Host Genetic Effects and Phenotypic Landscapes of Rumen Bacterial Enterotypes in a Large Sheep Population
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
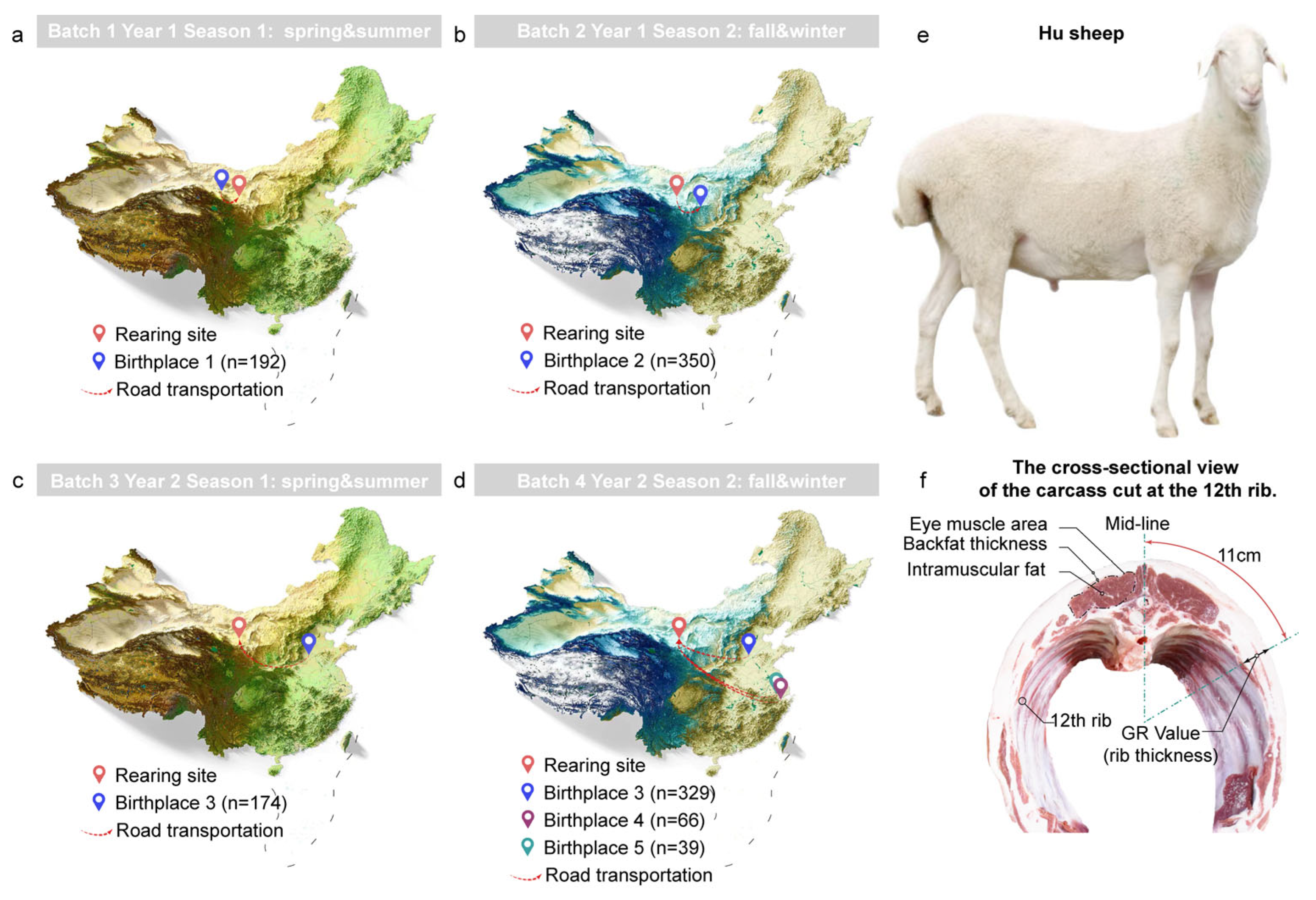
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. Animal Performance, Ruminal Fermentation, and Rumen Development Parameters
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Analysis
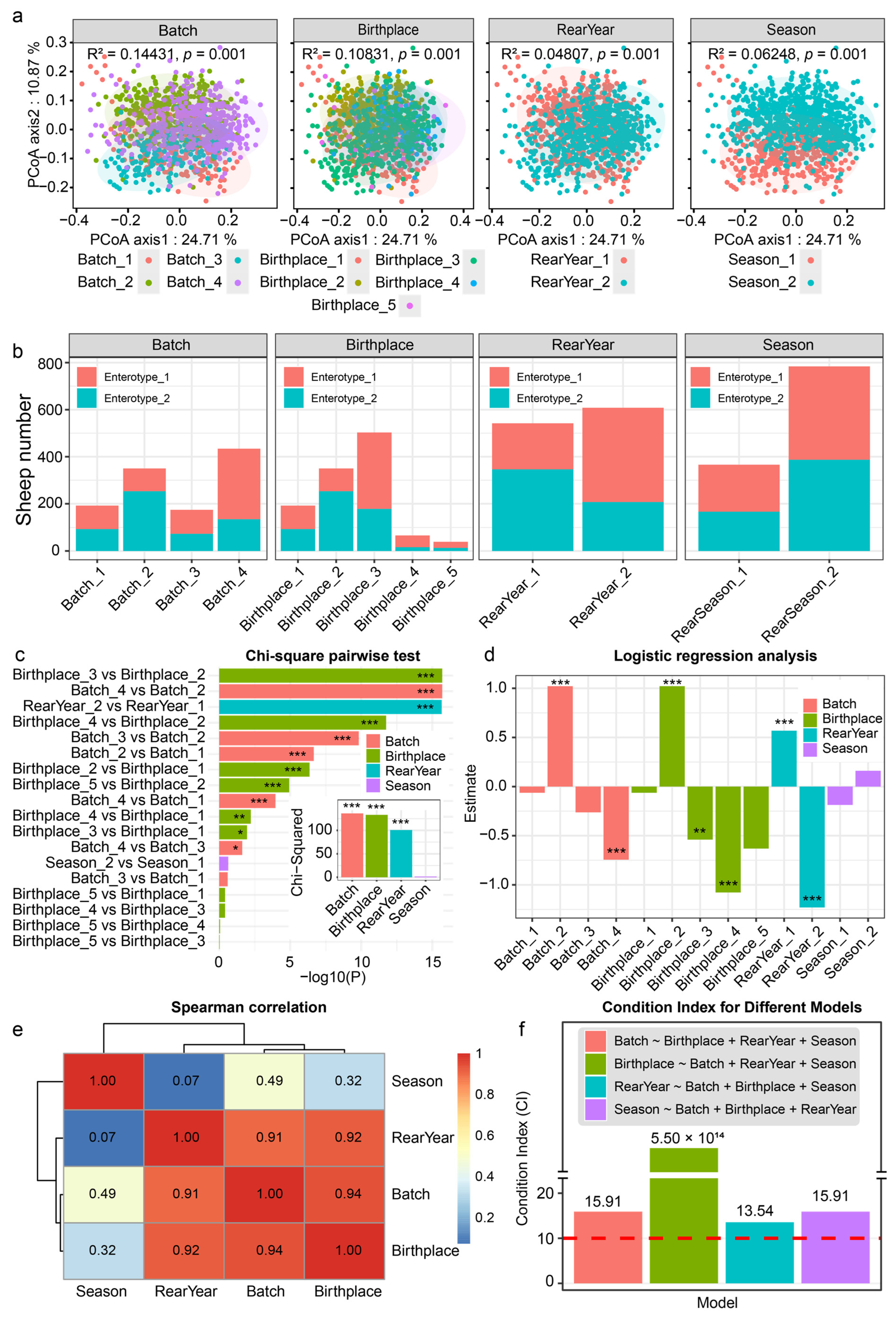
2.4. Analysis of Enterotype-Covariate Links and Covariate Collinearity
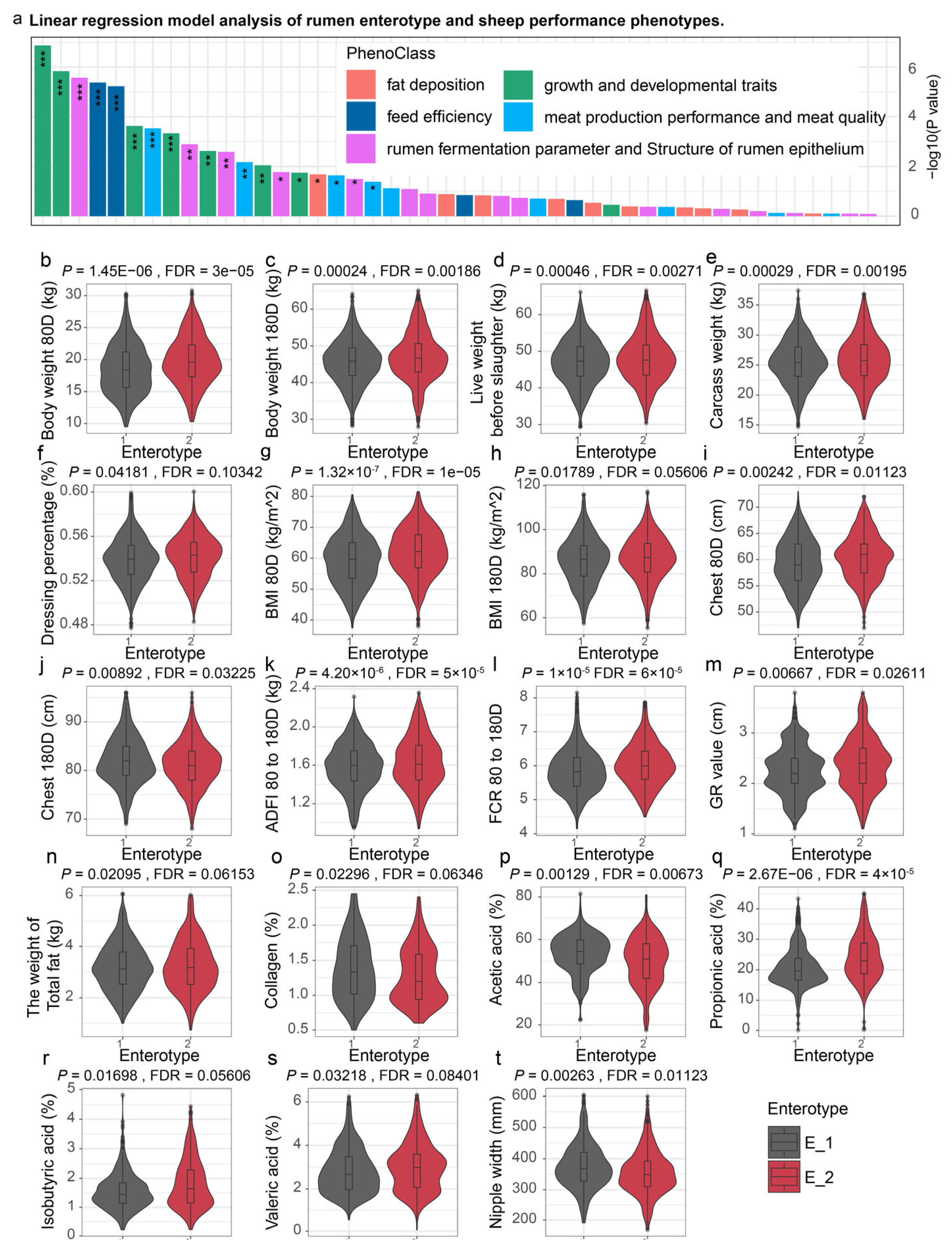
2.5. Linear Regression Model for Comparing Animal Phenotypes Across Enterotypes
2.6. Microbiota Differences Across Distinct Enterotypes
2.7. Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
2.8. Genotyping and Quality Control
2.9. Heritability, Genetic Correlation, and GWAS of Rumen Enterotypes
2.10. The Colocalization Relationship Between Enterotype GWAS Signals and Driving Bacteria GWAS Signals
2.11. The Influence of Significant Genetic Markers of Enterotype on Rumen Microbiota
3. Results
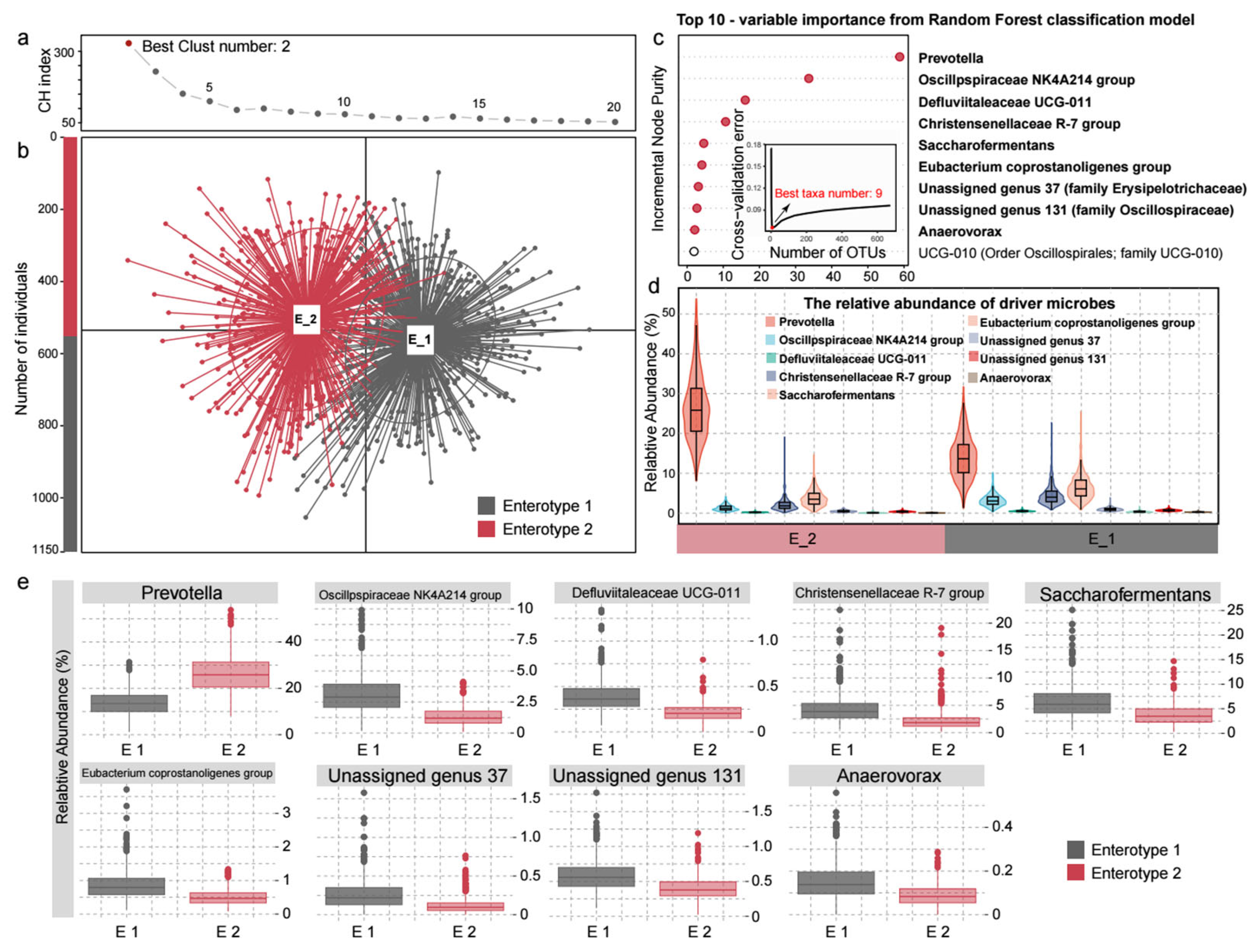
3.1. The Rumen-Enterotypes of the Hu Sheep and Associated Covariates
3.2. Association of Sheep Performance with Distinct Rumen Enterotypes
3.3. Enterotype-Specific Taxonomic Characteristics in Sheep Rumen Microbiome
3.4. The Co-Occurrence Network with Its Intrinsic Structure Revealed Enterotype-Specific Differences
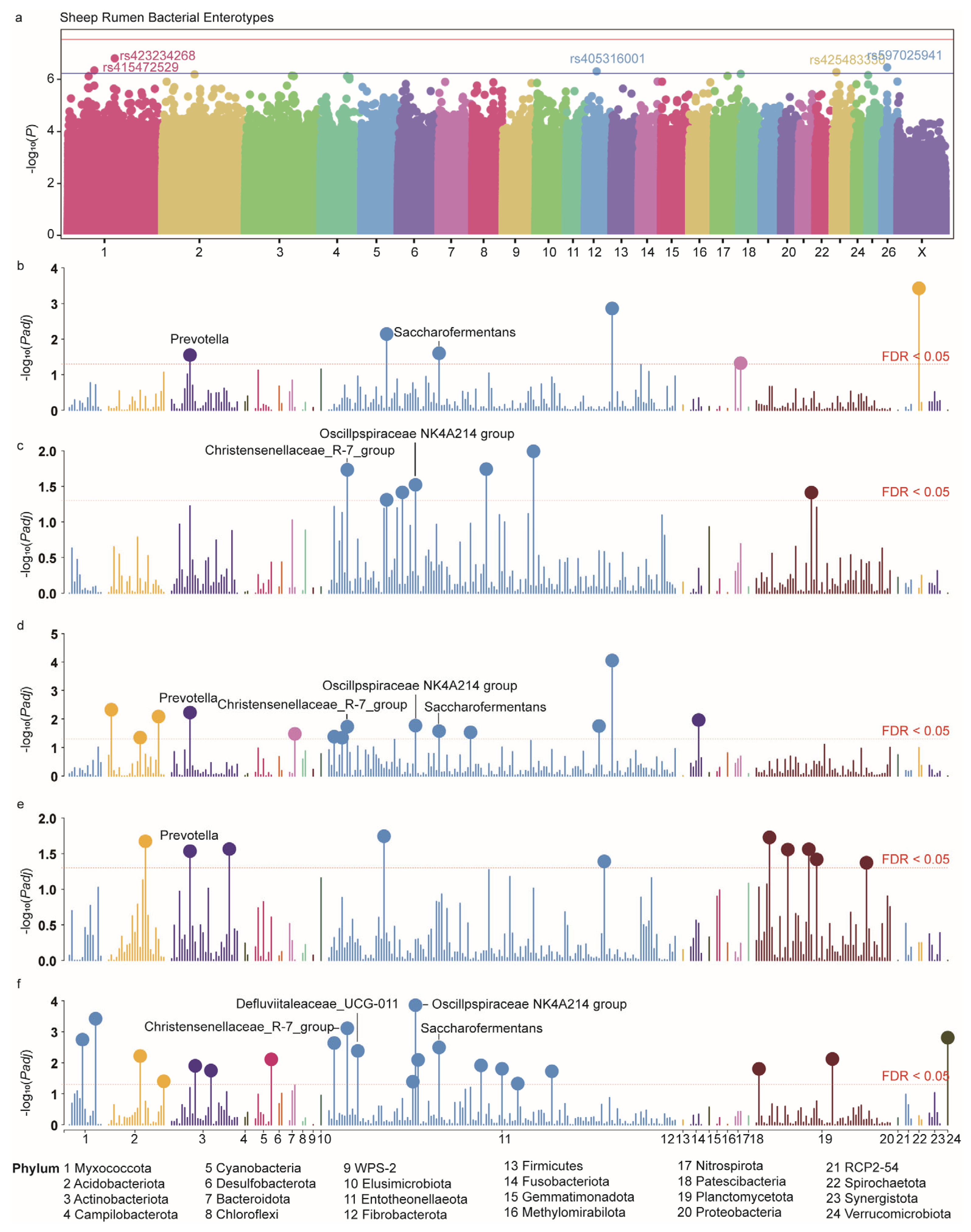
3.5. GWAS Identifies Several Genomic Variants Affecting Enterotype
3.6. Enterotype-Related Genetic Variations and Their Effects on Rumen Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E1 | Enterotype 1 |
| E2 | Enterotype 2 |
| INRAE | Institut National de Recherche pour l’Agriculture, l’Alimentation et l’Environnement |
| RF | Random Forest |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association studies |
| VFA | Volatile fatty acids |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| DMI | Dry matter intake |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| FI | Feed intake |
| ADFI | Average daily feed intake |
| FCR | Feed conversion ratio |
| ADG | Average daily gain |
| MBW | Mid-test metabolic weight |
| RFI | Residual feed intake |
| GR | Greville |
| EMA | Area of the eye muscle |
| ACE | Abundance-based Coverage Estimator |
| CI | Condition index |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| BH | Benjamini–Hochberg |
| ZIBR | Zero-Inflated Beta Regression |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| MAF | Minor Allele Frequency |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| REML | Restricted maximum likelihood |
| PCs | Principal components |
| GRM | Genomic relationship matrix |
| LRT | Likelihood ratio test |
| GLMM | Generalized linear mixed model |
| LEfse | Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| CH | Calinski–Harabasz |
