Interactive Effects of Vitamin A and All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, and Plasma Metabolomics of Broiler Chickens
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals, Diets, and Design
2.2. Growth Performance
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Intestinal Morphology
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.6. Plasma Metabolomics Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Intestinal Morphology
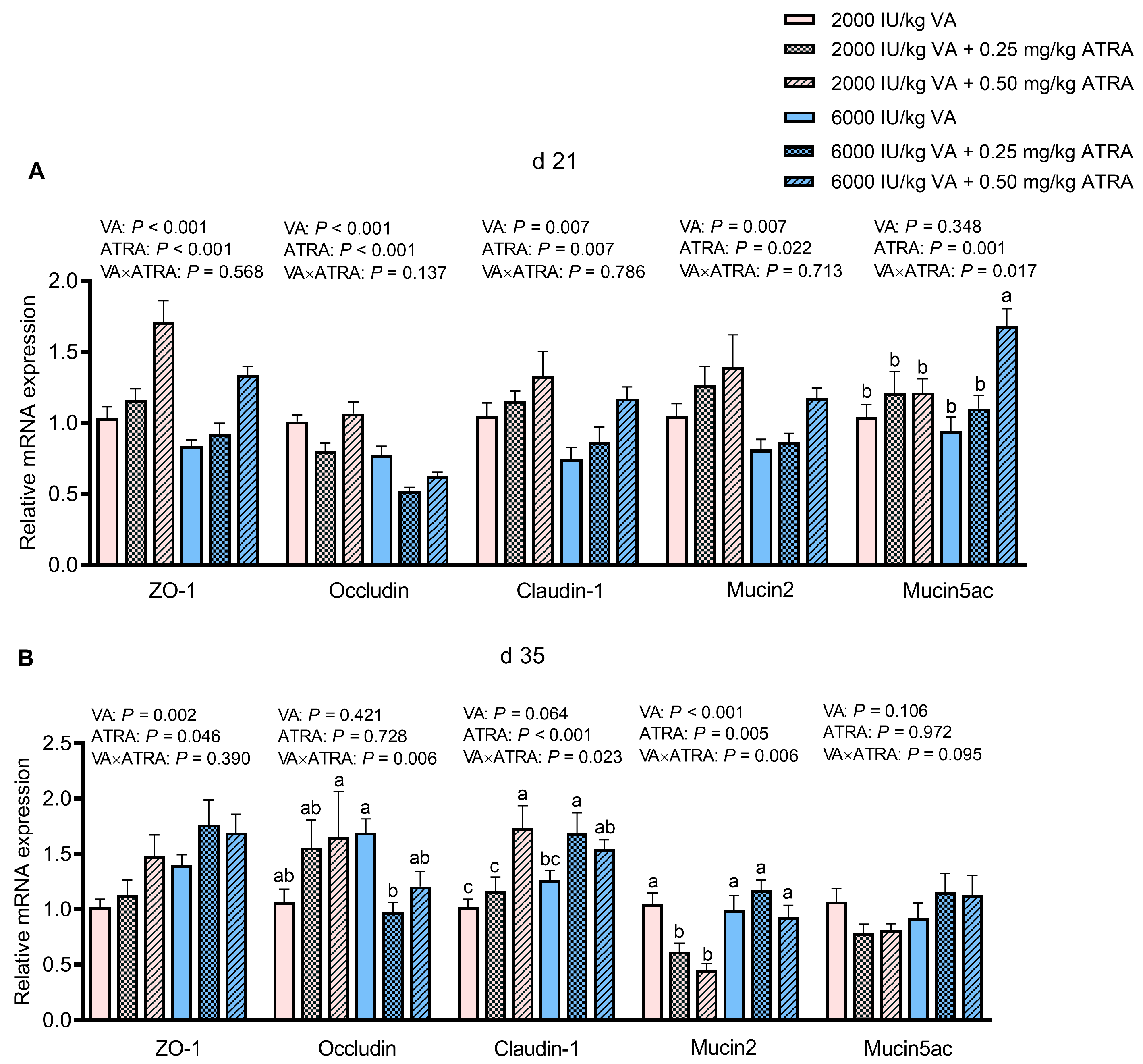
3.3. Gene Expression of Tight Junctions and Mucins in Jejunum
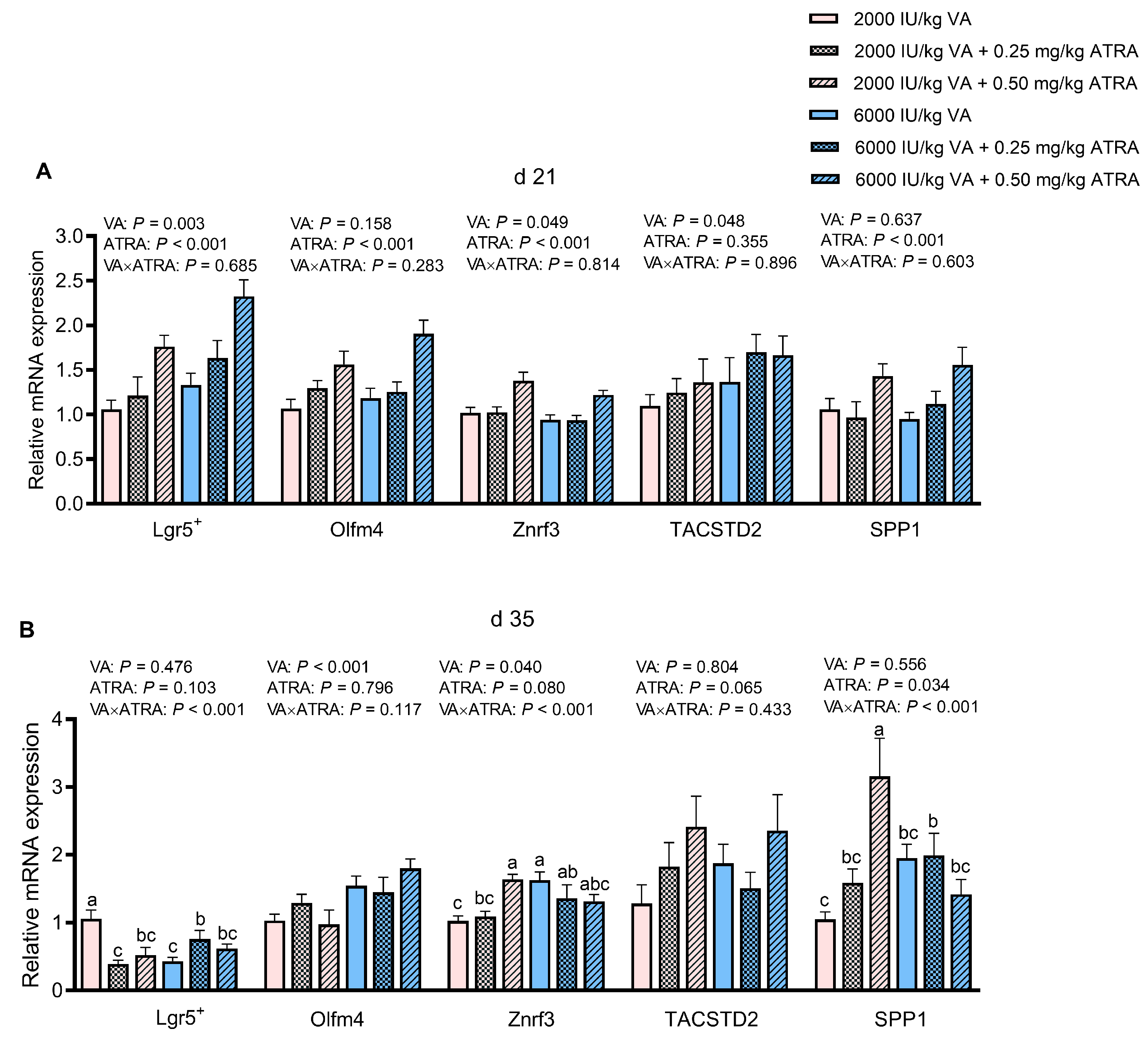
3.4. Gene Expression of Markers Indicating Stem Cell Proliferation in Jejunum
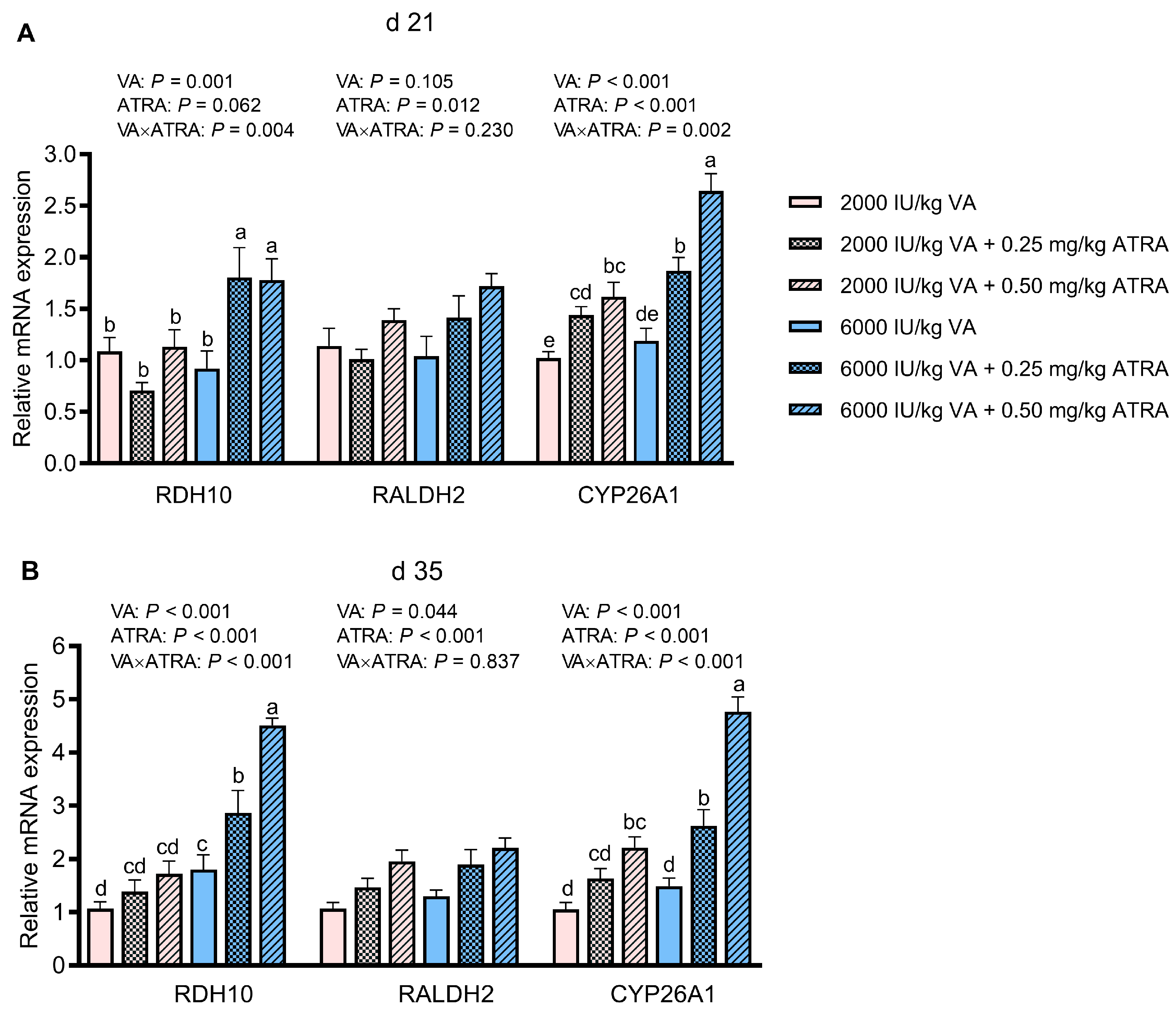
3.5. Gene Expression of Enzymes Involving in Retinoic Acid Metabolism
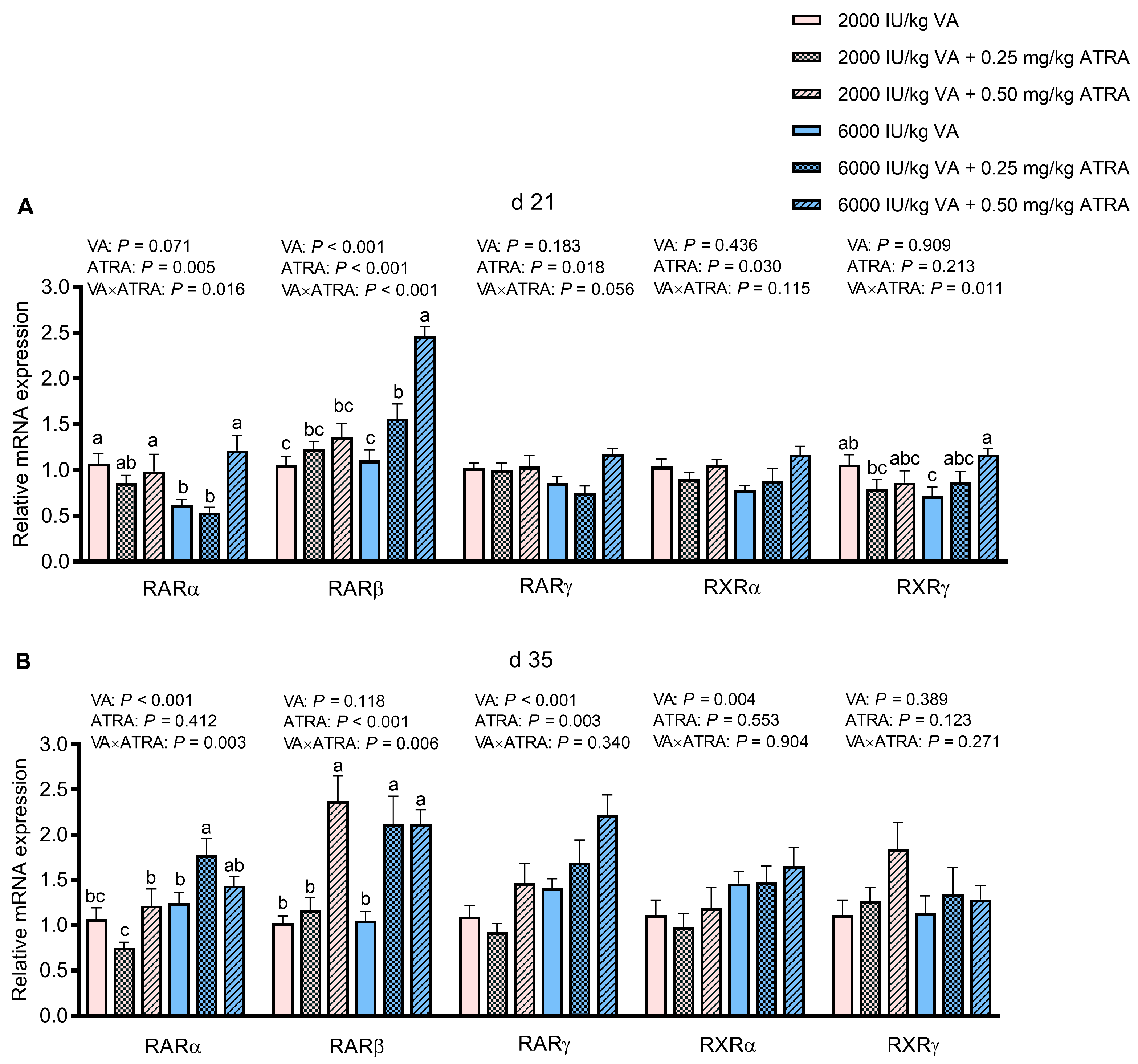
3.6. Gene Expression of Retinoic Acid Receptors and Retinoic Acid X Receptors
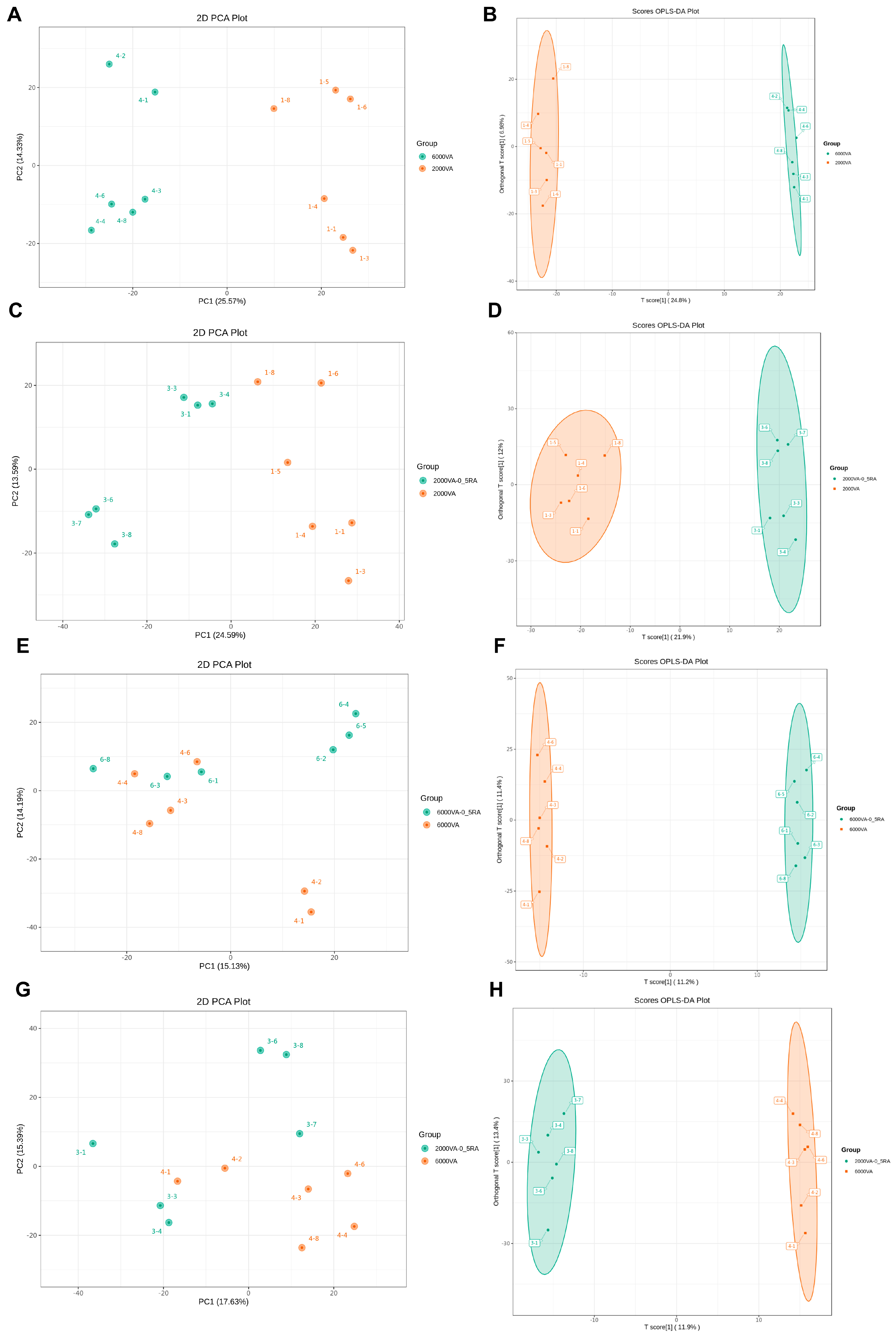
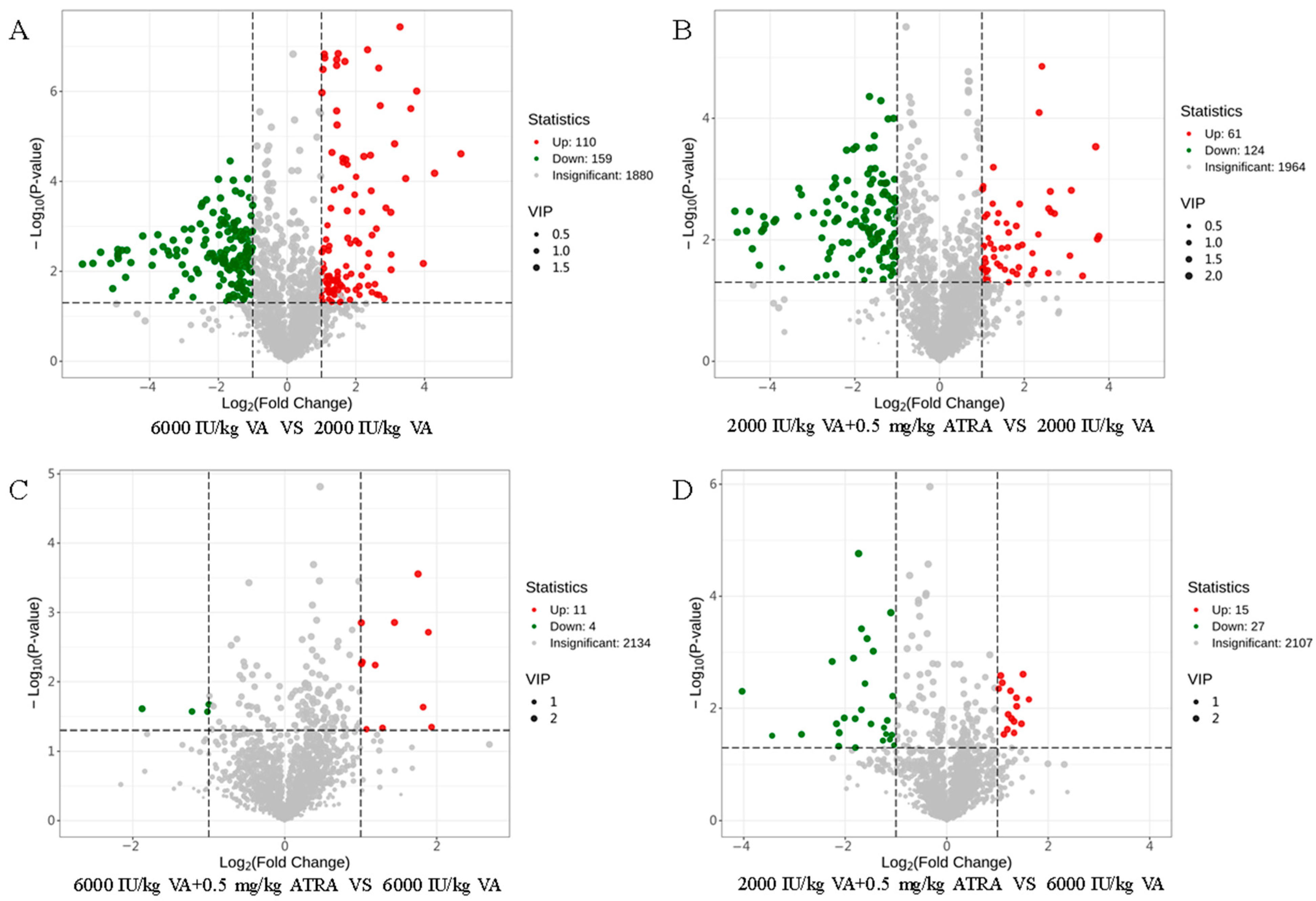
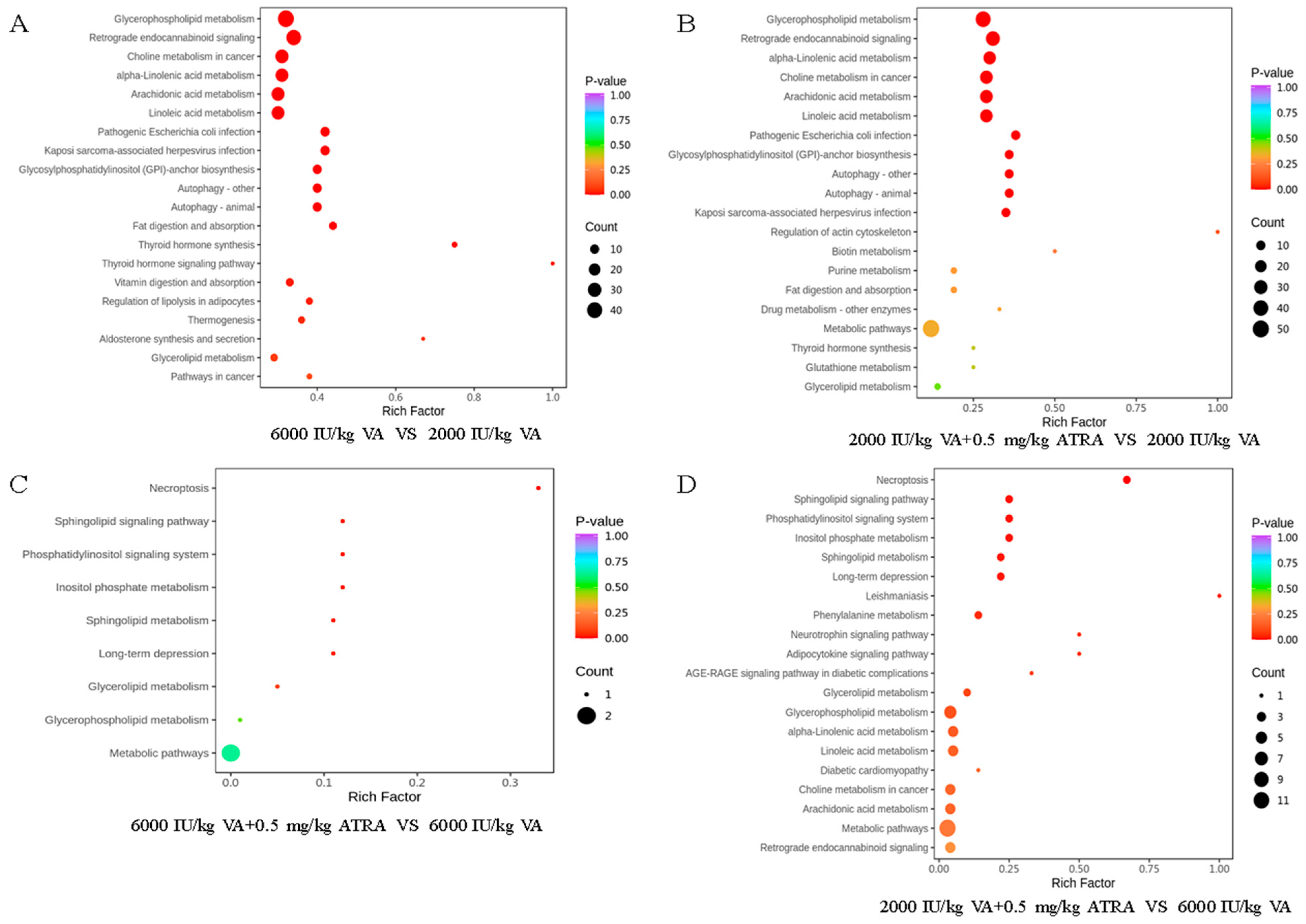
3.7. Plasma Metabolome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADFI | Average daily feed intake |
| ADG | Average daily gain |
| ATRA | All-trans retinoic acid |
| CD | Crypt depth |
| CRABP | Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein |
| CRBP | Cellular retinol-binding protein |
| CYP26A1 | Cytochrome P450, family 26, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 |
