Obesity-Associated Metabolomic and Functional Reprogramming in Neutrophils from Horses with Asthma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Polymorphonuclear Isolation
2.3. Sample Preparation for Metabolomics Analysis
2.4. Metabolomics Analysis by GC-MS
2.5. Respiratory Burst Production
2.6. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Analysis
2.7. Real Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.8. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
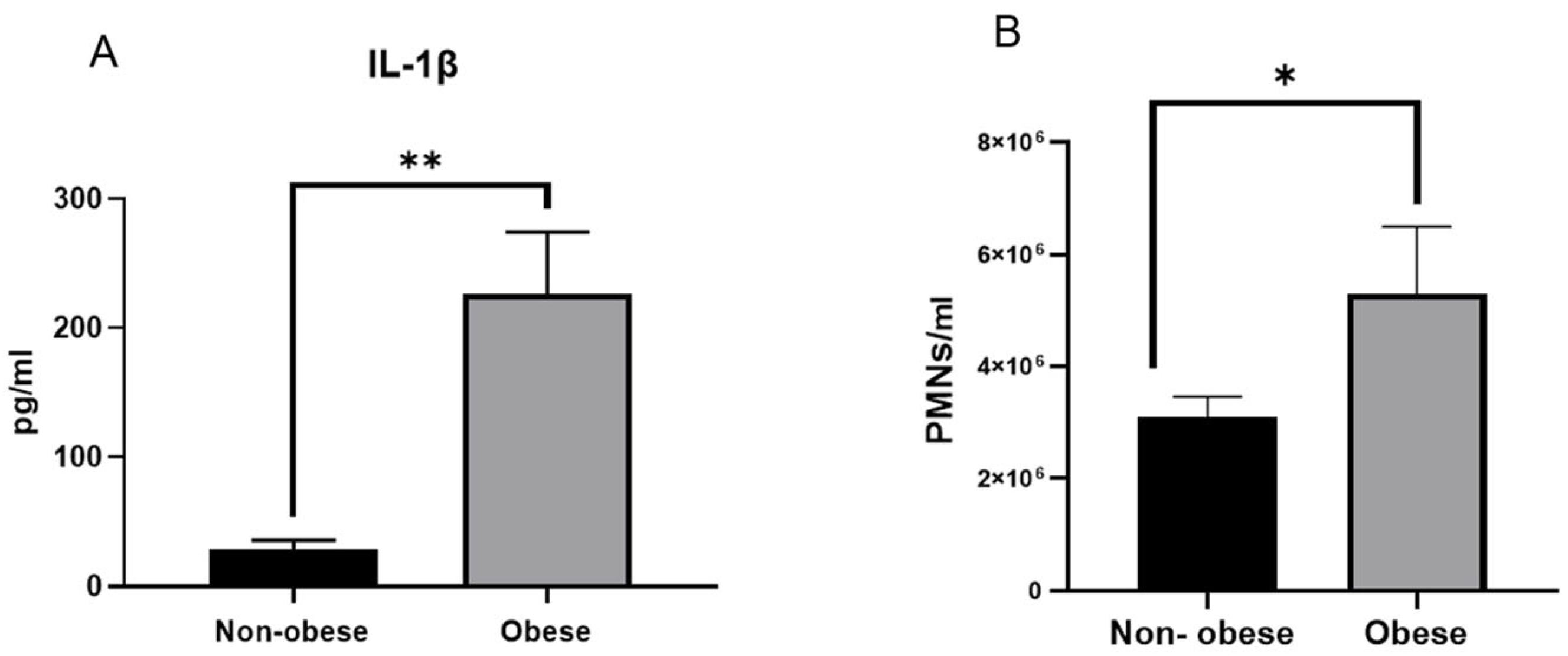
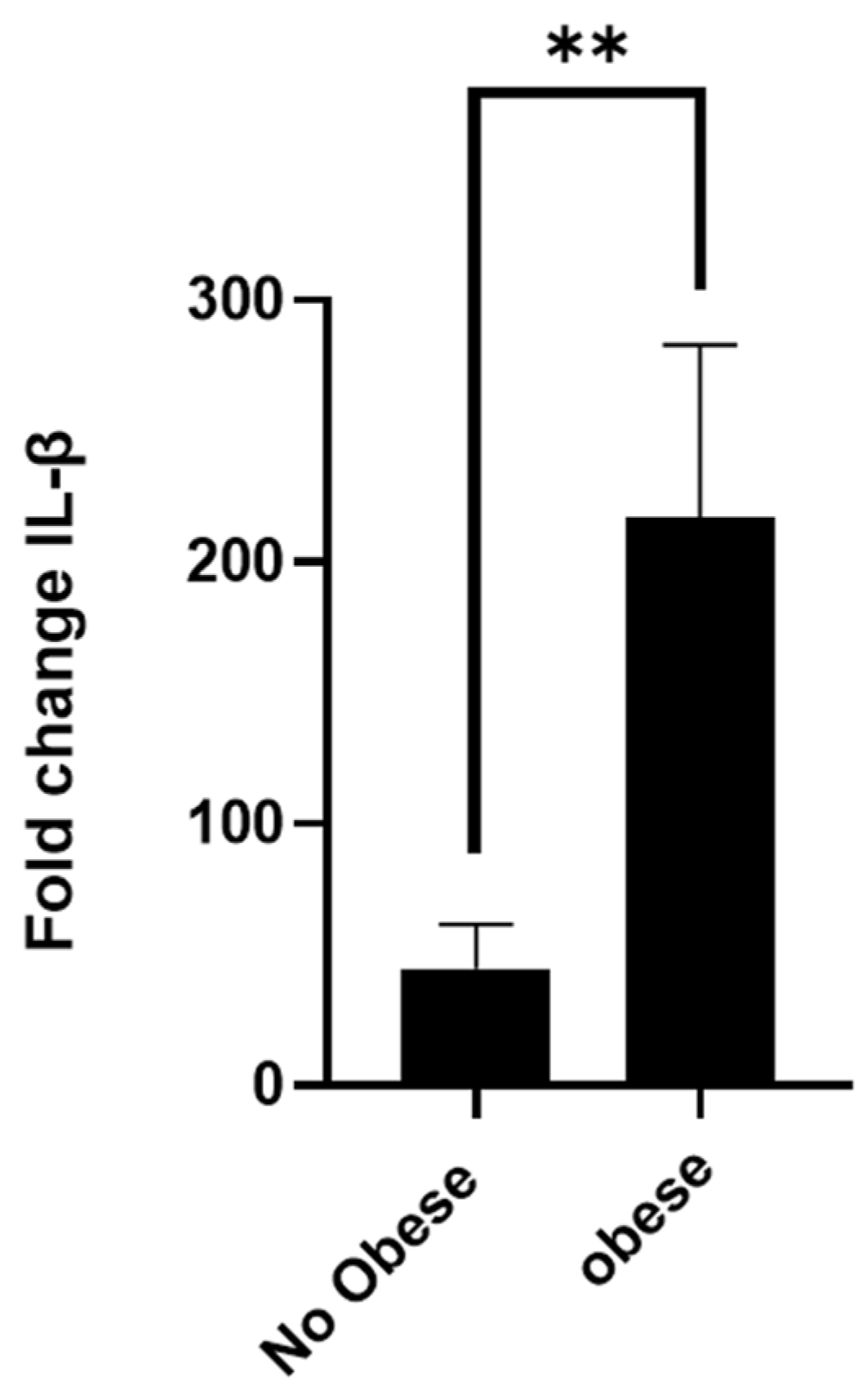
3.1. Asthmatic Obese Animals Exhibit Higher Levels of Circulating IL-1β
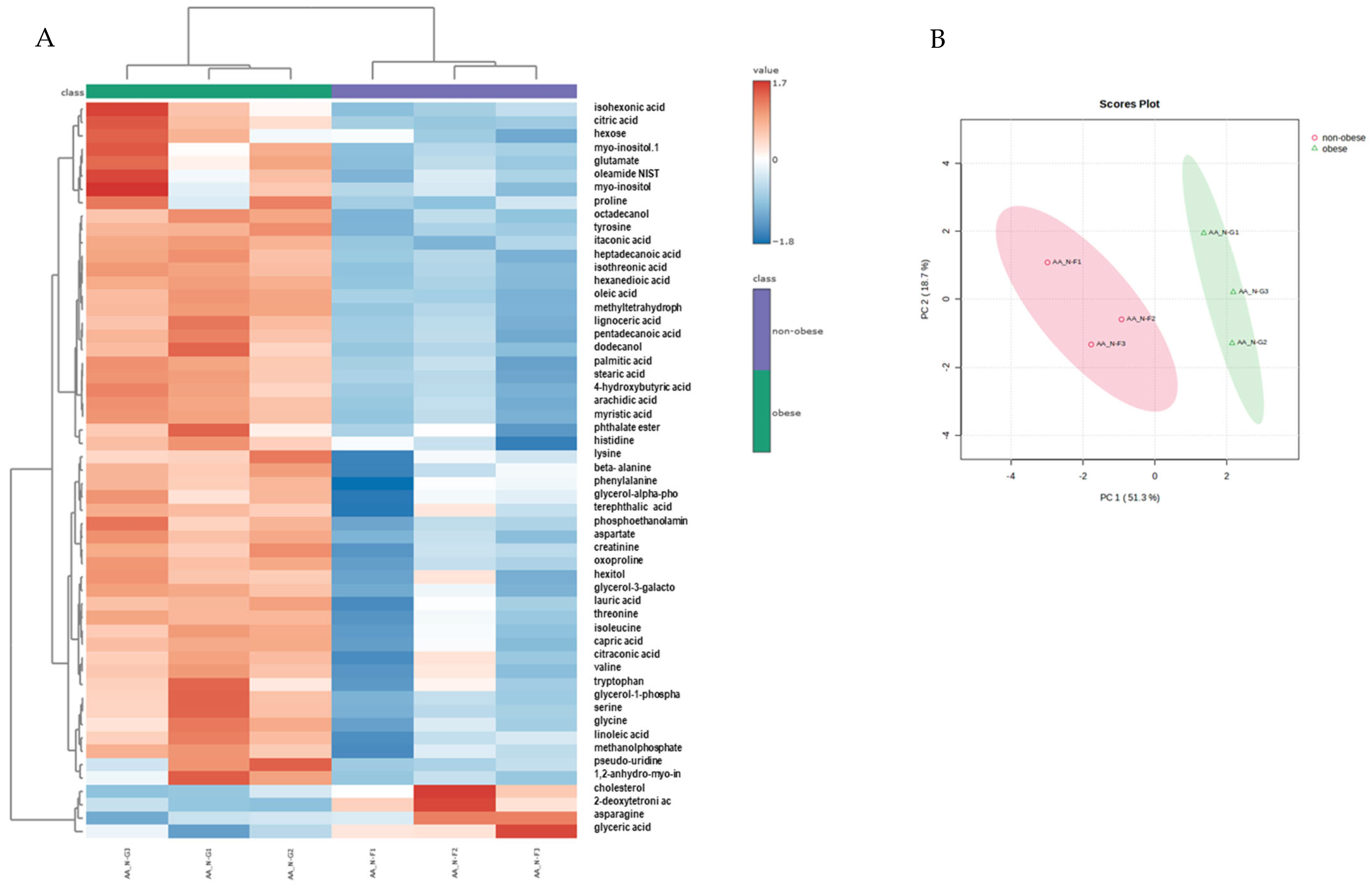
3.2. Neutrophils from Obese Asthmatic Animals Display a Distinct Metabolic Phenotype
