Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Aerobic Bacterial Isolates from Clinically Ill Pet Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) in Hong Kong
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Extraction
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Animals’ Demographic, Geographic, and Temporal Data
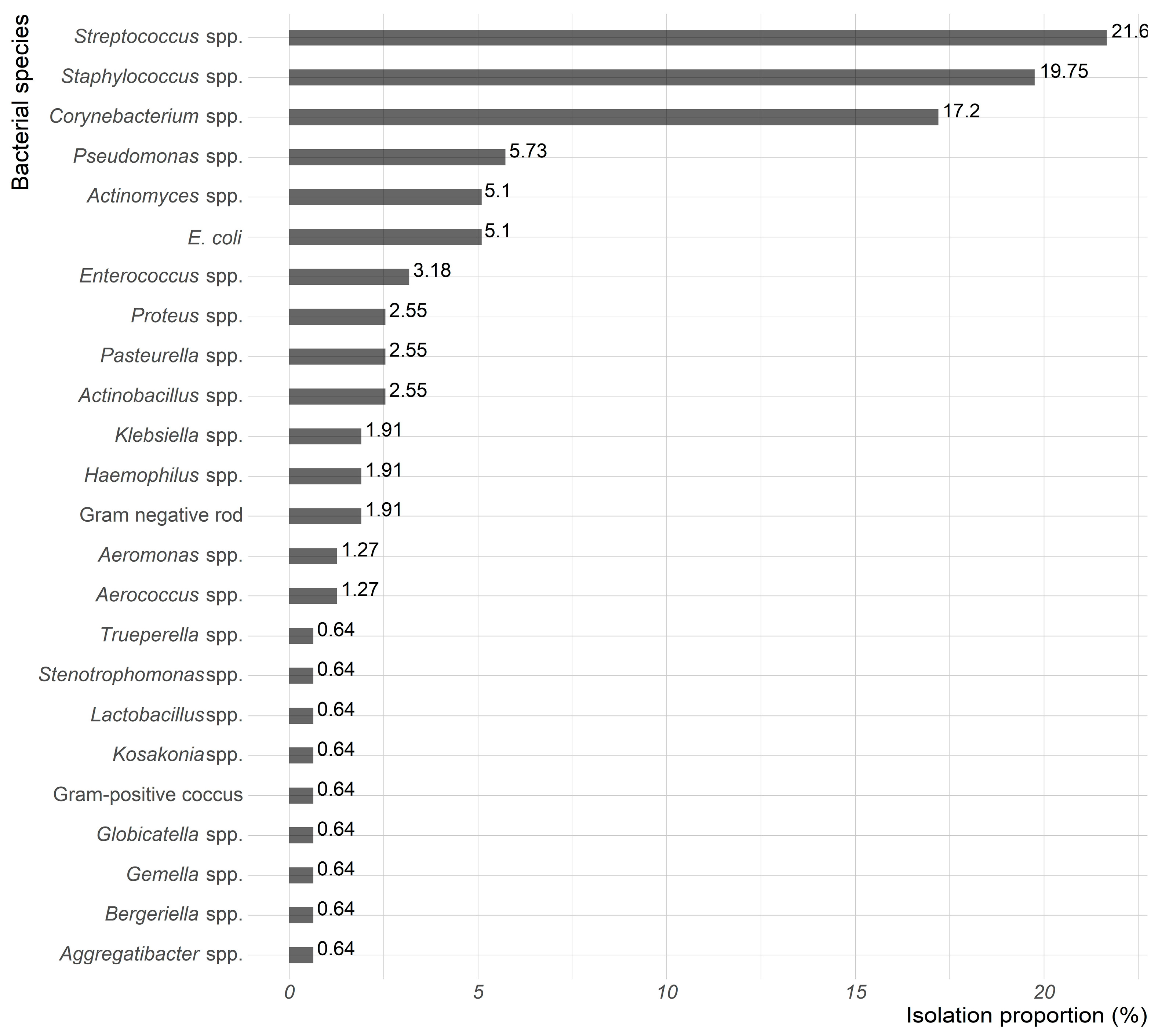
3.2. Bacterial Isolates
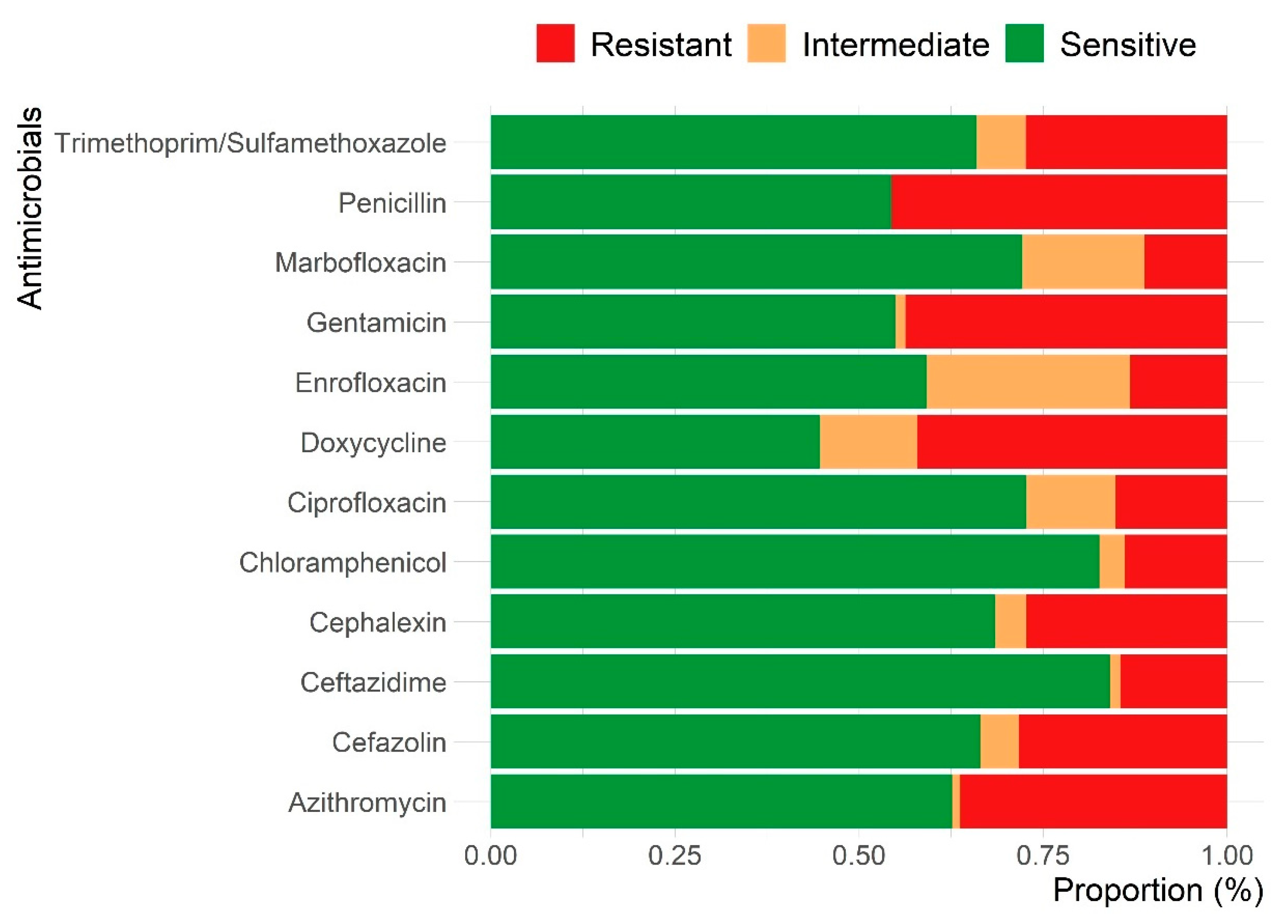
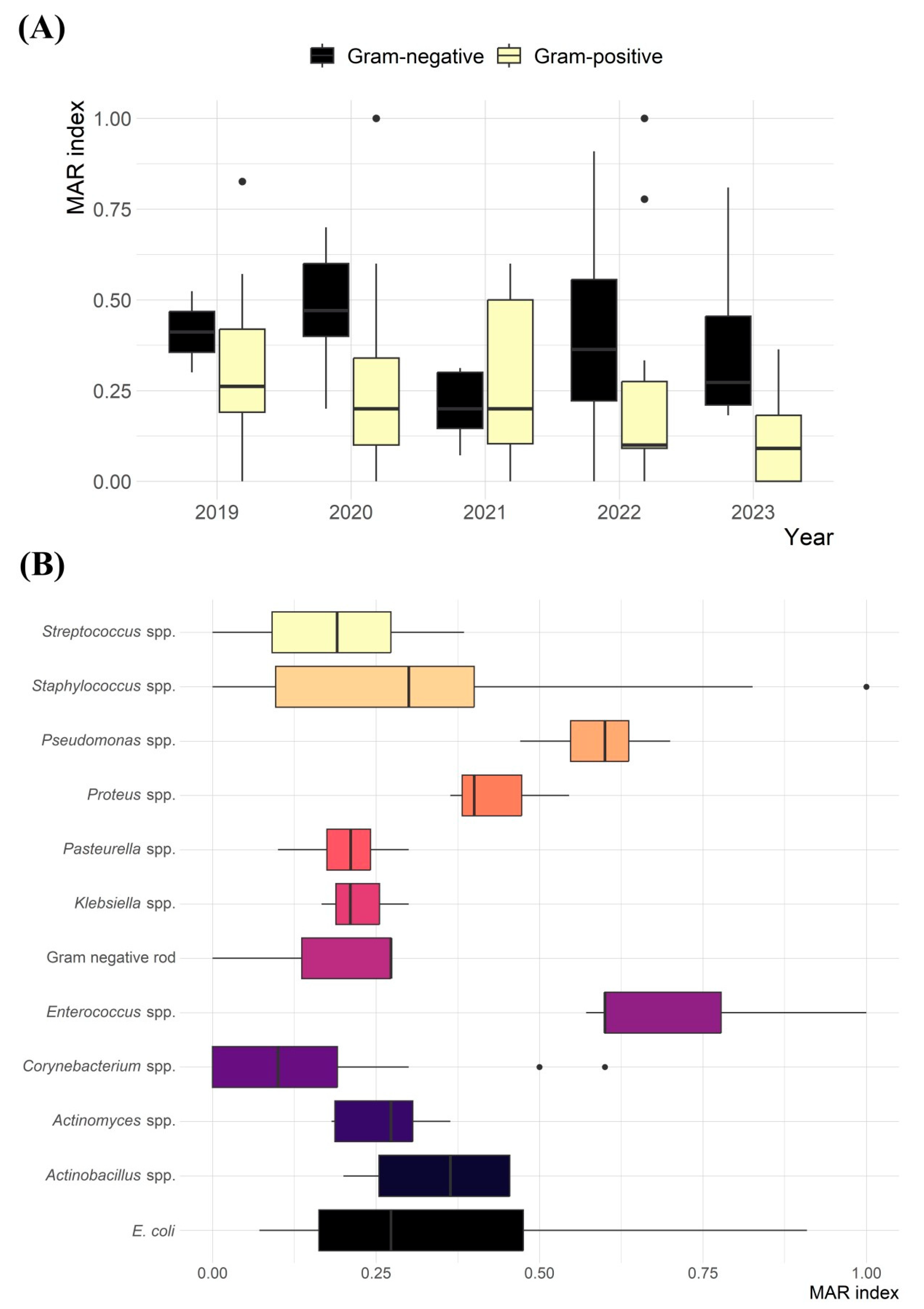
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
| MAR | Multiple antibiotic resistance index |
| AST | Antimicrobial susceptibility testing |
References
- Muñoz-Ibarra, E.; Molina-López, R.A.; Durán, I.; Garcias, B.; Martín, M.; Darwich, L. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from exotic pets: The situation in the Iberian Peninsula. Animals 2022, 12, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Livestock and Companion Animals; Schwarz, S., Cavaco, L.M., Shen, J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Osman, M.; Green, B.A.; Yang, Y.; Ahuja, A.; Lu, Z.; Cazer, C.L. Evidence for the transmission of antimicrobial resistant bacteria between humans and companion animals: A scoping review. One Health 2023, 17, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Hill, F.; Elsohaby, I. Retrospective analysis of antimicrobial resistance in bacterial pathogens from pet rabbits in Hong Kong, 2019–2022. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2024, 36, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minarikova, A.; Hauptman, K.; Knotek, Z.; Jekl, V. Microbial flora of odontogenic abscesses in pet guinea pigs. Vet. Rec. 2016, 179, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardhouse, S.; Sanchez-Migallon Guzman, D.; Paul-Murphy, J.; Byrne, B.A.; Hawkins, M.G. Bacterial isolates and antimicrobial susceptibilities from odontogenic abscesses in rabbits: 48 cases. Vet. Rec. 2017, 181, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts-Steel, S.; Oxley, J.A.; Carroll, A.; Wills, A.P. Frequency of owner-reported bacterial infections in pet guinea pigs. Animals 2019, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesenberry, K.; Mans, C.; Orcutt, C.; Carpenter, J.W. Ferrets, Rabbits and Rodents-E-Book; Elsevier, Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Devlin, J. Knowledge of pet-related zoonotic diseases and pet care in Hong Kong, a heavily crowded urban setting. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; le Clue, S. Threatened, Farmed: Hong Kong’s Invisible Pets; ADM Capital Foundation: Hong Kong SAR, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 35th ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing EUCAST Advice on Intrinsic Resistance and Exceptional Phenotypes v 1.2. 2023. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Expert_Rules/2020/Intrinsic_Resistance_and_Unusual_Phenotypes_Tables_v3.2_20200225.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.; Giske, C.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Garcias, B.; Duran, I.; Molina-López, R.A.; Darwich, L. Current situation of bacterial infections and antimicrobial resistance profiles in pet rabbits in Spain. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.P.; Brouwer, M.C.; van de Beek, D. Sex and gender differences in bacterial infections. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e0028322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, A. Management of husbandry-related problems in guinea pigs. Pract. 2011, 33, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minarikova, A.; Hauptman, K.; Jeklova, E.; Knotek, Z.; Jekl, V. Diseases in pet guinea pigs: A retrospective study in 1000 animals. Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.D.; Guzman, D.S.M.; Paul-Murphy, J.; Hawkins, M.G. Skin diseases in companion guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus): A retrospective study of 293 cases seen at the Veterinary Medical Teaching Hospital, University of California at Davis (1990–2015). Vet. Dermatol. 2016, 27, 395-e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reavill, D.R.; Lennox, A.M. Disease overview of the urinary tract in exotic companion mammals and tips on clinical management. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2020, 23, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.; Schröder, A.; Wenger, A.; Kamphues, J. The nutrition of the chinchilla as a companion animal–basic data, influences and dependences. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2003, 87, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Jota Baptista, C.; Oliveira, P.A.; Coelho, A.C. Urinary tract bacterial infections in small animal practice: Clinical and epidemiological aspects. Vet. Stanica 2024, 55, 703–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, M.G.; Ruby, A.L.; Drazenovich, T.L.; Westropp, J.L. Composition and characteristics of urinary calculi from guinea pigs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 234, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.A.; Barceló, A.M.; Nadeu, C.B.; Jekl, V. Respiratory diseases in guinea pigs, chinchillas and degus. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2021, 24, 419–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colby, L.A.; Nowland, M.H.; Kennedy, L.H. Clinical Laboratory Animal Medicine: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Harkness, J.E.; Murray, K.A.; Wagner, J.E. Chapter 6- Biology and diseases of guinea pigs. In Laboratory Animal Medicine; Fox, J.G., Anderson, L.C., Loew, F.M., Quimby, F.M., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 203–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamcak, A.; Otten, B. Rodent therapeutics. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2000, 3, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A. Perspectives in veterinary pharmacology and toxicology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartantyo, S.H.P.; Chau, M.L.; Fillon, L.; Ariff, A.Z.B.M.; Kang, J.S.L.; Aung, K.T.; Gutiérrez, R.A. Sick pets as potential reservoirs of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in Singapore. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2018, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmolka, A.; Nagy, B. Multidrug resistant commensal Escherichia coli in animals and its impact for public health. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, H.I.; Silva, V.; de Sousa, T.; Calouro, R.; Saraiva, S.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Antimicrobial resistance in european companion animals practice: A one health approach. Animals 2025, 15, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
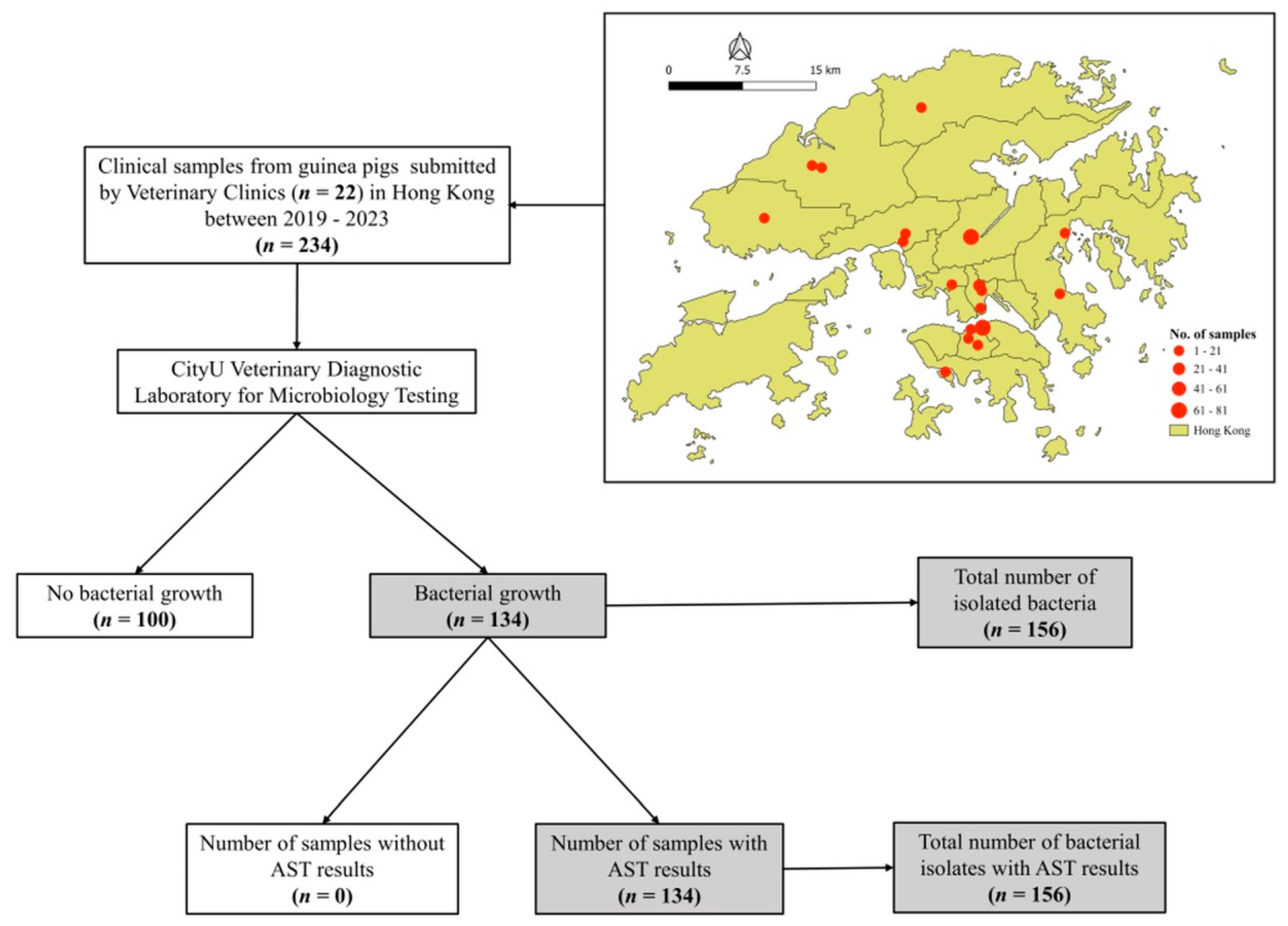

