Genomic Characterization of Four Novel Probiotic Strains with Enzymatic Activity and Their Effects on Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Isolation and Growth
2.2. Assessment of Strain Safety
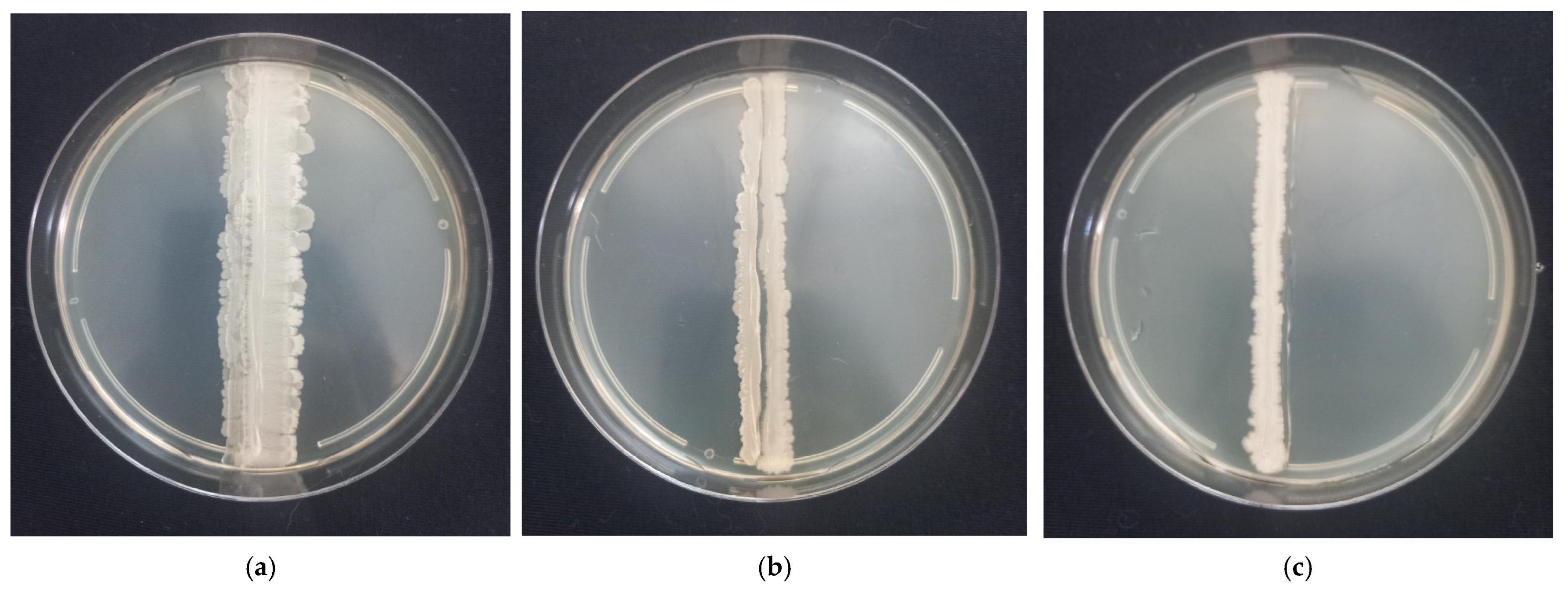
2.3. Strain Compatibility Testing
2.4. Probiotic Preparation Using Solid-Phase Fermentation
2.5. Experimental Diet
2.6. Experimental Design and Fish Conditions
- -
- Fulton’s fatness coefficient (QF, conventional units) according to the following formula:
- -
- individual biomass growth (WGi, g) using the following formula:
- -
- total biomass growth (WGt, kg) according to the following formula:
- -
- feed conversion rate (FCR, kg/kg) basing on the following formula:
- -
- fish survival rate (S, %) estimated with the following formula:
- -
- specific rate of weight growth (SGRW, %/day) determined according to the following formula:
- -
- specific growth rate of fish in length (SGRL, %/day) using the following formula:where t—duration of the experiment, days; l1—length at the end of the experiment, cm; l0—length at the beginning of the experiment, cm; m1—weight at the end of the experiment, g; m0—weight at the beginning of the experiment, g; N1—number of fish at the end of the experiment, specimens; N0—the number of fish at the beginning of the experiment, specimens; Mf—feed weight, kg; M1—feed weight, kg; M0—fish biomass at the beginning of the experiment, kg; m—weight, g; l—length, cm.
2.7. Determination of the Probiotic Bacteria Amount in Fish Intestinal Contents
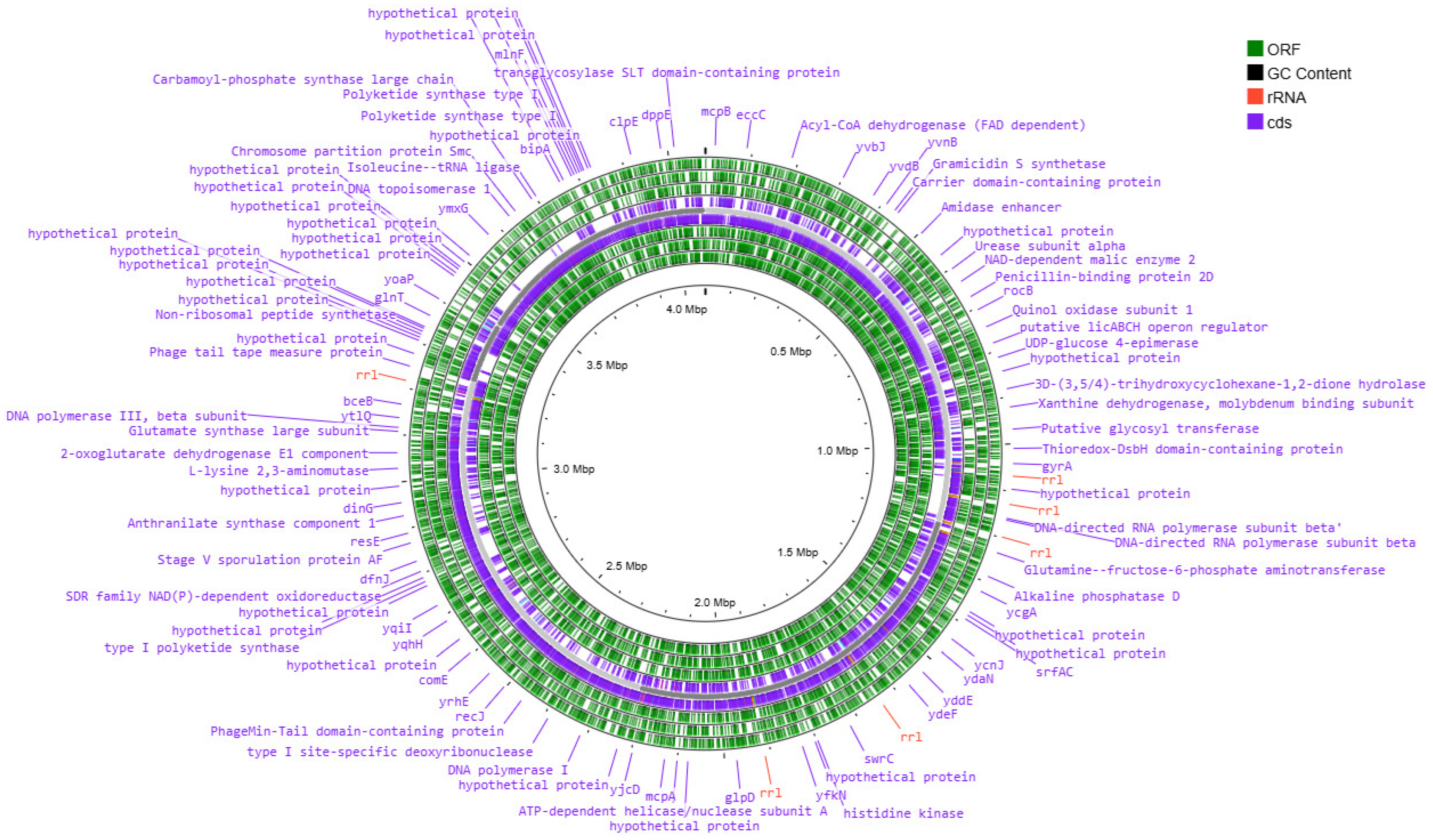
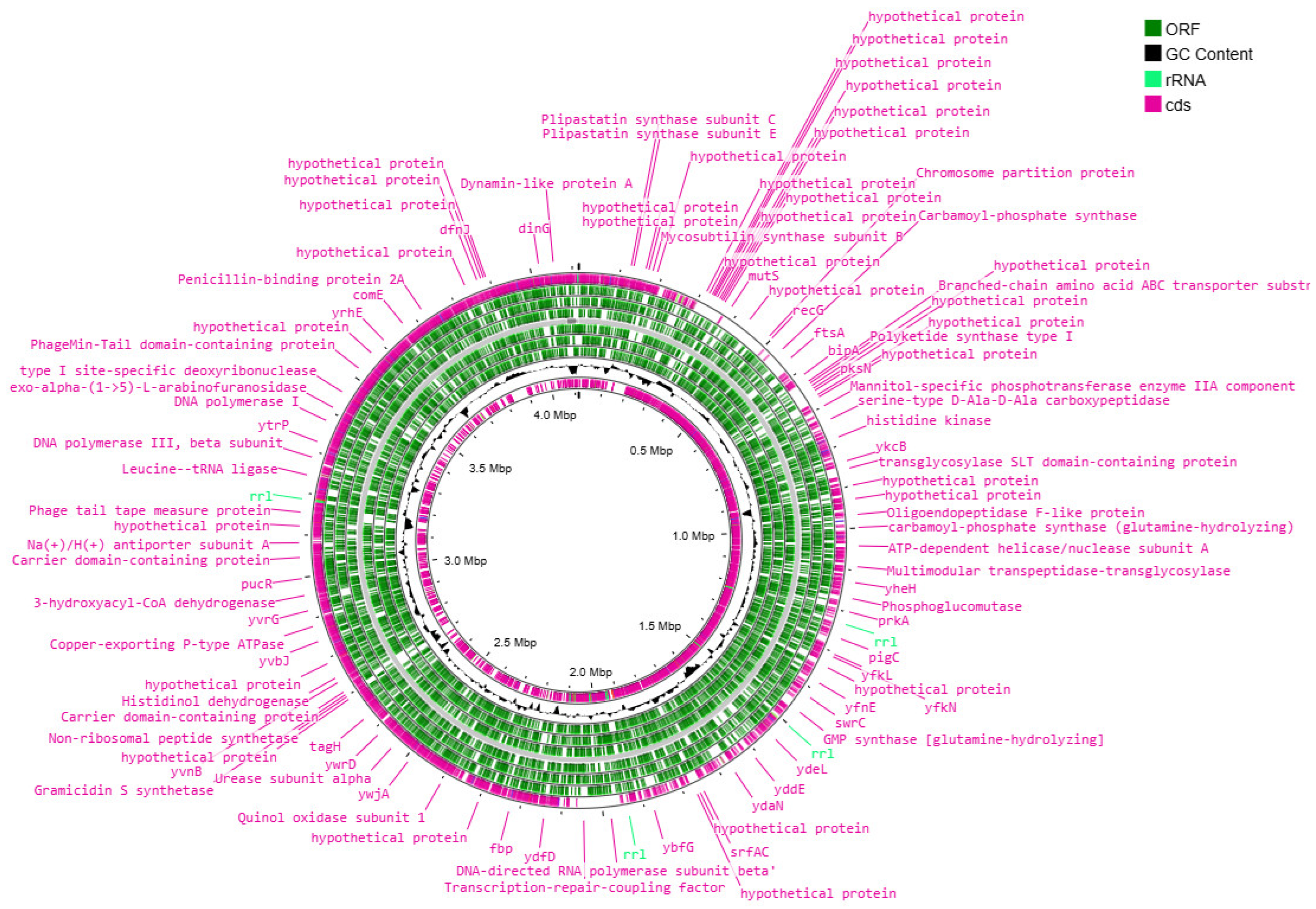
2.8. Genomic DNA Extraction, Sequencing, Assembly and Annotation
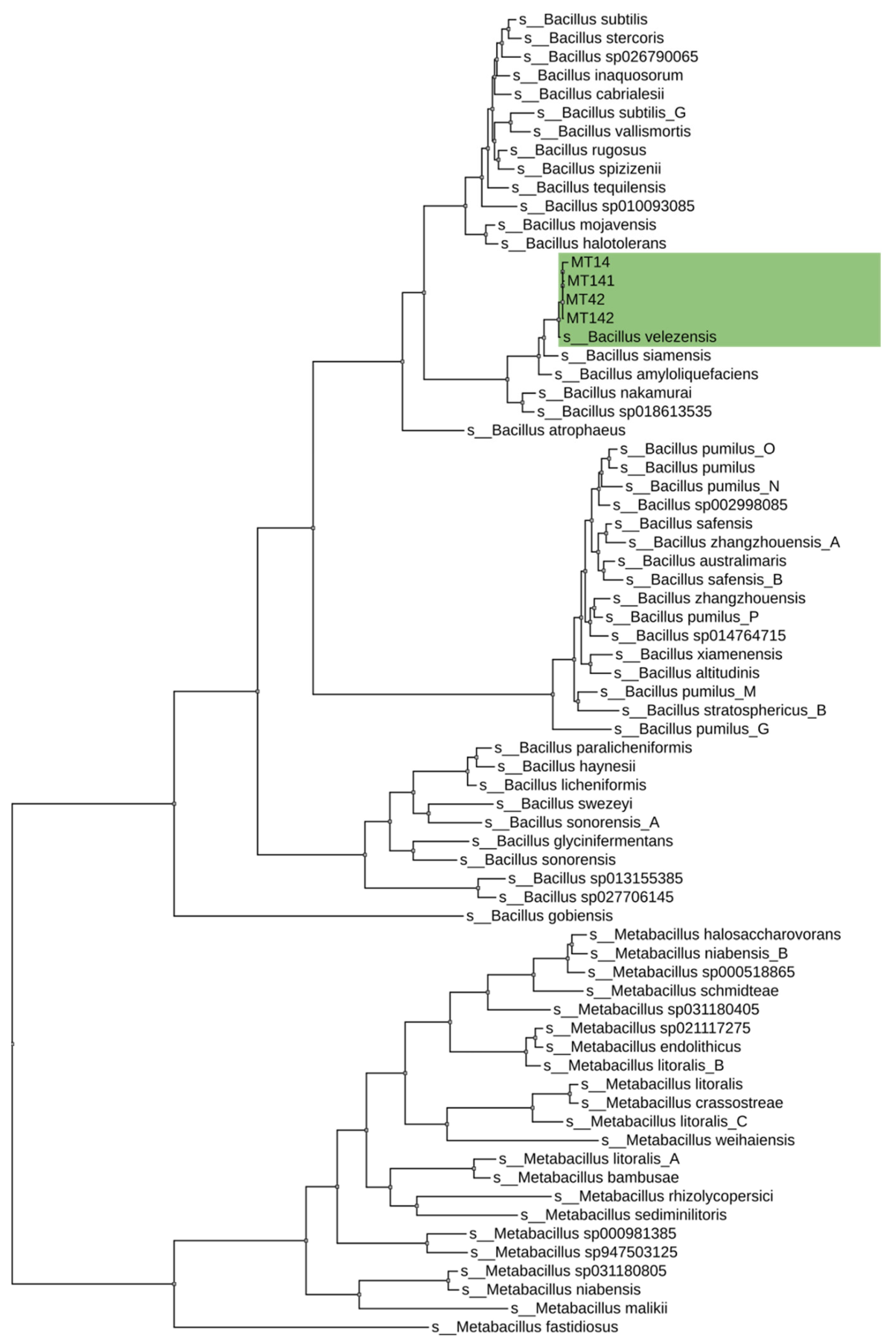
2.9. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.10. Analysis of the Differential Expression in Carp Tissues
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Screening and Selection of Probiotic Strains
3.2. Analysis of the Results of the Whole-Genome Sequencing
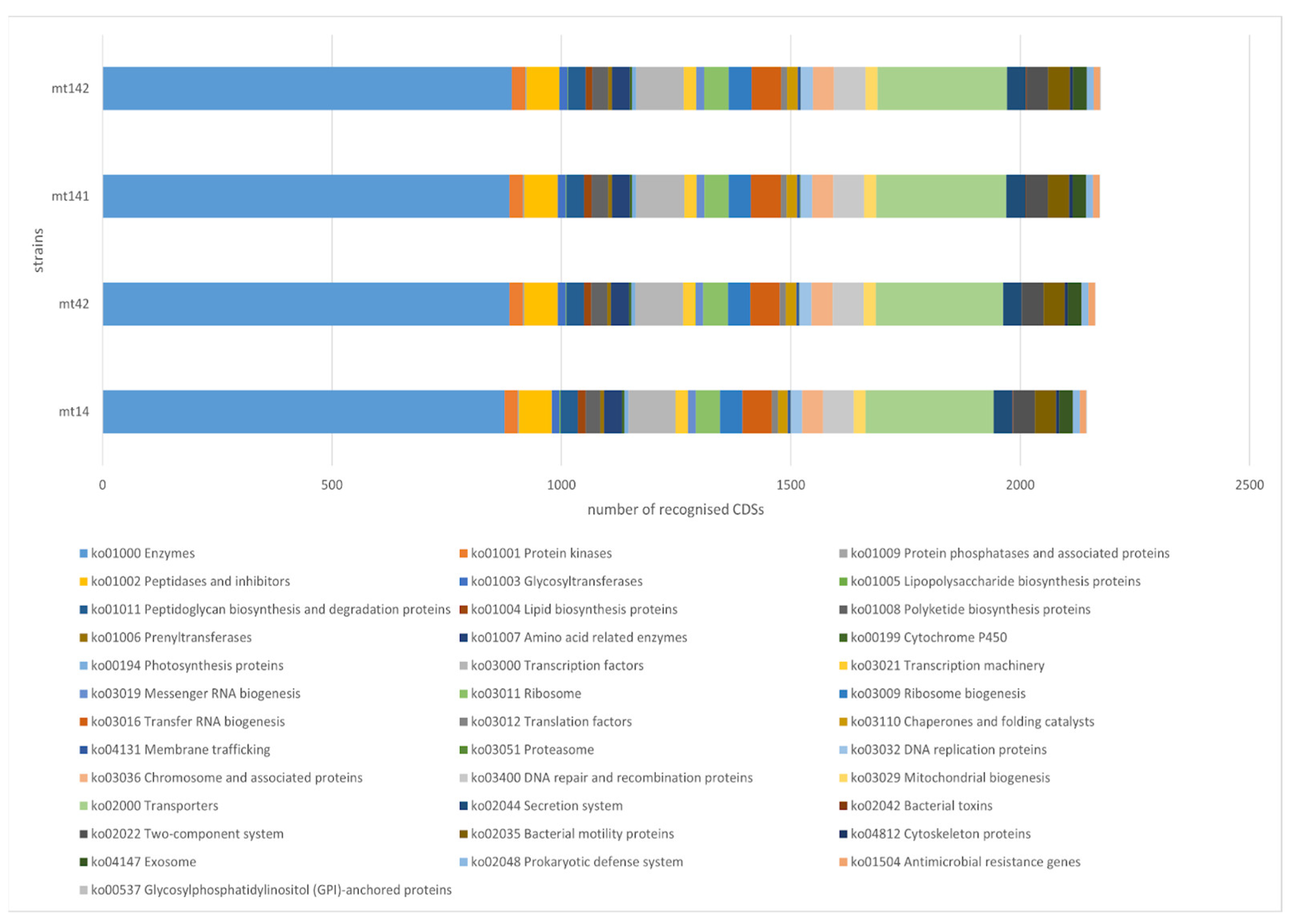
3.3. Functional Analysis of Genomes
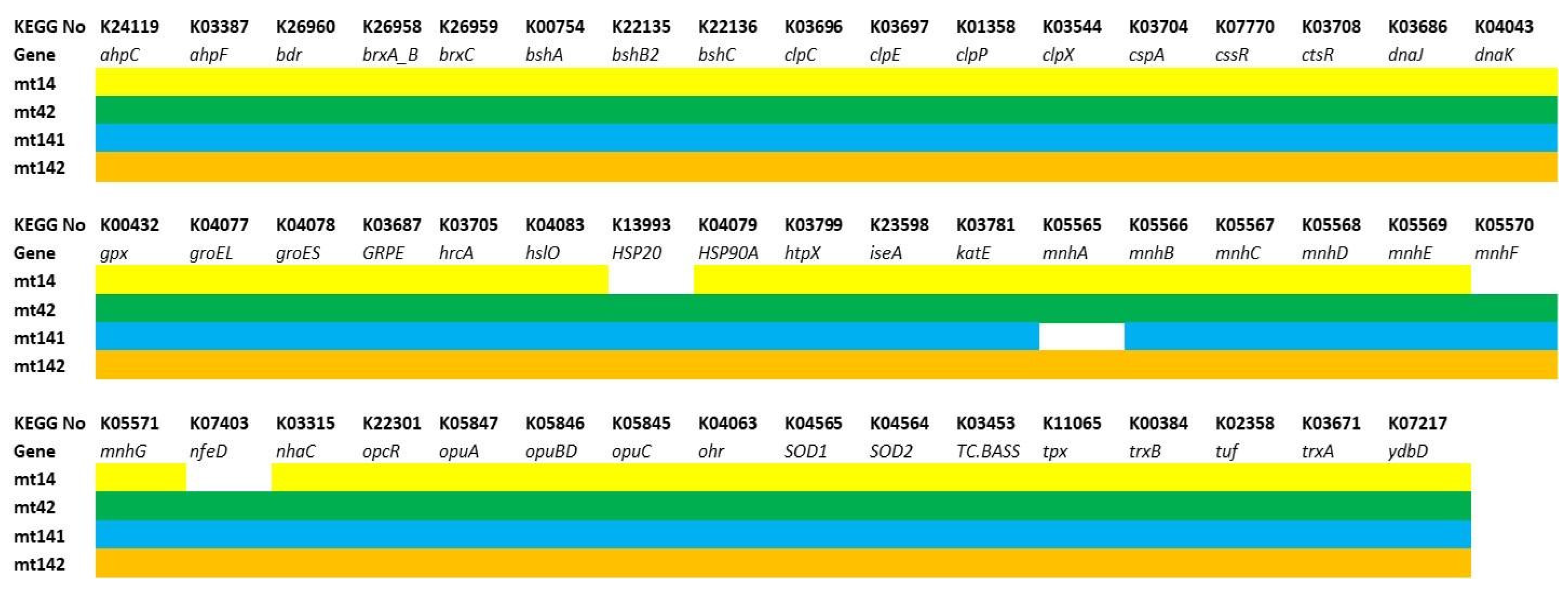
3.3.1. Genes of Probiotic Properties
3.3.2. Genes of Lytic Enzymes
3.4. Antibiotic Resistance Gene Screening
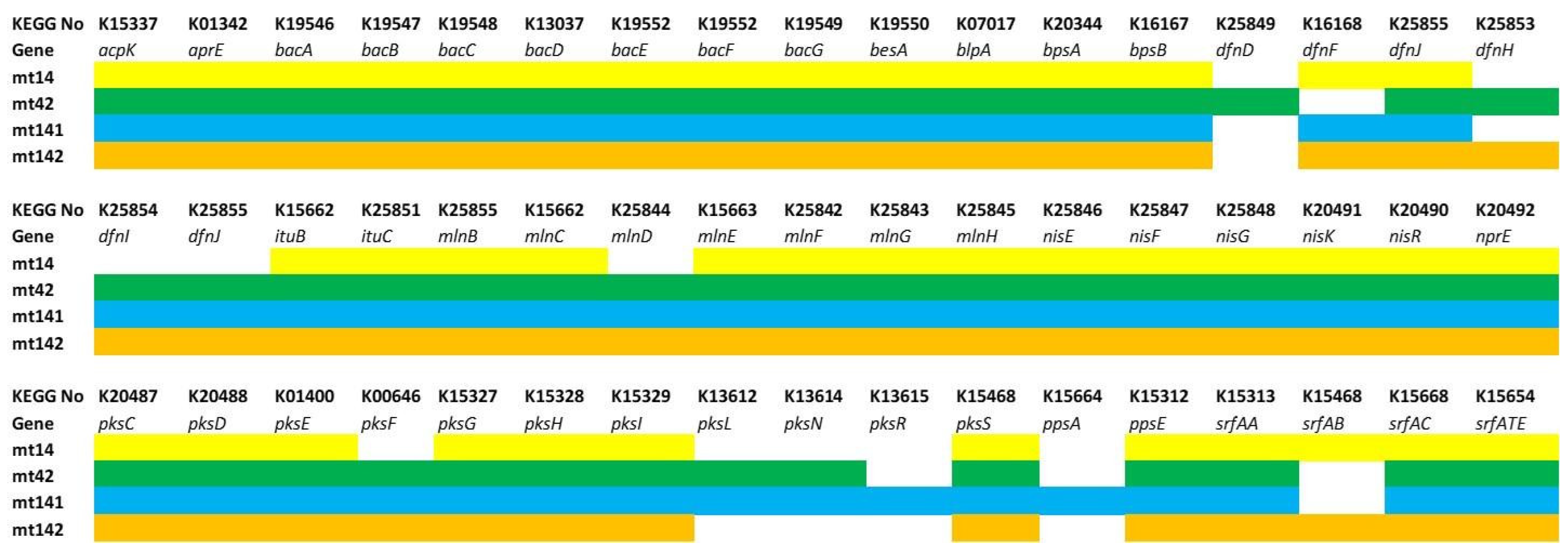
Secondary Metabolite Production: Non-Ribosomal Peptides and Polyketides
3.5. Fish Growth Parameters
3.6. Microbiological Tracking of Probiotic Colonization
3.7. Analysis of the Differential Expression of Fish Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. Bacilli as Probiotics for Aquaculture
4.2. Enzymatic Activity and Its Role in Improving Feed Digestibility
4.3. Effect on Fish Growth and Feed Conversion
4.4. Colonization and Stability of Preparations In Vivo
4.5. Secondary Metabolites and Antimicrobial Activity
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis and Mechanisms of Probiotic Action
4.7. Limitations and Future Directions
4.8. Practical Implications for Sustainable Aquaculture
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food And Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018 (SOFIA); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-5-130562-1. [Google Scholar]
- Food And Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; ISBN 978-92-5-132692-3. [Google Scholar]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Alagawany, M.; Patra, A.K.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Dhama, K.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. The Functionality of Probiotics in Aquaculture: An Overview. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, R.L.; Kishore, A.; Sumaila, U.R.; Issifu, I.; Hunter, B.P.; Belton, B.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Gelcich, S.; Gephart, J.A.; et al. Blue Food Demand across Geographic and Temporal Scales. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeckel, S.; Harjes, A.-G.E.; Roth, I.; Katz, H.; Wuertz, S.; Susenbeth, A.; Schulz, C. When a Turbot Catches a Fly: Evaluation of a Pre-Pupae Meal of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Fish Meal Substitute—Growth Performance and Chitin Degradation in Juvenile Turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture 2012, 364, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Xu, D.; Lin, K.; Sun, C.; Yang, X. Intelligent Feeding Control Methods in Aquaculture with an Emphasis on Fish: A Review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 975–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljasik, P.; Panicz, R.; Sobczak, M.; Sadowski, J. Key Performance Indicators of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Wintering in a Pond and RAS under Different Feeding Schemes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.A.F.; Reda, R.M.; Ismail, T.A.; Moustafa, A. Growth, Hemato-Biochemical Parameters, Body Composition, and Myostatin Gene Expression of Clarias gariepinus Fed by Replacing Fishmeal with Plant Protein. Animals 2021, 11, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.-L.; Niu, J. Growth Performance, Intestinal Histomorphology, Body Composition, Hematological and Antioxidant Parameters of Oncorhynchus mykiss Were Not Detrimentally Affected by Replacement of Fish Meal with Concentrated Dephenolization Cottonseed Protein. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusche, K.; Nagel, F.; Arning, S.; Wuertz, S.; Susenbeth, A.; Schulz, C. Effect of Different Dietary Levels of Potato Protein Concentrate Supplemented with Feed Attractants on Growth Performance of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2013, 183, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhar, A.K.; Bashir, Y.; Saikia, D.; Nath, D.; Gupta, K.; Konwar, B.K.; Mandal, M. Cellulolytic potential of probiotic Bacillus subtilis AMS6 isolated from traditional fermented soybean (Churpi): An in-vitro study with regards to application as an animal feed additive. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 186, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuertz, S.; Schroeder, A.; Wanka, K.M. Probiotics in fish nutrition—Long-standing household remedy or native nutraceuticals? Water 2021, 13, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, J.; Kundu, J.; Pramanik, A.; Patra, B.C. Effect of cellulolytic gut bacteria as a feed supplement on the growth performance and nutrient digestibility of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Int. J. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 2, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahem, M.D. Evolution of Probiotics in Aquatic World: Potential Effects, the Current Status in Egypt and Recent Prospectives. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y. A Review on the Application of Bacillus as Probiotics in Aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate Use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzón-Atienza, L.; Bravo, J.; Serradell, A.; Montero, D.; Gómez-Mercader, A.; Acosta, F. Current Status of Probiotics in European Sea Bass Aquaculture as One Important Mediterranean and Atlantic Commercial Species: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzón-Atienza, L.; Bravo, J.; Torrecillas, S.; Gómez-Mercader, A.; Montero, D.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Acosta, F. An In-Depth Study on the Inhibition of Quorum Sensing by Bacillus velezensis D-18: Its Significant Impact on Vibrio Biofilm Formation in Aquaculture. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y.; Hlordzi, V.; Sakyi, M.E.; Afriyie, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.X. Mechanisms and the Role of Probiotic Bacillus in Mitigating Fish Pathogens in Aquaculture. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 819–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Effect of Probiotic on Larvae Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Based on Water Quality, Survival Rate and Digestive Enzyme Activities. Aquaculture 2009, 287, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Dietary Administration of Bacillus Subtilis HAINUP40 Enhances Growth, Digestive Enzyme Activities, Innate Immune Responses and Disease Resistance of Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Jerusik, R.; Saavedra, M.J.; Enes, P.; Serra, C.R. Isolation and Characterization of Fish-Gut Bacillus spp. as Source of Natural Antimicrobial Compounds to Fight Aquaculture Bacterial Diseases. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, H.; Philip, B.; Philip, R.; Singh, I.S.B. Effect of Probiotics on Digestive Enzyme Activities and Growth of Cichlids, Etroplus suratensis (Pearl Spot) and Oreochromis mossambicus (Tilapia). Aquacult. Nutr. 2017, 23, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorian, T.J.; Jamali, H.; Farsani, H.G.; Darvishi, P.; Hasanpour, S.; Bagheri, T.; Roozbehfar, R. Effects of Probiotic Bacteria Bacillus on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Hematological Parameters of Asian Sea Bass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumon, M.S.; Ahmmed, F.; Khushi, S.S.; Ahmmed, M.K.; Rouf, M.A.; Chisty, A.H.; Sarower, G. Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity and Immune Response of Macrobrachium rosenbergii Fed with Probiotic Clostridium butyricum Incorporated Diets. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2018, 30, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrilasari, W.; Widanarni; Meryandini, A. Effect of Probiotic Bacillus megaterium PTB 1.4 on the Population of Intestinal Microflora, Digestive Enzyme Activity and the Growth of Catfish (Clarias sp.). HAYATI J. Biosci. 2016, 23, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl, A.; Olsen, R.E.; Dimitroglou, A.; Foey, A.; Davies, S.; et al. Effect of Dietary Components on the Gut Microbiota of Aquatic Animals. A Never-Ending Story? Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Cruz, P.; Ibáñez, A.L.; Monroy Hermosillo, O.A.; Ramírez Saad, H.C. Use of Probiotics in Aquaculture. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 916845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-F.; Li, Y.; Li, J.-R.; Cai, L.-Y.; Li, X.-X.; Chen, J.-R.; Lyu, S.-X. Isolation and Characterisation of Bacillus spp. Antagonistic to Vibrio parahaemolyticus for Use as Probiotics in Aquaculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidong, R.; Khotchanalekha, K.; Doolgindachbaporn, S.; Nagasawa, T.; Nakao, M.; Sakai, K.; Tongpim, S. Evaluation of Probiotic Bacillus aerius B81e Isolated from Healthy Hybrid Catfish on Growth, Disease Resistance and Innate Immunity of Pla-Mong Pangasius bocourti. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Katya, K.; Park, Y.; Won, S.; Seong, M.; Hamidoghli, A.; Bai, S.C. Comparative Evaluation of Dietary Probiotics Bacillus subtilis WB60 and Lactobacillus plantarum KCTC3928 on the Growth Performance, Immunological Parameters, Gut Morphology and Disease Resistance in Japanese Eel, Anguilla japonica. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 61, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.-M.; Kothari, D.; Lee, W.-D.; Lim, J.-M.; Khosravi, S.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, K.-W.; Han, H.-S.; Kim, S.-K. Autochthonous Bacillus licheniformis: Probiotic Potential and Survival Ability in Low-Fishmeal Extruded Pellet Aquafeed. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaylacı, E.U. Isolation and Characterization of Bacillus spp. from Aquaculture Cage Water and Its Inhibitory Effect against Selected Vibrio spp. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 204, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakharuthai, C.; Boonanuntanasarn, S.; Kaewda, J.; Manassila, P. Isolation of Potential Probiotic Bacillus spp. from the Intestine of Nile Tilapia to Construct Recombinant Probiotic Expressing CC Chemokine and Its Effectiveness on Innate Immune Responses in Nile Tilapia. Animals 2023, 13, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmnasser, N.; Hassen, W.; Zmantar, T.; Ashraf, S.A.; Hadj Lajimi, R.; Humaidi, J.R.; Alreshidi, M.; Hamadou, W.S.; Emira, N.; Snoussi, M. Antagonistic and Enzymatic Activities of Bacillus Species Isolated from the Fish Gastrointestinal Tract as Potential Probiotics Use in Artemia Culture. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2024, 70, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Y.; Chen, S.-W.; Hu, S.-Y. Improvements in the Growth Performance, Immunity, Disease Resistance, and Gut Microbiota by the Probiotic Rummeliibacillus stabekisii in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, F.; Shiu, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Puspitasari, A.W.; Danata, R.H.; Liu, C.-H.; Hu, S.-Y. Dietary Supplementation with Xylanase-Expressing B. Amyloliquefaciens R8 Improves Growth Performance and Enhances Immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 58, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.-H.; Shang, B.-J.; Shao, Y.-C.; Li, W.-Y.; Sun, J.-S. Screening of Intestinal Probiotics and the Effects of Feeding Probiotics on the Growth, Immune, Digestive Enzyme Activity and Intestinal Flora of Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.-C.; Liu, C.-H.; Chuang, K.-P.; Chang, Y.-T.; Hu, S.-Y. A Potential Probiotic Chromobacterium aquaticum with Bacteriocin-like Activity Enhances the Expression of Indicator Genes Associated with Nutrient Metabolism, Growth Performance and Innate Immunity against Pathogen Infections in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Saputra, F.