| FABP5 | Atty acid-binding protein 5 |
| FCR | Feed conversion ratios |
| IL | Interleukin |
| Lgr5+ | Leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5+ |
| Olfm4 | Olfactomedin 4 |
| RALDH | Retinal dehydrogenase |
| RAR | Retinoic acid receptor |
| RAREs | Retinoic acid-responsive elements |
| RBP4 | Retinol-binding protein |
| RDH | Retinol dehydrogenase |
| RDH10 | Retinol dehydrogenase 10 |
| RXR | Retinoid receptor X |
| SEM | Standard error |
| SPP1 | Secreted phosphoprotein 1 |
| TACSTD2 | Tumor associated calcium signal transducer 2 |
| VA | Vitamin A |
| VH | Villus height |
| Znrf3 | Zinc and ring finger 3 |
| ZO-1 | Zonula occludens-1 |
References
- Savaris, V.D.L.; Pozza, P.C.; Polese, C.; de Vargas, J.G.; Pavlak, M.S.D.; Wachholz, L.; Vieira, B.S.; Tesser, G.L.S.; de Oliveira Carvalho, P.L.; Eyng, C.; et al. Performance and Bone Characteristics of Broilers Fed Diets Supplemented with Vitamin a at Different Concentrations. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 108, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ratel, I.T.; Amara, M.M.; Beshara, M.M.; Basuini, M.F.E.; Fouda, S.F.; El-Kholy, K.H.; Ebeid, T.A.; Kamal, M.; Othman, S.I.; Rudayni, H.A.; et al. Effects of Supplemental Vitamin a on Reproduction and Antioxidative Status of Aged Laying Hens, and Growth, Blood Indices and Immunity of Their Offspring. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Xie, J.; Fan, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, Z.; Liu, S.; Ma, D. Effect of Oral Vitamin a Supplementation on Host Immune Response to Infectious Bronchitis Virus Infection in Specific Pathogen-Free Chicken. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uni, Z.; Zaiger, G.; Gal-Garber, O.; Pines, M.; Rozenboim, I.; Reifen, R. Vitamin a Deficiency Interferes with Proliferation and Maturation of Cells in the Chicken Small Intestine. Br. Poult. Sci. 2000, 41, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, A.M.; Kumar, S.R.; Steinberg, J.; Garcia-Buitrago, M.T.; Arosemena Benitez, L.R. Liver Damage due to Hypervitaminosis. ACG Case Rep. J. 2020, 7, e00431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Khan, A.; Naz, S.; Ullah, Q.; Puvača, N.; Laudadio, V.; Mazzei, D.; Seidavi, A.; Ayasan, T.; Tufarelli, V. Pros and Cons of Dietary Vitamin A and Its Precursors in Poultry Health and Production: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, C.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, S.; Ding, B. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Vitamin a on Antioxidant and Intestinal Barrier Function of Broilers Co-Infected with Coccidia and Clostridium perfringens. Animals 2022, 12, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Ding, B. Effects of Vitamin a on Immune Responses and Vitamin a Metabolism in Broiler Chickens Challenged with Necrotic Enteritis. Life 2023, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Goulart, R.A.; Batista, G.L.S.A. Vitamin