| Characteristics | 2019 N (%) | 2020 N (%) | 2021 N (%) | 2022 N (%) | 2023 N (%) | Total N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 21 (9.0) | 54 (23.1) | 44 (18.8) | 79 (33.8) | 36 (15.4) | 234 (100) | |
| Sampling Site | |||||||
| Dental | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | -- | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 6 (2.6) | |
| Gastrointestinal | 2 (28.5) | -- | 1 (14.3) | 3 (42.9) | 1 (14.3) | 7 (3.0) | |
| Integument | 8 (7.8) | 29 (28.4) | 17 (16.7) | 37 (36.3) | 11 (10.8) | 102 (43.6) | |
| Lymphatics | 2 (50.0) | 2 (50.0) | -- | -- | -- | 4 (1.7) | |
| Ocular | 1 (11.1) | 2 (22.2) | 2 (22.2) | 3 (33.4) | 1 (11.1) | 9 (3.8) | |
| Reproductive | 2 (25.0) | 2 (25.0) | 2 (25.0) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (12.5) | 8 (3.4) | |
| Respiratory | 1 (5.3) | 6 (31.6) | 1 (5.3) | 7 (36.8) | 4 (21.1) | 19 (8.1) | |
| Urinary | 4 (5.1) | 12 (15.2) | 21 (26.6) | 26 (32.9) | 16 (20.2) | 79 (33.8) | |
| Sample Type | |||||||
| Swab | 16 (10.3) | 44 (28.2) | 26 (16.7) | 49 (31.4) | 21 (13.5) | 156 (66.7) | |
| Fluid | 2 (8.7) | 4 (17.4) | 7 (30.4) | 8 (34.8) | 2 (8.7) | 23 (9.8) | |
| Cystocentesis | 2 (11.1) | 2 (11.1) | 6 (33.3) | 5 (27.8) | 3 (16.7) | 18 (7.7) | |
| Voided | -- | 3 (10.3) | 2 (6.9) | 14 (48.3) | 10 (34.5) | 29 (12.4) | |
| Other (feces, fresh tissue, flush, etc.) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (12.5) | 3 (37.5) | 3 (37.5) | -- | 8 (3.4) | |
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 10 (8.7) | 24 (20.9) | 23 (20.0) | 40 (34.8) | 18 (15.7) | 115 (49.1) | |
| Female | 2 (3.5) | 14 (24.1) | 11 (19.0) | 19 (32.7) | 12 (20.7) | 58 (24.8) | |
| Male (desex) | 8 (22.2) | 11 (30.6) | 4 (11.1) | 9 (25.0) | 4 (11.1) | 36 (15.4) | |
