Spatio-Temporal Pattern Analysis of African Swine Fever Spreading in Northwestern Italy—The Role of Habitat Interfaces
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
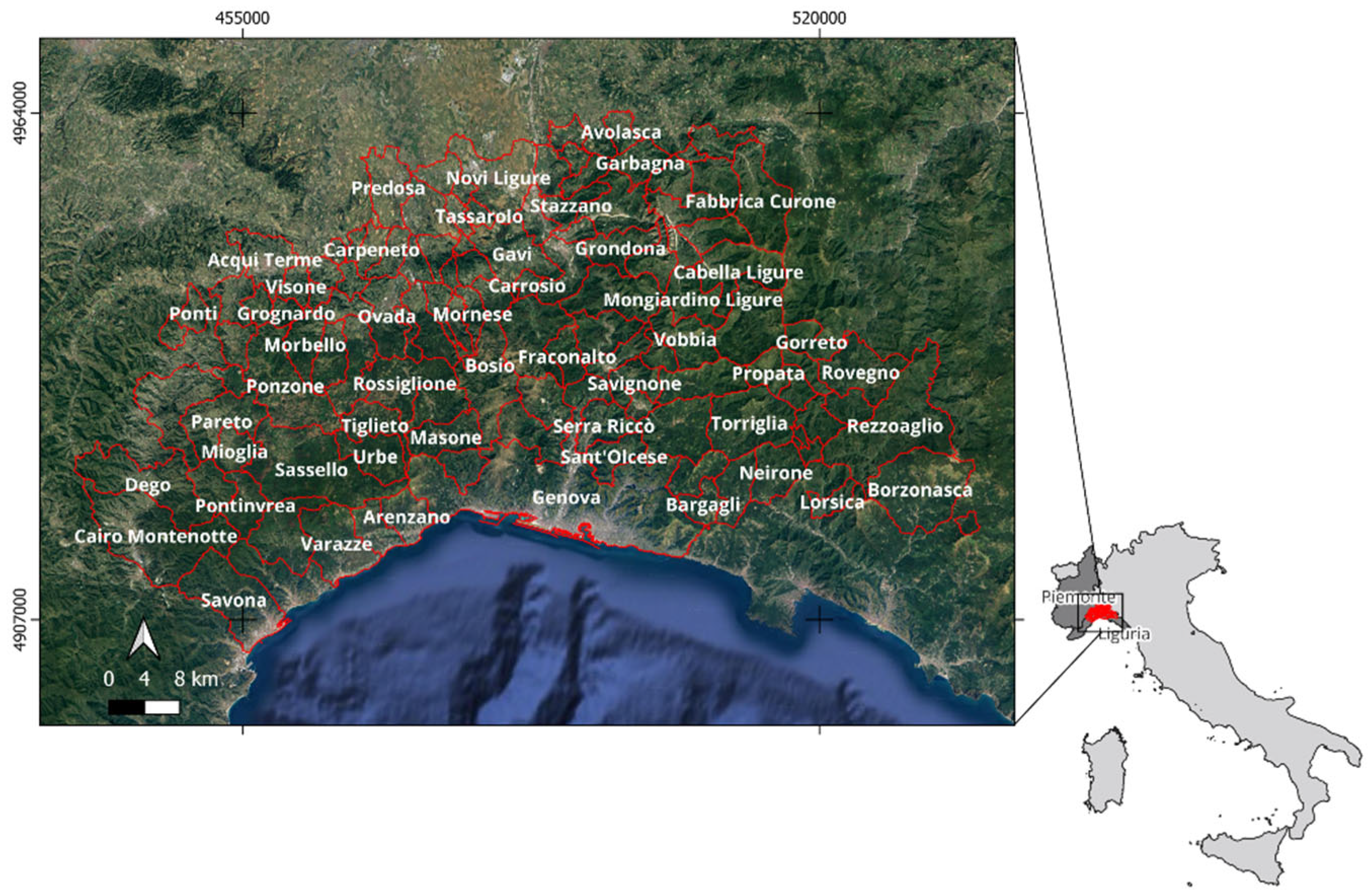
2.1. The Area of Interest
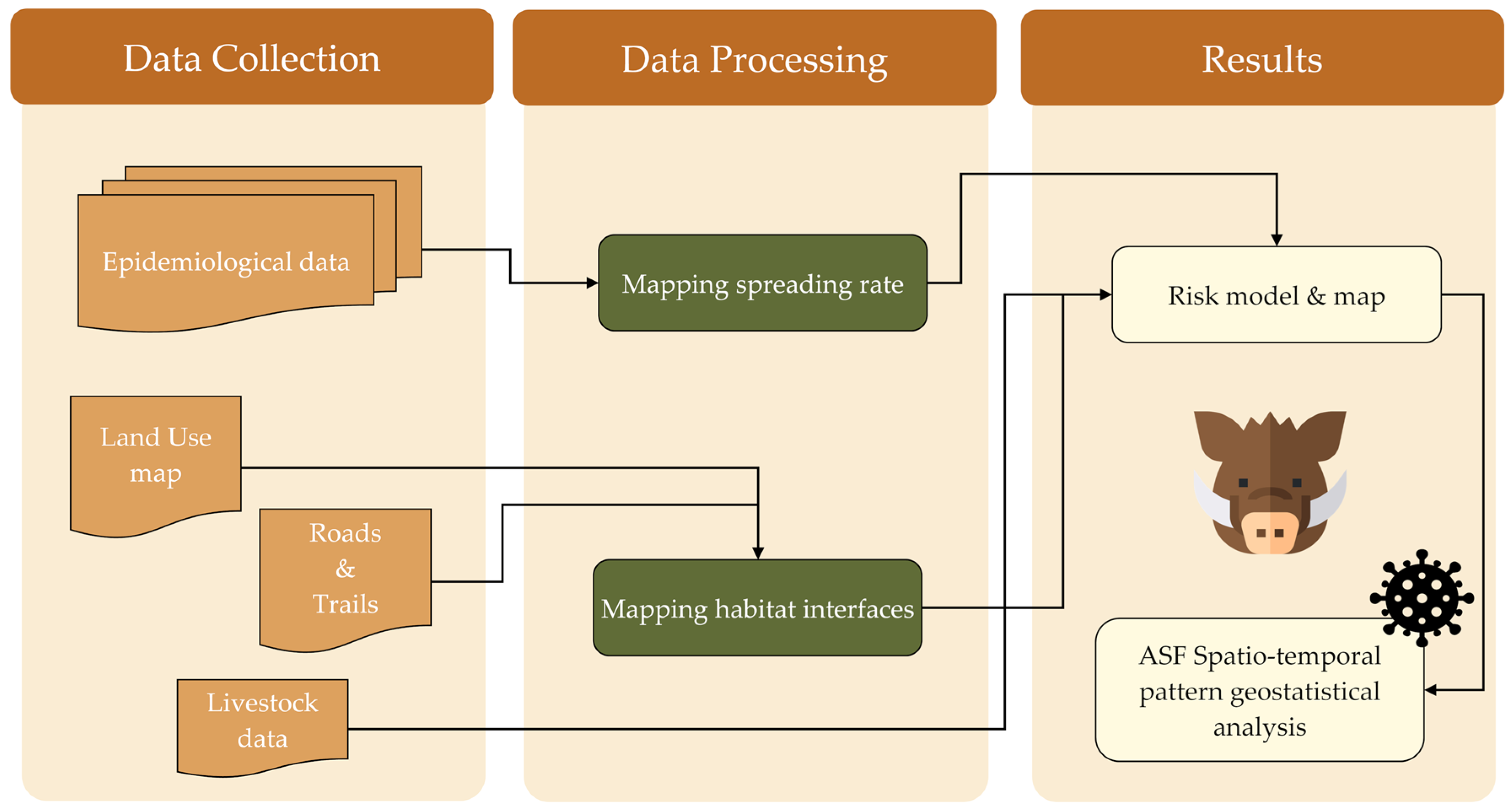
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Epidemiological Data
2.2.2. Land Use, Roads, and Trails Data
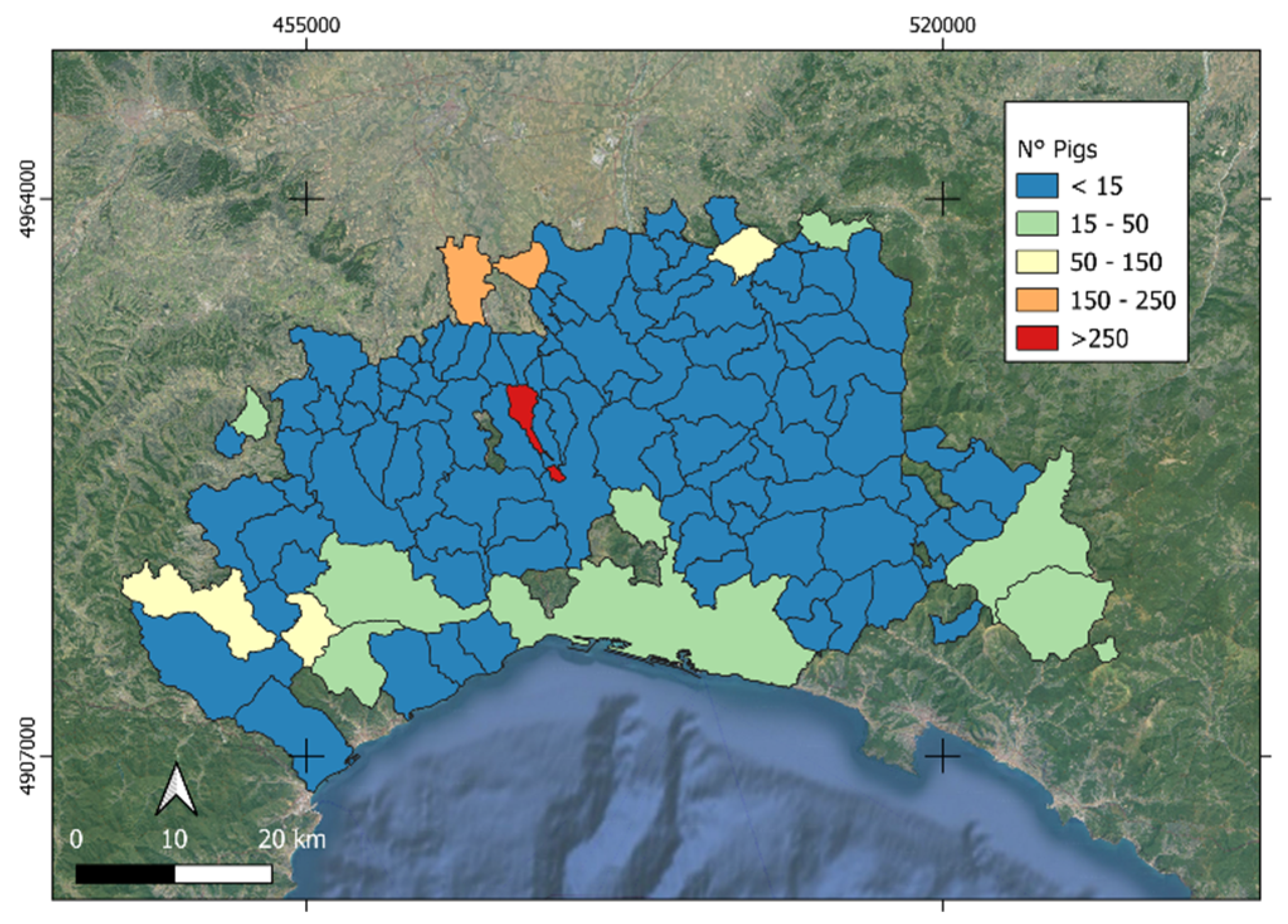
2.2.3. Livestock Data
2.3. Data Processing
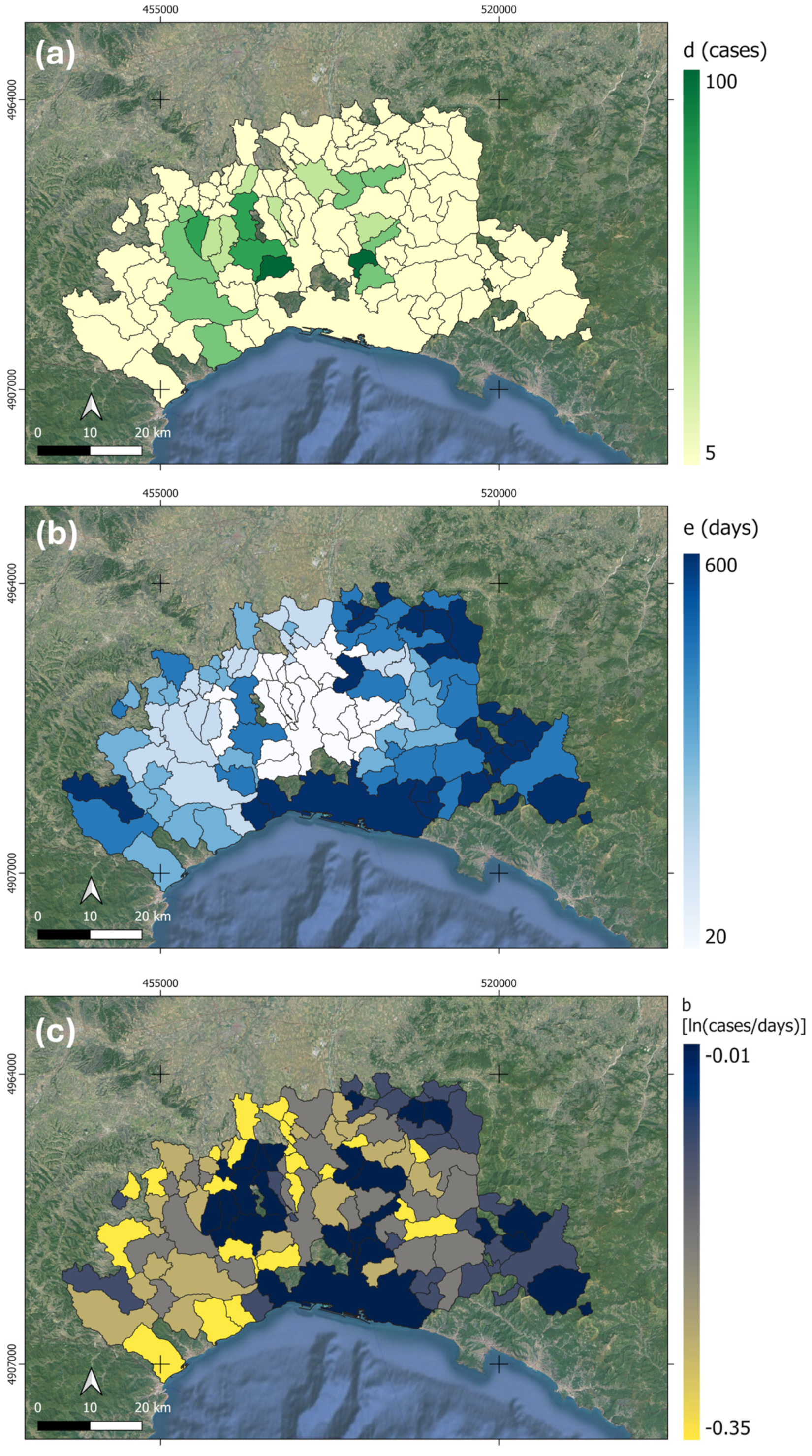
2.3.1. Mapping the Spreading Rate
2.3.2. Mapping the Habitat Interfaces
2.3.3. Livestock Risk Modeling
2.3.4. Geostatistical Analysis of ASF Spatio-Temporal Pattern
3. Results
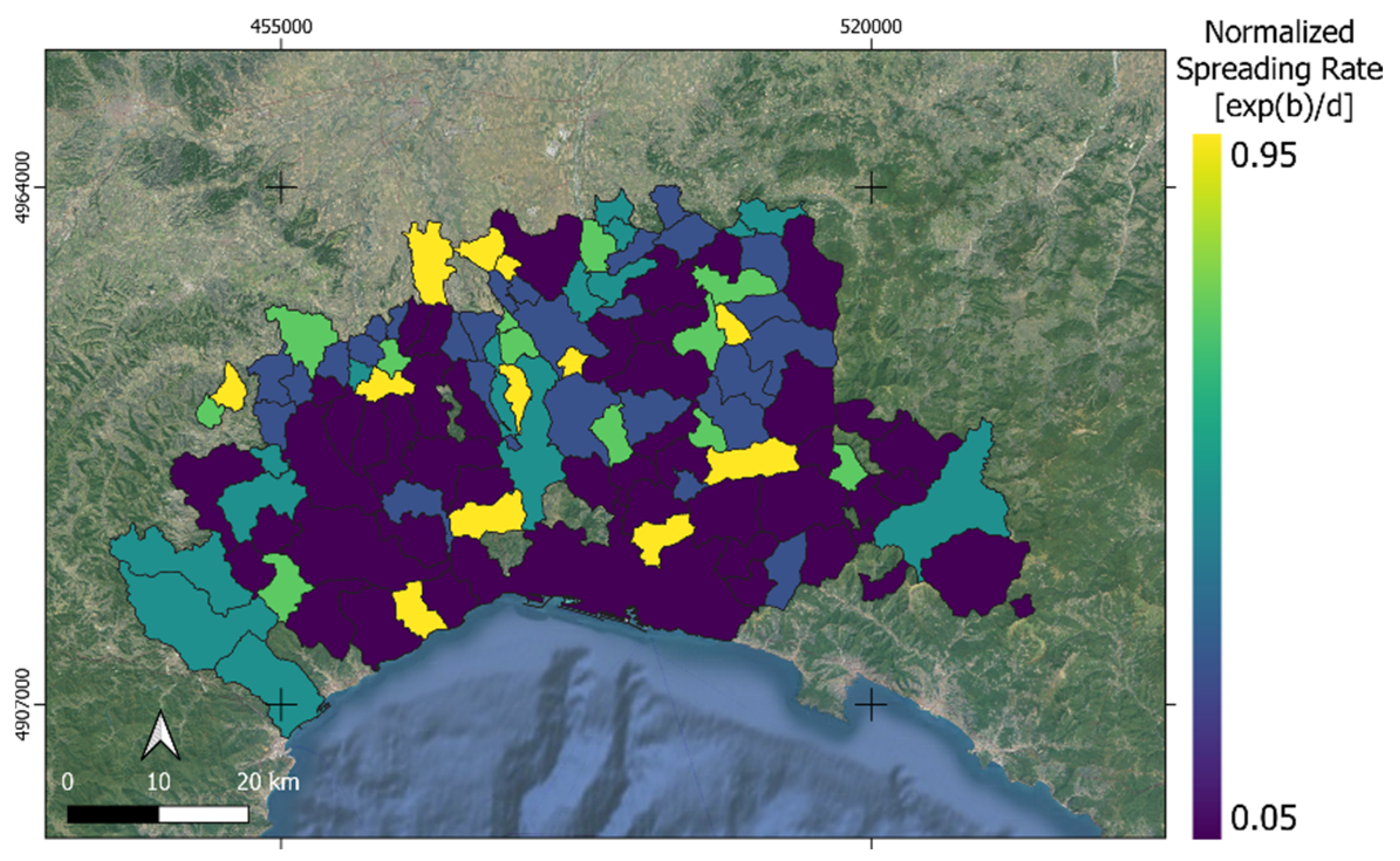
3.1. Mapping the Spreading Rate
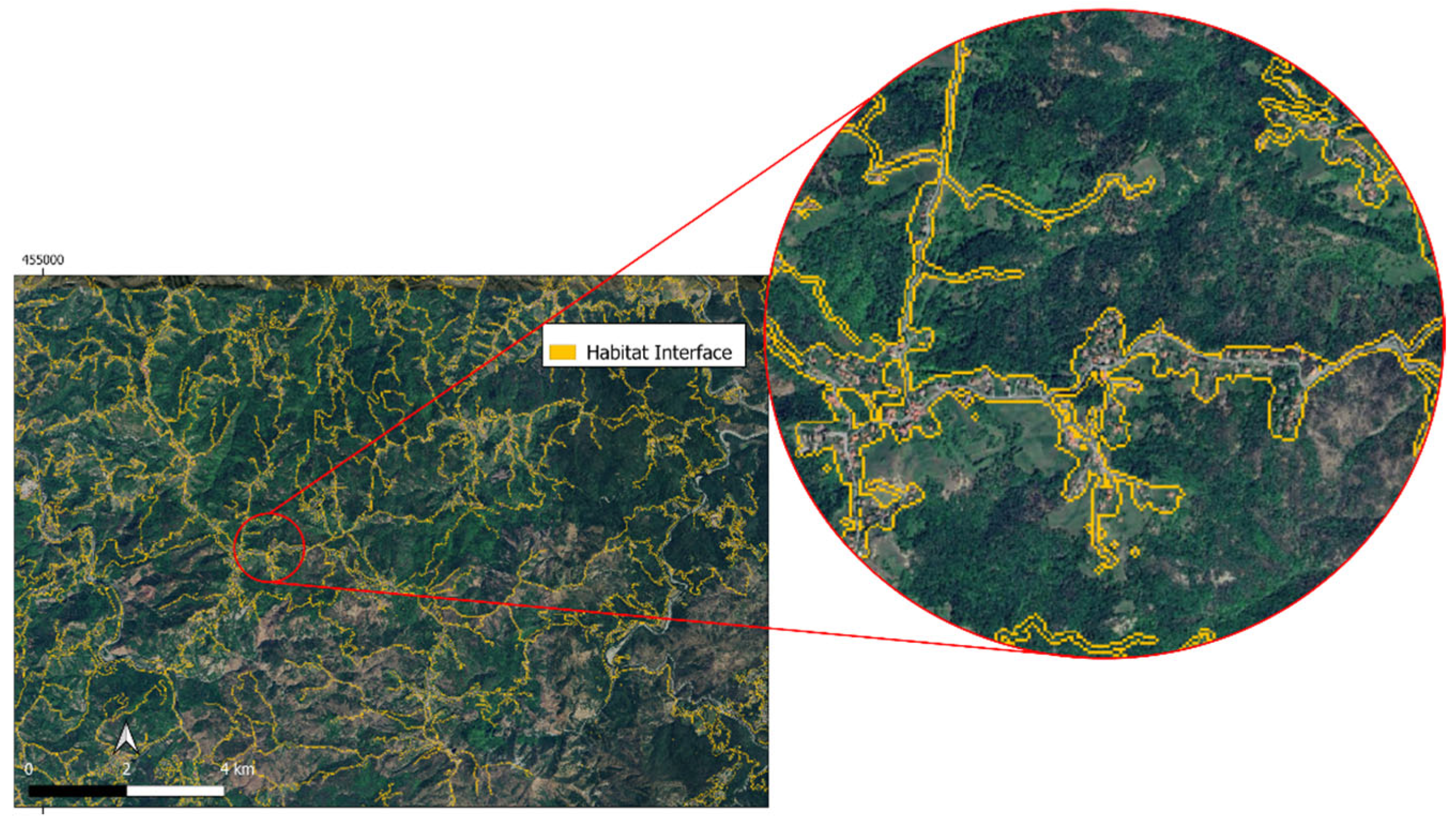
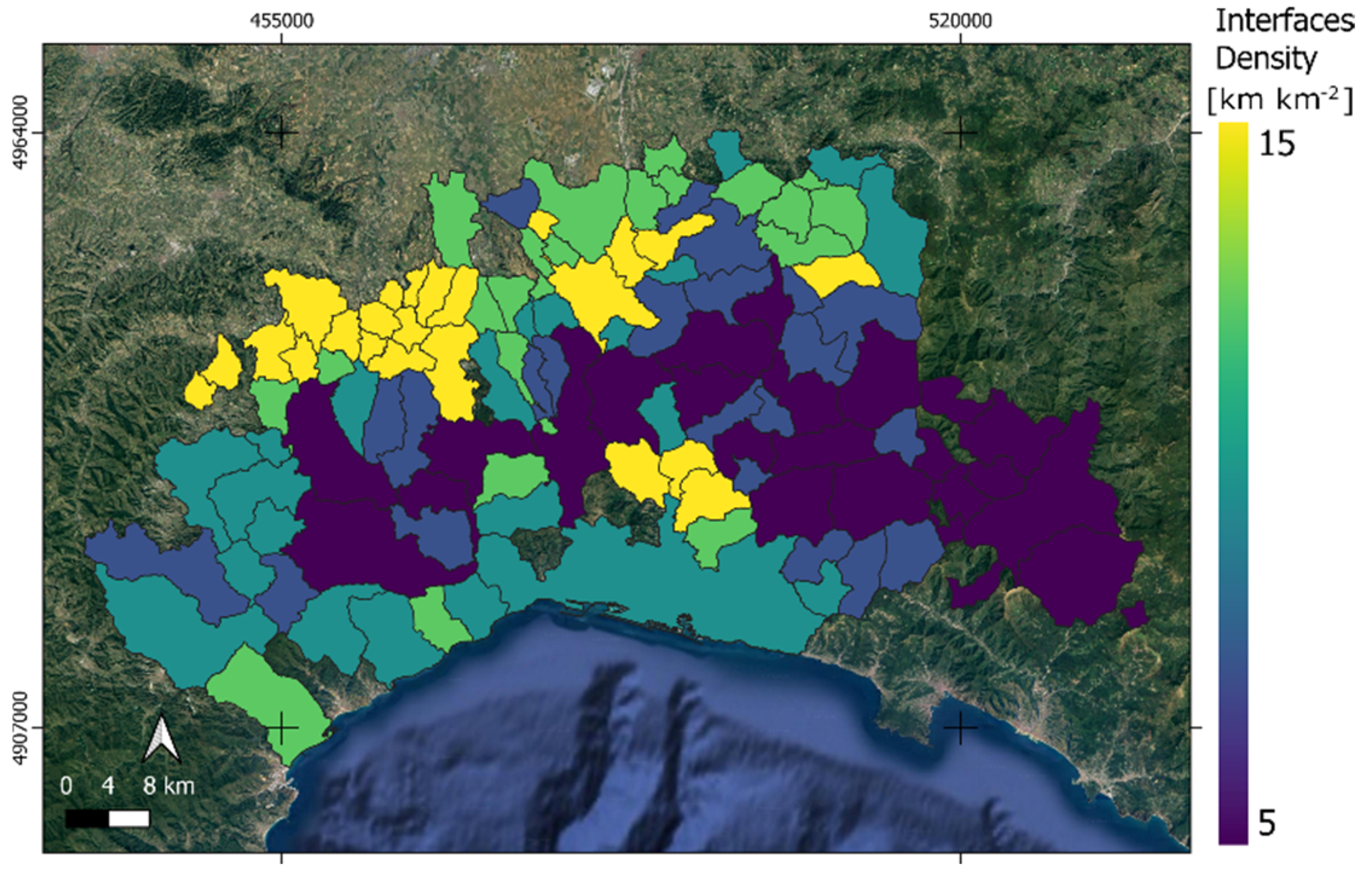
3.2. Mapping the Habitat Interfaces
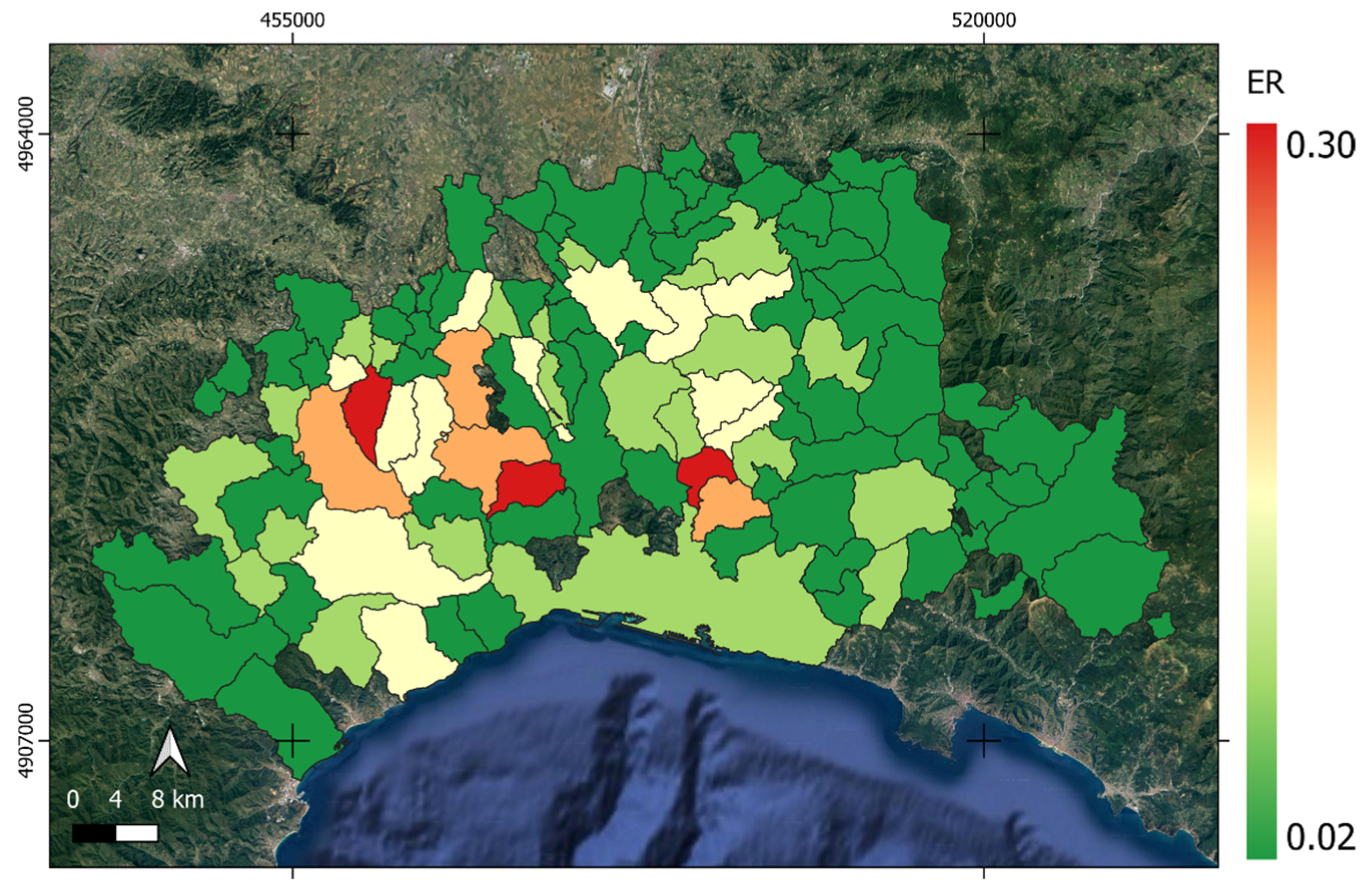
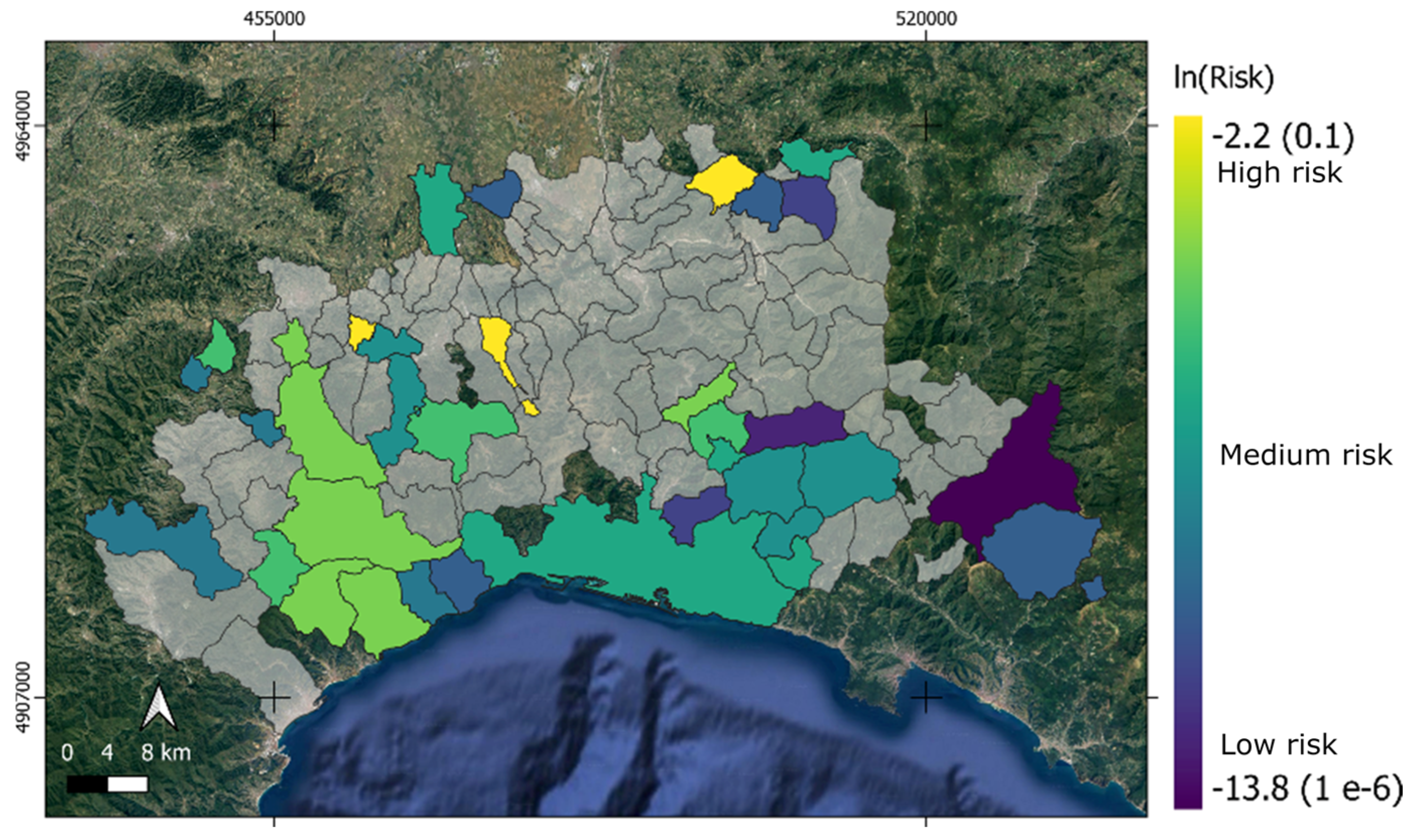
3.3. Livestock Risk Modeling
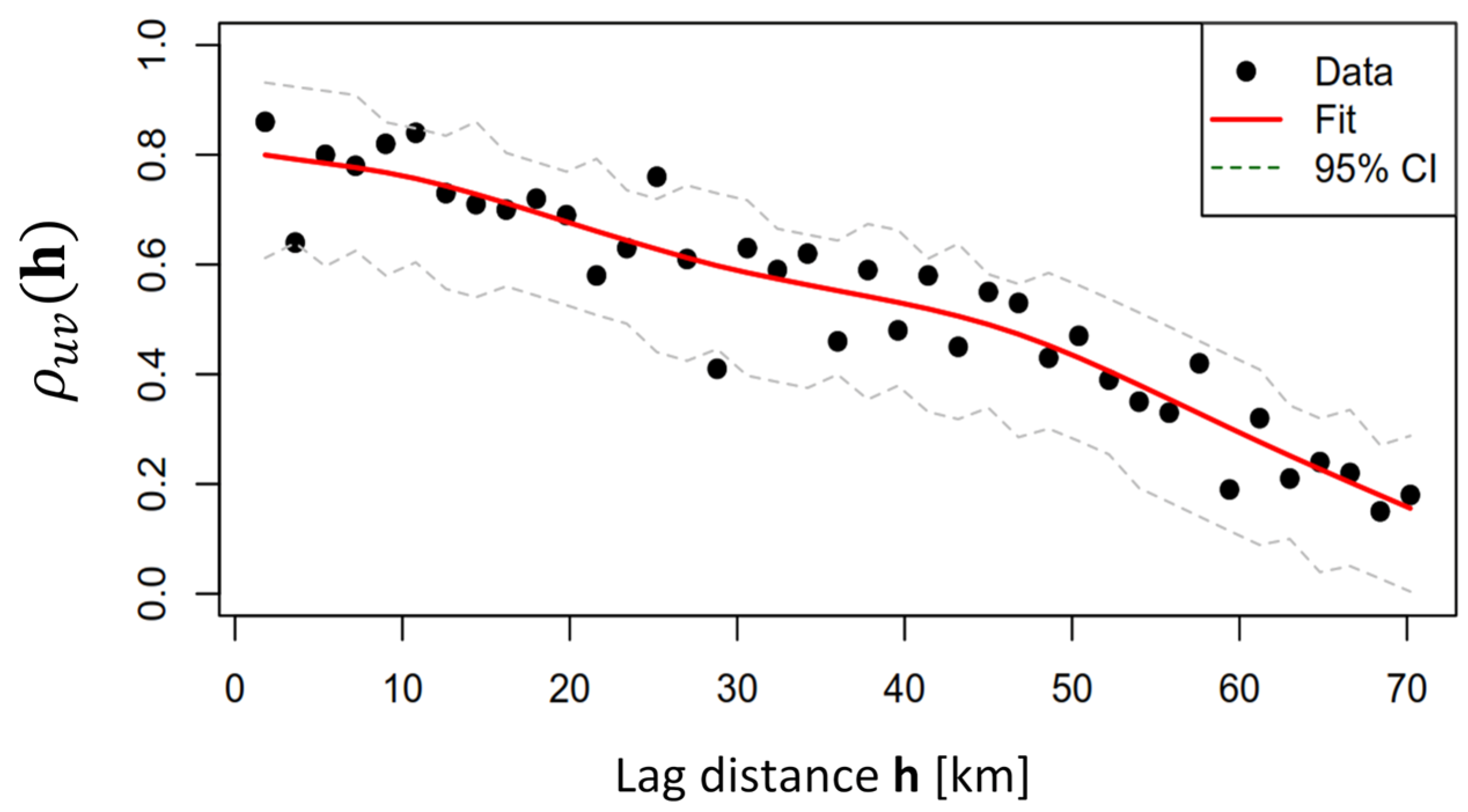
3.4. Geostatistical Analysis of Spreading Spatio-Temporal Pattern
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arias, M.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. African Swine Fever. In Trends in Emerging Viral Infections of Swine; Morilla, A., Yoon, K.-J., Zimmerman, J.J., Eds.; Iowa State Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2002; pp. 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, L.; Sun, H.; Roberts, H. African Swine Fever. Antivir. Res. 2019, 165, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, S.; Franzke, K.; Beer, M. African Swine Fever–A Review of Current Knowledge. Virus Res. 2020, 287, 198099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, S.H.; Mannelli, A.; Kitron, U.; Bellini, S. An Analysis of the Social, Cultural, and Ecological Factors That Affect the Implementation of Biosecurity Measures on Smallholder Commercial Swine Farms in Italy in the Context of an Emerging African Swine Fever Outbreak. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 229, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasa, T.; Bøtner, A.; Mortensen, S.; Christensen, H.; Toft, N.; Boklund, A. Simulating the Epidemiological and Economic Effects of an African Swine Fever Epidemic in Industrialized Swine Populations. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 193, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, V.R.; Miller, R.S.; McKee, S.C.; Ernst, K.H.; Didero, N.M.; Maison, R.M.; Grady, M.J.; Shwiff, S.A. Risks of Introduction and Economic Consequences Associated with African Swine Fever, Classical Swine Fever and Foot-and-Mouth Disease: A Review of the Literature. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1910–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason-D’Croz, D.; Bogard, J.R.; Herrero, M.; Robinson, S.; Sulser, T.B.; Wiebe, K.; Willenbockel, D.; Godfray, H.C.J. Modelling the Global Economic Consequences of a Major African Swine Fever Outbreak in China. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.; De la Torre, A.; Dixon, L.; Gallardo, C.; Jori, F.; Laddomada, A.; Martins, C.; Parkhouse, R.M.; Revilla, Y.; Rodriguez, F.; et al. Approaches and Perspectives for Development of African Swine Fever Virus Vaccines. Vaccines 2017, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.G.; Pérez-Núñez, D.; Revilla, Y. Development of Vaccines against African Swine Fever Virus. Virus Res. 2019, 265, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Camós, L.; López, E.; Rodriguez, F. African Swine Fever Vaccines: A Promising Work Still in Progress. Porc. Health Manag. 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jori, F.; Massei, G.; Licoppe, A.