A High Number of Ring-Down Artefacts and an Irregular Pleural Surface Are More Commonly Observed in WHWTs Suffering from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Compared to Control WHWTs
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Thoracic Ultrasonography
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dogs
3.2. Clinical Data
3.3. Thoracic Ultrasound Results
3.3.1. Transducers
3.3.2. Total Score and Repartition of the Lesions
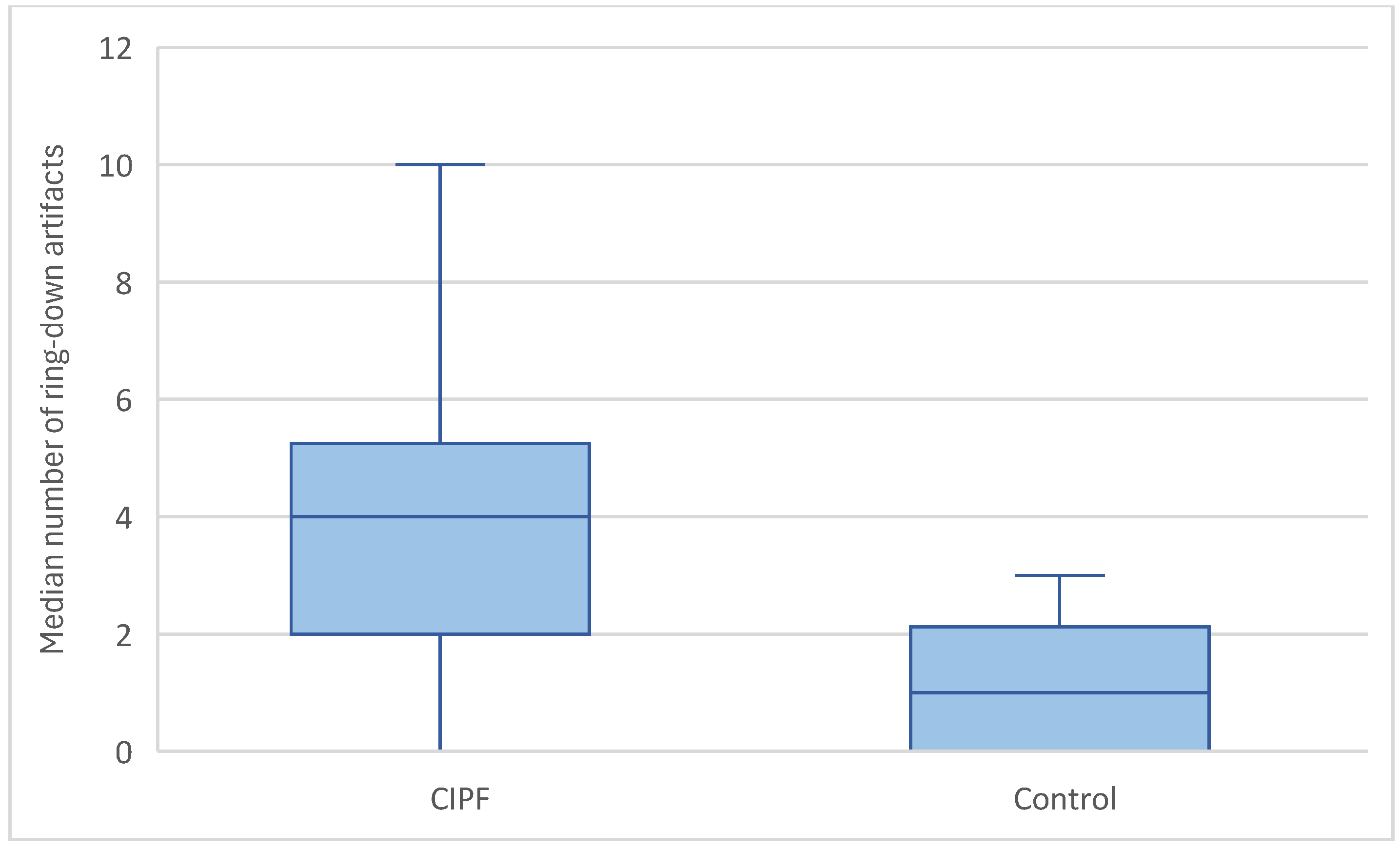
3.3.3. Ring-Down Artefacts
3.3.4. Pleural Surface
3.3.5. Other Lesions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIPF | Canine idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| WHWT | West Highland white terrier |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| US | Ultrasonography |
| UIP | Usual interstitial pneumonia |
| ILDs | Pulmonary interstitial disease |
References
- Laurila, H.P.; Rajamäki, M.M. Update on canine idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in West Highland White Terriers. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clercx, C.; Fastrès, A.; Roels, E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in West Highland White Terriers: An update. Vet. J. 2018, 242, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roels, E.; Couvreur, T.; Farnir, F.; Clercx, C.; Verschakelen, J.; Bolen, G. Comparison between sedation and general anesthesia for high resolution computed tomographic characterization of canine idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in West Highland White Terriers. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2017, 58, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, F.; Handel, I.; Hammond, G.; King, L.G.; Corcoran, B.M.; Schwarz, T. Further characterization of computed tomographic and clinical features for staging and prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in West Highland white terriers. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2017, 58, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä-Laurila, H.P.; Rajamäki, M.M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in West Highland White Terriers. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2014, 44, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkilä, H.P.; Lappalainen, A.K.; Day, M.J.; Clercx, C.; Rajamäki, M.M. Clinical, Bronchoscopic, Histopathologic, Diagnostic Imaging, and Arterial Oxygenation Findings in West Highland White Terriers with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, B.M.; King, L.G.; Schwarz, T.; Hammond, G.; Sullivan, M. Further characterisation of the clinical features of chronic pulmonary disease in West Highland white terriers. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Lisciandro, G.R.; Keene, B.W.; Tou, S.P.; DeFrancesco, T.C. Accuracy of point-of-care lung ultrasonography for the diagnosis of cardiogenic pulmonary edema in dogs and cats with acute dyspnea. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2017, 250, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzosi, T.; Mannucci, T.; Pistoresi, A.; Toma, F.; Tognetti, R.; Zini, E.; Domenech, O.; Auriemma, E.; Citi, S. Assessment of Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Dogs with Different Stages of Chronic Valvular Heart Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicker, S.A.; Lisciandro, G.R.; Newell, S.M.; Johnson, J.A. Diagnosis of pulmonary contusions with point of care lung ultrasonography and thoracic radiography compared to thoracic computed tomography in dogs with motor vehicle trauma: 29 cases (2017–2018). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2020, 30, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisciandro, G.R. Abdominal and thoracic focused assessment with sonography for trauma, triage, and monitoring in small animals. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2011, 21, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisciandro, G.R.; Fulton, R.M.; Fosgate, G.T.; Mann, K.A. Frequency and number of B-lines using a regionally based lung ultrasound examination in cats with radiographically normal lungs compared to cats with left-sided congestive heart failure. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2017, 27, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacholec, C.; Lisciandro, G.R.; Masseau, I.; Donnelly, L.; DeClue, A.; Reinero, C.R. Lung ultrasound nodule sign for detection of pulmonary nodule lesions in dogs: Comparison to thoracic radiography using computed tomography as the criterion standard. Vet. J. 2021, 275, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcetta, A.; Leccardi, S.; Testa, E.; Papaleo, F.; Fenoglio, L.; Melchio, R. The role of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease. Shanghai Chest 