| Female (desex) | 1 (4.4) | 4 (17.4) | 5 (21.7) | 11 (47.8) | 2 (8.7) | 23 (9.8) | |
| Unknown | -- | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | -- | -- | 2 (0.9) | |
| Age | |||||||
| <1 year | 5 (15.6) | 5 (15.6) | 11 (34.4) | 4 (12.5) | 7 (21.9) | 32 (13.7) | |
| 1–3 years | 11 (10.0) | 32 (29.1) | 20 (18.2) | 42 (38.2) | 5 (4.5) | 110 (47.0) | |
| >3 years | 5 (5.5) | 17 (18.9) | 13 (14.4) | 32 (35.6) | 23 (25.6) | 90 (38.5) | |
| Unknown | -- | -- | -- | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | 2 (0.9) | |
| Previously Reported Antimicrobial Use | |||||||
| Yes | 3 (27.3) | 2 (18.2) | 1 (9.1) | 4 (36.4) | 1 (9.1) | 11 (4.7) | |
| No | 18 (8.1) | 52 (23.3) | 43 (19.3) | 75 (33.6) | 35 (15.7) | 223 (95.3) | |
| Positive Bacterial Culture | |||||||
| Yes | 12 (9.0) | 35 (26.1) | 23 (17.2) | 38 (28.4) | 26 (19.4) | 134 (57.3) | |
| No | 9 (9.0) | 19 (19.0) | 21 (21.0) | 41 (41.0) | 10 (10.0) | 100 (42.7) | |
| Bacterial Isolates | No. of Resistances | MDR n (%) 1 | Average MAR Index (Range) 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total N | 0 n (%) | 1 n (%) | 2 n (%) | 3 n (%) | >3 n (%) | |||
| Enterococcus spp. | 5 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 5 (100) | 5 (100) | 0.71 (0.57–1.00) |
| Actinomyces spp. | 7 | -- | -- | 2 (28.6) | 2 (28.6) | 3 (42.8) | 3 (42.8) | 0.26 (0.18–0.36) |
| E. coli | 8 | -- | -- | 3 (37.5) | 2 (25.0) | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | 0.37 (0.07–0.91) |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 8 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 8 (100) | 8 (100) | 0.59 (0.47–0.70) |
