Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Inhibitory Mechanism of Fisetin Against the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Reagents
2.2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
2.3. Growth Curve Assay
2.4. Hemolytic Activity Assay
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.7. Animal Study
2.8. RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Fisetin on Bacterial Growth
3.2. Influence of Fisetin on the Hemolytic Activities of Bacterial Supernatants
3.3. Impact of Fisetin on Biofilm Production of A. hydrophila
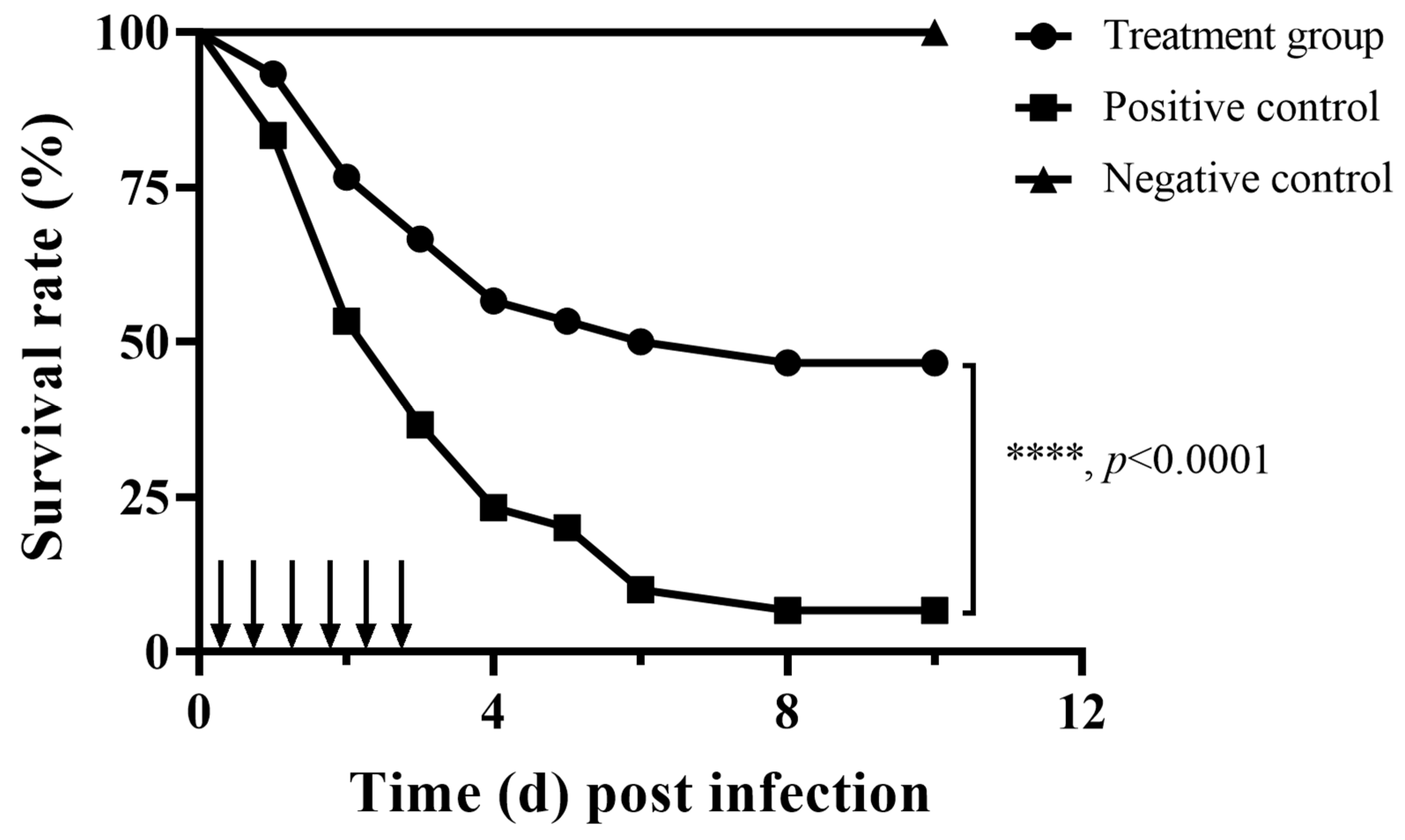
3.4. Impact of Fisetin on the Survivability of a Fish Infection Model
3.5. DEGs Determination
3.6. GO Function Analysis
3.7. GO Enrichment Analysis
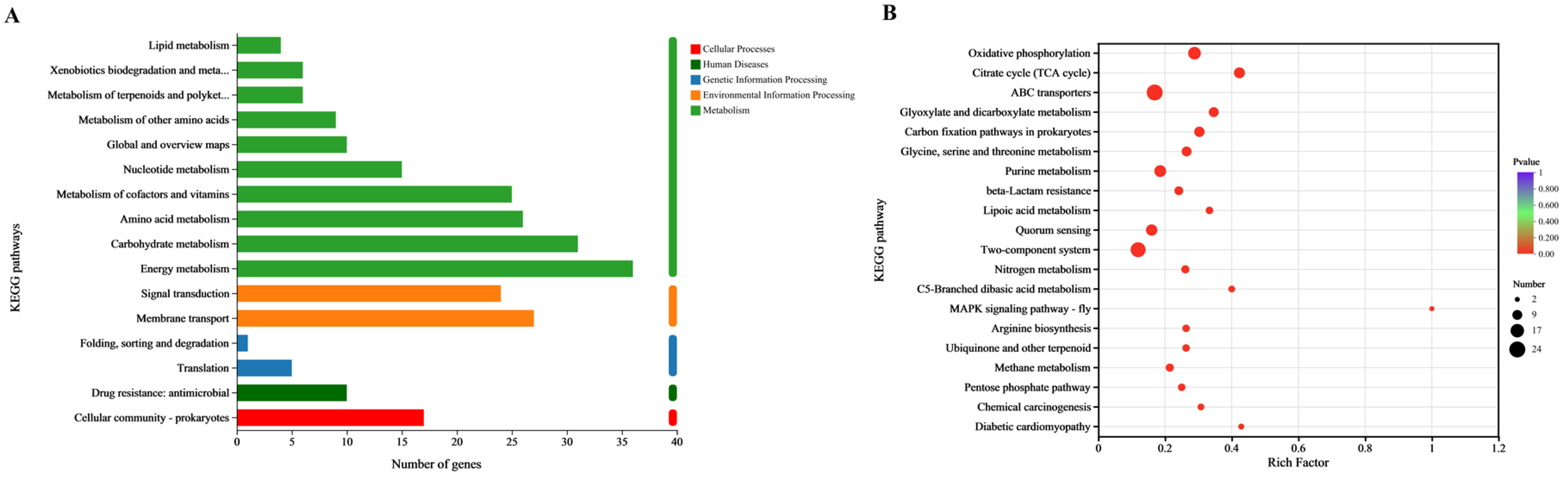
3.8. KEGG Function Analysis
3.9. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
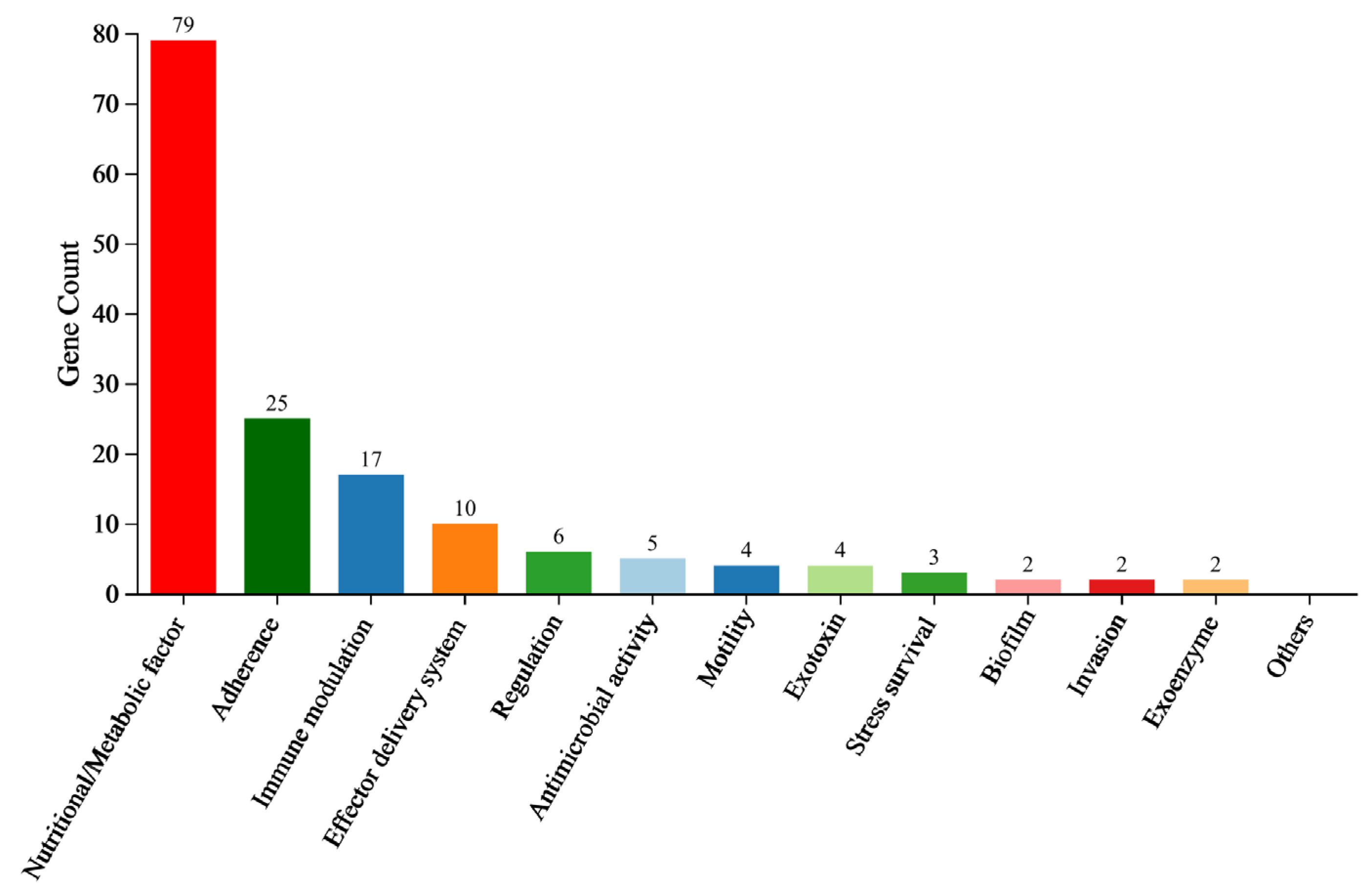
3.10. VFDB Classification Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Béné, C.; Arthur, R.; Norbury, H.; Allison, E.H.; Beveridge, M.; Bush, S.; Campling, L.; Leschen, W.; Little, D.; Squires, D.; et al. Contribution of Fisheries and Aquaculture to Food Security and Poverty Reduction: Assessing the Current Evidence. World Dev. 2016, 79, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlock, T.; Asche, F.; Anderson, J.; Ceballos-Concha, A.; Love, D.C.; Osmundsen, T.C.; Pincinato, R.B.M. Aquaculture: The missing contributor in the food security agenda. Glob. Food Secur. 2022, 32, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridgeon, J.; Klesius, P. Major bacterial diseases in aquaculture and their vaccine development. CABI Rev. 2012, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W. Social and economic impacts of aquatic animal health problems in aquaculture in China. In Primary Aquatic Animal Health Care in Rural, Small-Scale, Aquaculture Development; Arthur, J.R., Phillips, M.J., Subasinghe, R.P., Reantaso, M.B., MacRae, I.H., Eds.; FAO: Rome Italy, 2002; pp. 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Shirajum Monir, M.; Yusoff, S.M.; Mohamad, A.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y. Vaccination of tilapia against motile Aeromonas septicemia: A review. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2020, 32, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, K.; Borowiak, M.; Strauch, E.; Deneke, C.; Richter, M.H.; German Aeromonas Study, G. Emerging Aeromonas spp. infections in Europe: Characterization of human clinical isolates from German patients. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1498180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, D.R.; Ibarra, R.; Estevez, R.A.; Tlusty, M.F.; Nyberg, O.; Troell, M.; Avendano-Herrera, R.; Norden, W. Towards sustainable antibiotic use in aquaculture and antimicrobial resistance: Participatory experts’ overview and recommendations. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulijwa, R.; Rupia, E.J.; Alfaro, A.C. Antibiotic use in aquaculture, policies and regulation, health and environmental risks: A review of the top 15 major producers. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Song, H.; Xu, Y.; Lu, J.; Xu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Quantitative proteomics reveal the inherent antibiotic resistance mechanism against norfloxacin resistance in Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Figueras, M.J.; McGarey, D.; Liles, M.R. Virulence factors of Aeromonas hydrophila: In the wake of reclassification. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N. A review on pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and their mitigation through medicinal herbs in aquaculture. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; El Basuini, M.F.; Yilmaz, S.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Alagawany, M.; Kari, Z.A.; Abdul Razab, M.K.A.; Hamid, N.K.A.; Moonmanee, T.; Van Doan, H. Exploring the roles of dietary herbal essential oils in aquaculture: A review. Animals 2022, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Ge, H. The combined effect of a novel formula of herbal extracts on bacterial infection and immune response in Micropterus salmoides. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1185234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubina, R.; Iriti, M.; Kabala-Dzik, A. Anticancer potential of selected flavonols: Fisetin, kaempferol, and quercetin on head and neck cancers. Nutrients 2021, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Kimira, M.; Shimoi, K.; Mochizuki, R.; Kinae, N. Dietary intakes of flavonols, flavones and isoflavones by Japanese women and the inverse correlation between quercetin intake and plasma LDL cholesterol concentration. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, A.K.; Garg, G.; Rizvi, S.I. Fisetin as a caloric restriction mimetic protects rat brain against aging induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and neurodegeneration. Life Sci. 2018, 193, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.Y.; Lyu, J.