Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli from Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Admitted to a Wildlife Rescue Center
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals Involved in the Study and Housing Characteristics
- (i)
- Adult subjects;
- (ii)
- A clinical condition requiring hospitalization but not intensive care, as the aim was to investigate the effect of hospitalization without compromising the health or prognosis of critically ill individuals (e.g., with severe injuries or pathologies);
- (iii)
- Not showing gastrointestinal symptoms;
- (iv)
- An interval of no more than 12 h between their discovery and admission to the center, to minimize potential contamination from the rescuer’s environment;
- (v)
- Being alive and still hospitalized at the time of the second sampling.
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
2.4.2. Antimicrobial Resistance
2.4.3. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing E. coli
3. Results
3.1. Microbiological Analysis
3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Atb. | Antibiotic |
| AMC | Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid |
| AMI | Amikacin |
| AMP | Ampicillin |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| BPW | Buffered peptone water |
| CBP | Clinical breakpoint |
| CHL | Chloramphenicol |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CLE | Cefalexin |
| CPO | Cefpodoxime |
| CTZ | Ceftazidime |
| CVE | Cefovecin |
| CZO | Cefazolin |
| DOX | Doxycycline |
| ECOFF | Epidemiological cut-off |
| ENR | Enrofloxacin |
| ESBL | Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase |
| EUCAST | European committee on antimicrobial susceptibility testing |
| GEN | Gentamicin |
| IMI | Imipenem |
| MALDI-ToF | Matrix-assisted laser-desorption ionization—time of flight |
| McC3 | McConkey 3 agar |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MIC50 | 50th percentile of the minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MIC90 | 90th percentile of the minimum inhibitory concentration |
| nWT | Non-wild-type |
| PIT | Piperacillin–tazobactam |
| T0 | Time 0 (admission) |
| T1 | Time 1 (discharge or approx. 10 days post admission) |
| TET | Tetracycline |
| TECOFF | Tentative epidemiological cut-off |
| TSB | Tryptone soya broth |
| TRS | Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole |
| WRC | Wildlife rescue center |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- Tenaillon, O.; Skurnik, D.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. The Population Genetics of Commensal Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahian, S.; Graham, J.P.; Halaji, M. A Review of the Mechanisms That Confer Antibiotic Resistance in Pathotypes of E. coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1387497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster-Nyarko, E.; Pallen, M.J. The Microbial Ecology of Escherichia coli in the Vertebrate Gut. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.A.; Alcalá, L.; Simón, C.; Torres, C. Novel Sequence Types of Extended-Spectrum and Acquired AmpC Beta-Lactamase Producing Escherichia coli and Escherichia Clade V Isolated from Wild Mammals. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Ramatla, T.; Mafokwane, T.; Lekota, K.; Monyama, M.; Khasapane, G.; Serage, N.; Nkhebenyane, J.; Bezuidenhout, C.; Thekisoe, O. “One Health” Perspective on Prevalence of Co-Existing Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandachi, I.; Chabou, S.; Daoud, Z.; Rolain, J.M. Prevalence and Emergence of Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin-, Carbapenem- and Colistin-Resistant Gram Negative Bacteria of Animal Origin in the Mediterranean Basin. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; et al. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 627821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcês, A.; Pires, I. European Wild Carnivores and Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria: A Review. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabença, C.; Romero-Rivera, M.; Barbero-Herranz, R.; Sargo, R.; Sousa, L.; Silva, F.; Lopes, F.; Abrantes, A.C.; Vieira-Pinto, M.; Torres, C.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli from Fecal Samples of Wild Animals. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzard, A.; Rasmussen, S.L. Erinaceus Europaeus. IUCN Red List. Threat. Species 2024, e.T29650A213411773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, I.; Dervas, E.; Colombino, E.; Bonaffini, G.; Zanet, S.; Orusa, R.; Robetto, S.; Vacchetta, M.; Mauthe von Degerfeld, M.; Quaranta, G.; et al. Causes of Admission, Mortality and Pathological Findings in European Hedgehogs: Reports from Two University Centers in Italy and Switzerland. Animals 2024, 14, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, A.; Isomursu, M.; Valtonen, A.; Hirvelä-Koski, V.; Kunnasranta, M. Mortality, Diseases and Diet of European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in an Urban Environment in Finland. Mamm. Res. 2016, 61, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ai, L.; Zhu, C.; Lu, Y.; Lv, R.; Mao, Y.; Lu, N.; Tan, W. Co-Existence of Multiple Anaplasma Species and Variants in Ticks Feeding on Hedgehogs or Cattle Poses Potential Threats of Anaplasmosis to Humans and Livestock in Eastern China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 913650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcias, B.; Aguirre, L.; Seminati, C.; Reyes, N.; Allepuz, A.; Obón, E.; Molina-lopez, R.A.; Darwich, L. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactam Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae and Escherichia coli in Wild European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europeus) Living in Populated Areas. Animals 2021, 11, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Raisen, C.L.; Ba, X.; Sadgrove, N.J.; Padilla-González, G.F.; Simmonds, M.S.J.; Loncaric, I.; Kerschner, H.; Apfalter, P.; Hartl, R.; et al. Emergence of Methicillin Resistance Predates the Clinical Use of Antibiotics. Nature 2022, 602, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukešová, G.; Voslarova, E.; Vecerek, V.; Vucinic, M. Trends in Intake and Outcomes for European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) in the Czech Rescue Centers. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, P.; Ghorbani-Choboghlo, H. Isolation and Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Found in Free-Ranging Long-Eared Hedgehogs (Erinaceus concolor) from Tabriz, Iran. J. Exot. Pet. Med. 2015, 24, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yi, S.; Kim, W.-H.; Guk, J.-H.; Ha, M.; Kwak, I.; Han, J.; Yeon, S.-C.; Cho, S. Environmental Perturbations during the Rehabilitation of Wild Migratory Birds Induce Gut Microbiome Alteration and Antibiotic Resistance Acquisition. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0116322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, I.; Bellato, A.; Nebbia, P.; Stella, M.C.; Ala, U.; von Degerfeld, M.M.; Quaranta, G.; Robino, P. Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia coli in Wild Birds Hospitalised in a Wildlife Rescue Centre. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 93, 101945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.S.; Morton, J.M.; Cobbold, R.N.; Filippich, L.J.; Trott, D.J. Risk Factors for Dogs Becoming Rectal Carriers of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli during Hospitalization. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filius, P.M.G.; Gyssens, I.C.; Kershof, I.M.; Roovers, P.J.E.; Ott, A.; Vulto, A.G.; Verbrugh, H.A.; Endtz, H.P. Colonization and Resistance Dynamics of Gram-Negative Bacteria in Patients during and after Hospitalization. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2879–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.; Abreu, R.; Serrano, I.; Such, R.; Garcia-Vila, E.; Quirós, S.; Cunha, E.; Tavares, L.; Oliveira, M. Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Wild Mammals from Two Rescue and Rehabilitation Centers in Costa Rica: Characterization and Public Health Relevance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, T.W.; Williams, N.J.; Clegg, P.D.; O’Donnell, A.J.; Dawson, S.; Pinchbeck, G.L. Longitudinal Study of Antimicrobial-Resistant Commensal Escherichia coli in the Faeces of Horses in an Equine Hospital. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 100, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, M.J.P.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Schaafstra, F.J.W.C.; van Doorn, D.A.; Zomer, A.L. Longitudinal Study of the Short- and Long-Term Effects of Hospitalisation and Oral Trimethoprim-Sulfadiazine Administration on the Equine Faecal Microbiome and Resistome. Microbiome 2023, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, R.A.; Atwill, E.R.; Conrad, P.A.; Byrne, B.A.; Jang, S.; Lawrence, J.; McCowan, B.; Gulland, F.M.D. The Effect of Rehabilitation of Northern Elephant Seals (Mirounga angustirostris) on Antimicrobial Resistance of Commensal Escherichia coli. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 133, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baros Jorquera, C.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Sallaberry-Pincheira, N.; Munita, J.M.; Flores Navarro, C.; Tardone, R.; González-Rocha, G.; Singer, R.S.; Bueno, I. Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife and in the Built Environment in a Wildlife Rehabilitation Center. One Health 2021, 13, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law 11 February 1992, n. 157. Rules for the Protection of Homeothermic Wildlife and for Hunting. (OJ General Series n. 46 of 25-02-1992—Ordinary Supplement n. 41). [Legge 11 Febbraio 1992, n. 157. Norme per la Protezione della Fauna Selvatica Omeoterma e per il Prelievo Venatorio. (GU Serie Generale n. 46 del 25-02-1992—Suppl. Ordinario n. 41)]. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/1992/02/25/092G0211/sg (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Lagerstrom, K.M.; Hadly, E.A. Under-Appreciated Phylogroup Diversity of Escherichia coli within and between Animals at the Urban-Wildland Interface. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0014223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. LmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-387-98784-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Kosinski, M.; Biecek, P. survminer: Drawing Survival Curves Using “ggplot2”; CRAN: Contributed Packages; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing EUCAST MIC Distribution Website. Available online: https://mic.eucast.org/search/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Kahlmeter, G.; Turnidge, J. How to: ECOFFs—The Why, the How, and the Don’ts of EUCAST Epidemiological Cutoff Values. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlmeter, G.; Turnidge, J. Wild-Type Distributions of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations and Epidemiological Cut-off Values—Laboratory and Clinical Utility. Clin Microbiol Rev 2023, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegemann, M.R.; Passmore, C.A.; Sherington, J.; Lindeman, C.J.; Papp, G.; Weigel, D.J.; Skogerboe, T.L. Antimicrobial Activity and Spectrum of Cefovecin, a New Extended- Spectrum Cephalosporin, against Pathogens Collected from Dogs and Cats in Europe and North America. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter’s Exotic Animal Formulary, 6th ed.; Carpenter, J.W., Harms, C.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 9780323833929. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther, S.; Grobbel, M.; Heidemanns, K.; Schlegel, M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Ewers, C.; Wieler, L.H. First Insights into Antimicrobial Resistance among Faecal Escherichia coli Isolates from Small Wild Mammals in Rural Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3519–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.; Wang, J.; Fanning, S.; Mcmahon, B.