The Effects of Salinity on the Survival, Growth, and Eco-Physiological Parameters of Juvenile Sea Urchin Diadema setosum
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Measurement of Growth and Eco-Physiological Parameters
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Survival
3.2. Growth
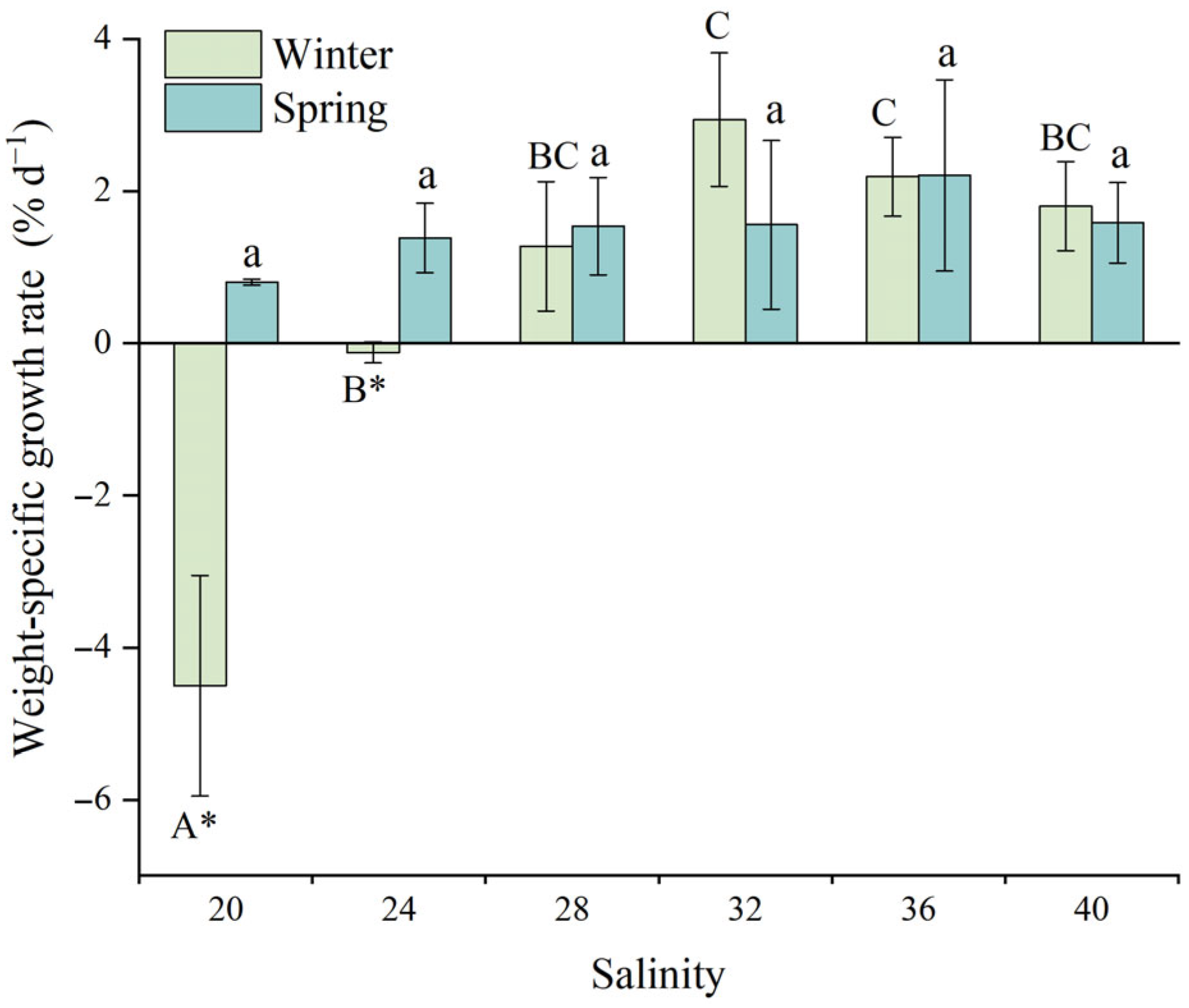
3.2.1. Weight-Specific Growth Rate
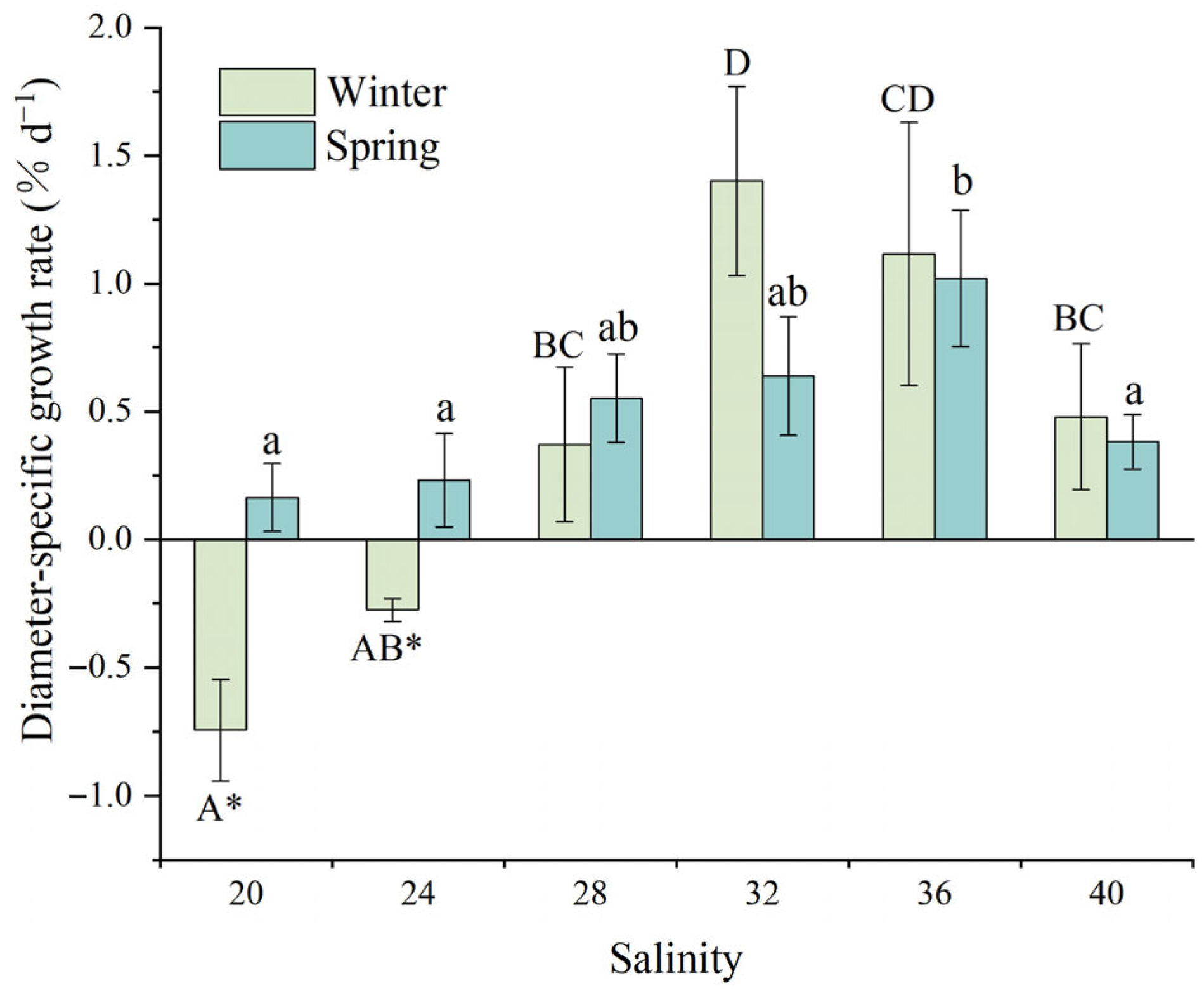
3.2.2. Test Diameter-Specific Growth Rate
3.3. Eco-Physiological Parameters
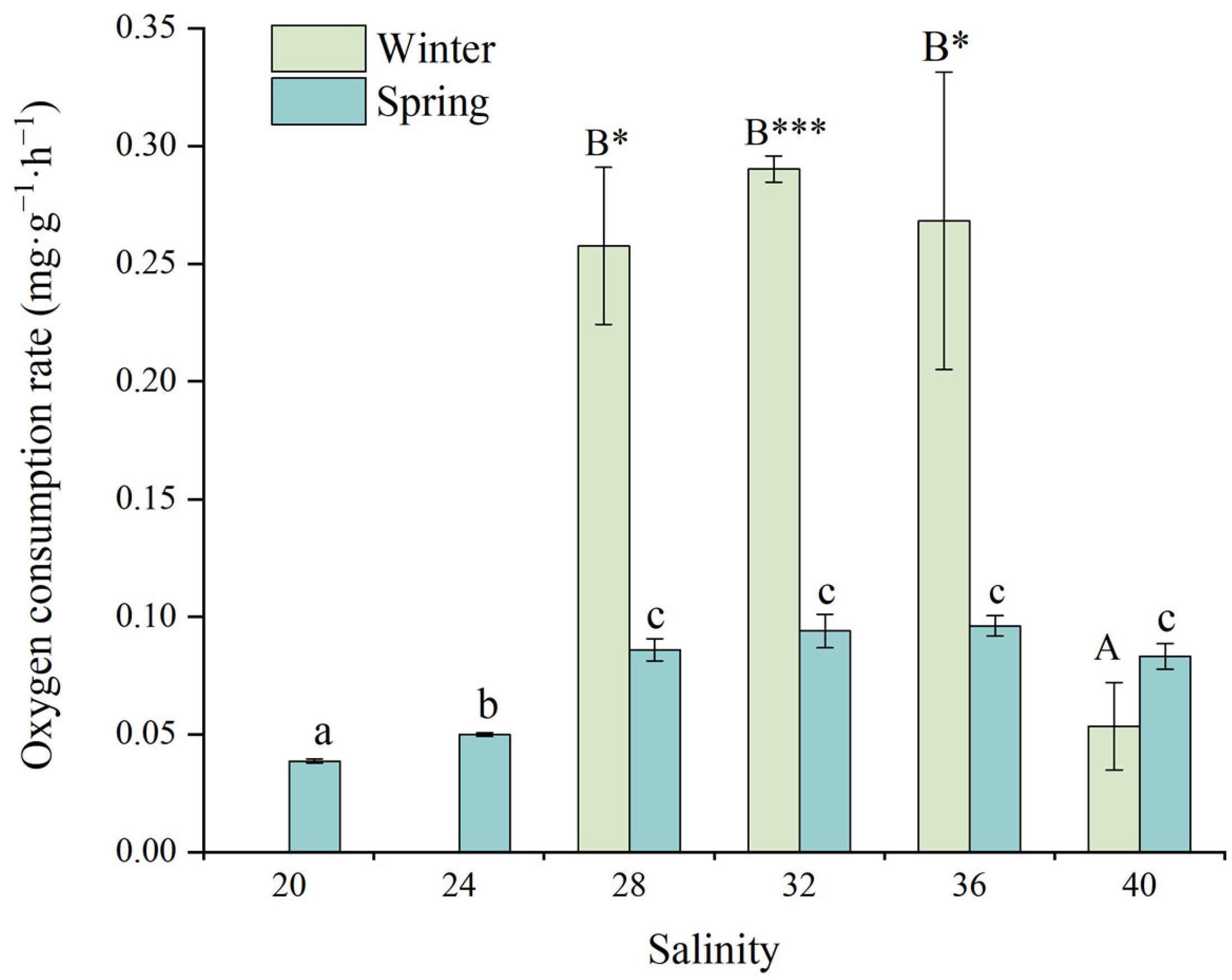
3.3.1. Oxygen Consumption Rate
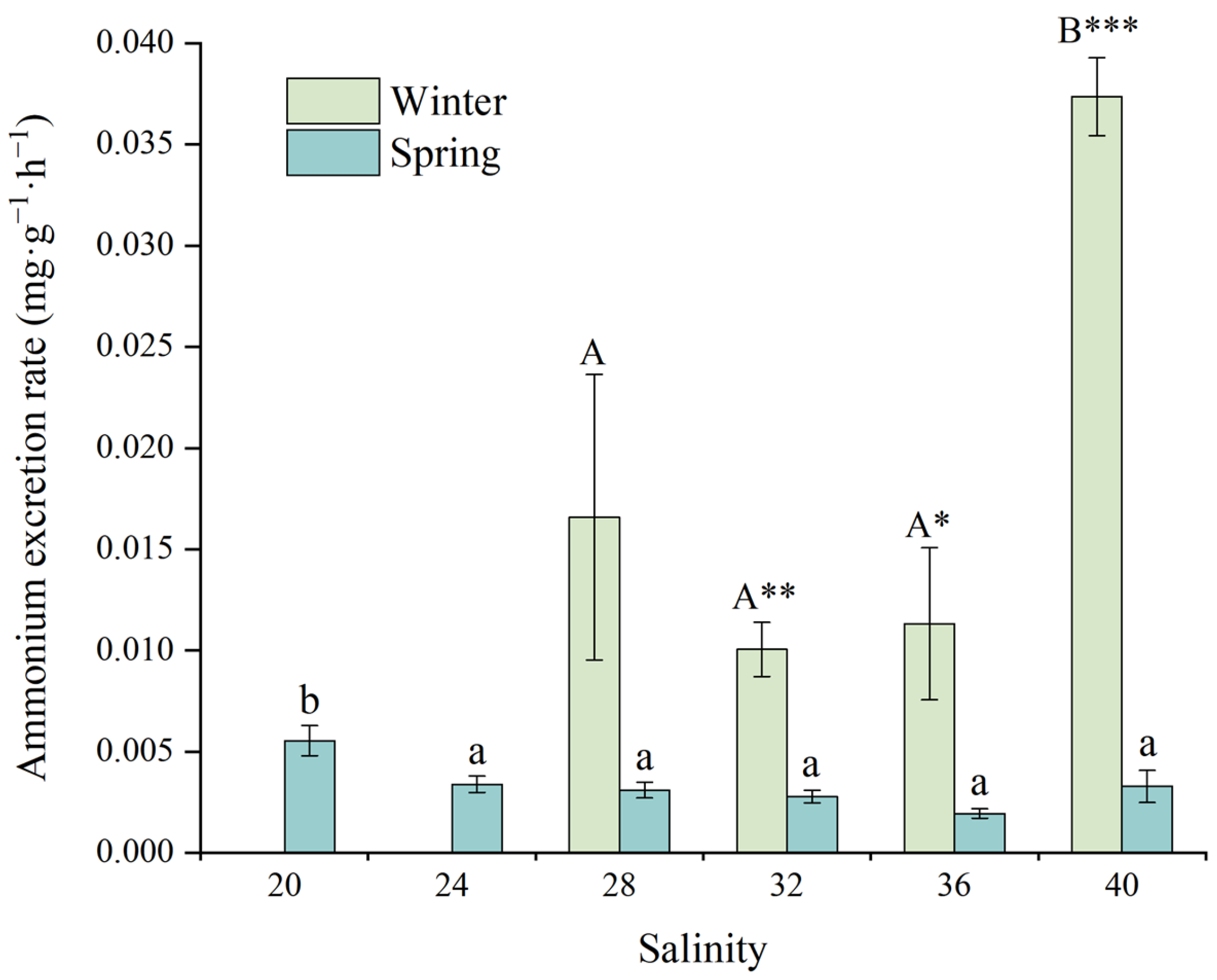
3.3.2. Ammonia Excretion Rate
3.3.3. Atomic O:N Ratio
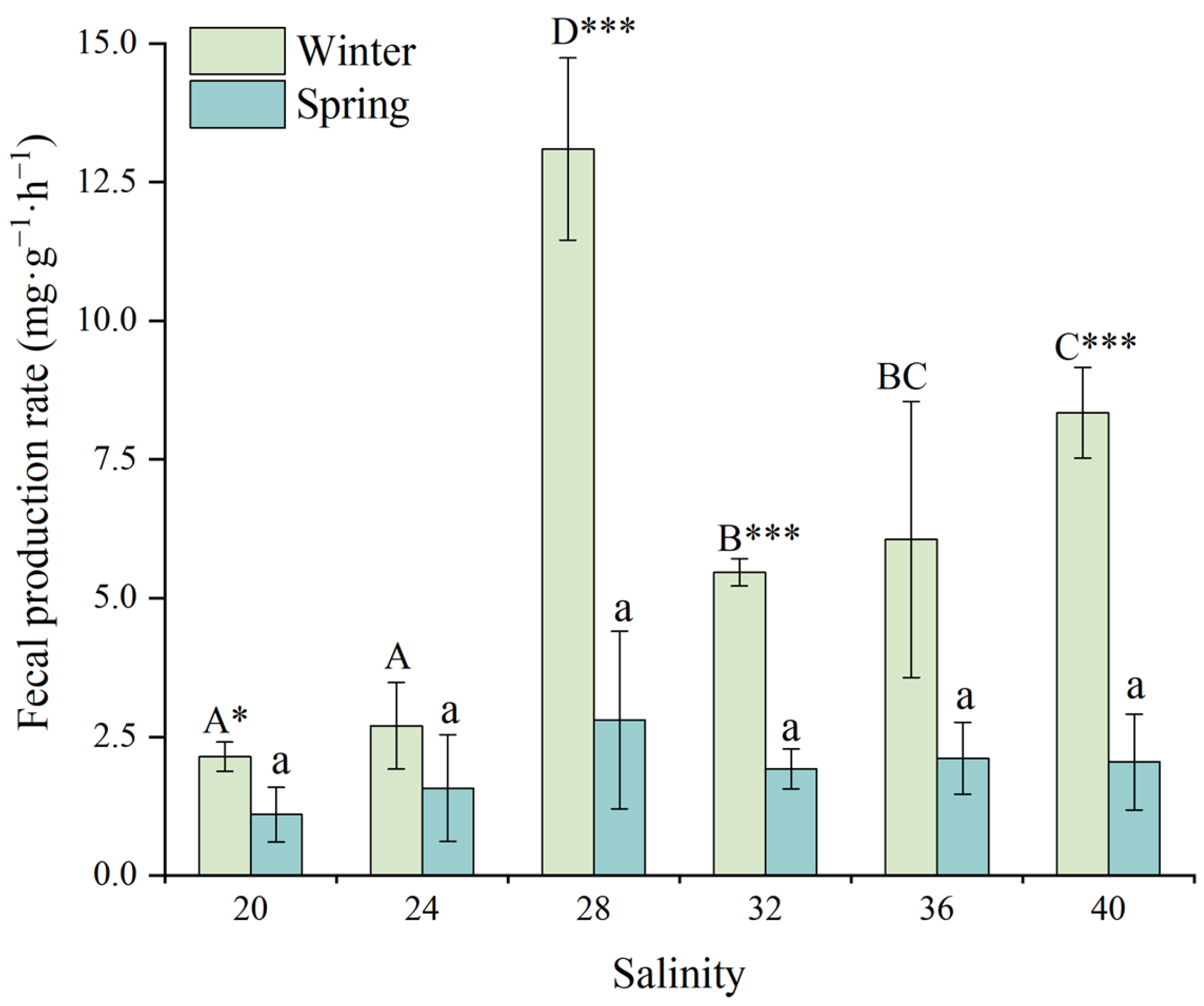
3.4. Fecal Production Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dincer, T.; Cakli, S. Chemical composition and biometrical measurements of the Turkish sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus, Lamarck, 1816). Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.; Pearse, J. Echinoderms from the Gulf of Suez and the northern Red Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. India 1971, 11, 78–125. [Google Scholar]
- Yokes, B.; Galil, B.S. The first record of the needle-spined urchin Diadema setosum (Leske, 1778)(Echinodermata: Echinoidea: Diadematidae) from the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2006, 1, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudhistira, C.Y. Sea Urchin as a Potential Fisheries Resources and Its Management Approach: A Case Study of Pari Island, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta Province, Indonesia. Master’s Thesis, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Distribution patterns and biological aspects of Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis (Echinoidea: Echinoida) in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Implications for commercial exploration. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2024, 34, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leske, N.G.; Klein, J.T. Additamenta ad Iacobi Theodori Klein Naturalem Dispositionim Echinodermatum et Lucubratiunculam de Aculeis Echinorum Marinorum/Nathanaelis Godofredi Leske; Ex Officina Gleditschiana: Leipzig, Germany, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Wu, P.; Gao, F. The community structure of echinoderms in sandy coral reef area in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya, China. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2020, 51, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers-Bennett, L.; Okamoto, D. Mesocentrotus franciscanus and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 43, pp. 593–608. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Aquaculture of green sea urchin in the Barents Sea: A brief review of Russian studies. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, Z. Effects of tourism disturbance on macrobenthic community in intertidal zones of Xisha’s Quanfu Island and Yinyu Island. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2024, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q. Ecological Functions and Ecological Environmental Significance of Sea Urchins in Luhuitou Coral Reef Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, B.; Liao, Y. Sea urchins in China. Bull. Biol. 1957, 7, 18–25+12. [Google Scholar]
- Flammang, P.; Warnau, M.; Temara, A.; Lane, D.J.W.; Jangoux, M.; Jangoux, M. Heavy metals in Diadema setosum (Echinodermata, Echinoidea) from Singapore coral reefs. J. Sea Res. 1997, 38, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinoto, S.; Sukaryono, I.D.; Siahay, Y. Kandungan Gizi Gonad dan Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Cangkang Bulu Babi (Diadema setosum). J. Pascapanen Dan Bioteknol. Kelaut. Dan Perikan. 2017, 12, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liao, Y. General Situation of Sea Urchin Biology. Fish. Sci. 1982, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalman, R.; Werorilangi, S.; Ukkas, M.; Mashoreng, S.; Tahir, A. Microplastic abundance in sea urchins (Diadema setosum) from seagrass beds of Barranglompo Island, Makassar, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 763, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçtürk, E.; Öndes, F.; Alan, V.; Dön, E. Mass Mortality of the Invasive Sea Urchin Diadema setosum in Türkiye, Eastern Mediterranean Possibly Reveals Vibrio Bacteria Infection. Mar. Ecol. 2024, 45, e12837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.Q.; Ding, J.; Song, J.; Yang, W. Biological Research and Culture of Sea Cucumber and Sea Urchin; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 211–215. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Freire, C.A.; Onken, H.; Mcnamara, J.C. A structure-function analysis of ion transport in crustacean gills and excretory organs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 151, 272–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garçon, D.P.; Lucena, M.N.; Pinto, M.R.; Fontes, C.F.L.; McNamara, J.C.; Leone, F.A. Synergistic stimulation by potassium and ammonium of K+-phosphatase activity in gill microsomes from the crab Callinectes ornatus acclimated to low salinity: Novel property of a primordial pump. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 530, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Tian, Y.; Shang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, Y. Effect of acute salinity stress on ion homeostasis, Na+/K+-ATPase and histological structure in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, T.D.; Lawrence, J.M. The effect of salinity on respiration, excretion, regeneration and production in Ophiophragmus filograneus (Echinodermata: Ophiuroidea). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 275, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarifudin, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Yusoff, F.M.; Arshad, A.; Tan, S.G. Influence of salinity variations on the embryonic and early larval development of long-spined black sea urchin (Diadema setosum). J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2017, 27, 316–324. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, Y.; Tu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z. The culture of the tropical sea urchin Salmacis sphaeroides: A new candidate for aquaculture in South China. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Tu, Y.; Luo, J.; Wu, H.; Hong, Z. Standardized Method for Artificial Breeding and Intermediate Cultivation of Tropical Sea Urchins. Chinese Patent CN202210067983, 3 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Luo, P.; Huang, W.; Hu, C. Temporal variations in physiological characteristics of the sea cucumber(Apostichopus japonicus) bottom-cultured in a subtropical fish farm. J. Fish. Sci. China 2018, 42, 863–869. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 12763.4-2007; Specifications for Oceanographic Survey—Part 4: Survey of Chemical Parameters in Sea Water. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Flores, M.; Diaz, F.; Medina, R.; Re, D.; Licea, A. The Effect of Dietary Astaxanthin on Physiological Responses of Juvenile White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Acclimated to Low-Salinity Water. J. Fish. Int. 2008, 3, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Oyervides-Figueroa, J.R.; Re-Araujo, A.D.; Díaz-Herrera, F.; Norzagaray-López, C.O.; Díaz-Castañeda, V.M.; Tripp-Valdez, M.A.; Galindo-Sánchez, C.E.; Cruz, F.L.-D.l. Improved growth performance and physiological state in hybrid abalone (Haliotis rufescens and Haliotis fulgens) facing ocean acidification conditions. Aquaculture 2025, 596, 741791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxas, A.; Young, C.M. Behaviour of echinoid larvae around sharp haloclines: Effects of the salinity gradient and dietary conditioning. Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.W.; Tremblay, R.; Bourget, E. Ontogenetic changes in hyposaline tolerance in the mussels Mytilus edulis and M. trossulus: Implications for distribution. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 228, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranchova, O.L.; Flyachinskaya, L.P. The Influence of Salinity on Early Ontogeny of the Mussel Mytilus edulisand the Starfish Asterias rubensfrom the White Sea. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2001, 27, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, T.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; He, Y. Effects of Low-Salinity Stress on Histology and Metabolomics in the Intestine of Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Animals 2024, 14, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roots, B.J.; Lim, R.; Fourie, S.A.; Rodgers, E.M.; Stout, E.J.; Cronin-O’Reilly, S.; Tweedley, J.R. Hypersalinity Drives Dramatic Shifts in the Invertebrate Fauna of Estuaries. Animals 2025, 15, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iko, R.; Gao, Z.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, H.; Jin, S.; Fu, H. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Macrobrachium nipponense Populations in the Saline–Alkaline Regions of China. Animals 2025, 15, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, B.; Dong, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yao, H. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the ALDH Gene Family in Sinonovacula constricta Bivalve in Response to Acute Hypersaline Stress. Animals 2025, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, N.J.; Sewell, M.A. Temperature and salinity: Two climate change stressors affecting early development of the New Zealand sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, H. Variation in embryonic temperature sensitivity among groups of the sea urchin, Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus, which differ in their habitats. Zool. Sci. 1995, 12, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, M.A.; Young, C.M. Temperature limits to fertilization and early development in the tropical sea urchin Echinometra lucunter. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 236, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam Azad, A.; McKinley, S.; Pearce, C.M. Factors influencing the growth and survival of larval and juvenile echinoids. Rev. Aquac. 2010, 2, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Kong, L. Effects of temperature and salinity on larval growth, survival, and development of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2011, 73, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, N.J.; Sewell, M.A. Temperature limits to early development of the New Zealand sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus (Valenciennes, 1846). J. Therm. Biol. 2013, 38, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, N.A.; Lamare, M.; Uthicke, S.; Wolfe, K.; Doo, S.; Dworjanyn, S.; Byrne, M. Thermal tolerance of early development in tropical and temperate sea urchins: Inferences for the tropicalization of eastern Australia. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, R.A.; Stickle, W.B. Effects of salinity on larval tolerance and early developmental rates of four species of echinoderms. Can. J. Zool. 1985, 63, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, R.A.; Stickle, W.B. Effects of temperature and salinity acclimation of adults on larval survival, physiology, and early development of Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Mar. Biol. 1993, 116, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxas, A. The effect of salinity on larval survival and development in the sea urchin Echinometra lucunter. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1998, 34, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowart, D.A.; Ulrich, P.N.; Miller, D.C.; Marsh, A.G. Salinity sensitivity of early embryos of the Antarctic sea urchin, Sterechinus neumayeri. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.D.; Pechenik, J.A. Understanding the effects of low salinity on fertilization success and early development in the sand dollar Echinarachnius parma. Biol. Bull. 2010, 218, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.F.; Blackburn, H.N.; Allen, J.D. A novel report of hatching plasticity in the phylum Echinodermata. Am. Nat. 2013, 181, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressan, M.; Marin, M.; Brunetti, R. Influence of temperature and salinity on embryonic development of Paracentrotus lividus (Lmk, 1816). Hydrobiologia 1995, 304, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashenko, S. The combined effect of temperature and salinity on development of the sea star Asterina pectinifera. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2006, 32, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Gao, X. The influence of salinity on development and growth of the sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus nudus). J. Fish. China 1991, 15, 72–76+81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Han, J.; LI, D. Effects of salinity on embryonic development, growth and metamorphosis in larval sea urchin Hybrids (Strongylocentrotus intermedius♀×S. nudus♂). Fish. Sci. 2009, 28, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zeng, X.; You, K. Effect of salinity and food on the growth and metamorphosis of the larva of Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2004, 4, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F. Metabolic characteristics of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) during aestivation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Qi, Z.; Hu, C.; Liu, W.; Huang, H. Effects of salinity on ingestion, oxygen consumption and ammonium excretion rates of the sea cucumber Holothuria leucospilota. Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Jiang, H.; Dong, S.; Tian, X. Comparison of oxygen consumption rate and ammonia-N excretion rate between green type and red type Apostichopus japonicus. J. Fish. China 2013, 37, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. The influence of diets containing dried bivalve feces and/or powdered algae on growth and energy distribution in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea). Aquaculture 2006, 256, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, B.L.; Widdows, J. The physiological ecology of two populations of Mytilus edulis L. Oecologia 1978, 37, 137–162. Oecologia 1978, 37, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T. Nutritional Ecology of Marine Zooplankton. In Memoirs of the Faculty of Fisheries; Hokkaido University: Sapporo, Japan, 1974; pp. 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Chen, P.; Qin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, N.; Qiao, P. Effects of temperature and weight on respiratory metabolism of wildlife Anthocidaris crassispina in South China Sea. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2012, 39, 123–125+131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Sun, M.; Hu, Q.; Li, G. Influence of temperature on various development stages of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus nudus A. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1993, 24, 634–640. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F. The Effects of Salinity and Temperature on Feeding and Survival of Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish. Sci. 2002, 6, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X. Effects of water temperature and macroalga species on feeding, respiration and ammonia excretion of sea urchin Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. Fish. Sci. 2020, 39, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Tan, B.; Ding, J.; Chang, Y. Construction of Growth Prediction Models of Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius Exposed to Different Water Temperatures. Chin. J. Fish. 2022, 35, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Luo, J.; Chang, Y. Review on the Effects of Temperature on the Survival, Feeding and Growth of Different—Sized Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Hebei Fish. 2019, 3, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Tong, S.; Zhang, S.; Qu, X. Effects of temperature and salinity on oxygen consumption rate and NH_ (3) excretion rate in sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Fish. Sci. China 1998, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, P.; Feng, Z.; You, X.; Zhang, B.; Song, D. Over—Summering net cage cultivation at seamedium culture andland pond culture of juvenile Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Fish. Sci. China 1999, 6, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. Experimental Studies on the Larval Development and Individual Energy Budget of Sea Urchin, Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; You, L.; Jin, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lin, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, Z. The Effects of Salinity on the Survival, Growth, and Eco-Physiological Parameters of Juvenile Sea Urchin Diadema setosum. Animals 2025, 15, 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162462
Wang X, Zhang J, You L, Jin Y, Lin Z, Lin J, Wu J, Yu Z. The Effects of Salinity on the Survival, Growth, and Eco-Physiological Parameters of Juvenile Sea Urchin Diadema setosum. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162462
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuanliang, Jieyu Zhang, Lei You, Yunyong Jin, Zhenhao Lin, Junhao Lin, Jinhui Wu, and Zonghe Yu. 2025. "The Effects of Salinity on the Survival, Growth, and Eco-Physiological Parameters of Juvenile Sea Urchin Diadema setosum" Animals 15, no. 16: 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162462
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, J., You, L., Jin, Y., Lin, Z., Lin, J., Wu, J., & Yu, Z. (2025). The Effects of Salinity on the Survival, Growth, and Eco-Physiological Parameters of Juvenile Sea Urchin Diadema setosum. Animals, 15(16), 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162462







