Assessing the Tolerance of Spotted Longbarbel Catfish as a Candidate Species for Aquaculture to Ammonia Nitrogen Exposure
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Care and Ethics Statement
2.2. Ammonia-N Exposure
2.3. Tissue Sampling and Pathological Analysis
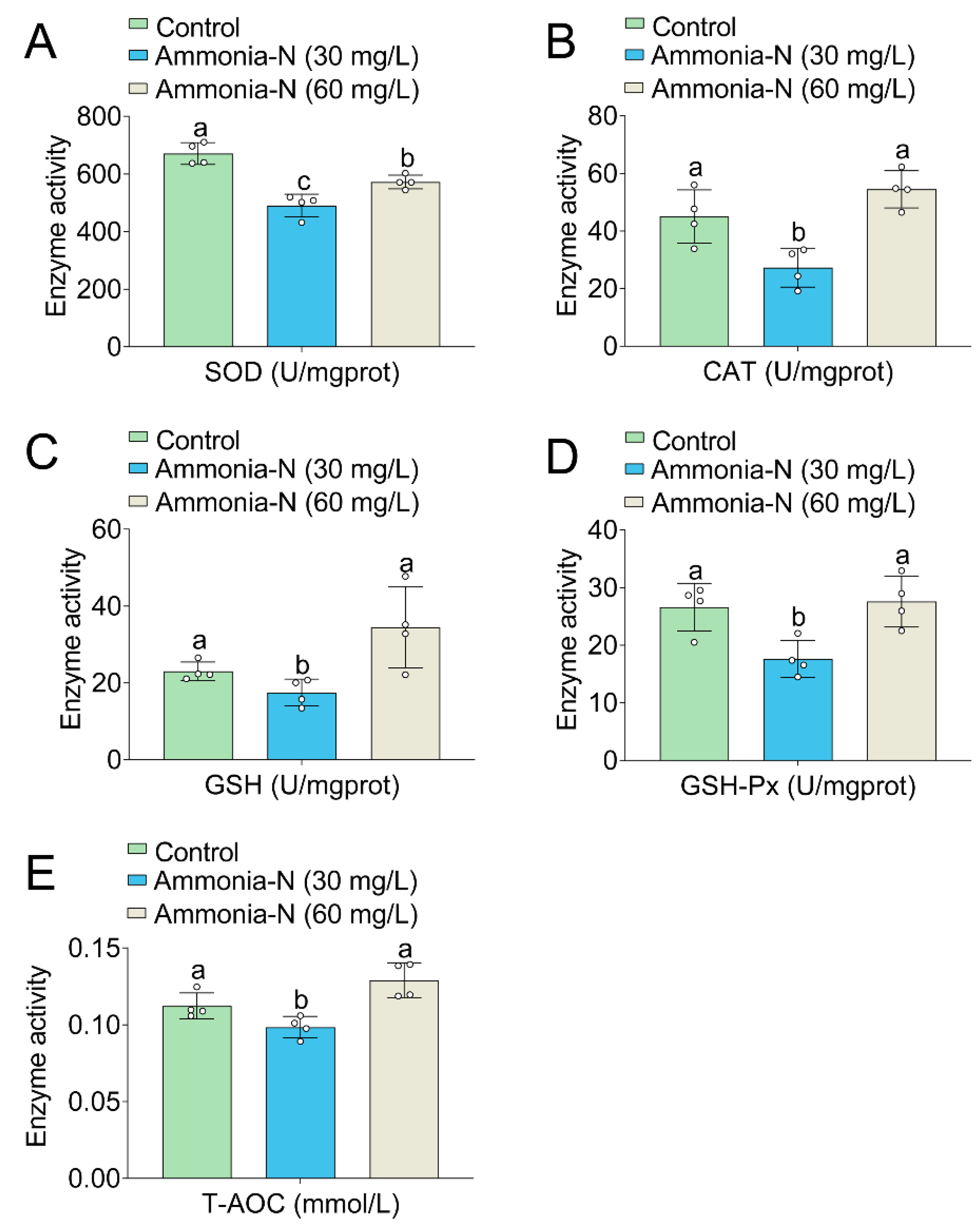
2.4. Enzyme Activity
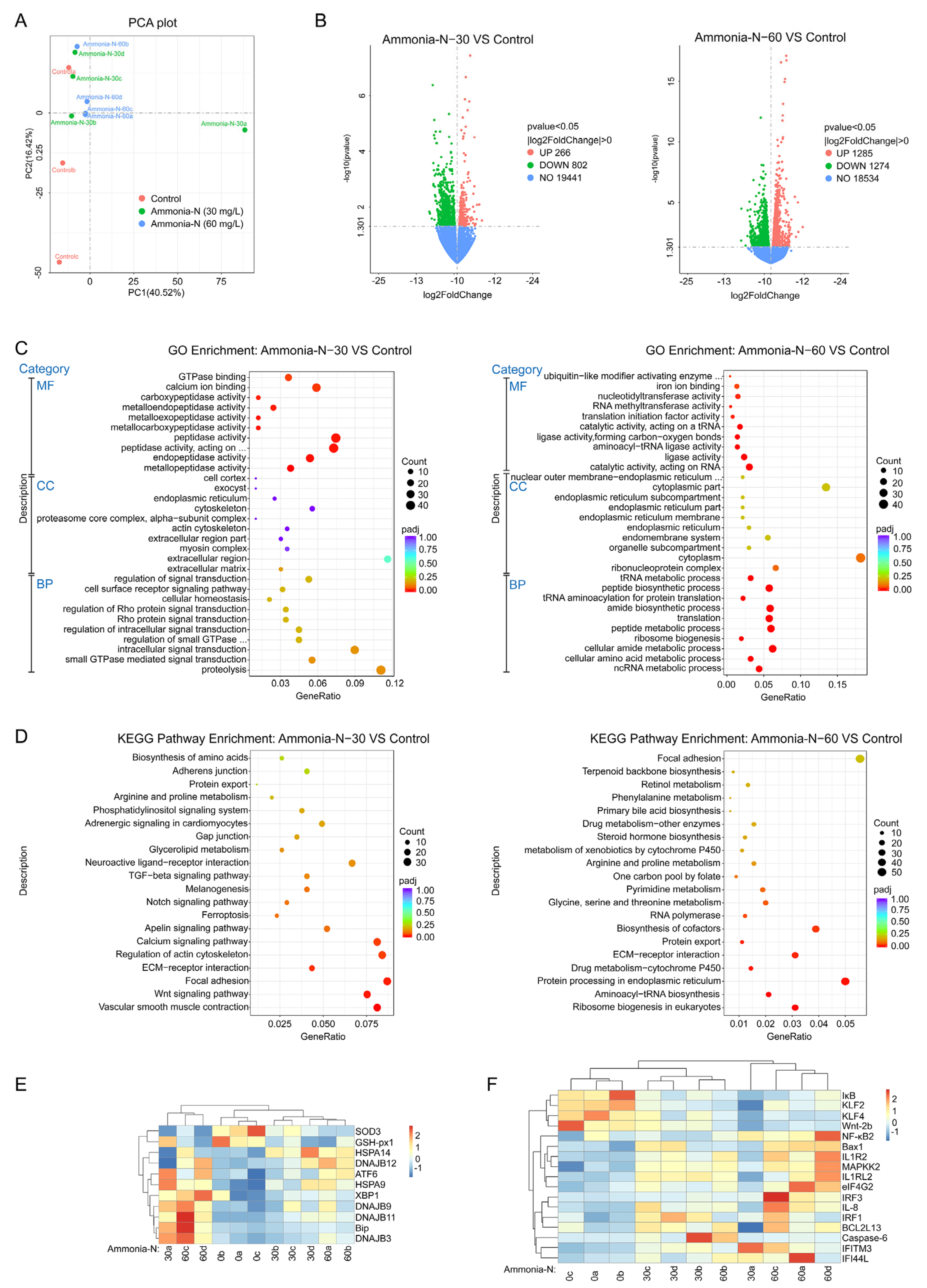
2.5. Transcriptomic Analysis
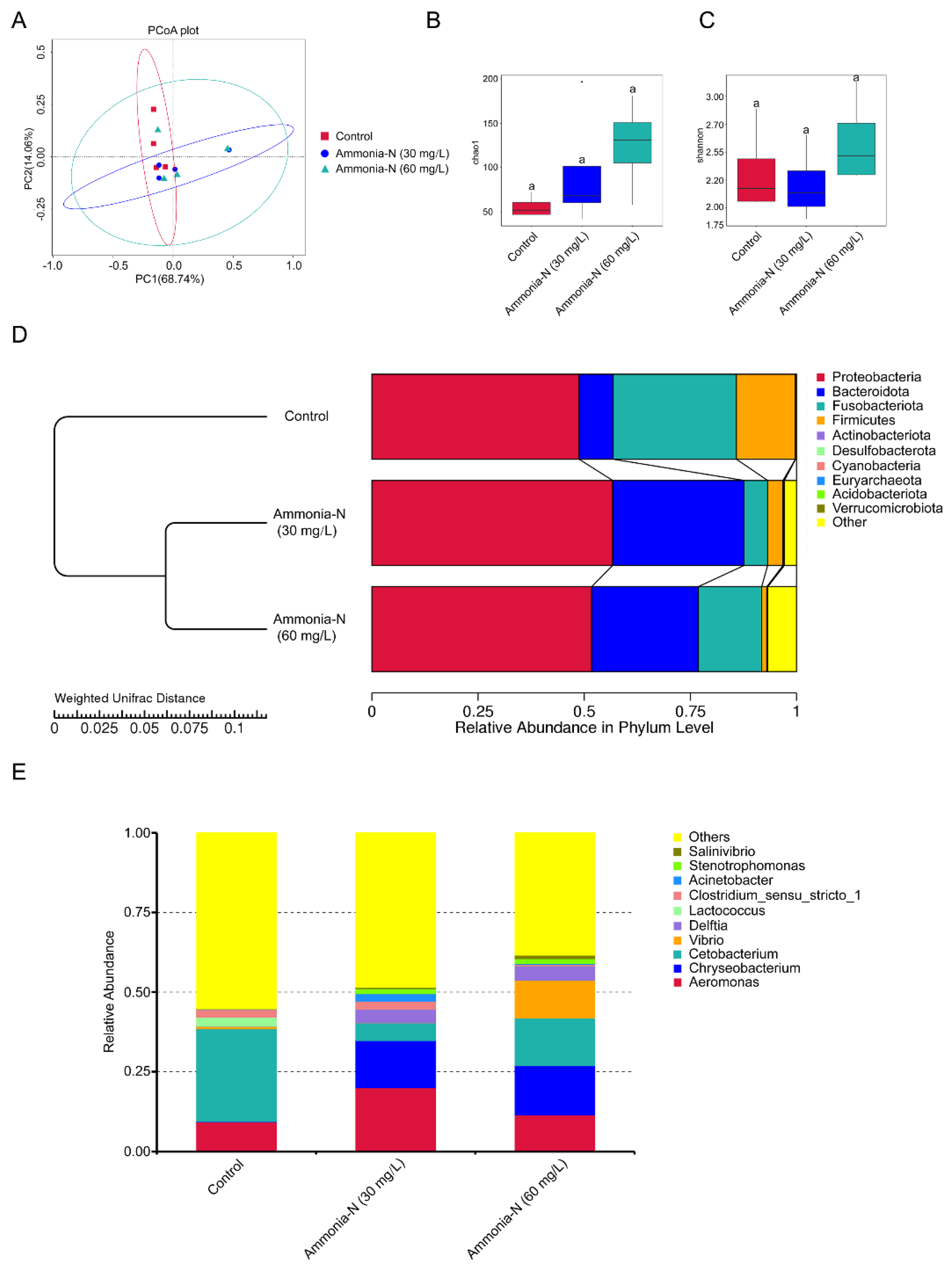
2.6. Microbiome Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ammonia-N Stress Decreased the Survival of the Spotted Longbarbel Catfish
3.2. Ammonia-N Stress Leads to Tissue Lesions
3.3. Transcriptomic Analysis
3.4. Oxidative Enzyme Activities
3.5. The Effects of Ammonia-N Stress on the Intestinal Microbial Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bureau of Fisheries. National Protected Aquatic Wildlife; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chu, Z. The biological character and breeding technology of Mystus guttatus. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2006, 34, 5882–5883. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Xie, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, H.; Zheng, G. The artificial propagation and embryonic development of spotted longbarbel catfish Mystus guttatus in ponds. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2005, 20, 352–354. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, S.; Zuo, F.; Geng, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Chen, D.; Yang, S.; Zheng, W.; Xiong, Y.; Cai, W.; et al. The IL17 signaling pathway: A potential signaling pathway mediating gill hyperplasia and inflammation under ammonia nitrogen stress was identified by multi-omics analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R. The harm and controlling measures of ammonia nitrogen in intensive aquaculture water. Henan Fish. 2018, 3, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Lin, Y.; Lee, C. Highly intensive culture study of tiger prawn Penaeus monodon in Taiwan. In Aquaculture—A Biotechnology in Progress; De Pauw, D., Jaspers, E., Ackefors, H., Wilkins, N., Eds.; European Aquaculture Society: Ghent, Belgium, 1989; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Hu, A.; Xiong, G.; Wu, W.; Shi, L.