Cellular Immune Response in Horses After West Nile Neuroinvasive Disease
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Samples
2.3. Cell Stimulants
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay (ELISpot)
2.5. WNV IgG ELISA and Virus Neutralization Tests
2.6. Statistical Analysis
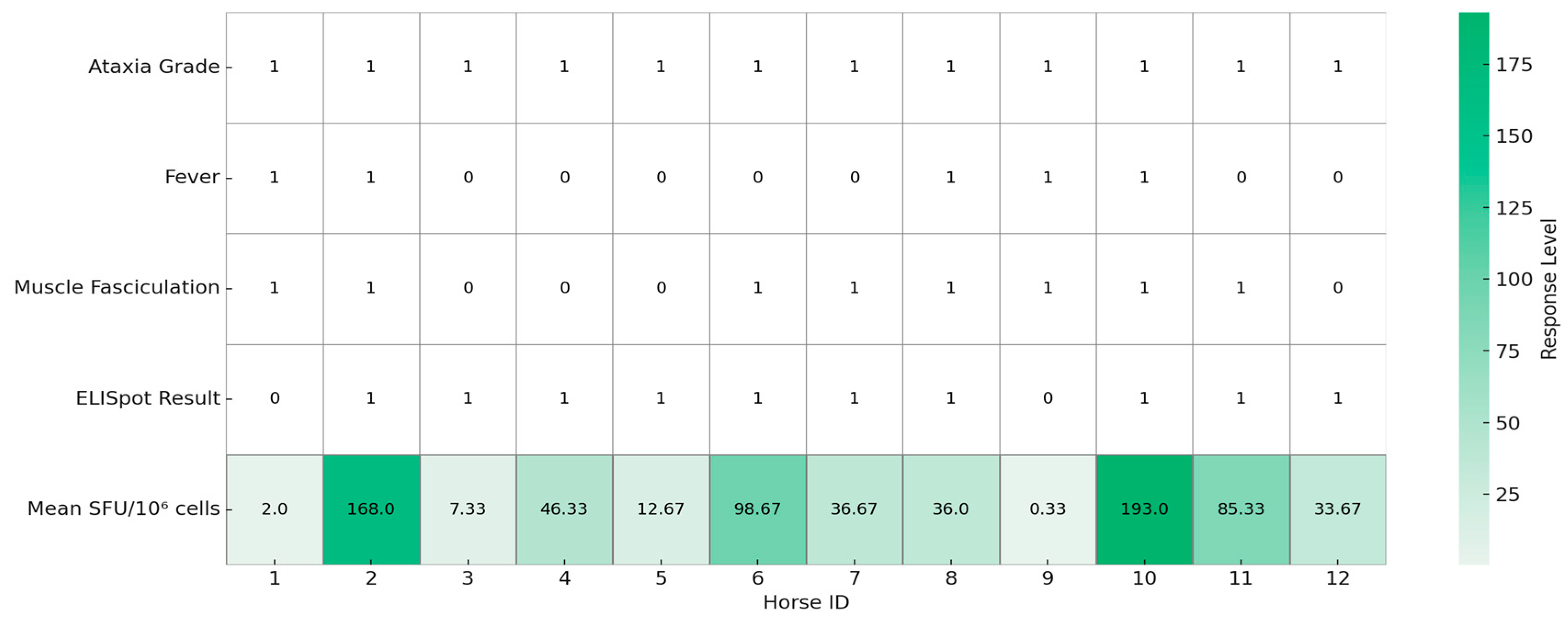
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Signs
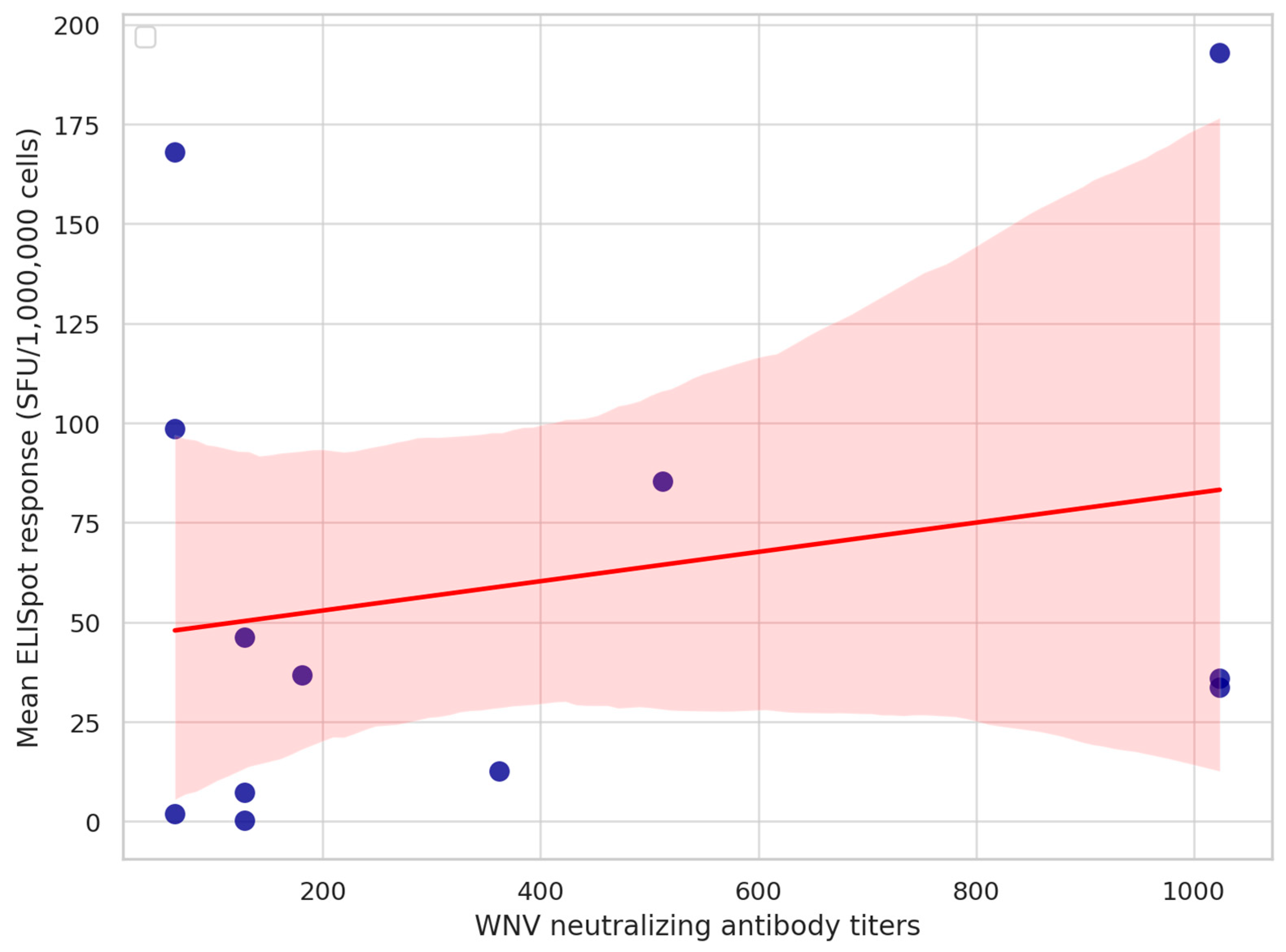
3.2. Cellular Immune Response
3.3. Humoral Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WNV | West Nile virus |
| WNND | West Nile neuroinvasive disease |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| VNT | Virus neutralization test |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood mononuclear cell |
| IFNγ | Interferon-gamma |
| ELISpot | Enzyme-linked immunospot |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| SFU | Spot-forming unit |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| TCM | Central memory T cell |
| TEM | Effector memory T cell |
| TRM | Tissue-resident memory T cell |
| USUV | Usutu virus |
| TBEV | Tick-borne encephalitis virus |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium |
References
- Sejvar, J.J. West Nile Virus: An Historical Overview. Ochsner J. 2003, 5, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chancey, C.; Grinev, A.; Volkova, E.; Rios, M. The Global Ecology and Epidemiology of West Nile Virus. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 376230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erazo, D.; Grant, L.; Ghisbain, G.; Marini, G.; Colón-González, F.J.; Wint, W.; Rizzoli, A.; Van Bortel, W.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Grubaugh, N.D.; et al. Contribution of Climate Change to the Spatial Expansion of West Nile Virus in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreychev, A.; Boyarova, E.; Nesterova, D. Climate Change’s Impact on Recording of West Nile Fever of Animals in the Middle Volga Region. BIO Web Conf. 2025, 181, 02023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postler, T.S.; Beer, M.; Blitvich, B.J.; Bukh, J.; de Lamballerie, X.; Drexler, J.F.; Imrie, A.; Kapoor, A.; Karganova, G.G.; Lemey, P.; et al. Renaming of the Genus Flavivirus to Orthoflavivirus and Extension of Binomial Species Names within the Family Flaviviridae. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byas, A.D.; Ebel, G.D. Comparative Pathology of West Nile Virus in Humans and Non-Human Animals. Pathogens 2020, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, L.; Nappo, M.A.; Frontoso, R.; Perrotta, M.G.; Di Lecce, R.; Guarnieri, C.; Ferrari, L.; Corradi, A. West Nile Virus (WNV): One-Health and Eco-Health Global Risks. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.R.; Long, M.T. Comparison of West Nile Virus Disease in Humans and Horses: Exploiting Similarities for Enhancing Syndromic Surveillance. Viruses 2023, 15, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.B.; Long, M.T.; Getman, L.M.; Giguère, S.; MacKay, R.J.; Lester, G.D.; Alleman, A.R.; Wamsley, H.L.; Franklin, R.P.; Jacks, S.; et al. West Nile Virus Encephalomyelitis in Horses: 46 Cases (2001). J. Am. Veter. Med Assoc. 2003, 222, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasi, O.; Bakonyi, T.; Lecollinet, S.; Biksi, I.; Ferenczi, E.; Bahuon, C.; Sardi, S.; Zientara, S.; Szenci, O. Equine Encephalomyelitis Outbreak Caused by a Genetic Lineage 2 West Nile Virus in Hungary. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Bocanegra, I.; Belkhiria, J.; Napp, S.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Jiménez-Ruiz, S.; Martínez-López, B. Epidemiology and Spatio-Temporal Analysis of West Nile Virus in Horses in Spain between 2010 and 2016. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heus, P.; Kolodziejek, J.; Camp, J.V.; Dimmel, K.; Bagó, Z.; Hubálek, Z.; van den Hoven, R.; Cavalleri, J.-M.V.; Nowotny, N. Emergence of West Nile Virus Lineage 2 in Europe: Characteristics of the First Seven Cases of West Nile Neuroinvasive Disease in Horses in Austria. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, O.E.; Fehérvári, P.; Tolnai, C.H.; Forgách, P.; Malik, P.; Jerzsele, Á.; Wagenhoffer, Z.; Szenci, O.; Korbacska-Kutasi, O. Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestation of West Nile Virus Infections of Equines in Hungary, 2007–2020. Viruses 2022, 14, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalleri, J.-M.V.; Korbacska-Kutasi, O.; Leblond, A.; Paillot, R.; Pusterla, N.; Steinmann, E.; Tomlinson, J. European College of Equine Internal Medicine Consensus Statement on Equine Flaviviridae Infections in Europe. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1858–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlers, L.R.H.; Goodman, A.G. The Immune Responses of the Animal Hosts of West Nile Virus: A Comparison of Insects, Birds, and Mammals. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trobaugh, D.; Green, S. Of Mice and Men: Protective and Pathogenic Immune Responses to West Nile Virus Infection. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2015, 2, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, M.S.; Diamond, M.S.; Gale, M., Jr. West Nile Virus Infection and Immunity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netland, J.; Bevan, M.J. CD8 and CD4 T Cells in West Nile Virus Immunity and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2013, 5, 2573–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Valenzuela, R.; Netland, J.; Seo, Y.-J.; Bevan, M.J.; Grakoui, A.; Suthar, M.S. Dynamics of Tissue-Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses during West Nile Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00014-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Diamond, M.S. Role of CD8+ T Cells in Control of West Nile Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8312–8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Diamond, M.S. Immune Responses to West Nile Virus Infection in the Central Nervous System. Viruses 2012, 4, 3812–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanteri, M.C.; Diamond, M.S.; Law, J.P.; Chew, G.M.; Wu, S.; Inglis, H.C.; Wong, D.; Busch, M.P.; Norris, P.J.; Ndhlovu, L.C. Increased Frequency of Tim-3 Expressing T Cells Is Associated with Symptomatic West Nile Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.S.; Lin, E.; Zhang, B.; Luster, A.D.; Tollett, J.; Samuel, M.A.; Engle, M.; Diamond, M.S. Neuronal CXCL10 Directs CD8+ T-Cell Recruitment and Control of West Nile Virus Encephalitis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11457–11466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, J.D.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Hirsch, A.; Wiley, C.A.; Nikolich-Žugich, J. Key Role of T Cell Defects in Age-Related Vulnerability to West Nile Virus. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, A.; Finlaison, D.; Gu, X.; Hick, P.; Moloney, B.; Wright, T.; Kirkland, P. Clinical and Epidemiological Features of West Nile Virus Equine Encephalitis in New South Wales, Australia, 2011. Aust. Vet. J. 2019, 97, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Kaech, S.M. Generation of Effector CD8+ T Cells and Their Conversion to Memory T Cells. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 236, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska, K.; Valkenburg, S.; Doherty, P.; Davenport, M.; Venturi, V. Use It or Lose It: Establishment and Persistence of T Cell Memory. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saade, F.; Gorski, S.A.; Petrovsky, N. Pushing the Frontiers of T-Cell Vaccines: Accurate Measurement of Human T-Cell Responses. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolnai, C.H.; Forgách, P.; Marosi, A.; Fehér, O.; Paszerbovics, B.; Tenk, M.; Wagenhoffer, Z.; Kutasi, O. Long-Term Humoral Immune Response After West Nile Virus Convalescence in Horses in a Geographic Area of Multiple Orthoflavivirus Co-Circulation. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2025, 39, e70176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, K.; Bakonyi, T.; Szenci, O.; Sárdi, S.; Ferenczi, E.; Barna, M.; Malik, P.; Hubalek, Z.; Fehér, O.; Kutasi, O. Comparison of Assays for the Detection of West Nile Virus Antibodies in Equine Serum after Natural Infection or Vaccination. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 183, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahav, G.; Hagin, M.; Maor, Y.; Yahalom, G.; Hindiyeh, M.; Mendelson, E.; Bin, H. Primary Versus Nonprimary West Nile Virus Infection: A Cohort Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Garch, H.; Minke, J.M.; Rehder, J.; Richard, S.; Edlund Toulemonde, C.; Dinic, S.; Andreoni, C.; Audonnet, J.C.; Nordgren, R.; Juillard, V. A West Nile Virus (WNV) Recombinant Canarypox Virus Vaccine Elicits WNV-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies and Cell-Mediated Immune Responses in the Horse. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 123, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagur, P.K.; McCoy, J.P. Collection, Storage, and Preparation of Human Blood Cells. CP Cytom. 2015, 73, 5.1.1–5.1.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerten, S.; Batoulis, H.; Recks, M.S.; Karacsony, E.; Zhang, W.; Subbramanian, R.A.; Lehmann, P.V. Resting of Cryopreserved PBMC Does Not Generally Benefit the Performance of Antigen-Specific T Cell ELISPOT Assays. Cells 2012, 1, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodie, Z.; Price, L.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Mander, A.; Janetzki, S.; Löwer, M.; Welters, M.J.P.; Ottensmeier, C.; van der Burg, S.H.; Britten, C.M. Response Definition Criteria for ELISPOT Assays Revisited. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2010, 59, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodie, Z.; Price, L.; Janetzki, S.; Britten, C.M. Response Determination Criteria for ELISPOT: Toward a Standard That Can Be Applied Across Laboratories. In Handbook of ELISPOT: Methods and Protocols; Kalyuzhny, A.E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 185–196. ISBN 978-1-61779-325-7. [Google Scholar]
- Tizard, I.R. Veterinary Immunology, 11th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MA, USA, 2025; ISBN 978-0-443-10975-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lanteri, M.C.; Heitman, J.W.; Owen, R.E.; Busch, T.; Gefter, N.; Kiely, N.; Kamel, H.T.; Tobler, L.H.; Busch, M.P.; Norris, P.J. Comprehensive Analysis of West Nile Virus–Specific T Cell Responses in Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calarota, S.A.; Baldanti, F. Enumeration and Characterization of Human Memory T Cells by Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assays. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 637649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimer, C.L.; Schnabel, C.L.; Perkins, G.; Babasyan, S.; Freer, H.; Stout, A.E.; Rollins, A.; Osterrieder, N.; Goodman, L.B.; Glaser, A.; et al. The Deletion of the ORF1 and ORF71 Genes Reduces Virulence of the Neuropathogenic EHV-1 Strain Ab4 without Compromising Host Immunity in Horses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.M.; Wagner, B. Characterization of Nasal Mucosal T Cells in Horses and Their Response to Equine Herpesvirus Type 1. Viruses 2024, 16, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclere, M.; Lavoie-Lamoureux, A.; Lavoie, J.