| Corynebacterium spp. | 27 | 9 (33.4) | 5 (18.5) | 7 (25.9) | 3 (11.1) | 3 (11.1) | 3 (11.1) | 0.20 (0.5–0.60) |
| Staphylococcus spp. | 31 | 5 (16.1) | 6 (19.4) | 2 (6.4) | 4 (12.9) | 14 (45.2) | 10 (32.3) | 0.34 (0.09–1.00) |
| Streptococcus spp. | 34 | 1 (2.9) | 10 (29.5) | 8 (23.5) | 7 (20.6) | 8 (23.5) | 14 (41.2) | 0.19 (0.09–0.38) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, D.; Elsohaby, I.; Hill, F.; Ferguson, A.; McDermott, C.T. Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Aerobic Bacterial Isolates from Clinically Ill Pet Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) in Hong Kong. Animals 2025, 15, 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142042
Hung D, Elsohaby I, Hill F, Ferguson A, McDermott CT. Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Aerobic Bacterial Isolates from Clinically Ill Pet Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) in Hong Kong. Animals. 2025; 15(14):2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142042
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Desiree, Ibrahim Elsohaby, Fraser Hill, Andrew Ferguson, and Colin T. McDermott. 2025. "Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Aerobic Bacterial Isolates from Clinically Ill Pet Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) in Hong Kong" Animals 15, no. 14: 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142042
APA StyleHung, D., Elsohaby, I., Hill, F., Ferguson, A., & McDermott, C. T. (2025). Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Aerobic Bacterial Isolates from Clinically Ill Pet Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) in Hong Kong. Animals, 15(14), 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142042









