Comparison of the Anxiolytic and Analgesic Effects of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Cats: A Systematic Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
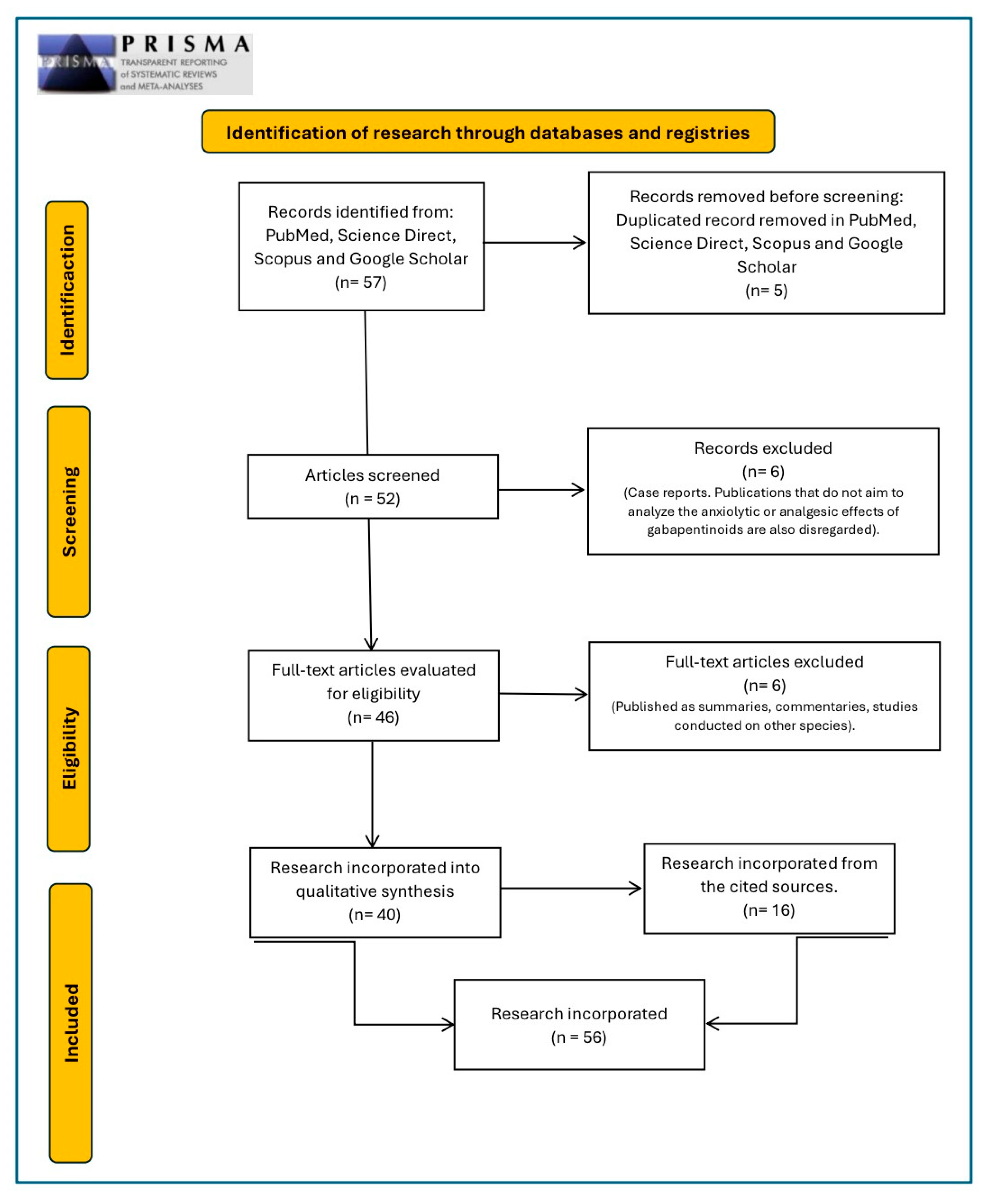
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Criteria
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Classification of Eligible Studies
- Gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin in felines.