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Linden, A.; Václavek, P.; Chenais, E.; Rosell, C. Management of Wild Boar Populations in the European Union before and during the ASF Crisis. In Understanding and Combatting African Swine Fever: A European Perspective; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Faustini, G.; Soret, M.; Defossez, A.; Bosch, J.; Conte, A.; Tran, A. Habitat Suitability Mapping and Landscape Connectivity Analysis to Predict African Swine Fever Spread in Wild Boar Populations: A Focus on Northern Italy. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0317577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, H.; Schulz, K.; Conraths, F.J.; Sauter-Louis, C. A Review of Environmental Risk Factors for African Swine Fever in European Wild Boar. Animals 2021, 11, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavone, S.; Iscaro, C.; Dettori, A.; Feliziani, F. African Swine Fever: The State of the Art in Italy. Animals 2023, 13, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasi, V.; Sordilli, M.; Loi, F.; Guberti, V. Estimating the Directional Spread of Epidemics in Their Early Stages Using a Simple Regression Approach: A Study on African Swine Fever in Northern Italy. Pathogens 2023, 12, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervasi, V.; Guberti, V. African Swine Fever Endemic Persistence in Wild Boar Populations: Key Mechanisms Explored through Modelling. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2812–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goicolea, T.; Cisneros-Araújo, P.; Vega, C.A.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Mateo-Sánchez, M.; Bosch, J. Landscape Connectivity for Predicting the Spread of ASF in the European Wild Boar Population. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possenti, L.; Savini, L.; Conte, A.; D’Alterio, N.; Danzetta, M.L.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Nardoia, M.; Migliaccio, P.; Tora, S.; Dalla Villa, P. A New Information System for the Management of Non-Epidemic Veterinary Emergencies. Animals 2020, 10, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, I.M.P.; Paiva, M.T.; da Costa, A.J.A.; Nicolino, R.R. African Swine Fever: Spread and Seasonal Patterns Worldwide. Prev. Vet. Med. 2025, 235, 106401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welle, T.; Birkmann, J. The World Risk Index–an Approach to Assess Risk and Vulnerability on a Global Scale. J. Extrem. Events 2015, 2, 1550003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavier-Widén, D.; Gortázar, C.; Ståhl, K.; Neimanis, A.S.; Rossi, S.; Hård av Segerstad, C.; Kuiken, T. African Swine Fever in Wild Boar in Europe: A Notable Challenge. Vet. Rec. 2015, 176, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palencia, P.; Blome, S.; Brook, R.K.; Ferroglio, E.; Jo, Y.-S.; Linden, A.; Montoro, V.; Penrith, M.-L.; Plhal, R.; Vicente, J.; et al. Tools and Opportunities for African Swine Fever Control in Wild Boar and Feral Pigs: A Review. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2023, 69, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosamilia, A.; Benedetti, S.; Cotugno, D.; Guarnieri, C.; Miraglia, V.; Riponi, A.; Capezzuto, S.; Siragusa, G.; Santini, N.; Pierantoni, M. African Swine Fever: Implications for the Italian Pork Trade. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2024, 13, 12489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orusa, T.; Farbo, A.; De Petris, S.; Sarvia, F.; Cammareri, D.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Characterization of Alpine Pastures Using Multitemporal Earth Observation Data within the Climate Change Framework. In Earth Observation: Current Challenges and Opportunities for Environmental Monitoring; Associazione Italiana di Telerilevamento (AIT): Firenze, Italy, 2024; Volume 3, pp. 