Production of Cloned Bighorn Sheep Embryos Using ISCNT via HMC from Domestic Sheep Oocytes Treated with Resveratrol During IVM
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Culture of Fibroblasts from Bighorn Sheep (O. c. mexicana)
2.2. In Vitro Maturation of Domestic Sheep (O. aries) Oocytes
2.3. Production of O. c. mexicana Cloned Embryos Through ISCNT via HMC
2.4. Statistical Analysis
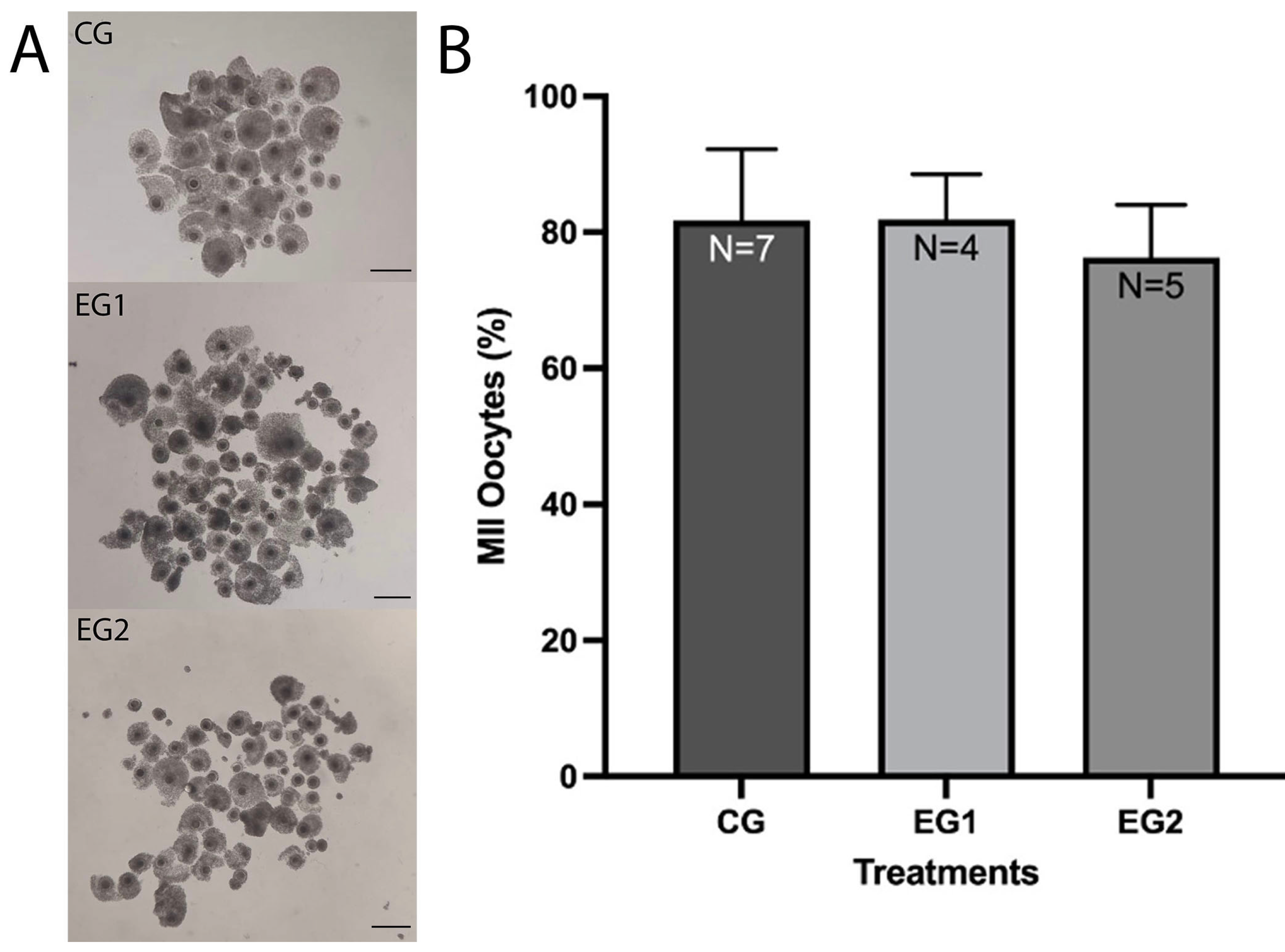
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Resveratrol on the IVM Rate of O. aries oocytes
3.2. Production of Cloned O. c. mexicana Embryos Using ISCNT via HMC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gobierno de México. Bancos de Germoplasma, Protectores de la Soberanía Nacional. 17 November 2023. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/agricultura/articulos/productor-productora-ya-conoces-los-bancos-de-germoplasma-aqui-te-contamos?idiom=es (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Festa-Bianchet, M. Ovis canadensis. IUCN Red List. Threat. Species 2020, E.T15735A22146699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antaño, A.D.L.; Mireya, G.C. Capítulo 3. Mamíferos en peligro de extinción: Un contexto global una solución local. In Estrategias para Recuperar Mamíferos en Riesgo, 1st ed.; Córdova, A.T., García, D.A., del Carmen Navarro Maldonado, M., Miranda, B.V., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Unidad Iztapalapa: Mexico City, Mexico, 2024; pp. 47–55, 50 Aniversario; ISBN 978-607-28-3321-0. [Google Scholar]
- Medrano, M.R. Capítulo 5. Plan de manejo estatal para la conservación, manejo y aprovechamiento sustentable del Borrego cimarrón de BCS (Un ejemplo de manejo in situ). In Acciones en México para Recuperar Poblaciones de Mamíferos en Riesgo, 1st ed.; del Carmen Navarro Maldonado, M., Miranda, B.V., Córdova, A.T., García, D.A., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Unidad Iztapalapa: Mexico City, Mexico, 2021; pp. 87–110. ISBN 978-607-28-2440-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gobierno de México. En Franja de Recuperación, Borrego Cimarrón en México. Secretaria de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. 5 March 2015. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/prensa/en-franca-recuperacion-borrego-cimarron-en-mexico (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Rosete Fernández, J.V.; Álvarez, G.H.; Urbán, D.D.; Fragoso, I.A.; Asprón, P.M.A.; Ríos, U.A.; Pérez, R.S.; De La Torre, S.J.F. Biotecnologías reproductivas en el ganado bovino: Cinco décadas de investigación en México. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2021, 12 (Suppl. 3), 39–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Maldonado, M.C.; García, A.D.; Serrrano, H. Técnicas de clonación de embriones. Cienc. Vet. 2003, 9, 2003–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lagutina, I.; Fulka, H.; Lazzari, G.; Galli, C. Interspecies somatic cell nuclear transfer: Advancements and problems. Cell. Reprogramming 2013, 15, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Cocero, M.J.; Chesné, P.; Alabart, J.L.; Domínguez, V.; Cognié, Y.; Roche, A.; Fernández-Arias, A.; Martí, J.I.; Sánchez, P.; et al. First birth of an animal