- Anxiolytic effects of gabapentinoids in cats.
- Gabapentin and pregabalin as treatment for acute and chronic pain in cats.
2.5. Collection and Evaluation of Additional Data
3. Results
3.1. Use of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in the Control and Treatment of Anxiety in Cats
3.2. Use of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Pain Control and Treatment in Cats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amat, M.; Camps, T.; Manteca, X. Stress in owned cats: Behavioural changes and welfare implications. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 18, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steagall, P.V. Analgesia: What Makes Cats Different/Challenging and What Is Critical for Cats? The Veterinary clinics of North America. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamminen, T.; Korpivaara, M.; Aspegrén, J.; Palestrini, C.; Overall, K.L. Pregabalin Alleviates Anxiety and Fear in Cats during Transportation and Veterinary Visits-A Clinical Field Study. Animals 2023, 13, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodan, I.; Dowgray, N.; Carney, H.C.; Carozza, E.; Ellis, S.L.; Heath, S.; Niel, L.; St Denis, K.; Taylor, S. 2022 AAFP/ISFM Cat Friendly Veterinary Interaction Guidelines: Approach and Handling Techniques. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 1093–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, S. The impact of paternity and early socialisation on the development of cats’ behaviour to people and novel objects. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1995, 45, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinlein, S.A.; Wilson, C.D.; Karatsoreos, I.N. Dysregulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis function con-tributes to altered endocrine and neurobehavioral responses to acute stress. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desborough, J.P. The stress response to trauma and surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 85, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.L.; Duke-Novakovski, T.; Singh, B. The immune response to anesthesia: Part 1. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2014, 41, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenadović, K.; Vučinić, M.; Radenković-Damnjanović, B.; Janković, L.; Teodorović, R.; Voslarova, E.; Becskei, Z. Cortisol concentration, pain and sedation scale in free roaming dogs treated with carprofen after ovariohysterectomy. Vet. World 2017, 10, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Avalos, I.; Flores-Gasca, E.; Mota-Rojas, D.; Casas-Alvarado, A.; Miranda-Cortés, A.E.; Domínguez-Oliva, A. Neurobiology of anesthetic-surgical stress and induced behavioral changes in dogs and cats: A review. Vet. World 2021, 14, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Papageorgiou, V.; Ververidis, C.; Mylonakis, M.E.; Savvas, I.; Kazakos, G. Orally administered gabapentin and alprazolam induce comparable levels of anxiolysis and sedation in cats. J. Am. Vet. Med.-Sociation 2024, 262, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucourt, L.; Masson, S. The Effect of Gabapentin on the Efficiency of a Desensitization-Counter-Conditioning Claw-Trimming Protocol for Cats with Healthcare Phobias: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Animals 2025, 15, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüelles, J.; Echaniz, M.; Bowen, J.; Fatjó, J. The impact of a stress-reducing protocol on the quality of pre-anaesthesia in cats. Vet. Rec. 2021, 188, e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steagall, P.V.; Benito, J.; Monteiro, B.P.; Doodnaught, G.M.; Beauchamp, G.; Evangelista, M.C. Analgesic effects of gabapentin and buprenorphine in cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy using two pain-scoring systems: A randomized clinical trial. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkar, A.; Bali, A.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Implications and mechanism of action of gabapentin in neuropathic pain. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013, 36, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, A.H.; Ullah, Q.; Naseer, O.; Gardezi, F.H.