| PAM | Partitioning around medoids |
References
- Lv, F.H.; Cao, Y.H.; Liu, G.J.; Luo, L.Y.; Lu, R.; Liu, M.J.; Li, W.R.; Zhou, P.; Wang, X.H.; Shen, M.; et al. Whole-Genome Resequencing of Worldwide Wild and Domestic Sheep Elucidates Genetic Diversity, Introgression, and Agronomically Important Loci. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msab353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cheng, J.; Li, X.; Huang, K.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X.; et al. Comprehensive multi-tissue epigenome atlas in sheep: A resource for complex traits, domestication, and breeding. iMeta 2024, 3, e254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bi, Y.; Ma, T.; Diao, Q.; Zhang, N. Sheep-derived butyrate-producing Clostridium beijerinckii R8 alleviates diarrhea by shaping the gut microbiota of goat kids. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 19, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Ma, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Jin, S.; Liu, S.; Zhong, J.; et al. Functional analysis of Parabacteroides distasonis F4: A novel probiotic strain linked to calf growth and rumen fermentation. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, E.N. Energy contributions of volatile fatty acids from the gastrointestinal tract in various species. Physiol. Rev. 1990, 70, 567–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Tian, H.; Weng, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, J.; et al. Rumen microbiome and fat deposition in sheep: Insights from a bidirectional mendelian randomization study. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Feng, X.R.; Zhao, W.; Bi, Y.L.; Diao, Q.Y.; Tu, Y. Rumen and hindgut microbiome regulate average daily gain of preweaning Holstein heifer calves in different ways. Microbiome 2024, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Dai, D.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Bi, Y.; et al. Rumen microbiome associates with postpartum ketosis development in dairy cows: A prospective nested case-control study. Microbiome 2025, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Zhu, S.; Xue, M.Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Song, M.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics across 2534 microbial species reveals functional heterogeneity in the rumen microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1884–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, P.I.; Hildebrand, F.; Arumugam, M.; Bäckhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Bushman, F.D.; de Vos, W.M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Hattori, M.; et al. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Sciellour, M.; Renaudeau, D.; Zemb, O. Longitudinal Analysis of the Microbiota Composition and Enterotypes of Pigs from Post-Weaning to Finishing. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Fang, S.; He, M.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Huang, L. Age-based dynamic changes of phylogenetic composition and interaction networks of health pig gut microbiome feeding in a uniformed condition. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Qi, Z.; Liu, C.; Ma, X. Micro-Coevolution of Genetics Rather Than Diet With Enterotype in Pigs. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 846974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarpong, N.; Seifert, J.; Bennewitz, J.; Rodehutscord, M.; Camarinha-Silva, A. Microbial signatures and enterotype clusters in fattening pigs: Implications for nitrogen utilization efficiency. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1354537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tröscher-Mußotter, J.; Saenz, J.S.; Grindler, S.; Meyer, J.; Kononov, S.U.; Mezger, B.; Borda-Molina, D.; Frahm, J.; Dänicke, S.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; et al. Microbiome Clusters Disclose Physiologic Variances in Dairy Cows Challenged by Calving and Lipopolysaccharides. mSystems 2021, 6, e0085621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gao, D.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Hou, G.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; et al. Maternal gastrointestinal microbiome shapes gut microbial function and resistome of newborns in a cow-to-calf model. Microbiome 2024, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Yin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Deng, L.; Yao, J.; et al. Multi-omics reveals that the host-microbiome metabolism crosstalk of differential rumen bacterial enterotypes can regulate the milk protein synthesis of dairy cows. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Choi, Y.; Seifert, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.J.; Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Guan, L.L.; Li, S. Temporal profiling of rumen and hindgut microbiota revealed enterotypes affecting the microbial interactions and assembly in the gut of dairy cows. ISME Commun. 2025, 5, ycaf130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lin, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Yang, X.; Xu, D.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity determines the gastrointestinal microbiome signatures and ecological processes that govern bacterial community assembly in sheep. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0111024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, J.; Lin, C.; et al. Heritability and recursive influence of host genetics on the rumen microbiota drive body weight variance in male Hu sheep lambs. Microbiome 2023, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larzul, C.; Estellé, J.; Borey, M.; Blanc, F.; Lemonnier, G.; Billon, Y.; Thiam, M.G.; Quinquis, B.; Galleron, N.; Jardet, D.; et al. Driving gut microbiota enterotypes through host genetics. Microbiome 2024, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W. Exploring the Ruminal Microbial Community Associated with Fat Deposition in Lambs. Animals 2021, 11, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Zhang, X.X.; Li, F.D.; Li, C.; Li, G.Z.; Zhang, D.Y.; Song, Q.Z.; Li, X.L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.M. Characterization of the rumen microbiota and its relationship with residual feed intake in sheep. Animal 2021, 15, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.M.; Morris, S.; Hopkins, D.L. Assessment of a probe to measure fat depth of lamb carcases. Meat Sci. 2020, 159, 107937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhu, S.L.; Zhong, Y.F.; Liu, J.X.; Sun, H.Z. Investigation of fiber utilization in the rumen of dairy cows based on metagenome-assembled genomes and single-cell RNA sequencing. Microbiome 2022, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Babraham Bioinformatics. 2013. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, S.N.; Qian, C.; Pan, J.; Rai, J.P.; Song, M.; Bagaitkar, J.; Merchant, M.; Cave, M.; Egilmez, N.K.; McClain, C.J. Microbiome data analysis with applications to pre-clinical studies using QIIME2: Statistical considerations. Genes Dis. 2021, 8, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.D.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2005. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Kim, S. ppcor: An R Package for a Fast Calculation to Semi-partial Correlation Coefficients. Commun. Stat. Appl. Methods 2015, 22, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinopoulos, D.M.; Rigby, R.A. Fitting non linear Generalized Additive Models for Location Scale and Shape (GAMLSS). J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 23, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. Complex Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wei, F.; Jin, X.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y.; Hu, Y. Quantitative microbiome profiling reveals the developmental trajectory of the chicken gut microbiota and its connection to host metabolism. iMeta 2023, 2, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasov, A.; Vilella, A.J.; Cuppen, E.; Nijman, I.J.; Prins, P. Sambamba: Fast processing of NGS alignment formats. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2032–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xia, X.; Hanif, Q.; Zhang, F.; Dang, R.; Huang, B.; Lyu, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Yan, H.; et al. Global genetic diversity, introgression, and evolutionary adaptation of indicine cattle revealed by whole genome sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Benyamin, B.; McEvoy, B.P.; Gordon, S.; Henders, A.K.; Nyholt, D.R.; Madden, P.A.; Heath, A.C.; Martin, N.G.; Montgomery, G.W.; et al. Common SNPs explain a large proportion of the heritability for human height. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wen, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.; Dong, Y.; Li, P.; et al. Genetic Basis and Identification of Candidate Genes for Alkalinity Tolerance Trait in Spotted Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) by Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS). Mar. Biotechnol. 2025, 27, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zeng, W.; Han, G.; Qiu, C.; Wang, T.; Tao, Z.; Wang, K.; et al. Linkage mapping combined with GWAS revealed the genetic structural relationship and candidate genes of maize flowering time-related traits. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wang, K.; Zhou, J.; Chen, D.; Jiang, A.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Qiu, X.; Li, X.; Tang, G. A combined GWAS approach reveals key loci for socially-affected traits in Yorkshire pigs. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Feng, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ren, G.; Wang, X.; et al. Fine mapping genetic variants affecting birth weight in sheep: A GWAS of 3007 individuals using low-coverage whole genome sequencing. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 16, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambartolomei, C.; Vukcevic, D.; Schadt, E.E.; Franke, L.; Hingorani, A.D.; Wallace, C.; Plagnol, V. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yan, W.; Sun, C.; Ji, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, J.; Yang, N. The gut microbiota is largely independent of host genetics in regulating fat deposition in chickens. Isme J. 2019, 13, 1422–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, D.; Yang, J.; Mao, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, C. Integrated multi-omics reveals the relationship between growth performance, rumen microbes and metabolic status of Hu sheep with different residual feed intakes. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 18, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Ma, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zou, Y.; Pu, L.; Yan, Q.; Kong, H.; Guo, X.; et al. Taeniasis impacts human gut microbiome composition and function. Isme J. 2024, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yao, J. Rumen bacterial cluster identification and its influence on rumen metabolites and growth performance of young goats. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 15, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.D.; Auffret, M.D.; Warr, A.; Walker, A.W.; Roehe, R.; Watson, M. Compendium of 4,941 rumen metagenome-assembled genomes for rumen microbiome biology and enzyme discovery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lee, Y.K.; Lu, W.; Li, M.; Chen, W. Chinese gut microbiota and its associations with staple food type, ethnicity, and urbanization. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Mahurkar, A.; Rahnavard, G.; Crabtree, J.; Orvis, J.; Hall, A.B.; Brady, A.; Creasy, H.H.; McCracken, C.; Giglio, M.G.; et al. Strains, functions and dynamics in the expanded Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2017, 550, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, D.; Mao, S.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J. Infusion of sodium butyrate promotes rumen papillae growth and enhances expression of genes related to rumen epithelial VFA uptake and metabolism in neonatal twin lambs. J. Anim Sci. 2019, 97, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Supplementation on Gas Production, Fermentation Characteristics, and Bacterial Community Profiles In Vitro. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, D.R.G.; de Souza Duarte, M.; La Reau, A.J.; Chaves, I.Z.; de Oliveira Mendes, T.A.; Detmann, E.; Bento, C.B.P.; Mercadante, M.E.Z.; Bonilha, S.F.M.; Suen, G.; et al. Assessing the relationship between the rumen microbiota and feed efficiency in Nellore steers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur-Murillo, C.L.; Aguilar-Marín, S.B.; Jovel, J. Prevotella: A Key Player in Ruminal Metabolism. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Grootaert, C.; Verstraete, W.; Van de Wiele, T. Propionate as a health-promoting microbial metabolite in the human gut. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.W.; Huang, H.J.; Wang, X.M.; Wei, R.Q.; Niu, H.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Luo, M.; Abdugheni, R.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, F.L.; et al. Christensenella strain resources, genomic/metabolomic profiling, and association with host at species level. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2347725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Feng, T.; Ding, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Cui, K.; Chen, W.; Pan, H.; Zhu, P.; Liu, Q. Age-related compositional and functional changes in the adult and breastfed buffalo rumen microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1342804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Yu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, W.; Luo, H.; Stergiadis, S.; Wang, B. Rumen microbiome-driven insight into bile acid metabolism and host metabolic regulation. Isme J. 2024, 18, wrae098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zubair, M.; Chen, L.; Chang, J.; Fang, W.; Nabi, M.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; et al. Rumen microbe fermentation of corn stalk to produce volatile fatty acids in a semi-continuous reactor. Fuel 2023, 350, 128905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.Y.