A Meta-Analysis on Quantitative Sodium, Potassium and Chloride Metabolism in Horses and Ponies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Sodium
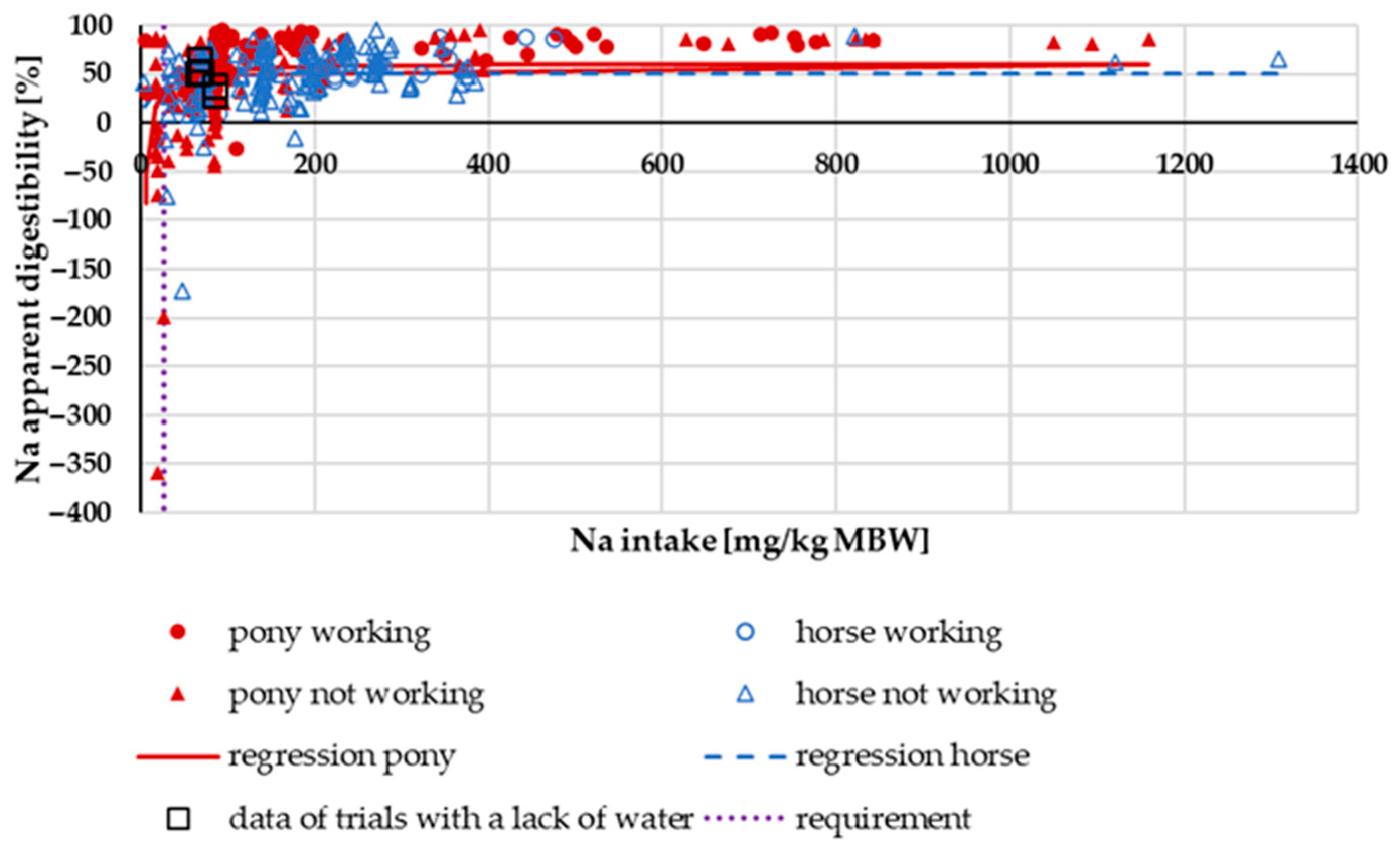
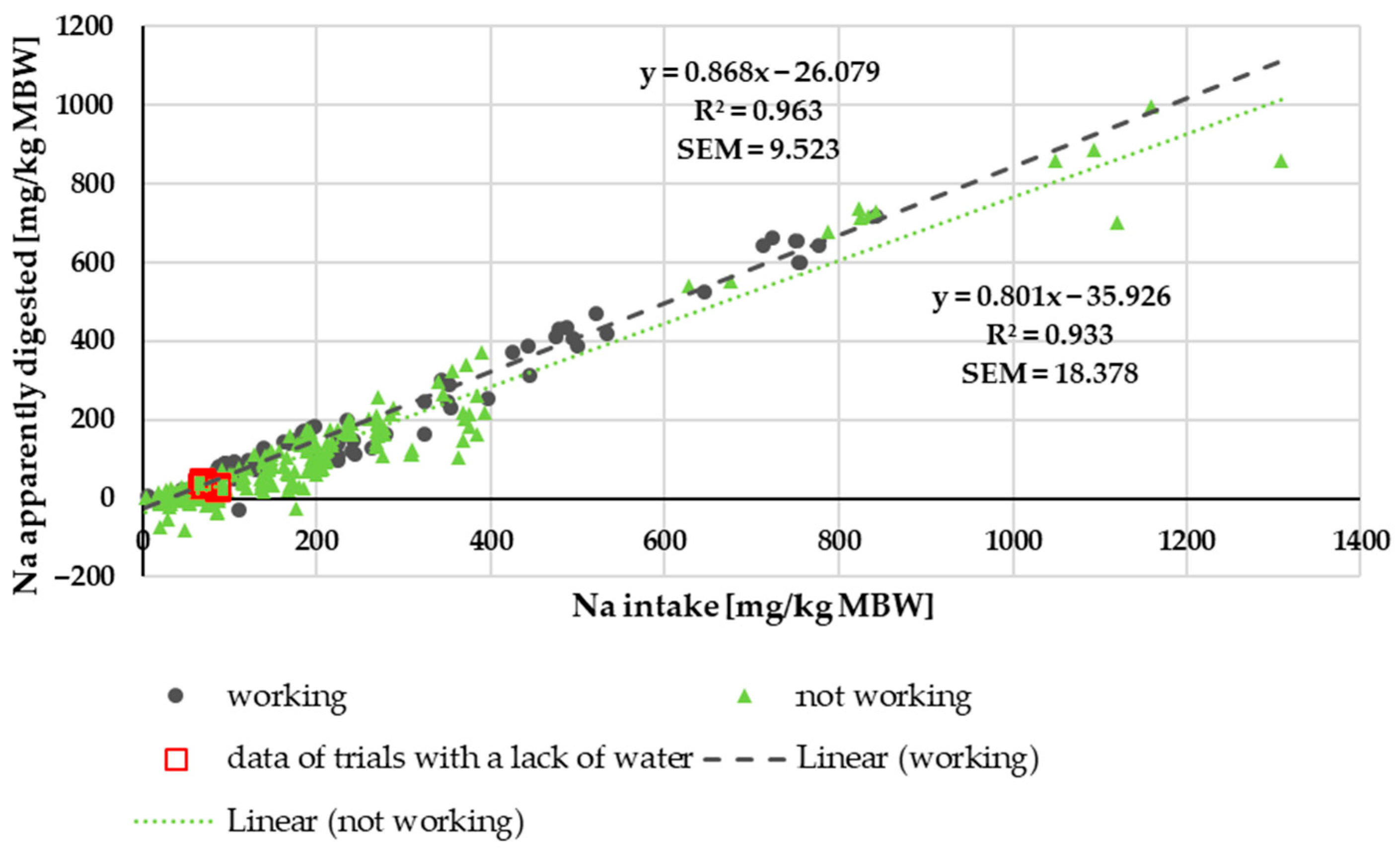
3.1.1. Na Digestibility
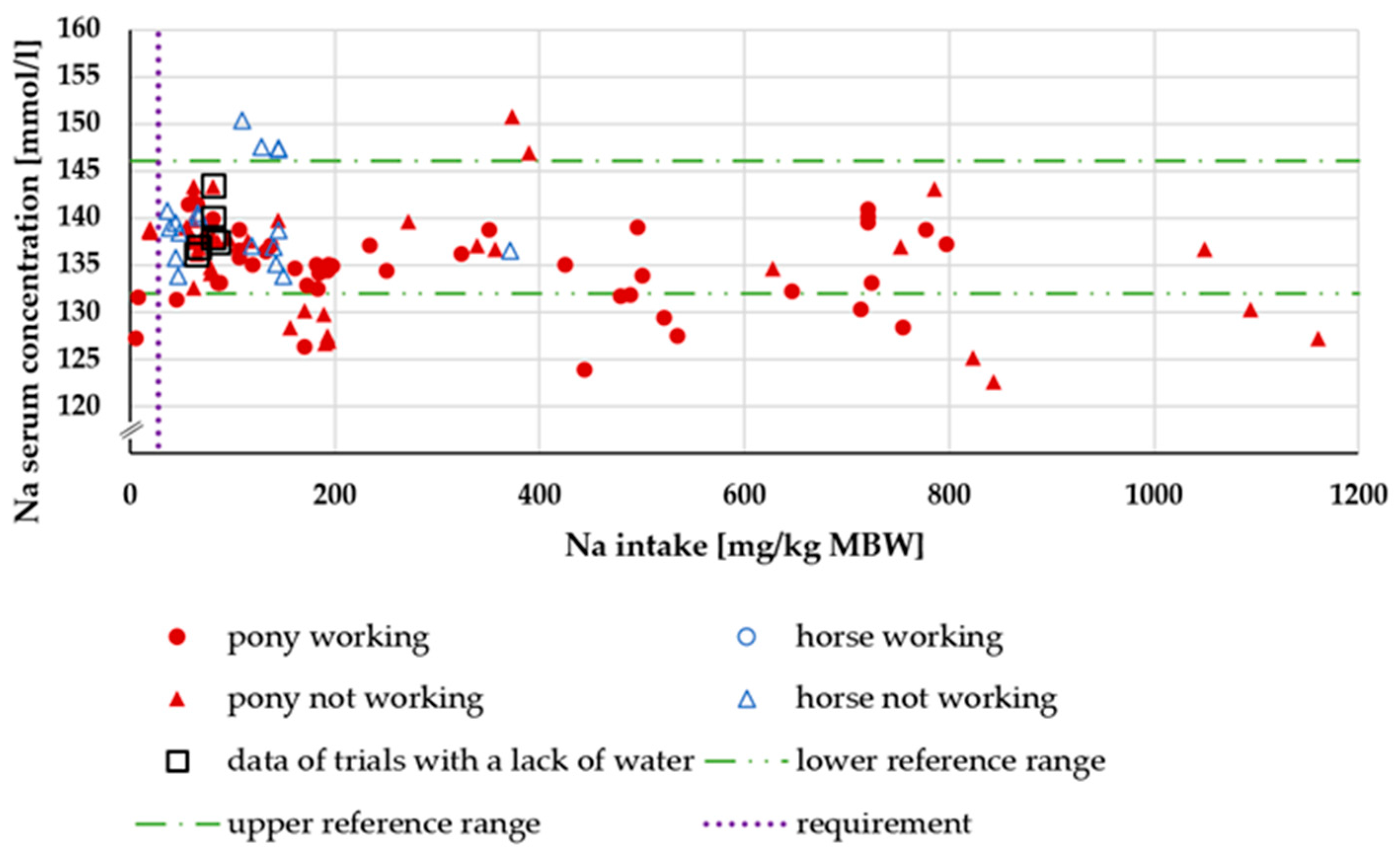
3.1.2. Serum Na Concentration
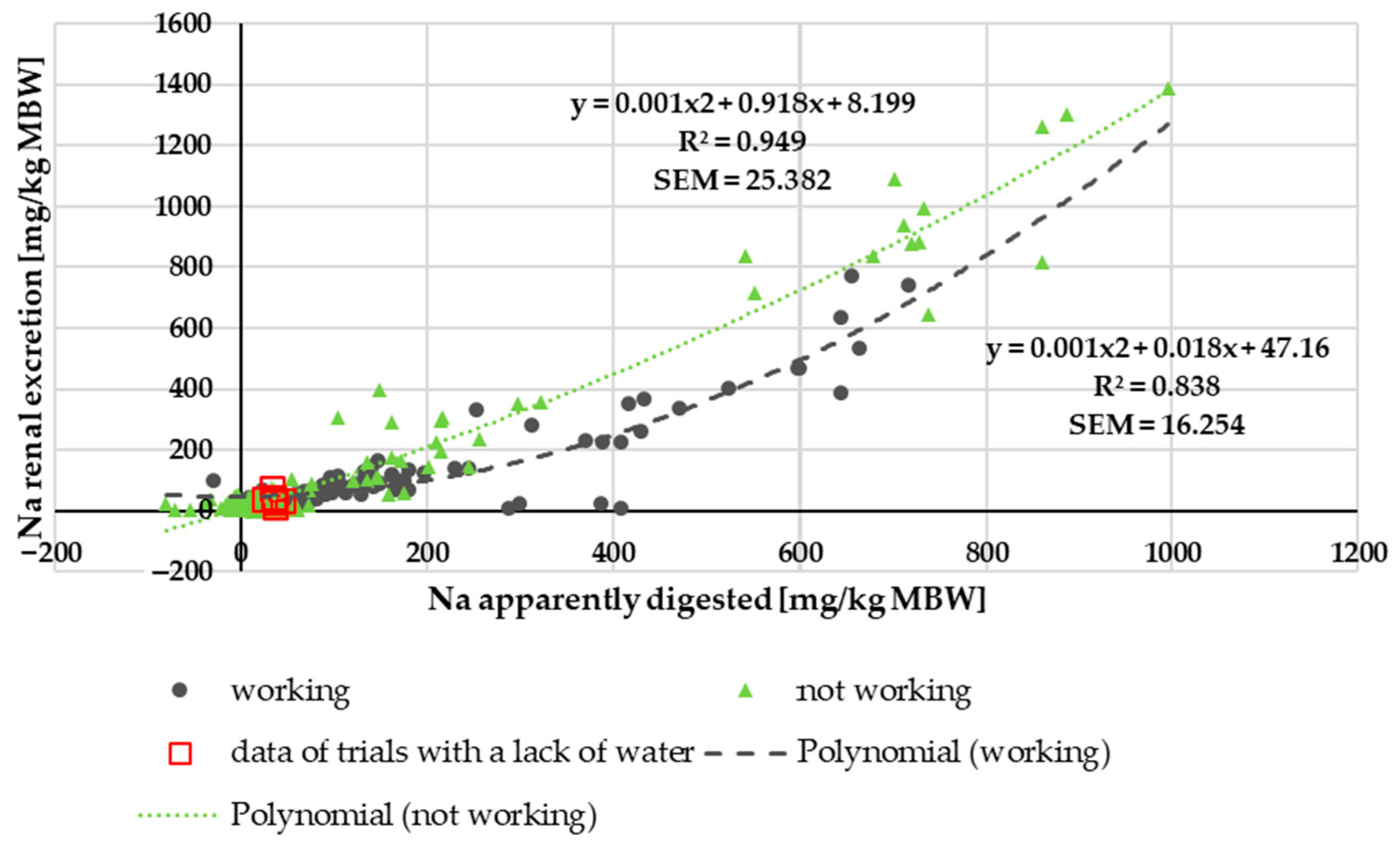
3.1.3. Na Renal Excretion
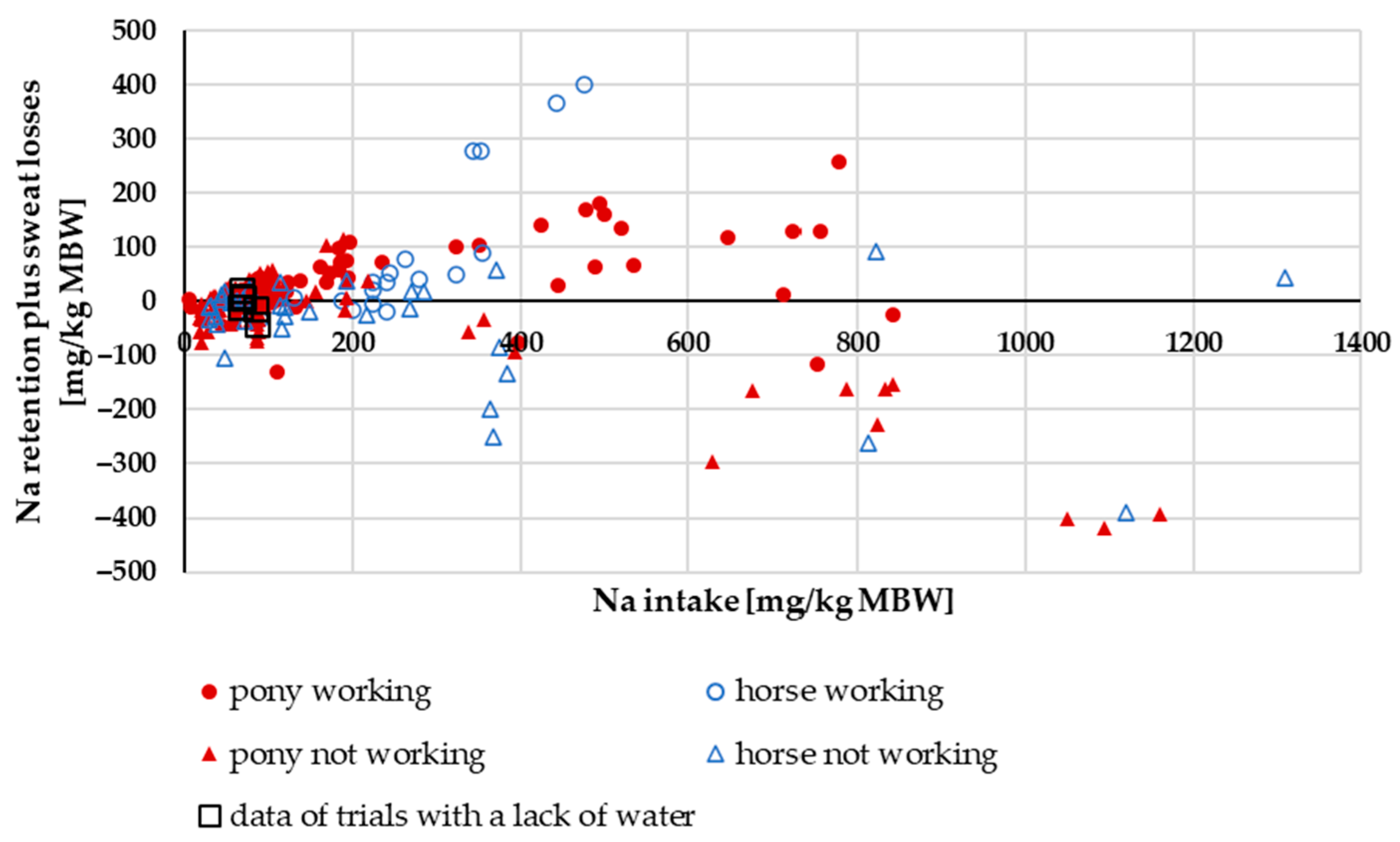
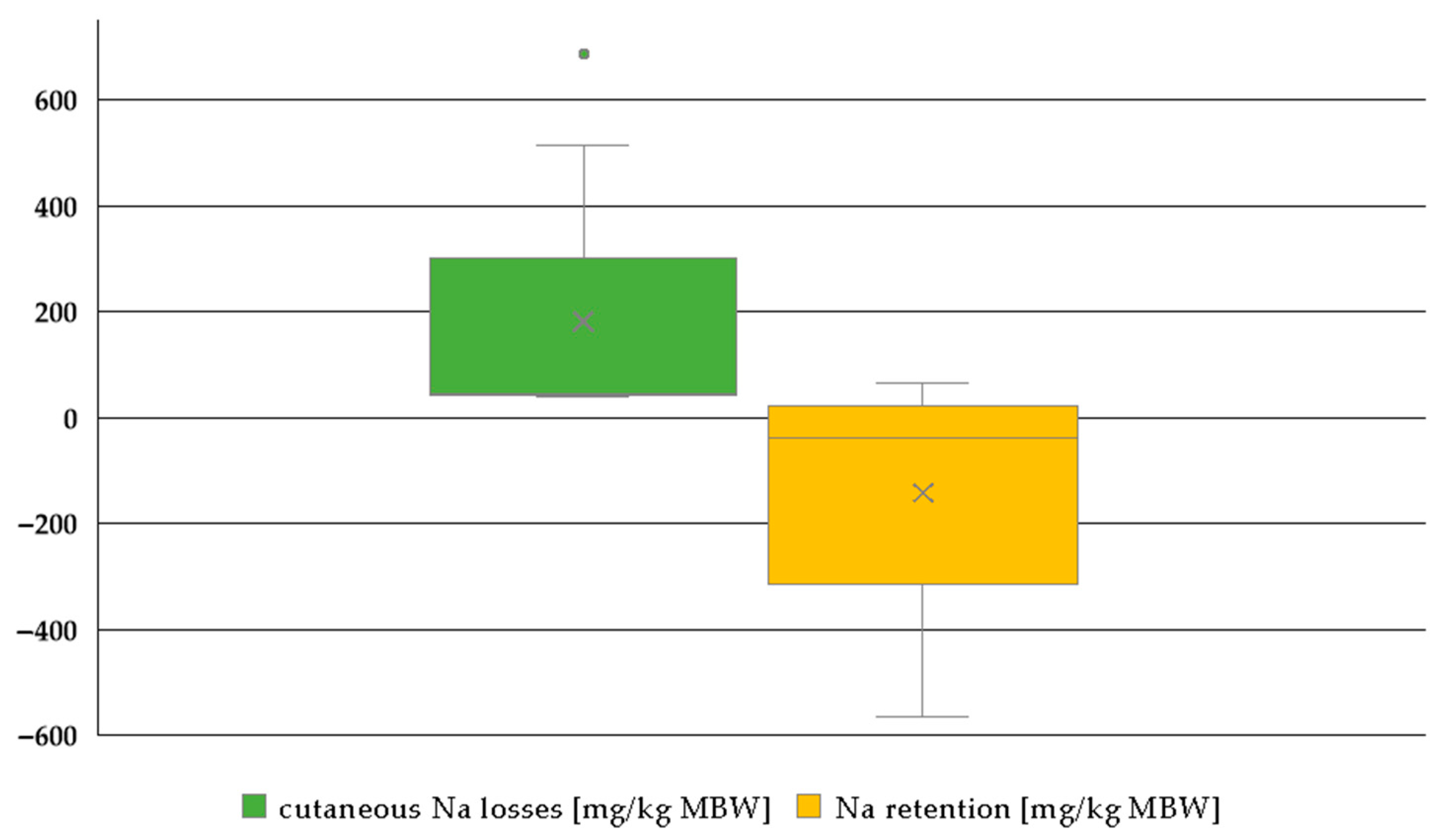
3.1.4. Na Retention (Plus Sweat Losses)
3.2. Potassium
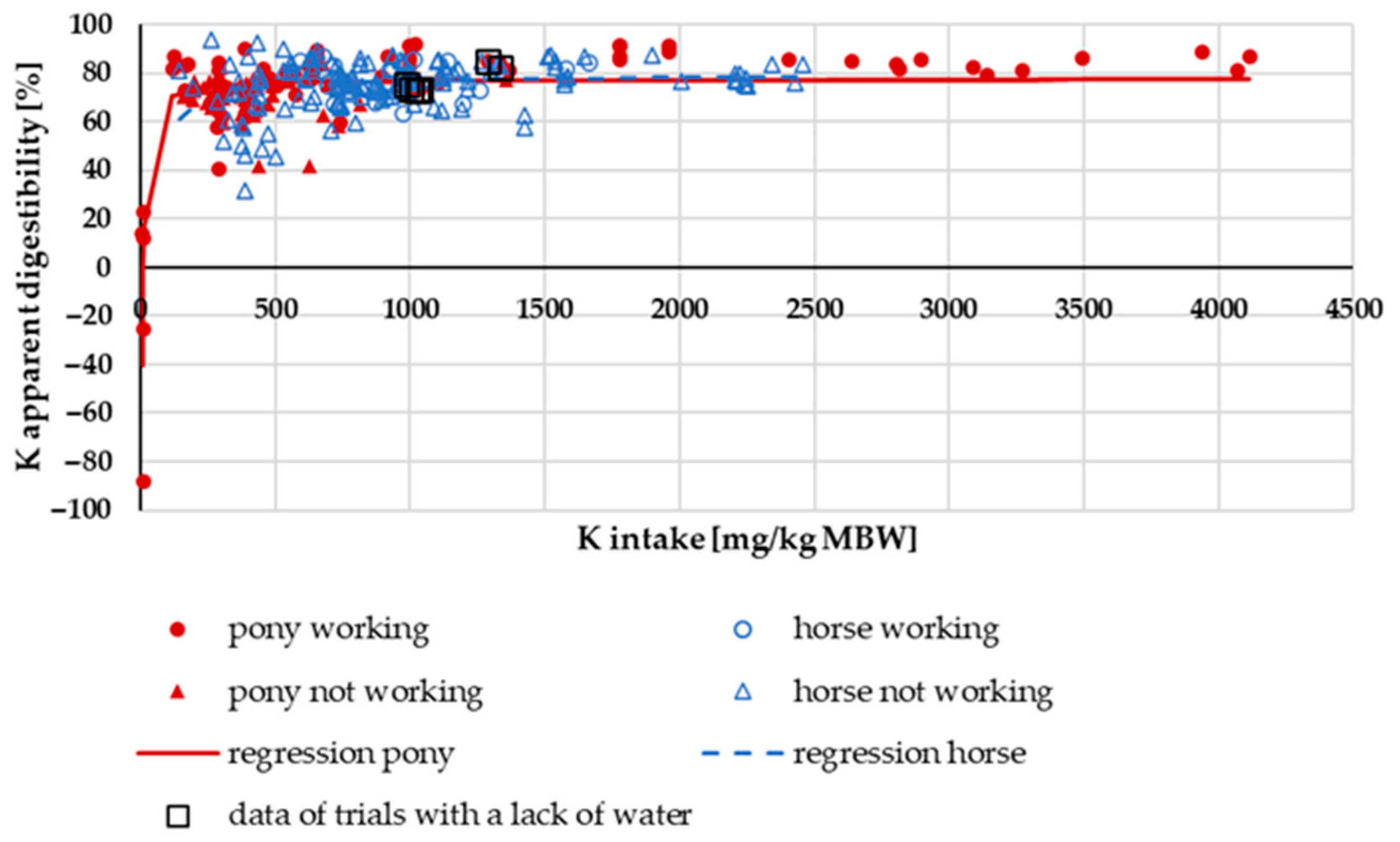
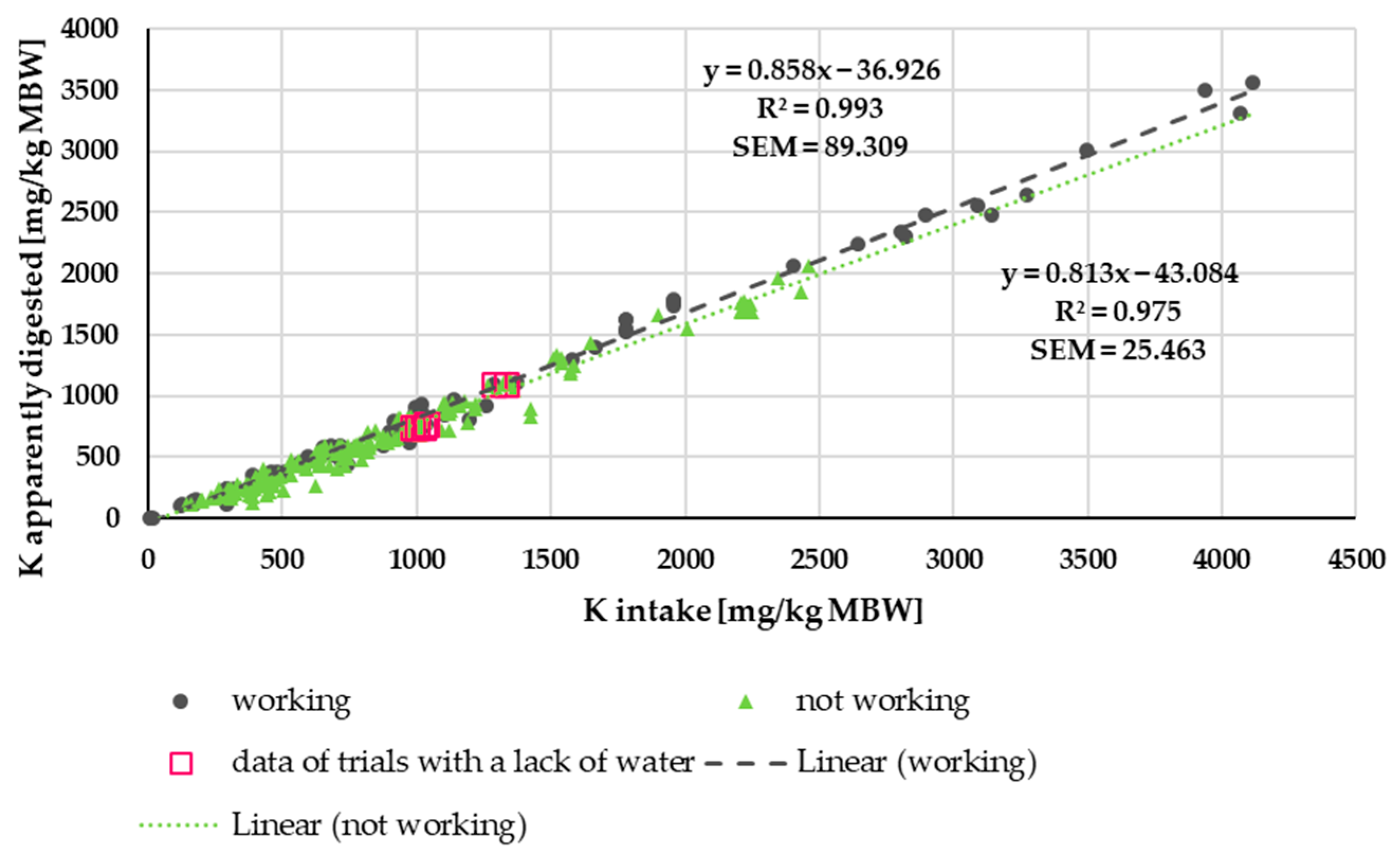
3.2.1. K Digestibility
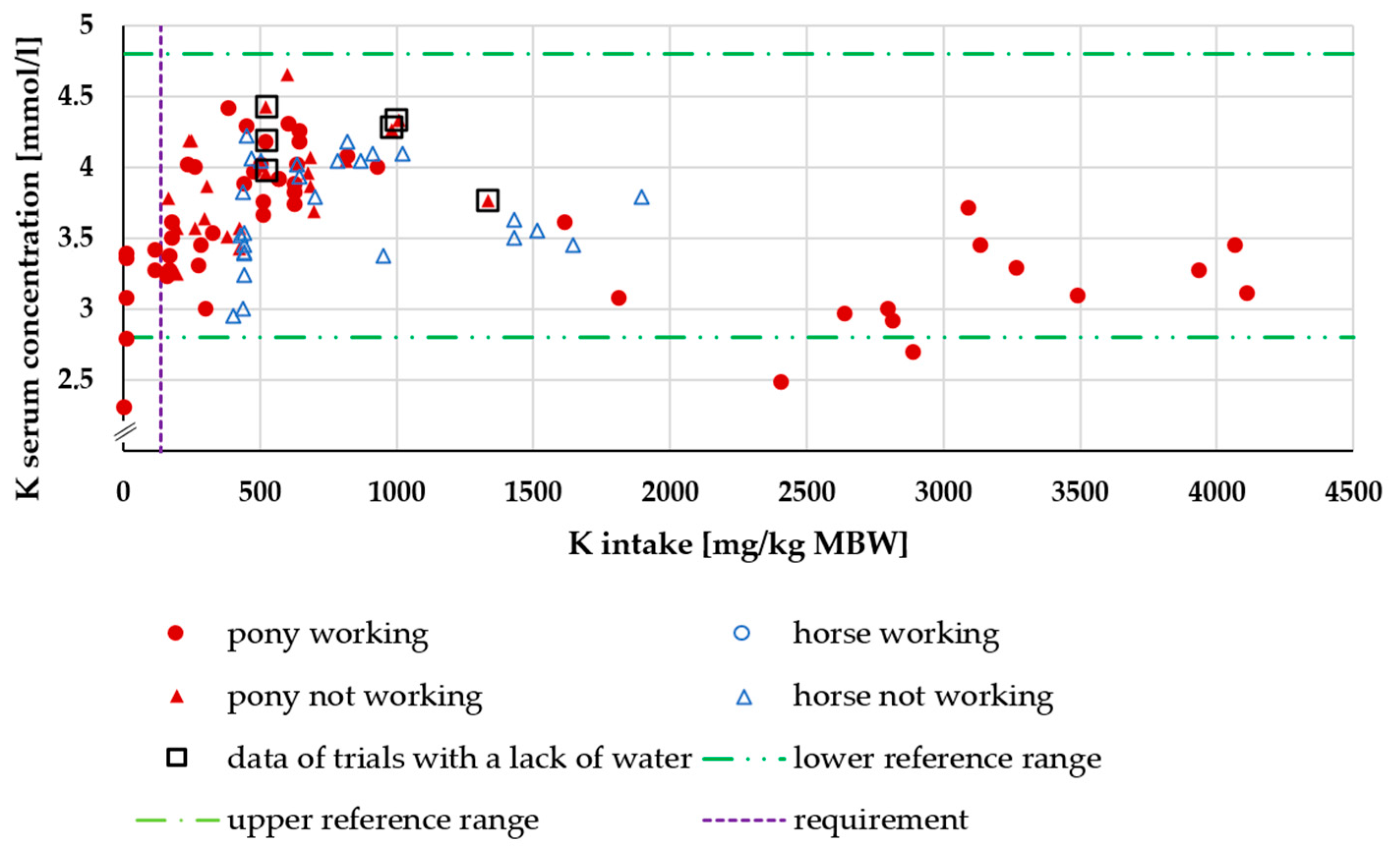
3.2.2. Serum K Concentration
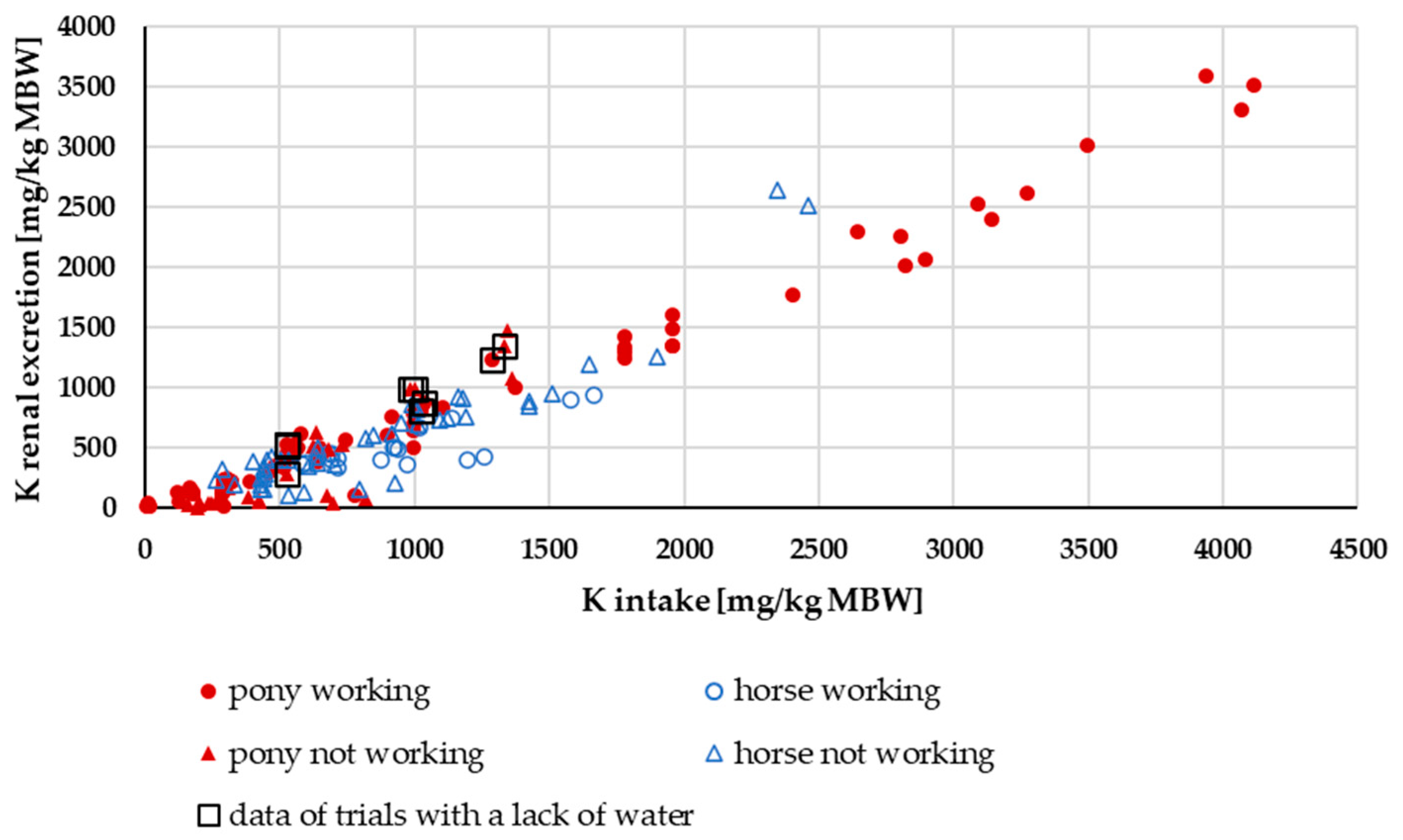
3.2.3. K Renal Excretion
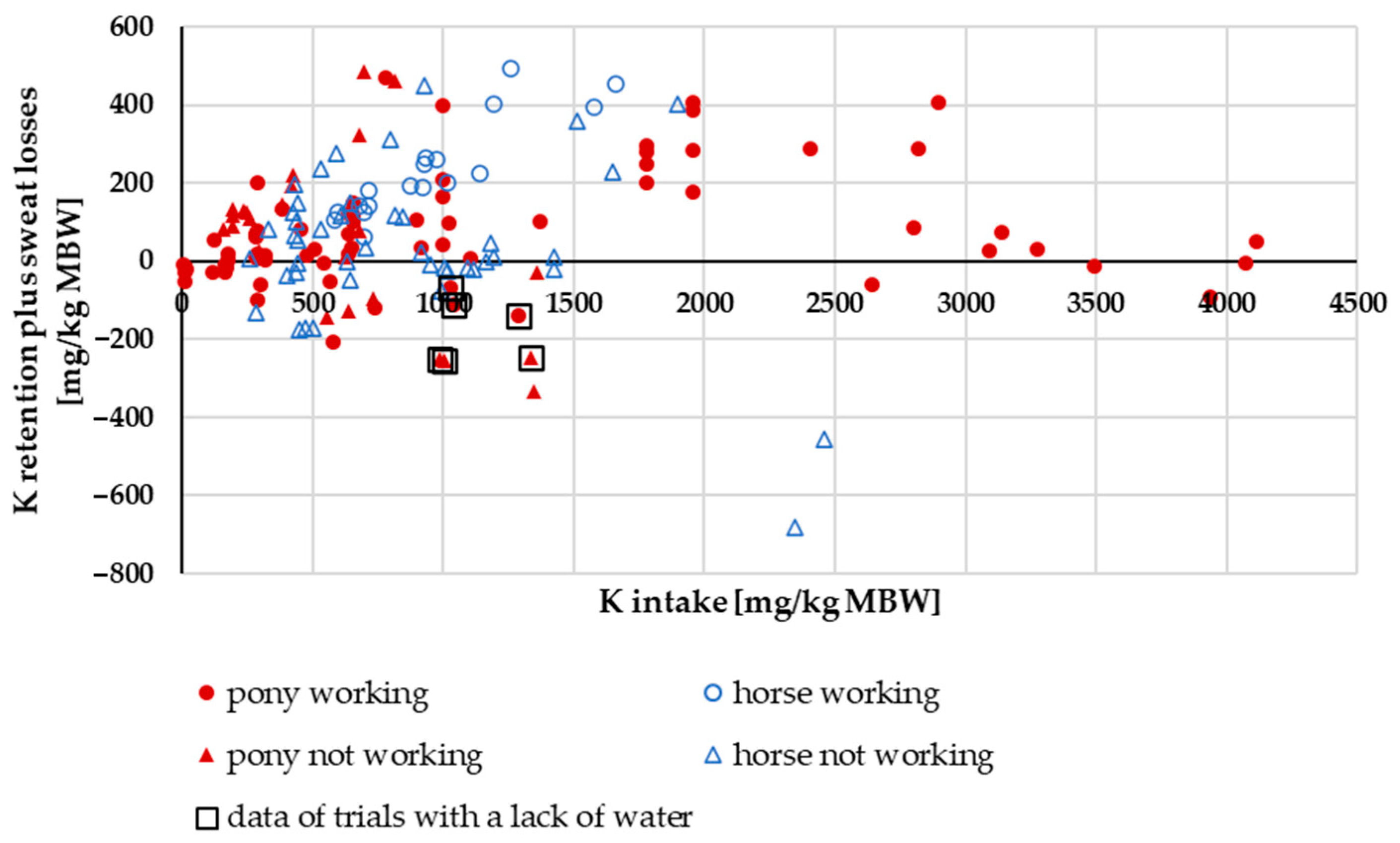
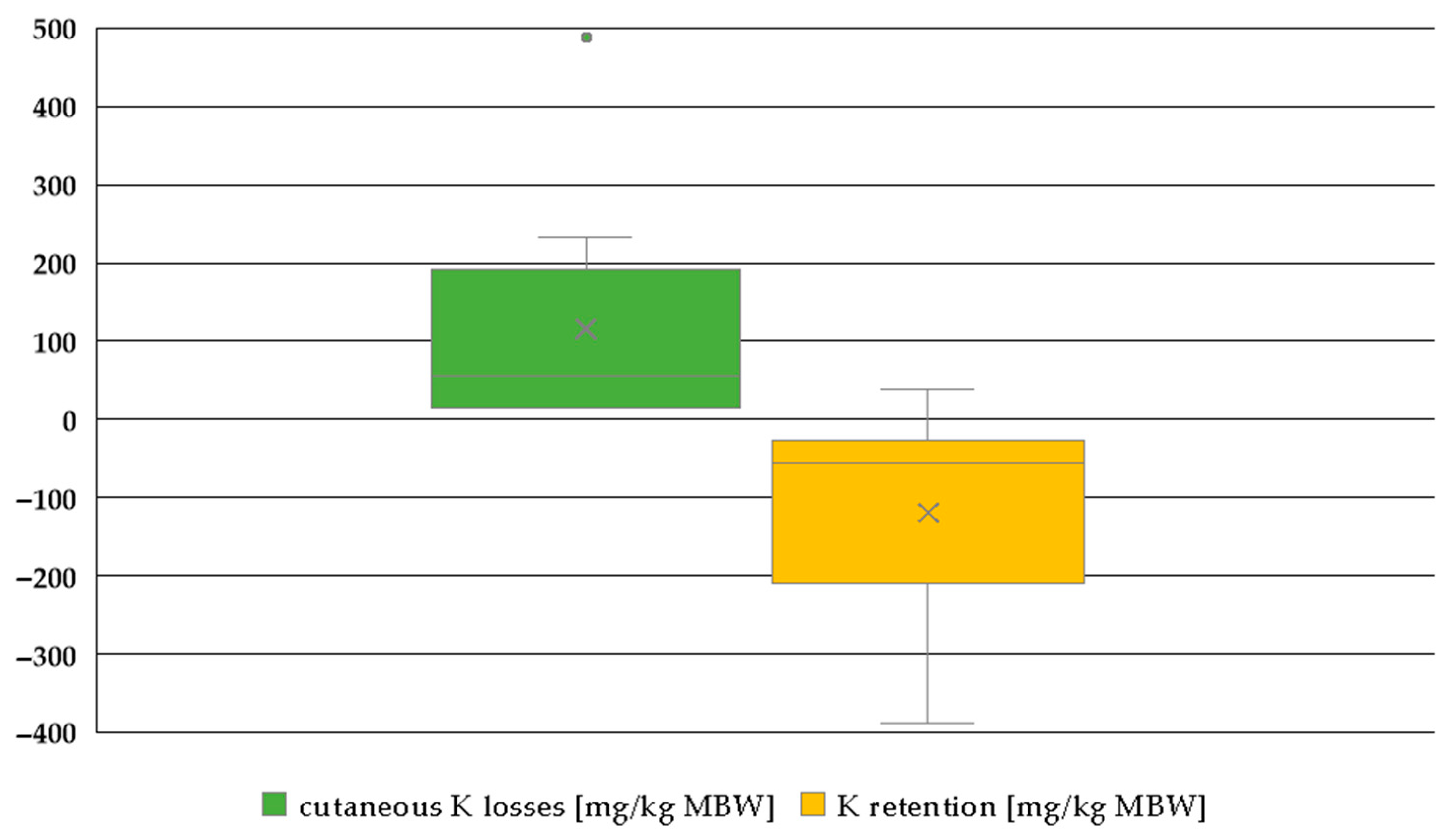
3.2.4. K Retention Plus Sweat Losses
3.3. Chloride
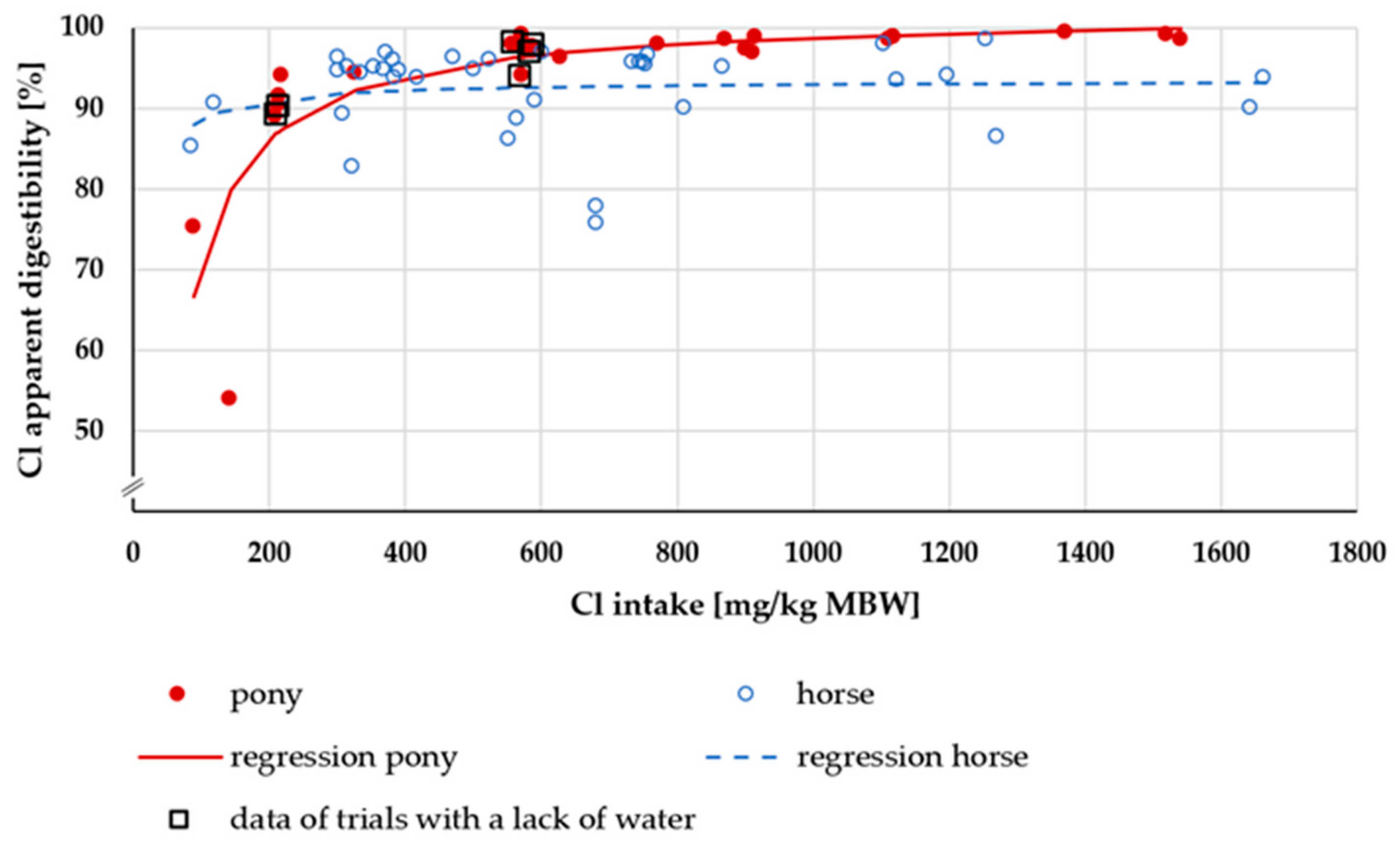
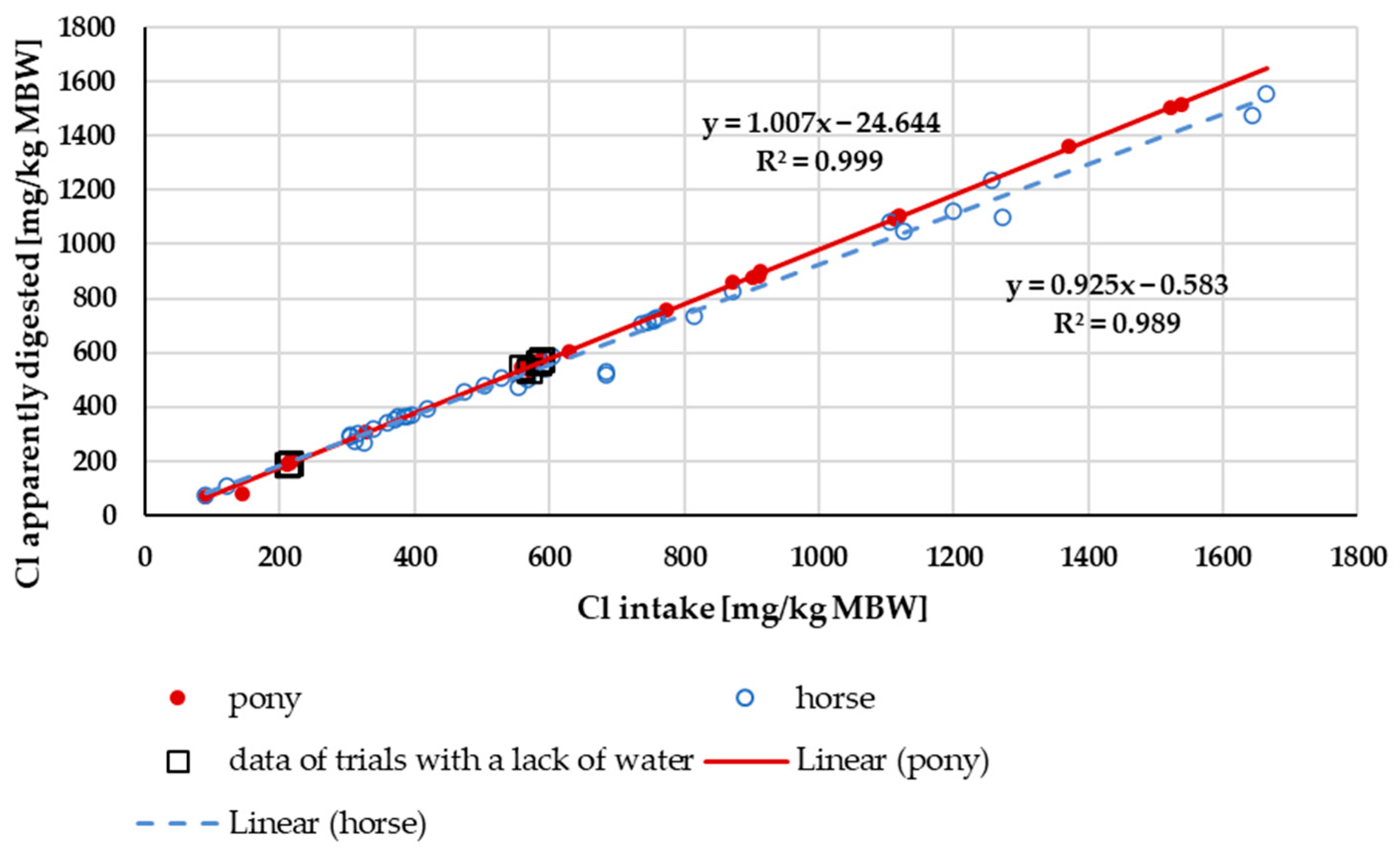
3.3.1. Cl Digestibility
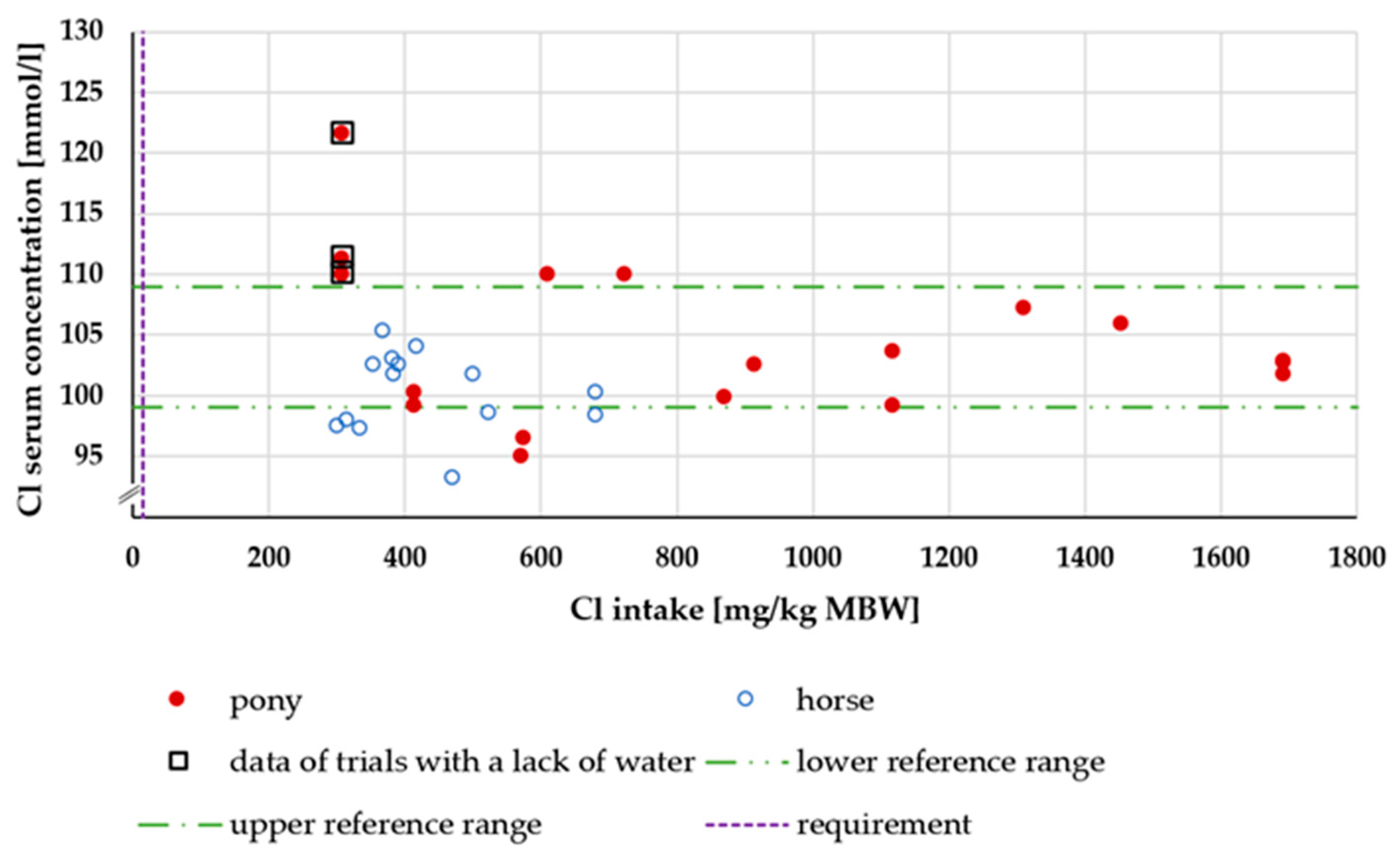
3.3.2. Serum Cl Concentration
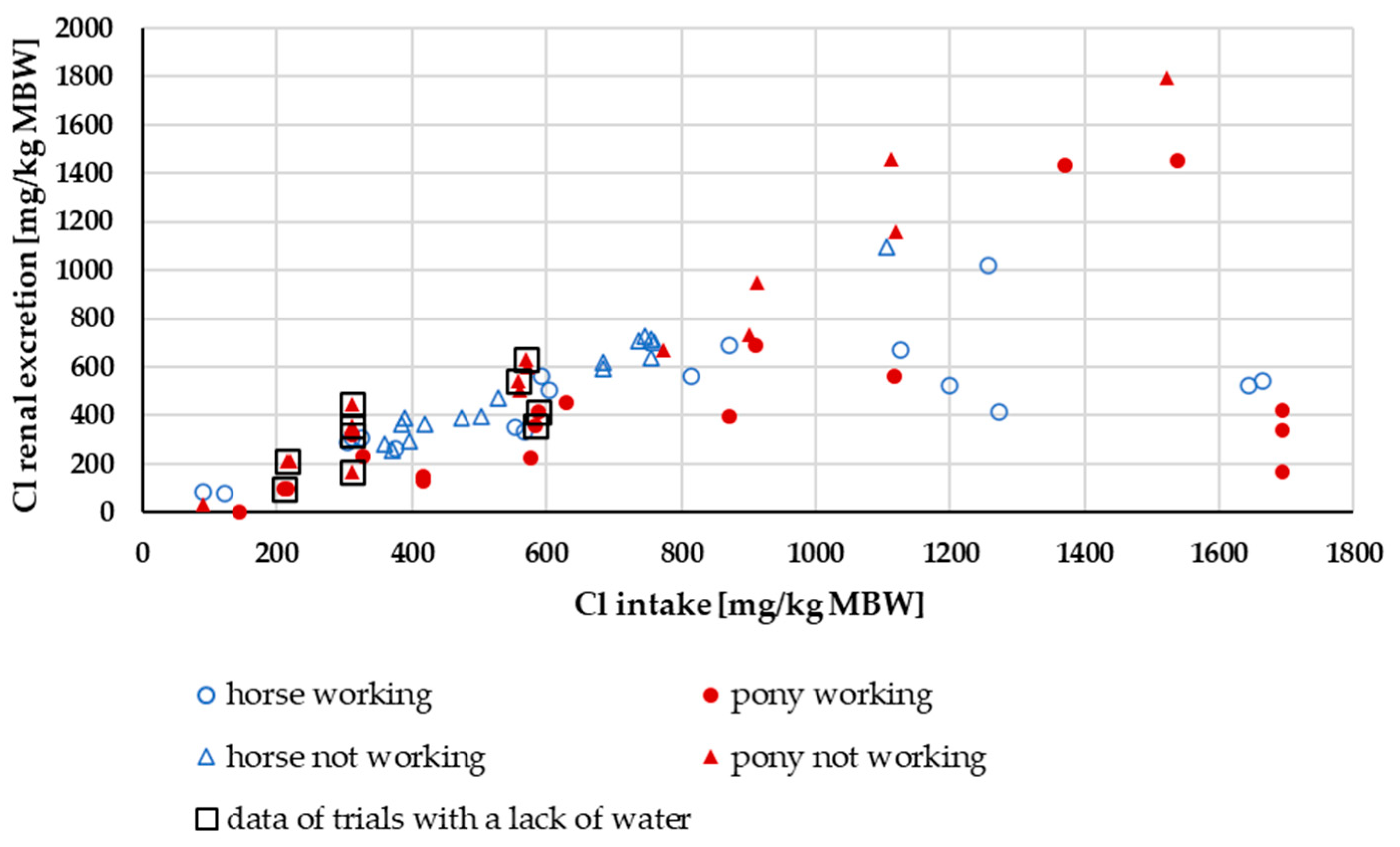
3.3.3. Cl Renal Excretion
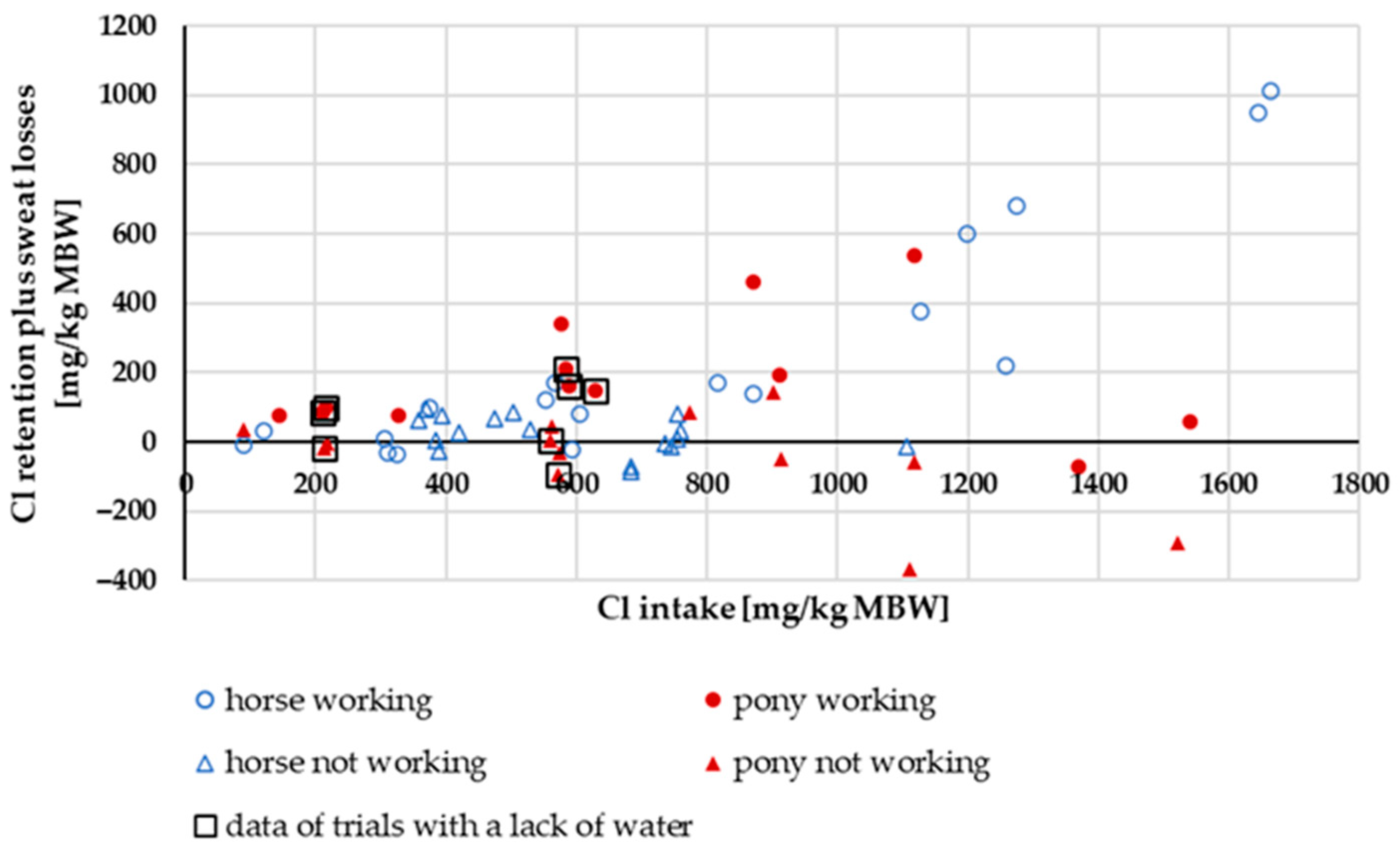
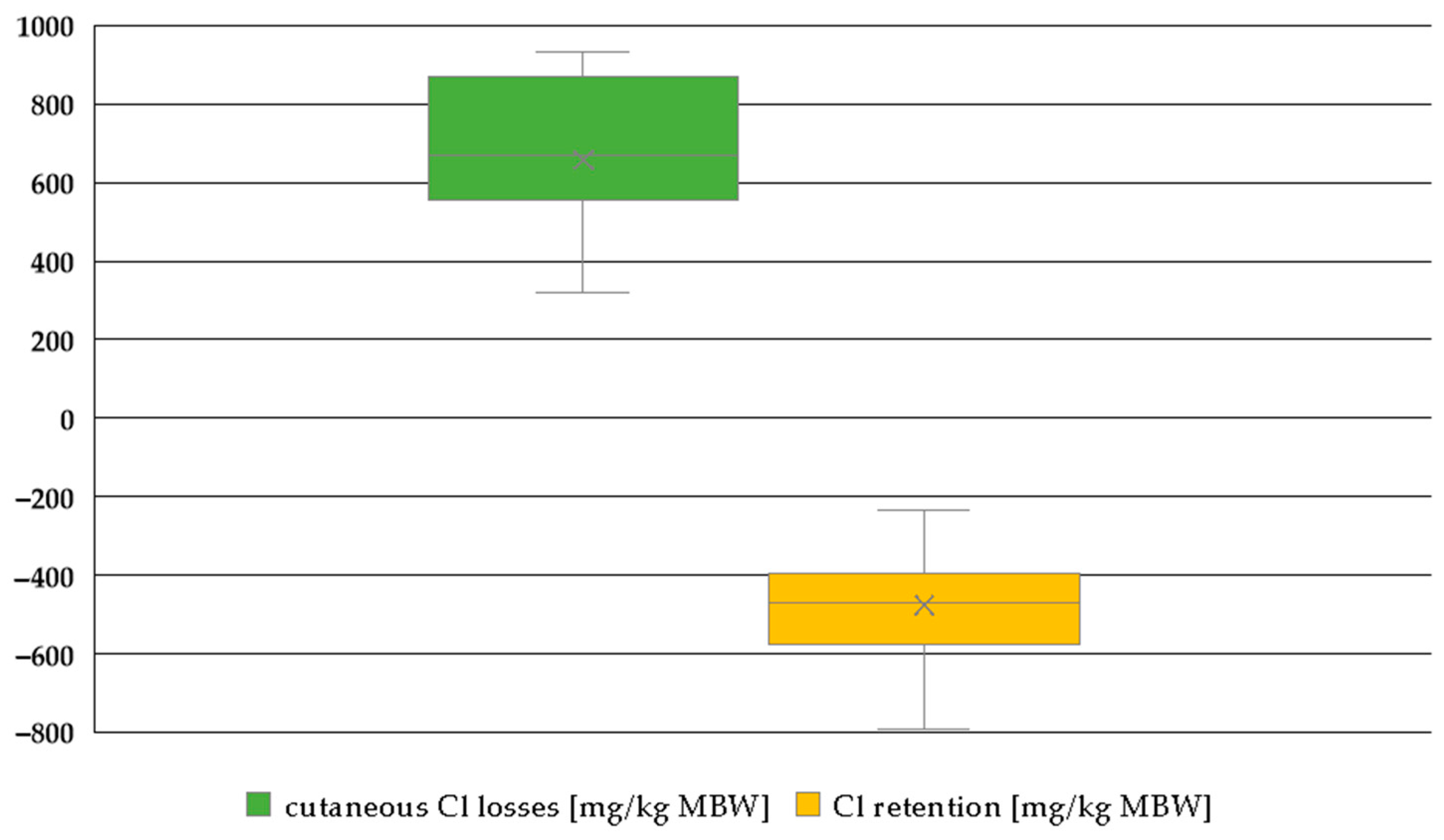
3.3.4. Cl Retention Plus Sweat Losses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirchgeßner, M.; Stangl, G.; Schwarz, F.; Roth, F.; Südekam, K.-H.; Eder, K. Tierernährung; DLG-Verlag: Frankfurt, Germany, 2014; Volume 14, p. 659. [Google Scholar]
- von Engelhardt, W.; Breves, G.; Diener, M.; Gäbel, G. Physiologie der Haustiere; Enke Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lindner, A. Untersuchungen zum Natriumstoffwechsel des Pferdes bei Marginaler Versorgung und Zusaetzlicher Bewegungsbelastung. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, M.J. Hyponatraemia. Br. Med. J. Clin. Res. Ed. 1985, 290, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Holbrook, T.; Simmons, R.; Payton, M.; MacAllister, C. Effect of repeated oral administration of hypertonic electrolyte solution on equine gastric mucosa. Equine Vet. J. 2005, 37, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyner, A.; Romanowski, K.; Vernunft, A.; Harris, P.; Müller, A.-M.; Wolf, C.; Kienzle, E. Effects of different oral doses of sodium chloride on the basal acid-base and mineral status of exercising horses fed low amounts of hay. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, B.D.; Post, T. Introduction to disorders of potassium balance. In Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders. BD Rose and TW Post, ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 822–836. [Google Scholar]