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hu, S.-Y. Dietary Administration of Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens R8 Reduces Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Enhances Nutrient Metabolism and Immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmani, H.; Daoud, L.; Jlidi, M.; Jalleli, K.; Ben Ali, M.; Hadj Brahim, A.; Bargui, M.; Dammak, A.; Ben Ali, M. A Bacillus subtilis Strain as Probiotic in Poultry: Selection Based on in Vitro Functional Properties and Enzymatic Potentialities. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midhun, S.J.; Neethu, S.; Vysakh, A.; Sunil, M.A.; Radhakrishnan, E.K.; Jyothis, M. Antibacterial Activity of Autochthonous Bacteria Isolated from Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792) and It’s in Vitro Probiotic Characterization. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos Soto, J. Bacillus Probiotic Enzymes: External Auxiliary Apparatus to Avoid Digestive Deficiencies, Water Pollution, Diseases, and Economic Problems in Marine Cultivated Animals. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 80, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, G.; Hafezieh, M.; Karimi, A.A.; Azra, M.N.; Van Doan, H.; Tapingkae, W.; Abdelrahman, H.A.; Dawood, M.A.O. The Synergistic Effects of Plant Polysaccharide and Pediococcus acidilactici as a Synbiotic Additive on Growth, Antioxidant Status, Immune Response, and Resistance of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Maravilla, E.; Parra, M.; Maisey, K.; Vargas, R.A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Tello, M.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Importance of Probiotics in Fish Aquaculture: Towards the Identification and Design of Novel Probiotics. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Du, J.; Luo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Long, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, L.; Du, Z.; Yan, T. Effects of Different Diets on the In-testinal Microbiota and Immunity of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setlow, P. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: Their Resistance to and Killing by Radiation, Heat and Chemicals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, R.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; He, K.; Wang, X. The Formation Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis Biofilm Surface Morphology under Competitive Environment. Can. J. Microbiol. 2023, 69, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Kong, R.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Fractal Morphology Facilitates Bacillus subtilis Biofilm Growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 56168–56177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tyler, B.M.; Wang, Y. Defense and Counterdefense During Plant-Pathogenic Oomycete Infection. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 667–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanko, M.S.; Gorlov, I.F.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Makarenko, M.S.; Usatov, A.V.; Bren, A.B.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Tutelyan, A.V.; Komarova, Z.B.; Mosolova, N.I.; et al. Bacillus Probiotic Supplementations Improve Laying Performance, Egg Quality, Hatching of Laying Hens, and Sperm Quality of Roosters. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazdnova, E.V.; Mazanko, M.S.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Denisenko, Y.V.; Makarenko, M.S.; Usatov, A.V.; Bren, A.B.; Tutelyan, A.V.; Komarova, Z.B.; Gorlov, I.F.; et al. Effect of Bacillus subtilis KATMIRA1933 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1895 on the Productivity, Reproductive Aging, and Physiological Characteristics of Hens and Roosters. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomareva, E.N.; Sorokina, M.N.; Grigoriev, V.A.; Mazanko, M.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Rudoy, D.V. Probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1895 Improved Growth of Juvenile Trout. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2024, 44, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, M.; Pakzad, K.; Taheri-Mirghaed, A.; Mirzargar, S.; Shekarabi, S.P.H.; Yosefi, P.; Soleymani, N. Dietary Application of the Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum 426951 Enhances Immune Status and Growth of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Vaccinated Against Yersinia ruckeri. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyugi, D.O.; Cucherousset, J.; Baker, D.J.; Britton, J.R. Effects of Temperature on the Foraging and Growth Rate of Juvenile Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio. J. Therm. Biol. 2012, 37, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarnejad, M. Survival and Growth of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Exposed to Different Water pH Levels. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2012, 36, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrati, M.; Hosseini Shekarabi, S.P.; Rajabi Islami, H.; Shenavar Masouleh, A.; Shamsaie Mehrgan, M. Singular or Combined Dietary Administration of Multi-strain Probiotics and Multi-enzyme Influences Growth, Body Composition, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Intestinal Morphology in Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Aquacult. Nutr. 2021, 27, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourgholam, M.A.; Khara, H.; Safari, R.; Sadati, M.A.Y.; Aramli, M.S. Dietary Administration of Lactobacillus plantarum Enhanced Growth Performance and Innate Immune Response of Siberian Sturgeon, Acipenser baerii. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2016, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobi, N.; Vaseeharan, B.; Chen, J.-C.; Rekha, R.; Vijayakumar, S.; Anjugam, M.; Iswarya, A. Dietary Supplementation of Probiotic Bacillus licheniformis Dahb1 Improves Growth Performance, Mucus and Serum Immune Parameters, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity as Well as Resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in Tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraylou, Z.; Souffreau, C.; Rurangwa, E.; De Meester, L.; Courtin, C.M.; Delcour, J.A.; Buyse, J.; Ollevier, F. Effects of Dietary Arabinoxylan-Oligosaccharides (AXOS) and Endogenous Probiotics on the Growth Performance, Non-Specific Immunity and Gut Microbiota of Juvenile Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Du, H.; Wei, Q. Evaluation of the Potential Probiotic Bacillus subtilis Isolated from Two Ancient Sturgeons on Growth Performance, Serum Immunity and Disease Resistance of Acipenser dabryanus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darafsh, F.; Soltani, M.; Abdolhay, H.A.; Shamsaei Mehrejan, M. Improvement of Growth Performance, Digestive Enzymes and Body Composition of Persian Sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) Following Feeding on Probiotics: Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, V.A. DNA and RNA Isolation Techniques for Non-Experts. In Techniques in Life Science and Biomedicine for the Non-Expert; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.