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Viani, A.; Orusa, T.; Borgogno-Mondino, E.; Orusa, R. Snow Metrics as Proxy to Assess Sarcoptic Mange in Wild Boar: Preliminary Results in Aosta Valley (Italy). Life 2023, 13, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Stahl, K.; Jori, F.; Vial, L.; Pfeiffer, D.U. African Swine Fever Epidemiology and Control. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2020, 8, 221–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. African Swine Fever Virus: A Review. Viruses 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orusa, T.; Orusa, R.; Viani, A.; Carella, E.; Borgogno Mondino, E. Geomatics and EO Data to Support Wildlife Diseases Assessment at Landscape Level: A Pilot Experience to Map Infectious Keratoconjunctivitis in Chamois and Phenological Trends in Aosta Valley (NW Italy). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, E.; Orusa, T.; Viani, A.; Meloni, D.; Borgogno-Mondino, E.; Orusa, R. An Integrated, Tentative Remote-Sensing Approach Based on NDVI Entropy to Model Canine Distemper Virus in Wildlife and to Prompt Science-Based Management Policies. Animals 2022, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penrith, M.-L.; Van Emmenes, J.; Hakizimana, J.N.; Heath, L.; Kabuuka, T.; Misinzo, G.; Odoom, T.; Wade, A.; Zerbo, H.L.; Luka, P.D. African Swine Fever Diagnosis in Africa: Challenges and Opportunities. Pathogens 2024, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, S.; Bellini, S.; Iscaro, C.; Farioli, M.; Chiari, M.; Lavazza, A.; Ruocco, L.; Lelli, D.; Pintus, G.; Prati, P.; et al. Strategic Challenges to the Eradication of African Swine Fever Genotype II in Domestic Pigs in North Italy. Animals 2024, 14, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Nie, T.; Ma, J.; Chen, H. Identification of Suitable Areas for African Swine Fever Occurrence in China Using Geographic Information System-Based Multi-Criteria Analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 209, 105794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórski, T.; Borowik, T.; Łyjak, M.; Woźniakowski, G. Spatial Epidemiology of African Swine Fever: Host, Landscape and Anthropogenic Drivers of Disease Occurrence in Wild Boar. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 177, 104691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenais, E.; Ahlberg, V.; Andersson, K.; Banihashem, F.; Björk, L.; Cedersmyg, M.; Ernholm, L.; Frössling, J.; Gustafsson, W.; Hellqvist Björnerot, L.; et al. First Outbreak of African Swine Fever in Sweden: Local Epidemiology, Surveillance, and Eradication Strategies. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 6071781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruedas-Torres, I.; Thi to Nga, B.; Salguero, F.J. Pathogenicity and Virulence of African Swine Fever Virus. Virulence 2024, 15, 2375550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradduzza, E.; Loi, F.; Porcu, F.; Mandas, D.; Secci, F.; Pisanu, M.E.; Pasini, C.; Zuddas, C.; Cherchi, M.; Denurra, D.; et al. Passive Surveillance as a Key Tool for African Swine Fever Eradication in Wild Boar: A Protocol to Find Carcasses Tested and Validated in the Mediterranean Island of Sardinia. Viruses 2024, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Guo, Z.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Wan, J. The Influencing Factors of “Post-African Swine Fever” Pig Farm Biosecurity: Evidence from Sichuan Province, China. Animals 2023, 13, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iscaro, C.; Dondo, A.; Ruocco, L.; Masoero, L.; Giammarioli, M.; Zoppi, S.; Guberti, V.; Feliziani, F. January 2022: Index Case of New African Swine Fever Incursion in Mainland Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhollander, S.; Cattaneo, E.; Cortiñas Abrahantes, J.; Boklund, A.; Szczotka-Bochniarz, A.; Mihalca, A.; Papanikolaou, A.; Mur, L.; Balmoș, O.; Frant, M.; et al. Prospective Case–Control Study of Determinants for African Swine Fever Introduction in Commercial Pig Farms in Poland, Romania, and Lithuania. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2025, 2025, 5419764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Dhakal, T.; Kim, T.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Jang, G.-S.; Oh, Y. Climate Change Influences the Spread of African Swine Fever Virus. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, A.; Orusa, T.; Borgogno-Mondino, E.; Orusa, R. A One Health Google Earth Engine Web-GIS Application to Evaluate and Monitor Water Quality Worldwide. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2024, 9, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, A.; Orusa, T.; Mandola, M.L.; Robetto, S.; Belvedere, M.; Renna, G.; Scala, S.; Borgogno-Mondino, E.; Orusa, R. R05. 4 Tick’s Suitability Habitat Maps and Tick-Host Relationships in Wildlife. A One Health Approach Based on Multitemporal Remote Sensed Data, Entropy and Meta® Population Dataset in Aosta Valley, NW Italy. In Proceedings of the GeoVet 2023 International Conference, Silvi Marina, Italy, 19–21 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Korennoy, F.; Gulenkin, V.; Malone, J.; Mores, C.; Dudnikov, S.; Stevenson, M. Spatio-Temporal Modeling of the African Swine Fever Epidemic in the Russian Federation, 2007–2012. Spat. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2014, 11, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, A.; Orusa, T.; Mandola, M.L.; Robetto, S.; Nogarol, C.; Mondino, E.B.; Orusa, R. Grading Habitats for Ticks by Mapping a Suitability Index Based on Remotely Sensed Data and Meta® Population Dataset in Aosta Valley, NW Italy. Vet. Ital. 2024, 60, 28-2. [Google Scholar]
- Orusa, T.; Viani, A.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Earth Observation Data and Geospatial Deep Learning AI to Assign Contributions to European Municipalities Sen4MUN: An Empirical Application in Aosta Valley (NW Italy). Land 2024, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, A.; Orusa, T.; Divari, S.; Lovisolo, S.; Zanet, S.; Orusa, R.; Borgogno-Mondino, E.; Bollo, E. Detection of Bartonella spp. in Foxes’ Populations in Piedmont and Aosta Valley (NW Italy) Coupling Geospatially-Based Techniques. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 11, 1388440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, K.A.; Lewis, B.L.; Marathe, M.; Eubank, S.; Blackburn, J.K. Modeling of Wildlife-Associated Zoonoses: Applications and Caveats. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranha, J.; Abrantes, A.C.; Gonçalves, R.; Miranda, R.; Serejo, J.; Vieira-Pinto, M. GIS as an Epidemiological Tool to Monitor the Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Tuberculosis in Large Game in a High-Risk Area in Portugal. Animals 2021, 11, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fioravante, P.; Strollo, A.; Assennato, F.; Marinosci, I.; Congedo, L.; Munafò, M. High Resolution Land Cover Integrating Copernicus Products: A 2012–2020 Map of Italy. Land 2021, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, G.; Bagliani, M.; Orusa, T. Lessico e Nuvole: Le Parole Del Cambiamento Climatico; Youcanprint: Siena, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, Z.; Cinderby, S.; Smart, J.C.R.; Raffaelli, D.; White, P. Mapping Wildlife: Integrating Stakeholder Knowledge with Modelled Patterns of Deer Abundance by Using Participatory GIS. Wildl. Res. 2009, 36, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Orusa, T.; Cammareri, D.; Freppaz, D.; Vuillermoz, P.; Borgogno Mondino, E. Sen4MUN: A Prototypal Service for the Distribution of Contributions to the European Municipalities from Copernicus Satellite Imagery. A Case in Aosta Valley (NW Italy). In Proceedings of the Italian Conference on Geomatics and Geospatial Technologies, Virtual, 18–20 December 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Blanton, J.D.; Manangan, A.; Manangan, J.; Hanlon, C.A.; Slate, D.; Rupprecht, C.E. Development of a GIS-Based, Real-Time Internet Mapping Tool for Rabies Surveillance. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2006, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Di Lorenzo, A.; Zenobio, V.; Cioci, D.; Dall’Acqua, F.; Tora, S.; Iannetti, S.; Rulli, M.; Di Sabatino, D. A Web-Based Geographic Information System Monitoring Wildlife Diseases in Abruzzo and Molise Regions, Southern Italy. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System; Open Source Geospatial Foundation: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Dobson, A.; Restif, O.; Wells, K. Challenges in Modelling the Dynamics of Infectious Diseases at the Wildlife–Human Interface. Epidemics 2021, 37, 100523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.J.; Razgour, O. Emerging Zoonotic Diseases Originating in Mammals: A Systematic Review of Effects of Anthropogenic Land-use Change. Mammal Rev. 2020, 50, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orusa, T.; Viani, A.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. IRIDE, the Euro-Italian Earth Observation Program: Overview, Current Progress, Global Expectations, and Recommendations. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2024, 29, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Aloi, D.; Rolesu, S.; Putzolu, A.; Scrugli, A.; Oggiano, A.; Chironi, P.; Dei Giudici, S.; Patta, C.; Basciu, G.; Piroddi, R. Use of Geographic Information Systems Technology in the Epidemiological Surveillance of African Swine Fever. Vet. Ital. 2007, 43, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, D.S.; Foody, G.M. An Overview of Recent Remote Sensing and GIS Based Research in Ecological Informatics. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Peterson, A.T.; Poulin, R.; de la Fuente, J. Effects of Environmental Change on Zoonotic Disease Risk: An Ecological Primer. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viani, A.; Orusa, T.; Divari, S.; Lovisolo, S.; Zanet, S.; Borgogno-Mondino, E.; Orusa, R.; Bollo, E. Bartonella spp. Distribution Assessment in Foxes Coupling Geospatially-Based Techniques. In Earth Observation: Current Challenges and Opportunities for Environmental Monitoring; Associazione Italiana di Telerilevamento (AIT): Firenze, Italy, 2024; Volume 3, pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Niu, B. Risk Analysis of African Swine Fever in Poland Based on Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Latin Hypercube Sampling, 2014–2017. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millington, A.C.; Walsh, S.J.; Osborne, P.E. GIS and Remote Sensing Applications in Biogeography and Ecology; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 626. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, A.C.; Windmeijer, F.A. An R-Squared Measure of Goodness of Fit for Some Common Nonlinear Regression Models. J. Econom. 1997, 77, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, S. Coefficients of Determination for Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis. Am. Stat. 2000, 54, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrusfield, M. Veterinary Epidemiology; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, M.C.; Reoyo, A.T.; Fernández-Pinero, J.; Iglesias, I.; Muñoz, M.J.; Arias, M.L. African Swine Fever: A Global View of the Current Challenge. Porc. Health Manag. 