In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Dietary Fibers Using Fecal Inoculum from Dogs Consuming a Dried Brewers Yeast Product
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates and Analysis
2.2. Animals, Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.3. In Vitro Fermentation Assay
2.4. Microbiota Analysis
2.5. Bioinformatics
2.6. Statistical Analyses
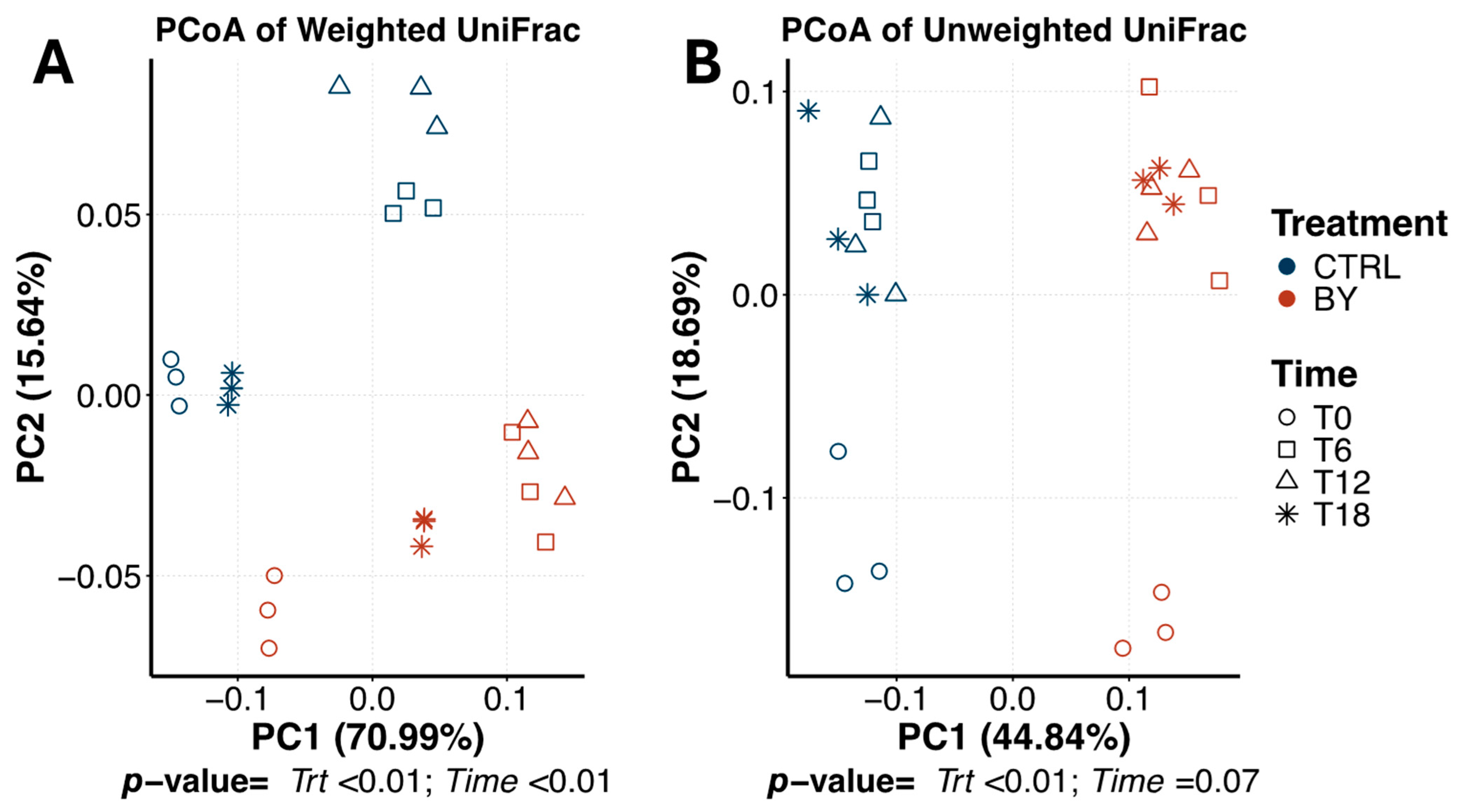
3. Results
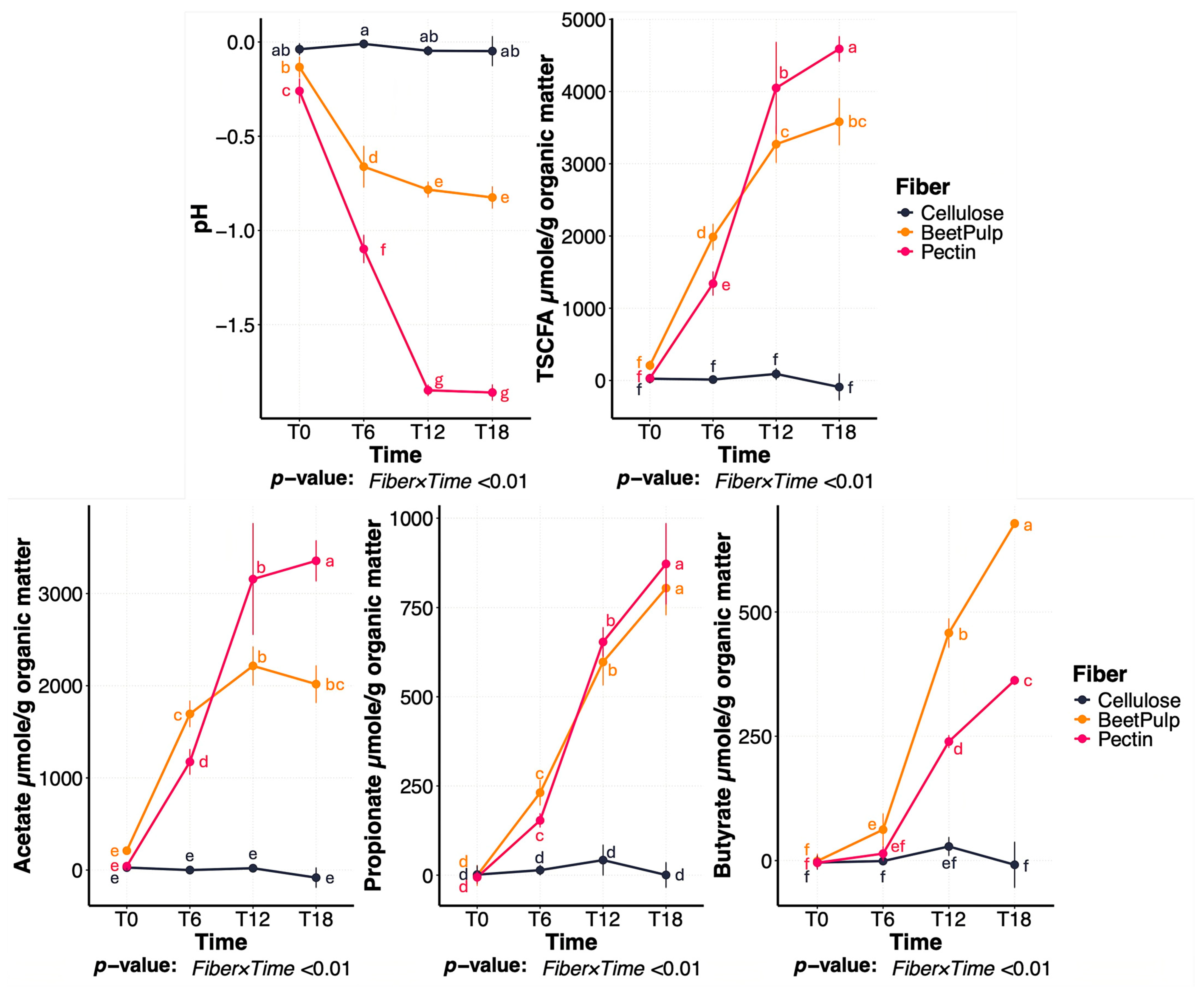
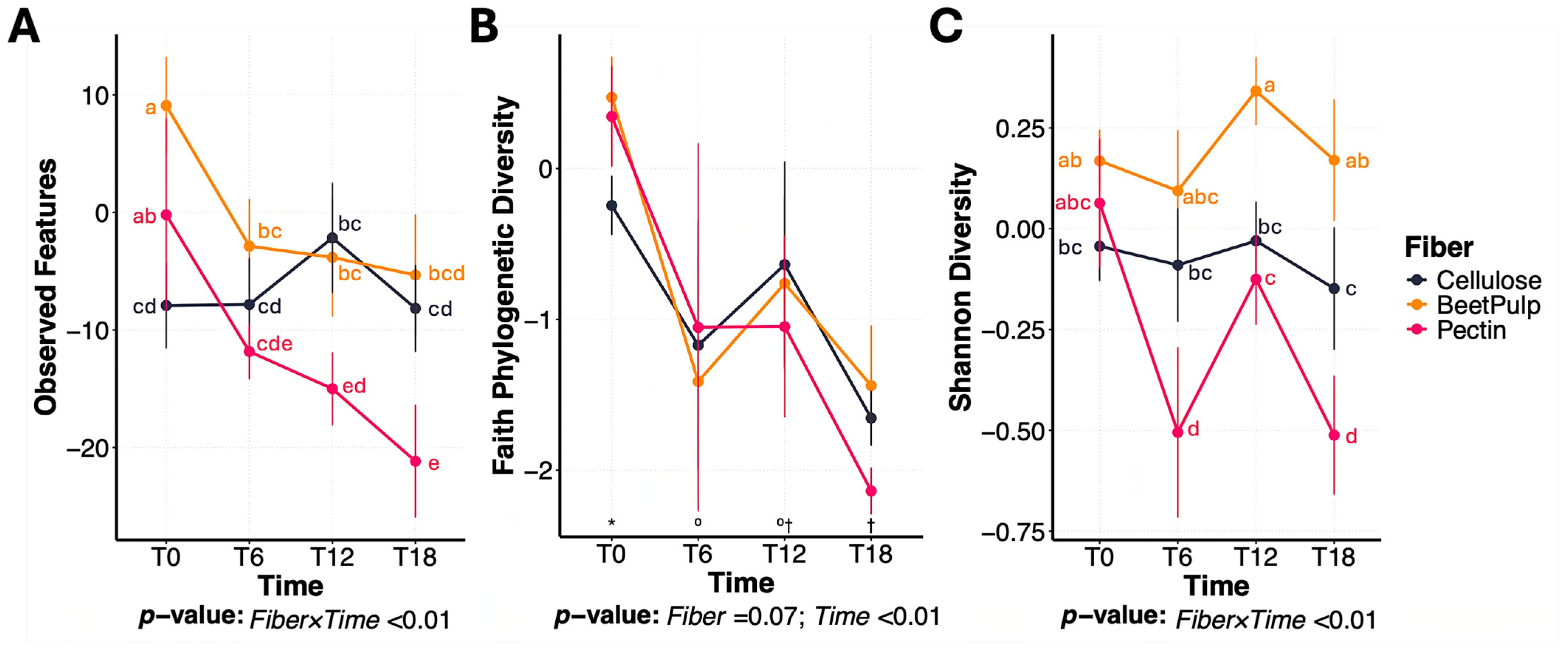
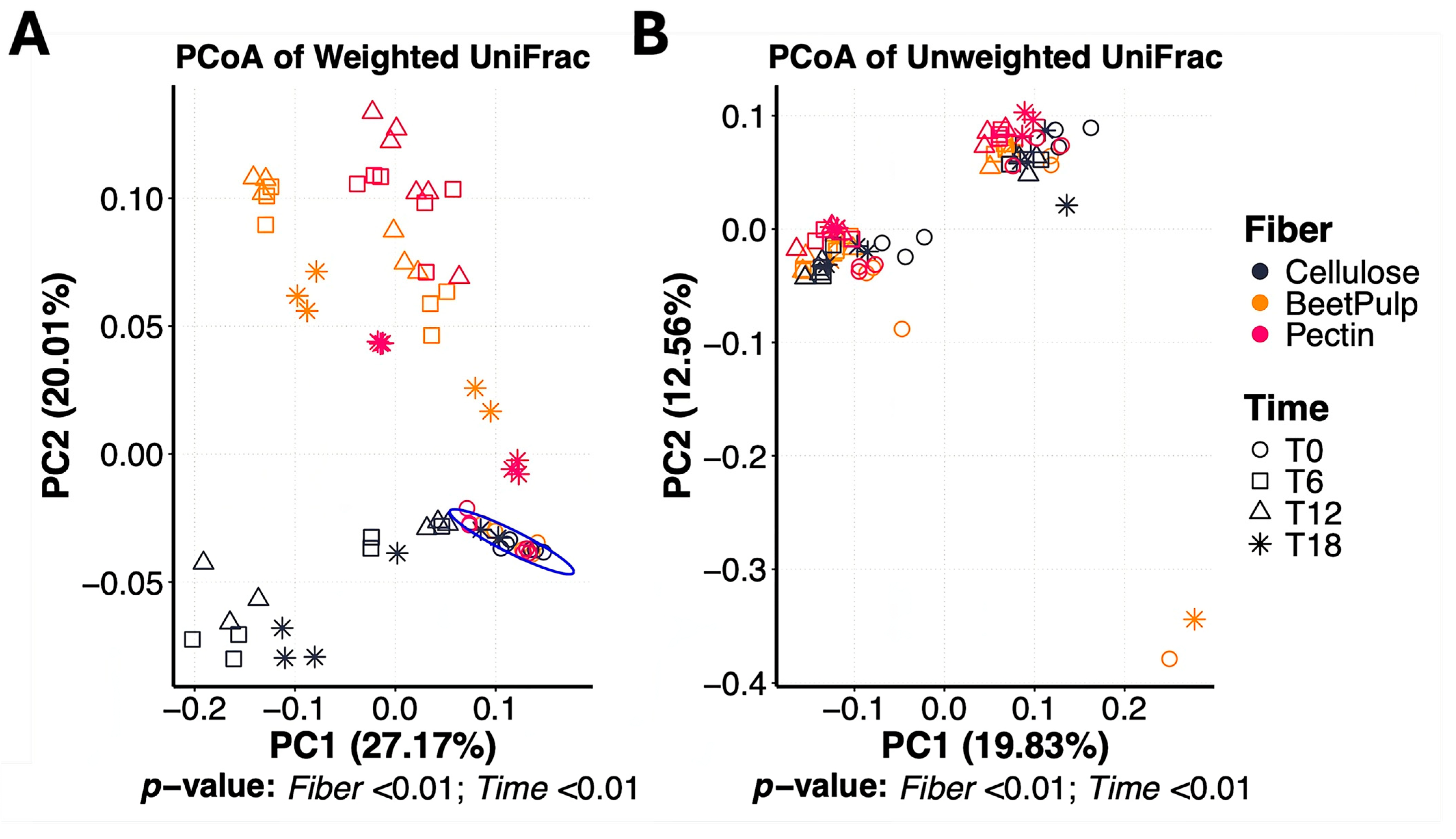
3.1. Differences Between Fiber Substrates
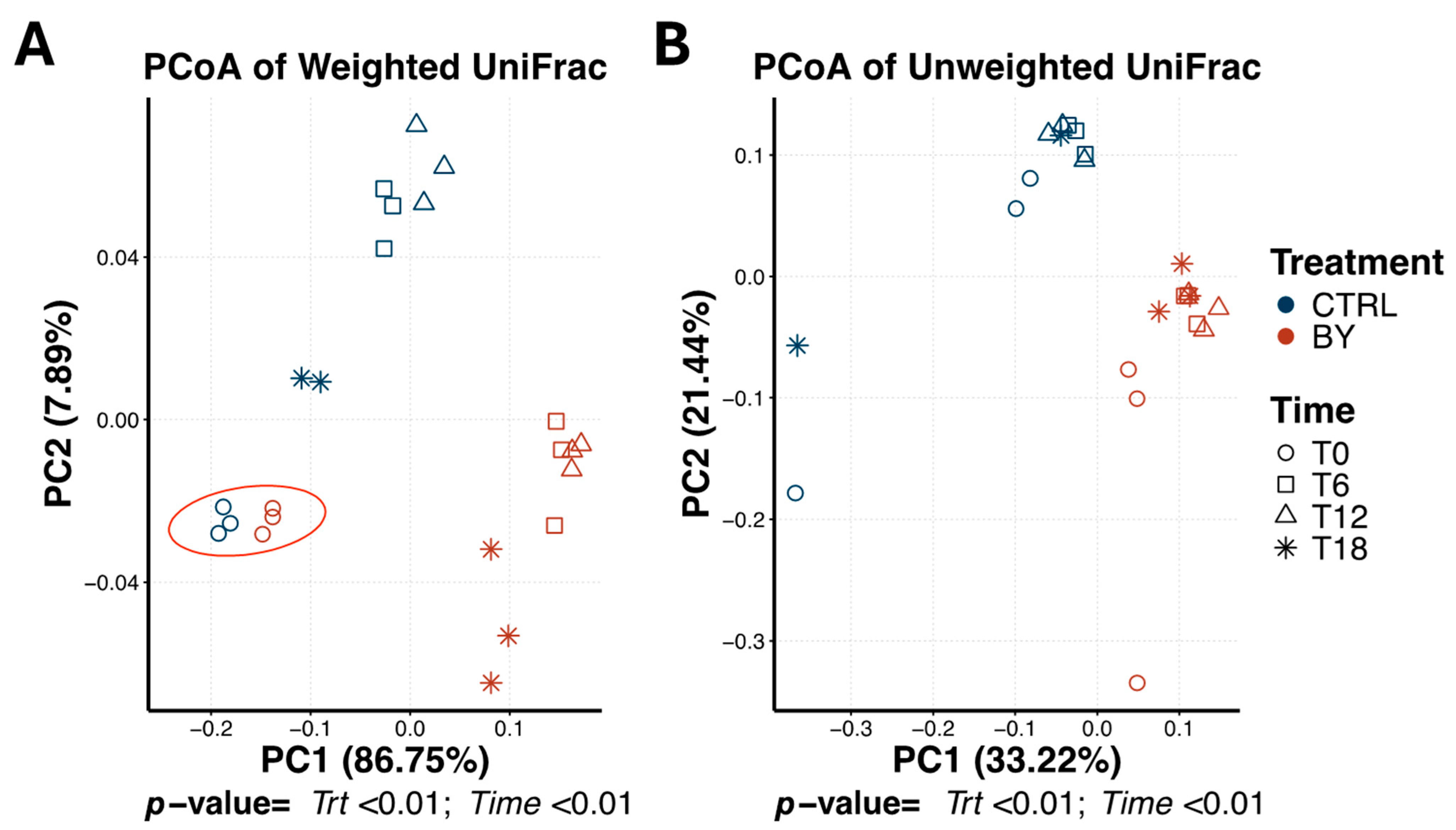
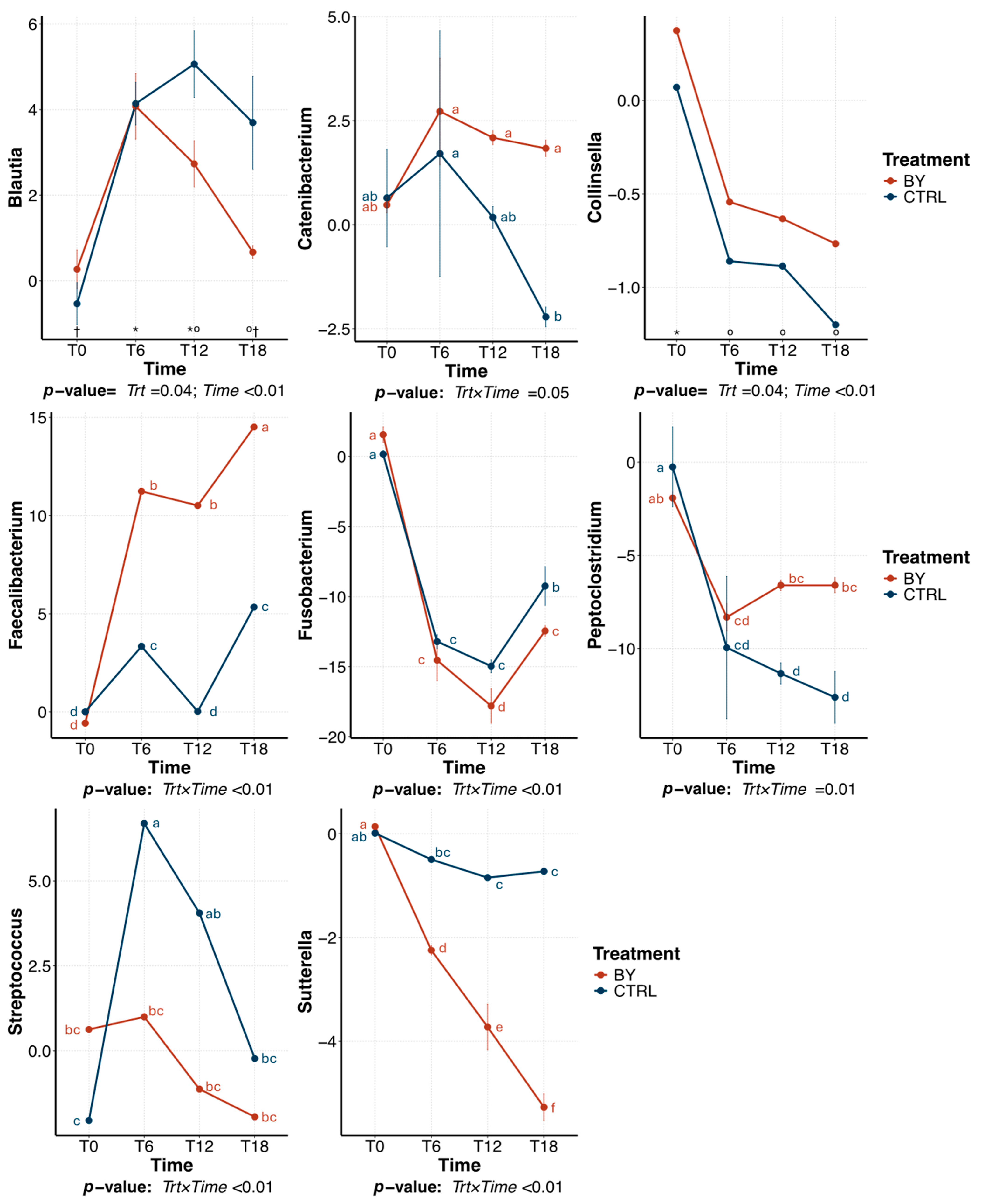
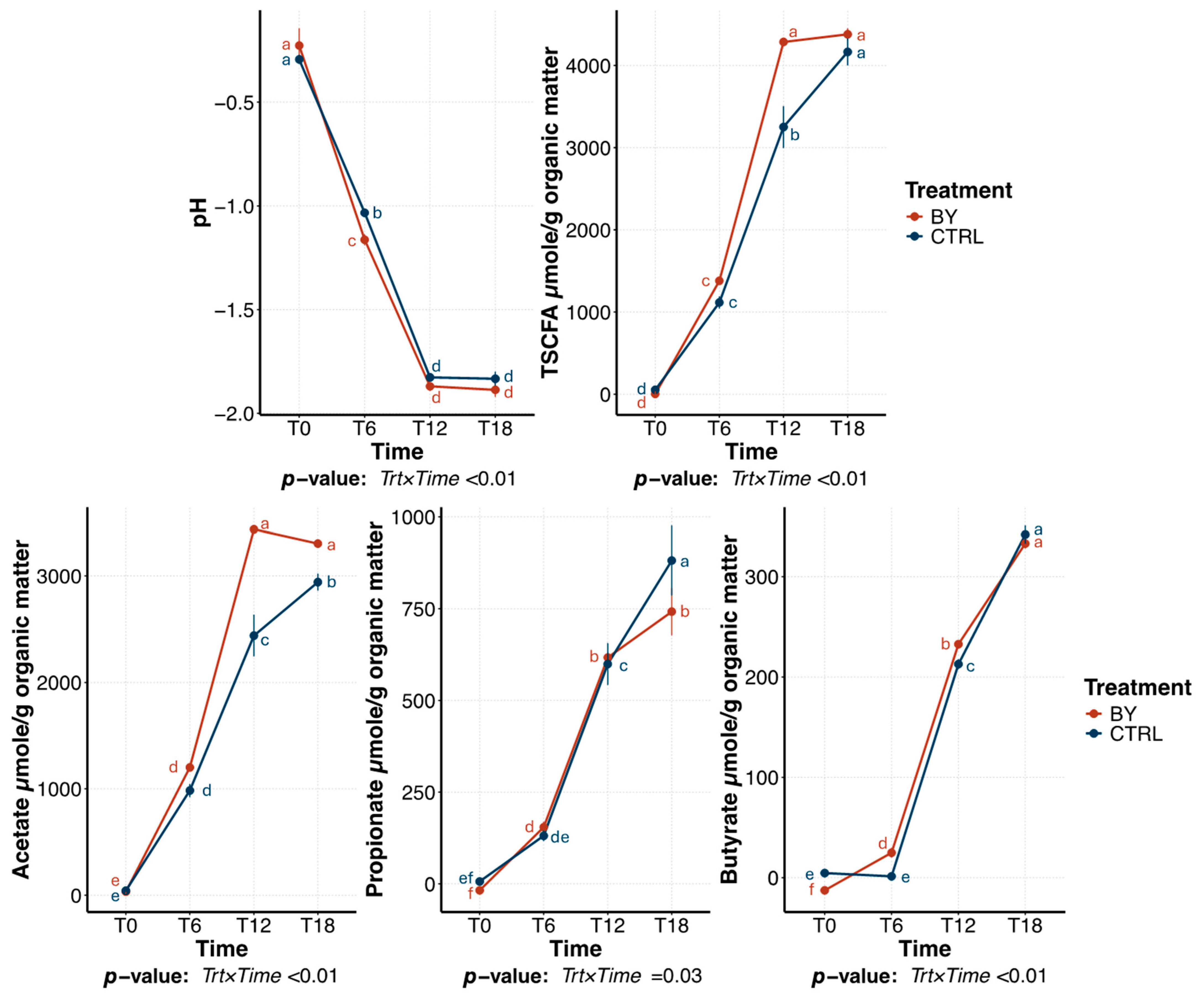
3.2. Change Between Treatments During Beet Pulp Fermentation
3.3. Change Between Treatments During Pectin Fermentation
3.4. Change Between Treatments During Cellulose Fermentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Maturana, M.; Castillejos, L.; Martin-Orue, S.M.; Minel, A.; Chetty, O.; Felix, A.P.; Adib Lesaux, A. Potential Benefits of Yeast Saccharomyces and Their Derivatives in Dogs and Cats: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1279506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurson, G.C. Yeast and Yeast Derivatives in Feed Additives and Ingredients: Sources, Characteristics, Animal Responses, and Quantification Methods. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2018, 235, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-González, M.E.; Gómez-Mejía, E.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; Madrid-Albarrán, Y. Residual Brewing Yeast as a Source of Polyphenols: Extraction, Identification and Quantification by Chromatographic and Chemometric Tools. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Abbeele, P.; Duysburgh, C.; Rakebrandt, M.; Marzorati, M. Dried Yeast Cell Walls High in Beta-Glucan and Mannan-Oligosaccharides Positively Affect Microbial Composition and Activity in the Canine Gastrointestinal Tract In Vitro. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Abbeele, P.; Moens, F.; Pignataro, G.; Schnurr, J.; Ribecco, C.; Gramenzi, A.; Marzorati, M. Yeast-Derived Formulations Are Differentially Fermented by the Canine and Feline Microbiome as Assessed in a Novel In Vitro Colonic Fermentation Model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13102–13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.F.; Methner, F.J.; Michel, M.; Zarnkow, M.; Hutzler, M. The Complexity of Yeast Extracts and Its Consequences on the Utility in Brewing: A Review. BrewingScience 2019, 72, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Alexander, C.; Steelman, A.J.; Warzecha, C.M.; De Godoy, M.R.C.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of a Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Fermentation Product on Fecal Characteristics, Nutrient Digestibility, Fecal Fermentative End-Products, Fecal Microbial Populations, Immune Function, and Diet Palatability in Adult Dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Guardia-Hidrogo, V.M.; Soto-Diaz, K.; Rummell, L.M.; Valizadegan, N.; Fields, C.J.; Steelman, A.J.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of Yeast-Enriched Functionalized Canola Meal Supplementation on Apparent Total Tract Macronutrient Digestibility and Fecal Characteristics, Fecal Microbiota, and Immune Function of Healthy Adult Dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Guardia Hidrogo, V.M.; Rummell, L.M.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of Yeast Products on the Apparent Total Tract Macronutrient Digestibility, Oxidative Stress Markers, Skin Measures, and Fecal Characteristics and Microbiota Populations of Healthy Adult Dogs. Animals 2025, 15, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummell, L.M.; Steele, M.A.; Templeman, J.R.; Yohe, T.T.; Akhtar, N.; Lambie, J.G.; Singh, P.; Asquith, T.; Verbrugghe, A.; Pearson, W.; et al. A Proof of Principle Study Investigating the Effects of Supplemental Concentrated Brewer’s Yeast on Markers of Gut Permeability, Inflammation, and Fecal Metabolites in Healthy Non-Challenged Adult Sled Dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.F.; Walton, G.E.; Jiang, L.; Plummer, S.; Garaiova, I.; Gibson, G.R. Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Tract Models. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venema, K.; Van Den Abbeele, P. Experimental Models of the Gut Microbiome. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Burillo, S.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Blasco, T.; Balzerani, F.; Lerma-Aguilera, A.; León, D.; Pastoriza, S.; Apaolaza, I.; Planes, F.J.; et al. Effect of Freezing on Gut Microbiota Composition and Functionality for In Vitro Fermentation Experiments. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, N.M.; Oliveira, D.L.; Saleh, M.A.D.; Pintado, M.; Madureira, A.R. Preservation of Human Gut Microbiota Inoculums for In Vitro Fermentations Studies. Fermentation 2021, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analitical Chemist (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Arlington, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Association of American Feed Control Officials. Dog and cat nutrient profiles. In Official Publication of the Association of American Feed Control Officials Incorporated; AAFCO: Oxford, IN, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Kump, P.; Satokari, R.; Sokol, H.; Arkkila, P.; Pintus, C.; Hart, A.; et al. European Consensus Conference on Faecal Microbiota Transplantation in Clinical Practice. Gut 2017, 66, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourquin, L.D.; Titgemeyer, E.C.; Fahey, G.C.; Garleb, K.A. Fermentation of Dietary Fibre by Human Colonic Bacteria: Disappearance of, Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production from, and Potential Water-Holding Capacity of, Various Substrates. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 28, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, E.S.; Marco, G.J.; Emery, E.M. Volatile Fatty Acid Analyses of Blood and Rumen Fluid by Gas Chromatography. J. Dairy. Sci. 1961, 44, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-High-Throughput Microbial Community Analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq Platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Costello, E.K.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Stombaugh, J.; Knights, D.; Gajer, P.; Ravel, J.; Fierer, N.; et al. Moving Pictures of the Human Microbiome. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing Taxonomic Classification of Marker-Gene Amplicon Sequences with QIIME 2’s Q2-Feature-Classifier Plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, M.S.; O’Rourke, D.R.; Kaehler, B.D.; Ziemski, M.; Dillon, M.R.; Foster, J.T.; Bokulich, N.A. RESCRIPt: Reproducible Sequence Taxonomy Reference Database Management. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation Evaluation and Phylogenetic Diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A New Phylogenetic Method for Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohnen, D. Pectin Structure and Biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Pérez, F.; Steigerwald, H.; Schülke, S.; Vieths, S.; Toda, M.; Scheurer, S. The Dietary Fiber Pectin: Health Benefits and Potential for the Treatment of Allergies by Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayser, E.; Finet, S.E.; de Godoy, M.R.C. The Role of Carbohydrates in Canine and Feline Nutrition. Anim. Front. 2024, 14, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.S.; Grieshop, C.M.; Clapper, G.M.; Shields, R.G.; Belay, T.; Merchen, N.R.; Fahey, G.C. Fruit and Vegetable Fiber Fermentation by Gut Microflora from Canines. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasevich, M.R.; Serao, M.C.R.; De Godoy, M.R.C.; Swanson, K.S.; Guérin-Deremaux, L.; Lynch, G.L.; Wils, D.; Fahey, G.C.; Dilger, R.N. Potato Fiber as a Dietary Fiber Source in Dog Foods. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5344–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutnan, M.; Drtil, M.; Mrafkova, L. Anaerobic Biodegradation of Sugar Beet Pulp. Biodegradation 2000, 11, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, G.C.; Merchen, N.R.; Corbin, J.E.; Hamilton, A.K.; Serbe, K.A.; Lewis, S.M.; Hirakawa, D.A. Dietary Fiber for Dogs: I. Effects of Beet Pulp on Nutrient Intake, Digestibility, Metabolizable Energy, and Digesta Mean Retention Time. J. Anim. Sci. 1992, 68, 4221–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, M.H.; Liaw, E.T. Utilization of Purified Cellulose in Fiber Studies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1990, 270, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciolacu, D.; Ciolacu, F.; Popa, V.I. Amorphous Cellulose Structure and Characterization. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2011, 45, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sunvold, G.D.; Fahey, G.C.; Merchen, N.R.; Titgemeyer, E.C.; Bourquin, L.D.; Bauer, L.L.; Reinhart, G.A. Dietary Fiber for Dogs: IV. In Vitro Fermentation of Selected Fiber Sources by Dog Fecal Inoculum and In Vivo Digestion and Metabolism of Fiber-Supplemented Diets. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Swanson, K.S. Gut Microbiota of Humans, Dogs and Cats: Current Knowledge and Future Opportunities and Challenges. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, S6–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchodolski, J.S. Analysis of the Gut Microbiome in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 50, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Guardia-Hidrogo, V.M.; Geary, E.L.; Wilson, S.M.; Bauer, L.L.; Menton, J.F.; Vinay, E.; Millette, M.; Kelly, M.R.; Dilger, R.N.; Swanson, K.S. In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Acacia Fiber Using Canine Fecal Inoculum. J. Anim. Sci. 2025, 103, skaf152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, E.C.; Kelly, A.G.; Tauzin, A.S.; Brumer, H. The Devil Lies in the Details: How Variations in Polysaccharide Fine-Structure Impact the Physiology and Evolution of Gut Microbes. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3851–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelbos, I.S.; Boler, B.M.V.; Qu, A.; White, B.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Fahey, G.C. Phylogenetic Characterization of Fecal Microbial Communities of Dogs Fed Diets with or without Supplemental Dietary Fiber Using 454 Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasevich, M.R.; Kerr, K.R.; Dilger, R.N.; Fahey, G.C.; Guérin-Deremaux, L.; Lynch, G.L.; Wils, D.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steer, J.M.; Dowd, S.E.; et al. Modulation of the Faecal Microbiome of Healthy Adult Dogs by Inclusion of Potato Fibre in the Diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröger, S.; Vahjen, W.; Zentek, J. Influence of Lignocellulose and Low or High Levels of Sugar Beet Pulp on Nutrient Digestibility and the Fecal Microbiota in Dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Brito, C.B.M.; Menezes Souza, C.M.; Bastos, T.S.; Mesa, D.; Oliveira, S.G.; Félix, A.P. Effect of Dietary Inclusion of Dried Apple Pomace on Faecal Butyrate Concentration and Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Dogs. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 75, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.M.M.; Bastos, T.S.; Kaelle, G.C.B.; Bortolo, M.; Vasconcellos, R.S.; De Oliveira, S.G.; Félix, A.P. Comparison of Cassava Fiber with Conventional Fiber Sources on Diet Digestibility, Fecal Characteristics, Intestinal Fermentation Products, and Fecal Microbiota of Dogs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 281, 115092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stercova, E.; Kumprechtova, D.; Auclair, E.; Novakova, J. Effects of Live Yeast Dietary Supplementation on Nutrient Digestibility and Fecal Microflora in Beagle Dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wichienchot, S.; He, X.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B. In Vitro Colonic Fermentation of Dietary Fibers: Fermentation Rate, Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production and Changes in Microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.; Phungviwatnikul, T.; De Godoy, M.R.C.; Swanson, K.S. Nutrient Digestibility and Fecal Characteristics, Microbiota, and Metabolites in Dogs Fed Human-Grade Foods. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mantrana, I.; Selma-Royo, M.; Alcantara, C.; Collado, M.C. Shifts on Gut Microbiota Associated to Mediterranean Diet Adherence and Specific Dietary Intakes on General Adult Population. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Zou, Y.; Dai, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, L. Characterization a Novel Butyric Acid-Producing Bacterium Collinsella Aerofaciens Subsp. Shenzhenensis Subsp. Nov. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.d.M.; Risolia, L.W.; Rentas, M.F.; Amaral, A.R.; Rodrigues, R.B.A.; Urrego, M.I.G.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; Ventura, R.V.; Balieiro, J.C.d.C.; Massoco, C.d.O.; et al. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Dehydrated Culture Modulates Fecal Microbiota and Improves Innate Immunity of Adult Dogs. Fermentation 2022, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karekar, S.; Stefanini, R.; Ahring, B. Homo-Acetogens: Their Metabolism and Competitive Relationship with Hydrogenotrophic Methanogens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, P.H.