from an extinct subspecies (Capra pyrenaica pyrenaica) by cloning. Theriogenology 2009, 71, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, P.; Ptak, G.; Barboni, B.; Fulka, J., Jr.; Cappai, P.; Clinton, M. Genetic rescue of an endangered mammal by cross-species nuclear transfer using post-mortem somatic cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, R.P.; Cibelli, J.B.; Diaz, F.; Moraes, C.T.; Farin, P.W.; Farin, C.E.; Hammer, C.J.; West, M.D.; Damiani, P. Cloning of an endangered species (Bos gaurus) using interspecies nuclear transfer. Cloning 2000, 2, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martínez, S.; Hernández-Pichardo, J.E.; Vazquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Ambríz-García, D.A.; Navarro-Maldonado, M.d.C. Developmental dynamics of cloned Mexican bighorn sheep embryos using morphological quality standards. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmut, I.; Schnieke, A.E.; McWhir, J.; Kind, A.J.; Campbell, K.H. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature 1997, 385, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Arora, J.S.; Sethi, R.S.; Mukhopadhyay, C.S.; Verma, R. Handmade cloning: Recent advances, potential and pitfalls. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, C.; Lazzari, G. Current applications of SCNT in advanced breeding and genome editing in livestock. Reproduction 2021, 162, F23–F32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ibarra, J.L.; Espinoza-Mendoza, E.A.; Rangel-Santos, R.; Ambriz-García, D.A.; Navarro-Maldonado, M.D.C. Effect of resveratrol on the in vitro maturation of ovine (Ovis aries) oocytes and the subsequent development of handmade cloned embryos. Vet. México 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Garzón, A.C.; Ramón-Ugalde, J.P.; Ambríz-García, D.A.; Vazquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Hernández-Pichardo, J.E.; Rodríguez-Suastegui, J.L.; Cortez-Romero, C.; Del Carmen Navarro-Maldonado, M. Resveratrol Reduces ROS by Increasing GSH in Vitrified Sheep Embryos. Animals 2023, 13, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambini, J.; López-Grueso, R.; Olaso-González, G.; Inglés, M.; Abdelazid, K.; Alami, M.E.; Bonet-Costa, V.; Borrás, C.; Viña, J. Resveratrol: Distribución, propiedades y perspectivas. Rev. Española Geriatría Gerontol. 2013, 48, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.S.; Cheong, S.A.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, E.; Choi, K.C.; Jeung, E.B.; Hyun, S.H. The effects of resveratrol on porcine oocyte in vitro maturation and subsequent embryonic development after parthenogenetic activation and in vitro fertilization. Theriogenology 2012, 78, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Hernández-Martínez, S.; Hernández- Pichardo, J.E.; Rivera-Rebolledo, J.A.; Ambriz-García, D.A.; Navarro-Maldonado, M.C. Efecto del uso de medio secuencial humano en la producción de blastocistos de hembra Ovis canadensis mexicana por clonación manual interespecies. Acta Zoológica Mex. 2017, 33, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Maldonado, M.C.; Hernández-Martínez, S.; Vázquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Martínez-Ibarra, J.L.; Zavala-Vega, N.L.; Vargas-Miranda, B.; Rivera-Rebolledo, J.A.; Ambríz-García, D.A. Deriva