Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Developmental Toxicity Induced by Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Fenvalerate and Sulfamethoxazole in Embryo and Juvenile Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma, McClelland, 1839)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Exposure Concentration Selection
2.2. Embryo Collection and Juvenile Fish Culture of Marine Medaka
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.5. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
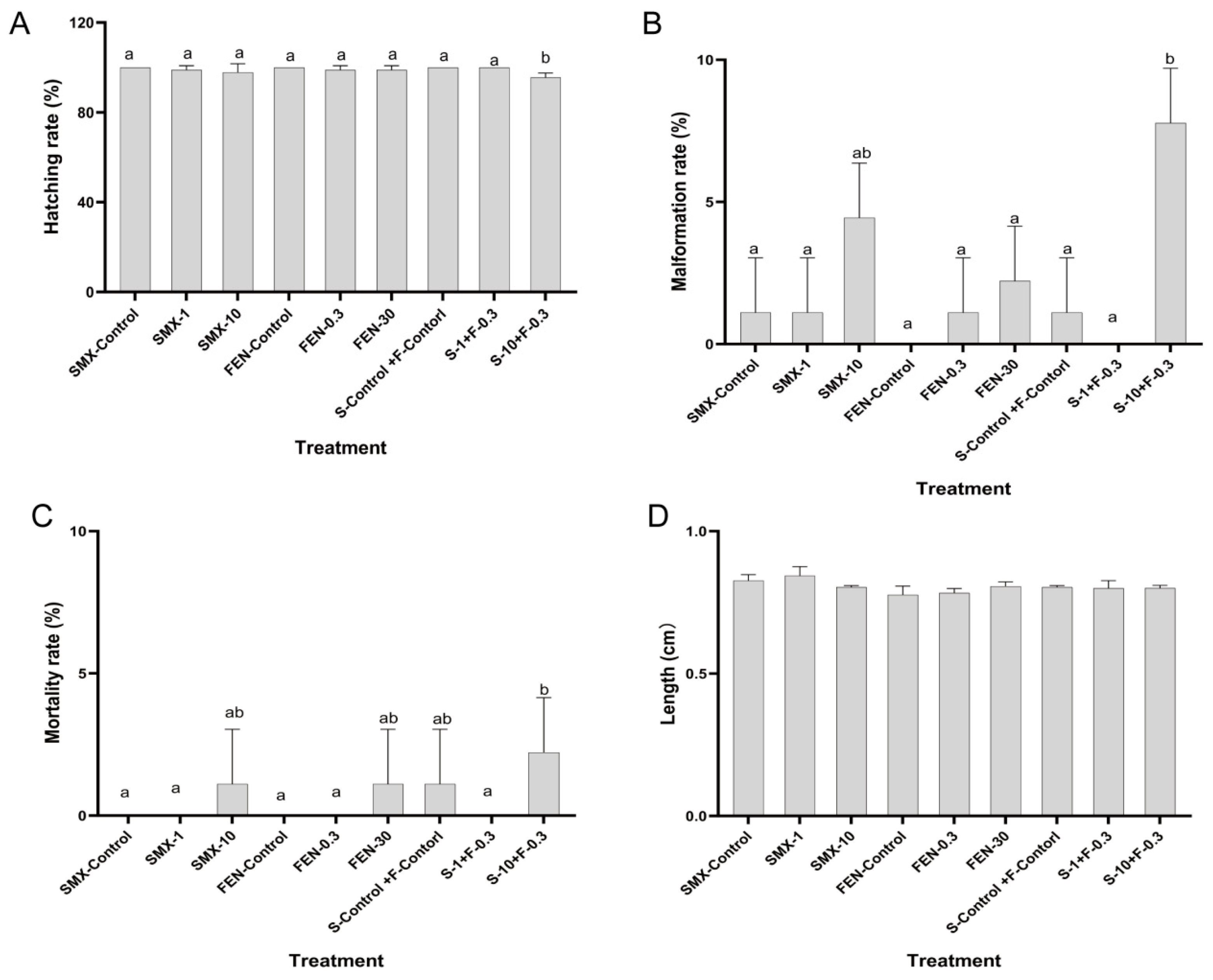
3.1. Effect of FEN and SMX on Development of Embryos of Marine Medaka
3.2. Effects of FEN and SMX on Juvenile Marine Medaka H&E Sections
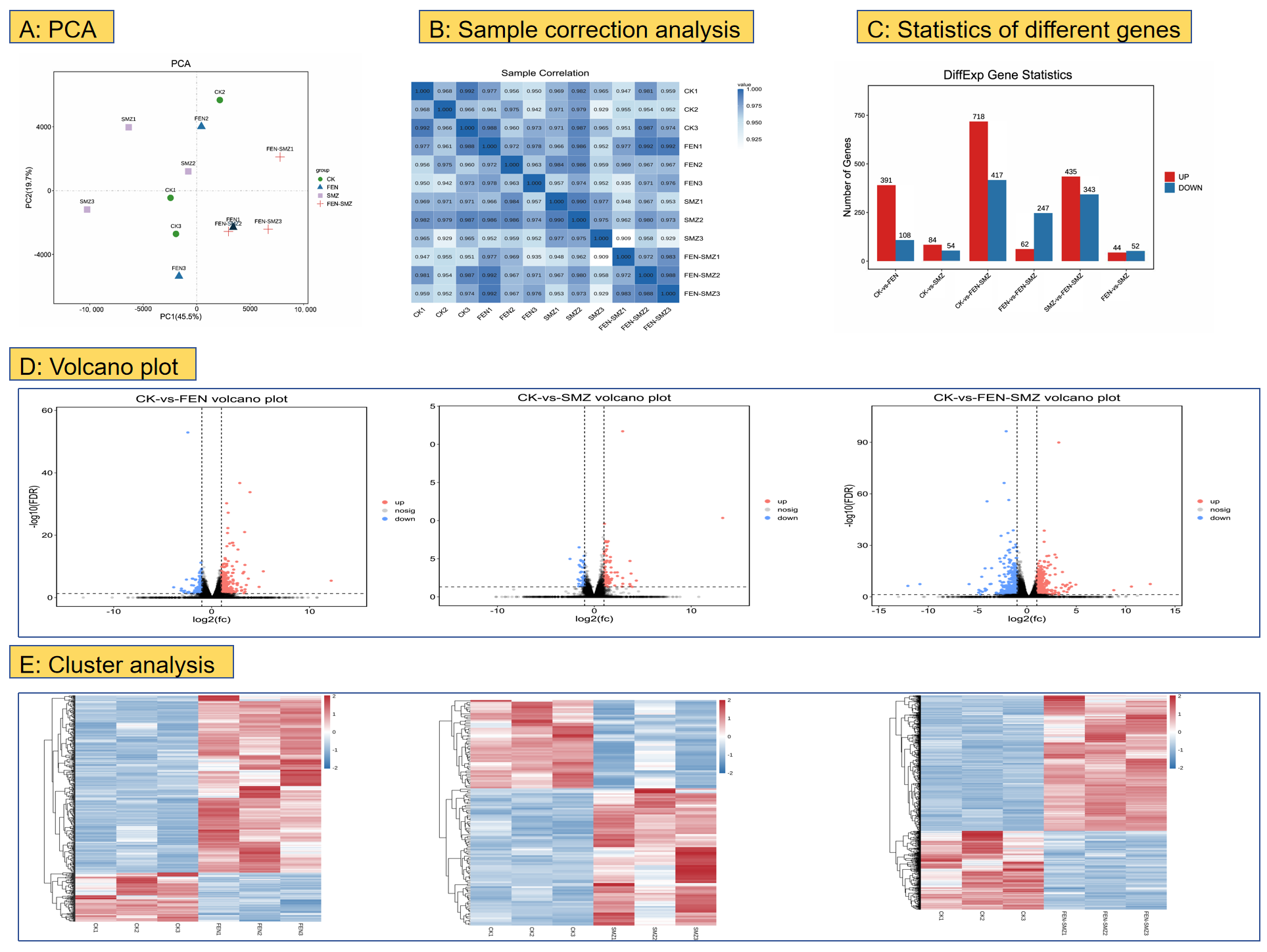
3.3. Transcriptomics
3.3.1. Analysis of DEGs
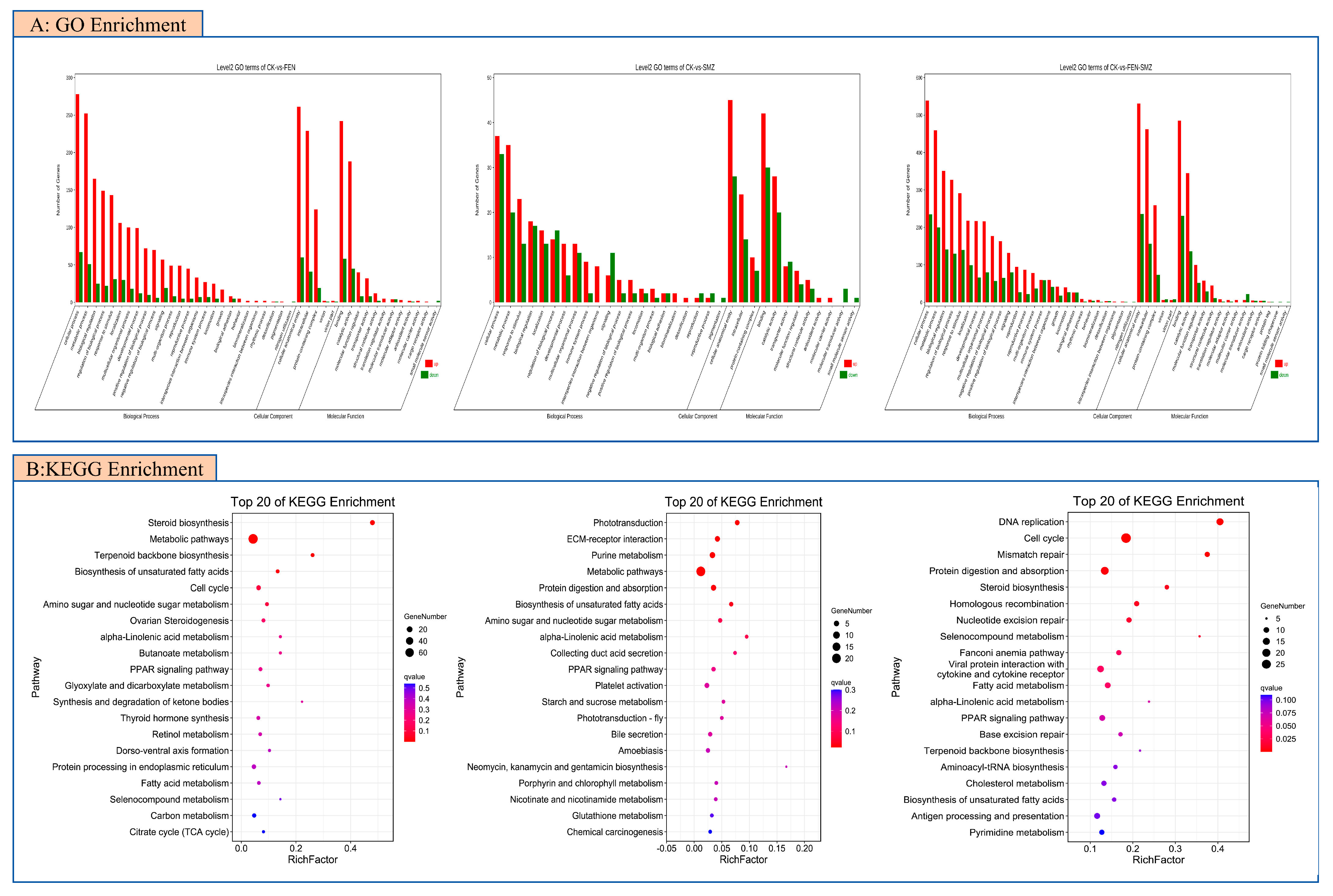
3.3.2. Gene Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Results of qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FEN | Fenvalerate |
| SMX | Sulfamethoxazole |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription PCR |
| LC-PUFA | Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| PCNA | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
References
- Zhu, H.M.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Shao, J.; Chen, H.R.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.H.; Li, J.J.; Wang, M.; Xu, D.X.; et al. Prenatal exposure to fenvalerate causes depressive-like behavior in adulthood by inhibiting brain-derived 5-HT synthesis. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafarifarsani, H.; Rohani, M.F.; Raeeszadeh, M.; Ahani, S.; Yousefi, M.; Talebi, M.; Hossain, M.S. Pesticides and heavy metal toxicity in fish and possible remediation—A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 1007–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodosan, C.; Gird, C.E.; Ghica, M.V.; Dinu-Pirvu, C.E.; Nistor, L.; Barbuica, I.S.; Marin, S.C.; Mihalache, A.; Popa, L. Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids: A Comprehensive Review of Natural Occurring Compounds and Their Synthetic Derivatives. Plants 2023, 12, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Y.; Ma, R.; Tong, G.; Wei, X.; Feng, D.; Hu, K. Transcriptome analysis to elucidate the toxicity mechanisms of fenvalerate, sulfide gatifloxacin, and ridomil on the hepatopancreas of Procambarus clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 116, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Weng, H.; Wang, Q. Mixture toxicity of thiophanate-methyl and fenvalerate to embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio) and its underlying mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.S.; Huang, M.T.