. Evaluation of acute kidney injury in dogs with complicated or uncomplicated Babesia rossi infection. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Breed (n = 3505) | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Mixed breed | 1608 (45.9) |
| Pomeranian | 333 (9.5) |
| Shih tzu | 299 (8.5) |
| Poodle | 291 (8.3) |
| Chihuahua | 213 (6.1) |
| Golden retriever | 105 (3) |
| Siberian husky | 103 (2.9) |
| Bangkaew | 76 (2.2) |
| Labrador retriever | 66 (1.9) |
| Pug | 43 (1.2) |
| Miniature Pincher | 40 (1.1) |
| French Bulldog | 37 (1.1) |
| Variables | Azotemia (N, %) | Odds Ratio (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Season | |||
| Summer | 850/1389 (61.2) | Reference | |
| Rainy | 1290/2272 (56.8) | 0.83 (0.73–0.95) | 0.009 |
| Winter | 1365/1874 (72.8) | 1.70 (1.47–1.97) | <0.001 |
| Breed | |||
| Mixed breed | 1608/2401 (67.0) | 1.32 (1.18–1.48) | <0.001 |
| Pure breed | 1895/3130 (60.5) | Reference | |
| Age | |||
| <6 months | 161/292 (55.1) | 1.42 (1.05–1.93) | 0.023 |
| 6 months–1 year | 184/397 (46.4) | Reference | |
| >1–7 years | 1230/2186 (56.3) | 1.49 (1.20–1.85) | <0.001 |
| >7–10 years | 798/1161 (68.7) | 2.54 (2.02–3.21) | <0.001 |
| >10 years | 1132/1499 (75.5) | 3.57 (2.84–4.49) | <0.001 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 1653/2678 (61.7) | Reference | |
| Male | 1846/2849 (64.8) | 1.14 (1.02–1.27) | 0.018 |
| Types of food | |||
| Commercial diet | 1188/2119 (56.1) | Reference | |
| Homemade | 991/1443 (68.7) | 1.72 (1.49–1.98) | <0.001 |
| Milk | 5/5 (100) | N/A | |
| Mixed | 1304/1949 (66.9) | 1.58 (1.39–1.80) | <0.001 |
| Raw | 2/3 (66.7) | 1.56 (0.14–17.31) | 0.714 |
| Lifestyle | |||
| Indoor | 1186/1830 (64.8) | Reference | |
| Outdoor | 1360/2091 (65.0) | 1.01 (0.89–1.15) | 0.879 |
| Mixed lifestyle | 945/1595 (59.3) | 0.79 (0.69–0.91) | 0.001 |
| Water source | |||
| Drinking water | 1011/1731 (58.4) | Reference | |
| Milk | 4/5 (80.0) | 2.85 (0.32–25.54) | 0.35 |
| Mixed water | 38/39 (97.4) | 27.06 (3.70–197.55) | 0.001 |
| Tap water | 2111/3413 (61.9) | 1.15 (1.03–1.30) | 0.017 |
| Natural water | 3/3 (100) | N/A | |
| Trauma | |||
| Yes | 304/318 (95.6) | 13.68 (7.98–23.44) | <0.001 |
| No | 3201/5217 (61.4) | Reference | |
| Diarrhea | |||
| Yes | 86/97 (86.7) | 4.62 (2.46–8.67) | <0.001 |
| No | 3419/5438 (62.9) | Reference | |
| Blood parasite | |||
| Yes | 98/144 (68.1) | 1.24 (0.87–1.77) | 0.233 |
| No | 3407/5391 (63.2) | Reference | |
| Kidney stone | |||
| Yes | 1/1 (100) | N/A | <0.001 * |
| No | 3504/5534 (63.3) | ||
| IMHA | |||
| Yes | 2/4 (50) | 0.58 (0.08–4.11) | 0.585 |
| No | 3503/5531 (63.3) | Reference | |
| Pancreatitis | |||
| Yes | 38/38 (100) | N/A | <0.001 * |
| No | 3467/5497 (63.1) | ||
| UB/Urethra injury | |||
| Yes | 42/42 (100) | N/A | <0.001 * |
| No | 3463/5493 (63.0) | ||
| UTIs | |||
| Yes | 23/23 (100) | N/A | <0.001 * |
| No | 3482/5512 (63.2) | ||
| Pyometra | |||
| Yes | 180/180 (100) | N/A | <0.001 * |
| No | 3325/5355 (62.1) | ||
| Respiratory | |||
| Yes | 50/68 (73.5) | 1.62 (0.94–2.78) | 0.082 |
