Effects of Different Ways of Music Stimulation on Exploring, Playing and Aggressive Behavior
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Management
2.2. Experimental Animal Grouping and Sample Collection
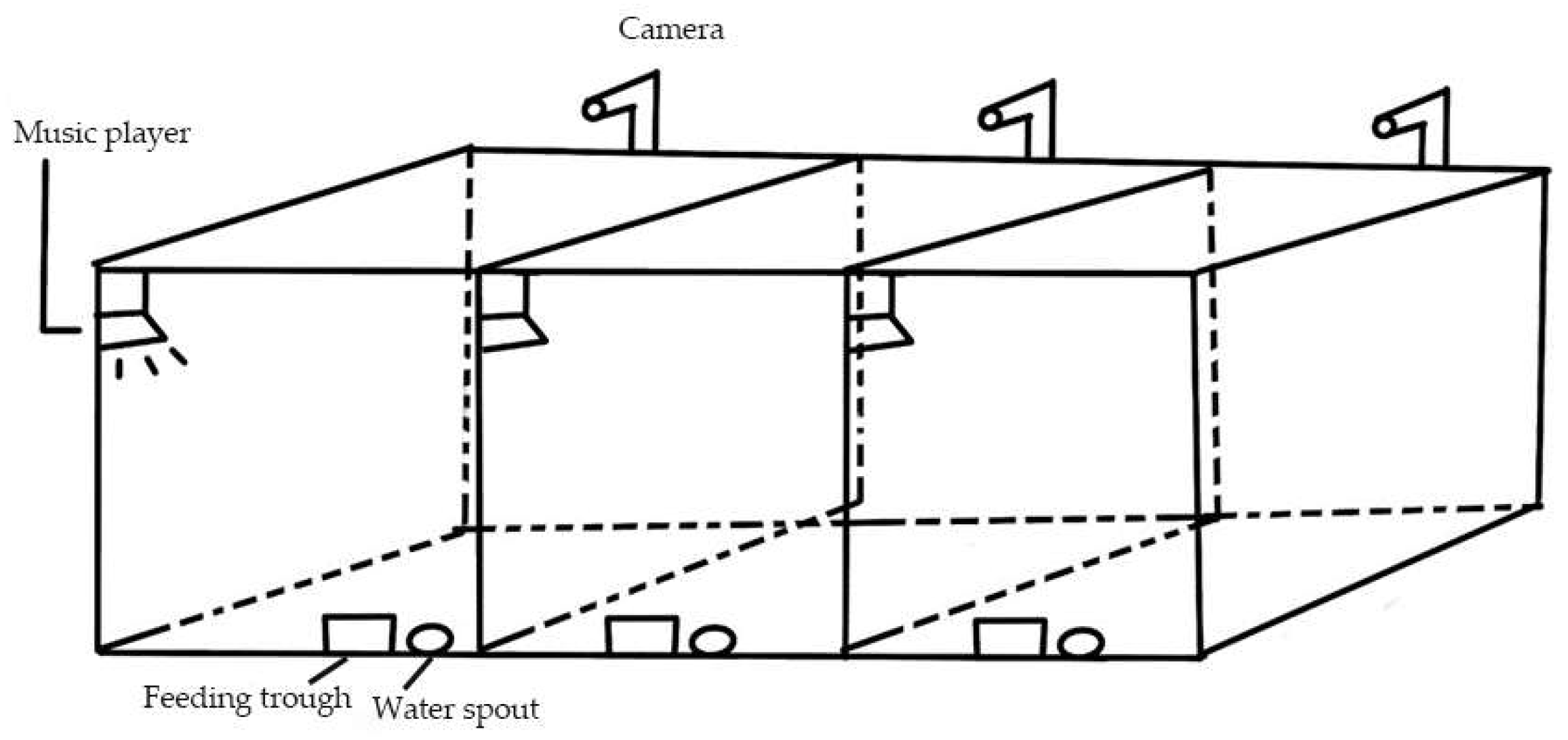
2.3. Behavior Video Capture
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Music Stimulation Methods on the Exploring Behavior of Piglets
3.2. Effects of Different Music Stimulation Methods on the Playing Behavior of Piglets
3.3. Effects of Different Music Stimulation Methods on the Aggressive Behavior of Piglets
3.4. mRNA Level of Neurodevelopment and Cognition in the Hippocampus
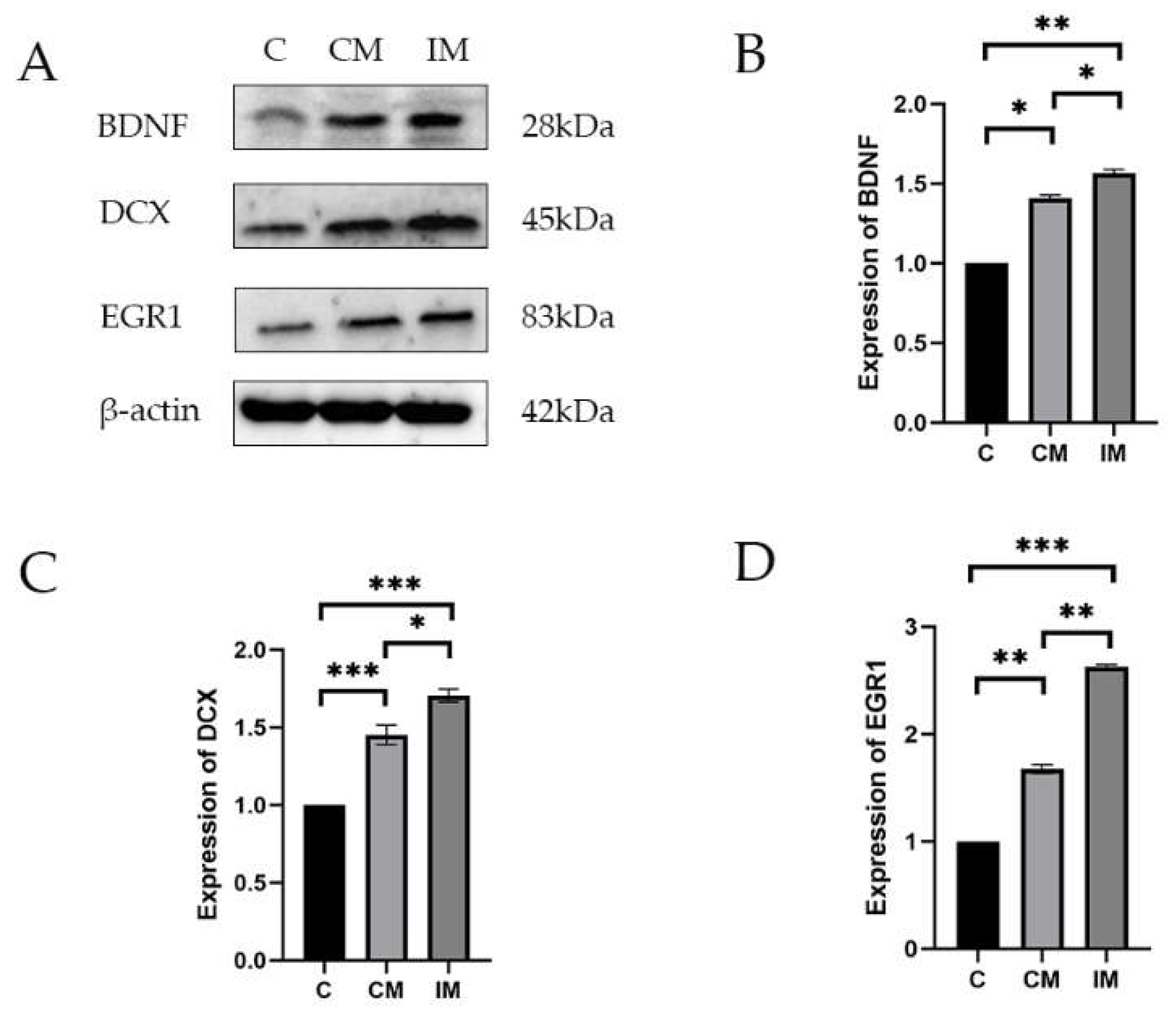
3.5. Protein Expression Related to Neurodevelopment and Cognition in the Hippocampus
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alworth, L.C.; Buerkle, S.C. The effects of music on animal physiology, behavior and welfare. Lab Anim. 2013, 42, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, B.L.; Sutherland, M.A.; Brooks, T.A. Relationship between Environmental Enrichment and the Response to Novelty in Laboratory-housed Pigs. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2017, 56, 735–741. [Google Scholar]
- Papadakakis, A.; Sidiropoulou, K.; Panagis, G. Music exposure attenuates anxiety- and depression-like behaviors and increases hippocampal spine density in male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 372, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, L.; Porta, C.; Sleight, P. Cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and respiratory changes induced by different types of music in musicians and non-musicians: The importance of silence. Heart 2006, 92, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, K.; Evans, B.; Montrose, V.T. The effects of auditory enrichment on the behaviour of dairy cows (Bos taurus). In Proceedings of the British Society of Animal Science Annual Conference, Edinburgh, UK, 9–11 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liang, T.; Zhou, F.H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, F.-Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, X.-F.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Li, C.-Q. Regular Music Exposure in Juvenile Rats Facilitates Conditioned Fear Extinction and Reduces Anxiety after Foot Shock in Adulthood. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8740674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xia, Y.; Kendrick, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Wu, D.; Yang, H.; Jing, W.; Guo, D.; Yao, D. Mozart, Mozart Rhythm and Retrograde Mozart Effects: Evidences from Behaviours and Neurobiology Bases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirste, I.; Nicola, Z.; Kronenberg, G.; Walker, T.L.; Liu, R.C.; Kempermann, G. Is silence golden? Effects of auditory stimuli and their absence on adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Anat. Embryol. 