- Coenen, M.; Vervuert, I. Pferdefütterung; Georg Thieme Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tasker, J. Fluid and electrolyte studies in the horse. 3. Intake and output of water, sodium, and potassium in normal horses. Cornell Vet. 1967, 57, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Bochnia, M.; Pietsch, C.; Wensch-Dorendorf, M.; Greef, M.; Zeyner, A. Effect of hay soaking duration on metabolizable energy, total and prececal digestible crude protein and amino acids, non-starch carbohydrates, macronutrients and trace elements. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 101, 103452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatter, M.; Bochnia, M.; Wensch-Dorendorf, M.; Greef, J.M.; Zeyner, A. Feed intake parameters of horses fed soaked or steamed hay and hygienic quality of hay stored following treatment. Animals 2021, 11, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, S.; Dugdale, A.; Argo, C.M.; Morgan, R.; McGowan, C. Impact of water-soaking on the nutrient composition of UK hays. Vet. Rec. 2014, 174, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, C.; Bowen, M. Cardiology of the Horse; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.J. Electrolyte and acid-base disturbances in the horse. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 1995, 11, 491–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaminio, M.J.B.; Rush, B.R. Fluid and electrolyte balance in endurance horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 1998, 14, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GfE (Gesellschaft für Ernährungsphysiologie). Energie- und Nährstoffbedarf landwirtschaftlicher Nutztiere. Empfehlungen zur Energie- und Nährstoffversorgung der Pferde. Mit Tabellen zur Berechnung der Nährstoffzufuhr; DLG-Verlag: Frankfurt, Germany, 1982; Volume 1, p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- NRC (National Research Council). Nutrient Requirements of Horses, 6th revised ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 360.
- GfE (Gesellschaft für Ernährungsphysiologie). Empfehlungen zur Energie-und Nährstoffversorgung von Pferden; DLG-Verlag: Frankfurt, Germany, 2014; Volume 11, p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- GfE (Gesellschaft für Ernährungsphysiologie). Empfehlungen zur Energie- und Nährstoffversorgung von Pferden. Mit Tabellen zur Berechnung der Nährstoffzufuhr; DLG-Verlag: Frankfurt, Germany, 1994; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, A. Literatur-Studie zur faktoriellen Ableitung des Mengenelement-Bedarfs für Erhaltung beim Pferd. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clauss, M.; Castell, J.; Kienzle, E.; Schramel, P.; Dierenfeld, E.; Flach, E.; Behlert, O.; Streich, W.J.; Hummel, J.; Hatt, J.M. Mineral absorption in the black rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis) as compared with the domestic horse. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2007, 91, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang-Deuerling, S.B. Untersuchungen zu Fütterung und Verdauungsphysiologie an Flachland-und Schabrackentapiren (Tapirus terrestris und Tapirus indicus). Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Holdø, R.M.; Dudley, J.P.; McDowell, L.R. Geophagy in the African elephant in relation to availability of dietary sodium. J. Mammal. 2002, 83, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, I.; Kienzle, E. A Meta-Analysis on Quantitative Calcium, Phosphorus and Magnesium Metabolism in Horses and Ponies. Animals 2024, 14, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipp-Quarton, A. Untersuchungen zur postprandialen Wasser-und Elektrolytretention beim Pferd in Abhängigkeit von der Natrium-und Wasseraufnahme. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Noriega, H.R. Untersuchungen über den postprandialen Wasser- und Elektrolythaushalt des Pferdes unter Variation des Wasser- und Futterangebots. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.A. The Comparison of Two Forms of Sodium and Potassium and Chloride Versus Sulfur in the Dietary Cation-Anion Balance Equation and Subsequent Effects on Acid-Base Status and Mineral Balance in Sedentary Horses; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, L.; Wall, D.; Topliff, D.; Freeman, D.; Teeter, R.; Breazile, J.; Wagner, D. Effect of dietary cation-anion balance in mineral balance in anaerobically exercised and sedentary horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 1993, 13, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsnick, R. Untersuchungen zur Akzeptanz und Verdaulichkeit von Trockenschnitzeln unterschiedlicher Konfektionierung beim Pferd. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold, L. Untersuchungen zum Einfluss der Anionen-Kationen-Bilanz auf den Mineralstoff-und Säure-Basen-Haushalt bei Ponys. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Eilmans, I. Fettverdauung beim Pferd Sowie die Folgen einer Marginalen Fettversorgung. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gomda, Y.M. Untersuchungen über die renale, fäkale und kutane Wasser-und Elektrolytausscheidung bei Pferden in Abhängigkeit von Fütterungszeit, Futtermenge sowie Bewegungsleistung. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Güldenhaupt, V. Verträglichkeit und Verdaulichkeit eines Alleinfutters für Pferde in Kombination mit Stroh. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, C. Untersuchungen über die Verdaulichkeit und Verträglichkeit von Hafer, Quetschhafer, Gerste und Mais beim Pferd. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Gürer, C. Untersuchungen zum Kaliumstoffwechsel des Pferdes bei marginaler Versorgung und zusätzlicher Belastung Dissertation TiHo Hannover. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt, J.; Potter, G.; Greene, L.; Vogelsang, M.; Anderson, J., Jr. Electrolyte balance in exercising horses fed a control and a fat-supplemented diet. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 1995, 15, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, J.; Potter, G.; Greene, L.; Anderson, J., Jr. Mineral balance in resting and exercised miniature horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 1995, 15, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krull, H. Untersuchungen über Aufnahme und Verdaulichkeit von Grünfutter beim Pferd. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann, G. Untersuchungen über den Einfluss von Lactose-und Stärkezulagen auf die Verdaulichkeit von NH3-aufgeschlossenem Stroh beim Pferd. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, R.K. Effect of Dietary Cation-Anion Difference on Acid-Base Status Energy Digestibility and Mineral Balance in Sedentary Horses Fed Varying Levels and Sources of Starch; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mundt, H.-C. Untersuchungen über die Verdaulichkeit von Aufgeschlossenem Stroh beim Pferd. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Neustädter, L.-T. Untersuchungen zu möglichen Auswirkungen einer Unterschiedlichen Mengenelementversorgung auf den Mineralstoffhaushalt von Pferden. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, C.; Nielsen, B.; Woodward, A.; Spooner, H.; Ventura, B.; Turner, K. Mineral balance in horses fed two supplemental silicon sources. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pferdekamp, M. Einfluss steigender Proteinmengen auf den Stoffwechsel des Pferdes. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Roose, K.; Hoekstra, K.; Pagan, J.; Geor, R. Effect of an Aluminum Supplement on Nutrient Digestibility and Mineral Metabolism in Thoroughbred Horses; Kentucky Equine Research: Versailles, KY, USA, 2001; pp. 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Schiele, K. Einfluss reduzierter Futterzuteilung zweier Verschiedener Heuqualitäten auf Passagedauer und Verdaulichkeit bei Ponies. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M. Untersuchungen über die Verträglichkeit und Verdaulichkeit eines pelletierten Mischfutters für Pferde in Kombination mit Heu und NH3-aufgeschlossenem Stroh. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Schryver, H.; Parker, M.; Daniluk, P.; Pagan, K.; Williams, J.; Soderholm, L.; Hintz, H. Salt consumption and the effect of salt on mineral metabolism in horses. Cornell Vet. 1987, 77, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulze, K. Untersuchungen zur Verdaulichkeit und Energiebewertung von Mischfuttermitteln für Pferde. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrenner, B. Einfluss eines NaCl-Supplements vor und während der Bewegung auf den Wasser-und Elektrolythaushalt des Pferdes. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Stürmer, K. Untersuchungen zum Einfluss der Fütterung auf den Säure-Basen-Haushalt bei Ponys. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munich, Ingolstadt, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Teleb, H. Untersuchungen über den intestinalen Ca-Stoffwechsel beim Pferd nach variierender Ca-Zufuhr und einer Oxalatzulage. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Verthein, B. Auswirkungen einer Enzymgabe auf die Futterverdaulichkeit beim Pferd. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, D.; Topliff, D.; Freeman, D.; Wagner, D.; Breazile, J.; Stutz, W. Effect of dietary cation-anion balance on urinary mineral excretion in exercised horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 1992, 12, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wedemeyer, H.C. Untersuchungen zum Calcium-, Phosphor-und Natrium-Umsatz des erwachsenen Pferdes; Georg-August-Universität Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Weidenhaupt, K. Untersuchungen zum Kaliumstoffwechsel des Pferdes. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Geor, R.J.; Harris, P.; Coenen, M. Equine Applied and Clinical Nutrition: Health, Welfare and Performance; Saunders Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013; p. 679. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, H.L. Stochastic elements in biological models; their sources and significance. Stoch. Models Med. Biol. 1964, 355–385. [Google Scholar]
- Böswald, L.; Dobenecker, B.; Clauss, M.; Kienzle, E. A comparative meta-analysis on the relationship of faecal calcium and phosphorus excretion in mammals. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, J.; Alexander, L.; Morris, P.; Dobenecker, B.; Kienzle, E. Demonstration of uniformity of calcium absorption in adult dogs and cats. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyner, A.; Romanowski, K.; Vernunft, A.; Harris, P.; Kienzle, E. Scoring of sweat losses in exercised horses—A pilot study. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 98, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theelen, M.J.; Luiken, R.E.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M.; Rossen, J.W.; Zomer, A.L. The equine faecal microbiota of healthy horses and ponies in the Netherlands: Impact of host and environmental factors. Animals 2021, 11, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, K.; Blaue, D.; Schedlbauer, C.; Starzonek, J.; Julliand, V.; Vervuert, I. Changes in the faecal microbiota of horses and ponies during a two-year body weight gain programme. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwin, K.-O.; Matsui, H. Comparative analysis of the methanogen diversity in horse and pony by using mcrA gene and archaeal 16S rRNA gene clone libraries. Archaea 2014, 2014, 483574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S.J.; Bamford, N.J.; Baskerville, C.L.; Harris, P.A.; Bailey, S.R. Comparison of feed digestibility between ponies, standardbreds and Andalusian horses fed three different diets. Vet. Sci. 2021, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermorel, M.; Vernet, J.; Martin-Rosset, W. Digestive and energy utilisation of two diets by ponies and horses. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1997, 51, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddeford, D.; Pearson, R.; Archibald, R.; Muirhead, R. Digestibility and gastro-intestinal transit time of diets containing different proportions of alfalfa and oat straw given to Thoroughbreds, Shetland ponies, Highland ponies and donkeys. Anim. Sci. 1995, 61, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Steinhöfel, O.; Fuchs, R. The digestibility of crude nutrients in horses. 2. Comparative studies on the digestive capacity of a thoroughbred horse, pony and wether. Arch. Fur Tierernahr. 1987, 37, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROSE, R.J.; Arnold, K.S.; Church, S.; Paris, R. Plasma and sweat electrolyte concentrations in the horse during long distance exercise. Equine Vet. J. 1980, 12, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, D.; Kerr, M.; Nimmo, M.; Abbott, E. Alterations in blood, sweat, urine and muscle composition during prolonged exercise in the horse. Vet. Rec. 1982, 110, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, J.; Hall, G. Further studies on the metabolic effects of long distance riding: Golden Horseshoe Ride 1979. Equine Vet. J. 1980, 12, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindinger, M.I.; Waller, A.P. Tracing oral Na+ and K+ in sweat during exercise and recovery in horses. Exp. Physiol. 2021, 106, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindinger, M.I. Oral electrolyte and water supplementation in horses. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, A.P.; Lindinger, M.I. Tracing acid-base variables in exercising horses: Effects of pre-loading oral electrolytes. Animals 2022, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, L.; Geor, R.; Hare, M.J.; ECKER, G.L.; Lindinger, M. Sweating rate and sweat composition during exercise and recovery in ambient heat and humidity. Equine Vet. J. 1995, 27, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, H.; Nielsen, B.; SCHOTT II, H.; Harris, P. Sweat composition in Arabian horses performing endurance exercise on forage-based, low Na rations. Equine Vet. J. 2010, 42, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucker, R. Allometric scaling, metabolic body size and interspecies comparisons of basal nutritional requirements. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2007, 91, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucker, R.; Storms, D. Interspecies comparisons of micronutrient requirements: Metabolic vs. absolute body size. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2999–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRC (National Research Council). Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 424.
