Topographic Correlation of Histopathological Subtypes in Canine Mammary Tumors: Evidence of Non-Random Tumor Distribution
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical Evaluation and Staging
2.3. Tissue Collection and Histopathology
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiology
3.2. Macroscopical Analysis and Nodule Anatomical Distribution
3.3. Histopathological Analysis and Tumor Subtypes’ Anatomical Distribution
3.3.1. Tumor Grading
3.3.2. TNM Score
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MGT | Mammary Gland Tumor. |
| CMT | Canine Mammary Tumor. |
| TNM | Tumor Node Metastasis. |
| HE | Hematoxylin and Eosin. |
| L.T1 | Left Cranial Thoracic Mammary Segment. |
| L.T2 | Left Caudal Thoracic Mammary Segment. |
| L.A1 | Left Cranial Abdominal Mammary Segment. |
| L.A2 | Left Cranial Abdominal Mammary Segment. |
| L.ING | Left Inguinal Mammary Segment. |
| R.T1 | Right Cranial Thoracic Mammary Segment. |
| R.T2 | Right Caudal Thoracic Mammary Segment. |
| R.A1 | Right Cranial Abdominal Mammary Segment. |
| R.A2 | Right Caudal Abdominal Mammary Segment. |
| R.ING | Right Inguinal Mammary Segment. |
| APC | Anaplastic Carcinoma. |
| ASQC | Adenosquamous Carcinoma. |
| BMT | Benign Mixed Tumor. |
| C | Mammary Carcinoma. |
| CA | Complex Adenoma. |
| CC | Complex Carcinoma. |
| CDC | Comedocarcinoma. |
| DA | Ductal Adenoma. |
| DC | Ductal Carcinoma. |
| FBS | Fibrosarcoma. |
| IFLC | Inflammatory Carcinoma. |
| IMPC | Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma. |
| IPA | Intraductal Papillary Adenoma. |
| IPC | Intraductal Papillary Carcinoma. |
| LRC | Lipid-Rich Carcinoma. |
| MXC | Mixed Carcinoma. |
| MC | Mucinous Carcinoma. |
| MME | Malignant Myoepithelioma. |
| OSA | Mammary Osteosarcoma. |
| S | Mammary Sarcoma. |
| SC | Solid Carcinoma. |
| TC | Tubular Carcinoma. |
| TPC | Tubulopapillary Carcinoma. |
References
- Ferreira, T.; Gama, A.; Seixas, F.; Faustino-Rocha, A.I.; Lopes, C.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F.; Medeiros, R.; Oliveira, P.A. Mammary Glands of Women, Female Dogs and Female Rats: Similarities and Differences to Be Considered in Breast Cancer Research. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, J.; Porto, C.; Franco, R.; Costa, I.D.; Bueno, L.; Girio, R.; Manhoso, F.; Bueno, P.; Repetti, C. Mammary Neoplasms in Female Dogs: Clinical, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects. Vet. Med. 2024, 69, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C. Cats, Cancer and Comparative Oncology. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, N.; Espadas, L.; Santella, M.; Ezquerra, L.J.; Tarazona, R.; Durán, M.E. Comparison between Histological Features and Strain Elastographic Characteristics in Canine Mammary Carcinomas. Vet. Sci. 2021, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedon, J.; Wehrend, A.; Failing, K.; Kessler, M. Canine Mammary Tumours: Size Matters–A Progression from Low to Highly Malignant Subtypes. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 19, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.D.S.; Valente, F.L.; Rocha, C.C.; Real Pereira, C.E.; Sarandy, T.B.; De Oliveira, F.L.D.; De Morais Calado, S.L.; Borges, A.P.B. Prognostic Factors for Cancer-Specific Survival and Disease-Free Interval of Dogs with Mammary Carcinomas. Vet. Med. Int. 2023, 2023, 6890707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, L.; Andrés, P.J.D.; Clemente, M.; Cuesta, P.; Pérez-Alenza, M.D. Prognostic Value of Histological Grading in Noninflammatory Canine Mammary Carcinomas in a Prospective Study With Two-Year Follow-Up: Relationship With Clinical and Histological Characteristics. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolka, I.; Czopowicz, M.; Stopka, D.; Wojtkowska, A.; Kaszak, I.; Sapierzyński, R. Risk Factor Analysis and Clinicopathological Characteristics of Female Dogs with Mammary Tumours from a Single-Center Retrospective Study in Poland. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, T.C.; Prado, M.E.; Ruiz Sueiro, F.A.; Cassali, G.D.; Jark, P.C. Small Canine Mammary Tumours Have Different Prognostic Factors: A Study of 3,470 Tumours. J. Comp. Pathol. 2025, 219, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaratirwa, S. Prognostic and Predictive Markers in Canine Tumours: Rationale and Relevance. A Review. Vet. Q. 2005, 27, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papparella, S.; Crescio, M.; Baldassarre, V.; Brunetti, B.; Burrai, G.; Cocumelli, C.; Grieco, V.; Iussich, S.; Maniscalco, L.; Mariotti, F.; et al. Reproducibility and Feasibility of Classification and National Guidelines for Histological Diagnosis of Canine Mammary Gland Tumours: A Multi-Institutional Ring Study. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassali, G.; Jark, P.; Gamba, C.; Damasceno, K.; Estrela-Lima, A.; Nardi, A.; Ferreira, E.; Horta, R.; Firmo, B.; Sueiro, F.; et al. Consensus Regarding the Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment of Canine and Feline Mammary Tumors—2019. BJVP 2020, 13, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, M.S.; Lewis, L.D. Small Animal Clinical Nutrition, 5th ed.; Mark Morris Institute: Topeka, KS, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-615-29701-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zappulli, V.; Peña, L.; Rasotto, R.; Goldschmidt, M.H.; Gama, A.; Scruggs, J.L.; Kiupel, M. Surgical Pathology of Tumors of Domestic Animals Volume 2: Mammary Tumors; Kiupel, M., Ed.; Davis-Thompson DVM Foundation: Gurnee, IL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-73374-911-4. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, E.; Lipovka, Y.; Cervantes-Arias, A.; Garibay-Escobar, A.; Haby, M.M.; Queiroga, F.L.; Velazquez, C. Canine Mammary Cancer: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Animals 2023, 13, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, Y.; Márquez, A.; Diaz, D.; Romero, L. Epidemiological Study of Mammary Tumors in Female Dogs Diagnosed during the Period 2002-2012: A Growing Animal Health Problem. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, R.; Dorn, C.R.; Taylor, D.O.N. Factors Influencing Canine Mammary Cancer Development and Postsurgical Survival. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1969, 43, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egenvall, A.; Bonnett, B.N.; Öhagen, P.; Olson, P.; Hedhammar, Å.; Euler, H.V. Incidence of and Survival after Mammary Tumors in a Population of over 80,000 Insured Female Dogs in Sweden from 1995 to 2002. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 69, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafalko, J.M.; Kruglyak, K.M.; McCleary-Wheeler, A.L.; Goyal, V.; Phelps-Dunn, A.; Wong, L.K.; Warren, C.D.; Brandstetter, G.; Rosentel, M.C.; DiMarzio, L.; et al. Age at Cancer Diagnosis by Breed, Weight, Sex, and Cancer Type in a Cohort of More than 3,000 Dogs: Determining the Optimal Age to Initiate Cancer Screening in Canine Patients. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyarathna, H.; De Silva, N.; Aberdein, D.; Kodikara, D.; Jayasinghe, M.; Adikari, R.; Munday, J.S. Clinicopathological Diversity of Canine Mammary Gland Tumors in Sri Lanka: A One-Year Survey on Cases Presented to Two Veterinary Practices. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.-H.; Du, C.-T.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Huang, R.-L.; Tang, X.-Y.; Xie, G.-H. Epidemiological Investigation of Canine Mammary Tumors in Mainland China Between 2017 and 2021. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 843390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanians’ Mentality and Attitudes towards Dogs. Available online: https://hopeforromaniandogs.weebly.com/the-current-situation.html (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Terzian, A.C.B.; Zuccari, D.A.P.D.C.; Pereira, R.S.; Pavam, M.V.; Ruiz, C.M.; Sueiro, F.A.R.; Coelho, J. Avaliação Da Caspase-3 e Ki-67 Como Marcadores Prognósticos Nas Neoplasias Mamárias Em Cadelas. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2007, 44, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Santana, Á.; Herráez, P.; Killick, D.R.; De Los Monteros, A.E. Epidemiology of Canine Mammary Tumours on the Canary Archipelago in Spain. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.T.; Niza-Ribeiro, J.; Amorim, I.; Queiroga, F.; Severo, M.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Pinello, K. Comparative Epidemiological Study of Breast Cancer in Humans and Canine Mammary Tumors: Insights from Portugal. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1271097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmunds, G.; Beck, S.; Kale, K.U.; Spasic, I.; O’Neill, D.; Brodbelt, D.; Smalley, M.J. Associations Between Dog Breed and Clinical Features of Mammary Epithelial Neoplasia in Bitches: An Epidemiological Study of Submissions to a Single Diagnostic Pathology Centre Between 2008–2021. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2023, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, E.M.G.; Dos Santos, T.R.; Silva, M.J.B. Identifying the Risk Factors for Malignant Mammary Tumors in Dogs: A Retrospective Study. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.; Miranda, M.; Pinto-Leite, R.; Mano, J.F.; Medeiros, R.; Oliveira, P.A.; Gama, A. Integrated Study of Canine Mammary Tumors Histopathology, Immunohistochemistry, and Cytogenetic Findings. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.G.; Iturriaga, M.P.; Cruz, P. Hormonal Carcinogenesis in Canine Mammary Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms of Estradiol Involved in Malignant Progression. Animals 2021, 11, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withrow and MacEwen’s Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 5th ed.; Withrow, S.J., Ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4377-2362-5. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, F.H.; Figueiroa, F.C.; Bersano, P.R.; Bissacot, D.Z.; Rocha, N.S. Malignant Mammary Tumor in Female Dogs: Environmental Contaminants. Diagn. Pathol. 