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Difference in muscle metabolism caused by metabolism disorder of rainbow trout liver exposed to ammonia stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Ma, H.L.; Su, Y.L.; Deng, Y.Q.; Feng, J.; Xie, J.W.; Chen, X.L.; Guo, Z.X. Ammonia toxicity in the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain): The mechanistic insight from physiology to transcriptome analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 179, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Si, M.R.; Jiang, S.G.; Yang, Q.B.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.S.; Huang, J.H.; Zhou, F.L. First transcriptome profiling in gill and hepatopancrease tissues of Metapenaeus ensis in response to acute ammonia-N stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Yu, R.; Zhou, M. Modulatory effects of ammonia-N on the immune system of Penaeus japonicus to virulence of white spot syndrome virus. Aquaculture 2004, 241, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; He, J.; Li, C. Ammonia nitrogen stress increases susceptibility to bacterial infection via blocking IL-1R–Relish axis mediated antimicrobial peptides expression in shrimp. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, M.M.; Attia, Z.I.; Ashour, O.A. Oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in liver and white muscle of Nile tilapia juveniles in chronic ammonia exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 99, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geihs, M.A.; Vargas, M.A.; Maciel, F.E.; Vakkuri, O.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Allodi, S.; Nery, L.E. Effects of hypoxia and reoxygenation on the antioxidant defense_system of the locomotor muscle of the crab Neohelice granulata (Decapoda, Varunidae). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2016, 186, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.H.; Ma, H.L.; Liu, G.X.; Fan, S.G.; Deng, Y.Q.; Jiang, J.J.; Feng, J.; Guo, Z.X. Toxic effects of cadmium exposure on intestinal histology, oxidative stress, microbial community, and transcriptome change in the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain). Chemosphere 2023, 326, 138464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yun, J.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, W.