Molecular Constraints of Sperm Sex Sorting via TLR7/8 Activation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sperm Sex Sorting via the TLR7/8 Receptor Activation Method
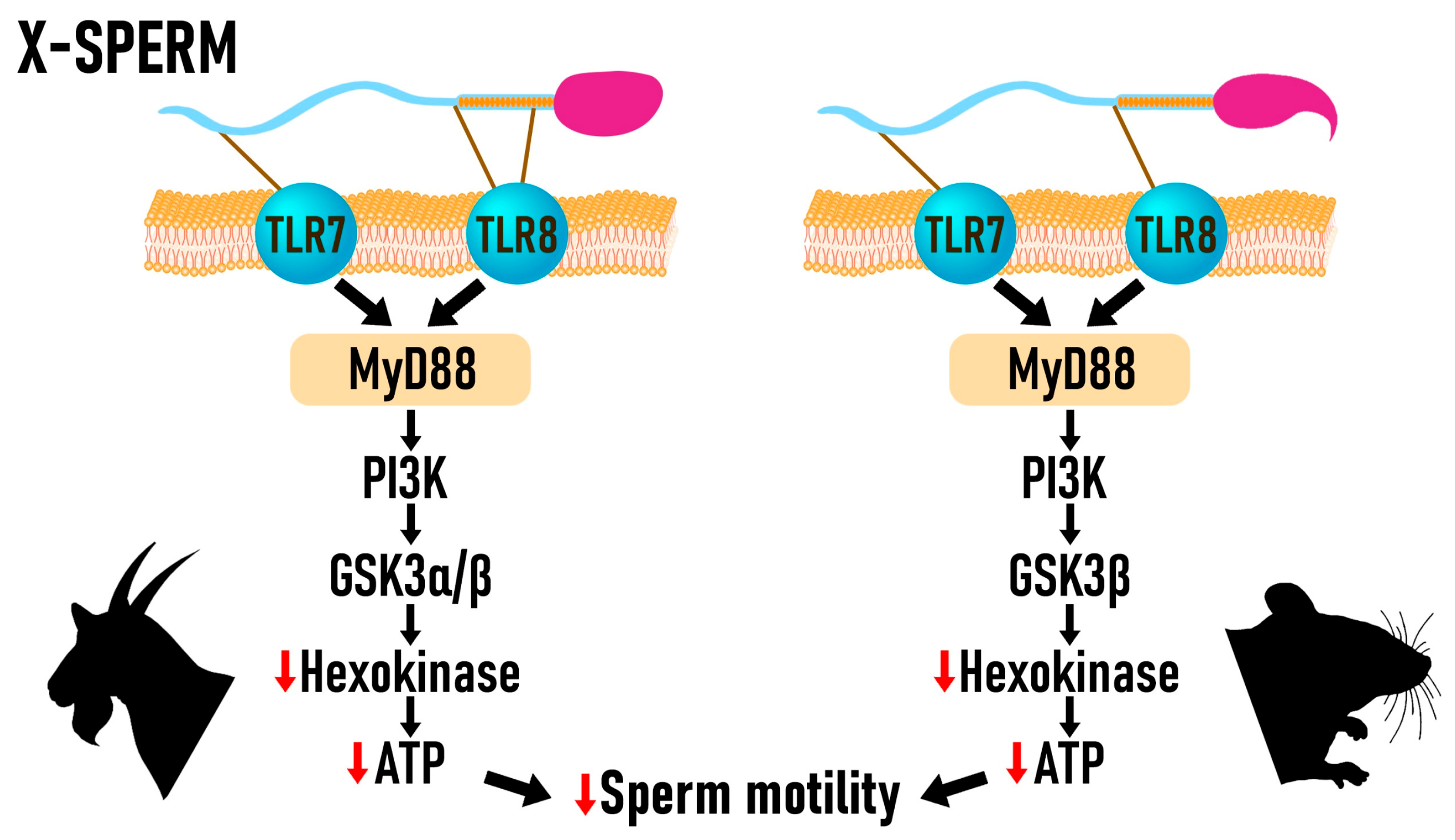
2.1. Activation of TLR7/8
2.2. Swim-Up Technique to Separate Sperm Based on Sex Chromosome Type
2.3. Sperm Motility and ATP Generation
2.4. Sperm Motility and Glucose Concentration
2.5. Other Factors Affecting the Efficiency of the Method
3. Application of Sperm Sorting Based on the TLR7/8 Receptor Activation Method in Different Mammalian Species
3.1. Species with Successful Application of the TLR7/8 Receptor Activation Method
3.2. Species with Unsuccessful Application of the TLR7/8 Receptor Activation Method
3.2.1. Swine
3.2.2. Canine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The expression patterns: in murine, TLR7 is predominantly expressed at the elongated spermatid stage, a period when functional differences between X- and Y-spermatozoa may already manifest. In swine and canine, either stage-specific expression is absent, or TLR7/8 expression levels are insufficient to initiate a signaling response.