2010, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontas, B.; Yüzbaşıoğlu Öztürk, G.; Toydemir, T.; Arun, S.; Ekici, H. Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Canine Mammary Gland Tumours: A Comparison Between Cytology and Histopathology. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Yoo, D.S.; Park, C.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Ahn, T.; Jung, B.-G.; Park, J.-G.; Park, S.-I.; Bae, C.-S. Radical Mastectomy Efficiently Improves Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in Dogs with Malignant Mammary Tumors. Animals 2024, 14, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, F.; Gudea, A.; Damian, A.; Gal, A.F.; Papuc, I.; Pop, A.R.; Martonos, C. Ultrasonographic Algorithm for the Assessment of Sentinel Lymph Nodes That Drain the Mammary Carcinomas in Female Dogs. Animals 2020, 10, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, N.; Failing, K.; Richter, A.; Wehrend, A. Mammary Tumor Recurrence in Bitches After Regional Mastectomy. Vet. Surg. 2008, 37, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Anaesthesia and Analgesia. In British Small Animal Veterinary Association, 3rd ed.; BSAVA Manual Series; Duke-Novakovski, T., Vries, M., de Seymour, C., Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association: Quedgeley, Gloucester, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-1-905319-61-9. [Google Scholar]
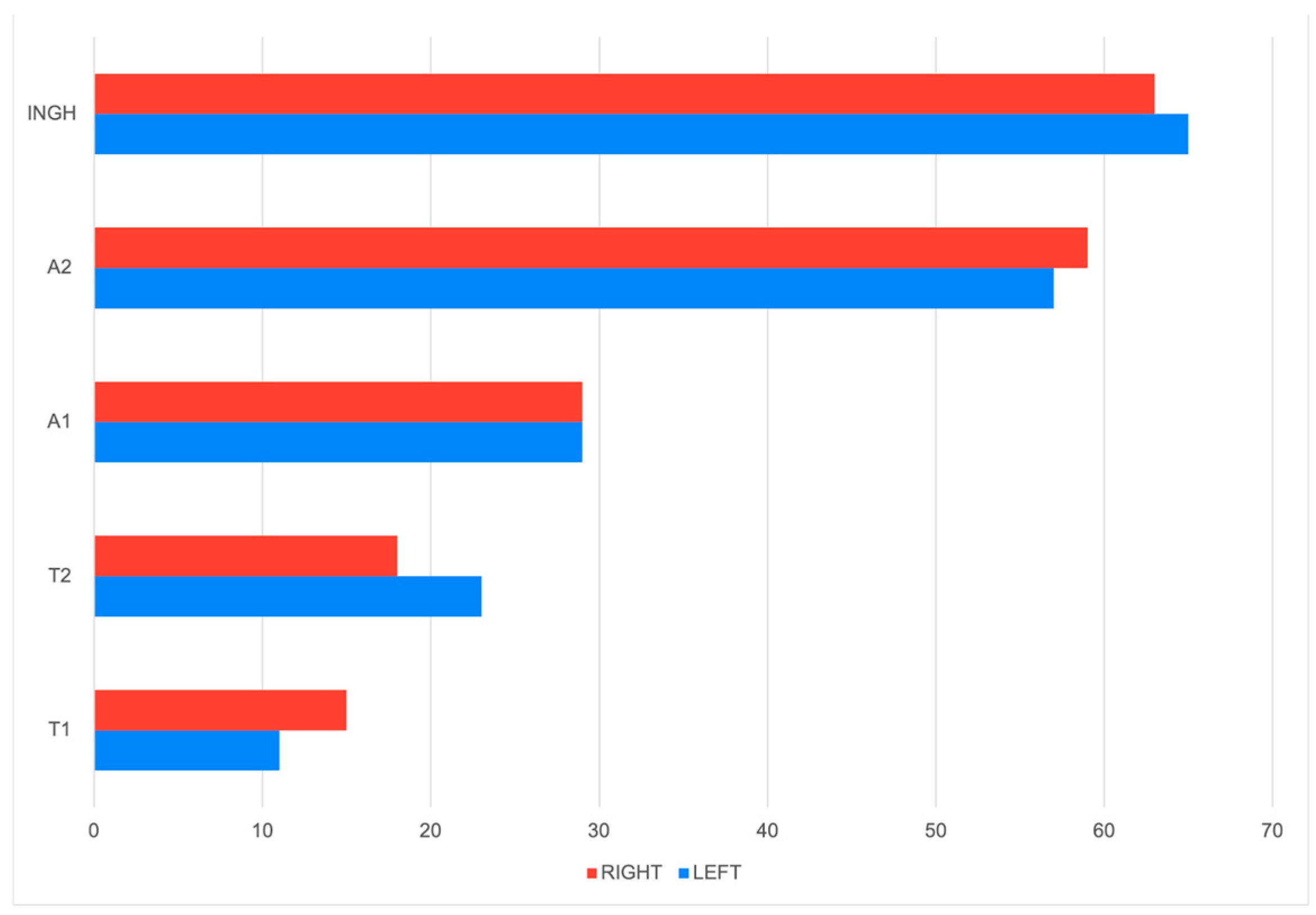
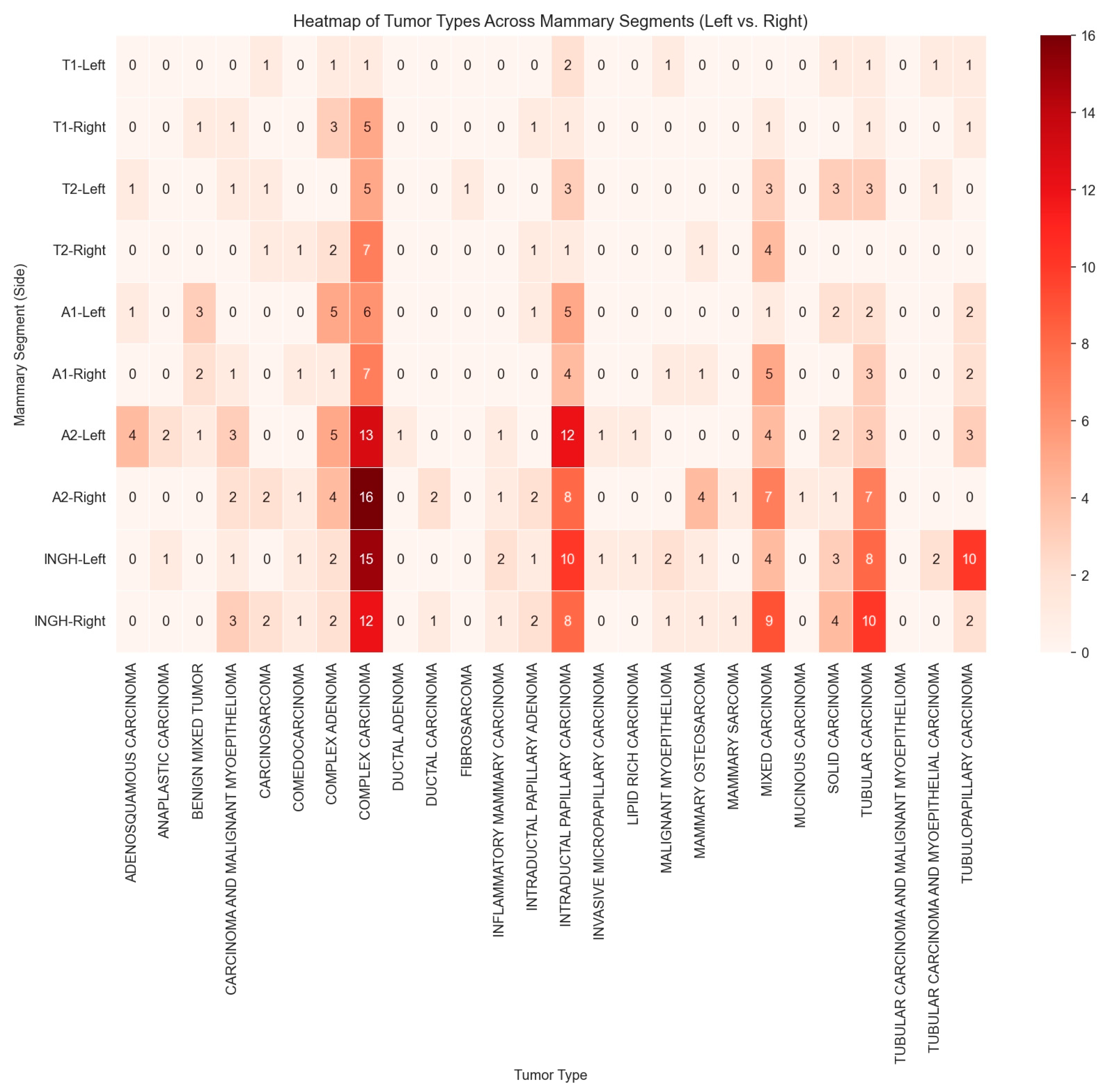

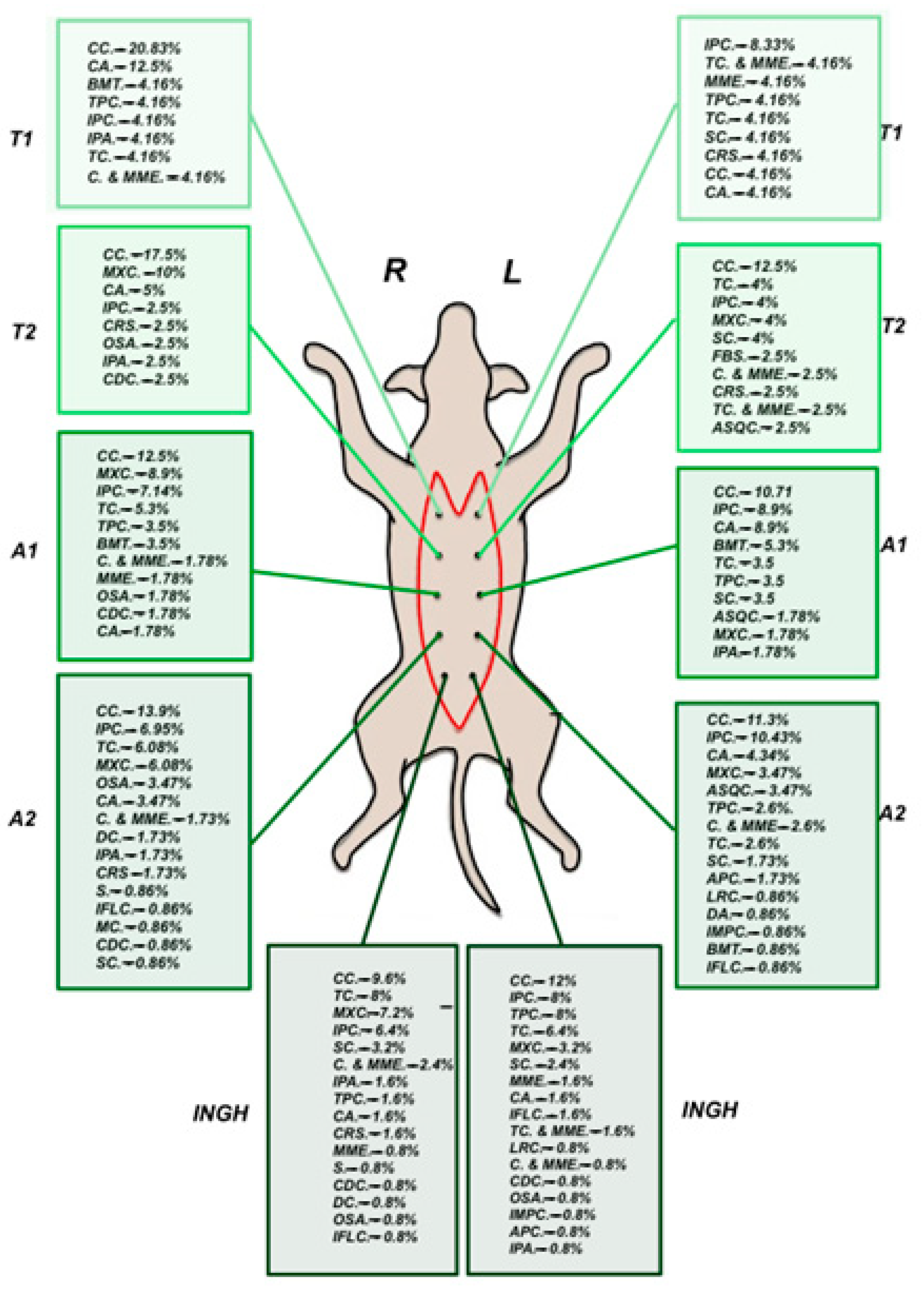
| Histological Type | Number of Tumors on the Left Mammary Chain | Number of Tumors on the Right Mammary Chain | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complex Carcinoma | 40 | 47 | 87 |
| Intraductal Papillary Carcinoma | 32 | 22 | 54 |
| Tubular Carcinoma | 17 | 21 | 38 |
| Mixed Carcinoma | 12 | 26 | 38 |
| Complex Adenoma | 13 | 12 | 25 |
| Tubulopapillary Carcinoma | 16 | 5 | 21 |
| Solid Carcinoma | 11 | 5 | 16 |
| Carcinoma And Malignant Myoepithelioma | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Mammary Osteosarcoma | 1 | 7 | 8 |
| Intraductal Papillary Adenoma | 2 | 6 | 8 |
| Benign Mixed Tumor | 4 | 3 | 7 |
| Carcinosarcoma | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| Adenosquamous Carcinoma | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| Malignant Myoepithelioma | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Inflammatory Mammary Carcinoma | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Comedocarcinoma | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| Tubular