2015, 220, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, M.-H.; Chang, H.-K.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, H.-H.; Shin, M.-C.; Shin, M.-S.; Won, R.; Shin, H.-S.; Kim, C.-J. Influence of prenatal noise and music on the spatial memory and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of developing rats. Brain Dev. 2006, 28, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Shin, J.W.; Chung, K.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Shin, M.-S.; Baek, S.-B.; Sung, Y.-H.; Kim, C.-J.; Kim, K.-H. Exposure to Music and Noise During Pregnancy Influences Neurogenesis and Thickness in Motor and Somatosensory Cortex of Rat Pups. Int. Neurourol. J. 2013, 17, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindig, A.M.; McGreevy, P.D.; Crean, A.J. Musical Dogs: A Review of the Influence of Auditory Enrichment on Canine Health and Behavior. Animals 2020, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, G.; Afonso, P.M.; Salazar, I.L.; Duarte, C.B. Regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by BDNF. Brain Res. 2015, 1621, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuso, S.; La Rosa, P.; Fiorenza, M.T.; Canterini, S. Pleiotropic effects of BDNF on the cerebellum and hippocampus: Implications for neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 163, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Inoue, T.; Hayashi, M.; Maejima, H. Exercise enhances the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus accompanied by epigenetic alterations in senescence-accelerated mice prone 8. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 706, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclot, F.; Kabbaj, M. The Role of Early Growth Response 1 (EGR1) in Brain Plasticity and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappeler, C.; Saillour, Y.; Baudoin, J.-P.; Tuy, F.P.D.; Alvarez, C.; Houbron, C.; Gaspar, P.; Hamard, G.; Chelly, J.; Métin, C.; et al. Branching and nucleokinesis defects in migrating interneurons derived from doublecortin knockout mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkbeiner, S.; Tavazoie, S.F.; Maloratsky, A.; Jacobs, K.M.; Harris, K.M.; Greenberg, M.E. CREB: A major mediator of neuronal neurotrophin responses. Neuron 1997, 19, 1031–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Mao, L. The ERK Pathway: Molecular Mechanisms and Treatment of Depression. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6197–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Bao, J. Behavioural responses of piglets to different types of music. Animal 2019, 13, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, Q.