Population Genomic Survey of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix in the Yangtze River Basin: A RAD Sequencing Perspective
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Sampling Site and Methods
2.3. Library Preparation, Construction, and Sequencing of RAD-Seq
2.4. The Genotyping of Silver Carp
2.5. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis and Genetic Diversity Assessment
2.6. Structure Assessment and Population Differentiation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RAD-Sequencing and Statistic
3.2. Genetic Diversity Assessment
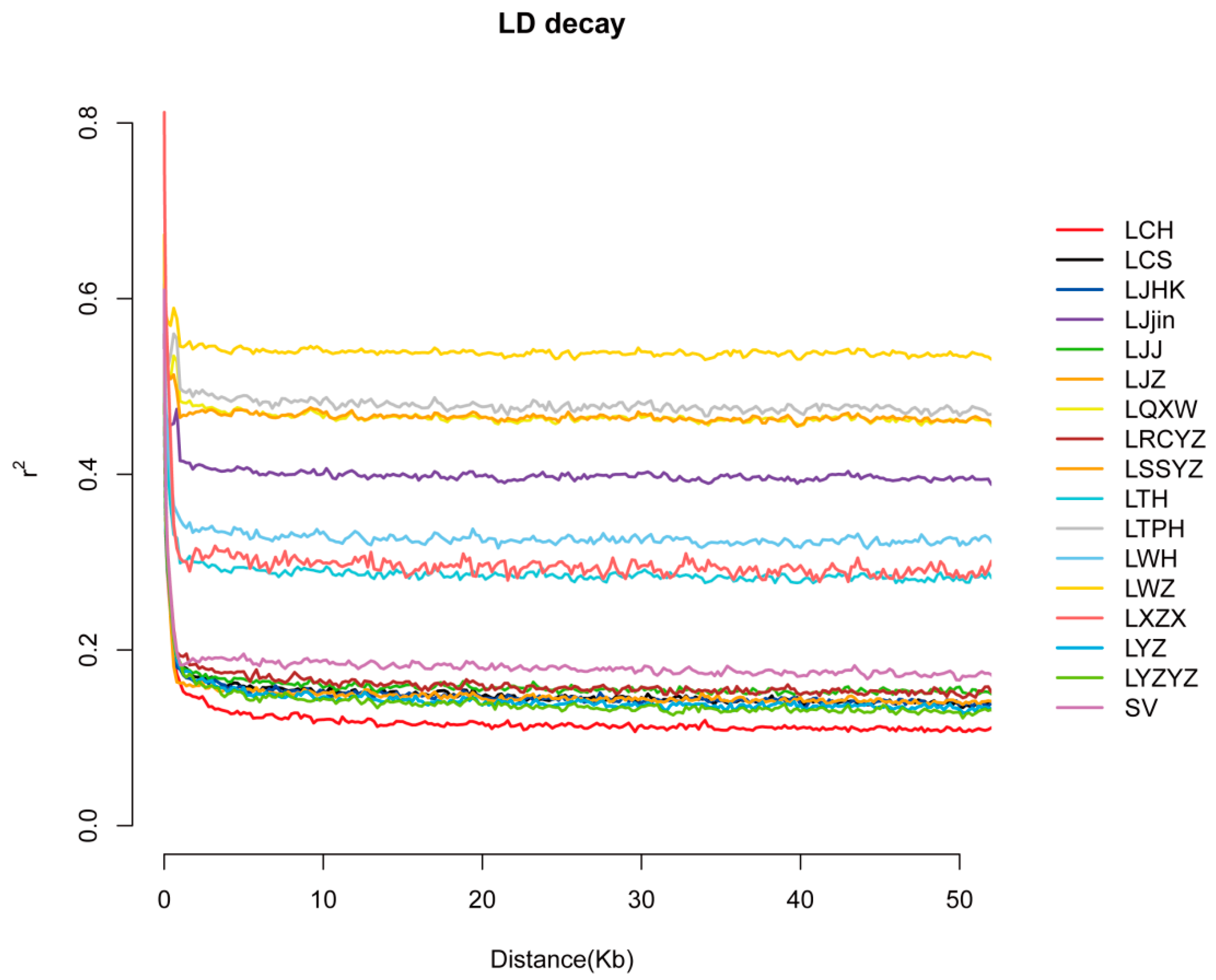
3.3. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
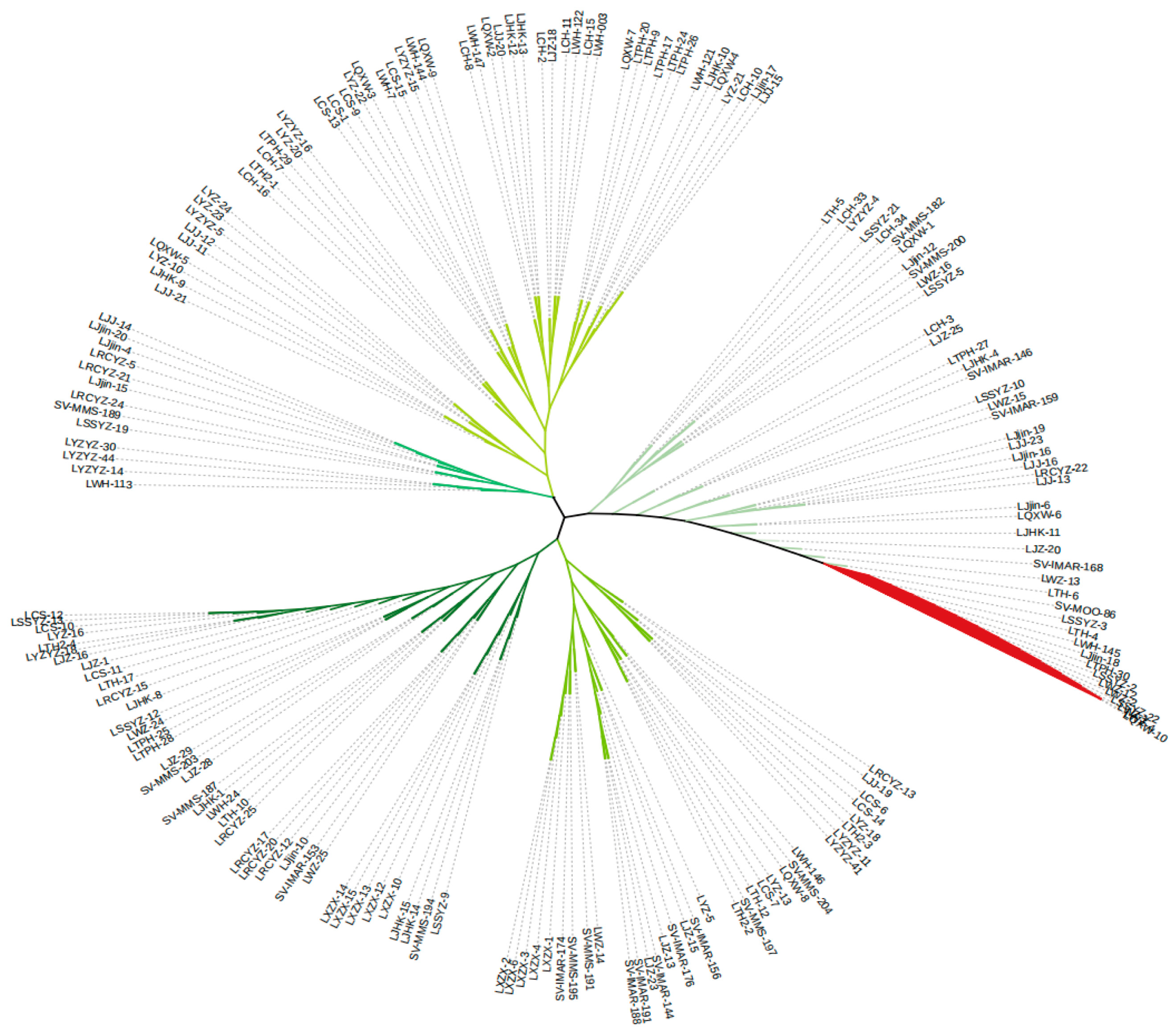
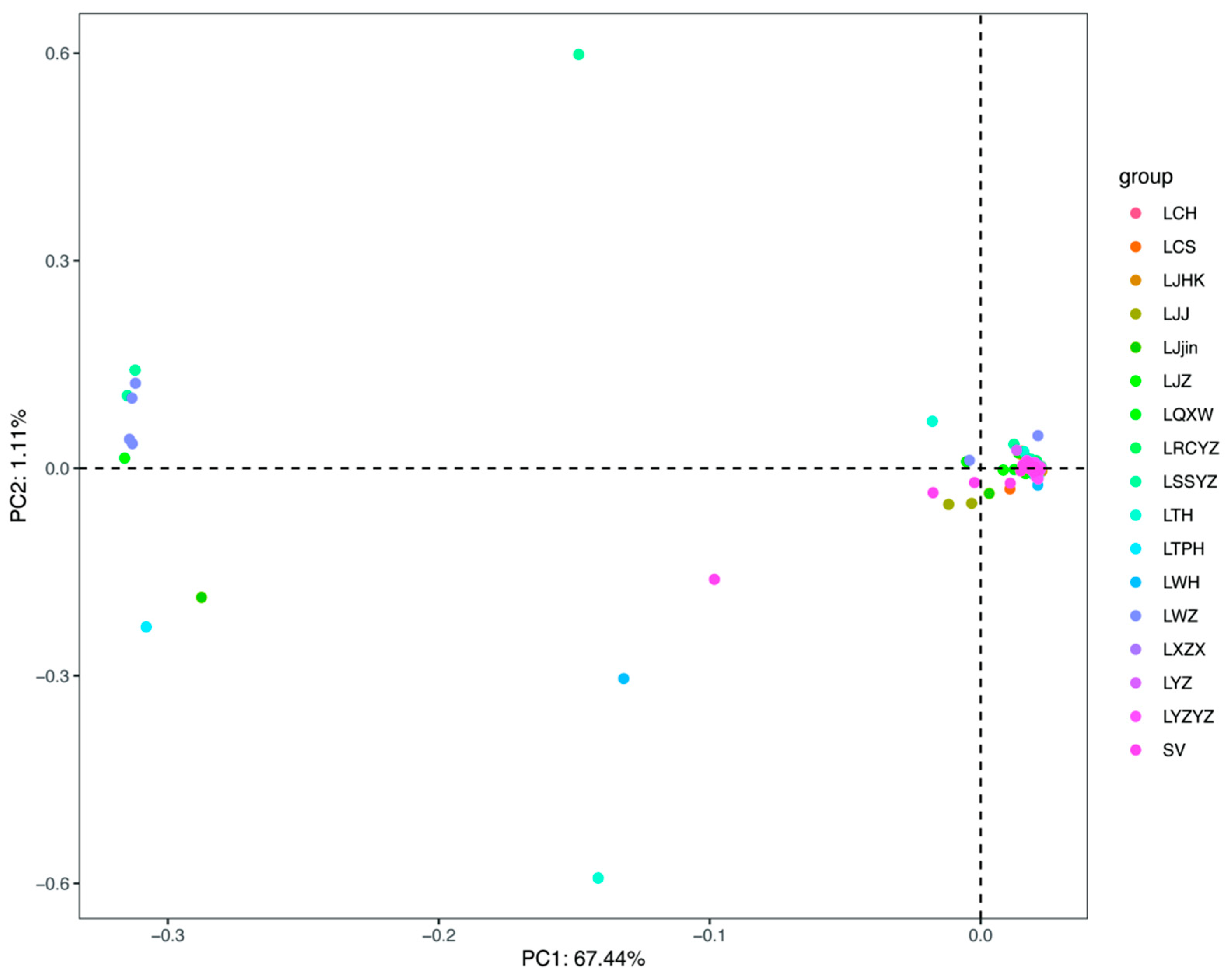
3.4. Genetic Differentiation Assessment
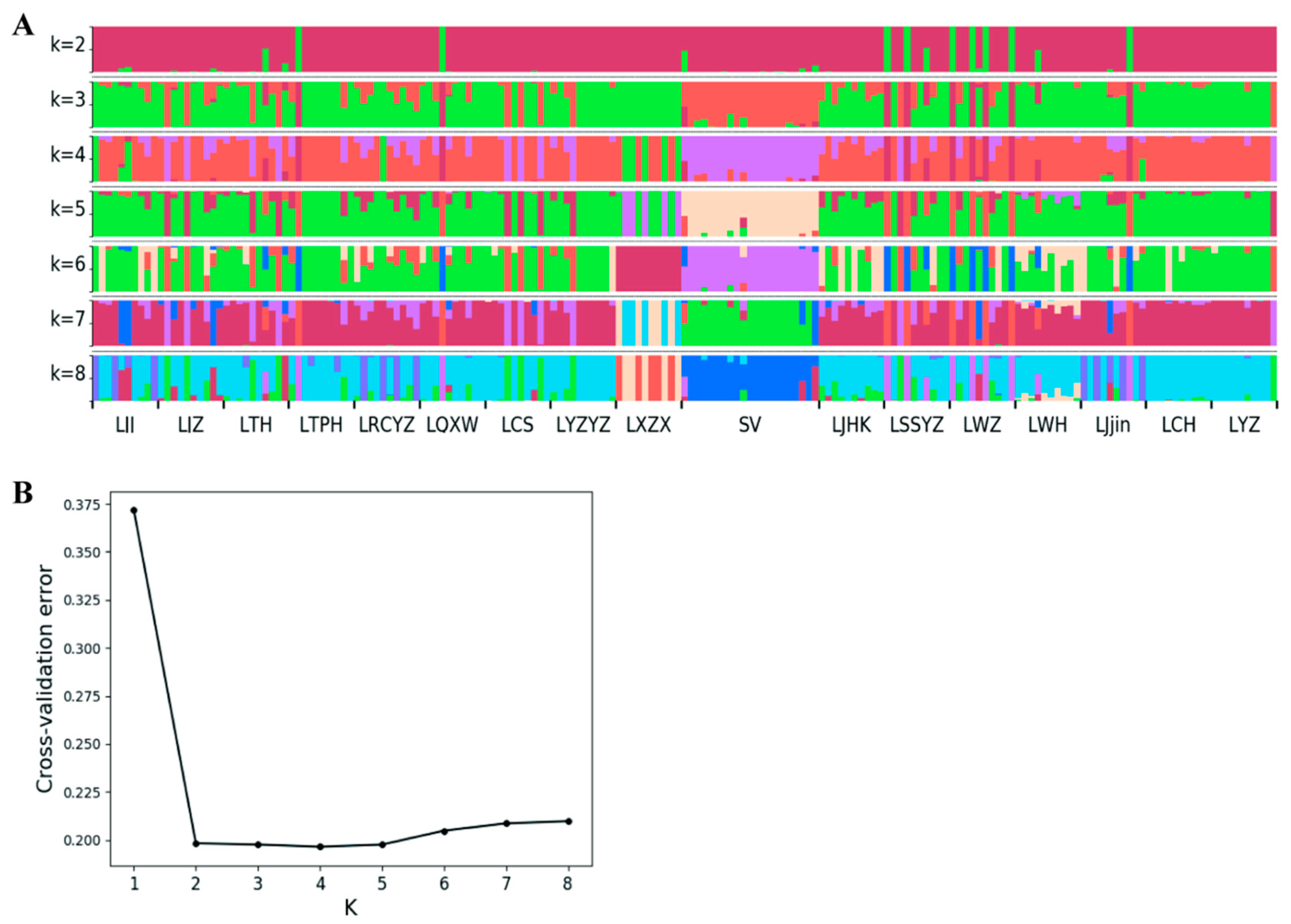
3.5. Population Structure Analysis
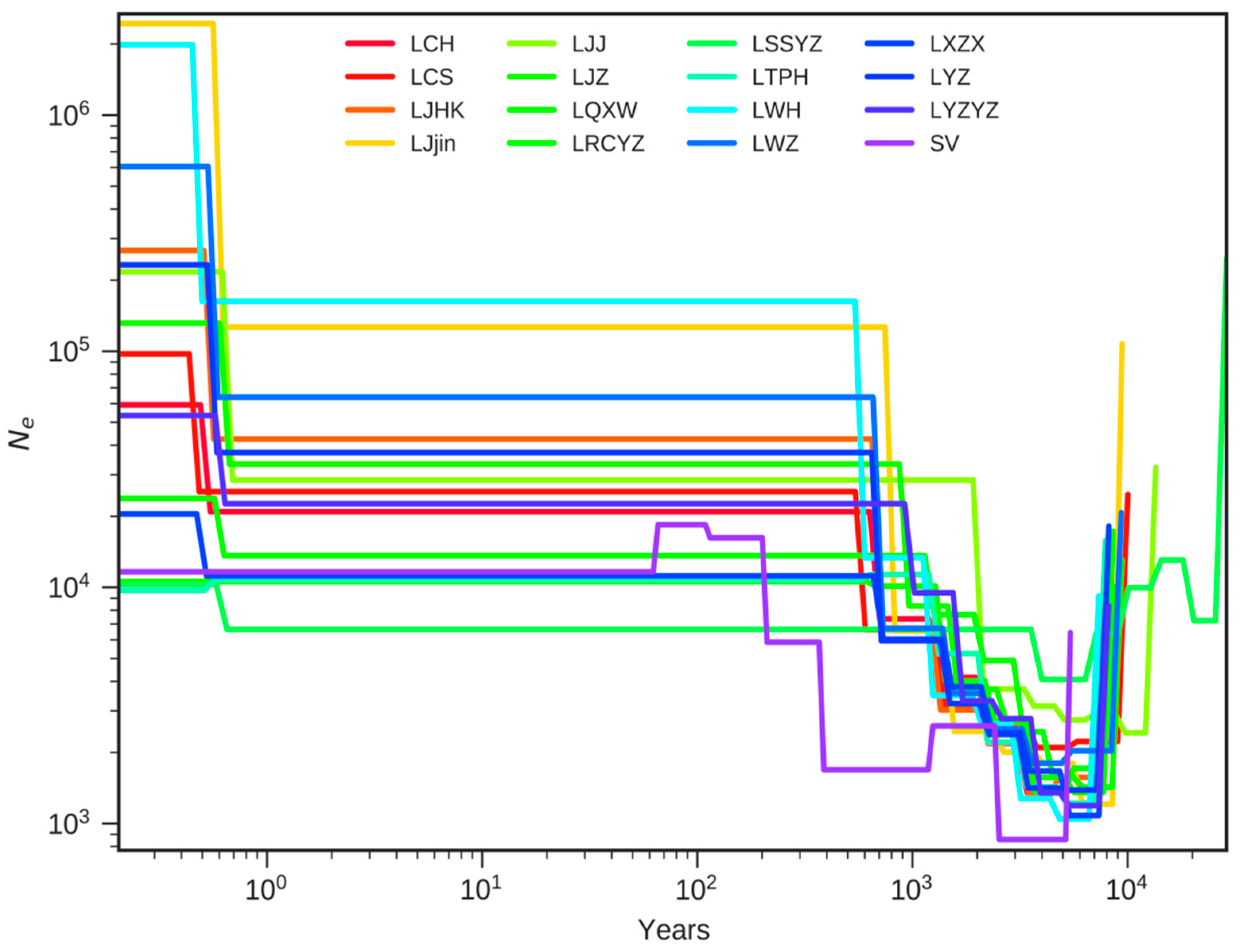
3.6. Population Demographic History Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Shi, W.; Tu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Yuan, C. Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) utilization: Surimi innovations based on seasonal variation in muscle proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 153, 104737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, J.; Que, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, E.; Liao, X.; Zhu, B. Population Genetic Investigation of Hypophthalmichthys nobilis in the Yangtze River Basin Based on RAD Sequencing Data. Biology 2024, 13, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024—Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; pp. 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Belton, B.; Bush, S.R.; Little, D.C. Not just for the wealthy: Rethinking farmed fish consumption in the Global South. Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 16, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisheries Administration Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2025; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Luo, M.; Zhu, L.; Bernatzhez, L.; Li, S. Evolution and genetics of bighead and silver carps: Native population conservation versus invasive species control. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Fang, F. On the geographical distribution of the four kinds of pond-cultured carps in China. Acta Zool. Sin. 1990, 36, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.Q.; Li, S.; Bernatchez, L. Mitochondrial DNA diversity, population structure, and conservation genetics of four native carps within the Yangtze River, China. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, J.; Xu, X.; Yue, G.H.; Li, J. Population structure, demographic history and local adaptation of the grass carp. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.J.; Zhang, S.H. Habitat suitability model of the four major Chinese carps. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2011, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Gardner, C.; Wu, F. Threats and protection policies of the aquatic biodiversity in the Yangtze River. J. Nat. Conserv. 2020, 58, 125931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.P.; Chen, D.Q.; Duan, X.B.; Qiu, S.L.; Huang, M.G. Monitoring of the four famous Chinese carps resources in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2004, 13, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Sokta, L.; Jiang, T.; Liu, H.; Xuan, Z.; Qiu, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. Loss of Coilia nasus habitats in Chinese freshwater lakes: An otolith microchemistry assessment. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Rutschmann, P. Three high flow experiment releases from Glen Canyon Dam on rainbow trout and flannelmouth sucker habitat in Colorado River. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.R.; Inouye, B.D.; Johnson, M.T.; Underwood, N.; Vellend, M. Ecological consequences of genetic diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yue, G. Current status of research on aquaculture genetics and genomics-information from ISGA 2018. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 4, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, J.L.; Egan, S.P.; Nosil, P. The genomics of speciation-with-gene-flow. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delph, L.F.; Kelly, J.K. On the importance of balancing selection in plants. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, M.; Díez-del-Molino, D.; García-Marín, J.L. Genomic survey provides insights into the evolutionary changes that occurred during European expansion of the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki). Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Lundquist, L.L. Introduction: Population biology, evolution, and control of invasive species. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Zhou, B.Y.; Ni, C.K.; Chen, Z.Q. Morphological variations of silver carp, bighead and grass carp from Changjiang, Zhujiang and Heilongjiang rivers. Acta Zool. Sin. 1989, 35, 390–398. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, F.; Ma, X.; Zhu, G.; Song, D.; Nie, G.; Li, X. Analysis on genetic diversity and selective pressure in farmed bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) from Henan province. Freshw. Fish 2018, 48, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, H.; Luo, X.; Zou, G.; Liang, H. Genetic diversity analysis of Aristichthys nobilis in middle reaches of Yangtze River based on the microsatellite makers. Freshw. Fish 2020, 50, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, S.S.; Xu, J.Y.; He, W.M.; Yang, T.L. PopLDdecay: A fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilella, A.J.; Severin, J.; Ureta-Vidal, A.; Heng, L.; Durbin, R.; Birney, E. EnsemblCompara GeneTrees: Complete, duplication-aware phylogenetic trees in vertebrates. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant graphics for data analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 2011, 174, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffels, S.; Wang, K. MSMC and MSMC2: The Multiple Sequentially Markovian Coalescent. In Statistical Population Genomics; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 147–165. [Google Scholar]
- Lowell, N.; Suhrbier, A.; Tarpey, C.; May, S.; Carson, H.; Hauser, L. Population structure and adaptive differentiation in the sea cucumber Apostichopus californicus and implications for spatial resource management. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urvois, T.; Perrier, C.; Roques, A.; Sauné, L.; Courtin, C.; Kajimura, H.; Hulcr, J.; Cognato, A.I.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.A.; Kerdelhué, C. The worldwide invasion history of a pest ambrosia beetle inferred using population genomics. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 4381–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, J.A.; Hallerman, E.M.; Haak, D.C. Genotyping and Sequencing Technologies in Population Genetics and Genomics. In Population Genomics: Concepts, Approaches and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 83–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, C.H.; Huang, J.L.; Lao, Y.L.; Chang, X.Y.; Cao, J.N. Genetic diversity of Hapalogenys analis in the northwest Pacific assessed using dd-RAD sequencing. Front. Eco. Evo. 2024, 12, 1345739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Hu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Huo, B.; Li, D.; Tang, R. Genetic diversity and population structure of Hemiculter leucisculus (basilesky, 1855) in Xinjiang Tarim River. Genes 2022, 13, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchilla-Vargas, J.; Meerbeek, J.R.; Rothschild, M.F.; Bertolini, F. Signatures of Selection and Genomic