Analysis of the Role of KLF4 in the Regulation of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses, and Reagents
2.2. Generation of Gene Knockout and Overexpression Cells
2.3. PEDV Infection
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Assay
2.5. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
2.6. The 50% Cell Culture Infectious Dose (TCID50) Assay
2.7. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay
2.8. Transcriptome Data Analysis
2.9. Functional Annotation of DEGs
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
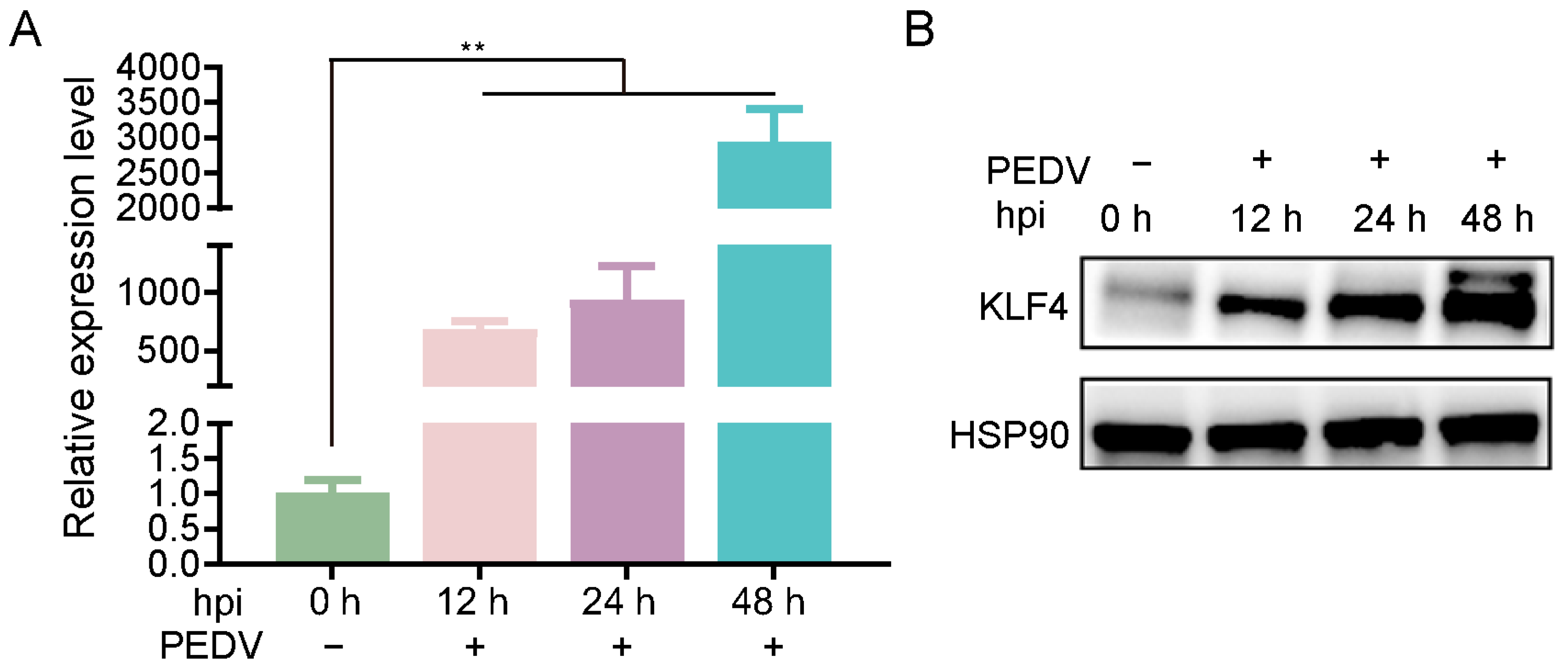
3.1. KLF4 Expression Is Increased in PEDV-Infected Host Cells
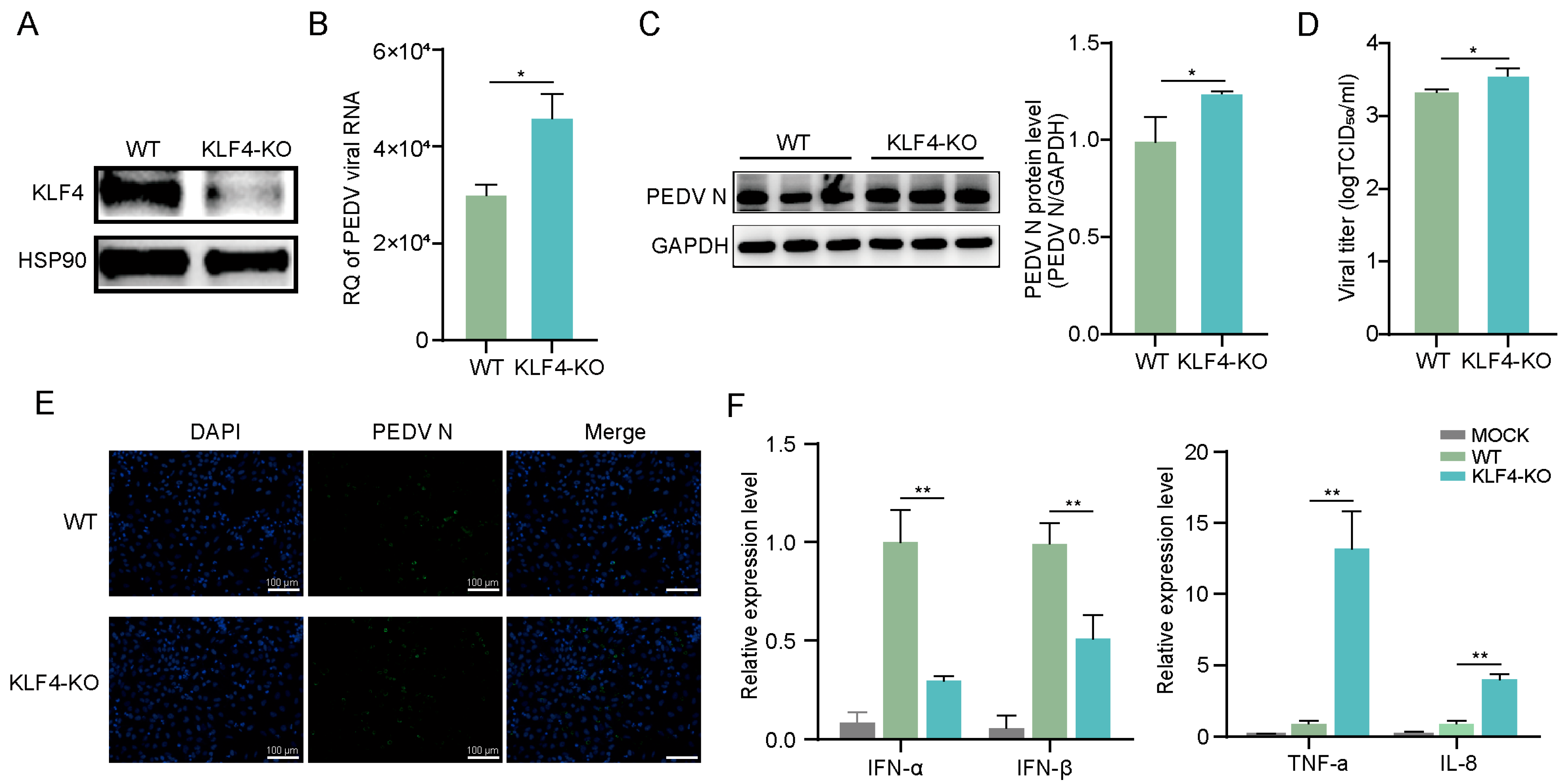
3.2. Knockout of KLF4 Promotes PEDV Replication in IPEC-J2 Cells
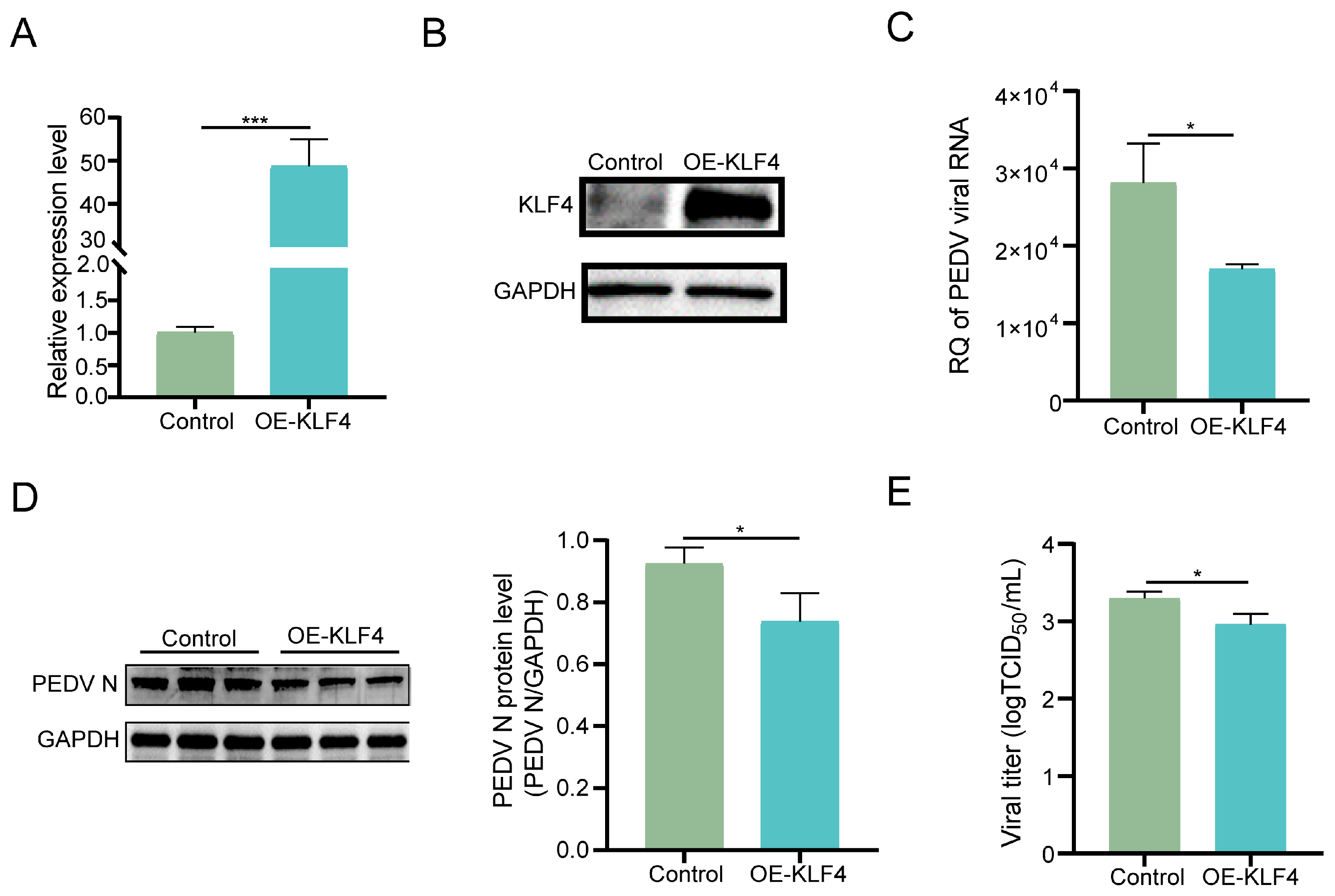
3.3. Overexpression of KLF4 Suppresses PEDV Replication in IPEC-J2 Cells
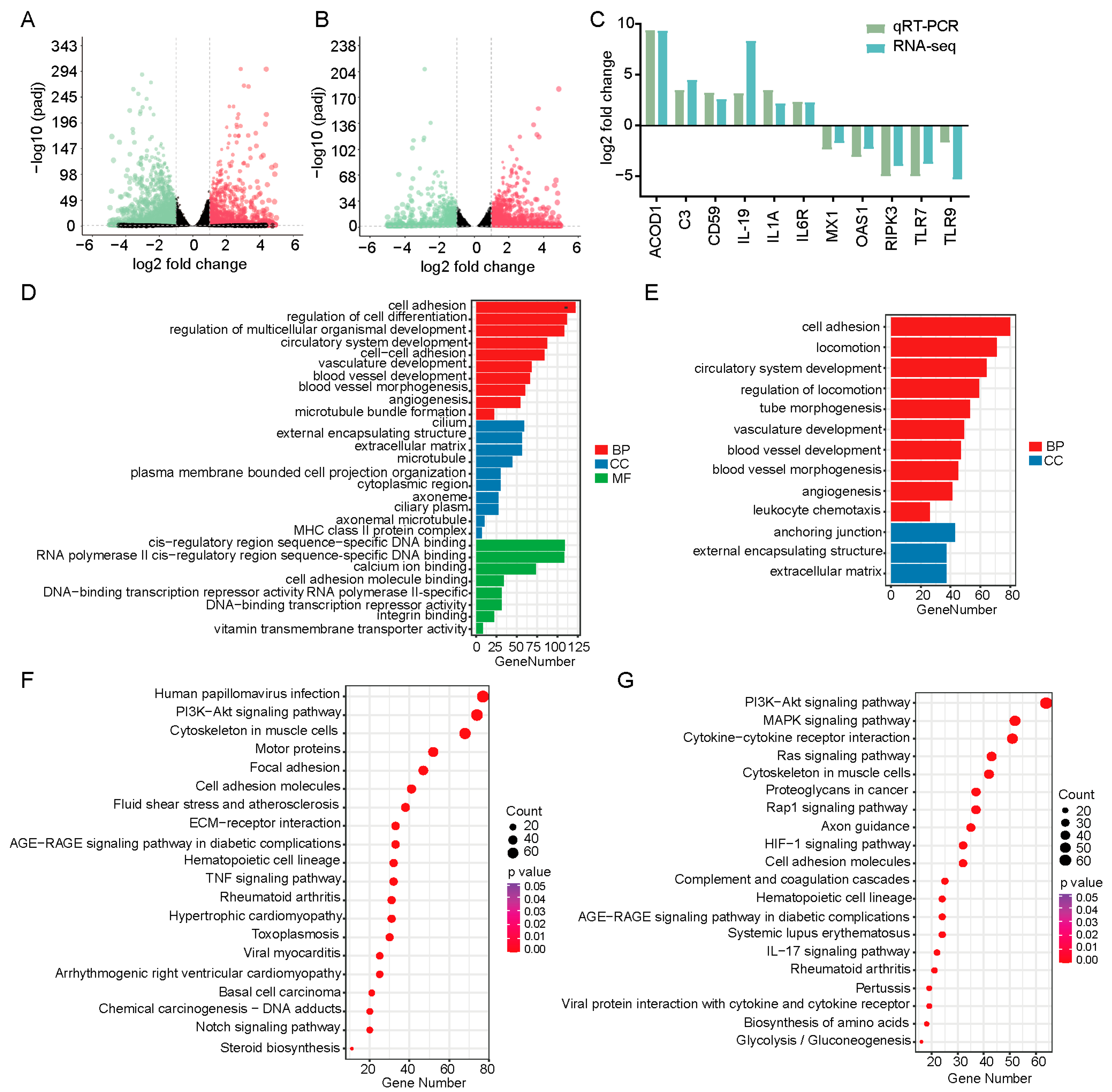
3.4. Transcriptomics Analysis of KLF4 Knockout Cells Infected with PEDV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, Z.F.; Xu, Z.C.; Zhou, Q.F.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.Y.; Du, Y.P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.Y.; Cao, Y.C. Oral administration of coated PEDV-loaded microspheres elicited PEDV-specific immunity in weaned piglets. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6803–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Wei, S.; Chen, J.F.; Feng, L. Epidemiology and vaccine of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in China: A mini-review. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, S.; Strugnell, B.; Thomson, J.; Webster, G.; McOrist, S.; Clarke, H. Emergence of severe porcine epidemic diarrhoea in pigs in the USA. Vet. Rec. 2013, 173, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, S.; Neill, C.; Singrey, A.; Clement, T.; Cochrane, R.; Jones, C.; Patterson, G.; Spronk, G.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E. Modeling the transboundary risk of feed ingredients contaminated with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasick, J.; Berhane, Y.; Ojkic, D.; Maxie, G.; Embury-Hyatt, C.; Swekla, K.; Handel, K.; Fairles, J.; Alexandersen, S. Investigation into the role of potentially contaminated feed as a source of the first-detected outbreaks of porcine epidemic diarrhea in Canada. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Wu, Q.X.; Huang, L.L.; Yuan, C.; Wang, J.L.; Yang, Q. An alternative pathway of enteric PEDV dissemination from nasal cavity to intestinal mucosa in swine. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W.; Mallipattu, S.K. Krüppel-like factors in mammalian stem cells and development. Development 2017, 144, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Feng, Y.P.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, L.; Chen, J.Y.; Song, Y.X.; Zhu, W.B.; Hu, X.L.; Li, Z.S.; Kong, F.Y.; et al. Optimized rAAV8 targeting acinar KLF4 ameliorates fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis via exosomes-enriched let-7s suppressing pancreatic stellate cells activation. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 2624–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Yang, V.W. Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4): What we currently know. Gene 2017, 611, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawandar, D.M.; Wang, A.; Makielski, K.; Lee, D.; Ma, S.; Barlow, E.; Reusch, J.; Jiang, R.; Wille, C.K.; Greenspan, D.; et al. Differentiation-Dependent KLF4 Expression Promotes Lytic Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Epithelial Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.W.; Lian, H.; Zhong, B.; Shu, H.B.; Li, S. Krüppel-like factor 4 negatively regulates cellular antiviral immune response. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Qu, H.; Feng, H.; Wu, S.; Bao, W. Global Mapping of H3K4 Trimethylation (H3K4me3) and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal Genes Involved in the Response to Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infections in Pigs. Animals 2019, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, H.; Ren, J.; Zheng, X.; Wei, K.; Liu, J. Transcriptome analysis reveals modulation of the STAT family in PEDV-infected IPEC-J2 cells. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labun, K.; Montague, T.G.; Krause, M.; Torres Cleuren, Y.N.; Tjeldnes, H.; Valen, E. CHOPCHOP v3: Expanding the CRISPR web toolbox beyond genome editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W171–W174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, T.C.; Ai, W.; Liu, C. Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates intestinal epithelial cell morphology and polarity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.H.; Spindler, K.R. Identifying host factors that regulate viral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klann, K.; Bojkova, D.; Tascher, G.; Ciesek, S.; Münch, C.; Cinatl, J. Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Inhibition Prevents SARS-CoV-2 Replication. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 164–174.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, B.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; He, K.; Fan, H. Nonstructural protein 6 of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus induces autophagy to promote viral replication via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, C.; Ming, X.; Zhang, C.; Jung, Y.S.; Qian, Y. Veratramine inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus entry through macropinocytosis by suppressing PI3K/Akt pathway. Virus Res. 2024, 339, 199260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, M.M.; Lindkvist, M.; Fälker, K.; Kumawat, A.K.; Paramel, G.; Grenegård, M.; Sirsjö, A.; Ljungberg, L.U. Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, A.; Bonni, A.; Zigmond, M.J.; Lin, M.Z.; Juo, P.; Hu, L.S.; Anderson, M.J.; Arden, K.C.; Blenis, J.; Greenberg, M.E. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 1999, 96, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Khandelwal, N.; Thachamvally, R.; Tripathi, B.N.; Barua, S.; Kashyap, S.K.; Maherchandani, S.; Kumar, N. Role of MAPK/MNK1 signaling in virus replication. Virus Res. 2018, 253, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, C.A.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Bonaventure, B.; Kurland, A.P.; Ye, C.; Yaron, T.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Adhikary, P.; Golynker, I.; Panis, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 hijacks p38β/MAPK11 to promote virus replication. mBio 2023, 14, e0100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Gong, T.; Kuang, Q.; Xiang, Q.; Gong, L.; Zhang, G. Deoxycholic acid inhibits ASFV replication by inhibiting MAPK signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266 Pt 1, 130939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, J.H. JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways contribute to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection. Virus Res. 2016, 222, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.S.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, S.; Feng, M.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Huang, X.; Wu, S.; Bao, W. Analysis of the Role of KLF4 in the Regulation of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Animals 2025, 15, 2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162343
Wang H, Zhou Y, Gu S, Feng M, Wang J, Jin J, Huang X, Wu S, Bao W. Analysis of the Role of KLF4 in the Regulation of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162343
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haifei, Yajing Zhou, Shanshen Gu, Mengke Feng, Jie Wang, Jian Jin, Xiaoguo Huang, Shenglong Wu, and Wenbin Bao. 2025. "Analysis of the Role of KLF4 in the Regulation of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection" Animals 15, no. 16: 2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162343
APA StyleWang, H., Zhou, Y., Gu, S., Feng, M., Wang, J., Jin, J., Huang, X., Wu, S., & Bao, W. (2025). Analysis of the Role of KLF4 in the Regulation of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Animals, 15(16), 2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162343