-Y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-Depth Characterization and Visualization of Bacterial Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwengers, O.; Jelonek, L.; Dieckmann, M.A.; Beyvers, S.; Blom, J.; Goesmann, A. Bakta: Rapid and Standardized Annotation of Bacterial Genomes via Alignment-Free Sequence Identification. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded Curation, Support for Machine Learning, and Resistome Prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Fetter, A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Metcalf, W.W.; Helfrich, E.J.N.; et al. antiSMASH 7.0: New and Improved Predictions for Detection, Regulation, Chemical Structures and Visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W46–W50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.-A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk v2: Memory Friendly Classification with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 5315–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Rinke, C.; Mussig, A.J.; Chaumeil, P.-A.; Hugenholtz, P. GTDB: An Ongoing Census of Bacterial and Archaeal Diversity through a Phylogenetically Consistent, Rank Normalized and Complete Genome-Based Taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D785–D794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, D.; Zubaidah, A.; Cahya Putra, R.D.; Anne, O.; Ariansyah, F. Growth Performance of Tilapia Fed Commercial Feed with Cellulolytic Bacteria from Ruminants. In Proceedings of the BIO Web of Conferences: The 3rd and 4th International Conference on Bioenergy and Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture Technology (ICoN BEAT 2022 and 2023), Les Ulis, France, 1 May 2024; Volume 104, p. 00009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Hatamleh, A.A.; Biji, G.D.; Rady, A.M. Host Associated Mixed Probiotic Bacteria Induced Digestive Enzymes in the Gut of Tiger Shrimp Penaeus Monodon. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Follador, R. Metabolism of Oligosaccharides and Starch in Lactobacilli: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Reales-Calderon, J.A.; Corona, F.; Lira, F.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Bernardini, A.; Sanchez, M.B.; Martinez, J.L. Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps: Much More Than Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsamad, A.E.M.; Said, R.E.M.; Assas, M.; Gaafar, A.Y.; Hamouda, A.H.; Mahdy, A. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus velezensis on the Growth Performance, Body Composition, Antioxidant, Immune-Related Gene Expression, and Histology of Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barale, S.S.; Ghane, S.G.; Sonawane, K.D. Purification and Characterization of Antibacterial Surfactin Isoforms Produced by Bacillus velezensis SK. AMB Express 2022, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.J.; Song, J.W.; Lee, C.; Kim, B.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.E.; Park, J.H. Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Strains against Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease-Causing Vibrio campbellii in Pacific White Leg Shrimp. Fishes 2022, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam-On, M.F.S.; Mustafa, S.; Mohd Hashim, A.; Yusof, M.T.; Zulkifly, S.; Malek, A.Z.A.; Roslan, M.A.H.; Mohd Asrore, M.S. Mining the Genome of Bacillus velezensis FS26 for Probiotic Markers and Secondary Metabolites with Antimicrobial Properties against Aquaculture Pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 181, 106161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; You, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Aimaier, R.; Zhang, J.; Han, S.; Zhao, H.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Reveal That Bacillus subtilis BS-Z15 Lipopeptides Mycosubtilin Homologue Mediates Plant Defense Responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1088220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Ho, M.T.; Weselowski, B.; McDowell, T.; Solomon, O.; Renaud, J.; Yuan, Z.-C. Characterization and Complete Genome Analysis of the Surfactin-Producing, Plant-Protecting Bacterium Bacillus velezensis 9D-6. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Shi, G.; Wu, L.; Lou, Z.; Huo, R.; Wu, H.; Borriss, R.; Gao, X. Bacillomycin D Produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Is Involved in the Antagonistic Interaction with the Plant-Pathogenic Fungus Fusarium graminearum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01075-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibe, V.; Kulikov, M.; Prazdnova, E.; Mazanko, M.; Chistyakov, V.; Rudoy, D.; Shevchenko, V.; Kulikova, N. Effect of Growth Medium Composition on the Efficiency of Non-Ribosomal Synthesis in Bacteria of the Genus Bacillus. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 113, 02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sword, T.T.; Abbas, G.S.K.; Bailey, C.B. Cell-Free Protein Synthesis for Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetic Biology. Front. Nat. Prod. 2024, 3, 1353362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xin, Z.; Sang, Z.; Li, X.; Xie, J.; Wu, J.; Pang, S.; Wen, Y.; Wang, W. A Rational Multi-Target Combination Strategy for Synergistic Improvement of Non-Ribosomal Peptide Production. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripnichenko, R.V.; Chelombitskaya, D.S.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Kulikov, M.P.; Neurov, A.M.; Zaikina, A.A.; Grigoryev, V.A.; Sorokina, M.N.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Chikindas, M.L.; et al. Potential Probiotic Bacillus Strains with Antioxidant and Antimutagenic Activity Increased Weight Gain and Altered Hsp70, Cxc, Tnfα, Il1β, and lysC Gene Expression in Clarias gariepinus. Fishes 2024, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, K.; Konkol, D.; Korczyński, M. Overview of the Use of Probiotics in Poultry Production. Animals 2021, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Vidal, E.; Martín-Orúe, S.M.; Castillejos, L. Practical Aspects of the Use of Probiotics in Pig Production: A Review. Livest. Sci. 2019, 223, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, D. Research Progress of Biological Feed in Beef Cattle. Animals 2023, 13, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ringø, E.; Ángeles Esteban, M.; Dadar, M.; Dawood, M.A.; Faggio, C. Host-associated probiotics: A key factor in sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.L.; Yang, D.H.; Hao, Q.; Yang, H.W.; Meng, D.L.; Zhou, Z.G. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG triggers intestinal epithelium injury in zebrafish revealing host dependent beneficial effects. IMeta 2024, 3, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, S.; Amoah, K.; Huang, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, B.; Shija, V.M.; Jiang, M. Probiotics application in aquaculture: Its potential effects, current status in China and future prospects. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1455905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.H. Evolutionary Loss of Acid-Secreting Stomach and Endoskeletal Ossification: A Phosphorus Perspective. Fishes 2025, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radchikov, V.F.; Astrenkov, A.V.; Gadlevskaya, N.N.; Prodennia, V.I.; Djulić, E.L.; Rohalskaia, S.U. Improvement of carp production efficiency through reduction of the cost of feed combinations. Mech. Electrif. Agric. 2022, 55, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Hou, D.; Zhou, R.; Zeng, S.; Xing, C.; Wei, D.; He, J. Environmental water and sediment microbial communities shape intestine microbiota for host health: The central dogma in an anthropogenic aquaculture ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 772149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xiao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhai, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xia, M. Vertical habitat preferences shape the fish gut microbiota in a shallow lake. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1341303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, F.; Khalid, A.; Fu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Khan, S.; Wang, Z. Potential of Bacillus velezensis as a Probiotic in Animal Feed: A Review. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Z.; Gao, J. Exploring the Antibiotic Potential of Cultured ‘Unculturable’ Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.-B.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, J.-W.; Qu, S.-Y.; Qi, X.-Z.; Wang, G.-X.; Ling, F. Effects of Potential Probiotic Bacillus velezensis K2 on Growth, Immunity and Resistance to Vibrio harveyi Infection of Hybrid Grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × E. fuscoguttatus♀). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 93, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Lai, H.; Zhao, X.; Bi, S.; Guo, D.; Chen, X.; Yi, H.; et al. Identifying the Related Genes of Muscle Growth and Exploring the Functions by Compensatory Growth in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 553563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, Z.; Wu, A.; Pan, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Muscle Transcriptome Analysis Provides New Insights into the Growth Gap between Fast- and Slow-Growing Sinocyclocheilus grahami. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1217952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anee, I.J.; Alam, S.; Begum, R.A.; Shahjahan, R.M.; Khandaker, A.M. The Role of Probiotics on Animal Health and Nutrition. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2021, 82, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlidi, M.; Akremi, I.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Brabra, W.; Ali, M.B.; Ali, M.B. Probiotic Properties of Bacillus Strains Isolated from the Gastrointestinal Tract against Pathogenic Vibriosis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 884244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Hu, S.-Y. Probiotic Bacillus safensis NPUST1 Administration Improves Growth Performance, Gut Microbiota, and Innate Immunity against Streptococcus iniae in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assan, D.; Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Hlordzi, V.; Chen, H.; Mraz, J.; Mustapha, U.F.; Abarike, E.D. Effects of Probiotics on Digestive Enzymes of Fish (Finfish and Shellfish); Status and Prospects: A Mini Review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 257, 110653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K. Diverse LXG Toxin and Antitoxin Systems Specifically Mediate Intraspecies Competition in Bacillus subtilis Biofilms. PLoS Genet 2021, 17, e1009682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Kong, J.; Zhang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, M.; Guo, T. New Crosstalk between Probiotics Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus subtilis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, J.; Bellmer, D.; Jadeja, R.; Muriana, P. The Potential of Bacillus Species as Probiotics in the Food Industry: A Review. Foods 2024, 13, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanko, M.S.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Kulikov, M.P.; Maltseva, T.A.; Rudoy, D.V.; Chikindas, M.L. Antioxidant and Antimutagenic Properties of Probiotic Lactobacilli Determined Using LUX-Biosensors. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 155, 109980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Fu, S.-J.; Zhang, Y.-G. Acclimation Temperature Alters the Relationship between Growth and Swimming Performance among Juvenile Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 199, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanbo, W.; Zirong, X. Effect of Probiotics for Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Based on Growth Performance and Digestive Enzyme Activities. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2006, 127, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Lu, X.; Xue, M.; Fan, Y.; Tian, J.; Dong, L.; Zhu, C.; Wen, H.; Jiang, M. The Probiotic Effects of Host-Associated Bacillus velezensis in Diets for Hybrid Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco ♀ × Pelteo-bagrus vachelli ♂). Anim. Nutr. 2023, 15, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lv, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Sun, C.; Hu, S. Effects of Bacillus velezensis Supplementation on the Growth Performance, Immune Responses, and Intestine Microbiota of Litopenaeus vannamei. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 744281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-X.; Kang, Y.-H.; Zhan, S.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Jin, S.