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zang, X.W.; Zhong, Y.F.; Ma, X.J.; Sun, H.Z.; Liu, J.X. Deciphering functional groups of rumen microbiome and their underlying potentially causal relationships in shaping host traits. iMeta 2024, 3, e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Maistrenko, O.M.; Andrejev, S.; Kim, Y.; Bork, P.; Patil, K.R.; Patil, K.R. Polarization of microbial communities between competitive and cooperative metabolism. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Boggio, G.; Meynadier, A.; Buitenhuis, A.J.; Marie-Etancelin, C. Host genetic control on rumen microbiota and its impact on dairy traits in sheep. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2022, 54, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wei, Z.; Li, Z.; Ren, J.; Song, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, A.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Fan, H.; et al. Integrating genome- and transcriptome-wide association studies to uncover the host-microbiome interactions in bovine rumen methanogenesis. iMeta 2024, 3, e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, G.; Dimauro, C.; Daghio, M.; Serra, A.; Mannelli, F.; McAmmond, B.M.; Van Hamme, J.D.; Buccioni, A.; Viti, C.; Mantino, A.; et al. Exploring the relationship between bacterial genera and lipid metabolism in bovine rumen. Animal 2022, 16, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Henniger, M.T.; Izzo, A.S.; Melchior, E.A.; Clemmons, B.A.; Oliver, M.A.; Gaffney, J.R.; Martino, C.; Ault-Seay, T.B.; Striluk, M.L.; et al. Performance improvements and increased ruminal microbial interactions in Angus heifers via supplementation with native rumen bacteria during high-grain challenge. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Rumen fermentation and microbial diversity of sheep fed a high-concentrate diet supplemented with hydroethanolic extract of walnut green husks. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhen, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Min, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Woods, J.; et al. Mouse spermatogenesis-associated protein 1 (SPATA1), an IFT20 binding partner, is an acrosomal protein. Dev. Dyn. 2020, 249, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, K.; Li, B. Integrating single-cell and spatial transcriptomic analysis to unveil heterogeneity in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1420847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, J.; Slack, E.; Foster, K.R. Host control of the microbiome: Mechanisms, evolution, and disease. Science 2024, 385, eadi3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

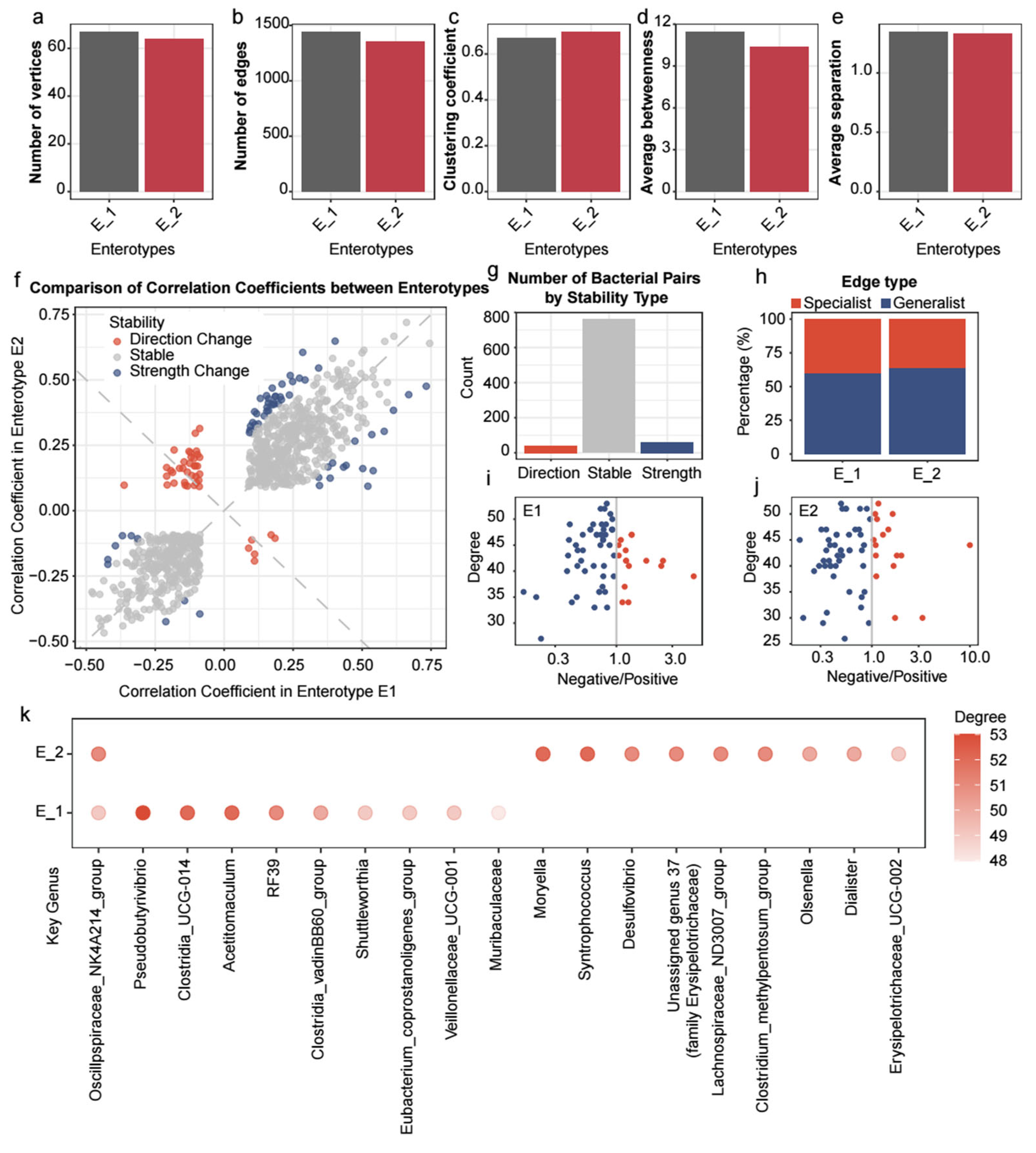
| Taxa_A | Taxa_B | r (E1) | r (E2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetitomaculum | Shuttleworthia | −0.21 | 0.13 |
| Butyrivibrio | Eubacterium nodatum group | −0.13 | 0.09 |