2015, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orusa, T.; Viani, A.; Cammareri, D.; Borgogno Mondino, E. A Google Earth Engine Algorithm to Map Phenological Metrics in Mountain Areas Worldwide with Landsat Collection and Sentinel-2. Geomatics 2023, 3, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, A.; Mangone, I.; Colangeli, P.; Cioci, D.; Curini, V.; Vincifori, G.; Mercante, M.T.; Di Pasquale, A.; Radomski, N.; Iannetti, S. One Health System Supporting Surveillance during COVID-19 Epidemic in Abruzzo Region, Southern Italy. One Health 2023, 16, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.; Kassié, D.; Herbreteau, V. Applications of Remote Sensing to the Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases: Some Examples. In Land Surface Remote Sensing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 295–315. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira-Pinto, M.; Alberto, J.; Aranha, J.; Serejo, J.; Canto, A.; Cunha, M.V.; Botelho, A. Combined Evaluation of Bovine Tuberculosis in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) and Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) from Central-East Portugal. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2011, 57, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wong, H.; Belanger, P.; Moore, K.; Peterson, M.; Cunningham, J. Analyzing the Correlation between Deer Habitat and the Component of the Risk for Lyme Disease in Eastern Ontario, Canada: A GIS-Based Approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orusa, T.; Viani, A.; d’Alessio, S.G.; Orusa, R.; Caminade, C. One Health Approaches and Modeling in Parasitology in the Climate Change Framework and Possible Supporting Tools Adopting GIS and Remote Sensing. Front. Parasitol. 2025, 4, 1560799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.; Masuoka, P.; Murrell, K.D. Swine Trichinella Infection and Geographic Information System Tools. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Dunn, J.E.; Smith, K.G. A Multivariate Model of Female Black Bear Habitat Use for a Geographic Information System. J. Wildl. Manag. 1993, 57, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.S.; Carpenter, S.R.; Barber, M.; Collins, S.; Dobson, A.; Foley, J.A.; Lodge, D.M.; Pascual, M.; Pielke, R., Jr.; Pizer, W.; et al. Ecological Forecasts: An Emerging Imperative. Science 2001, 293, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colby, M.M.; Johnson, Y.J. Potential Uses for Geographic Information System-Based Planning and Decision Support Technology in Intensive Food Animal Production. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2002, 3, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danson, F.; Bowyer, P.; Pleydell, D.; Craig, P. Echinococcus Multilocularis: The Role of Satellite Remote Sensing, GIS and Spatial Modelling. South-East Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2004, 35, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, M.; Ferrari, N.; Fanelli, A.; Muset, S.; Thompson, L.; Sleeman, J.M.; White, C.; Walsh, D.; Wannous, C.; Tizzani, P.; et al. Wildlife Health Surveillance: Gaps, Needs and Opportunities. Rev. Sci. ET Tech.-Off. Int. DES Epizoot. 2023, 42, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Dorotea, T.; Riuzzi, G.; Franzago, E.; Posen, P.; Tavornpanich, S.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Ferroni, L.; Martelli, W.; Mazzucato, M.; Soccio, G.; et al. A Scoping Review on GIS Technologies Applied to Farmed Fish Health Management. Animals 2023, 13, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, M.L.; Hoeting, J.A.; Hobbs, N.T.; Conner, M.M.; Burnham, K.P.; Wolfe, L.L.; Williams, E.S.; Theobald, D.M.; Miller, M.W. The Role of Geographic Information Systems Inwildlife Epidemiology: Models of Chronic Wasting Disease in Colorado Mule Deer. Vet. Ital. 2007, 43, 581. [Google Scholar]