Diversity of Muskellunge (Esox masquinongy) from Two Populations in North America. Genes 2021, 12, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, G.; Xu, P. Whole-genome resequencing of three Coilia nasus population reveals genetic variations in genes related to immune, vision, migration, and osmoregulation. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatkin, M. Linkage disequilibrium—Understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, R.S. Practical application of the linkage disequilibrium method for estimating contemporary effective population size: A review. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2024, 24, e13879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosil, P.; Funk, D.J.; Ortiz-Barrientos, D.A. Divergent selection and heterogeneous genomic divergence. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xia, J.H.; Bai, Z.Y.; Fu, J.J.; Li, J.L.; Yue, G.H. High genetic diversity and substantial population differentiation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) revealed by microsatellite analysis. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Fu, J.; Luo, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Z. Genetic diversity and population structure of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) from the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River revealed using microsatellite markers. Aquacult. Rep. 2022, 27, 101377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tong, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, X. Development of microsatellite markers and genetic diversity in wild and cultured populations of black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) along the Yangtze River. Aquacult. Int. 2020, 28, 1867–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Luikart, G.H.; Aitken, S.N. Conservation and the Genetics of Populations; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, T.; Lehoczky, I.; Edviné Meleg, E.; Boros, G.; Specziár, A.; Mozsár, A.; Vitál, Z.; Józsa, V.; Allele, W.; Urbányi, B.; et al. Comparison of the Genetic Structure of Invasive Bigheaded Carp (Hypophthalmichthys spp.) Populations in Central-European Lacustrine and Riverine Habitats. Animals 2021, 11, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.; Bhandari, M.S.; Meena, R.K.; Pandey, S.; Kant, R. Contemporary spatial association of genetic diversity determinants in Asian Dipterocarps: A systematic review. Ann. Silvic. Res. 2023, 48, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, D.D.; Cai, J.; Yu, J.X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Xiong, F.; Duan, X.B.; Liu, S.P.; Chen, D.Q. Genetic diversity and population differentiation of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Beijing Normal. Univ. (Natur. Sci.) 2021, 57, 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Dai, F.B.; Tang, W.Q.; Liu, D. Genetic diversity status of silver carp and its contributing factors in the Yangtze River. J. Fish. Sci. China 2022, 29, 1612–1624. [Google Scholar]

| Population ID | Sampling Site | River System | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| LJjin | Jiangjin, Chongqing, China | Upper reach of the Yangtze River | 10 |
| LWZ | Wanzhou, Chongqing, China | 10 | |
| LTPH | Taipingxi, Hubei, China | 10 | |
| LJZ | Jingzhou, Hubei, China | Middle reach of the Yangtze River | 10 |
| LQXW | Qixingwan, Hubei, China | 10 | |
| LJJ | Jiujiang, Jiangxi, China | 10 | |
| LWH | Wuhu, Anhui, China | Lower reach of the Yangtze River | 10 |
| LYZ | Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China | 10 | |
| LCS | Changsu, Jiangsu, China | 10 | |
| LJHK | Dongting lake, Hunan, Chian | Major Yangtze-connected Lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River | 10 |
| LXZX | Poyang lake, Jiangxi, China | 10 | |
| LCH | Chaohu lake, Anhui, China | 10 | |
| LTH | Taihu lake, Jiangsu, China | 10 | |