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Chien, T.Y.; Hsu, H.C.; Wen, K.C.; Chiang, H.M. Fisetin regulates Nrf2 expression and the inflammation-related signaling pathway to prevent UVB-induced skin damage in hairless mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Saeed, F.; Gilani, S.A.; Shariati, M.A.; Imran, A.; Afzaal, M.; Atif, M.; Tufail, T.; Anjum, F.M. Fisetin: An anticancer perspective. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria, 3rd ed.; CLSI Guideline M45-ED3; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman, S.; Rajendhran, N.; Kannan, M.A.; Ramasamy, T. Quercetin disrupts biofilm formation and attenuates virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfarland, J. The nephelometer: An instrument for estimating the number of bacteria in suspensions used for calculating the posonic index and for vaccines. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1907, 49, 1176–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W. The impact of mutations in the quorum sensing systems of Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio harveyi on their virulence towards gnotobiotically cultured Artemia franciscana. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Expression and activity of recombinant proaerolysin derived from Aeromonas hydrophila cultured from diseased channel catfish. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, T.; Huhle, B.; Hof, H.; Bergbauer, H.; Goebel, W. Marker exchange mutagenesis of the aerolysin determinant in Aeromonas hydrophila demonstrates the role of aerolysin in A. hydrophila-Associated Systemic Infections. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Nagano, I.; Masunaga, S.; Kitazawa, D.; Matsuda, H. Antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Risks, current concern, and future thinking. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 11054–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Deng, L.; Li, T.; Feng, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Huang, X.; Chen, D.; et al. Genotype diversity and antibiotic resistance risk in Aeromonas hydrophila in Sichuan, China. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhinh, D.T.; Le, D.V.; Van, K.V.; Huong Giang, N.T.; Dang, L.T.; Hoai, T.D. Prevalence, virulence gene distribution and alarming the multidrug resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila associated with disease outbreaks in freshwater aquaculture. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Lv, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.J. A review of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Occurrence, contamination, and transmission. Toxics 2023, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, N.; Yang, Q.; Ai, X. Resveratrol influences the pathogenesis of Aeromonas hydrophila by inhibiting production of aerolysin and biofilm. Food Control 2021, 126, 108083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SobhZahedi, M.; Zamani, H.; YektaKooshali, M.H. Curcumin aattenuates the expression of metalloprotease (AHA_0978) and serine protease (AHA_3857) genes in Aeromonas hydrophila. Galen Med. J. 2023, 12, e3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.S.; Cavaleiro, E.; Pereira, C.; Merino, S.; Esteves, A.C.; Duarte, E.P.; Tomas, J.M.; Correia, A.C. Aeromonas piscicola AH-3 expresses an extracellular collagenase with cytotoxic properties. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 60, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Rosenzweig, J.A.; Kozlova, E.V.; Wang, S.; Erova, T.E.; Kirtley, M.L.; van Lier, C.J.; Chopra, A.K. Evaluation of the roles played by Hcp and VgrG type 6 secretion system effectors in Aeromonas hydrophila SSU pathogenesis. Microbiology 2013, 159, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, C.; Luypaert, M.; Maag, J.L.V.; Cheng, Q.X.; Dinger, M.E.; Hellemans, J.; Mestdagh, P. Benchmarking of RNA-sequencing analysis workflows using whole-transcriptome RT-qPCR expression data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenye, T. Do results obtained with RNA-sequencing require independent verification? Biofilm 2021, 3, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, H.; Shu, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; et al. Fisetin inhibits Salmonella Typhimurium type III secretion system regulator HilD and reduces pathology in vivo. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0240623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zong, B.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Tan, C. Fisetin lowers Streptococcus suis serotype 2 pathogenicity in mice by inhibiting the hemolytic activity of suilysin. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, J.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Feng, H.; Li, W.; Niu, X.; et al. Fisetin inhibits Listeria monocytogenes virulence by interfering with the oligomerization of listeriolysin O. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Sheng, Q.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Qiu, J.; Cui, M.