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y. Comparison of antioxidant capacity and immune response between low salinity tolerant hybrid and normal variety of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Int. 2023, 32, 1879–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Fu, Q.; Su, B.; Zhou, S.; Liu, F.; Song, L.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Dong, X.; Tan, F.; et al. Transcriptomic profiling revealed the signatures of intestinal barrier alteration and pathogen entry in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) following Vibrio anguillarum challenge. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 65, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, H.; Wang, R.; Qian, Y.; Li, M. Ammonia stress disrupts intestinal microbial community and amino acid metabolism of juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Xue, M.; Yang, S.; Zha, J.; Wang, G.; Ling, F. Ammonia exposure alters the expression of immune-related and antioxidant enzymes-related genes and the gut microbial community of crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, K.; Huo, D. Assembly process and co-occurrence network of microbial community in response to free ammonia gradient distribution. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0105124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, A.J.; Das, B.C.; Jifiriya, M.J.; Varghese, T.; Pillai, D.; Rejish Kumar, V.J. Ammonia induced toxico-physiological responses in fish and management interventions. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 15, 452–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Perez-Gracia, J.; Rouzaut, A.; Sanmamed, M.; Le Bon, A.; Melero, I. Direct effects of type I interferons on cells of the immune system. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhao, Y. Comparison of immune defense and antioxidant capacity between broodstock and hybrid offspring of juvenile shrimp (Macrobrachium nipponense): Response to acute ammonia stress. Anim. Genet. 2022, 53, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, C.; Yao, D.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Aweya, J.J.; Zhang, Y. Penaeid shrimp counteract high ammonia stress by generating and using functional peptides from hemocyanin, such as HMCs27. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Qin, J.; Fu, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, A.; Gu, Z.; Yu, F.; Liu, C. Transcriptomic analysis revealed the dynamic response mechanism to acute ammonia exposure in the ivory shell, Babylonia areolata. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 143, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, M.; Song, L. Ammonia exposure induces oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in hepatopancreas of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011, 334, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, F.; Bi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yue, H.; Yuan, K.; Chen, Y.; Wen, S.; He, J. Transcriptome analysis endoplasmic reticulum-stress response in Litopenaeus vannamei hemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 124, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, F.; Bi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yue, H.; Yuan, K.; Chen, Y.; Wen, S.; He, J. Transcriptome analysis of the unfolded protein response in hemocytes of Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Geng, R.; Deng, H.; Niu, S.; Zuo, H.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xu, X. White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) inhibits hippo signaling and activates Yki to promote its infection in Penaeus vannamei. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0236322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Gan, Y.; Zuo, H.; Deng, H.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xu, X. Basigin binds bacteria and activates Dorsal signaling to promote antibacterial defense in Penaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 142, 109123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Yang, L.; Zheng, R.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xie, J. Nervous necrosis virus capsid protein and Protein A dynamically modulate the fish cGAS-mediated IFN signal pathway to facilitate viral evasion. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0068624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hong, Q.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. Study of the antivirus function mediated by STING in Micropterus salmoides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 149, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-a.; Zheng, J.; Yang, L.; Zuo, H.; Niu, S.