a and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Cellular Studies and Animal Models to Human Disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer, J.E.; Blomhoff, R. Gene Expression Regulation by Retinoic Acid. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1773–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Shin, B.J.; Ryu, B.Y.; Lee, K. Short Communication: In Ovo Injection of All-Trans Retinoic Acid Causes Adipocyte Hypertrophy in Embryos but Lost Its Effect in Posthatch Chickens. Animal 2023, 17, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Chen, D.; Tian, G.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Huang, Z.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. All-Trans Retinoic Acid Alleviates Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus-Induced Intestinal Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction in Weaned Piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaris, V.D.L.; Souza, C.; Wachholz, L.; Broch, J.; Polese, C.; Carvalho, P.L.O.; Pozza, P.C.; Eyng, C.; Nunes, R.V. Interactions Between Lipid Source and Vitamin A on Broiler Performance, Blood Parameters, Fat and Protein Deposition Rate, and Bone Development. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.Y.; Sell, J.L. Effect of All-Trans Retinol and Retinoic Acid Nutriture on the Immune System of Chicks. J. Nutr. 1983, 113, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 33-2004; Feeding Standard of Chicken. The National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Tables of Feed Composition and Nutritive Values in China (Version 33); National Agricultural Science Data Center: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Li, P.; Gao, M.; Fu, J.; Yan, S.; Liu, Y.; Mahmood, T.; Lv, Z.; Guo, Y. Dietary Soya Saponin Improves the Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Health of Laying Hens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, K.; Qiao, H.; Xu, R.; Liu, S.; Xu, C. Selection and Validation of Reference Genes for Gene Expression in Bactericera gobica Loginova under Different Insecticide Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Wu, S.G.; Zhang, H.J.; Qi, G.H.; Wang, J. Dynamic Alterations in Early Intestinal Development, Microbiota and Metabolome Induced by in Ovo Feeding of L-Arginine in a Layer Chick Model. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, D.A.; Remolue, L.; Becker, J.; Perret, M.; Bunescu, A.; Hennig, K.; Biliaut, E.; Badin, A.; Giacomini, C.; Reynier, F.; et al. An Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Study of the Immune Response of Newly Hatched Chicks to the Cytosine-Phosphate-Guanine Oligonucleotide Stimulation. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4360–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human Metabolome Database. Available online: https://hmdb.ca/ (accessed on 26 February 2020).
- Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Databases. Available online: http://www.genome.jp/kegg/ (accessed on 26 February 2020).
- Feng, Y.L.; Xie, M.; Tang, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, S.S. Effects of Vitamin A on Growth Performance and Tissue Retinol of Starter White Pekin Ducks. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2189–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.R.; Xiao, X.; Yang, H.M.; Wang, Z.Y. Assessment of Vitamin A Requirement of Gosling in 0–28 D Based on Growth Performance and Bone Indexes. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, W.K.; Aji, B.S.P.; Fikri, F.; Purnomo, A.; Maslamama, S.T.; Caliskan, H.; Purnama, M.T.E. Strategies to Combat Heat Stress in Isa Brown Layer Hens: Unveiling the Roles of Vitamin A, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Vitamin C, Selenium, Folic Acid, and in Combination. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yin, Y.; Yin, L.; Yang, H.; Yin, Y. Dietary Vitamin A Affects Growth Performance, Intestinal Development, and Functions in Weaned Piglets by Affecting Intestinal Stem Cells. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Qin, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Yang, H.S.; Yin, Y. Effects of Iron, Vitamin a, and the Interaction between the Two Nutrients on Intestinal Development and Cell Differentiation in Piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastak, Y.; Pelletier, W. Delving into Vitamin A Supplementation in Poultry Nutrition: Current Knowledge, Functional Effects, and Practical Implications. World Poult. Sci. J. 2024, 80, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Liang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Pi, J.; Zhang, H. Whole-Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effect of Retinoic Acid on Small Intestinal Mucosal Injury in Cage-Stressed Young Laying Ducks. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Yu, D.; Yu, M. Ascorbic Acid and All-Trans Retinoic Acid Promote Proliferation of Chicken Blastoderm Cells (Cbcs) by Mediating DNA Demethylation. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2022, 58, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Chen, D.; Tian, G.; He, J.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. All-Trans Retinoic Acid Attenuates Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus-Induced Apoptosis in Ipec-J2 Cells Via Inhibiting Ros-Mediated P(38)Mapk Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uni, Z.; Zaiger, G.; Reifen, R. Vitamin a Deficiency Induces Morphometric Changes and Decreased Functionality in Chicken Small Intestine. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Kou, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Dietary Genistein Supplementation Improves Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Escherichia coli O78-Challenged Broilers. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 77, 108267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, K.; Lin, X.; Liu, H.C.; Odle, J.; See, M.T.; Cui, X.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; et al. Dietary Zn Proteinate with Moderate Chelation Strength Alleviates Heat Stress-Induced Intestinal Barrier Function Damage by Promoting Expression of Tight Junction Proteins Via the A20/Nf-Kappab P65/Mmp-2 Pathway in the Jejunum of Broilers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib-Naseri, K.; Kheravii, S.; Keerqin, C.; Swick, R.A.; Choct, M.; Wu, S.B. Differential Expression of Intestinal Genes in Necrotic Enteritis Challenged Broiler Chickens with 2 Different Clostridium Perfringens Strains. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Jiao, H.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Lin, H. Vitamin a Deficiency Impairs Mucin Expression and Suppresses the Mucosal Immune Function of the Respiratory Tract in Chicks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Cui, B.; Wen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, S. Effects of Vitamin a on Growth Performance, Antioxidants, Gut Inflammation, and Microbes in Weaned Piglets. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, N. Adult Intestinal Stem Cells: Critical Drivers of Epithelial Homeostasis and Regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.S.; Janda, C.Y.; Chang, J.; Zheng, G.X.Y.; Larkin, K.A.; Luca, V.C.; Chia, L.A.; Mah, A.T.; Han, A.; Terry, J.M.; et al. Non-Equivalence of Wnt and R-Spondin Ligands During Lgr5(+) Intestinal Stem-Cell Self-Renewal. Nature 2017, 545, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.J.M.; Lo, Y.H.; Mah, A.T.; Kuo, C.J. The Intestinal Stem Cell Niche: Homeostasis and Adaptations. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, T.F.; Hammer, L.; Furtado, S.; Mathiowitz, E.; Nicoletti, F.; Mangano, K.; Egilmez, N.K.; Auci, D.L. Oral Delivery of Particulate Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 and All-Trans Retinoic Acid Reduces Gut Inflammation in Murine Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2015, 9, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, F.S.; Northrop-Clewes, C.A.; Thurnham, D.I. The Effect of Vitamin a on Epithelial Integrity. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1999, 58, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.K.; Spit, M.; Jordens, I.; Low, T.Y.; Stange, D.E.; van de Wetering, M.; van Es, J.H.; Mohammed, S.; Heck, A.J.; Maurice, M.M.; et al. Tumour Suppressor Rnf43 Is a Stem-Cell E3 Ligase That Induces Endocytosis of Wnt Receptors. Nature 2012, 488, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, Y.; He, T.; Lu, Y.; Szeto, I.M.; Duan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Synergistic Effect of Lactoferrin and Osteopontin on Intestinal Barrier Injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabut, K.C.B.; Isoherranen, N. Crabps Alter All-Trans-Retinoic Acid Metabolism by Cyp26a1 Via Protein-Protein Interactions. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Cockrum, M.A.; Napoli, J.L. Cyp26a1 Supports Postnatal Retinoic Acid Homeostasis and Glucoregulatory Control. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, K.; McCaffery, P.; Drager, U.; Forehand, C.J. Differential Distribution of Retinoic Acid Synthesis in the Chicken Embryo as Determined by Immunolocalization of the Retinoic Acid Synthetic Enzyme, RALDH-2. Dev. Biol. 1999, 210, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yu, P.; Leghari, I.H.; Ge, C.; Mi, Y.; Zhang, C. Raldh2, the Enzyme for Retinoic Acid Synthesis, Mediates Meiosis Initiation in Germ Cells of the Female Embryonic Chickens. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zimmerman, T.L.; Thevananther, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kurie, J.M.; Karpen, S.J. Interleukin-1 Beta-Mediated Suppression of Rxr:Rar Transactivation of the Ntcp Promoter Is Jnk-Dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31416–31422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Neerven, S.; Kampmann, E.; Mey, J. Rar/Rxr and Ppar/Rxr Signaling in Neurological and Psychiatric Diseases. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, M.; Hirakiyama, A.; Eshima, Y.; Kagechika, H.; Kato, C.; Song, S.Y. Retinoic Acid Imprints Gut-Homing Specificity on T Cells. Immunity 2004, 21, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Yokota, A.; Ohoka, Y.; Kagechika, H.; Kato, C.; Song, S.Y.; Iwata, M. Efficient Induction of Ccr9 on T Cells Requires Coactivation of Retinoic Acid Receptors and Retinoid X Receptors (Rxrs): Exaggerated T Cell Homing to the Intestine by Rxr Activation with Organotins. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5289–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farouk, S.M.; Abdel-Rahman, H.G.; Abdallah, O.A.; El-Behidy, N.G. Comparative Immunomodulatory Efficacy of Rosemary and Fenugreek against Escherichia coli Infection Via Suppression of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Broilers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 40053–40067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklan, D. Effect of High Vitamin a or Tocopherol Intake on Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Absorption and Secretion of Lipids and Bile Acids in the Chick. Br. J. Nutr. 1983, 50, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.; Suh, Y.; Ko, J.K.; Lee, K. Transdifferentiation of Myoblasts into Adipocytes by All-Trans-Retinoic Acid in Avian. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 856881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Lee, K. Hypertrophy of Adipose Tissues in Quail Embryos by in Ovo Injection of All-Trans Retinoic Acid. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 681562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.; Atkinson, S.N.; Taylor, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, D.; Flejsierowicz, P.; Wang, L.S.; Morse, M.; Liu, C.; Gunsolus, I.L.; et al. Retinoic Acid Signaling Modulates Recipient Gut Barrier Integrity and Microbiota After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 749002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Bai, J.; Song, J.; Hao, B.; Zhang, L.; Xia, G. Effects of Vitamin A on Yanbian Yellow Cattle and Their Preadipocytes by Activating AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Intestinal Microflora. Animals 2022, 12, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients | Contents (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Starter (Days 1–21) | Grower (Days 22–35) | |
| Maize | 51.90 | 61.11 |
| Soybean meal | 39.80 | 31.15 |
| Soybean oil | 4.20 | 4.50 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.80 | 1.30 |
| Limestone | 1.16 | 0.83 |
| Sodium chloride | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| L-Lysine | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| D, L-Methionine | 0.19 | 0.17 |
| Threonine | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| Choline chloride (50%) | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Mineral premix 1 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Vitamin premix 2 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Calculated nutrients 3 | ||
| Metabolizable energy, MJ/kg | 12.38 | 12.89 |
| Crude protein, % | 21.50 | 18.50 |
| Calcium, % | 0.95 | 0.70 |
| Available phosphorus, % | 0.45 | 0.35 |
| Lysine, % | 1.19 | 1.01 |
| Methionine, % | 0.48 | 0.43 |
| Threonine, % | 0.83 | 0.79 |
| Gene Names | NCBI Number | Forward Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZO-1 | XM_040706827.2 | CTTCAGGGTGTTTCTCTTCCTCCTC | CTGTGGTTTCATGGCTGGATC |
| Occludin | NM_205128.1 | ACGGCAGCACCTACCTCAA | GGGCGAAGAAGCAGATGAG |
| Claudin-1 | NM_001013611.2 | CATACTCCTGGGTCTGGTTGGT | GACAGCCATCCGCATCTTCT |
| Mucin2 | XM_040701656.2 | TTCATGATGCCTGCTCTTGTG | CCTGAGCCTTGGTACATTCTTGT |
| Mucin5ac | XM_040701669.2 | TGTGGTTGCTATGAGAATGGA | TTGCCATGGTTTGTGCAT |
| Lgr5+ | XM_205518.1 | CCTTTATCAGCCCAGAAGTGA | TGGAACAAATGCTACGGATG |
| Olfm4 | NM_001040463.1 | GACTGGCTCTCTGGATGACC | AGCGTTGTGGCTATCACTTG |
| Znrf3 | XM_015275473.1 | GCCTCTACCAAGCCCAATCT | GGTCGTCGGAAGTTGTGAG |
| TACSTD2 | NM_001277676.2 | TGAGAAGCCACCAGTGTTTAG | CTCCGCTGGCACAGAATAAT |