-P. Heaves, an Asthma-like Disease of Horses. Respirology 2011, 16, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O.; Malin, K.; Dąbrowska, I.; Grzędzicka, J.; Ostaszewski, P.; Carter, C. Immunology of Physical Exercise: Is Equus Caballus an Appropriate Animal Model for Human Athletes? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, R.; Lelic, A.; Hayes, L.; Carter, A.; Marshall, L.; Evelegh, C.; Drebot, M.; Andonova, M.; McMurtrey, C.; Hildebrand, W.; et al. The Memory T Cell Response to West Nile Virus in Symptomatic Humans Following Natural Infection Is Not Influenced by Age and Is Dominated by a Restricted Set of CD8+ T Cell Epitopes1. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felippe, M.J.B. Equine Clinical Immunology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Ames, IA, USA; West Sussex, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-1-119-08651-2. [Google Scholar]
- Horohov, D.W.; Adams, A.A.; Chambers, T.M. Immunosenescence of the Equine Immune System. J. Comp. Pathol. 2010, 142, S78–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.; Baptiste, K.E.; Fjeldborg, J.; Horohov, D.W. A Review of the Equine Age-Related Changes in the Immune System: Comparisons between Human and Equine Aging, with Focus on Lung-Specific Immune-Aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 20, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNotta, S.; McFarlane, D. Immunosenescence and Inflammaging in the Aged Horse. Immun. Ageing 2023, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, G.A.; Wagner, B. The Development of Equine Immunity: Current Knowledge on Immunology in the Young Horse. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, K.W.; Lee, J.J.; Foster, G.A.; Krysztof, D.; Stramer, S.L.; Lim, J.K. Sex Differences in Cytokine Production Following West Nile Virus Infection: Implications for Symptom Manifestation. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftz016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, J.D.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Nikolich-Žugich, J. Protective Capacity and Epitope Specificity of CD8+ T Cells Responding to Lethal West Nile Virus Infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanteri, M.C.; O’Brien, K.M.; Purtha, W.E.; Cameron, M.J.; Lund, J.M.; Owen, R.E.; Heitman, J.W.; Custer, B.; Hirschkorn, D.F.; Tobler, L.H.; et al. Tregs Control the Development of Symptomatic West Nile Virus Infection in Humans and Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3266–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNab, F.; Mayer-Barber, K.; Sher, A.; Wack, A.; O’Garra, A. Type I Interferons in Infectious Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, F.-M.; Thompson, P.N.; Venter, M. Epidemiology and Clinical Presentation of West Nile Virus Infection in Horses in South Africa, 2016–2017. Pathogens 2020, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.-H.; Wang, T. West Nile Virus Induced Cell Death in the Central Nervous System. Pathogens 2019, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, E.M.; Bauer, L.; Nelemans, T.; Sooksawasdi Na Ayudhya, S.; Benavides, F.; Lanko, K.; de Vrij, F.M.S.; Kushner, S.A.; Koopmans, M.; van Riel, D.; et al. Differential Susceptibility of Human Motor Neurons to Infection with Usutu and West Nile Virus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortuna, P.R.J.