- Meyer, H.; Zentek, J.; Habernoll, H.; Maskell, I. Digestibility and compatibility of mixed diets and faecal consistency in different breeds of dog. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 1999, 46, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeier, H.U. Auswirkungen des Natrium-und Rohproteingehalts sowie der Proteinqualität im Futter auf die Harnzusammensetzung von gesunden Katzen. Ph.D. Thesis, Freie Universitä Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Entringer, R.; Plumlee, M.; Conrad, J.; Cline, T.; Wolfe, S. Influence of diet on passage rate and apparent digestibility by growing swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1975, 40, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böswald, L.F.; Wenderlein, J.; Siegert, W.; Straubinger, R.K.; Kienzle, E. True mineral digestibility in C57Bl/6J mice. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böswald, L.F.; Matzek, D.; Popper, B. Digestibility of crude nutrients and minerals in C57Bl/6J and CD1 mice fed a pelleted lab rodent diet. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauss, M.; Loehlein, W.; Kienzle, E.; Wiesner, H. Studies on feed digestibilities in captive Asian elephants (Elephas maximus). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2003, 87, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, P. Mechanisms of sodium balance: Total body sodium, surrogate variables, and renal sodium excretion. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R945–R962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michell, A. The Clinical Biology of Sodium: The Physiology and Pathophysiology of Sodium in Mammals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Selkurt, E.E. Sodium excretion by the mammalian kidney. Physiol. Rev. 1954, 34, 287–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ost, S. Eine Feldstudie zu Energiebedarf und Rationsgestaltung bei Hochleistungsspringpferden. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schott II, H.C.; Hinchcliff, K.W. Treatments affecting fluid and electrolyte status during exercise. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 1998, 14, 175–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M.G. Biochemical and Physiological Aspects of Endurance Exercise in the Horse. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Clauss, M.; Lang-Deuerling, S.; Kienzle, E.; Medici, E.P.; Hummel, J. Mineral absorption in tapirs (Tapirus spp.) as compared to the domestic horse. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2009, 93, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshima, E.; Brunetto, M.; Vasconcellos, R.; Gonçalves, K.; De-Oliveira, L.; Valério, A.; Carciofi, A. Nutrient digestibility, but not mineral absorption, is age-dependent in cats. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2010, 94, e251–e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervuert, I.; Kienzle, E. Assessment of nutritional status from analysis of blood and other tissue samples. In Equine Applied and Clinical Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, R.W.; Couto, C.G. Innere Medizin der Kleintiere; Elsevier GmbH: München, Germany, 2010; p. 1564. [Google Scholar]