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L. Enhancing the effectiveness of Polymyxin E with a Fisetin Nanoemulsion against a Colistin-resistant Salmonella typhimurium infection. Phytomedicine 2024, 130, 155768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, G.; Wei, L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J. Metallo-beta-lactamases inhibitor fisetin attenuates meropenem resistance in NDM-1-producing Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 231, 114108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Oh, M.J. Antiviral activities of flavonoids isolated from the bark of Rhus verniciflua stokes against fish pathogenic viruses in vitro. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmo, R. Strengths and weaknesses of different challenge methods. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1997, 90, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molagoda, I.M.N.; Jayasingha, J.A.C.C.; Choi, Y.H.; Jayasooriya, R.G.P.T.; Kang, C.-H.; Kim, G.-Y. Fisetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by activating β-catenin, leading to a decrease in endotoxic shock. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample Name | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Bases (bp) | Clean Error Rate (%) | Clean Q20 (%) | Clean Q30 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 20,530,174 | 20,314,872 | 2,993,496,680 | 0.0117 | 98.92 | 96.59 |
| C2 | 22,833,722 | 22,606,096 | 3,359,219,377 | 0.0117 | 98.95 | 96.61 |
| C3 | 21,288,572 | 21,109,952 | 3,138,989,218 | 0.0116 | 98.98 | 96.70 |
| F1 | 22,743,550 | 22,537,754 | 3,356,574,698 | 0.0116 | 98.98 | 96.71 |
| F2 | 22,389,376 | 22,194,338 | 3,299,969,664 | 0.0116 | 99.01 | 96.78 |
| F3 | 23,764,044 | 23,490,540 | 3,483,066,492 | 0.0116 | 98.99 | 96.73 |
| Sample Name | Total Reads | Genome Mapped Reads | Genome Mapped Ratio (%) | Unmapped Reads | Unmapped Reads Ratio (%) | Uniq Mapped Reads | Uniq Mapped Reads Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 20,314,872 | 18,679,762 | 91.95 | 1,635,110 | 8.05 | 18,188,830 | 89.53 |
| C2 | 22,606,096 | 21,479,423 | 95.02 | 1,126,673 | 4.98 | 21,275,355 | 94.11 |
| C3 | 21,109,952 | 20,056,686 | 95.01 | 1,053,266 | 4.99 | 19,876,725 | 94.16 |
| F1 | 22,537,754 | 21,468,942 | 95.26 | 1,068,812 | 4.74 | 21,295,334 | 94.49 |
| F2 | 22,194,338 | 21,203,091 | 95.53 | 991,247 | 4.47 | 21,065,749 | 94.91 |
| F3 | 23,490,540 | 2,235,0070 | 95.14 | 1,140,470 | 4.86 | 22,169,827 | 94.38 |
| Gene ID | Log2 Fold Change | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Genes related to exotoxins | ||