- French, N.P.; White, P.C. The Use of GIS in Modelling the Spatial and Temporal Spread of Animal Diseases. In GIS and Spatial Analysis in Veterinary Science; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 177–203. [Google Scholar]
- Benjelloun, A.; El Harrak, M.; Calistri, P.; Loutfi, C.; Kabbaj, H.; Conte, A.; Ippoliti, C.; Danzetta, M.L.; Belkadi, B. Seroprevalence of West Nile Virus in Horses in Different Moroccan Regions. Vet. Med. Amp. Sci 2017, 3, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippoliti, C.; Candeloro, L.; Gilbert, M.; Goffredo, M.; Mancini, G.; Curci, G.; Falasca, S.; Tora, S.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Quaglia, M. Defining Ecological Regions in Italy Based on a Multivariate Clustering Approach: A First Step towards a Targeted Vector Borne Disease Surveillance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, L.; Weiss, C.; Colangeli, P.; Conte, A.; Ippoliti, C.; Lelli, R.; Santucci, U. A Web-Based Geographic Information System for the Management of Animal Disease Epidemics. Vet. Ital. 2007, 43, 761–772. [Google Scholar]
- Sauter-Louis, C.; Conraths, F.J.; Probst, C.; Blohm, U.; Schulz, K.; Sehl, J.; Fischer, M.; Forth, J.H.; Zani, L.; Depner, K.; et al. African Swine Fever in Wild Boar in Europe—A Review. Viruses 2021, 13, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, L.; Brülisauer, F.; Willoughby, K.; Cousens, C. Identifying Environmental Risk Factors for Louping Ill Virus Seroprevalence in Sheep and the Potential to Inform Wildlife Management Policy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, G.E.; Aron, J.L.; Ellis, J.H.; Yoon, S.S. Applications of GIS Technology to Disease Control; The Johns Hoph University: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hattendorf, J.; Bardosh, K.L.; Zinsstag, J. One Health and Its Practical Implications for Surveillance of Endemic Zoonotic Diseases in Resource Limited Settings. Acta Trop. 2017, 165, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomenko, S.; Rozstalnyy, A.; Dhingra, M. African Swine Fever Epidemiology and Geographic Information Systems; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, W.; Damrongwatanapokin, T.; Larntz, K.; Morrison, R. The Use of a Geographic Information System in an Epidemiological Study of Pseudorabies (Aujeszky’s Disease) in Minnesota Swine Herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 1991, 11, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, J.S. The Use of GIS in the Management of Wildlife Diseases. In GIS and Spatial Analysis in Veterinary Science; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 249–283. [Google Scholar]
- Llonch, P.; Guevara, R.D.; Camerlink, I. Effects of Climate Change on Pig Welfare. In Advances in Pig Welfare; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 557–576. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, S.; Bosch, J.; Martínez-Avilés, M.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. The Evolution of African Swine Fever in China: A Global Threat? Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 828498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orusa, T.; Viani, A.; Moyo, B.; Cammareri, D.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Risk Assessment of Rising Temperatures Using Landsat 4–9 LST Time Series and Meta® Population Dataset: An Application in Aosta Valley, NW Italy. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.A.; Carpenter, T.E. Spatial Analytical Methods and Geographic Information Systems: Use in Health Research and Epidemiology. Epidemiol. Rev. 1999, 21, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, A.; Khashoggi, B.F. Using GIS for Disease Mapping and Clustering in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.J.; Byrne, A.W.; Marples, N.; O’Hagan, M.J.; Kelly, D.J.; Quinn, D.; Breslin, P.; Morera-Pujol, V.; Khouri, R.M.; Barrett, D.; et al. Wildlife Response to Land-Use Change Forces Encounters between Zoonotic Disease Hosts and Farms in Agricultural Landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 386, 109561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, S.A. Spatial Epidemiology and GIS in Marine Mammal Conservation Medicine and Disease Research. EcoHealth 2008, 5, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, S.A.; DiGiacomo, R.F.; Gulland, F.M.; Meschke, J.S.; Lowry, M.S. Risk Factors for an Outbreak of Leptospirosis in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus) in California, 2004. J. Wildl. Dis. 2008, 44, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norstrøm, M. Geographical Information System (GIS) as a Tool in Surveillance and Monitoring of Animal Diseases. Acta Vet. Scand. 2001, 42, S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusser, S.M.; Clark, W.R.; Otis, D.L.; Huang, L. Sampling Considerations for Disease Surveillance in Wildlife Populations. J. Wildl. Manag. 2008, 72, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeyinka, O.T.; Omaghomi, T.T. Wildlife as Sentinels for Emerging Zoonotic Diseases: A Review of Surveillance Systems in the USA. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 21, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, R.S.; Glass, G.E.; Keesing, F. Spatial Epidemiology: An Emerging (or Re-Emerging) Discipline. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, F. Spatial Epidemiology and Its Role in Prevention and Control of Swine Viral Disease. Animals 2024, 14, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Laddomada, A.; Arias, M.L. African Swine Fever Virus. In Diseases of Swine; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Ryser-Degiorgis, M.-P. Wildlife Health Investigations: Needs, Challenges and Recommendations. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Lv, C. Modern Technologies and Solutions to Enhance Surveillance and Response Systems for Emerging Zoonotic Diseases. Sci. One Health 2024, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Petris, S.; Orusa, T.; Viani, A.; Feliziani, F.; Sordilli, M.; Troisi, S.; Zoppi, S.; Ragionieri, M.; Orusa, R.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Spatio-Temporal Pattern Analysis of African Swine Fever Spreading in Northwestern Italy—The Role of Habitat Interfaces. Animals 2025, 15, 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192886
De Petris S, Orusa T, Viani A, Feliziani F, Sordilli M, Troisi S, Zoppi S, Ragionieri M, Orusa R, Borgogno-Mondino E. Spatio-Temporal Pattern Analysis of African Swine Fever Spreading in Northwestern Italy—The Role of Habitat Interfaces. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192886
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Petris, Samuele, Tommaso Orusa, Annalisa Viani, Francesco Feliziani, Marco Sordilli, Sabatino Troisi, Simona Zoppi, Marco Ragionieri, Riccardo Orusa, and Enrico Borgogno-Mondino. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Pattern Analysis of African Swine Fever Spreading in Northwestern Italy—The Role of Habitat Interfaces" Animals 15, no. 19: 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192886
APA StyleDe Petris, S., Orusa, T., Viani, A., Feliziani, F., Sordilli, M., Troisi, S., Zoppi, S., Ragionieri, M., Orusa, R., & Borgogno-Mondino, E. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Pattern Analysis of African Swine Fever Spreading in Northwestern Italy—The Role of Habitat Interfaces. Animals, 15(19), 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192886