2018, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frongillo, E.; Gaudioso, G.; Feragalli, B. Ultrasound and interstitial lung disease: Use and limitations. Radiol. Medica 2020, 125, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolescu, D.; Davidescu, L.; Traila, D.; Oancea, C.; Tudorache, V. The reliability of lung ultrasound in assessment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. CIA 2018, 13, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolescu, D.; Oancea, C.; Timar, B.; Traila, D.; Malita, D.; Birsasteanu, F.; Tudorache, V. Ultrasound mapping of lung changes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin. Respir. J. 2020, 14, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacedonia, D.; Scioscia, G.; Giardinelli, A.; Quarato, C.M.I.; Sassani, E.V.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Maci, F.; Sperandeo, M. The Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in the Study of Interstitial Lung Diseases: High-Resolution Computed Tomography Versus Ultrasound Patterns: Our Preliminary Experience. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoon, J.S.; Nyland, T.G. Chapter 1—Fundamentals of Diagnostic Ultrasound. In Small Animal Diagnostic Ultrasound; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, M.K.; Katyal, S.; Blackwood, M.S. US Artifacts. RadioGraphics 2009, 29, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Lisciandro, G.R.; DeFrancesco, T.C. Distribution of alveolar-interstitial syndrome in dogs and cats with respiratory distress as assessed by lung ultrasound versus thoracic radiographs. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2018, 28, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Lo, P.-Y.; Lam, M.-C.; Wu, H.-D. Usefulness of Chest Ultrasonography in Predicting Diagnosis in Non-emergency Small Animal Patients With Lung Parenchymal and Pleural Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 616882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Mézière, G.; Biderman, P.; Gepner, A.; Barré, O. The Comet-tail Artifact: An Ultrasound Sign of Alveolar-Interstitial Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reef, V.B.; Whittier, M.; Allam, L.G. Thoracic Ultrasonography. Clin. Tech. Equine Pract. 2004, 3, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reißig, A.; Kroegel, C. Transthoracic Sonography of Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease. J. Ultrasound Med. 2003, 22, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G. Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2020, 158, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Sakakibara, K.; Sano, T.; Hori, A. Usefulness of pericardial lung ultrasonography for the diagnosis of cardiogenic pulmonary edema in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 81, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.D.; Ward, J.L.; Viall, A.K.; Tropf, M.A.; Walton, R.L.; Fowler, J.L.; Ware, W.A.; DeFrancesco, T.C. Utility of point of care lung ultrasound for monitoring cardiogenic pulmonary edema in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademacher, N.; Pariaut, R.; Pate, J.; Saelinger, C.; Kearney, M.T.; Gaschen, L. Transthoracic Lung Ultrasound in Normal Dogs and Dogs with Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema: A Pilot Study. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2014, 55, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Lisciandro, G.R.; Ware, W.A.; Miles, K.G.; Viall, A.K.; DeFrancesco, T.C. Lung ultrasonography findings in dogs with various underlying causes of cough. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 255, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.; Pivetta, M.; Humm, K. Diagnostic accuracy of a lung ultrasound protocol (Vet BLUE) for detection of pleural fluid, pneumothorax and lung pathology in dogs and cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishniw, M.; Caivano, D.; Dickson, D.; Vatne, L.; Harris, J.; Matos, J.N. Two-dimensional echocardiographic left- atrial-to-aortic ratio in healthy adult dogs: A reexamination of reference intervals. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, K.; Häggström, J.; Kvart, C.; Lord, P. Left atrial to aortic root indices using two-dimensional and M-mode echocardiography in cavalier King Charles spaniels with and without left atrial enlargement. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2002, 43, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrall, D.E. Canine and Feline Lung. In Textbook of Veterinary Diagnostic Radiology; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 710–734. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes Rodrigues, N.; Giraud, L.; Bolen, G.; Fastrès, A.; Clercx, C.; Boysen, S.; Billen, F.; Gommeren, K. Comparison of lung ultrasound, chest radiographs, C-reactive protein, and clinical findings in dogs treated for aspiration pneumonia. Vet. Intern. Medicne 2022, 36, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, D.A.; Sverzellati, N.; Travis, W.D.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Galvin, J.R.; Goldin, J.G.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A Fleischner Society White Paper. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusmirek, J.E.; Martin, M.D.; Kanne, J.P. Imaging of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 2016, 54, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizioli, L.; Ciccarese, F.; Forti, P.; Chiesa, A.M.; Giovagnoli, M.; Mughetti, M.; Zompatori, M.; Zoli, M. Integrated Use of Lung Ultrasound and Chest X-Ray in the Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease. Respiration 2017, 93, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-H.; Pan, L.; Gao, Y.-B.; Cui, G.-H.; Wang, Y.-H. Utility of lung ultrasound to identify interstitial lung disease: An observational study based on the STROBE guidelines. Medicine 2021, 100, e25217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Vázquez, N.; Jimenez-Núñez, F.G.; Godoy-Navarrete, F.J.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Aguilar-Hurtado, M.C.; Romero-Barco, C.M.; Ureña-Garnica, I.; Espildora, F.; Padin-Martín, M.I.; Fernández-Nebro, A. Utility of pulmonary ultrasound to identify interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, G.; Chokhani, A.; Verma, A.; Siddiqui, Z. Transthoracic ultrasonography in patients with interstitial lung disease. Lung India 2020, 37, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrjä, P.; Heikkilä, H.P.; Lilja-Maula, L.; Krafft, E.; Clercx, C.; Day, M.J.; Rönty, M.; Myllärniemi, M.; Rajamäki, M.M. The Histopathology of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in West Highland White Terriers Shares Features of Both Non-specific Interstitial Pneumonia and Usual Interstitial Pneumonia in Man. J. Comp. Pathol. 2013, 149, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, J.; Rubio, G.A.; Limper, A.H.; Williams, K.; Elliot, S.J.