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Bao, J. Effects of music stimulus on behavior response, cortisol level and immunity horizontal of growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Bao, J.; Xing, H. Selenomethionine protects against ammonia-induced apoptosis through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress in pig kidneys. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, J.Z.; Ceballos, M.C.; Morales, A.M.T.; Jaramillo, E.D.; Rodríguez, B.d.J. Music modulates emotional responses in growing pigs. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, B.M.B.; Lisa, R. From Fearful to Fear Free: A Positive Program to Free Your Dog from Anxiety, Fears, and Phobias; Health Communications, Inc.: Deerfield Beach, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reimert, I.; Bolhuis, J.E.; Kemp, B.; Rodenburg, T.B. Indicators of positive and negative emotions and emotional contagion in pigs. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 109, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immordino-Yang, M.H.; Singh, V. Hippocampal contributions to the processing of social emotions. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Zaben, N.; Vithanage, N.M.; Al Shdefat, A.; Choi, H.-K. Comparison of active contour and fast marching methods of hippocampus segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), Amman, Jordan, 7–9 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Angelucci, F.; Ricci, E.; Padua, L.; Sabino, A.; Tonali, P.A. Music exposure differentially alters the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in the mouse hypothalamus. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 429, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horner, C.H.; Arbuthnott, E. Methods of estimation of spine density--are spines evenly distributed throughout the dendritic field? J. Anat. 1991, 177, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Kentner, A.C.; Khoury, A.; Queiroz, E.L.; MacRae, M. Environmental enrichment rescues the effects of early life inflammation on markers of synaptic transmission and plasticity. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2016, 57, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Pan, J.; Sun, J.; Ding, L.; Ruan, L.; Reed, M.; Yu, X.; Klabnik, J.; Lin, D.; Li, J.; et al. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 2 reverses impaired cognition and neuronal remodeling caused by chronic stress. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieraci, A.; Mallei, A.; Popoli, M. Social Isolation Stress Induces Anxious-Depressive-Like Behavior and Alterations of Neuroplasticity-Related Genes in Adult Male Mice. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 6212983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, F.; Brégère, C.; Laws, G.C.; Armstrong, E.A.; Wylie, N.J.; Moxham, T.T.; Guzman, R.; Boswell, T.; Smulders, T.V. Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Doublecortin and BDNF Expression along the Dorso-Ventral Axis of the Dentate Gyrus. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, E.A.; Voelkl, B.; Voegeli, S.; Gebhardt-Henrich, S.G.; Guy, J.H.; Sandilands, V.; Boswell, T.; Toscano, M.J.; Smulders, T.V. Cell Proliferation in the Adult Chicken Hippocampus Correlates With Individual Differences in Time Spent in Outdoor Areas and Tonic Immobility. Front. Veter Sci. 2020, 7, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Behavioral Categories | Behavior Definition |
|---|---|
| Event behavior | |
| Exploring | Nose sniffing, touching, or arching on the floor; nose or mouth sniffing, arching, gnawing, or biting ring bar and chute. |
| Playing | Turning and jumping, suddenly lying down; the target pig is close to the other pig, sniffing, arching the neck and back, with the nose; pigs place two front legs on the front or back of a companion. |
| Aggressive | Two piggy heads pushing, fighting, biting, banging, or pushing each other head-to-head. |
| Gene | Serial Number | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| BDNF | NM_214259.2 | Forward: GAACTCCCAGTGCCGAACTACC |
| Reverse: CCTTATGAACCGCCAGCCAATTC | ||
| DCX | XM_013986335.2 | Forward: ATGCTCTCCTGGCTGACCTGAC |
| Reverse: AGCTCATCCATGCTTCCAATCTTCC | ||
| EGR1 | XM_003123974.6 | Forward: AGTTTGCCAGGAGCGATGAA |
| Reverse: AGGCCACACTTTTGTCTGCT | ||
| TRKB | XM_021064645.1 | Forward: GACGCTGAAGGATGCCAGTGAC |
| Reverse: AGACGCCATAGAACTTGACGATGTG | ||
| CREB | WP_185668273.1 | Forward: CACCTGCCATCACCACTGTAACG |
| Reverse: CTGAATTGCTCCTCCCTGGGTAATG | ||
| PDGFA | XM_021085925.1 | Forward: ACGGGCTCCAGCAGTTCTACC |
| Reverse: CCACCAGGTCCGAGGAGTCTATG | ||
| NGFR | XM_021067136.1 | Forward: GGAGGTGGAGAAGCTGCTGAATG |
| Reverse: AGTCTATGTGCTCGGGCTGGTAG | ||
| β-actin | NM_001170517.2 | Forward: GGCACCACACCTTCTACAACGAG |
| Reverse: TCATCTTCTCACGGTTGGCTTTGG |
| Antibody | Dilution Multiple | kDa | Source | Producer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF | 1:1000 | 28 | rabbit | WANLEIBIO, Shenyang, China |
| DCX | 1:1000 | 40–45 | rabbit | WANLEIBIO, Shenyang, China |
| EGR1 | 1:1000 | 82 | rabbit | WANLEIBIO, Shenyang, China |
| β-actin | 1:5000 | 42 | rabbit | Beyotime, Shanghai, China |
| Group | Day 1(n) | Day 2(n) | Day 3(n) | Main Effect (Grouping) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C group | 56.67 ± 1.43 c | 55.33 ± 1.20 c | 54.33 ± 0.71 c | 55.44 ± 0.67 c |
| CM group | 77.16 ± 1.92 bx | 70.50 ± 1.09 by | 59.33 ± 0.84 bz | 69.00 ± 1.93 b |
| IM group | 86.17 ± 2.39 ax | 82.50 ± 1.43 ax | 75.50 ± 1.18 ay | 81.38 ± 1.43 a |