- Gennari, F.J. Disorders of potassium homeostasis: Hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. Crit. Care Clin. 2002, 18, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.H.; Menouar, M.A.; Dunn, R.J. Physiology, Aldosterone; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, S.N. Regulation of thirst. Nutr. Today 2013, 48, S4–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockham, S.L. Interpretation of equine serum biochemical profile results. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 1995, 11, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, T.; Pinchbeck, G.; McGowan, C. Prevalence, risk factors and clinical signs predictive for equine pituitary pars intermedia dysfunction in aged horses. Equine Vet. J. 2013, 45, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumnitz, M.S. Qualitativ-histologische und quantitativ-stereologische Veränderungen der Nebennieren bei Equiden. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, D.; Foster, S.; Hopper, B.; Staudte, K.; O’hara, A.; Irwin, P. Hypokalaemic paresis, hypertension, alkalosis and adrenal-dependent hyperadrenocorticism in a dog. Aust. Vet. J. 2008, 86, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayzer, J.; Jones, B. Canine hyperadrenocorticism. New Zealand Vet. J. 1993, 41, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.A.; Mullins, J.J.; Kenyon, C.J. Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors stimulate epithelial sodium channel activity in a mouse model of Cushing syndrome. Hypertension 2009, 54, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zondek, H.; Leszynsky, H.E. Transient Cushing Syndrome. Br. Med. J. 1956, 1, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maier, I.; Kienzle, E. A Meta-Analysis on Quantitative Sodium, Potassium and Chloride Metabolism in Horses and Ponies. Animals 2025, 15, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020191
Maier I, Kienzle E. A Meta-Analysis on Quantitative Sodium, Potassium and Chloride Metabolism in Horses and Ponies. Animals. 2025; 15(2):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020191
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaier, Isabelle, and Ellen Kienzle. 2025. "A Meta-Analysis on Quantitative Sodium, Potassium and Chloride Metabolism in Horses and Ponies" Animals 15, no. 2: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020191
APA StyleMaier, I., & Kienzle, E. (2025). A Meta-Analysis on Quantitative Sodium, Potassium and Chloride Metabolism in Horses and Ponies. Animals, 15(2), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020191