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Glassberg, M.K. Exploring Animal Models That Resemble Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, O.; Agha, M.; Al-Asdody, A.; Mehana, N.; Habib, R. Sonographic features of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2018, 67, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venco, L.; Colaneri, G.; Formaggini, L.; De Franco, M.; Rishniw, M. Utility of thoracic ultrasonography in a rapid diagnosis of angiostrongylosis in young dogs presenting with respiratory distress. Vet. J. 2021, 271, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenise, A.; Boysen, R.S.; Rudloff, E.; Neri, L.; Spattini, G.; Storti, E. Veterinary-focused assessment with sonography for trauma-airway, breathing, circulation, disability and exposure: A prospective observational study in 64 canine trauma patients. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 60, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudas, M.; Orde, S.; Nalos, M. Bedside lung ultrasound in the care of the critically ill. Crit. Care Resusc. 2017, 19, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.G. Diagnostic accuracy of lung ultrasound for interstitial lung disease in patients with connective tissue diseases: A meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Quarato, C.M.I.; Venuti, M.; Sperandeo, M. The artificial count of artifacts for thoracic ultrasound: What is the clinical usefulness? J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2020, 34, 1379–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, G.M.; Sperandeo, M. Sounds, Ultrasounds, and Artifacts: Which Clinical Role for Lung Imaging? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo, M.; Rotondo, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Catalano, D.; Feragalli, B.; Trovato, G.M. Transthoracic ultrasound in the assessment of pleural and pulmonary diseases: Use and limitations. Radiol. Medica 2014, 119, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łobaczewski, A.; Czopowicz, M.; Moroz, A.; Mickiewicz, M.; Stabińska, M.; Petelicka, H.; Frymus, T.; Szaluś-Jordanow, O. Lung Ultrasound for Imaging of B-Lines in Dogs and Cats—A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement between Three Types of Transducers and the Accuracy in Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema, Pneumonia and Lung Neoplasia. Animals 2021, 11, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
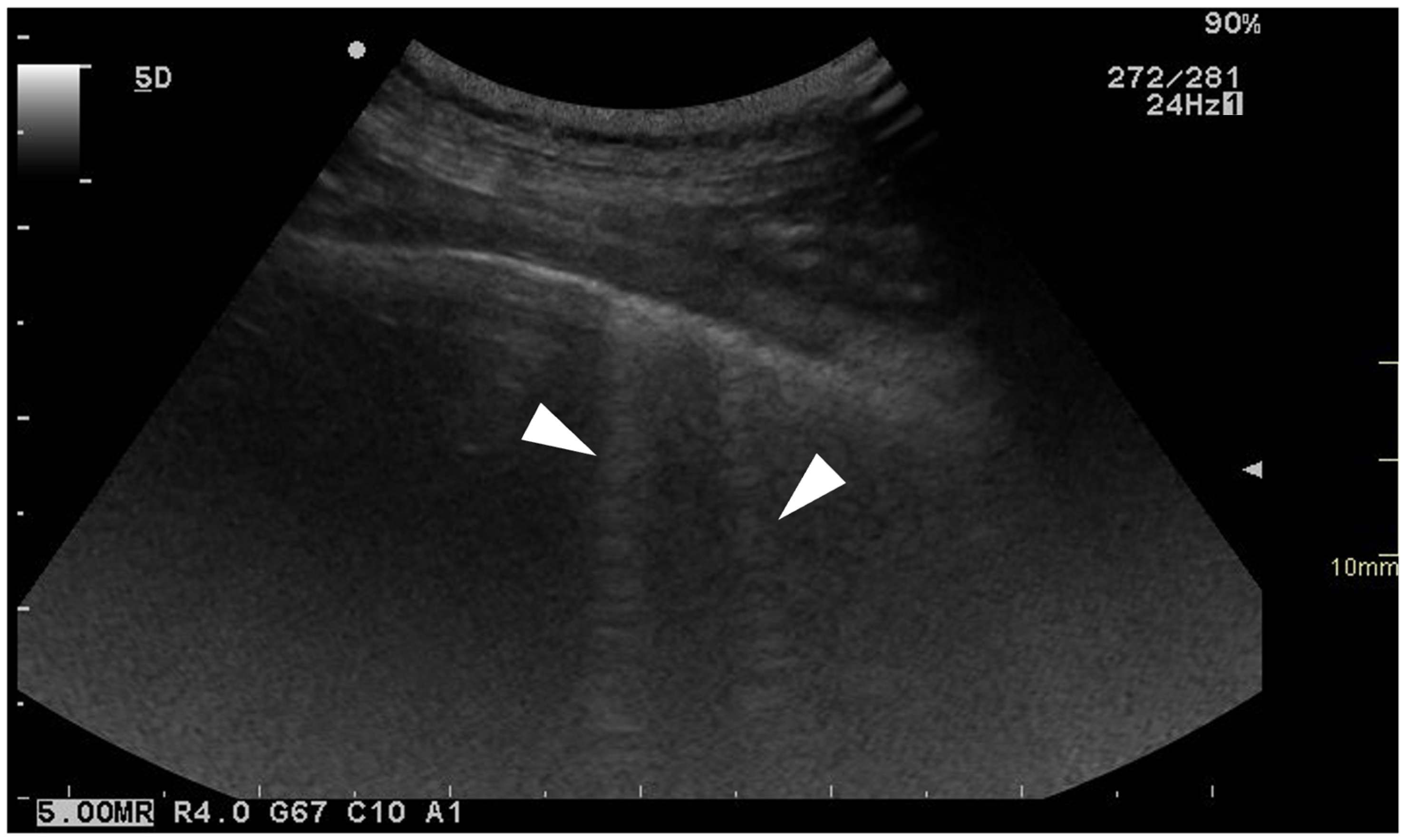
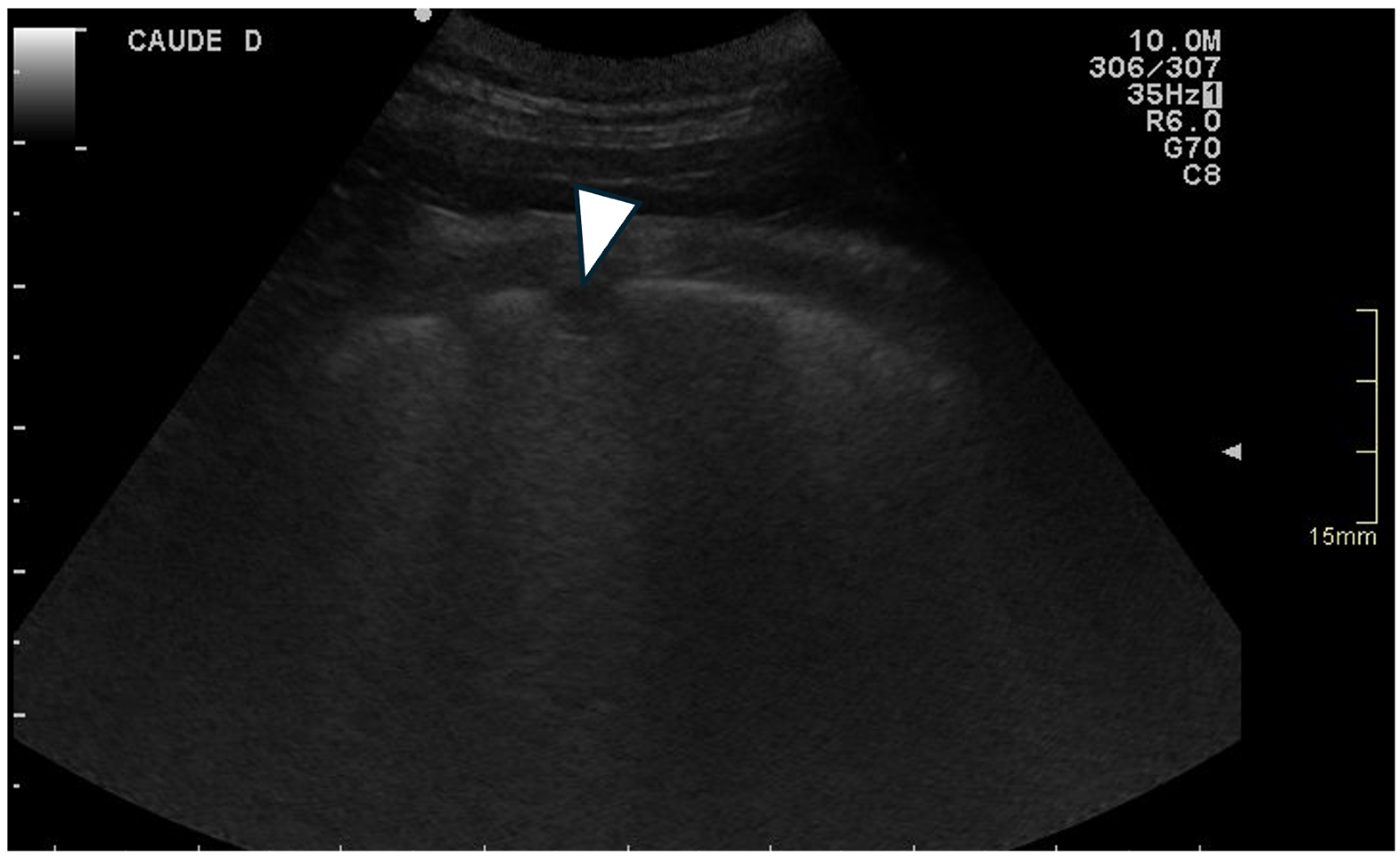
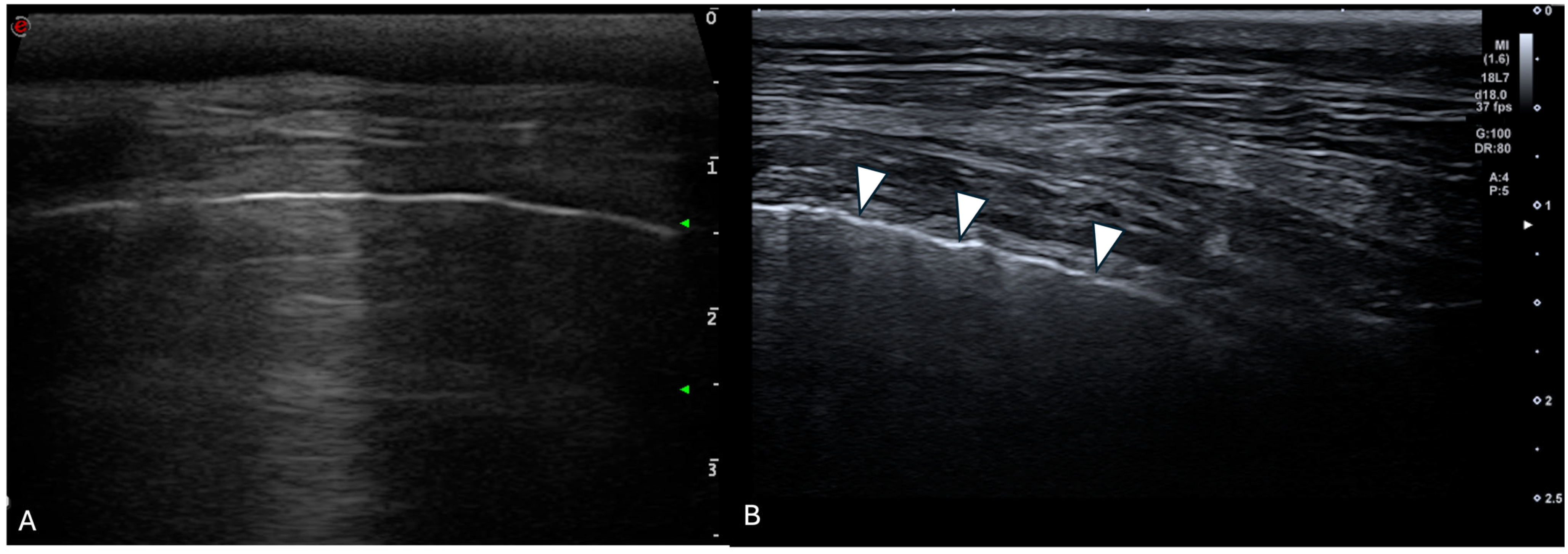

