Positive Correlation Between Economic Activities and Fish Diversity in Small River Basins of Less Developed Regions: A Case Study of the Lixian River Basin
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Total eDNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Economic Data Collection of Yunnan’s Counties and Districts in the Lixian River Basin
2.5. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
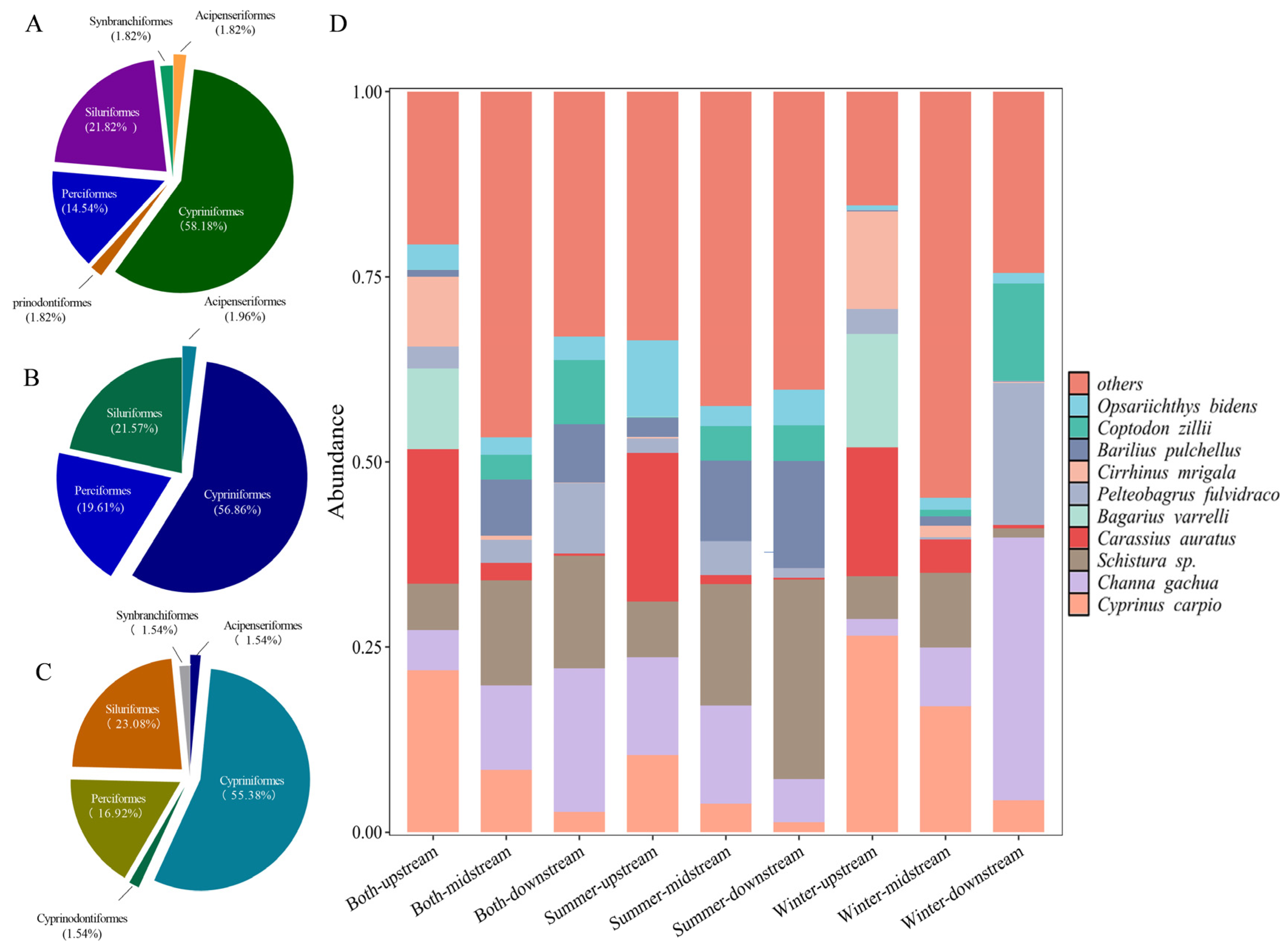
3.1. Species Identification and Composition in the Lixian River
3.2. Fish Diversity and Spatial Distribution Pattern in the Lixian River
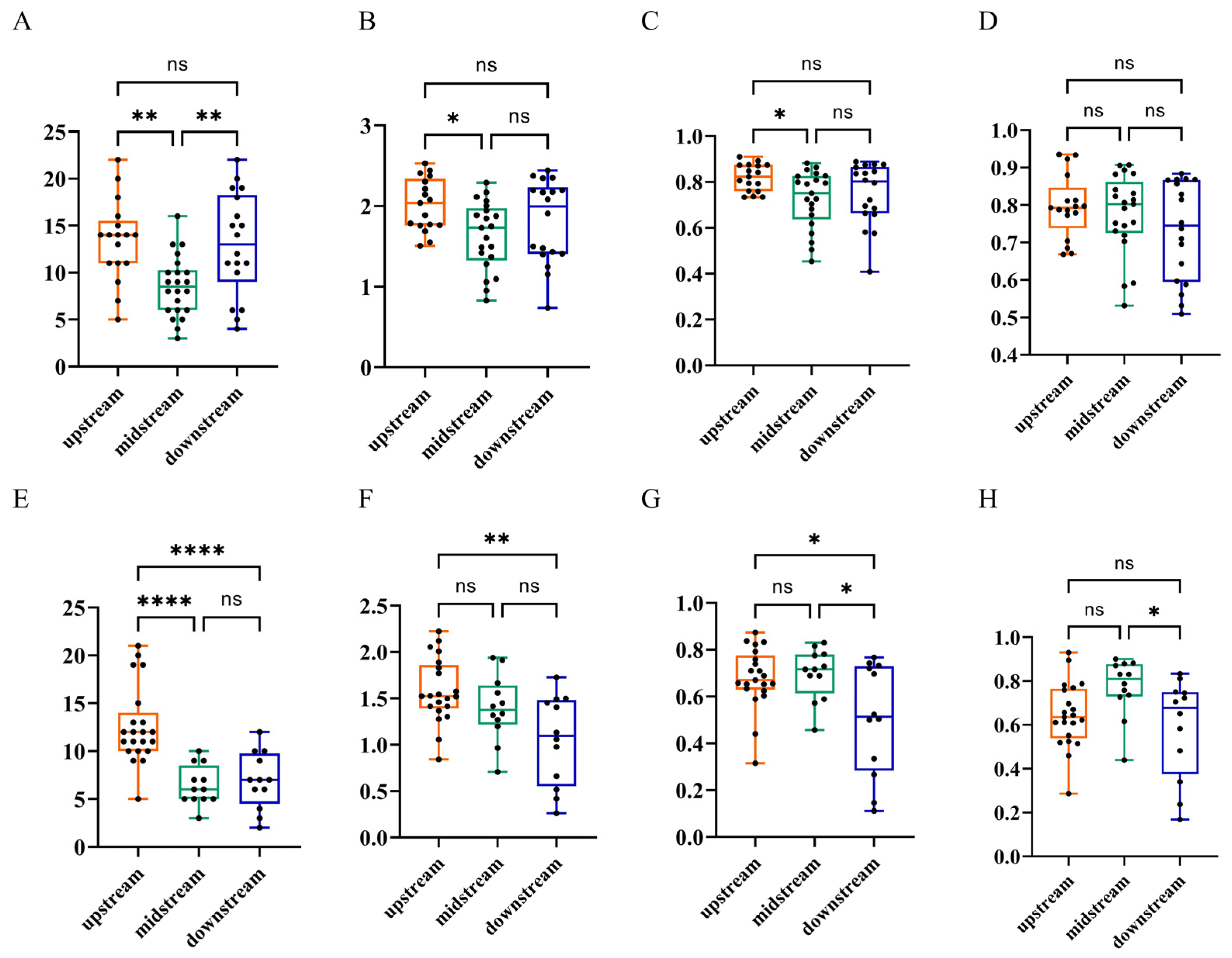
3.2.1. Fish Diversity in the Upstream, Midstream and Downstream Reaches of the Lixian River
3.2.2. Relationship Between the Spatial Distribution Pattern of Fish and Natural Environmental Factors
3.3. The Impacts of Economic Development Level on the Fish Diversity in the Lixian River
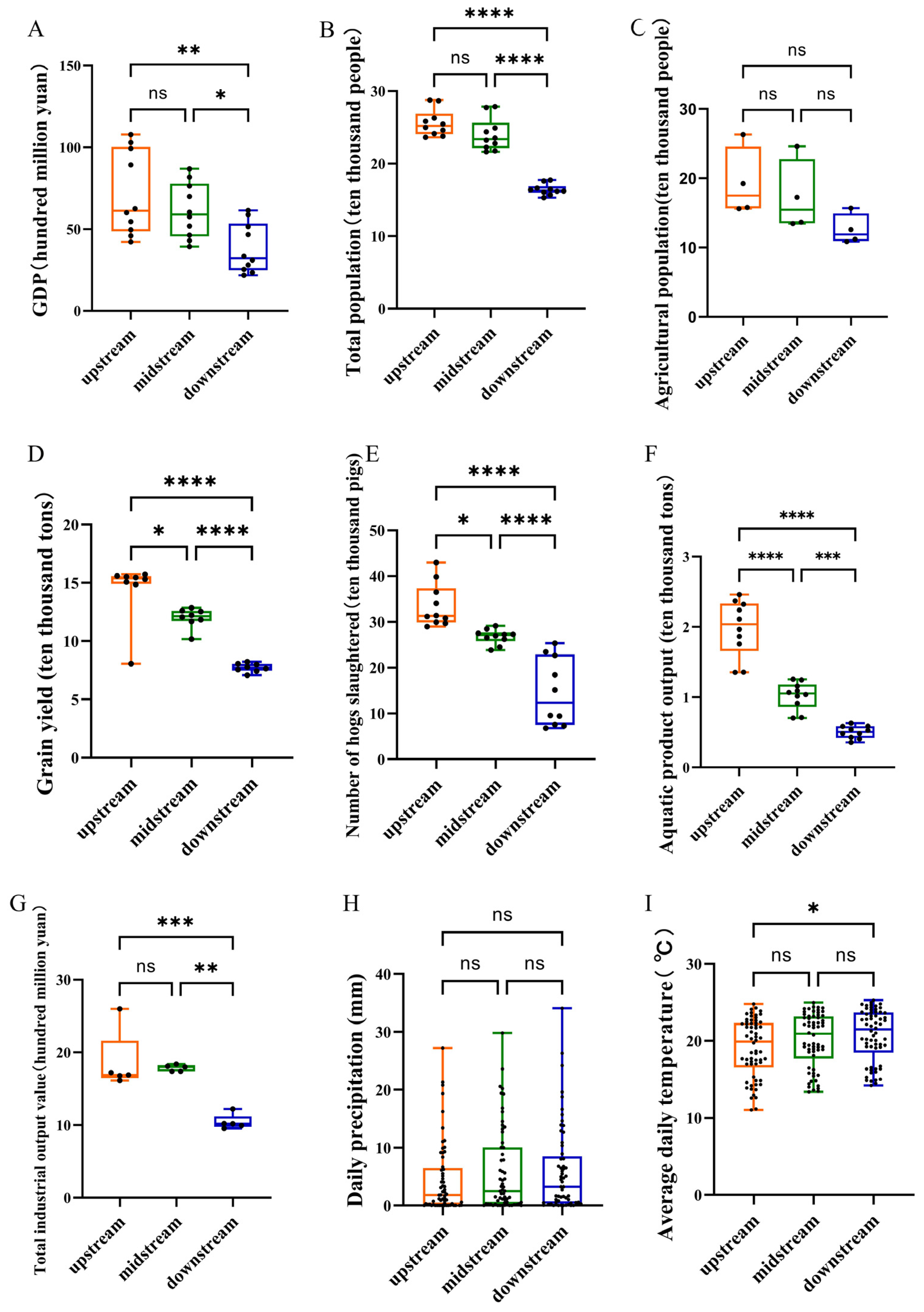
3.3.1. Economic Development and Climate Status of the Upper, Middle, and Lower Reaches of the Lixian River
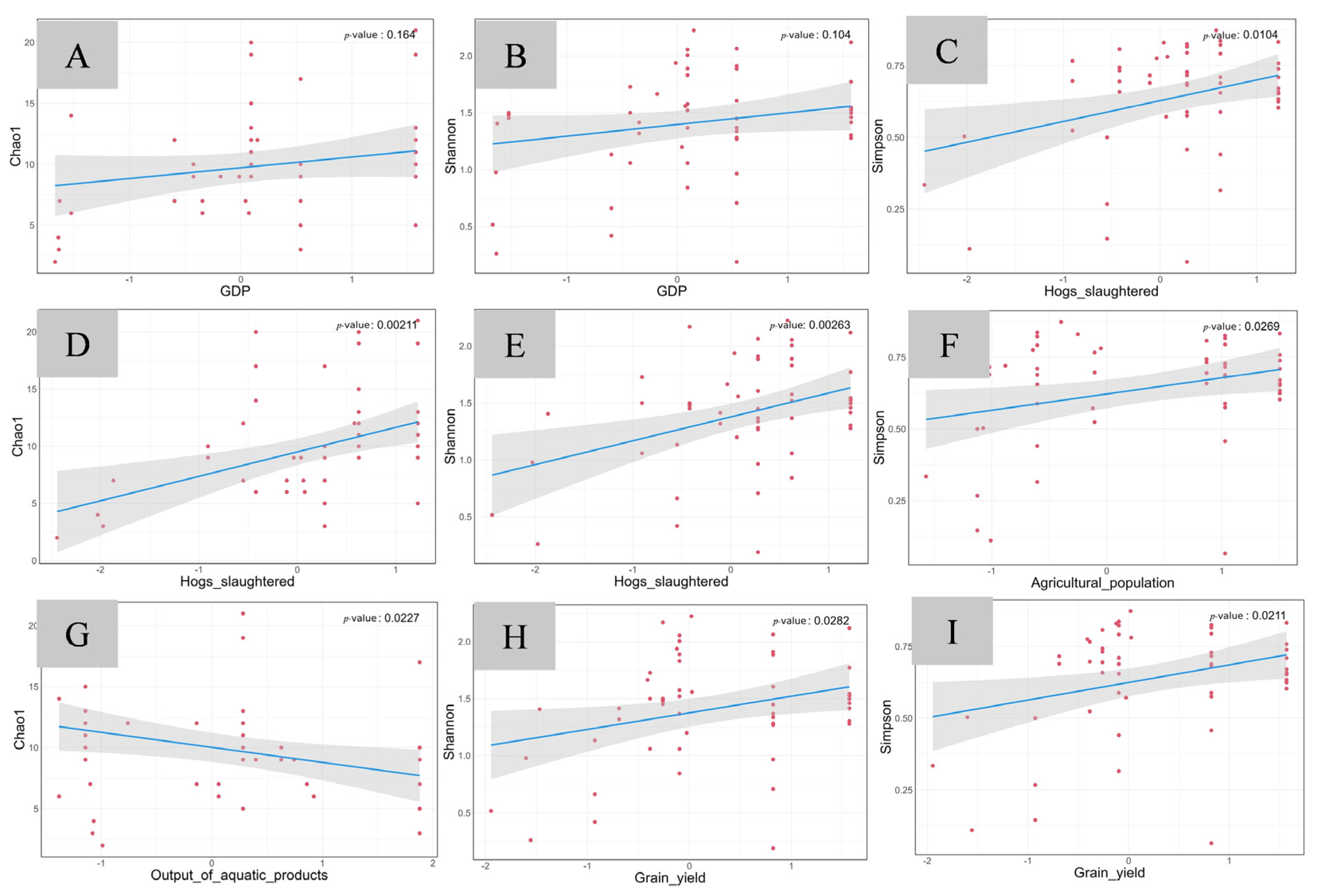
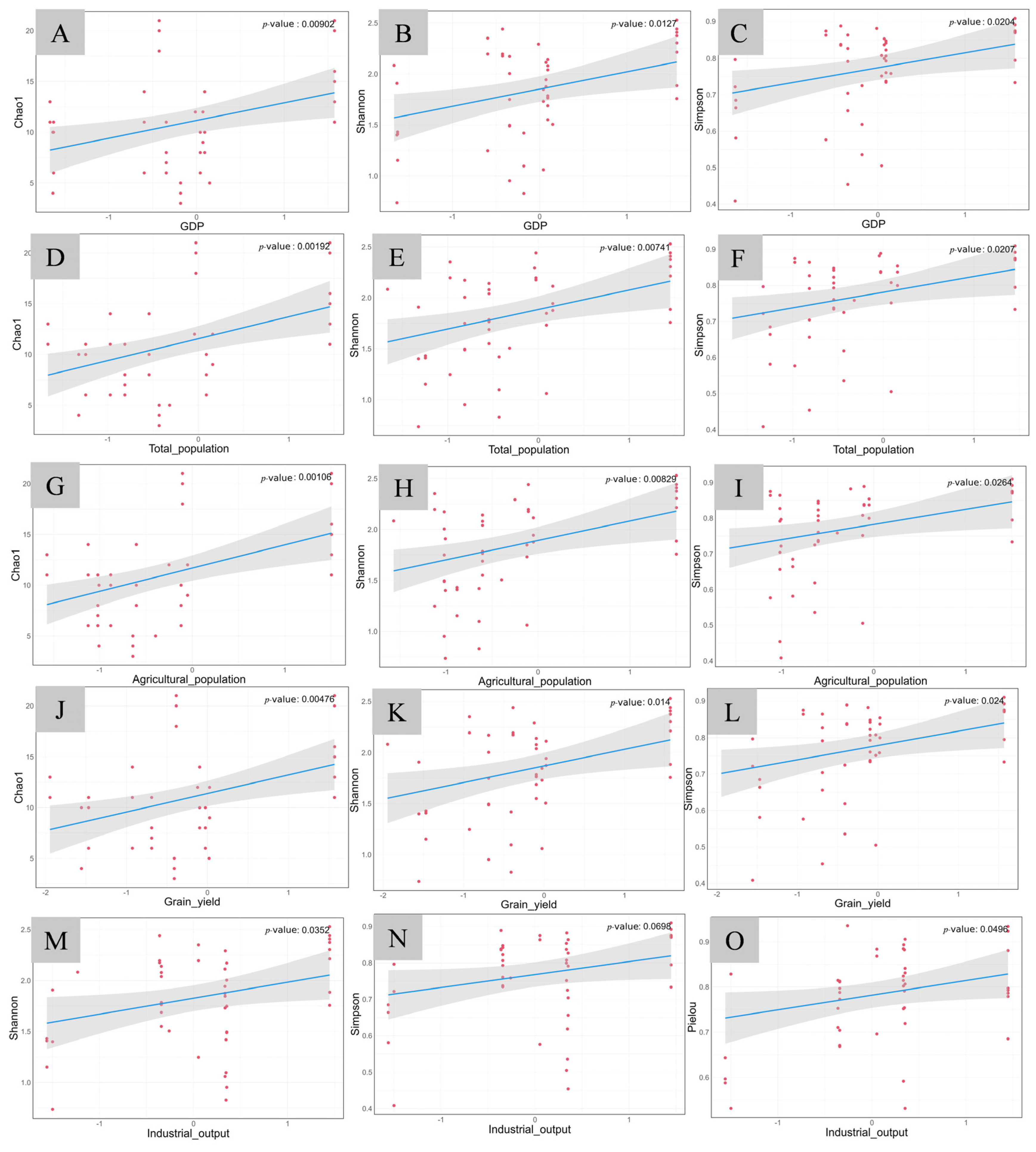
3.3.2. The Relationship Between Fish Diversity and Economic Development in the Lixian River
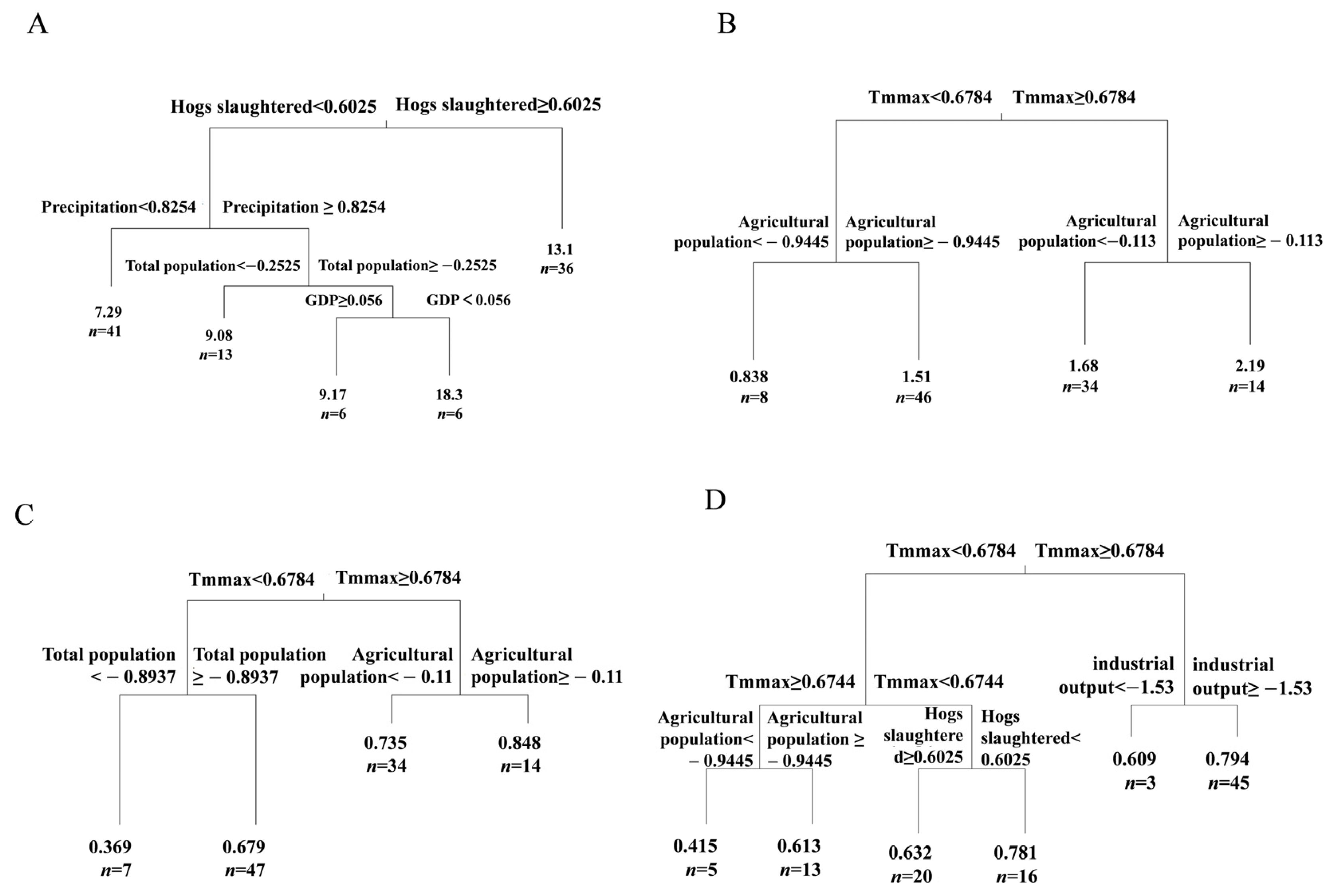
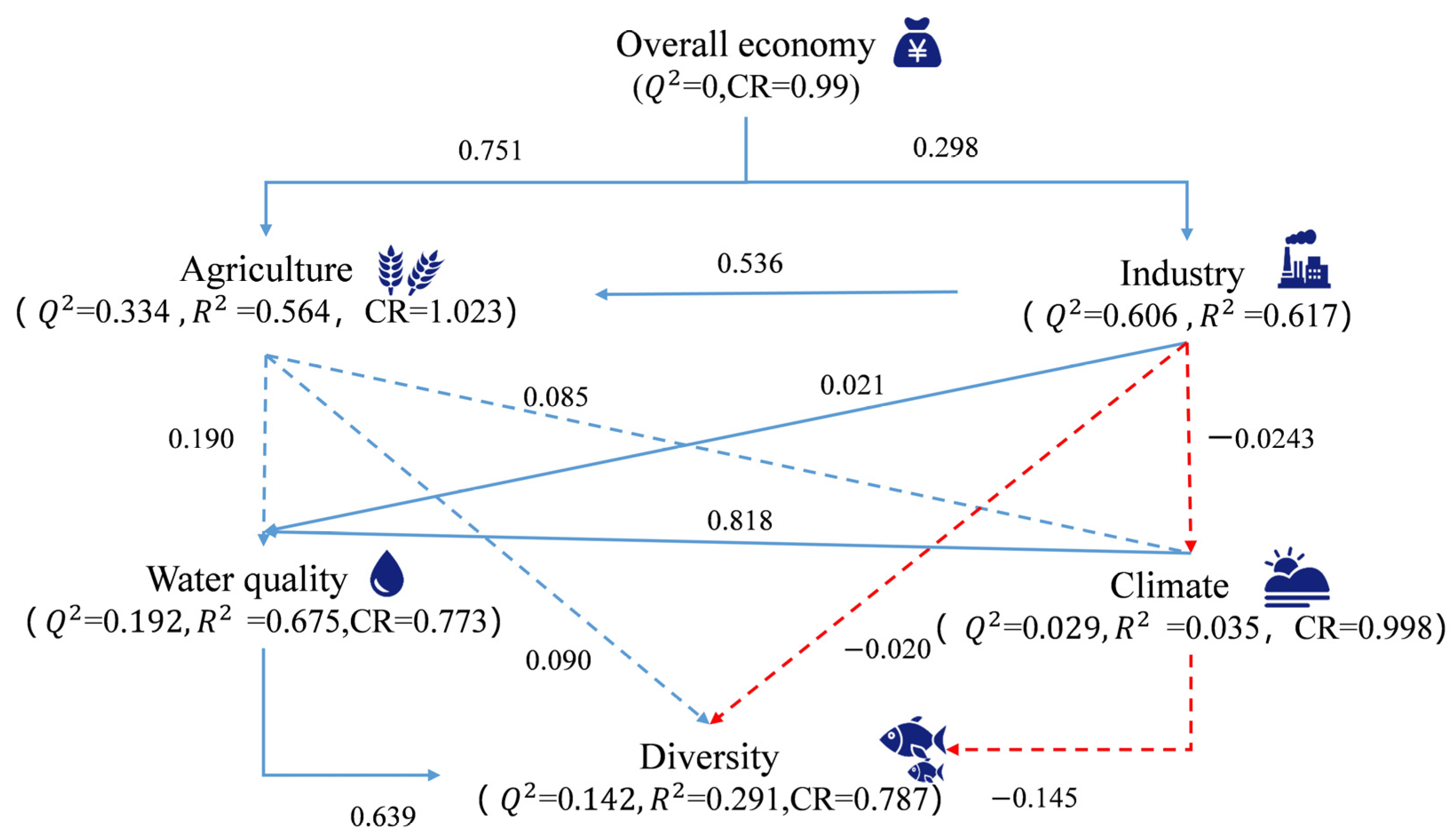
3.4. Mechanisms of Effects of Economic Development Level on Fish Diversity in the Lixian River
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in the Fish Composition of the Lixian River Basin
4.2. Effects of Climate on the Fish Diversity in the Lixian River
4.3. The Impact of Economic Development on Fish Diversity in the Lixian River
4.4. Pathways of the Effects of Economic Development on Fish Diversity in the Lixian River
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| eDNA | Environmental deoxyribonucleic acid |
| OTUs | Operational taxonomic units |
| Temp | Water temperature |
| Tmmax | Maximum temperature |
| Tmmin | Minimum temperature |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| SAL | Salinity |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ASVs | Amplicon sequence variants |
| PCoA | Principal Co-ordinates Analysis |
| CCA | Canonical Correlation Analysis |
| PLS-PM | Partial least-squares path modeling |
References
