Pulsed Radiofrequency for Lumbosacral Radicular Pain in Dogs: Description and Assessment of an Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Technique in a Cadaveric Model
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phase I: Anatomical Study
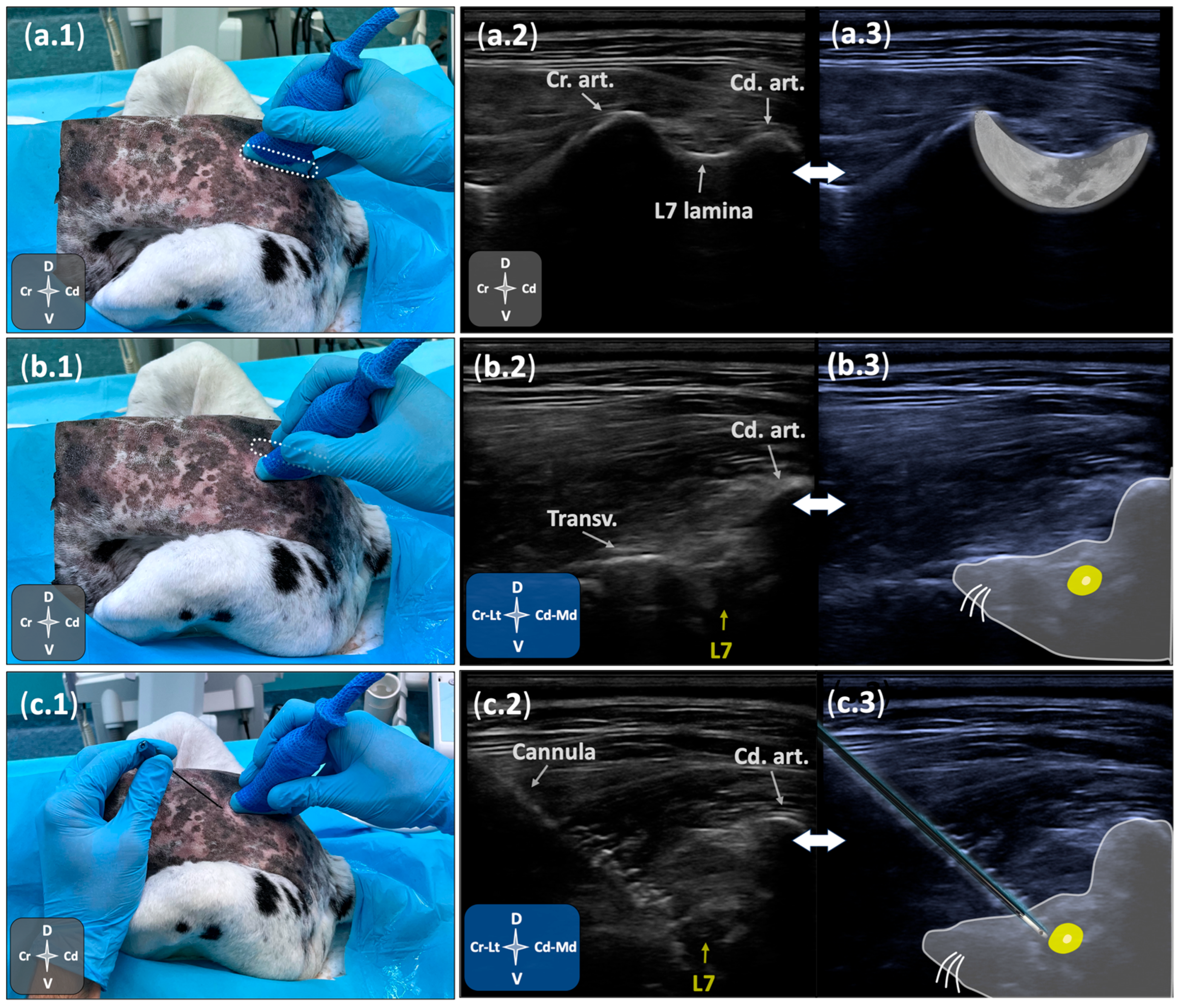
2.1.1. Ultrasonographic Study
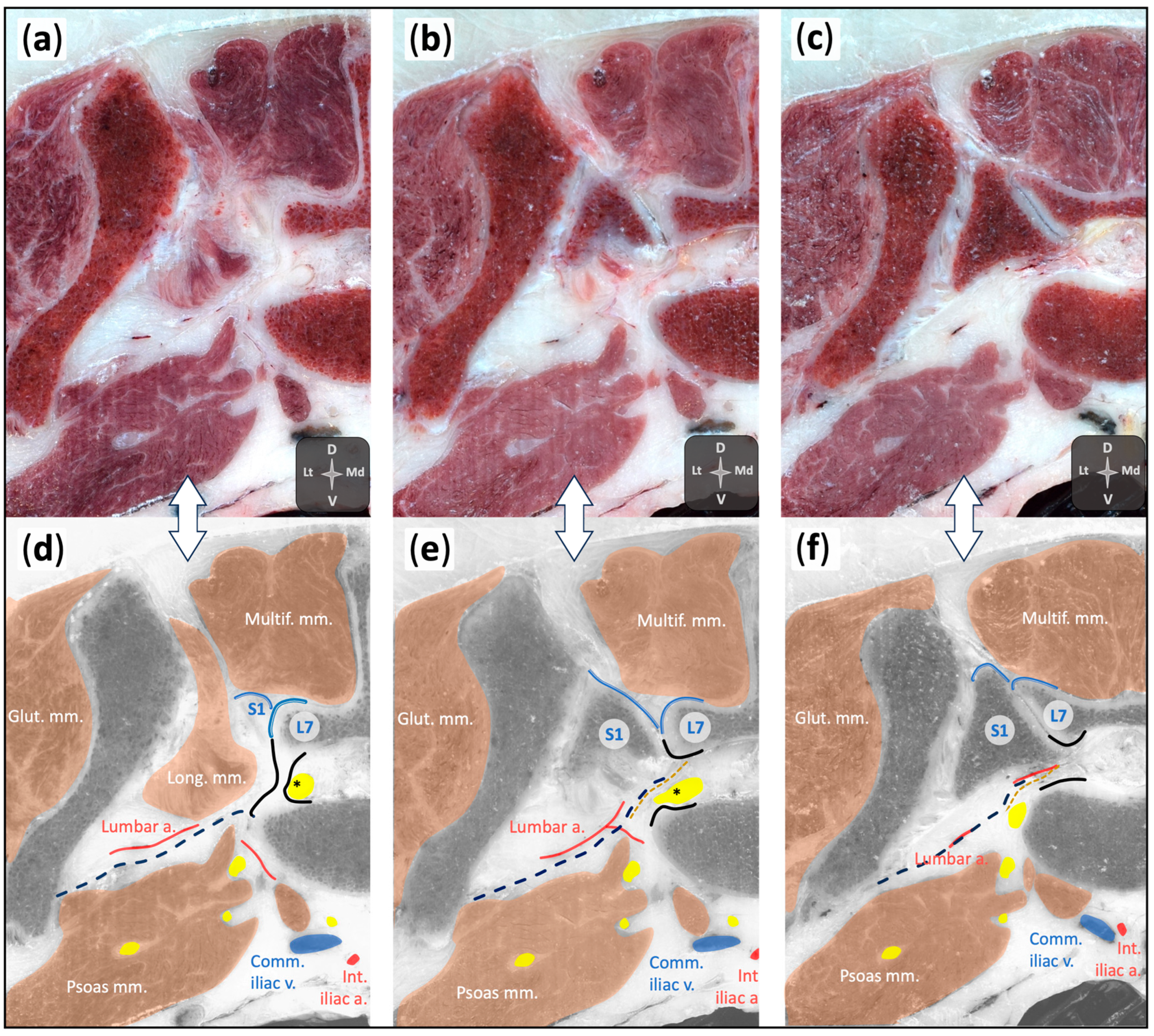
2.1.2. Anatomical Dissections
2.2. Phase II: Technique Performance and Assessment
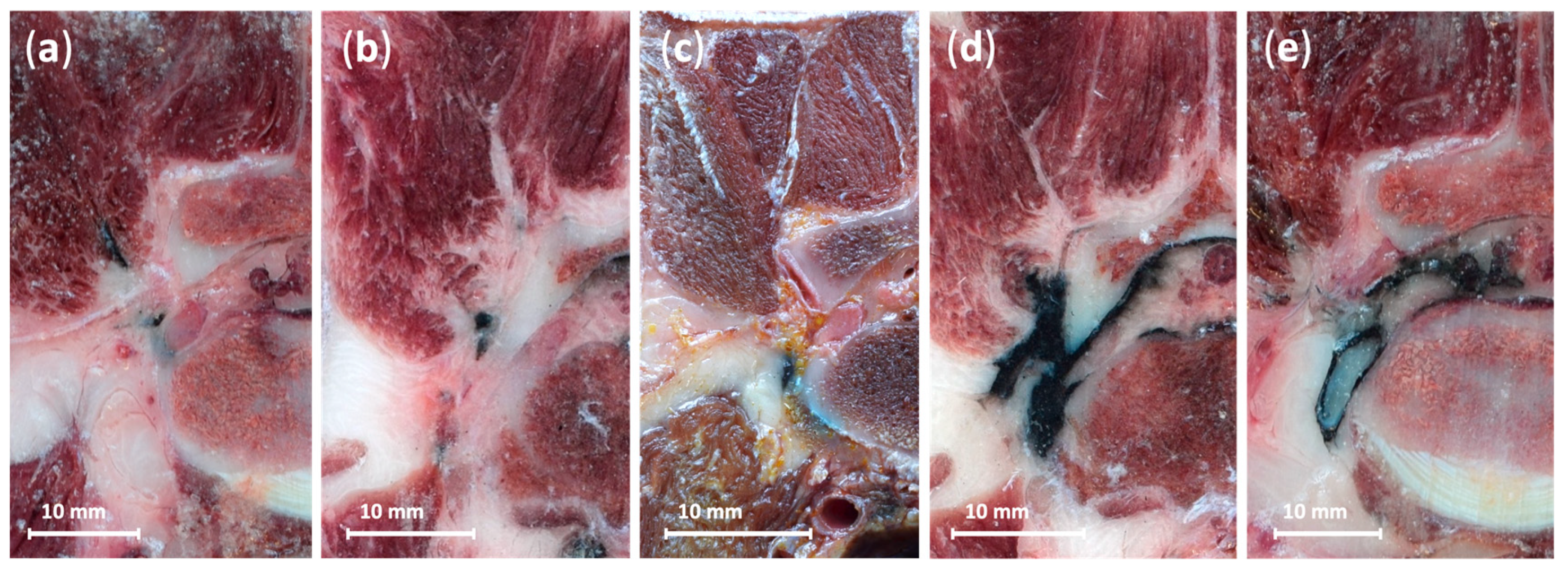
2.2.1. Preliminary Dye Testing and Selection
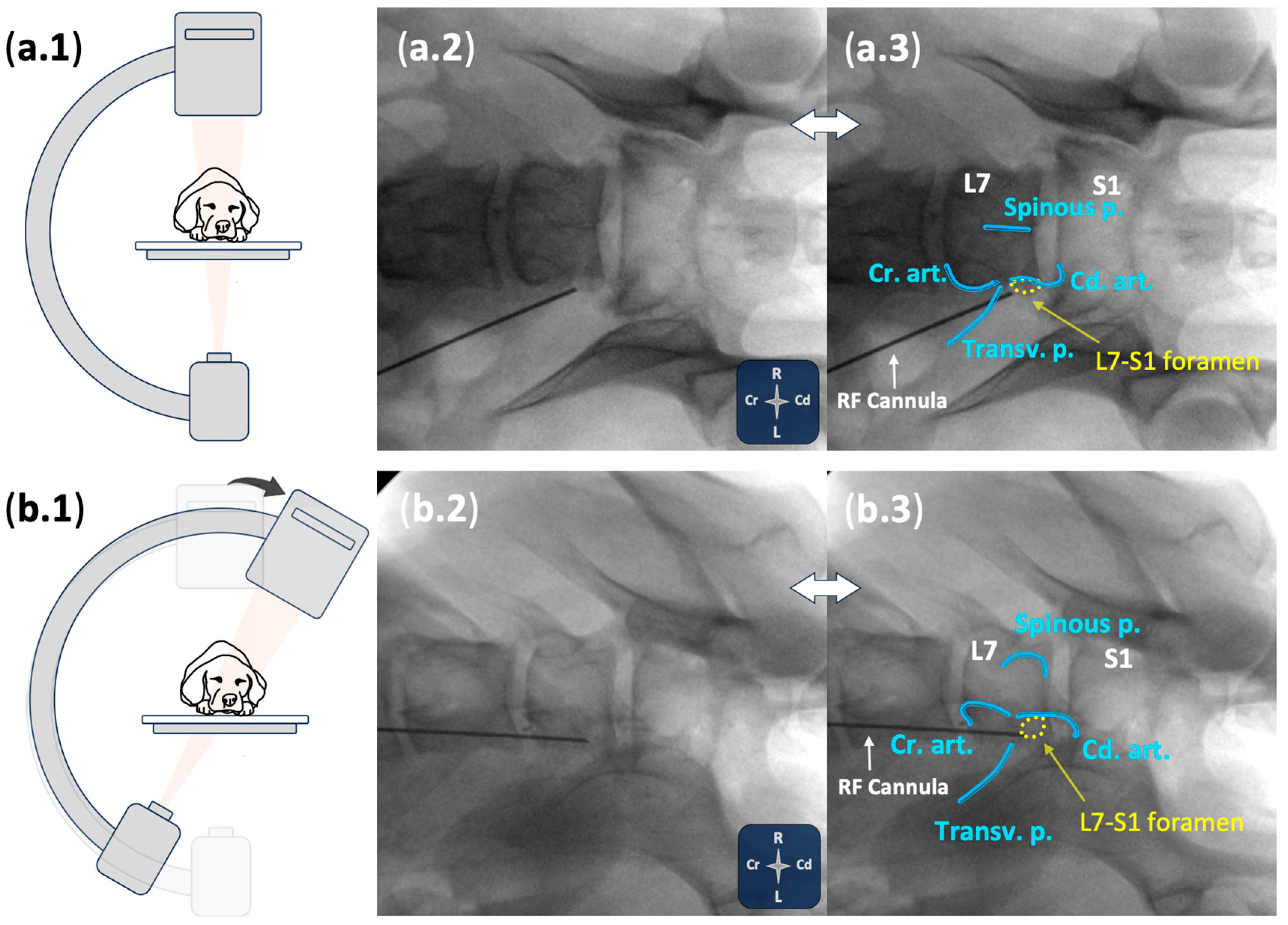
2.2.2. Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Technique
2.2.3. Anatomical Dissections and Technique Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phase I: Anatomical Study
3.2. Phase II: Technique Performance and Assessment
3.2.1. Demographics
3.2.2. Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Technique
3.2.3. Anatomical Dissections and Technique Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ball, R.D. The Science of Conventional and Water-Cooled Monopolar Lumbar Radiofrequency Rhizotomy: An Electrical Engineering Point of View. Pain Physician 2014, 17, E175–E211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosman, E.R.; Cosman, E.R. Electric and Thermal Field Effects in Tissue Around Radiofrequency Electrodes. Pain Med. 2005, 6, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluijter, M.E.; Imani, F. Evolution and Mode of Action of Pulsed Radiofrequency. Anesth. Pain Med. 2013, 2, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.F.; Malayil, R.; Hanes, M.; Deer, T. Unique Characteristics of the Dorsal Root Ganglion as a Target for Neuromodulation. Pain Med. 2019, 20, S23–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krames, E.S. The Dorsal Root Ganglion in Chronic Pain and as a Target for Neuromodulation: A Review. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2015, 18, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Fu, S.; Shi, X.; Liu, R. Microglial BDNF, PI3K, and p-ERK in the Spinal Cord Are Suppressed by Pulsed Radiofrequency on Dorsal Root Ganglion to Ease SNI-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Pain Res. Manag. 2019, 2019, 5948686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.-R. Rapid and Delayed Effects of Pulsed Radiofrequency on Neuropathic Pain: Electrophysiological, Molecular, and Behavioral Evidence Supporting Long-Term Depression. Pain Physician 2017, 2, E269–E283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laksono, R.M.; Kalim, H.; Rohman, M.S.; Widodo, N.; Ahmad, M.R.; Halim, W. Pulsed Radiofrequency Decreases PERK and Affects Intracellular Ca2+ Influx, Cytosolic ATP Level, and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in the Sensitized Dorsal Root Ganglion Neuron Induced by N-Methyl D-Aspartate. J. Pain Res. 2023, 16, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, J.; Catapano, M.; Sahni, S.; Ma, F.; Abd-Elsayed, A.; Visnjevac, O. Pulsed Radiofrequency in Interventional Pain Management: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action—An Update and Review. Pain Physician 2021, 24, 525–532. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Chang, M.C. Efficacy of Pulsed Radiofrequency in Controlling Pain Caused by Spinal Disorders: A Narrative Review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 3528–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuka, I.; Marciuš, T.; Došenović, S.; Ferhatović Hamzić, L.; Vučić, K.; Sapunar, D.; Puljak, L. Efficacy and Safety of Pulsed Radiofrequency as a Method of Dorsal Root Ganglia Stimulation in Patients with Neuropathic Pain: A Systematic Review. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 3320–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Park, J.; Jang, J.N.; Choi, S.; Song, Y.; Kim, Y.U.; Park, S. Pulsed Radiofrequency of Lumbar Dorsal Root Ganglion for Lumbar Radicular Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pain Pract. 2024, 24, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanneste, T.; Van Lantschoot, A.; Van Boxem, K.; Van Zundert, J. Pulsed Radiofrequency in Chronic Pain. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2017, 30, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.N.; Park, S.; Park, J.-H.; Song, Y.; Kim, Y.U.; Kim, D.S.; Sohn, J.E.; Park, S. Output Current and Efficacy of Pulsed Radiofrequency of the Lumbar Dorsal Root Ganglion in Patients with Lumbar Radiculopathy: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized Pilot Study. Pain Physician 2023, 26, E797–E804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erken, B.; Edipoglu, I.S. Efficacy of High-Voltage Pulsed Radiofrequency of the Dorsal Root Ganglion for Treatment of Chronic Lumbosacral Radicular Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2024, 27, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.; Choi, S.-S.; Karm, M.H.; Suh, J.H.; Leem, J.G.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, Y.K.; Shin, J. Treatment of Chronic Lumbosacral Radicular Pain Using Adjuvant Pulsed Radiofrequency: A Randomized Controlled Study. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, A.; Meij, B.; Jeffery, N. Canine Degenerative Lumbosacral Stenosis: Prevalence, Impact and Management Strategies. Vet. Med. 2019, 10, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Serra, R.; López-Abradelo, P.; Belda, E.; Riding-Medina, H.; Laredo, F.G.; Marwood, R.; Mortera, V.; Redondo, J.I. Multivariable Analysis of the Association Between Lumbar and Lumbosacral MRI-Diagnosed Spinal Pathologies and Pain in Dogs. Animals 2025, 15, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.; Becvarova, I.; Cave, N.; MacKay, C.; Nguyen, P.; Rama, B.; Takashima, G.; Tiffin, R.; van Beukelen, P.; Yathiraj, S. WSAVA Nutritional Assessment Guidelines. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heavner, J.E.; Racz, G.B.; Jenigiri, B.; Lehman, T.; Day, M.R. Sharp Versus Blunt Needle: A Comparative Study of Penetration of Internal Structures and Bleeding in Dogs. Pain Pract. 