-N.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.-Y.; Wang, C.-F.; Wang, G.-Q.; et al. Effect of Bacillus velezensis on Aeromonas veronii-Induced Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function Damage and Inflammation in Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, K.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, X. Host Gut-Derived Bacillus Probiotics Supplementation Improves Growth Performance, Serum and Liver Immunity, Gut Health, and Resistive Capacity against Vibrio harveyi Infection in Hybrid Grouper (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂Epinephelus lanceolatus). Anim. Nutr. 2023, 14, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyanto, Y.S.; Anika, M. Probiotics on Commercial Fish Growth: A Meta-Analysis. J. Sumberd. Hayati 2024, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yi, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, X.; Bi, S.; Lai, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, G. Probiotics Improve Eating Disorders in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) Induced by a Pellet Feed Diet via Stimulating Immunity and Regulating Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Nguyen, T.L.; Roh, H.; Kim, A.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, Y.-R.; Kang, H.; Sohn, M.-Y.; Park, C.-I.; et al. Mechanisms Underlying Probiotic Effects on Neurotransmission and Stress Resilience in Fish via Transcriptomic Profiling. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 141, 109063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, M.; Feng, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Meng, X.; Chang, X. Effect of Beneficial Colonization of Bacillus coagulans NRS 609 on Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, Antioxidant Capacity, and Immune Response of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquac. Nutr. 2023, 2023, 1451394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Acharya, D.; Adholeya, A.; Barrow, C.J.; Deshmukh, S.K. Nonribosomal Peptides from Marine Microbes and Their Antimicrobial and Anticancer Potential. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, A.C.R.; Smeralda, W.; Cugnet, A.; Brostaux, Y.; Deleu, M.; Garigliany, M.; Jacques, P. The Structure of Lipopeptides Impacts Their Antiviral Activity and Mode of Action against SARS-CoV-2 in Vitro. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistikow, K.R.; May, D.S.; Suh, W.S.; Vargas Asensio, G.; Schaenzer, A.J.; Currie, C.R.; Hristova, K.R. Bacillus subtilis-Derived Peptides Disrupt Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Assembly in Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. mSystems 2024, 9, e00712-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, Y.-B.; Yu, Y.-H.; Dybus, A.; Hsiao, F.S.-H.; Cheng, Y.-H. Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Species-Derived Surfactin on Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and Clostridium perfringens. AMB Express 2019, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Borriss, R.; Gao, X. Difficidin and Bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 Have Antibacterial Activity against Xanthomonas oryzae Rice Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannan, C.; Vu, H.Q.; Gillis, A.; Caulier, S.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Mahillon, J. Bacilysin within the Bacillus subtilis Group: Gene Prevalence versus Antagonistic Activity against Gram-Negative Foodborne Pathogens. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 327, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, X.; Dong, Y.; Xu, S.; Chen, C.; Feng, Y.; Cui, Q.; Li, W. Bacillaenes: Decomposition Trigger Point and Biofilm Enhancement in Bacillus. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M.; Dhara, S. Difficidin Class of Polyketide Antibiotics from Marine Macroalga-Associated Bacillus as Promising Antibacterial Agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 6395–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, R.; Huang, Q.; Rensing, C.; Raza, W.; Shen, Q. Antibacterial Compounds-Macrolactin Alters the Soil Bacterial Community and Abundance of the Gene Encoding PKS. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Y.; Ali, Q.; Mohamed, M.S.R.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Gao, X.; et al. Mycosubtilin Produced by Bacillus subtilis ATCC6633 Inhibits Growth and Mycotoxin Biosynthesis of Fusarium graminearum and Fusarium verticillioides. Toxins 2021, 13, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Shao, J.; Li, B.; Yan, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Contribution of Bacillomycin D in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 to Antifungal Activity and Biofilm Formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.; Alam, S.T.; Kang, K.; Choi, J.; Seo, M.-H. Anti-Staphylococcal Activity of a Cyclic Lipopeptide, C15 -Bacillomycin D, Produced by Bacillus velezensis NST6. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Oh, T.; Kang, B.; Ahn, J.S.; Cho, Y. Throughput Screening of Bacillus subtilis Strains That Abundantly Secrete Surfactin in Vitro Identifies Effective Probiotic Candidates. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurov, A.M.; Zaikina, A.A.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Anuj, R.; Rudoy, D.V. Modulation of Stress-Related Protein in the African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Using Bacillus-Based Non-Ribosomal Peptides. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 2743–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wei, Q. Quantifying the Colonization of Environmental Microbes in the Fish Gut: A Case Study of Wild Fish Populations in the Yangtze River. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 828409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, R.; Abel, C.; Malachi, A.W.; Nancy, C.; Bui, C.T.D.; Joseph, C.N.; Mark, R.L. Identification of Bacillus strains for biological control of catfish pathogens. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Giatsis, C.; Sipkema, D.; Ramiro-Garcia, J.; Bacanu, G.M.; Abernathy, J.; Verreth, J.; Verdegem, M. Probiotic legacy effects on gut microbial assembly in tilapia larvae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Sofia, E.; Shakil, A.; Haque, N.F.; Khan, M.N.A.; Ikeda, D.; Kinoshita, S.; Abol-Munafi, A.B. Host Gut-Derived Probiotic Bacteria Promote Hypertrophic Muscle Progression and Upregulate Growth-Related Gene Expression of Slow-Growing Malaysian Mahseer Tor tambroides. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 9, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, J.; Chaganti, S.R.; Heath, D.D. Regulation of Host Gene Expression by Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiota in Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 4427–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. Effects of Probiotics on Gut Microbiota: Mechanisms of Intestinal Immunomodulation and Neuromodulation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, I.S.; Santiago-Morales, K.D.; Ferguson, C.S.; Clarington, J.; Thompson, M.; Rauschenbach, M.; Levine, U.; Drahos, D.; Aylward, F.O.; Smith, S.A.; et al. Steelhead Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fed Probiotic during the Earliest Developmental Stages Have Enhanced Growth Rates and Intestinal Microbiome Bacterial Diversity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1021647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Hassan, H.; Mohammad Ali, Q.; Ahmad, N.; Masood, Z.; Hossain, Y.; Gabol, K.; Khan, W.; Hussain, M.; Ali, A.; Attaullah, M.; et al. Assessment of Growth Characteristics, the Survival Rate and Body Composition of Asian Sea Bass Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790) under Different Feeding Rates in Closed Aquaculture System. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrack, R.S.; Manabu, I.; Yokoyama, S. Efficacy of Single and Mix Probiotic Bacteria Strain on Growth Indices, Physiological Condition and Bio-Chemical Composition of Juvenile Amberjack (Seriola dumerili). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speare, D.J.; MacNair, N.; Hammell, K.L. Demonstration of Tank Effect on Growth Indices of Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during an Ad Libitum Feeding Trial. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Aquaculture Society. Meeting Abstract. Experimental Design and Statistical Power of Fish Growth Studies. Available online: https://www.was.org/MeetingAbstracts/ShowAbstract/42356 (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Rwezawula, P.; Waiswa Mwanja, W.; Vereecke, N.; Bossier, P.; Vanrompay, D. Advancing Aquaculture Probiotic Discovery via an Innovative Protocol for Isolation of Indigenous, Heat and Salt Tolerant, Quorum Quenching Probiotic Candidates. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1558238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Men, X.; Dang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, Y. Probiotics Mediate Intestinal Microbiome and Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Regulating the Growth and Immunity of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0398022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, C.R.; Almeida, E.M.; Guerreiro, I.; Santos, R.; Merrifield, D.L.; Tavares, F.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P. Selection of Carbohydrate-Active Probiotics from the Gut of Carnivorous Fish Fed Plant-Based Diets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Target Gene | Forward Primer Sequence (F, 5′-3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (R, 5′-3′) | Product Length | Melting Point of Primers, °C | GC Content, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| act | GTCTACCACTTCGCCCTCATC | CAGTGTACAGAGACACCCTGG | 247 | F: 60.20 R: 59.73 | F:57.14 R:57.14 |
| cxc | CTGGGATTCCTGACCATTGGT | GTTGGCTCTCTGTTTCAATGCA | 88 | F: 55.87 R: 57.46 | F: 52 R: 45 |
| lyz | GTGTCTGATGTGGCTGTGCT | TTCCCCAGGTATCCCATGAT | 359 | F: 60.38 R: 57.46 | F: 55 R: 50 |
| hsp70 | TGAGAACATCAACGAGCCCA | TTGTCAAAGTCCTCCCCACC | 195 | F: 59.59 R: 59.62 | F: 50 R: 55 |
| il-1β | ACTGGAGCTGTCTTCGCATC | CTCCAAGATGAAGCCGAGCA | 136 | F: 58.48 R: 59.25 | F: 55 R: 55 |
| il-10 | GCTGTCACGTCATGAACGAGAT | CCCGCTTGAGATCCTGAAATAT | 132 | F: 58.89 R: 57.01 | F: 50 R: 45 |
| igf-1 | CCGTCTCCTGTTCGCTAAATCT | CTTTGGTGTCCTGGGACTGT | 554 | F: 60.86 R: 59.02 | F: 50 R: 55 |
| gst | TACAATACTTTCACGCTTTCCC | GGCTCAACACCTCCTTCAC | 149 | F: 54.41 R: 54.25 | F: 41 R: 58 |
| β2m | CCAAATACCCAGCAGACGGA | CAGTTGCTAGGCAGACGTTTA | 784 | F: 56.75 R: 57.2 | F: 55 R: 48 |
| mt1 | ATGGATCCTTGCGATTGCGCCA | CGAACAGGTTCACATAGGTGA | 232 | F: 62.94 R: 55.04 | F: 55 R: 48 |
| Strain | Proteolytic Activity (Width of the Clearing Zone in the Milk Medium, mm) | Amylolytic Activity (Width of the Clearing Zone in the Starch Medium, mm) | Cellulolytic Activity (Width of the Clearing Zone in the Carboxymethilcellulose Medium, mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MT14 | 8 ± 0.3 | 8 ± 0.6 | 16 ± 0.3 |
| MT27 | 8 ± 0.6 | 8 ± 1.0 | - |
| MT42 | 8 ± 0.3 | 11 ± 1.0 | 17 ± 1.0 |
| MT48 | 6 ± 1.0 | 11 ± 0.3 | 16 ± 0.3 |
| MT49 | 6 ± 0.6 | 10 ± 1.0 | - |
| MT56 | 5 ± 1.0 | 10 ± 0.3 | - |
| MT64 | 9 ± 0.3 | 4 ± 1.0 | 12 ± 0.6 |
| MT73 | 5 ± 0.6 | 10 ± 0.3 | - |
| MT74 | 8 ± 1.0 | 8 ± 1.0 | 16 ± 1.0 |
| MT77 | 3 ± 0.6 | 10 ± 0.3 | 6 ± 0.3 |
| MT84 | 9 ± 0.3 | 2 ± 0.6 | - |
| MT102 | 10 ± 0.6 | 4 ± 1.0 | 18 ± 1.0 |
| MT141 | 11 ± 0.3 | 6 ± 0.3 | 14 ± 0.3 |
| MT142 | 10 ± 1.0 | 5 ± 1.0 | 15 ± 0.6 |
| B1895a | 5 ± 0.3 | 7 ± 0.6 | - |
| Katmira | 5 ± 1.0 | 4 ± 0.3 | - |
| MT14 | MT27 | MT42 | MT48 | MT49 | MT56 | MT64 | MT73 | MT74 | MT77 | MT84 | MT102 | MT141 | MT142 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT14 | % | = | + | + | = | = | + | = | − | − | − | − | + | + |
| MT27 | = | % | = | = | = | = | = | = | − | − | = | − | = | = |
| MT42 | + | = | % | = | = | = | = | = | = | = | = | = | + | = |
| MT48 | + | = | = | % | = | = | = | = | = | = | − | = | + | = |
| MT49 | = | = | = | = | % | = | = | = | = | = | = | − | = | = |
| MT56 | = | = | = | = | = | % | = | = | = | = | = | = | = | + |
| MT64 | + | = | = | = | = | = | % | + | = | − | − | − | = | = |
| MT73 | = | = | = | = | = | = | + | % | − | = | − | = | + | = |
| MT74 | − | − | = | = | = | = | = | − | % | − | − | = | − | = |
| MT77 | − | − | = | = | = | = | − | = | − | % | − | − | − | − |
| MT84 | − | = | = | − | = | = | − | − | − | − | % | − | − | = |
| MT102 | − | − | = | = | − | = | − | = | = | − | − | % | − | + |
| MT141 | + | = | + | + | = | = | = | + | − | − | − | − | % | + |
| MT142 | + | = | = | = | = | + | = | = | = | − | = | + | + | % |
| Strain | MT14 | MT42 | MT141 | MT142 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length b.p. | 4,080,572 | 4,115,985 | 4,432,692 | 4,434,607 |
| Contigs count | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| GC % | 46.2 | 46.1 | 45.4 | 45.4 |
| N50 b.p. | 1,035,922 | 4,080,892 | 4,303,216 | 4,305,438 |
| Coding density % | 88.8 | 89.4 | 88.8 | 88.9 |
| tRNAs | 87 | 92 | 97 | 93 |
| tmRNAs | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| rRNAs | 26 | 30 | 31 | 31 |
| ncRNAs | 31 | 31 | 34 | 34 |
| ncRNA regions | 58 | 58 | 58 | 58 |
| CRISPR arrays | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CDSs | 4571 | 4433 | 4918 | 4813 |
| pseudogenes | 343 | 245 | 280 | 215 |