- Lundberg, J.G.; Kottelat, M.; Smith, G.R.; Melanie, L.J.S.; Gill, A.C. So many fishes, so little time: An overview of recent ichthyological discovery in continental waters. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2000, 87, 26–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erős, T.; Takács, P.; Specziár, A.; Schmera, D.; Sály, P. Effect of landscape context on fish metacommunity structuring in stream networks. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Bremerich, V.; Zarfl, C.; Geldmann, J.; Langhans, S.D.; David, J.N.W.; Darwall, W.; Tockner, K.; Jähnig, S.C. Freshwater megafauna diversity: Patterns, status and threats. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegotto, A.; Dambros, C.S.; Netto, S.A. The scale-dependent effect of environmental filters on species turnover and nestedness in an estuarine benthic community. Ecology 2019, 100, e2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, D. Pattern and process in the ecological biogeography of european freshwater fish. J. Anim. Ecol. 2006, 75, 734–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissi, E.; Schiebinger, L.; Hadly, E.A.; Crowder, L.B.; Santoleri, R.; Micheli, F. Exploring climate-induced sex-based differences in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems to mitigate biodiversity loss. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Chen, Y.; Lek, S.; Li, Z. Large scale patterns in the diversity of lake fish assemblages in China and the effect of environmental factors. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2016, 188, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.S.; Tedesco, P.A.; Hugueny, B.; Jézéquel, C.; Beauchard, O.; Brosse, S.; Oberdorff, T. Anthropogenic stressors and riverine fish extinctions. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 79, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Pédron, S.; Mehner, T.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Argillier, C.; Winfield, I.J.; Volta, P.; Emmrich, M.; Hesthagen, T.; Holmgren, K.; et al. Fish diversity in European lakes: Geographical factors dominate over anthropogenic pressures. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, C.; Beilin, R.; Folke, C.; Lindborg, R. Farmland abandonment: Threat or opportunity for biodiversity conservation? A global review. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; Jamoneau, A.; Rosebery, J.; Passy, S.I. Global patterns and drivers of species and trait composition in diatoms. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limburg, K.E.; Hughes, R.M.; Jackson, D.C.; Czech, B. Human population increase, economic growth, and fish conservation: Collision course or savvy stewardship? Fisheries 2011, 36, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, R.; York, R. Global biodiversity decline of marine and freshwater fish: A cross-national analysis of economic, demographic, and ecological influences. Soc. Sci. Res. 2008, 37, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Chen, Y.; Gozlan, R.E.; Li, Z.; Mehner, T.; Lek, S.; Paukert, C.P. Biogeographic freshwater fish pattern legacy revealed despite rapid socio-economic changes in China. Fish. Fish. 2019, 20, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, K.M.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, M.S. Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DAN (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e547. [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson, M.D.; Kelly, R.P.; Duda, J.J.; Hoy, M.; Kralj, J.; Quinn, T.P. Concentrations of environmental DNA (eDNA) reflect spawning salmon abundance at fine spatial and temporal scales. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 220, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, J.J.; BENSON, B.J.; MCLAIN, A.S. Insights on species richness and turnover from long-term ecological research: Fishes in North Temperate Lakes. Am. Zool. 1994, 34, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Ma, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, G.; Geng, Y.; Yu, D.W. Using eDNA to detect the distribution and density of invasive crayfish in the honghe-hani rice terrace world heritage site. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e177724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, C.M.; Kidd, A.G.; Wilson, C.C. Development and validation of environmental DNA (eDNA) markers for detection of freshwater turtles. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e130965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, A.D.; Thomsen, P.F.; Sveegaard, S.; Wahlberg, M.; Kielgast, J.; Kyhn, L.A.; Salling, A.B.; Galatius, A.; Orlando, L.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Investigating the potential use of environmental DNA (eDNA) for genetic monitoring of marine mammals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilliod, D.; Goldberg, C.; Arkle, R.; Waits, L. Estimating occupancy and abundance of stream amphibians using environmental DNA from filtered water samples. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.T.; Olds, B.P.; Renshaw, M.A.; Turner, C.R.; Li, Y.; Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Pfrender, M.E.; Lamberti, G.A.; Lodge, D.M. Quantification of mesocosm fish and amphibian species diversity via environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, F.; Gao, W.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Environmental DNA biomonitoring reveals the interactive effects of dams and nutrient enrichment on aquatic multitrophic communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16952–16963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. The current status and protection strategies of fish resources in Lixian river. J. Water Ecol. 2010, 31, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, X.; Zhou, W.; Yang, M. Fish resource protection in hydropower development of Lixian river basin in Yunnan province. Zool. Res. 2011, 32, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Deiner, K.; Walser, J.; Mächler, E.; Altermatt, F. Choice of capture and extraction methods affect detection of freshwater biodiversity from environmental DNA. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Bonin, A.; Zinger, L.; Coissac, E. Environmental DNA: For Biodiversity Research and Monitoring; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. Vsearch: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. Peer J. 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y. Yunnan Fish Atlas; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Hou, Y.; He, D.; Ji, Y. Color Atlas of Pu’er Indigenous Fish; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y. Species and Distribution of Inland Fish in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Balasingham, K.D.; Walter, R.P.; Mandrak, N.E.; Heath, D.D. Environmental DNA detection of rare and invasive fish species in two great lakes tributaries. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Gao, H.; Qu, W.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Duan, Z. Fish communities and diversity in river ecosystems on the qinghai-tibet plateau revealed by environmental DNA (eDNA) method. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Computing 2022, 1, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau, T.M.; Atkinson, B.; Riple, B.; Oksanen, J.; De’Ath, G. Mvpart: Multivariate Partitioning. R Package Version 1.6-2. 