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Whitworth, D.J. Cortical Neurons Derived from Equine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Are Susceptible to Neurotropic Flavivirus Infection and Replication: An In Vitro Model for Equine Neuropathic Diseases. Stem Cells Dev. 2018, 27, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toplu, N.; Oğuzoğlu, T.Ç.; Ural, K.; Albayrak, H.; Ozan, E.; Ertürk, A.; Epikmen, E.T. West Nile Virus Infection in Horses: Detection by Immunohistochemistry, In Situ Hybridization, and ELISA. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Kim, C.Y.; Dean, A.; Kulas, K.E.; St. George, K.; Hoang, H.E.; Thakur, K.T. Clinical and Diagnostic Features of West Nile Virus Neuroinvasive Disease in New York City. Pathogens 2024, 13, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Reina, C.; Martínez-Moya, M.; Piñero-González de la Peña, P.; Caro-Domínguez, P. Neuroinvasive Disease Due to West Nile Virus: Clinical and Imaging Findings Associated with a Re-Emerging Pathogen. Radiologia 2022, 64, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, A.; Kamat, A.; Mittal, S.O. Spectrum of Movement Disorders in Patients with Neuroinvasive West Nile Virus Infection. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratkin, J.D.; Leis, A.A.; Stokic, D.S.; Slavinski, S.A.; Geiss, R.W. Spinal Cord Neuropathology in Human West NileVirus Infection. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2004, 128, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackhurst, B.M.; Funk, K.E. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Underlying Neurologic Manifestations of Mosquito-Borne Flavivirus Infections. Viruses 2023, 15, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Boudewijns, R.; Schmid, M.A.; Marques, R.E.; Sharma, S.; Neyts, J.; Dallmeier, K. A Chimeric Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Protects against Lethal Yellow Fever Virus Infection without Inducing Neutralizing Antibodies. mBio 2020, 11, e02494-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yauch, L.E.; Zellweger, R.M.; Kotturi, M.F.; Qutubuddin, A.; Sidney, J.; Peters, B.; Prestwood, T.R.; Sette, A.; Shresta, S. A Protective Role for Dengue Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4865–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Oswal, N.; Chawla, A.S.; Agrawal, T.; Biswas, M.; Vrati, S.; Rath, S.; George, A.; Bal, V.; Medigeshi, G.R. CD8 T Cells Protect Adult Naive Mice from JEV-Induced Morbidity via Lytic Function. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesh, R.B.; Travassos Da Rosa, A.P.A.; Guzman, H.; Araujo, T.P.; Xiao, S.-Y. Immunization with Heterologous Flaviviruses Protective Against Fatal West Nile Encephalitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrig, J.T.; Staudinger, L.A.; Hunt, A.R.; Mathews, J.H.; Blair, C.D. Antibody Prophylaxis and Therapy for Flavivirus Encephalitis Infections. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, D.; Draves, K.E.; Young, L.B.; Roe, K.; Bryan, M.A.; Dresch, C.; Richner, J.M.; Diamond, M.S.; Gale, M.; Clark, E.A. Protection of Mice Deficient in Mature B Cells from West Nile Virus Infection by Passive and Active Immunization. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreil, T.R.; Maier, E.; Fraiss, S.; Eibl, M.M. Neutralizing Antibodies Protect against Lethal Flavivirus Challenge but Allow for the Development of Active Humoral Immunity to a Nonstructural Virus Protein. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3076–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.R.; Ismail, A.A.; Thergarajan, G.; Raju, C.S.; Yam, H.C.; Rishya, M.; Sekaran, S.D. Serological Cross-Reactivity among Common Flaviviruses. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 975398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, J.; Nishi, H.; Matsuda, H.; Tsunemitsu, H.; Shimiz, S. Cross-Reactivity of Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Vaccinated Horse Sera in Serodiagnosis of West Nile Virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, A.; Medhin, G.; Darfiro, K.; Kebede, N.; Legesse, M. Magnitude of Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Medically Important Mosquito-Borne Flaviviruses: A Systematic Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 4291–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, A.P.S.; St. John, A.L. Cross-Reactive Immunity Among Flaviviruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.M.; Tesh, R.B.; Siirin, M.; da Rosa, A.T.; Newman, P.C.; Clements, D.E.; Ogata, S.; Coller, B.-A.; Weeks-Levy, C.; Lieberman, M.M. Efficacy and Durability of a Recombinant Subunit West Nile Vaccine Candidate in Protecting Hamsters from West Nile Encephalitis. Vaccine 2007, 25, 2913–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Kooi, K.; Hawks, S.A.; Duggal, N.K. Cross-Protection between West Nile Virus and Emerging Flaviviruses in Wild Birds. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 112, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.L.; McKinstry, K.K.; Strutt, T.M. Expanding Roles for CD4+ T Cells in Immunity to Viruses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuddin, S.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Chan, Y.F.Z.; Hang, S.K.; Kunasegaran, K.; Chia, A.; Chan, C.Y.Y.; Ng, D.H.L.; Sim, J.X.Y.; Tan, H.-C.; et al. Vaccine-Induced T Cell Responses Control Orthoflavivirus Challenge Infection without Neutralizing Antibodies in Humans. Nat. Microbiol. 2025, 10, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.A.S.; Mathew, A.; Rothman, A.L. T Lymphocyte Responses to Flaviviruses—Diverse Cell Populations Affect Tendency toward Protection and Disease. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 43, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzan-Rivera, N.; Serrano-Collazo, C.; Cruz, L.; Pantoja, P.; Ortiz-Rosa, A.; Arana, T.; Martinez, M.I.; Burgos, A.G.; Roman, C.; Mendez, L.B.; et al. Infection Order Outweighs the Role of CD4+ T Cells in Tertiary Flavivirus Exposure. iScience 2022, 25, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, V.; Natrajan, M.S.; Huerta, C.; Xu, Y.; Lai, L.; Mulligan, M.J. Immunological Cross-Reactivity to Dengue Virus among Persons with Neuroinvasive West Nile Virus Infection. medRxiv 2022. [CrossRef]
- Percivalle, E.; Cassaniti, I.; Sarasini, A.; Rovida, F.; Adzasehoun, K.M.G.; Colombini, I.; Isernia, P.; Cuppari, I.; Baldanti, F. West Nile or Usutu Virus? A Three-Year Follow-Up of Humoral and Cellular Response in a Group of Asymptomatic Blood Donors. Viruses 2020, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauswein, M.; Eid, E.; Eidenschink, L.; Schmidt, B.; Gessner, A.; Tappe, D.; Cadar, D.; Böhmer, M.M.; Jockel, L.; van Wickeren, N.; et al. Detection of Virus-Specific T Cells via ELISpot Corroborates Early Diagnosis in Human Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1) Encephalitis. Infection 2024, 52, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, R.; Wang, M.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, A. Structure and Function of Capsid Protein in Flavivirus Infection and Its Applications in the Development of Vaccines and Therapeutics. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunning, M.L.; Bowen, R.A.; Cropp, B.C.; Sullivan, K.G.; Davis, B.S.; Komar, N.; Godsey, M.; Baker, D.; Hettler, D.L.; Holmes, D.A.; et al. Experimental Infection of Horses with West Nile Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genus: Orthoflavivirus|ICTV. Available online: https://ictv.global/report/chapter/flaviviridae/flaviviridae/orthoflavivirus (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- van den Elsen, K.; Quek, J.P.; Luo, D. Molecular Insights into the Flavivirus Replication Complex. Viruses 2021, 13, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothan, H.A.; Kumar, M. Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Proteins in Flavivirus Replication and Assembly Complexes. Pathogens 2019, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Elsen, K.; Alvin, C.B.L.; Sheng, H.J.; Dahai, L. Flavivirus Nonstructural Proteins and Replication Complexes as Antiviral Drug Targets. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2023, 59, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, M.; Sharma, N.; Singh, S.K. Flavivirus NS1: A Multifaceted Enigmatic Viral Protein. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.D.; Pierson, T.C.; DeGrace, M.M.; Mattei, L.M.; Hanna, S.L.; Del Piero, F.; Doms, R.W. The Neutralizing Antibody Response against West Nile Virus in Naturally Infected Horses. Virology 2007, 359, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.V.; Lelic, A.; Parsons, R.; Nielsen, M.; Hoof, I.; Lamberth, K.; Loeb, M.B.; Buus, S.; Bramson, J.; Lund, O. Identification of CD8+ T Cell Epitopes in the West Nile Virus Polyprotein by Reverse-Immunology Using NetCTL. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaabinejadian, S.; Piazza, P.A.; McMurtrey, C.P.; Vernon, S.R.; Cate, S.J.; Bardet, W.; Schafer, F.B.; Jackson, K.W.; Campbell, D.M.; Buchli, R.; et al. Identification of Class I HLA T Cell Control Epitopes for West Nile Virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, F.M.; Reche, P.A.; Flower, D.R. West Nile Virus Vaccine Design by T Cell Epitope Selection: In Silico Analysis of Conservation, Functional Cross-Reactivity with the Human Genome, and Population Coverage. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 7235742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurtrey, C.P.; Lelic, A.; Piazza, P.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Yablonsky, E.J.; Wahl, A.; Bardet, W.; Eckerd, A.; Cook, R.L.; Hess, R.; et al. Epitope Discovery in West Nile Virus Infection: Identification and Immune Recognition of Viral Epitopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, P.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, A. Analysis of Promiscuous T Cell Epitopes for Vaccine Development Against West Nile Virus Using Bioinformatics Approaches. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2018, 24, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblischke, M.; Spitzer, F.S.; Florian, D.M.; Aberle, S.W.; Malafa, S.; Fae, I.; Cassaniti, I.; Jungbauer, C.; Knapp, B.; Laferl, H.; et al. CD4 T Cell Determinants in West Nile Virus Disease and Asymptomatic Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblischke, M.; Stiasny, K.; Aberle, S.W.; Malafa, S.; Tsouchnikas, G.; Schwaiger, J.; Kundi, M.; Heinz, F.X.; Aberle, J.H. Structural Influence on the Dominance of Virus-Specific CD4 T Cell Epitopes in Zika Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A Quest for Better Vaccines Against a Virus on the Rise. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/8/3/451 (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- De Filette, M.; Chabierski, S.; Andries, O.; Ulbert, S.; Sanders, N.N. T Cell Epitope Mapping of the E-Protein of West Nile Virus in BALB/c Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, J.D.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Nikolich-Zugich, J. West Nile Virus-Specific CD4 T Cells Exhibit Direct Antiviral Cytokine Secretion and Cytotoxicity and Are Sufficient for Antiviral Protection. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8568–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körber, N.; Behrends, U.; Protzer, U.; Bauer, T. Evaluation of T-Activated Proteins as Recall Antigens to Monitor Epstein–Barr Virus and Human Cytomegalovirus-Specific T Cells in a Clinical Trial Setting. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzfeldt, N.; Chambers, T.M.; Reedy, S.; Spann, K.M.; Pusterla, N. Effect of Dexamethasone on Antibody Response of Horses to Vaccination with a Combined Equine Influenza Virus and Equine Herpesvirus-1 Vaccine. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 38, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O.; Pingwara, R.; Szczepaniak, J.; Winnicka, A. The Effect of the Clenbuterol—Β2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonist on the Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Proliferation, Phenotype, Functions, and Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Race Horses In Vitro. Cells 2021, 10, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, I.; Grzędzicka, J.; Niedzielska, A.; Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O. Impact of Chlorogenic Acid on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Proliferation, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Responses in Racehorses during Exercise. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couëtil, L.L.; Cardwell, J.M.; Gerber, V.; Lavoie, J.-P.; Léguillette, R.; Richard, E.A. Inflammatory Airway Disease of Horses—Revised Consensus Statement. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couetil, L.; Cardwell, J.M.; Leguillette, R.; Mazan, M.; Richard, E.; Bienzle, D.; Bullone, M.; Gerber, V.; Ivester, K.; Lavoie, J.-P.; et al. Equine Asthma: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, D.; Tan, J.; Niewold, P.; Spiteri, A.G.; Pinget, G.V.; Stanley, D.; King, N.J.C.; Macia, L. Impact of Dietary Fiber on West Nile Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 784486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-C.; Zhao, F.R.; Janova, H.; Gervais, A.; Rucknagel, S.; Murray, K.O.; Casanova, J.-L.; Diamond, M.S. Blockade of Interferon Signaling Decreases Gut Barrier Integrity and Promotes Severe West Nile Virus Disease. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/epidemiological-update-west-nile-virus-transmission-season-europe-2023-0 (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Jameson, S.C.; Masopust, D. Understanding Subset Diversity in T Cell Memory. Immunity 2018, 48, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolnai, C.; O’Sullivan, C.; Lőrincz, M.; Karvouni, M.; Tenk, M.; Marosi, A.; Forgách, P.; Paszerbovics, B.; Wagenhoffer, Z.; Kutasi, O. Cellular Immune Response in Horses After West Nile Neuroinvasive Disease. Animals 2025, 15, 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162352
Tolnai C, O’Sullivan C, Lőrincz M, Karvouni M, Tenk M, Marosi A, Forgách P, Paszerbovics B, Wagenhoffer Z, Kutasi O. Cellular Immune Response in Horses After West Nile Neuroinvasive Disease. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162352
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolnai, Csenge, Ciara O’Sullivan, Márta Lőrincz, Maria Karvouni, Miklós Tenk, András Marosi, Petra Forgách, Bettina Paszerbovics, Zsombor Wagenhoffer, and Orsolya Kutasi. 2025. "Cellular Immune Response in Horses After West Nile Neuroinvasive Disease" Animals 15, no. 16: 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162352
APA StyleTolnai, C., O’Sullivan, C., Lőrincz, M., Karvouni, M., Tenk, M., Marosi, A., Forgách, P., Paszerbovics, B., Wagenhoffer, Z., & Kutasi, O. (2025). Cellular Immune Response in Horses After West Nile Neuroinvasive Disease. Animals, 15(16), 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162352