Carcinoma And Myoepithelial Carcinoma | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| Ductal Carcinoma | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Anaplastic Carcinoma | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Mammary Sarcoma | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Lipid-Rich Carcinoma | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Fibrosarcoma | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Mucinous Carcinoma | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Ductal Adenoma | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| T1 | T2 | A1 | A2 | INGH | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRADE (n) | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III |
| LEFT | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 14 | 16 | 13 | 22 | 8 | 20 |
| RIGHT | 6 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 21 | 12 | 7 | 19 | 11 | 15 |
| TNM Score (n) | Clinical Stage (%) | Number of Patients | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1N0M0 | 1 | 130 (52%) | |
| T2N0M0 | 2 | 40 (1.6%) | |
| T3N0M0 | 3 | 53 (21.2%) | |
| T1N1M0 | 4 | 5 (2%) | 25 (10%) |
| T2N1M0 | 4 (1.6%) | ||
| T3N1M0 | 16 (6.4%) | ||
| T3N1M1 | 5 | 2 (0.8%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hîruța, A.; Irimie, A.; Bocăneț, V.I.; Gál, Z.M.; Pop, A.R.; Gal, C.; Gagniuc, E.; Cătoi, C. Topographic Correlation of Histopathological Subtypes in Canine Mammary Tumors: Evidence of Non-Random Tumor Distribution. Animals 2025, 15, 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172604
Hîruța A, Irimie A, Bocăneț VI, Gál ZM, Pop AR, Gal C, Gagniuc E, Cătoi C. Topographic Correlation of Histopathological Subtypes in Canine Mammary Tumors: Evidence of Non-Random Tumor Distribution. Animals. 2025; 15(17):2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172604
Chicago/Turabian StyleHîruța, Ana, Alexandra Irimie, Vlad Ioan Bocăneț, Zoltán Miklós Gál, Alexandru Raul Pop, Claudiu Gal, Elvira Gagniuc, and Cornel Cătoi. 2025. "Topographic Correlation of Histopathological Subtypes in Canine Mammary Tumors: Evidence of Non-Random Tumor Distribution" Animals 15, no. 17: 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172604
APA StyleHîruța, A., Irimie, A., Bocăneț, V. I., Gál, Z. M., Pop, A. R., Gal, C., Gagniuc, E., & Cătoi, C. (2025). Topographic Correlation of Histopathological Subtypes in Canine Mammary Tumors: Evidence of Non-Random Tumor Distribution. Animals, 15(17), 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172604