| SPP1 | NM_204535.4 | GCCCAACATCAGAGCGTAGA | ACGGGTGACCTCGTTGTTTT |
| RDH10 | NM001199459.1 | AATGCTGGCGTGGTCTC | TCATCGGCTGGTCTGTAAG |
| RALDH2 | AF064253 | CAAGACATGAACCCATCG | GAGCTGGAGCAATCTTCC |
| CYP26A1 | NM001001129.1 | TACCGACAAGGACGAGTTCA | CATTGTAGGAGGTCCATTTAGC |
| RARα | NM_204536.1 | AGGAGCTGATCGAGAAGG | GAGCTGTTGTTCGTGGTG |
| RARβ | NM_205326 | GCATCAGTGCAAAAGGTG | TGTCAGTGGTTCGTGTCC |
| RARγ | NM_205294 | GATGAAGATCACCGACCTG | TCCTCCTCGAACATCTCG |
| RXRα | XM_003642291.6 | GATGCGAGACATGCAGATG | GTCGGGGTATTTGTGCTTG |
| RXRγ | NM_205294.2 | CCAAGACGGAGGCATACAG | GGAGCGATGGGAGAAGGAT |
| β-actin | NM_205518 | GAGAAATTGTGCGTGACATCA | CCTGAACCTCTCATTGCCA |
| VA (IU/kg) | 2000 | 6000 | SEM | p Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATRA (mg/kg) | 0 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.50 | VA | ATRA | VA × ATRA | |
| BW | ||||||||||
| Day 1 | 40.70 | 40.66 | 40.61 | 40.42 | 40.71 | 40.89 | 0.06 | 0.893 | 0.469 | 0.208 |
| Day 21 | 612.30 | 647.65 | 654.16 | 632.71 | 631.79 | 644.37 | 4.84 | 0.851 | 0.071 | 0.242 |
| Day 35 | 1474.79 | 1595.04 | 1636.89 | 1670.47 | 1666.42 | 1699.63 | 19.55 | 0.002 | 0.202 | 0.333 |
| Days 1–21 | ||||||||||
| ADG (g) | 26.41 | 28.69 | 28.99 | 27.75 | 27.72 | 28.74 | 0.27 | 0.935 | 0.018 | 0.156 |
| ADFI (g) | 40.99 | 41.44 | 40.57 | 40.25 | 39.76 | 40.91 | 0.50 | 0.518 | 0.993 | 0.740 |
| FCR | 1.55 | 1.44 | 1.40 | 1.45 | 1.44 | 1.42 | 0.02 | 0.402 | 0.105 | 0.326 |
| Mortality (%) | 0 | 1.39 | 1.39 | 6.94 | 2.78 | 1.39 | 0.18 | 0.055 | 0.488 | 0.094 |
| Days 22–35 | ||||||||||
| ADG (g) | 62.77 | 68.02 | 70.29 | 75.52 | 75.33 | 75.37 | 1.37 | 0.002 | 0.331 | 0.329 |
| ADFI (g) | 126.31 | 132.97 | 131.55 | 136.96 | 138.34 | 132.81 | 1.09 | 0.005 | 0.190 | 0.144 |
| FCR | 2.11 | 2.00 | 1.88 | 1.82 | 1.84 | 1.77 | 0.05 | 0.057 | 0.357 | 0.610 |
| Days 1–35 | ||||||||||
| ADG (g) | 40.95 | 44.42 | 45.51 | 46.86 | 46.76 | 47.39 | 0.58 | 0.001 | 0.105 | 0.189 |
| ADFI (g) | 75.11 | 78.05 | 76.96 | 78.93 | 79.20 | 77.67 | 0.52 | 0.070 | 0.395 | 0.403 |
| FCR | 1.86 | 1.77 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 1.64 | 0.02 | 0.044 | 0.196 | 0.560 |
| VA (IU/kg) | 2000 | 6000 | SEM | p Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATRA (mg/kg) | 0 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.50 | VA | ATRA | VA × ATRA | |
| Duodenum | ||||||||||
| VH (μm) | 1338.32 | 1216.35 | 1256.85 | 1324.06 | 1276.51 | 1208.38 | 24.03 | 0.986 | 0.208 | 0.644 |
| CD (μm) | 128.02 | 142.32 | 120.90 | 125.00 | 113.97 | 108.49 | 2.67 | 0.004 | 0.056 | 0.099 |
| VH/CD | 10.95 a | 8.56 b | 10.64 a | 10.72 a | 11.22 a | 11.19 a | 0.20 | 0.006 | 0.031 | 0.003 |
| Jejunum | ||||||||||
| VH (μm) | 706.39 | 780.42 | 870.88 | 849.97 | 707.74 | 820.86 | 23.97 | 0.883 | 0.203 | 0.132 |
| CD (μm) | 102.93 | 104.98 | 108.82 | 107.62 | 98.64 | 112.56 | 2.08 | 0.868 | 0.220 | 0.493 |
| VH/CD | 6.96 | 7.43 | 8.01 | 7.86 | 7.06 | 7.19 | 0.16 | 0.754 | 0.641 | 0.073 |
| Ileum | ||||||||||
| VH (μm) | 604.80 cd | 623.16 bc | 631.55 b | 618.31 bc | 594.34 d | 671.84 a | 4.10 | 0.189 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| CD (μm) | 96.37 ab | 100.24 a | 99.03 ab | 98.46 ab | 95.23 b | 99.33 a | 0.53 | 0.394 | 0.317 | 0.018 |
| VH/CD | 6.28 | 6.22 | 6.38 | 6.28 | 6.26 | 6.72 | 0.04 | 0.068 | 0.001 | 0.106 |
| VA (IU/kg) | 2000 | 6000 | SEM | p Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATRA (mg/kg) | 0 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.50 | VA | ATRA | VA × ATRA | |
| Duodenum | ||||||||||
| VH (μm) | 1427.09 | 1222.44 | 1395.95 | 1440.13 | 1432.53 | 1412.95 | 29.97 | 0.182 | 0.327 | 0.302 |
| CD (μm) | 153.87 | 164.04 | 141.43 | 149.50 | 175.26 | 127.82 | 5.24 | 0.826 | 0.021 | 0.592 |
| VH/CD | 10.85 | 8.07 | 10.03 | 9.76 | 8.26 | 11.14 | 0.22 | 0.846 | <0.001 | 0.060 |
| Jejunum | ||||||||||
| VH (μm) | 946.15 | 916.34 | 964.52 | 863.19 | 989.23 | 924.34 | 23.39 | 0.727 | 0.676 | 0.397 |
| CD (μm) | 117.52 | 111.76 | 111.77 | 103.92 | 118.27 | 94.29 | 2.80 | 0.137 | 0.203 | 0.170 |
| VH/CD | 8.16 | 8.37 | 8.66 | 8.35 | 8.58 | 9.87 | 0.20 | 0.161 | 0.082 | 0.465 |
| Ileum | ||||||||||
| VH (μm) | 704.19 | 823.11 | 725.88 | 725.15 | 793.91 | 643.07 | 19.51 | 0.425 | 0.026 | 0.537 |
| CD (μm) | 110.00 | 114.26 | 104.26 | 114.64 | 109.89 | 87.59 | 2.34 | 0.205 | 0.003 | 0.133 |
| VH/CD | 6.41 | 7.21 | 7.01 | 6.38 | 7.26 | 7.33 | 0.14 | 0.692 | 0.021 | 0.863 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Xiong, Y.; He, L.; Yan, J.; Li, P.; Li, C.; Ding, B. Interactive Effects of Vitamin A and All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, and Plasma Metabolomics of Broiler Chickens. Animals 2025, 15, 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203005
Guo S, Xiong Y, He L, Yan J, Li P, Li C, Ding B. Interactive Effects of Vitamin A and All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, and Plasma Metabolomics of Broiler Chickens. Animals. 2025; 15(20):3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Shuangshuang, Yushu Xiong, Lai He, Jiakun Yan, Peng Li, Changwu Li, and Binying Ding. 2025. "Interactive Effects of Vitamin A and All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, and Plasma Metabolomics of Broiler Chickens" Animals 15, no. 20: 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203005
APA StyleGuo, S., Xiong, Y., He, L., Yan, J., Li, P., Li, C., & Ding, B. (2025). Interactive Effects of Vitamin A and All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, and Plasma Metabolomics of Broiler Chickens. Animals, 15(20), 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203005