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife: Implications for Public Health. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munley, J.A.; Kelly, L.S.; Pons, E.E.; Kannan, K.B.; Coldwell, P.S.; Whitley, E.M.; Gillies, G.S.; Efron, P.A.; Nagpal, R.; Mohr, A.M. Multicompartmental Traumatic Injury and the Microbiome: Shift to a Pathobiome. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023, 94, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelloni, F.; Cilia, G.; Bogi, S.; Ebani, V.V.; Turini, L.; Nuvoloni, R.; Cerri, D.; Fratini, F.; Turchi, B. Pathotypes and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Escherichia coli Isolated from Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) in Tuscany. Animals 2020, 10, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2021–2022. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Dashboard on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/microstrategy/dashboard-antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Darwich, L.; Vidal, A.; Seminati, C.; Albamonte, A.; Casado, A.; López, F.; Molina-López, R.A.; Migura-Garcia, L. High Prevalence and Diversity of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase and Emergence of OXA-48 Producing Enterobacterales in Wildlife in Catalonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Usui, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Izumi, K.; Ikeda, T.; Andoh, M. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Escherichia coli Isolates Obtained from Wild Mammals between 2013 and 2017 in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoglica, C.; Vergara, A.; Angelucci, S.; Festino, A.R.; Antonucci, A.; Moschetti, L.; Farooq, M.; Marsilio, F.; Di Francesco, C.E. Resistance Patterns, Mcr-4 and OXA-48 Genes, and Virulence Factors of Escherichia coli from Apennine Chamois Living in Sympatry with Domestic Species, Italy. Animals 2022, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, M.; Su, J. Spread of Plasmids Carrying Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Soil-Lettuce-Snail Food Chain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 34295–34308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbanegavi, T.T.; Makuvara, Z.; Marumure, J.; Alufasi, R.; Karidzagundi, R.; Chaukura, N.; Musvuugwa, T.; Okiobe, S.T.; Rzymski, P.; Gwenzi, W. Are Earthworms the Victim, Facilitator or Antidote of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance at the Soil-Animal-Human Interface? A One-Health Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.S.; Morton, J.M.; Cobbold, R.N.; Filippich, L.J.; Trott, D.J. Risk Factors for Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Rectal Colonization of Dogs on Admission to a Veterinary Hospital. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocca, G.; Piva, S.; Del Magno, S.; Scarpellini, R.; Giacometti, F.; Serraino, A.; Giunti, M. Prevalence and Patterns of Antimicrobial Resistance among Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus spp. In a Veterinary University Hospital. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.M.; Pinchbeck, G.; McIntyre, K.M.; Nuttall, T.; McEwan, N.; Dawson, S.; Williams, N.J. Routine Antibiotic Therapy in Dogs Increases the Detection of Antimicrobial-Resistant Faecal Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3305–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, J.W.; Weese, J.S. Hospital-Associated Infections in Small Animal Practice. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 45, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogeer-Gyles, J.; Mathews, K.A.; Sears, W.; Prescott, J.F.; Weese, J.S.; Boerlin, P. Development of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance in Rectal Escherichia coli Isolates from Dogs Hospitalized in an Intensive Care Unit. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerstein, R.; Atkinson, A.; Lo Priore, E.F.; Kronenberg, A.; Marschall, J.; Burnens, A.; Cherkaoui, A.; Dubuis, O.; Egli, A.; Gaia, V.; et al. Characterizing Non-Linear Effects of Hospitalisation Duration on Antimicrobial Resistance in Respiratory Isolates: An Analysis of a Prospective Nationwide Surveillance System. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bexton, S. Hedgehogs. In BSAVA Manual of Wildlife Casualties; Mullineaux, E., Keeble, E., Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association: Glouchester, UK, 2016; pp. 117–132. ISBN 9781905319800. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Sui, J. Gut Microbiome Differences in Rescued Common Kestrels (Falco tinnunculus) Before and After Captivity. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chng, K.R.; Li, C.; Bertrand, D.; Ng, A.H.Q.; Kwah, J.S.; Low, H.M.; Tong, C.; Natrajan, M.; Zhang, M.H.; Xu, L.; et al. Cartography of Opportunistic Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in a Tertiary Hospital Environment. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofte, D.; Jepson, R.E. PRO: Environmental Microbiological Surveillance Does Support Infection Control in Veterinary Hospitals. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 6, dlae113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.P.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Boerlin, P.; Weese, J.S.; Prescott, J.F.; Janecko, N.; Hassard, L.; McEwen, S.A. Escherichia coli and Selected Veterinary and Zoonotic Pathogens Isolated from Environmental Sites in Companion Animal Veterinary Hospitals in Southern Ontario. Can. Vet. J. 2010, 51, 963–972. [Google Scholar]
- Suthar, N.; Roy, S.; Call, D.R.; Besser, T.E.; Davis, M.A. An Individual-Based Model of Transmission of Resistant Bacteria in a Veterinary Teaching Hospital. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Yeo, Y.G.; Lee, Y.T.; Han, J.I. Antimicrobial Resistance of Commensal Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis Isolated from Clinically Healthy Captive Wild Animals in Seoul Zoo. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.C.M.; Murray, M.; Tseng, F.; Widmer, G. The Fecal Microbiota of Wild and Captive Raptors. Anim. Microbiome 2020, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
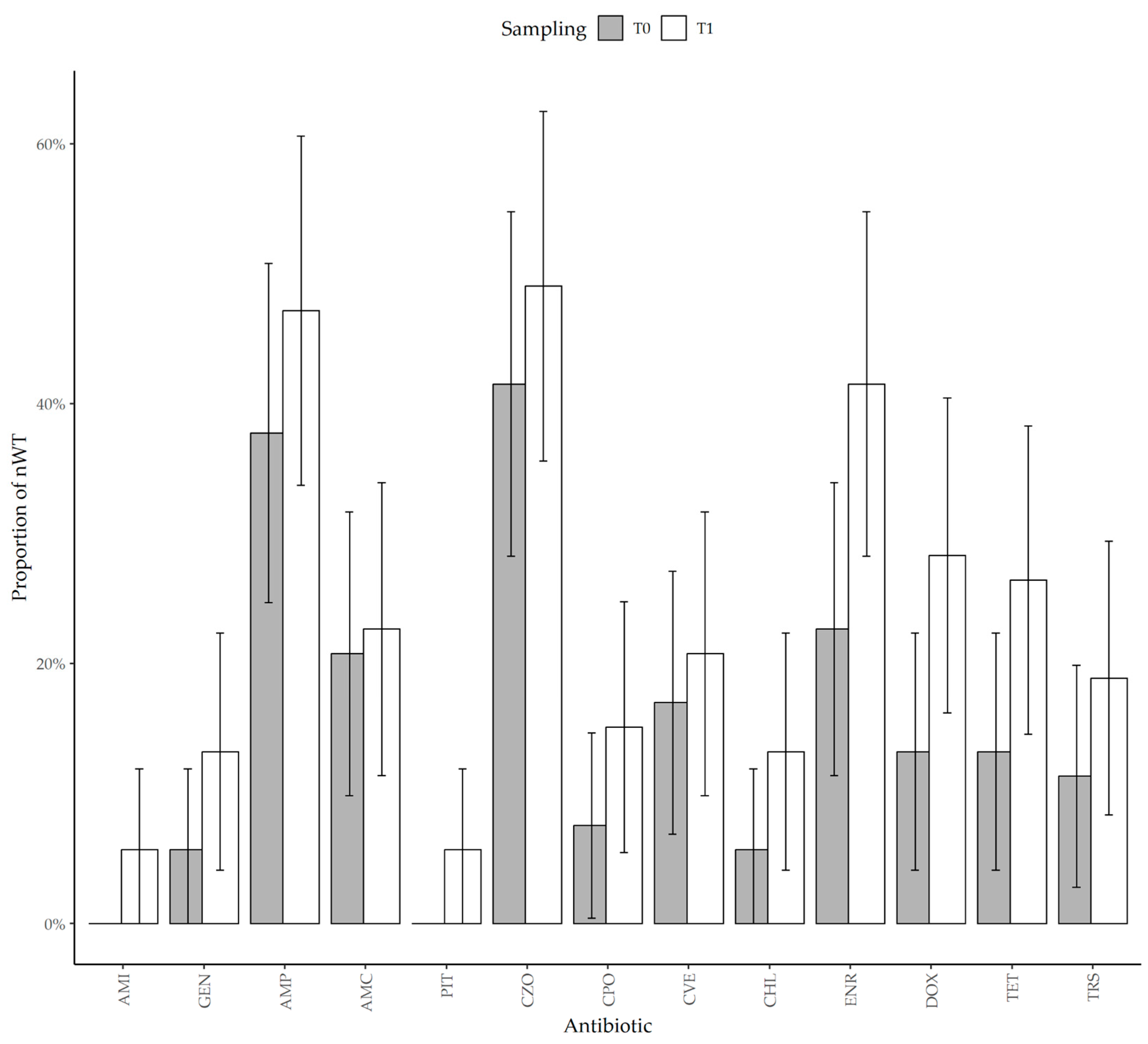
| Tested MIC (µg/mL) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atb. | Time | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | MIC50 | MIC90 | (T)ECOFF | %nWT |
| AMI | T0 | 50 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 8 [4–8] | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | ||||||
| T1 | 42 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 5.7 (0.0–11.9) | ||||||||
| GEN | T0 | 0 | 13 | 21 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 [1,2] | 5.7 (0.0–11.9) | ||||
| T1 | 1 | 7 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 13.2 (4.1–22.3) | ||||||
| AMP | T0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 20 | 4 | 16 | 8 [4–16] | 37.7 (24.7–50.8) | ||||
| T1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 14 | 3 | 25 | 8 | 16 | 47.2 (33.7–60.6) | ||||||
| AMC | T0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 17 | 16 | 11 | 8 | 16 | (8) [2–64] | 20.8 (9.8–31.7) | ||||
| T1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 17 | 17 | 12 | 8 | 16 | 22.6 (11.4–33.9) | ||||||
| PIT | T0 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 8 [4–16] | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | ||||||
| T1 | 50 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 5.7 (0.0–11.9) | ||||||||
| CLE | T0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 21 | 16 | 14 | 16 | 32 | (32) [4–32] | † | ||||
| T1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 16 | 19 | 16 | 32 | † | ||||||
| CZO | T0 | 0 | 19 | 12 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 4 | 64 | 4 [0.5–16] | 41.5 (28.2–54.8) | ||||
| T1 | 0 | 16 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 15 | 4 | 64 | 49.1 (35.6–62.5) | ||||||