| hypotheticals proteins | 515 | 388 | 605 | 522 |
| signal peptides | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| sORFs | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| gaps | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| oriCs | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Assembly completeness % | 97.35 | 99.97 | 99.94 | 99.91 |
| Assembly contamination % | 2.19 | 2.1 | 1.19 | 2.32 |
| Enzyme | MT14 | MT42 | MT141 | MT142 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycosyl hydrolases of the alpha-amylase family | +++ | + | +++ | + |
| Alpha-amylase | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Glucosidase/amylase (phosphorylase) | + | + | + | |
| Beta-glucanase | + | + | + | + |
| 6-phosphorus-beta-glucosidase | ++++ | ++ | ++ | ++++ |
| 6-beta-D-glucan-glucanohydrolase | + | ++ | ++ | + |
| Alpha-D-1,4-glucosidase | + | + | ||
| Oligo-1,6-glucosidase | + | |||
| Aryl-phosphorus-beta-D-glucosidase BglC | + | + | ++ | + |
| Aryl-phosphorus-beta-D-glucosidase BglH | + | |||
| Maltodextrin-glucosidase | + | + | + | |
| Maltose-6′-phosphate glucosidase | + | + | +++ | + |
| Chitobiose-specific 6-phosphorus-beta-glucosidase ChbF | + | ++ | + | |
| Neopullalanase | + | + | + | |
| Levansaccharase | + | + | ++ | ++ |
| Alpha, alpha-phosphotregalase | + | + | ||
| DNA-recombinase SpoIVCA/DNA-invertase PinE | + | + | ||
| DNA-invertase hin | + | + | ||
| Cellulose | + | + | ||
| Endoglucanase | + | + | ++ | + |
| Protein of the lysozyme family | + | + | + | |
| CwlT-like protein containing lysozyme domain | + | + | + | ++ |
| Hemolysin C | + | + | ||
| Hemolysin III family protein | + | + | + | + |
| Hemolysins and related proteins containing CBS domains | +++ | + |
| Drug Resistance Cluster | Strain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 42 | 141 | 142 | |
| M00627 beta-Lactam resistance, Bla system (1) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) |
| M00704 Tetracycline resistance, efflux pump Tet38 (1) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) |
| M00726 Cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) resistance, lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol (L-PG) synthase MprF (1) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) | (2 blocks missing 1/3) |
| M00700 Efflux pump AbcA (2) | (complete 2/2) | (complete 2/2) | (complete 2/2) | (complete 2/2) |
| M00702 Multidrug resistance, efflux pump NorB (1) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) |
| M00714 Multidrug resistance, efflux pump QacA (1) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) | (1 block missing 1/2) |
| Substance/Strain | B. velezensis MT14 | B. velezensis MT42 | B. velezensis MT141 | B. velezensis MT142 | Possible Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacilysin | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | Antimicrobial [76] |
| Surfactin | 78 | 78 | 78 | 78 | Antimicrobial, immunostimulation [77,78] |
| Microlactin (H) | 88 | 100 | 90 | 90 | Antiviral [79] |
| Bacillaene | 100 | 100 | 100 | 71 | Antibacterial [79] |
| Mycosubtilin | 100 | - | 100 | - | Antifungal [80] |
| Difficidin | 8 | 100 | 100 | 93 | Antibacterial [81] |
| Bacillomycin | - | 100 | - | 100 | Antifungal [82] |
| Parameter | Control Group | Experimental Group No. 1 MT14 + MT42 | Experimental Group No. 2 MT141 + MT142 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 76 | Day 1 | Day 76 | Day 1 | Day 76 | |
| Individual weight (g) | ||||||
| min | 1.65 | 6.51 | 1.78 | 10.54 | 1.37 | 7.82 |
| max | 6.69 | 32.87 | 6.42 | 44.71 | 5.69 | 45.63 |
| Average value ± SD | 3.79 ± 0.96 | 17.97 ± 3.73 | 3.67 ± 0.86 | 23.82 ± 6.23 | 2.91 ± 0.72 | 21.61 ± 7.11 |
| Individual length (cm) | ||||||
| min | 4.26 | 8.91 | 4.19 | 9.51 | 3.64 | 7.48 |
| max | 6.51 | 12.46 | 6.32 | 13.49 | 5.78 | 13.10 |
| Average value ± SD | 5.05 ± 0.44 | 10.41 ± 0.73 | 5.02 ± 0.41 | 11.32 ± 0.73 | 4.51 ± 0.36 | 10.61 ± 0.99 |
| Fulton’s fatness coefficient, standard units | 2.94 | 1.59 | 2.91 | 1.64 | 3.17 | 1.81 |
| Criteria | Control Group | Experimental Group No. 1 MT14 + MT42 | Experimental Group No. 2 MT141 + MT142 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish biomass, kg (during the end of the experiment) | 2.55 | 3.48 | 3.07 |
| Total increase in biomass, kg | 1.98 | 2.93 | 2.63 |
| Biomass growth, % | 448.85 | 631.74 | 703.00 |
| Individual biomass growth, g | 14.18 | 20.15 | 18.7 |
| Individual biomass growth, % | 474.14 | 649.05 | 742.61 |
| Specific mass growth rate, %/day | 2.04 | 2.47 | 2.63 |
| Specific growth rate of fish by length, %/day | 0.95 | 1.08 | 1.12 |
| Feed conversion rate, kg/kg | 1.39 | 1.32 | 1.30 |
| Survival rate, % | 94.67 | 97.33 | 94.67 |
| Probiotic Used | Total Amount | Spore Form |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.2 ± 0.2·104 | 5.3 ± 0.4·103 |
| Experiment 1 (MT14 + MT42) | 2.7 ± 0.4·106 | 1.5 ± 0.2·104 |
| Experiment 2 (MT141 + MT142) | 2.3 ± 0.3·106 | 1.1 ± 0.4·104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prazdnova, E.V.; Mazanko, M.S.; Shevchenko, V.N.; Skripnichenko, R.V.; Kulikov, M.P.; Golovko, L.S.; Grigoriev, V.A.; Maltseva, T.A.; Kulikova, D.B.; Rudoy, D.V. Genomic Characterization of Four Novel Probiotic Strains with Enzymatic Activity and Their Effects on Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Animals 2025, 15, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131998
Prazdnova EV, Mazanko MS, Shevchenko VN, Skripnichenko RV, Kulikov MP, Golovko LS, Grigoriev VA, Maltseva TA, Kulikova DB, Rudoy DV. Genomic Characterization of Four Novel Probiotic Strains with Enzymatic Activity and Their Effects on Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Animals. 2025; 15(13):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131998
Chicago/Turabian StylePrazdnova, Evgeniya Valeryevna, Maria Sergeevna Mazanko, Victoria Nikolaevna Shevchenko, Radomir Viktorovich Skripnichenko, Maksim Pavlovich Kulikov, Lilia Sergeevna Golovko, Vadim Alexeevich Grigoriev, Tatiana Alexandrovna Maltseva, Daria Borisovna Kulikova, and Dmitry Vladimirovich Rudoy. 2025. "Genomic Characterization of Four Novel Probiotic Strains with Enzymatic Activity and Their Effects on Carp (Cyprinus carpio)" Animals 15, no. 13: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131998
APA StylePrazdnova, E. V., Mazanko, M. S., Shevchenko, V. N., Skripnichenko, R. V., Kulikov, M. P., Golovko, L. S., Grigoriev, V. A., Maltseva, T. A., Kulikova, D. B., & Rudoy, D. V. (2025). Genomic Characterization of Four Novel Probiotic Strains with Enzymatic Activity and Their Effects on Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Animals, 15(13), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131998










