Exploring Monthly Variation of Gait Asymmetry During In-Hand Trot in Thoroughbred Racehorses in Race Training
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Horses
2.2. Gait Assessment
2.3. Movement Variables
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Movement Symmetry Distribution
2.4.2. Variability of Gait Symmetry and Range of Motion at Monthly Intervals
2.4.3. Frequency of Switches Between Left- and Right-Sided Asymmetry
3. Results
3.1. Movement Symmetry Characteristics of Thoroughbred Horses in Training Included in This Study
3.2. Variability of Repeat Gait Analysis Measurements
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estberg, L.; Gardner, I.A.; Stover, S.M.; Johnson, B.J.; Case, J.T.; Ardans, A. Cumulative Racing-Speed Exercise Distance Cluster as a Risk Factor for Fatal Musculoskeletal Injury in Thoroughbred Racehorses in California. Prev. Vet. Med. 1995, 24, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estberg, L.; Stover, S.M.; Gardner, I.A.; Drake, C.M.; Johnson, B.; Ardans, A. High-Speed Exercise History and Catastrophic Racing Fracture in Thoroughbreds. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 37, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estberg, L.; Gardner, I.A.; Stover, S.M.; Johnson, B.J. A Case-Crossover Study of Intensive Racing and Training Schedules and Risk of Catastrophic Musculoskeletal Injury and Lay-up in California Thoroughbred Racehorses. Prev. Vet. Med. 1998, 33, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.D.; Berry, S.M.; Peloso, J.G.; Mundy, G.D.; Howard, I. Association of High-Speed Exercise with Racing Injury in Thoroughbreds. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2000, 216, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, J.A.; Scollay, M.C.; Hawkins, D.L.; Corda, J.A.; Krueger, T.M. Evaluation of Horseshoe Characteristics and High-Speed Exercise History as Possible Risk Factors for Catastrophic Musculoskeletal Injury in Thoroughbred Racehorses. AJVR 2005, 66, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, T.H.; Hirst, C.V.; Wilson, A.M. Effect of Speed on Stride Parameters in Racehorses at Gallop in Field Conditions. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 4389–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, M. Analysis of Asymmetrical Gaits. J. Mammal. 1977, 58, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, B.; Ho, W.; Parkes, R.S.V.; Sepulveda Caviedes, M.F.; Pfau, T.; Martel, D.R. Associations between Racing Thoroughbred Movement Asymmetries and Racing and Training Direction. Animals 2024, 14, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda Caviedes, M.F.; Forbes, B.S.; Pfau, T. Repeatability of Gait Analysis Measurements in Thoroughbreds in Training. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringmark, S.; Jansson, A.; Lindholm, A.; Hedenström, U.; Roepstorff, L. A 2.5 Year Study on Health and Locomotion Symmetry in Young Standardbred Horses Subjected to Two Levels of High Intensity Training Distance. Vet. J. 2016, 207, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, A.; Ringmark, S.; Johansson, L.; Roepstorff, L. Locomotion Asymmetry in Young Standardbred Trotters in Training and Links to Future Racing Career. CEP 2022, 18, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, K.G.; MacAllister, C.G.; Wilson, D.A.; Gedon, C.A.; Kramer, J.; Yonezawa, Y.; Maki, H.; Pai, P.F. Comparison of an Inertial Sensor System with a Stationary Force Plate for Evaluation of Horses with Bilateral Forelimb Lameness. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.P.; Reed, S.K.; Schoonover, M.J.; Whitfield, C.T.; Yonezawa, Y.; Maki, H.; Pai, P.F.; Keegan, K.G. Associations of Force Plate and Body-Mounted Inertial Sensor Measurements for Identification of Hind Limb Lameness in Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 77, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.S.M.; Morrice-West, A.V.; Whitton, R.C.; Hitchens, P.L. Changes in Thoroughbred Speed and Stride Characteristics over Successive Race Starts and Their Association with Musculoskeletal Injury. Equine Vet. J. 2022, 55, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCracken, M.J.; Kramer, J.; Keegan, K.G.; Lopes, M.; Wilson, D.A.; Reed, S.K.; LaCarrubba, A.; Rasch, M. Comparison of an Inertial Sensor System of Lameness Quantification with Subjective Lameness Evaluation. Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfau, T.; Witte, T.H.; Wilson, A.M. A Method for Deriving Displacement Data during Cyclical Movement Using an Inertial Sensor. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, S.M.; Koch, T.O.; Pfau, T. Inertial Sensors for Assessment of Back Movement in Horses during Locomotion over Ground. Equine Vet. J. 2010, 42 (Suppl. S3), 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, T.; Reilly, P. How Low Can We Go? Influence of Sample Rate on Equine Pelvic Displacement Calculated from Inertial Sensor Data. Equine Vet. J. 2020, 53, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starke, S.D.; Witte, T.H.; May, S.A.; Pfau, T. Accuracy and Precision of Hind Limb Foot Contact Timings of Horses Determined Using a Pelvis-Mounted Inertial Measurement Unit. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, S.A.; Wyn-Jones, G. Identification of Hindleg Lameness. Equine Vet. J. 1987, 19, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, T.; Boultbee, H.; Davis, H.; Walker, A.; Rhodin, M. Agreement between Two Inertial Sensor Gait Analysis Systems for Lameness Examinations in Horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2016, 28, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byström, A.; Hardeman, A.M.; Engell, M.T.; Swagemakers, J.H.; Koene, M.H.W.; Serra-Bragança, F.M.; Rhodin, M.; Hernlund, E. Normal Variation in Pelvic Roll Motion Pattern during Straight-Line Trot in Hand in Warmblood Horses. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, T.; Starke, S.D.; Tröster, S.; Roepstorff, L. Estimation of Vertical Tuber Coxae Movement in the Horse from a Single Inertial Measurement Unit. Vet. J. 2013, 198, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawin, F.J.; Byström, A.; Roepstorff, C.; Rhodin, M.; Almlöf, M.; Silva, M.; Andersen, P.H.; Kjellström, H.; Hernlund, E. Is Markerless More or Less? Comparing a Smartphone Computer Vision Method for Equine Lameness Assessment to Multi-Camera Motion Capture. Animals 2023, 13, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, K.G.; Kramer, J.; Yonezawa, Y.; Maki, H.; Pai, P.F.; Dent, E.V.; Kellerman, T.E.; Wilson, D.A.; Reed, S.K. Assessment of Repeatability of a Wireless Inertial Sensor-Based Lameness Evaluation System for Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 72, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeman, A.M.; Serra Bragança, F.M.; Swagemakers, J.H.; Weeren, P.R.; Roepstorff, L. Variation in Gait Parameters Used for Objective Lameness Assessment in Sound Horses at the Trot on the Straight Line and the Lunge. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeman, A.M.; Byström, A.; Roepstorff, L.; Swagemakers, J.H. Range of Motion and Between-Measurement Variation of Spinal Kinematics in Sound Horses at Trot on the Straight Line and on the Lunge. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0222822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Chateau, H.; Pourcelot, P.; Duray, L.; Cheze, L. Comparison between Inertial Sensors and Motion Capture System to Quantify Flexion-Extension Motion in the Back of a Horse. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsbergen, K.; Davis, B.; Garcia, K.; Kenny, O.; Kernot, N.; Scott, W.; Sparks, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Toth, K.; Pfau, T. Movement Symmetry and Back Range of Motion in Reining Quarter Horses. J. Equine Rehabil. 2024, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, J.A.; Blake, S.; Ferro De Godoy, R. Surface Electromyography (sEMG) of Equine Core Muscles and Kinematics of Lumbo-Sacral Joint during Core Strengthening Exercises. J. Equine Rehabil. 2023, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peham, C.; Schobesberger, H. A Novel Method to Estimate the Stiffness of the Equine Back. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2845–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaneb, H.; Kaufmann, V.; Stanek, C.; Peham, C.; Licka, T.F. Quantitative Differences in Activities of Back and Pelvic Limb Muscles during Walking and Trotting between Chronically Lame and Nonlame Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. George, L.B.; Spoormakers, T.J.P.; Hobbs, S.J.; Clayton, H.M.; Roy, S.H.; Richards, J.; Serra Bragança, F.M. Classification Performance of sEMG and Kinematic Parameters for Distinguishing between Non-Lame and Induced Lameness Conditions in Horses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1358986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoormakers, T.J.P.; St. George, L.; Smit, I.H.; Hobbs, S.J.; Brommer, H.; Clayton, H.M.; Roy, S.H.; Richards, J.; Serra Bragança, F.M. Adaptations in Equine Axial Movement and Muscle Activity Occur during Induced Fore- and Hindlimb Lameness: A Kinematic and Electromyographic Evaluation during In-hand Trot. Equine Vet. J. 2023, 55, 1112–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, T.; Shaw, K.; Levine, D.; Steve Adair, H.; Richards, J. Electromyography of the Multifidus Muscle in Horses Trotting over Firm and Soft Surfaces. J. Equine Rehabil. 