| CPO | T0 | 43 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 [0.5–4] | 7.5 (0.4–14.7) | ||||||
| T1 | 41 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 15.1 (5.5–24.7) | ||||||||
| CTZ | T0 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 1 [0.5–1] | † | |||||||
| T1 | 51 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 4 | † | |||||||||
| CVE | T0 | 2 | 19 | 23 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 17.0 (6.9–27.1) | ||||
| T1 | 0 | 16 | 26 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 20.8 (9.8–31.7) | ||||||
| IMI | T0 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 [0.25–0.5] | † | ||||||
| T1 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | † | ||||||||
| CHL | T0 | 0 | 24 | 21 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 16 | 16 [8–16] | 5.7 (0.0–11.9) | |||||
| T1 | 0 | 16 | 21 | 9 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 64 | 13.2 (4.1–22.3) | |||||||
| ENR | T0 | 41 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0.12 | 8 | 0.125 | 22.6 (11.4–33.9) | ||||
| T1 | 31 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0.12 | 8 | 41.5 (28.2–54.8) | ||||||
| MAR | T0 | 38 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0.12 | 8 | * | |||||
| T1 | 32 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 0.12 | 8 | |||||||
| ORB | T0 | 40 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 16 | * | |||||||
| T1 | 34 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 16 | |||||||||
| PRA | T0 | 45 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0.25 | 4 | * | |||||||
| T1 | 36 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0.25 | 4 | |||||||||
| DOX | T0 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 21 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 4 [4–8] | 13.2 (4.1–22.3) | ||||
| T1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 29 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 2 | 16 | 28.3 (16.2–40.4) | ||||||
| TET | T0 | 46 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 4 | 32 | 8 [2–4] | 13.2 (4.1–22.3) | |||||||
| T1 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 4 | 32 | 26.4 (14.5–38.3) | |||||||||
| TRS | T0 | 47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0.5 | 8 | 0.5 [0.125–1] | 11.3 (2.8–19.9) | ||||||
| T1 | 43 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0.5 | 8 | 18.9 (8.3–29.4) | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prandi, I.; Bellato, A.; Nebbia, P.; Roch-Dupland, O.; Stella, M.C.; Passarino, E.; Mauthe von Degerfeld, M.; Quaranta, G.; Robino, P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli from Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Admitted to a Wildlife Rescue Center. Animals 2025, 15, 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152206
Prandi I, Bellato A, Nebbia P, Roch-Dupland O, Stella MC, Passarino E, Mauthe von Degerfeld M, Quaranta G, Robino P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli from Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Admitted to a Wildlife Rescue Center. Animals. 2025; 15(15):2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152206
Chicago/Turabian StylePrandi, Ilaria, Alessandro Bellato, Patrizia Nebbia, Onésia Roch-Dupland, Maria Cristina Stella, Elena Passarino, Mitzy Mauthe von Degerfeld, Giuseppe Quaranta, and Patrizia Robino. 2025. "Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli from Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Admitted to a Wildlife Rescue Center" Animals 15, no. 15: 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152206
APA StylePrandi, I., Bellato, A., Nebbia, P., Roch-Dupland, O., Stella, M. C., Passarino, E., Mauthe von Degerfeld, M., Quaranta, G., & Robino, P. (2025). Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli from Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Admitted to a Wildlife Rescue Center. Animals, 15(15), 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152206