- The proteolytic maturation of receptors: activation of TLR7/8 requires cleavage of the Z-loop within the LRR domain, enabling receptor dimerization. In the absence of proteolytic activity, as is presumed in swine and canine, the receptors remain inactive and fail to initiate the signaling cascade.
- The mRNA distribution via cytoplasmic bridges: in many species, haploid spermatids exchange molecular information through cytoplasmic bridges, which tend to minimize differences between X- and Y-cells. However, certain genes, referred to as genoinformative markers (GIMs), can partially evade this exchange. These genes are more actively expressed during the late stages of spermatogenesis and may contribute to phenotypic differences between X- and Y-spermatozoa. While this mechanism could potentially explain species-specific differences in sorting efficiency, including the limited success observed in swine and canine, further molecular studies are required to confirm such associations.
- The alternative splicing and polymorphisms. In humans, TLR8 exists in multiple splice variants, one of which (TLR8v2) may encode a truncated protein. Such variations potentially reduce the receptor’s capacity for dimerization and activation. As a result, the application of TLR7/8-mediated sperm sorting is feasible only under strictly defined conditions, including receptor expression at post-meiotic stages, their full proteolytic activation, and the absence of intercellular equilibration compensatory mechanisms.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magauiya, A.; Zhumadil Kh Temirkhan, A.; Umorbekova, G.; Sadyk, T. Sperm sexing methods and recent developments in this field: Systematic review. Nor. J. Dev. Int. Sci. 2024, 124, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, E.; Malama, E.; Bozukova, S.; Siuda, M.; Wyck, S.; Witschi, U.; Bauersachs, S.; Bollwein, H. The micro-RNA content of unsorted cryopreserved bovine sperm and its relation to the fertility of sperm after sex-sorting. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quelhas, J.; Santiago, J.; Matos, B.; Rocha, A.; Lopes, G.; Fardilha, M. Bovine semen sexing: Sperm membrane proteomics as candidates for immunological selection of X- and Y-chromosome-bearing sperm. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, T.; Tsujita, N.; Shimada, M. Activation of Toll-like receptor 7/8 encoded by the X chromosome alters sperm motility and provides a novel simple technology for sexing sperm. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Xi, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Wen, F.; Xian, M.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, D.; Wang, L.; Lei, A.; et al. TLR7/8 signalling affects X-sperm motility via the GSK3 α/β-hexokinase pathway for the efficient production of sexed dairy goat embryos. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Song, M. Expression of TLR7/8 in canine sperm and evaluation of the effect of ligand R848 on the sorting of canine X/Y sperm. Theriogenology 2025, 231, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Gui, H.; Chen, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Jing, Q.; Lv, H.; Wan, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.; et al. Regulating Tumor-Associated Macrophage Polarization by Cyclodextrin-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded with R848 for Treating Colon Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 3589–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Umehara, T.; Okazaki, T.; Goto, M.; Fujita, Y.; Hoque, S.A.M.; Kawai, T.; Zeng, W.; Shimada, M. Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis in Mitochondria Enhance the Duration of High-Speed Linear Motility in Boar Sperm. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.; Herrmann, B.G. RAC1 controls progressive movement and competitiveness of mammalian spermatozoa. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; McGoldrick, L.L.; Chung, J.J. Sperm ion channels and transporters in male fertility and infertility. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, T.; Tsujita, N.; Zhu, Z.; Ikedo, M.; Shimada, M. A simple sperm-sexing method that activates TLR7/8 on X sperm for the efficient production of sexed mouse or cattle embryos. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2645–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, T.; Kawai, T.; Goto, M.; Richards, J.S.; Shimada, M. Creatine enhances the duration of sperm capacitation: A novel factor for improving in vitro fertilization with small numbers of sperm. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Keshtgar, S. The Effects of EGTA on the Quality of Fresh and Cryopreserved-Thawed Human Spermatozoa. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 45, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Peng, J.; Hong, L.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, E.; Li, Z. Gender Control of Mouse Embryos by Activation of TLR7/8 on X Sperm via Ligands dsRNA-40 and dsRNA-DR. Molecules 2024, 29, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, L.; McKim, C.; Desaulniers, J.P. Effective carrier-free gene-silencing activity of cholesterol-modified siRNAs. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22963–22966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mageed, A.M.; Isobe, N.; Yoshimura, Y. Effects of Virus-associated Molecular Patterns on the Expression of Cathelicidins in the Hen Vagina. J. Poult. Sci. 2016, 53, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Sinhari, A.; Jain, P.; Jadhav, H.R. A perspective on oligonucleotide therapy: Approaches to patient customization. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1006304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, S.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, F. Effects of Diluent pH on Enrichment and Performance of Dairy Goat X/Y Sperm. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 747722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, S.; Gao, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, F. Diluent pH affects sperm motility via GSK3 α/β-hexokinase pathway for the efficient enrichment of X-sperm to increase the female kids rate of dairy goats. Theriogenology 2023, 201, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Cao, X.Y.; He, Q.F.; Yang, H.W.; Chen, Y.Z.; Zhao, J.L.; Ma, H.W.; Kang, J.; Liu, J.; Quang, F.S. Alkaline semen diluent combined with R848 for separation and enrichment of dairy goat X-sperm. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 10020–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.P.; Shah, T.M.; George, L.B.; Joshi, C.G. Effect of the pH in the enrichment of X or Y sex chromosome-bearing sperm in bovine. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadjieva, D.; Kistanova, E.; Yotov, S.; Atanasov, A.; Ivanova, B.; Yarkov, D.; Sinapov, B. Sexing of fresh ram semen by activation of the toll-like receptors 7/8 (TLR7/8). Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2022, 57 (Suppl. 4), 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Yang, W.; Mo, J.; Hong, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S. Expression of Toll-like Receptors 7/8 in Boar Reproductive System and Evaluation of Effect of their Ligands on Boar X/Y Sperm Sorting. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2023, 54, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Doğan, G.; Sandıkçı, M.; Karagenç, L. Stage-specific expression of Toll-like receptors in the seminiferous epithelium of mouse testis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 162, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shi, D.; Li, X.; Gong, W.; Wu, F.; Guo, X.; Xiao, H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H. TLR signalling affects sperm mitochondrial function and motility via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and glycogen synthase kinase-3α. Cell Signal 2016, 28, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutani, K.; Stansifer, K.; Ticau, S.; Bojic, L.; Villani, A.C.; Slisz, J.; Cremers, C.M.; Roy, C.; Donovan, J.; Fiske, B.; et al. Widespread haploid-biased gene expression enables sperm-level natural selection. Science 2021, 371, eabb1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, J.M.; Nachman, M.W. Rates of protein evolution are positively correlated with developmental timing of expression during mouse spermatogenesis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielcarska, M.B.; Bossowska-Nowicka, M.; Toka, F.N. Cell Surface Expression of Endosomal Toll-Like Receptors-A Necessity or a Superfluous Duplication? Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 620972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ohto, U.; Shimizu, T. Toward a structural understanding of nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors in the innate immune system. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 3167–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ohto, U.; Shibata, T.; Krayukhina, E.; Taoka, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Tanji, H.; Isobe, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Miyake, K.; et al. Structural Analysis Reveals that Toll-like Receptor 7 Is a Dual Receptor for Guanosine and Single-Stranded RNA. Immunity 2016, 45, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shao, Y.; Bennett, T.A.; Shankar, R.A.; Wightman, P.D.; Reddy, L.G. The functional effects of physical interactions among Toll-like receptors 7, 8, and 9. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37427–37434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.L.; Weinerman, B.; Basole, C.; Salazar, J.C. TLR8: The forgotten relative revindicated. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantier, M.P.; Irving, A.T.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Xu, D.; Evans, V.A.; Cameron, P.U.; Bourne, J.A.; Ferrero, R.L.; John, M.; Beh-lke, M.A.; et al. Genetic modulation of TLR8 response following bacterial phagocytosis. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, F.; Mbengue, N.; Winge, S.B.; Trefzer, T.; Leushkin, E.; Sepp, M.; Cardoso-Moreira, M.; Schmidt, J.; Schneider, C.; Mößinger, K.; et al. The molecular evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals. Nature 2023, 613, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Specie | TLR7 Localization | TLR8 Localization | Expression Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umehara et al., 2019 [4] | Murine | Tail region of X-sperm | Midpiece of X-sperm | Both TLR7 and TLR8 expressed; X-sperm enriched for TLR7/8 |
| Ren et al., 2021 [5] | Caprine | Entire tail | Connecting and midpiece regions | Both receptors are active and cooperatively reduce ATP levels in X-spermatozoa. |
| Pan et al., 2025 [6] | Canine | Tail and post-acrosomal region | Not detected | Only TLR7 detected; TLR8 absent in canine spermatozoa |
| Source | Culture Medium | Specie | Results | Agonist Concentration | Sex Gamete Detection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umehara et al., 2019 [4] | R848 + mHTF containing 2 mM glucose | Murine 1 | Y-sperm: >90% | 0.3 μM | PCR |
| Hou et al., 2024 [14] | dsRNA-40/cholesterol + HTF | Murine 1 | Y-sperm: 71.59% ± 3.73% X-sperm: 79.48% ± 1.44% | 0.3 μM | PCR |
| dsRNA/cholesterol + HTF | Y-sperm: 68.17% ± 2.72% X-sperm: 60.43% ± 23.07% | ||||
| Umehara et al., 2020 [11] | R848 + mHTF containing 2 mM glucose + creatine | Murine 1 | XY embryos: 92 ± 4.2% | 0.3 μM | PCR |
| R848 + mHTF containing 2 mM glucose + creatine | Bovine 2 | XY embryos: 91.3 ± 2.8% XX embryos: 84.2 ± 5.3% | 0.3 μM | PCR | |
| Ren et al., 2021 [5] | R848 + goat semen extender | Caprine 1 | Y-sperm: 90.50% ± 2.86% X-sperm: 80.30% ± 2.91% | 1 μmol/L | Flow cytometry |
| Huang et al., 2022 [20] | R848 + semen extender at pH 7.4 | Caprine 1 | X-sperm: 85.62% ± 2.37% | 0.2 μg/mL | PCR |
| Abadjieva et al., 2022 [22] | R848 + modified human tubal fluid medium | Ovine 1 | Y-sperm: 74–78% X-sperm: 64–70% | 0.3 μM | PCR |
| Source | Culture Medium | Specie | Results | Agonist Concentration | Sex Gamete Detection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al., 2023 [23] | R848 + semen extender | Swine 1 | X-sperm: 46.49 ± 2.27% Y-sperm: 53.51 ± 2.27% | 0.3 μM | PCR |
| Pan et al., 2025 [6] | R848 | Canine 1 | Y-sperm: 49.51 ± 1.12% X-sperm: 50.68 ± 0.98% | 0.4 μM | PCR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magauiya, A.; Torebek, K.; Savvulidi, F.G.; Ptáček, M.; LeBrun, C.; Langerová, L.; Sagdat, E.; Baikoshkarova, S.; Malmakov, N. Molecular Constraints of Sperm Sex Sorting via TLR7/8 Activation. Animals 2025, 15, 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202976
Magauiya A, Torebek K, Savvulidi FG, Ptáček M, LeBrun C, Langerová L, Sagdat E, Baikoshkarova S, Malmakov N. Molecular Constraints of Sperm Sex Sorting via TLR7/8 Activation. Animals. 2025; 15(20):2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202976
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagauiya, Alikhan, Kausar Torebek, Filipp Georgijevič Savvulidi, Martin Ptáček, Christopher LeBrun, Lucie Langerová, Elbosyn Sagdat, Saltanat Baikoshkarova, and Nurlan Malmakov. 2025. "Molecular Constraints of Sperm Sex Sorting via TLR7/8 Activation" Animals 15, no. 20: 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202976
APA StyleMagauiya, A., Torebek, K., Savvulidi, F. G., Ptáček, M., LeBrun, C., Langerová, L., Sagdat, E., Baikoshkarova, S., & Malmakov, N. (2025). Molecular Constraints of Sperm Sex Sorting via TLR7/8 Activation. Animals, 15(20), 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202976