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogossian, P.M.; Nattala, U.; Wong, A.S.M.; Morrice-West, A.; Zhang, G.Z.; Rana, P.; Whitton, R.C.; Hitchens, P.L. A Machine Learning Approach to Identify Stride Characteristics Predictive of Musculoskeletal Injury, Enforced Rest and Retirement in Thoroughbred Racehorses. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.D.H.; Clegg, P.D.; French, N.P.; Proudman, C.J.; Riggs, C.M.; Singer, E.R.; Webbon, P.M.; Morgan, K.L. Horse-Level Risk Factors for Fatal Distal Limb Fracture in Racing Thoroughbreds in the UK. Equine Vet. J. 2010, 36, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, S.P.; Parkin, T.D.H. Risk Factors for Equine Fractures in Thoroughbred Flat Racing in North America. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 139, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

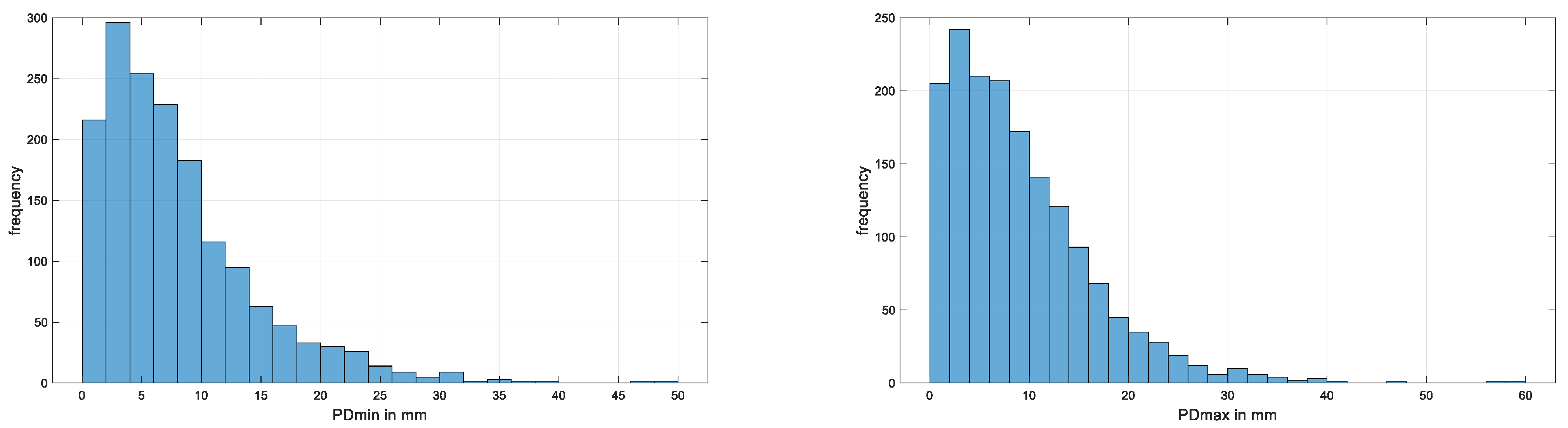
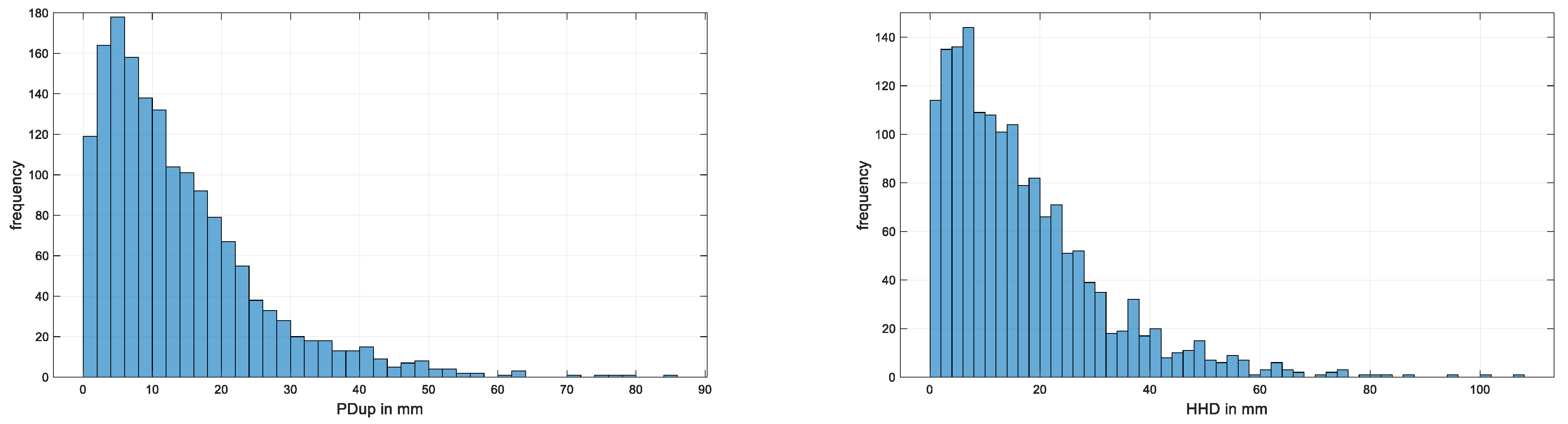
| # Data Sets Per Horse | Number of Horses | Accumulative Number of Horses | Accumulative Number of Data Sets |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 * | 30 * | not included |
| 2 | 32 | 62 | 64 |
| 3 | 40 | 102 | 184 |
| 4 | 32 | 134 | 312 |
| 5 | 25 | 159 | 437 |
| 6 | 18 | 177 | 545 |
| 7 | 23 | 200 | 706 |
| 8 | 19 | 219 | 858 |
| 9 | 15 | 234 | 993 |
| 10 | 10 | 244 | 1093 |
| 11 | 11 | 255 | 1214 |
| 12 | 9 | 264 | 1322 |
| 13 | 7 | 271 | 1413 |
| 14 | 8 | 279 | 1525 |
| 15 | 5 | 284 | 1600 |
| 16 | 2 | 286 | 1632 |
| Statistic | Days Lapsed |
|---|---|
| Minimum | 5 |
| 5th percentile | 26 |
| 10th percentile | 28 |
| 25th percentile | 29 |
| Median | 35 |
| 75th percentile | 42 |
| 90th percentile | 63 |
| 95th percentile | 77 |
| Maximum | 315 |
| HDmin | HDmax | HDup | HROM | Pdmin | PDmax | PDup | HHD | PROM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | −74 | −55 | −105 | 28 | −49 | −56 | −79 | −101 | 36 |
| 5th | −27 | −18 | −36 | 46 | −16 | −19 | −29 | −39 | 53 |
| 10th | −18 | −13 | −25 | 50 | −10 | −15 | −21 | −28 | 57 |
| 25th | −7 | −6 | −11 | 57 | −5 | −8 | −11 | −15 | 64 |
| Median | 2 | 1 | 3 | 66 | 1 | −1 | 0 | −2 | 73 |
| 75th | 11 | 8 | 16 | 75 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 80 |
| 90th | 20 | 14 | 29 | 84 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 22 | 86 |
| 95th | 26 | 19 | 39 | 91 | 17 | 16 | 27 | 31 | 90 |
| Max | 86 | 56 | 102 | 125 | 34 | 59 | 85 | 108 | 109 |
| HDmin | HDmax | HDup | PDmin | PDmax | PDup | HHD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Left | 371 (22.7) | 297 (18.2) | 448 (27.5) | 418 (25.6) | 622 (38.1) | 628 (38.5) | 721 (44.2) |
| # Sym | 761 (46.6) | 947 (58.0) | 565 (34.6) | 647 (39.6) | 550 (33.7) | 368 (22.5) | 326 (20.0) |
| # Right | 500 (30.6) | 388 (23.8) | 619 (37.9) | 567 (34.7) | 460 (28.2) | 636 (39.0) | 585 (35.8) |
| # Right−# Left | +129 | +91 | +171 | +149 | −162 | +8 | −136 |