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, K.; Saleem, T.; Ali, A.; Khan, Y.R.; Waheed, A. Comparative Multimodal Palliative efficacy of gabapentin and tramadol by Using Two Pain Scoring Systems in Cats Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy. Acta Vet. 2021, 71, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, M.; Gower, L. Randomised clinical trial evaluating the effect of a single preappointment dose of gabapentin on signs of stress in hyperthyroid cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, e85–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lombaert, M.C.; Lourenço, B.N.; Coleman, A.E.; Arne, A.M.; Berghaus, R.D.; Schmiedt, C.W. Effect of gabapentin on ambulatory, direct, systemic arterial blood pressure in apparently healthy cats in the at-home and in-clinic environments. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X231188770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steagall, P.V.; Robertson, S.; Simon, B.; Warne, L.N.; Shilo-Benjamini, Y.; Taylor, S. 2022 ISFM Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Acute Pain in Cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudec, C.P.; Griffin, C.E. Changes in the stress markers cortisol and glucose before and during intradermal testing in cats after single administration of pre-appointment gabapentin. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, Y.C.; Groth, A.D.; Billson, F.M.; White, J.; Coall, S.M.; Yates, K.L.; Premont, J.E. Gabapentin reduces stress and does not affect ocular parameters in clinically normal cats. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2022, 25, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruviaro Tuleski, G.L.; Silveira, M.F.; Bastos, R.F.; Pscheidt, M.J.G.R.; Prieto, W.D.S.; Sousa, M.G. Behavioral and cardiovascular effects of a single dose of gabapentin or melatonin in cats: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, e524–e534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronezi, T.M.; Lopes, D.J.; Zardo, I.L.; Ferronatto, J.V.; Trojan, M.M.; Franck, K.R.; de Azevedo, A.F.; Spiering, A.G.; Nunes, L.N.; Fadel, L.; et al. Evaluation of the effects of gabapentin on the physiologic and echocardiographic variables of healthy cats: A prospective, randomized and blinded study. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, e498–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.F.; Veronezi, T.M.; Zardo, I.L.; Ferronatto, J.V.; Franck, K.R.; Spiering, A.G.; Nunes, L.N.; da Costa, F.V. Does pre-appointment gabapentin affect neurological examination findings? A prospective, randomized and blinded study in healthy cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X221149384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- DuPont, A.; Zidan, N.; Lueck, L.C.; Cameron, S. Evaluation of gabapentin administration on neurologic examination in 2 different age groups of healthy cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024, 38, 3129–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, K.; DePorter, T. Feline Stress Management During air Travel: A Multimodal Approach. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X221145521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haaften, K.A.; Forsythe, L.R.E.; Stelow, E.A.; Bain, M.J. Effects of a single preappointment dose of gabapentin on signs of stress in cats during transportation and veterinary examination. J. Am. Veteri-Nary Med. Assoc. 2017, 251, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszka, M.; Graff, E.; Medam, T.; Masson, S. Clinical evaluation of the effects of a single oral dose of gabapentin on fear-based aggressive behaviors in cats during veterinary examinations. J. Am. Vet. Med-Ical Assoc. 2021, 259, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, A.; Harbin, K.; MacPherson, J.; Rundle, K.; Overall, K.L. A review of pre-appointment medications to reduce fear and anxiety in dogs and cats at veterinary visits. Can. Vet. J. 2021, 62, 952–960. [Google Scholar]
- Spano, V.; Springer, C.M.; Christensen, E.L.; Albright, J.D. Effects of transdermal mirtazapine and oral gabapentin as pre-veterinary visit pharmaceuticals for shelter Cats. J. Vet. Behav. 2023, 64–65, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteg, N.; Dias, T.P.; de Freitas, V.R.; das Neves, V.B.; Gomes, M.R.; Meinerz, A.R.M.; Jorge, S.; Rondelli, M.C.H.; Cleff, M.B. A comparative study between integrative practices and preappointement gabapentin on serum cortisol in cats. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 3469–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratz, K.E.; Ferris, K.K.; Griffith, E.H.; Sherman, B.L. Use of single-dose oral gabapentin to attenuate fear responses in cage-trap confined community cats: A double-blind, placebo-controlled field trial. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagan, B.H.; Van Haaften, K.; Protopopova, A. Daily gabapentin improved behavior modification progress and decreased stress in shelter cats from hoarding environments in a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2023, 261, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarbeglou, M.; Arkan, P. Retrospective evaluation of preanesthetic oral gabapentin in cats receiving total injectable anesthesia in a high-quality, high-volume spay-neuter setting. Res. Vet. Sci. 2025, 189, 105635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, V.; Ververidis, C.; Mylonakis, M.E.; Savvas, I.; Kazakos, G. Use of Gabapentin or Alprazolam in Cats during Postoperative, Short-Term Hospitalization. Animals 2024, 14, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamminen, T.; Korpivaara, M.; Suokko, M.; Aspegrén, J.; Palestrini, C.; Overall, K. Efficacy of a Single Dose of Pregabalin on Signs of Anxiety in Cats During Transportation-A Pilot Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 711816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamminen, T.; Doedée, A.; Hyttilä-Hopponen, M.; Kaskinoro, J. Pharmacokinetics of single and repeated oral doses of pregabalin oral solution formulation in cats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 45, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigner, D.R.; Breitreiter, K.; Carmack, T.; Cox, S.; Downing, R.; Robertson, S.; Rodan, I. 2023 AAFP/IAAHPC feline hospice and palliative care guidelines. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X231201683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; Peng, H.; Wei, B.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z. Effect of oral administration of pregabalin on physiological and echocardiographic variables in healthy cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2024, 26, 1098612X241250245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbrook, C.; Clark, L. State of the art analgesia-Recent developments pharmacological approaches to acute pain management in dogs and cats: Part 2. Vet. J. 2018, 236, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovak, J.E.; Costa, A.P. A pilot study of transdermal gabapentin in cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, F.; Negro, V.; Ravasio, G.; Villa, R.; Draghi, S.; Cagnardi, P. Gabapentin: Clinical Use and Pharmaco-kinetics in Dogs, Cats, and Horses. Animals 2023, 13, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, D.; Papich, M.; Baynes, R.; Murrell, J.; Lascelles, B.D.X. Chronic maladaptive pain in cats: A review of current and future drug treatment options. Vet. J. 2017, 230, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, D.E.; Rishniw, M.; Scherk, M.; Lascelles, B.D.X. Prescribing practices of veterinarians in the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain in cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.G.P.; Meadows, J.M.; Pypendop, B.H.; Johnson, E.G.; Zaffarano, B. Assessment of the effects of gabapentin on activity levels and owner-perceived mobility impairment and quality of life in osteoarthritic geriatric cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2018, 253, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusbridge, C. Neuropathic pain in cats: Mechanisms and multimodal management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2024, 26, 1098612X241246518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Gruen, M.; KuKanich, K.; XLascelles, B.D.; Monteiro, B.P.; Sampietro, L.R.; Robertson, S.; Steagall, P.V. 2024 ISFM and AAFP consensus guidelines on the long-term use of NSAIDs in cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2024, 26, 1098612X241241951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goich, M.; Bascuñán, A.; Faúndez, P.; Valdés, A. Multimodal analgesia for treatment of allodynia and hyperalgesia after major trauma in a cat. JFMS Open Rep. 2019, 5, 2055116919855809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertelt, K.; Dörner, J. Successful treatment of a Himalayan cat with feline orofacial pain syndrome. Vet. Rec. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, K.; Matsunami, E.; Tazawa, K.; Wang, W.; DiNardo, J.A.; Koutsogiannaki, S. Pediatric perioperative stress responses and anesthesia. Transl. Perioper. Pain Med. 2017, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Srithunyarat, T.; Höglund, O.V.; Hagman, R.; Olsson, U.; Stridsberg, M.; Lagerstedt, A.; Pettersson, A. Catestatin, vasostatin, cortisol, temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate, scores of the short form of the Glasgow composite measure pain scale and visual analog scale for stress and pain behavior in dogs before and after ovariohysterectomy. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby-Madden, T.; Waring, C.T.; Herron, M. Effects of Gabapentin on the Treatment of Behavioral Disorders in Dogs: A Retrospective Evaluation. Animals 2024, 14, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockbrader, H.N.; Wesche, D.; Miller, R.; Chapel, S.; Janiczek, N.; Burger, P. A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steagall, P.V.; Monteiro, B.P. Acute pain in cats: Recent advances in clinical assessment. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Bernal, F.; Martínez-Burnes, J.; Hernández-Avalos, I.; Olmos-Hernández, A.; Domínguez-OIiva, A.; Reyes-Sotelo, B.; González-López, C.; Villanueva-Pereyra, D.; Mota-Rojas, D. Infrared Thermography and Physiological Variables as Methods for Recognizing Fear in Domestic Cats (Felis catus) Using Three Pharmacological Models: Cannabidiol, Gabapentin, and Synthetic Facial Pheromones. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | Study Design | Pharmacological Action | Stress, Anxiety, or Pain Measuring Instrument(s) | Dose | Certainty | Conclusions of the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABAPENTIN | ||||||
| Azevedo, et al., 2023 [25] | Prospective, randomized, and blinded study | Anxiolytic (neurological examination) | NE | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Reduced stress, fear, and anxiety Facilitated the neurological examination |
| Crowe, et al., 2022 [22] | Crossover, randomized, controlled, and blinded study | Anxiolytic (neurologic examination) | CSS | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Reduced stress Increased sedation Did not affect the pupillary diameter and the Schirmer test 1 |
| DuPont, et al., 2024 [26] | Prospective, double-blind, closed clinical trial | Anxiolytic (Neurologic examination) | CSS | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Anxiolytic Increased sedation in geriatric cats |
| Eagan, et al., 2023 [34] | Randomized, blinded, and prospective study | Anxiolytic | CSS LTE VR | 10 mg/kg | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Decreased stress in shelter cats Behavioral changes |
| Gurney and Gower 2022 [18] | Prospective clinical trial | Anxiolytic | NE | 20 mg/kg | ⊕⊕⊕ | In cats with hyperthyroidism, decreased transport stress and facilitated animal handling during consultation |
| Van Haaften, et al., 2017 [28] | Randomized clinical trial | Anxiolytic | CSS VR CS | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Reduced stress and aggression Increased compliance during transportation, resulting in safe and effective treatment |
| Hudec and Griffin 2020 [21] | Crossover, prospective, and blinded study | Anxiolytic | ECS OA G C | 25–30.5 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Did not reduce serum cortisol/glucose concentrations Lower stress scores when measured by veterinarians and caregivers |
| Kruszka, et al., 2021 [29] | Clinical, crossover, double-blind, randomized, and controlled | Anxiolytic Aggression management | CS | 100 mg/cat (<7 kg) and 200 mg/cat (≥7 kg) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Improves compliance during physical examination |
| De Lombaert, et al., 2023 [19] | Experimental, prospective, randomized, and controlled study | Anxiolytic | CS CSS | 100 mg/cat | ⊕ | Did not affect blood pressure Lower evaluation score, but without statistically significant differences |
| Papageorgiou, et al., 2024 [11] | Prospective, blinded, controlled clinical trial | Anxiolytic | CSS VSS EAS | 100 mg/cat | ⊕ | There were no differences between treatment (gabapentin/alprazolam) Lower CSS scores Increased sedation scores |
| Papageorgiou, et al., 2024 [36] | Prospective, blinded, controlled clinical trial | Anxiolytic | CSS VSS GCMPS | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Gabapentin/alprazolam are effective anxiolytics during the postsurgical hospitalization |
| Pankratz, et al., 2018 [33] | Double-blind, randomized, controlled study | Anxiolytic | CSS GSS | 50 and 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Both doses reduced stress in confined cats without sedation |
| Spano, et al., 2023 [31] | Double-blind, controlled, and randomized | Anxiolytic | CSS GSS EHS | 5–30 mg/kg | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Reduced fear and stress during medical management in shelter cats |