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; Zafalon, R.V.A.; Príncipe, L.d.A.; Cesar, C.G.L.; Perini, M.P.; Putarov, T.C.; Gomes, C.O.M.S.; Balieiro, J.C.d.C.; Brunetto, M.A. Effects of Increasing Levels of Purified Beta-1,3/1,6-Glucans on the Fecal Microbiome, Digestibility, and Immunity Variables of Healthy Adult Dogs. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.H.; Hold, G.L.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Stewart, C.S.; Flint, H.J. Growth Requirements and Fermentation Products of Fusobacterium Prausnitzii, and a Proposal to Reclassify It as Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii Gen. Nov., Comb. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, S.; Martín, R.; Rossi, O.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Chatel, J.M.; Sokol, H.; Thomas, M.; Wells, J.M.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii and Human Intestinal Health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diether, N.E.; Willing, B.P. Microbial Fermentation of Dietary Protein: An Important Factor in Diet–Microbe–Host Interaction. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Gut Microbiome of Dogs and Cats, and the Influence of Diet. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShawaqfeh, M.K.; Wajid, B.; Minamoto, Y.; Markel, M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Serpedin, E.; Suchodolski, J.S. A Dysbiosis Index to Assess Microbial Changes in Fecal Samples of Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, C.D.; Young, W.; Maclean, P.H.; Cookson, A.L.; Bermingham, E.N. Metagenomic Insights into the Roles of Proteobacteria in the Gastrointestinal Microbiomes of Healthy Dogs and Cats. Microbiologyopen 2018, 7, e677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greetham, H.L.; Collins, M.D.; Gibson, G.R.; Giffard, C.; Falsen, E.; Lawson, P.A. Sutterella Stercoricanis Sp. Nov., Isolated from Canine Faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1581–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Markel, M.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Unterer, S.; Heilmann, R.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Kachroo, P.; Ivanov, I.; Minamoto, Y.; Dillman, E.M.; et al. The Fecal Microbiome in Dogs with Acute Diarrhea and Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Component | Concentration in Medium |