2003, 3, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smuck, M.; Paulus, S.; Patel, A.; Demirjian, R.; Ith, M.A.; Kennedy, D.J. Differential Rates of Inadvertent Intravascular Injection during Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections Using Blunt-Tip, Pencil-Point, and Catheter-Extension Needles. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 2084–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuck, M.; Yu, A.J.; Tang, C.-T.; Zemper, E. Influence of Needle Type on the Incidence of Intravascular Injection during Transforaminal Epidural Injections: A Comparison of Short-Bevel and Long-Bevel Needles. Spine J. 2010, 10, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkhchoui, Y.; Koshkin, E. A Blunt Needle (Epimed ®) Does Not Eliminate the Risk of Vascular Penetration during Transforaminal Epidural Injection. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laredo, F.G.; Belda, E.; Soler, M.; Gil, F.; Murciano, J.; Sánchez-Campillo, J.; Agut, A. Short-Term Effects of Deliberate Subparaneural or Subepineural Injections with Saline Solution or Bupivacaine 0.75% in the Sciatic Nerve of Rabbits. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belda, E.; Laredo, F.G.; Gil, F.; Soler, M.; Murciano, J.; Ayala, M.D.; Gómez, S.; Castells, M.T.; Escobar, M.; Agut, A. Ultrasound-Guided Administration of Lidocaine into the Sciatic Nerve in a Porcine Model: Correlation between the Ultrasonographic Evolution of the Lesions, Locomotor Function and Histological Findings. Vet. J. 2014, 200, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzic, A.; Dilberovic, F.; Shah, S.; Kulenovic, A.; Kapur, E.; Zaciragic, A.; Cosovic, E.; Vuckovic, I.; Divanovic, K.; Mornjakovic, Z. Combination of Intraneural Injection and High Injection Pressure Leads to Fascicular Injury and Neurologic Deficits in Dogs. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2004, 29, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfeldt, T.; Nimphius, W.; Werner, T.; Vassiliou, T.; Kill, C.; Karakas, E.; Wulf, H.; Graf, J. Nerve Injury by Needle Nerve Perforation in Regional Anaesthesia: Does Size Matter? Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 104, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-J.; Park, H.S.; Park, M.K. The Effect of Needle Tip Position on the Analgesic Efficacy of Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment in Patients with Chronic Lumbar Radicular Pain: A Retrospective Observational Study. Korean J. Pain 2019, 32, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahana, A.; Vutskits, L.; Muller, D. Acute Differential Modulation of Synaptic Transmission and Cell Survival during Exposure to Pulsed and Continuous Radiofrequency Energy. J. Pain 2003, 4, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, F.W.; Chan, V.W.S. Monitoring Intraneural Needle Injection. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 118, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.M.; Melton, M.S.; Grill, W.M.; Nielsen, K.C. Peripheral Nerve Stimulation in Regional Anesthesia. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2012, 37, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.D.; Kenny, G.N.; Parbrook, G.D. Basic Physics and Measurement in Anaesthesia, 5th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Croydon, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Paśnicki, M.; Król, A.; Kosson, D.; Kołacz, M. The Safety of Peripheral Nerve Blocks: The Role of Triple Monitoring in Regional Anaesthesia, a Comprehensive Review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, M.; Dolan, J. Challenges, Solutions, and Advances in Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anaesthesia. BJA Educ. 2016, 16, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, J.; Ma, L.; Cai, Z.; Meng, C.; Qi, S.; Zhou, H. Ultrasound-Guided Versus Fluoroscopy-Controlled Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Serra, R.; Belda, E.; López-Abradelo, P.; Zoff, A.; Sanchís-Mora, S. Radiation Exposure during Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Spinal Interventional Pain Management Procedures in Dogs: A Retrospective Analysis in a Single Institution. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, S.; Smith, H.; Meleger, A.; Seibert, J. Radiation Safety in Pain Medicine. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2002, 27, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonkoue, L.; Behets, C.W.; Steyaert, A.; Kouassi, J.-E.K.; Detrembleur, C.; De Waroux, B.L.; Cornu, O. Current versus Revised Anatomical Targets for Genicular Nerve Blockade and Radiofrequency Ablation: Evidence from a Cadaveric Model. Reg. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2020, 45, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina-Serra, R.; Gil-Cano, F.; Laredo, F.G.; Belda, E. Pulsed Radiofrequency for Lumbosacral Radicular Pain in Dogs: Description and Assessment of an Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Technique in a Cadaveric Model. Animals 2025, 15, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172586
Medina-Serra R, Gil-Cano F, Laredo FG, Belda E. Pulsed Radiofrequency for Lumbosacral Radicular Pain in Dogs: Description and Assessment of an Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Technique in a Cadaveric Model. Animals. 2025; 15(17):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172586
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina-Serra, Roger, Francisco Gil-Cano, Francisco G. Laredo, and Eliseo Belda. 2025. "Pulsed Radiofrequency for Lumbosacral Radicular Pain in Dogs: Description and Assessment of an Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Technique in a Cadaveric Model" Animals 15, no. 17: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172586
APA StyleMedina-Serra, R., Gil-Cano, F., Laredo, F. G., & Belda, E. (2025). Pulsed Radiofrequency for Lumbosacral Radicular Pain in Dogs: Description and Assessment of an Ultrasound- and Fluoroscopy-Guided Technique in a Cadaveric Model. Animals, 15(17), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15172586