| HDmin | HDmax | HDup | HROM | PDmin | PDmax | PDup | HHD | PROM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5th | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 10th | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 25th | 4 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| 50th | 9 (8) | 7 | 13 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 9 (8) | 11 (10) | 5 |
| 75th | 15 | 13 | 24 | 13 (12) | 9 | 10 | 16 | 19 | 9 |
| 90th | 25 (24) | 20 | 37 | 21 (20) | 13 | 16 (15) | 24 | 30 (29) | 13 |
| 95th | 33 (32) | 23 | 49 (48) | 26 | 17 | 20 (19) | 30 | 38 (37) | 17 (16) |
| max | 89 | 67 | 134 | 76 | 38 (34) | 60 | 80 | 105 | 70 (67) |
| daily90 * | 14 | 16 | NA | 12 | 11 | 9 | NA | 12 | 15 |
| daily95 * | 16 | 20 | NA | 18 | 11 | 11 | NA | 15 | 18 |
| weekly90 * | 19 | 18 | NA | 17 | 12 | 13 | NA | 11 | 19 |
| weekly95 * | 26 | 22 | NA | 17 | 13 | 18 | NA | 15 | 27 |
| HDmin | HDmax | HDup | AnyHead | PDmin | PDmax | PDup | HHD | AnyPelvis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no switch | 963 (69.99) | 914 (66.42) | 907 (65.92) | 562 (40.84) | 1002 (72.82) | 996 (72.38) | 946 (68.75) | 951 (69.11) | 607 (44.11) |
| switch | 413 (30.01) | 462 (33.58) | 469 (34.08) | 814 (59.16) | 374 (27.18) | 380 (27.62) | 430 (31.25) | 425 (30.89) | 769 (55.89) |
| HDmin | HDmax | HDup | AnyHead | PDmin | PDmax | PDup | HHD | AnyPelvis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no switch | 1289 (93.68) | 1325 (96.29) | 1229 (89.32) | 1179 (85.68) | 1274 (92.59) | 1250 (90.84) | 1151 (83.65) | 1138 (82.70) | 995 (72.31) |
| switch LR | 87 (6.32) | 51 (3.71) | 147 (10.68) | 197 (14.32) | 102 (7.41) | 126 (9.16) | 225 (16.35) | 238 (17.30) | 381 (27.69) |
| HDmin | HDmax | HDup | AnyHead | PDmin | PDmax | PDup | HHD | AnyPelvis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no switch | 1362 (98.98) | 1372 (99.71) | 1327 (96.44) | 1322 (96.08) | 1368 (99.42) | 1361 (98.91) | 1311 (95.28) | 1280 (93.02) | 1262 (91.72) |
| switch LR | 14 (1.02) | 4 (0.29) | 49 (3.56) | 54 (3.92) | 8 (0.58) | 15 (1.09) | 65 (4.72) | 96 (6.98) | 114 (8.28) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pfau, T.; Forbes, B.; Sepulveda-Caviedes, F.; Chan, Z.; Weller, R. Exploring Monthly Variation of Gait Asymmetry During In-Hand Trot in Thoroughbred Racehorses in Race Training. Animals 2025, 15, 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162449
Pfau T, Forbes B, Sepulveda-Caviedes F, Chan Z, Weller R. Exploring Monthly Variation of Gait Asymmetry During In-Hand Trot in Thoroughbred Racehorses in Race Training. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162449
Chicago/Turabian StylePfau, Thilo, Bronte Forbes, Fernanda Sepulveda-Caviedes, Zoe Chan, and Renate Weller. 2025. "Exploring Monthly Variation of Gait Asymmetry During In-Hand Trot in Thoroughbred Racehorses in Race Training" Animals 15, no. 16: 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162449
APA StylePfau, T., Forbes, B., Sepulveda-Caviedes, F., Chan, Z., & Weller, R. (2025). Exploring Monthly Variation of Gait Asymmetry During In-Hand Trot in Thoroughbred Racehorses in Race Training. Animals, 15(16), 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162449