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Zou, L.; Yang, F.; Zhu, R.F. Curcumin protects against fenvalerate-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae through inhibition of oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Ji, C.; Guo, Y.; Yan, R.; Hong, T.; Dou, Y.; An, Y.; Tao, S.; Qin, F.; Nie, J.; et al. Mechanisms underlying melatonin-mediated prevention of fenvalerate-induced behavioral and oxidative toxicity in zebrafish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2017, 80, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, R.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Gong, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Fenvalerate triggers Parkinson-like symptom during zebrafish development through initiation of autophagy and p38 MAPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archundia, D.; Boithias, L.; Duwig, C.; Morel, M.C.; Flores Aviles, G.; Martins, J.M.F. Environmental fate and ecotoxicological risk of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole across the Katari catchment (Bolivian Altiplano): Application of the GREAT-ER model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wang, X.D.; Yang, S.S.; Gu, J.; Deng, J.Y.; Zhang, X.E. Anti-folates potentiate bactericidal effects of other antimicrobial agents. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, N.; Yonar, M.E. Effects of sulfamerazine on selected haematological and immunological parameters in rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum, 1792). Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, T.; Wu, X.; Zhong, H.; Qiu, W.; Zheng, Y. Early exposure to environmental levels of sulfamethoxazole triggers immune and inflammatory response of healthy zebrafish larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, M. Effects of environmentally relevant cypermethrin and sulfamethoxazole on intestinal health, microbiome, and liver metabolism in grass carp. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 265, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbu, S.M.; Zhou, L.; Sun, S.X.; Zhang, M.L.; Du, Z.Y. Chronic exposure to low environmental concentrations and legal aquaculture doses of antibiotics cause systemic adverse effects in Nile tilapia and provoke differential human health risk. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurais, D.; Ernande, B.; Quazuguel, P.; Severe, A.; Huelvan, C.; Madec, L.; Mouchel, O.; Soudant, P.; Robbens, J.; Huvet, A.; et al. Evaluation of the impact of polyethylene microbeads ingestion in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 112, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hong, X.S.; Yan, S.H.; Zha, J.M. Environmentally relevant concentrations of fenvalerate induces immunotoxicity and reduces pathogen resistance in Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, M.R. Environmentally relevant levels of λ-cyhalothrin, fenvalerate, and permethrin cause developmental toxicity and disrupt endocrine system in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, B.; Senthilkumaar, P.; Karthikeyan, S. Toxicity impact of fenvalerate on the gill tissue of Oreochromis mossambicus with respect to biochemical changes utilizing FTIR and principal component analysis. J. Biol. Phys. 2018, 44, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Shi, H.Q.; Peng, Y.L.; Han, M.L.; Hu, T.L.; Liao, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G.X. Enhanced hepatotoxicity in zebrafish due to co-exposure of microplastics and sulfamethoxazole: Insights into ROS-mediated MAPK signaling pathway regulation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buah-Kwofie, A.; Humphries, M.S.; Pillay, L. Bioaccumulation and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in fish from a global biodiversity hotspot: ISimangaliso Wetland Park, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Osachoff, H.L.; Kennedy, C.J. Physiological disturbances in juvenile sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) exposed to the water-soluble fraction of diluted bitumen. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 220, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Feng, C.; Gu, E.; Tian, C.; Shen, Z. Spatial distribution, source apportionment and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water and sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.X.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.Q.; Wu, Z.W.; Li, L.Y.; Huang, M.L.; Xu, S.H.; Yan, D.Y. Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: An overview. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Xing, M. Environmentally relevant concentration of cypermethrin or/and sulfamethoxazole induce neurotoxicity of grass carp: Involvement of blood-brain barrier, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, H.; Duan, S. Multigenerational reproduction and developmental toxicity, and HPG axis gene expression study on environmentally-relevant concentrations of nonylphenol in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 144259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Q.; Fang, C.; Ye, T.; Qiu, L.; Dong, S. PFOS induced precocious hatching of Oryzias melastigma—From molecular level to individual level. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Chen, M.Y.; He, S.Q.; Fang, C.; Chen, M.L.; Li, D.; Wu, D.; Chernick, M.; Hinton, D.E.; Bo, J.; et al. Microplastics decrease the toxicity of triphenyl phosphate (TPhP) in the marine medaka (Oryzias Melastigma) larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wu, X.; Huang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Liu, L.; Qiu, L.; Shen, H.; Dong, S. PFOS elicits transcriptional responses of the ER, AHR and PPAR pathways in Oryzias melastigma in a stage-specific manner. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 106, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhong, D.; Shi, D. Bone developmental toxicity of organophosphorus flame retardants TDCIPP and TPhP in marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Kang, M.; Huang, Q.; Fang, C.; Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; Dong, S. Exposure to DEHP and MEHP from hatching to adulthood causes reproductive dysfunction and endocrine disruption in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 146, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ding, H.; Jin, C.; Wang, M.; Li, P.; Bao, Z.; Wang, B.; Hu, J. Theoretical Analysis and Expression Profiling of 17beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Genes in Gonadal Development and Steroidogenesis of Leopard Coral Grouper (Plectropomus leopardus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, V.; Mauro, M.; Celi, M.; Cammilleri, G.; Vizzini, A.; Luparello, C.; Bellini, P.; Ferrantelli, V.; Vazzana, M. Effects of Sulfamethoxazole on Fertilization and Embryo Development in the Arbacia lixula Sea Urchin. Animals 2022, 12, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, M.; Xu, H.; Nasir, S.; Wu, M.; Qiu, J.; Li, M. Combined exposure to fenvalerate and tebuconazole induces apoptosis, leading to developmental and endocrine toxicity in early life stages of Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 297, 110280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Lu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Guo, R.; Chen, J. Integrated toxic evaluation of sulfamethazine on zebrafish: Including two lifespan stages (embryo-larval and adult) and three exposure periods (exposure, post-exposure and re-exposure). Chemosphere 2018, 195, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Xing, M.; Wang, Y. Lycopene regulates Nrf2 to Ameliorate Sulfamethoxazole -induced renal injury and apoptosis via inhibiting oxidative stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum stress. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 283, 107348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.F.; Li, X.H.; Cheng, P.; Mai, J.Q.; Sun, Y.Q.; Wang, J.C.; Shi, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Chen, S.L. Characterization of emopamil binding protein (Cs-ebp) reveals its potential role in cholesterol biosynthesis and growth performance of Chinese tongue sole. Aquaculture 2024, 581, 740382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, G. ANGPTL4-A protein involved in glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and tumor development. J. Gene Med. 2024, 26, e3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.P.; Xiao, Y.B.; Huang, R.; Zhao, D.F.; Xu, W.Q.; Li, S.T.; Tang, J.Z.; Qu, F.F.; Jin, J.Y.; Xie, S.Q.; et al. Dietary Supplementation With Hydroxyproline Enhances Growth Performance, Collagen Synthesis and Muscle Quality of Triploid. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 913800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Ogawa, M.; Ayer, A.; Britton, W.J.; Stocker, R.; Kikuchi, K.; Oehlers, S.H. Zebrafish Heme Oxygenase 1a Is Necessary for Normal Development and Macrophage Migration. Zebrafish 2022, 19, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotti, S.; Di Biagio, C.; Huysseune, A.; Koppe, W.; Forlino, A.; Witten, P.E. Matrix first, minerals later: Fine-tuned dietary phosphate increases bone formation in zebrafish. JBMR Plus 2024, 8, ziae081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.Z.; Hu, Y.C.; Chen, P.; Zhu, X.; Wang, B.Z.; Cheng, C.; Tian, T.; Zhang, D.Z.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, Y. Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of fatty acyl desaturase (fads2) gene in Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Aquacult Rep. 2024, 38, 102338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemilainen, H.; Adam, M.; Maki-Jouppila, J.; Damdimopoulou, P.; Damdimopoulos, A.E.; Kere, J.; Hovatta, O.; Laajala, T.D.; Aittokallio, T.; Adamski, J.; et al. The Hydroxysteroid (17beta) Dehydrogenase Family Gene HSD17B12 Is Involved in the Prostaglandin Synthesis Pathway, the Ovarian Function, and Regulation of Fertility. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3719–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Chen, F.; Xu, T.; Cao, M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Guo, X.; Yin, D. BDE-99 Disrupts the Photoreceptor Patterning of Zebrafish Larvae via Transcription Factor six7. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5673–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, C.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Q. The functional differentiation of four smad4 paralogs in TGF-beta signaling pathway of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Cell. Signal. 2020, 71, 109601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Alexander, P.B.; Wang, X.-F. TGF-β Family Signaling in the Control of Cell Proliferation and Survival. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Holzschuh, J.; Erhardt, S.; Ettl, A.K.; Driever, W. Depletion of minichromosome maintenance protein 5 in the zebrafish retina causes cell-cycle defect and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18467–18472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Sense Primer (5′-3′) | Antisense Primer (5′-3′) | GeneBank Number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18s | AACGCTGTGCTGCGTAGCCTCAATT | AGAAGAAGCCCCACTTTTCCTCGCA | DQ105650 | [28] |
| Six3 | GACTGACCCCGACTCAAGTG | CCGAGTCACTGTCCGTTACT | XM_024285009 | [29] |
| Cyp1a | TCGTCGTTCTAAGTGGCAATGAAAC | AGAAAGAGCGCAATGCACTGTAGG | [30] | |
| Runx2 | TCTACGGACCTGAGCCCGTT | GGAGGAGGCGCCGTAGTAGA | [31] | |
| Hsd17B | CGCTACCTCCACAAAGTTGTTGTC | AGTTCTGCCTCAACAGTTTCACCT | KF742611 | [32] |
| AR | TTTGATGAACTGCGGACCTCCTAC | AACTGGTGCAATTTCCTCACAACC | KF742606 | [32] |
| ERα | TCGCCGCTGTTGTGCTGTGATGTT | TCCTGGATCTGAGTGCGGGTCCGA | JF907629 | [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Duan, M.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Sun, D. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Developmental Toxicity Induced by Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Fenvalerate and Sulfamethoxazole in Embryo and Juvenile Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma, McClelland, 1839). Animals 2025, 15, 2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182765
Chen S, Duan M, Liu Q, Huang Y, Sun D. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Developmental Toxicity Induced by Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Fenvalerate and Sulfamethoxazole in Embryo and Juvenile Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma, McClelland, 1839). Animals. 2025; 15(18):2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182765
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuyuan, Meina Duan, Qian Liu, Yuna Huang, and Dong Sun. 2025. "Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Developmental Toxicity Induced by Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Fenvalerate and Sulfamethoxazole in Embryo and Juvenile Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma, McClelland, 1839)" Animals 15, no. 18: 2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182765
APA StyleChen, S., Duan, M., Liu, Q., Huang, Y., & Sun, D. (2025). Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Developmental Toxicity Induced by Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Fenvalerate and Sulfamethoxazole in Embryo and Juvenile Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma, McClelland, 1839). Animals, 15(18), 2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182765