| Ruviaro, et al., 2022 [23] | Randomized, double-blind, controlled, prospective trial | Anxiolytic | CS GSS | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Effectively increased compliance without altering cardiovascular parameters |
| Veronezi, et al., 2022 [24] | Prospective, randomized, blinded study | Anxiolytic | NE | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕ | Reduced anxiety without physiological or hemodynamic alterations |
| Versteg, et al., 2024 [32] | Randomized, double-blind clinical trial | Anxiolytic | C | 50–100 mg/cat | ⊕ | Gabapentin and integrative practices reduced stress and cortisol levels |
| Jafarbeglou and Arkan 2025 [35] | Retrospective and blinded study | Anxiolytic | NE | 100 mg/cat | ⊕ | An anxiolytic that improves sedation Fewer animals received rescue analgesia |
| Raucourt and Masson 2025 [12] | Prospective, double-blind, randomized, crossover study | Anxiolytic | NRSAFE | 100 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Supports early integration into behavioral therapy protocols Reduced fear and increased welfare Prevented phobias |
| Rabbani, et al., 2021 [16] | Experimental, prospective, randomized study | Acute pain | GCMPS DIVAS | 10 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | The combination of gabapentin/tramadol improved analgesia and increased the mechanical nociceptive threshold |
| Slovak and Costa 2021 [42] | Randomized study | Acute pain | GCMPS UNESP—Botucatu | 10 mg/kg | ⊕⊕ | The transdermal route may be suitable Scores decreased Preliminary study with a small number of study animals |
| Steagall, et al., 2018 [14] | Prospective, blinded, randomized, controlled study | Acute pain | GCMPS UNESP—Botucatu DIVAS | 50 mg/cat | ⊕⊕⊕ | No differences between groups Gabapentin in combination with opioids is an alternative for perioperative pain |
| Guedes, et al., 2018 [46] | Randomized, controlled, crossover study | Chronic pain | CSOM Omnidirectional piezoelectric accelerometer | 10 mg/kg | ⊕⊕⊕ | Improved averages of tutors’ informational outcomes Decreased signs of pain |
| PREGABALIN | ||||||
| Lamminen, et al., 2021 [37] | Randomized, blinded, controlled study | Anxiolytic | VR RSDAF Ethogram (external observer) | 5 and 10 mg/kg | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Reduces signs of anxiety and fear associated with traveling by car |
| Lamminen, et al., 2023 [3] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter study | Anxiolytic | NRST NRSCE VR | 5 mg/kg | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Relief from anxiety and fear related to transportation and veterinary visits Improved medical management and feline welfare |
| Li, et al., 2024 [40] | Randomized, blinded, crossover trial | Anxiolytic Sedative | The 13—point sedation scores | 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/kg | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | Causes sedation and anxiolytic effects The effects are dose-dependent. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda-Cortés, A.E.; Prado-Ochoa, M.G.; Díaz-Torres, R.; Pérez-Sánchez, A.P.; Del Río-García, J.C.; Mota-Rojas, D.; Hernández-Avalos, I. Comparison of the Anxiolytic and Analgesic Effects of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Cats: A Systematic Review. Animals 2025, 15, 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162346
Miranda-Cortés AE, Prado-Ochoa MG, Díaz-Torres R, Pérez-Sánchez AP, Del Río-García JC, Mota-Rojas D, Hernández-Avalos I. Comparison of the Anxiolytic and Analgesic Effects of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Cats: A Systematic Review. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162346
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda-Cortés, Agatha Elisa, María Guadalupe Prado-Ochoa, Roberto Díaz-Torres, Alicia Pamela Pérez-Sánchez, Juan Carlos Del Río-García, Daniel Mota-Rojas, and Ismael Hernández-Avalos. 2025. "Comparison of the Anxiolytic and Analgesic Effects of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Cats: A Systematic Review" Animals 15, no. 16: 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162346
APA StyleMiranda-Cortés, A. E., Prado-Ochoa, M. G., Díaz-Torres, R., Pérez-Sánchez, A. P., Del Río-García, J. C., Mota-Rojas, D., & Hernández-Avalos, I. (2025). Comparison of the Anxiolytic and Analgesic Effects of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Cats: A Systematic Review. Animals, 15(16), 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162346