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xu, X. Wnt11 positively regulates immune defense against Vibrio parahaemolyticus but promotes white spot syndrome virus infection in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.A.; Zuo, H.; Guo, Z.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xu, X. Wnt5b plays a negative role in antibacterial response in Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 133, 104411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Wnt gene family members and their expression profiling in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 77, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Weng, S.; He, J. Nitrite nitrogen stress disrupts the intestine bacterial community by altering host-community interactions in shrimp. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limborg, M.T.; Alberdi, A.; Kodama, M.; Roggenbuck, M.; Kristiansen, K.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Applied hologenomics: Feasibility and potential in aquaculture. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Xiong, J.; Hou, D.; Zhou, R.; Xing, C.; Wei, D.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Microecological Koch’s postulates reveal that intestinal microbiota dysbiosis contributes to shrimp white feces syndrome. Microbiome 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Yang, L.; Xu, X. Assessing the Tolerance of Spotted Longbarbel Catfish as a Candidate Species for Aquaculture to Ammonia Nitrogen Exposure. Animals 2025, 15, 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142035
Guo S, Yang L, Xu X. Assessing the Tolerance of Spotted Longbarbel Catfish as a Candidate Species for Aquaculture to Ammonia Nitrogen Exposure. Animals. 2025; 15(14):2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142035
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Song, Linwei Yang, and Xiaopeng Xu. 2025. "Assessing the Tolerance of Spotted Longbarbel Catfish as a Candidate Species for Aquaculture to Ammonia Nitrogen Exposure" Animals 15, no. 14: 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142035
APA StyleGuo, S., Yang, L., & Xu, X. (2025). Assessing the Tolerance of Spotted Longbarbel Catfish as a Candidate Species for Aquaculture to Ammonia Nitrogen Exposure. Animals, 15(14), 2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142035