| Ring-Down Artefacts | Lung Lesions | Pleural Surface | Pleural Sliding | Pleural Effusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score 0 | 0 | 0 | Smooth | Present | Absent |
| Score 1 | 1–5 | Small hypoechoic nodules | Irregular | Absent | Present |
| Score 2 | 6–10 | Larger hypoechoic areas | |||
| Score 3 | >10 | Both |
| Score | Ring-Down Artefacts (Dogs = n) | Lung Lesions (Dogs = n) | Pleural Surface (Dogs = n) | Pleural Sliding (Dogs = n) | Pleural Effusion (Dogs = n) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control dogs | 0 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 10 | 10 |
| 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| 3 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| CIPF dogs | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 17 | 17 |
| 1 | 5 | 2 | 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 9 | 10 | ||||
| 3 | 3 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soliveres, E.; Pierrot, E.; Fastrès, A.; Roels, E.; Clercx, C.; Bolen, G. A High Number of Ring-Down Artefacts and an Irregular Pleural Surface Are More Commonly Observed in WHWTs Suffering from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Compared to Control WHWTs. Animals 2025, 15, 2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202964
Soliveres E, Pierrot E, Fastrès A, Roels E, Clercx C, Bolen G. A High Number of Ring-Down Artefacts and an Irregular Pleural Surface Are More Commonly Observed in WHWTs Suffering from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Compared to Control WHWTs. Animals. 2025; 15(20):2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202964
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoliveres, Eugénie, Emilie Pierrot, Aline Fastrès, Elodie Roels, Cécile Clercx, and Géraldine Bolen. 2025. "A High Number of Ring-Down Artefacts and an Irregular Pleural Surface Are More Commonly Observed in WHWTs Suffering from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Compared to Control WHWTs" Animals 15, no. 20: 2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202964
APA StyleSoliveres, E., Pierrot, E., Fastrès, A., Roels, E., Clercx, C., & Bolen, G. (2025). A High Number of Ring-Down Artefacts and an Irregular Pleural Surface Are More Commonly Observed in WHWTs Suffering from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Compared to Control WHWTs. Animals, 15(20), 2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202964