| AHA_1194 | −1.5085 | multidrug resistance efflux pump |
| AHA_0663 | −1.1876 | putative transporter |
| AHA_0438 | −1.2324 | aerolysin |
| AHA_0739 | −1.1749 | putative amidase |
| Genes related to two-component systems | ||
| AHA_2453 | −2.2819 | tricarboxylic transport membrane protein TctB |
| AHA_2454 | −2.1815 | tricarboxylic transport membrane protein TctA |
| AHA_2526 | −3.3417 | hydrogenase small subunit HydA |
| AHA_2523 | −4.0288 | hydrogenase-2 large chain HyaB |
| AHA_3288 | −1.0205 | two-component system sensor histidine kinase TtrS |
| Genes related to quorum sensing | ||
| AHA_1305 | −1.2950 | LasA protease |
| AHA_2613 | −1.1305 | oligopeptide transport system substrate OppA |
| AHA_2517 | −1.3323 | peptide/nickel transport system ATP DdpD |
| AHA_2519 | −1.4034 | peptide/nickel transport system permease protein |
| AHA_2520 | −1.8038 | peptide/nickel transport system substrate |
| Genes related to secretory systems | ||
| AHA_1835 | −1.1672 | type VI secretion system protein ImpG |
| AHA_1827 | −1.1736 | type VI secretion system secreted protein VgrG |
| AHA_1833 | −1.2388 | type VI secretion system protein ImpC |
| AHA_1118 | −1.1621 | type VI secretion system secreted protein Hcp |
| AHA_3786 | −1.2232 | general secretion pathway protein B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, J.; Ma, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Q.; Ai, X. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Inhibitory Mechanism of Fisetin Against the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. Animals 2025, 15, 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162415
Dong J, Ma X, Li S, Zhou S, Yang Q, Ai X. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Inhibitory Mechanism of Fisetin Against the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162415
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Jing, Xinwei Ma, Shengping Li, Shun Zhou, Qiuhong Yang, and Xiaohui Ai. 2025. "Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Inhibitory Mechanism of Fisetin Against the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila" Animals 15, no. 16: 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162415
APA StyleDong, J., Ma, X., Li, S., Zhou, S., Yang, Q., & Ai, X. (2025). Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Inhibitory Mechanism of Fisetin Against the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. Animals, 15(16), 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162415