2014. Available online: https://r-forge.r-project.org/projects/mvpart (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 183–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, G.; Trinchera, L.; Russolillo, G. Plspm: Partial Least Squares Path Modeling (PLS-PM). R Package Version 0.5.1. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/gastonstat/plspm (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Epskamp, S. Semplot: Path Diagrams and Visual Analysis of Various Sem Packages Output. R Package Version 1.1.6. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/SachaEpskamp/semPlot (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, V.; Tamam, M.B. First record of the invasive nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Perciformes, Cichlidae), on Bawean Island, Indonesia. Check List. 2019, 15, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Dai, Y.; Gong, Y. Economic profitability of tilapia farming in China. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C.; Yohe, G. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 2003, 421, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorosmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, D. Large-scale hydrological changes in tropical asia: Prospects for riverine biodiversity. Bioscience 2000, 50, 793–806. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, N.; Sen, R.; Chowdhury, M.A. Consequences of climate change on fish diversity in Dekhar Haor Bangladesh. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019, 7, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Smalås, A.; Primicerio, R.; Kahilainen, K.K.; Terentyev, P.M.; Kashulin, N.A.; Zubova, E.M.; Amundsen, P.A. Increased importance of cool-water fish at high latitudes emerges from individual-level responses to warming. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Knust, R. Climate change affects marine fishes through the oxygen limitation of thermal tolerance. Science 2007, 315, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinaya, W.; Lobon-Cervia, F.J.; Pita, P.; de Souza, R.B.; Freire, J.; Isaac, V.J. Multispecies fisheries in the lower amazon river and its relationship with the regional and global climate variability. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e157050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehanen, T.; Sutela, T.; Huusko, A. Potential impact of climate change on salmonid smolt ecology. Fishes 2023, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, T.; Martinsen, K.T.; Kristensen, E.; Sand-Jensen, K. From drought to flood: Sudden carbon inflow causes whole-lake anoxia and massive fish kill in a large shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, M.; Martinez-Andrade, F.; Wells, R.J.D.; Fisher, M.; Pawluk, M.; Livernois, M.C. Climate-related factors cause changes in the diversity of fish and invertebrates in subtropical coast of the Gulf of Mexico. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabia, I.D.; García Molinos, J.; Hirata, T.; Mueter, F.J.; David, C.L. Pan-arctic marine biodiversity and species co-occurrence patterns under recent climate. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4076. [Google Scholar]
- Siwertsson, A.; Lindström, U.; Aune, M.; Berg, E.; Skardhamar, J.; Varpe, O.; Primicerio, R. Rapid climate change increases diversity and homogenizes composition of coastal fish at high latitudes. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, A.L.; Low, P.J.; Ellis, J.R.; Reynolds, J.D. Climate change and distribution shifts in marine fishes. Science 2005, 308, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Vander Zanden, M.J.; Magnuson, J.J.; Lyons, J. Comparing climate change and species invasions as drivers of coldwater fish population extirpations. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.W.; Schaefer, C. The absolute general law of environmental degradation under capitalism. Capital. Nat. Social. 1992, 21, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Thieme, M.; Zarfl, C.; Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Hogan, Z.; Tockner, K.; Jähnig, S.C. Impacts of loss of free-flowing rivers on global freshwater megafauna. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 263, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Guo, F.; Kainz, M.J.; Li, F.; Gao, W.; Bunn, S.E.; Zhang, Y. The importance of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as high-quality food in freshwater ecosystems with implications of global change. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2024, 99, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Fan, J.; Guo, F.; Carpenter-Bundhoo, L.; Huang, G.; Shi, Y.; Ao, Y.; Wang, J. Assessing the impact of river connectivity on fish biodiversity in the Yangtze River basin using a multi-index evaluation framework. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. The ecological consequences of changes in biodiversity: A search for general principles. Ecology 1999, 80, 1455–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamees, R.; Püssa, K.; Zobel, K.; Zobel, M. Restoration potential of the persistent soil seed bank in successional calcareous (alvar) grasslands in Estonia. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2012, 15, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Dalsgaard, J.; Froese, R.; Torres, F. Fishing down marine food webs. Science 1998, 279, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.M.; Arenas, F.; Neto, A.I.; Jenkins, S.R. Effects of fishing and regional species pool on the functional diversity of fish communities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Ling, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, L.; Xie, G. Evolution of corresponding resistance genes in the water of fish tanks with multiple stresses of antibiotics and heavy metals. Water Res. 2017, 124, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, R.L.; Goldburg, R.J.; Primavera, J.H.; Kautsky, N.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Clay, J.; Folke, C.; Lubchenco, J.; Mooney, H.; Troell, M. Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 2000, 405, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, I.; Fonseca-Alves, C. Impact of introduced nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) on non-native aquatic ecosystems. Pak. J. Bio Sci. 2013, 16, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kou, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, S. Fish gut microbiome analysis provides insight into differences in physiology and behavior of invasive Nile tilapia and indigenous fish in a large subtropical river in China. Animals 2023, 13, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, C.O.; Buckley, C.; Chyzheuskaya, A.; Green, S.; Howley, P.; Hynes, S.; Upton, V.; Ryan, M. The spatial impact of rural economic change on river water quality. Land. Use Pol. 2021, 103, 105322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, L.; Li, Y.; Zou, G.; Wu, J.; Zheng, J. Using modern coexistence theory to understand the distinct states of phytoplankton communities in a subtropical eutrophic river network. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smucker, N.; Becker, M.; Detenbeck, N.; Morrison, A. Using algal metrics and biomass to evaluate multiple ways of defining concentration-based nutrient criteria in streams and their ecological relevance. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 32, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, R.F.; Everett, J.D.; Blanchard, J.L.; Sykes, P.; Richardson, A.J. Climate-driven zooplankton shifts cause large-scale declines in food quality for fish. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Palmer, M.A.; Collins, S.L. Species diversity enhances ecosystem functioning through interspecific facilitation. Nature 2002, 415, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, L.; Nicolle, A.; Graneli, W.; Hallgren, P.; Kritzberg, E.; Persson, A.; Björk, J.; Nilsson, A.; Brönmark, C. Food chain length alters community response to global change in aquatic systems. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, R.; Everett, J.; Blanchard, J.; Richardson, A. Zooplankton are not fish: Improving zooplankton realism in size-spectrum models mediates energy transfer in food webs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Schoeman, D.S. Climate impact on plankton ecosystems in the northeast atlantic. Science 2004, 305, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, R.; Chen, B.; Ma, C.; Deng, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Positive Correlation Between Economic Activities and Fish Diversity in Small River Basins of Less Developed Regions: A Case Study of the Lixian River Basin. Animals 2025, 15, 2416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162416
Huang R, Chen B, Ma C, Deng C, Zhang J, Xiao Z, Wang Z, Liu Y, Liu X. Positive Correlation Between Economic Activities and Fish Diversity in Small River Basins of Less Developed Regions: A Case Study of the Lixian River Basin. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162416
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Rong, Bolin Chen, Chengcheng Ma, Chao Deng, Jiaqi Zhang, Zhihui Xiao, Zhijian Wang, Yaqiu Liu, and Xiaohong Liu. 2025. "Positive Correlation Between Economic Activities and Fish Diversity in Small River Basins of Less Developed Regions: A Case Study of the Lixian River Basin" Animals 15, no. 16: 2416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162416
APA StyleHuang, R., Chen, B., Ma, C., Deng, C., Zhang, J., Xiao, Z., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., & Liu, X. (2025). Positive Correlation Between Economic Activities and Fish Diversity in Small River Basins of Less Developed Regions: A Case Study of the Lixian River Basin. Animals, 15(16), 2416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162416