| Main effect (test days) | 73.33 ± 3.18 x | 69.44 ± 2.78 xy | 63.06 ± 2.25 y | -- |
| -- | Test days | Grouping | Test days × Grouping | -- |
| Group | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Main effect (grouping) |
| P ratio | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | -- |
| F ratio | 38.847 | 242.916 | 7.489 | -- |
| Group | Day 1(n) | Day 2(n) | Day 3(n) | Main Effect (Grouping) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C group | 20.00 ± 1.15 b | 19.17 ± 0.40 b | 20.00 ± 1.03 b | 19.11 ± 0.46 b |
| CM group | 30.33 ± 1.45 ax | 27.17 ± 0.83 axy | 25.17 ± 0.75 ay | 27.56 ± 0.77 a |
| IM group | 32.33 ± 1.33 ax | 28.33 ± 1.12 ay | 27 ± 0.93 ay | 29.22 ± 0.83 a |
| Main effect (test days) | 27.56 ± 1.49 x | 24.89 ± 1.09 xy | 23.44 ± 1.01 y | -- |
| -- | Test days | Grouping | Test days × Grouping | -- |
| P ratio | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.352 | -- |
| F ratio | 12.985 | 87.727 | 1.136 | -- |
| Group | Day 1(n) | Day 2(n) | Day 3(n) | Main Effect (Grouping) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C group | 11.33 ± 0.71 a | 10.83 ± 0.80 a | 11.00 ± 1.21 a | 9.56 ± 0.58 a |
| CM group | 8 ± 0.37 bx | 7 ± 0.45 by | 7.83 ± 1.07 bx | 6.44 ± 0.35 b |
| IM group | 5.67 ± 0.33 c | 5.17 ± 0.48 c | 4.33 ± 0.61 c | 5.06 ± 0.30 c |
| Main effect (grouping) | 8.72 ± 0.73 x | 6.61 ± 0.45 y | 5.72 ± 0.41 y | |
| Test days | Grouping | Test days × Grouping | ||
| P ratio | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |
| F ratio | 33.449 | 74.797 | 5.254 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, B.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Zhao, W. Effects of Different Ways of Music Stimulation on Exploring, Playing and Aggressive Behavior. Animals 2025, 15, 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182721
Wu M, Wang Z, Zhou S, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Liu X, Bai B, Liu R, Liu H, Zhao W. Effects of Different Ways of Music Stimulation on Exploring, Playing and Aggressive Behavior. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182721
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Mengyao, Zhonghui Wang, Sitong Zhou, Xiaolong Zhang, Yunlong Zhao, Xuanning Liu, Bin Bai, Runze Liu, Honggui Liu, and Wenzhong Zhao. 2025. "Effects of Different Ways of Music Stimulation on Exploring, Playing and Aggressive Behavior" Animals 15, no. 18: 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182721
APA StyleWu, M., Wang, Z., Zhou, S., Zhang, X., Zhao, Y., Liu, X., Bai, B., Liu, R., Liu, H., & Zhao, W. (2025). Effects of Different Ways of Music Stimulation on Exploring, Playing and Aggressive Behavior. Animals, 15(18), 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182721