| No | 3455/5467 (63.2) | Reference | |
| CVS | |||
| Yes | 89/103 (86.4) | 3.75 (2.13–6.61) | <0.001 |
| No | 3416/5432 (62.9) | Reference | |
| Toxin | |||
| Yes | 12/12 (100) | N/A | 0.005 * |
| No | 3493/5523 (63.2) | ||
| Anemia | |||
| Yes | 1424/1716 (83.0) | 4.07 (3.54–4.70) | <0.001 |
| No | 2081/3819 (54.5) | Reference | |
| WBCs | |||
| Normal | 1748/3211 (54.4) | Reference | |
| Leukocytosis | 1619/2130 (76.0) | 2.65 (2.35–2.99) | <0.001 |
| Leukopenia | 138/194 (71.1) | 2.06 (1.50–2.84) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils | |||
| Normal (3020) | 1585/3020 (52.5) | Reference | |
| Neutropenia (256) | 198/256 (77.3) | 3.09 (2.29–4.18) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophilia (2259) | 1722/2259 (76.2) | 2.90 (2.57–3.27) | <0.001 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| >1–7 years | 1.77 (1.36–2.29) | <0.001 |
| >7–10 years | 2.77 (2.10–3.67) | <0.001 |
| >10 years | 4.28 (3.25–5.64) | <0.001 |
| Male | 1.18 (1.04–1.34) | 0.010 |
| Homemade | 1.41 (1.18–1.69) | <0.001 |
| Mixed types of food | 1.36 (1.16–1.60) | <0.001 |
| Outdoor | 0.70 (0.57–0.87) | 0.001 |
| Indoor-outdoor | 0.65 (0.54–0.78) | <0.001 |
| Mixed type of water | 24.00 (3.19–180.67) | 0.001 |
| Rainy | 0.67 (0.57–0.78) | <0.001 |
| Winter | 1.65 (1.39–1.95) | <0.001 |
| Anemia | 3.85 (3.29–4.52) | <0.001 |
| Leukocytosis | 1.30 (1.04–1.63) | 0.019 |
| Neutropenia | 2.70 (1.86–3.95) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophilia | 1.94 (1.56–2.41) | <0.001 |
| Trauma | 17.95 (10.32–31.21) | <0.001 |
| Diarrhea | 5.93 (3.05–11.51) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 4.00 (2.18–7.35) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saardarwut, P.; Piyarungsri, K.; Manachai, N.; Tangtrongsup, S. Risk Factors Associated with Azotemia in Dogs Presented to the Chiang Mai University Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Thailand: A Retrospective Study (2017–2021). Animals 2025, 15, 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223313
Saardarwut P, Piyarungsri K, Manachai N, Tangtrongsup S. Risk Factors Associated with Azotemia in Dogs Presented to the Chiang Mai University Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Thailand: A Retrospective Study (2017–2021). Animals. 2025; 15(22):3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaardarwut, Pattara, Kakanang Piyarungsri, Nawin Manachai, and Sahatchai Tangtrongsup. 2025. "Risk Factors Associated with Azotemia in Dogs Presented to the Chiang Mai University Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Thailand: A Retrospective Study (2017–2021)" Animals 15, no. 22: 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223313
APA StyleSaardarwut, P., Piyarungsri, K., Manachai, N., & Tangtrongsup, S. (2025). Risk Factors Associated with Azotemia in Dogs Presented to the Chiang Mai University Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Thailand: A Retrospective Study (2017–2021). Animals, 15(22), 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223313