|---|---|
| ---mL/L--- | |
| Mineral solution A 1 | 330 |
| Mineral solution B 2 | 330 |
| Trace mineral solution 3 | 10 |
| Water-soluble vitamins 4 | 20 |
| Folate:biotin solution 5 | 5 |
| Riboflavin solution 6 | 5 |
| Hemin solution 7 | 2.5 |
| Short-chain fatty acid mix 8 | 0.4 |
| Resazurin solution 9 | 1.0 |
| Distilled H2O | 296 |
| ---g/L--- | |
| Yeast extract | 0.5 |
| Trypticase | 0.5 |
| Na2CO3 | 4.0 |
| Cysteine HCl·H2O | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De La Guardia Hidrogo, V.M.; Oba, P.M.; Holt, D.A.; Bauer, L.L.; Rummell, L.M.; Dilger, R.N.; Swanson, K.S. In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Dietary Fibers Using Fecal Inoculum from Dogs Consuming a Dried Brewers Yeast Product. Animals 2025, 15, 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213117
De La Guardia Hidrogo VM, Oba PM, Holt DA, Bauer LL, Rummell LM, Dilger RN, Swanson KS. In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Dietary Fibers Using Fecal Inoculum from Dogs Consuming a Dried Brewers Yeast Product. Animals. 2025; 15(21):3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213117
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe La Guardia Hidrogo, Vanessa M., Patricia M. Oba, Dalton A. Holt, Laura L. Bauer, Lindsey M. Rummell, Ryan N. Dilger, and Kelly S. Swanson. 2025. "In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Dietary Fibers Using Fecal Inoculum from Dogs Consuming a Dried Brewers Yeast Product" Animals 15, no. 21: 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213117
APA StyleDe La Guardia Hidrogo, V. M., Oba, P. M., Holt, D. A., Bauer, L. L., Rummell, L. M., Dilger, R. N., & Swanson, K. S. (2025). In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Dietary Fibers Using Fecal Inoculum from Dogs Consuming a Dried Brewers Yeast Product. Animals, 15(21), 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213117