de células epiteliales de tejido de piel descongelado de Ovis canadensis mexicana para la formación de un banco de germoplasma. Acta Zoológica Mex. 2015, 31, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asociación para el Estudio de la Biología Reproductiva (ASEBIR). Criterios ASEBIR de valoración morfológica de ovocitos, embriones tempranos y blastocistos humanos. In Cuadernos de Embriología Clínica, 3rd ed.; ASEBIR: Madrid, Spain, 2015; pp. 9–75. [Google Scholar]
- Vajta, G.; Korösi, T.; Du, Y.; Nakata, K.; Ieda, S.; Kuwayama, M.; Nagy, Z.P. The Well-of-the-Well system: An efficient approach to improve embryo development. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2008, 17, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakayama, S.; Ito, D.; Hayashi, E.; Ishiuchi, T.; Wakayama, T. Healthy cloned offspring derived from freeze-dried somatic cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.K.; Kang, M.H.; Gurunathan, S.; Cho, S.G.; Park, C.; Park, J.K.; Kim, J.H. Pifithrin-α ameliorates resveratrol-induced two-cell block in mouse preimplantation embryos in vitro. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itami, N.; Shirasuna, K.; Kuwayama, T.; Iwata, H. Resveratrol improves the quality of pig oocytes derived from early antral follicles through sirtuin 1 activation. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagafuchi, A.; Shirayoshi, Y.; Okazaki, K.; Yasuda, K.; Takeichi, M. Transformation of cell adhesión properties by exogenously introduced E-cadherin cDNA. Nature 1987, 29, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.J.; Barcroft, L.C. Regulation of blastocyst formation. Front. Biosci. 2001, 6, d708–d730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabeer, S.W.; Riaz, A.; Ul-Rahman, A.; Shahbakht, R.M.; Anjum, A.; Khera, H.U.R.A.; Haider, A.; Riaz, F.; Yasin, R.; Yaseen, M.; et al. Effect of different concentrations of resveratrol on nuclear maturation and in-vitro development competence of oocytes of Nili Ravi buffalo. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 56, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonekam, K.; Anthakat, Y.; Polrachom, A.; Samruan, W.; Anwised, P.; Boonchuen, P.; Ketudat-Cairns, M.; Parnpai, R. Resveratrol Supplementation in In Vitro Maturation and Culture Medium: Enhancing Blastocyst Viability After Vitrification. Anim. Sci. J. = Nihon Chikusan Gakkaiho 2025, 96, e70061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, A.; Shabankareh, H.K.; Hajarian, H.; Foroutanifar, S. Resveratrol addition to in vitro maturation and in vitro culture media enhances developmental competence of sheep embryos. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2019, 68, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, T.K.; Xiang, T.; Romo, S.; Kjelland, M.E. Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis canadensis) embryos produced using somatic cell nuclear transfer. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2014, 26, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajta, G.; Lewis, I.M.; Hyttel, P.; Thouas, G.A.; Trounson, A.O. Somatic cell cloning without micromanipulators. Cloning 2001, 3, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Kragh, P.; Zhang, X.; Purup, S.; Yang, H.; Bolund, L.; Vajta, G. High Overall In Vitro Efficiency of Porcine Handmade Cloning (HMC) Combining Partial Zona Digestion and Oocyte Trisection with Sequential Culture. Cloning Stem Cells 2005, 7, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbha, R.; Hosny, N.; Matson, A.; Steinhoff, M.; Hering, B.J.; Burlak, C. Efficient production of GGTA1 knockout porcine embryos using a modified handmade cloning (HMC) method. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 128, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, P.; Dou, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Lin, L.; Tan, P.; Vajta, G.; Gao, J.; Du, Y.; et al. Handmade cloned transgenic sheep rich in omega-3 Fatty acids. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecirlioglu, R.T.; Cooney, M.A.; Lewis, I.M.; Korfiatis, N.A.; Hodgson, R.; Ruddock, N.T.; Vajta, G.; Downie, S.; Trounson, A.O.; Holland, M.K.; et al. Comparison of two approaches to nuclear transfer in the bovine: Hand-made cloning with modifications and the conventional nuclear transfer technique. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2005, 17, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajta, G.; Lewis, I.M.; Trounson, A.O.; Purup, S.; Maddox-Hyttel, P.; Schmidt, M.; Pedersen, H.G.; Greve, T.; Callesen, H. Handmade somatic cell cloning in cattle: Analysis of factors contributing to high efficiency in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, J.; Murga, N.; Segura, G.; Rodríguez, L.; Vásquez, H.; Maicelo-Quintana, J. Capacidad de Dos Líneas Celulares para la Producción de Embriones Clonados mediante Transferencia Nuclear de Células Somáticas. Rev. De Investig. Vet. Del Perú 2017, 28, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagutina, I.; Lazzari, G.; Duchi, R.; Colleoni, S.; Ponderato, N.; Turini, P.; Crotti, G.; Galli, C. Somatic cell nuclear transfer in horses: Effect of oocyte morphology, embryo reconstruction method, and donor cell type. Reproduction 2005, 130, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selokar, N.L.; George, A.; Saha, A.P.; Sharma, R.; Muzaffer, M.; Shah, R.A.; Palta, P.; Chauhan, M.S.; Manik, R.S.; Singla, S.K. Production of interspecies handmade cloned embryos by nuclear transfer of cattle, goat, and rat fibroblasts to buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) oocytes. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 123, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, D.; Selokar, N.L.; Raja, A.K.; Saini, M.; Sahare, A.A.; Nala, N.; Palta, P.; Chauhan, M.S.; Manik, R.S.; Singla, S.K. Production of wild buffalo (Bubalus arnee) embryos by interspecies somatic cell nuclear transfer using domestic buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) oocytes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. = Zuchthygiene 2014, 49, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duah, E.K.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Sood, T.J.; Sandhu, A.; Singla, S.K.; Chauhan, M.S.; Manik, R.S.; Palta, P. Production of hand-made cloned buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos from non-viable somatic cells. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2016, 52, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, F. Development of interspecies nuclear transfer embryos reconstructed with argali (Ovis ammon) somatic cells and sheep ooplasm. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Forouzanfar, M.; Abedi, P.; Ostadhosseini, S.; Hosseini, L.; Moulavi, F.; Gourabi, H.; Shahverdi, A.H.; Vosough Taghi Dizaj, A.; et al. “Conservation cloning” of vulnerable Esfahan mouflon (Ovis orientalis isphahanica): In vitro and in vivo studies. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2011, 57, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmet, K.; Wolf, E.; Zakhartchenko, V. Manipulating the Epigenome in Nuclear Transfer Cloning: Where, When and How. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Ambríz-García, D.A.; Cortez-Romero, C.; Trejo-Córdova, A.; del Carmen Navarro-Maldonado, M. Current state of the efficiency of sheep embryo production through somatic cell nuclear transfer. Small Rum. Res. 2022, 212, 106702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
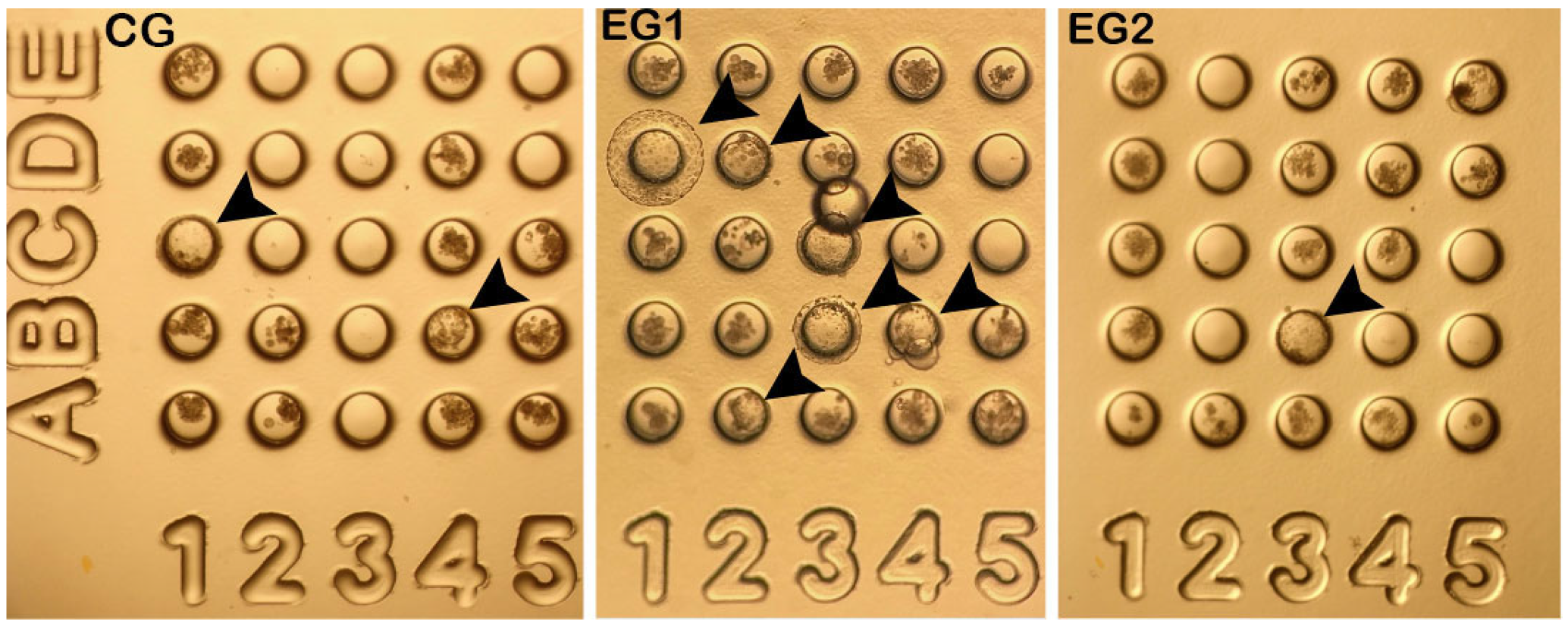
| Group | No. | Cleavage N (%) | 4–16 Cells N (%) | Morula N (%) | Blastocysts N (%) | Fragmented N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 40 | 38 (94 ± 8.0) | 6 (16 ± 18.5) | 9 (21 ± 15.4) | 6 (16 ± 3.2) a | 17 (46 ± 8.8) a |
| EG1 | 69 | 69 (100) | 12 (20 ± 22.9) | 16 (24 ± 6.5) | 22 (31 ± 12.0) b | 19 (25 ± 10.4) b |
| EG2 | 32 | 32 (100) | 8 (20 ± 19.9) | 8 (26 ± 17.3) | 2 (6 ± 6.3) a | 14 (42 ± 6.4) a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vazquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Ambríz-García, D.A.; Trejo-Córdova, A.; Sandoval-Zárate, J.A.; Gual-Sill, F.; Nuñez-Macias, J.E.; Casillas, F.; Navarro-Maldonado, M.d.C. Production of Cloned Bighorn Sheep Embryos Using ISCNT via HMC from Domestic Sheep Oocytes Treated with Resveratrol During IVM. Animals 2025, 15, 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192872
Vazquez-Avendaño JR, Ambríz-García DA, Trejo-Córdova A, Sandoval-Zárate JA, Gual-Sill F, Nuñez-Macias JE, Casillas F, Navarro-Maldonado MdC. Production of Cloned Bighorn Sheep Embryos Using ISCNT via HMC from Domestic Sheep Oocytes Treated with Resveratrol During IVM. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192872
Chicago/Turabian StyleVazquez-Avendaño, José Roberto, Demetrio Alonso Ambríz-García, Alfredo Trejo-Córdova, José Antonio Sandoval-Zárate, Fernando Gual-Sill, Jessica Elivier Nuñez-Macias, Fahiel Casillas, and María del Carmen Navarro-Maldonado. 2025. "Production of Cloned Bighorn Sheep Embryos Using ISCNT via HMC from Domestic Sheep Oocytes Treated with Resveratrol During IVM" Animals 15, no. 19: 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192872
APA StyleVazquez-Avendaño, J. R., Ambríz-García, D. A., Trejo-Córdova, A., Sandoval-Zárate, J. A., Gual-Sill, F., Nuñez-Macias, J. E., Casillas, F., & Navarro-Maldonado, M. d. C. (2025). Production of Cloned Bighorn Sheep Embryos Using ISCNT via HMC from Domestic Sheep Oocytes Treated with Resveratrol During IVM. Animals, 15(19), 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192872