| Christensenellaceae R-7 group | Anaerovibrio | −0.21 | 0.16 |
| Christensenellaceae R-7 group | Eubacterium ruminantium group | −0.10 | 0.21 |
| Christensenellaceae R-7 group | Pseudobutyrivibrio | −0.10 | 0.23 |
| Christensenellaceae R-7 group | Veillonellaceae UCG-001 | −0.18 | 0.23 |
| Clostridia UCG-014 | Acetitomaculum | −0.10 | 0.30 |
| Defluviitaleaceae UCG-011 | Veillonellaceae UCG-001 | −0.12 | 0.18 |
| Eubacterium coprostanoligenes group | Anaerovibrio | −0.21 | 0.10 |
| Eubacterium ruminantium group | NK4A214 group | −0.09 | 0.12 |
| F082 | Fibrobacter | −0.15 | 0.16 |
| F082 | Saccharofermentans | −0.13 | 0.23 |
| Fibrobacter | Lachnospiraceae ND3007 group | −0.09 | 0.14 |
| Oribacterium | Veillonellaceae UCG-001 | 0.11 | −0.19 |
| Prevotellaceae Ga6A1 group | Lachnospiraceae XPB1014 group | −0.14 | 0.11 |
| Prevotellaceae UCG-001 | Desulfovibrio | 0.10 | −0.11 |
| Prevotellaceae UCG-001 | NK4A214 group | −0.19 | 0.15 |
| Prevotellaceae UCG-001 | Succiniclasticum | 0.11 | −0.17 |
| Prevotellaceae YAB2003 group | Eubacterium ruminantium group | 0.09 | −0.14 |
| Pseudobutyrivibrio | UCG-010 | −0.12 | 0.20 |
| RF39 | Acetitomaculum | −0.16 | 0.16 |
| RF39 | Succiniclasticum | −0.14 | 0.10 |
| Rikenellaceae RC9 gut group | Eubacterium ruminantium group | −0.18 | 0.11 |
| Rikenellaceae RC9 gut group | Saccharofermentans | −0.11 | 0.20 |
| Ruminococcus gauvreauii group | probable genus 10 | −0.09 | 0.31 |
| Saccharofermentans | Dialister | 0.17 | −0.09 |
| Saccharofermentans | Pseudobutyrivibrio | −0.13 | 0.15 |
| Saccharofermentans | Veillonellaceae UCG-001 | −0.36 | 0.10 |
| UCG-004 | Anaerovibrio | −0.15 | 0.19 |
| UCG-004 | Pseudobutyrivibrio | −0.12 | 0.13 |
| UCG-010 | Veillonellaceae UCG-001 | −0.09 | 0.20 |
| Veillonellaceae UCG-001 | Candidatus Saccharimonas | −0.10 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W. Host Genetic Effects and Phenotypic Landscapes of Rumen Bacterial Enterotypes in a Large Sheep Population. Animals 2025, 15, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182724
Zhang Y, Li F, Zhang X, Zhang D, Wang W. Host Genetic Effects and Phenotypic Landscapes of Rumen Bacterial Enterotypes in a Large Sheep Population. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182724
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yukun, Fadi Li, Xiaoxue Zhang, Deyin Zhang, and Weimin Wang. 2025. "Host Genetic Effects and Phenotypic Landscapes of Rumen Bacterial Enterotypes in a Large Sheep Population" Animals 15, no. 18: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182724
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, F., Zhang, X., Zhang, D., & Wang, W. (2025). Host Genetic Effects and Phenotypic Landscapes of Rumen Bacterial Enterotypes in a Large Sheep Population. Animals, 15(18), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182724