| LYZYZ | Yangzhou Hatchery, Jiangsu, China | The broodstock of a national hatchery in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River | 10 |
| LRCYZ | Ruichang Hatchery, Jiangxi, China | 10 | |
| LSSYZ | Shishou Hatchery, Hubei, China | 10 | |
| SV | The Marseilles Reach of the Illinois River | Mississippi River | 21 |
| Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Squares | MeanSqs | Fmodel | R2 | Pr (>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among populations | 16 | 148.9617 | 9.3101 | 2.8813 | 21.94% | 0.002 |
| Within populations | 164 | 529.9067 | 3.2311 | 78.06% | ||
| Total | 180 | 678.8684 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Hu, X.; Que, Y.; Wang, E.; Xu, N.; Shao, K.; Lu, G.; Liao, X.; Zhu, B. Population Genomic Survey of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix in the Yangtze River Basin: A RAD Sequencing Perspective. Animals 2025, 15, 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192906
Li W, Hu X, Que Y, Wang E, Xu N, Shao K, Lu G, Liao X, Zhu B. Population Genomic Survey of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix in the Yangtze River Basin: A RAD Sequencing Perspective. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192906
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Weitao, Xingkun Hu, Yanfu Que, Ezhou Wang, Nian Xu, Ke Shao, Guoqing Lu, Xiaolin Liao, and Bin Zhu. 2025. "Population Genomic Survey of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix in the Yangtze River Basin: A RAD Sequencing Perspective" Animals 15, no. 19: 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192906
APA StyleLi, W., Hu, X., Que, Y., Wang, E., Xu, N., Shao, K., Lu, G., Liao, X., & Zhu, B. (2025). Population Genomic Survey of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix in the Yangtze River Basin: A RAD Sequencing Perspective. Animals, 15(19), 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192906