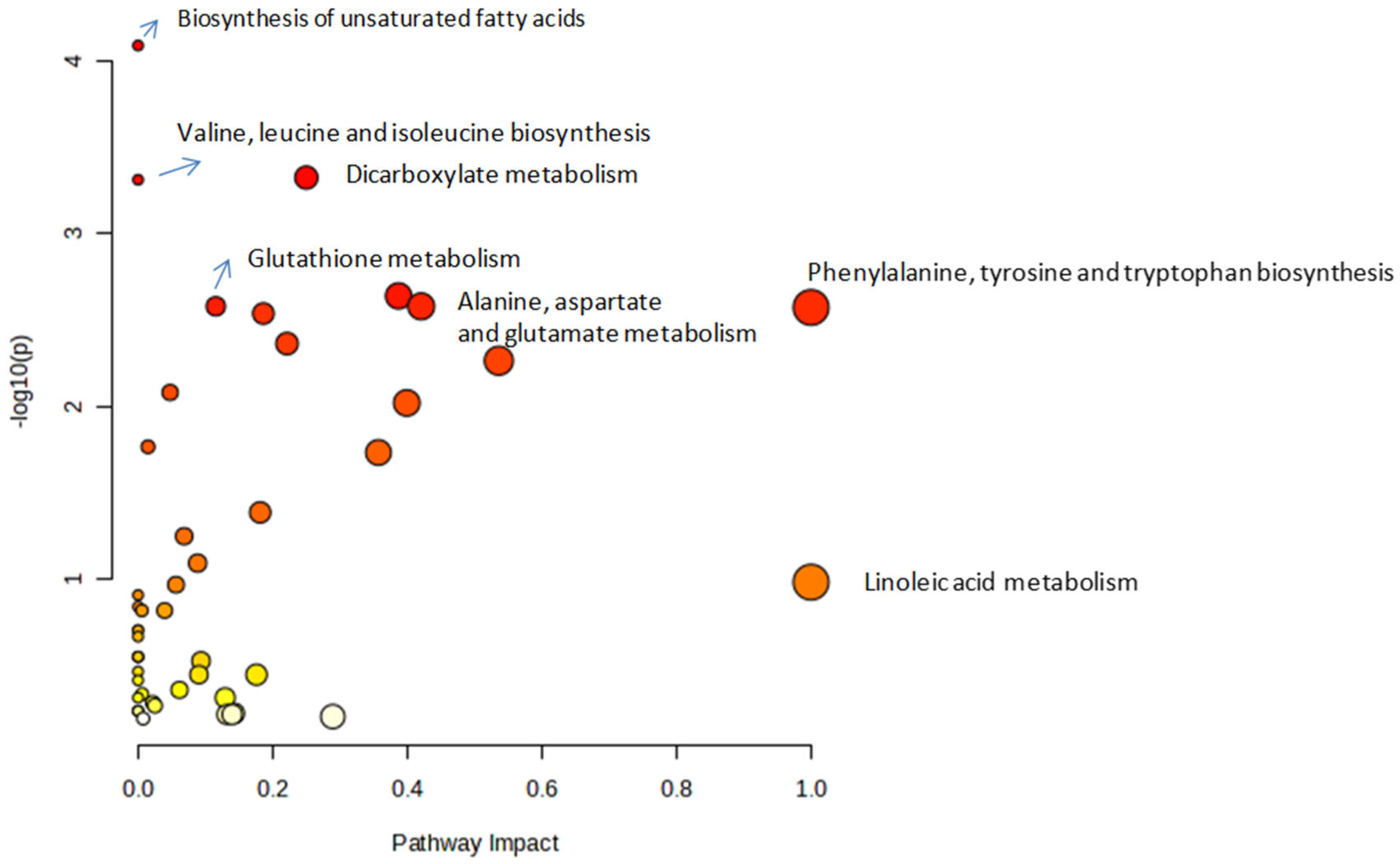
3.3. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
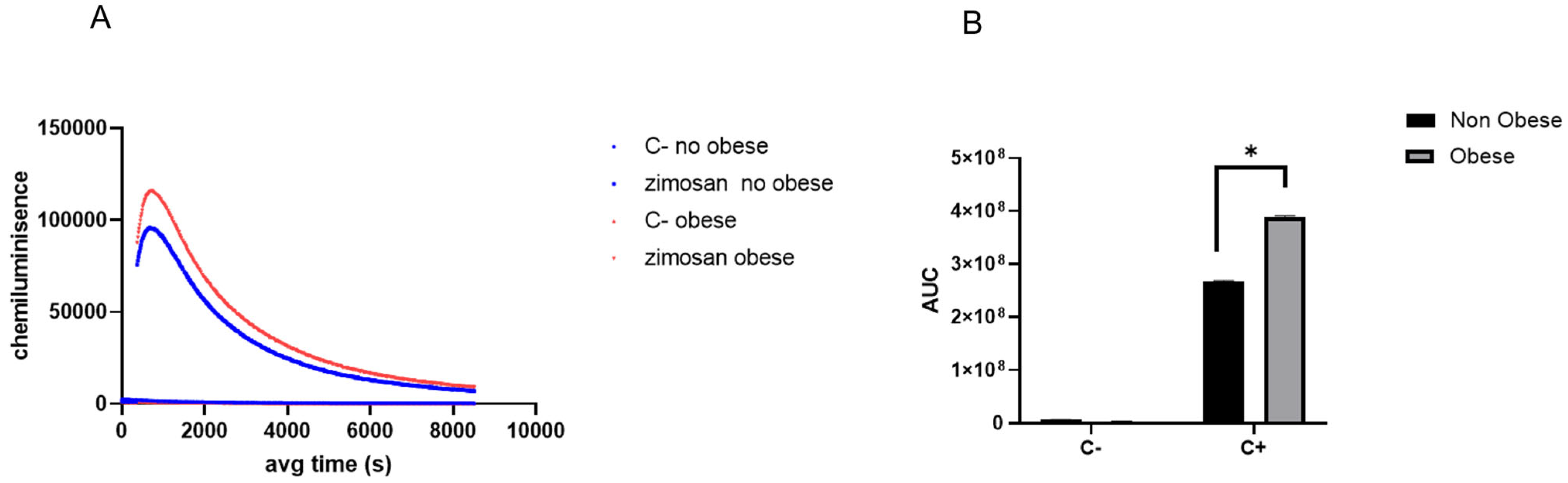
3.4. Neutrophils Isolated from Obese Asthmatic Animals Demonstrate a Heightened Responsiveness to Pro-Inflammatory Stimuli
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Couetil, L.; Cardwell, J.M.; Leguillette, R.; Mazan, M.; Richard, E.; Bienzle, D.; Bullone, M.; Gerber, V.; Ivester, K.; Lavoie, J.P.; et al. Equine Asthma: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullone, M.; Lavoie, J.-P. Asthma “of Horses and Men”—How Can Equine Heaves Help Us Better Understand Human Asthma Immunopathology and Its Functional Consequences? Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirie, R.S.; Couëtil, L.L.; Robinson, N.E.; Lavoie, J.-P. Equine Asthma: An Appropriate, Translational and Comprehendible Terminology? Equine Vet. J. 2016, 48, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.U.; Sheats, M.K. The Role of Neutrophils in the Pathophysiology of Asthma in Humans and Horses. Inflammation 2021, 44, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, N.E. International Workshop on Equine Chronic Airway Disease. Michigan State University 16–18 June 2000. Equine Vet. J. 2001, 33, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, B.; Morán, G. Role of Neutrophils in Equine Asthma. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2018, 19, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, U.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose Tissue Regulates Insulin Sensitivity: Role of Adipogenesis, de Novo Lipogenesis and Novel Lipids. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Llorente, M.A.; Romero, R.; Chueca, N.; Martinez-Cañavate, A.; Gomez-Llorente, C. Obesity and Asthma: A Missing Link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandøe, P.; Palmer, C.; Corr, S.; Astrup, A.; Bjørnvad, C.R. Canine and Feline Obesity: A One Health Perspective. Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosolofski, H.R.; Gow, S.P.; Robinson, K.A. Prevalence of Obesity in the Equine Population of Saskatoon and Surrounding Area. Can. Vet. J. 2017, 58, 967–970. [Google Scholar]
- Wyse, C.A.; McNie, K.A.; Tannahil, V.J.; Murray, J.K.; Love, S. Prevalence of Obesity in Riding Horses in Scotland. Vet. Rec. 2008, 162, 590–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, C.D.; Pleasant, R.S.; Geor, R.J.; Elvinger, F. Prevalence of Overconditioning in Mature Horses in Southwest Virginia during the Summer. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaqueth, A.L.; Iwaniuk, M.E.; Burk, A.O. Characterization of the Prevalence and Management of Over-Conditioned Ponies and Horses in Maryland. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 68, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, A.E. Endocrine Disease in Aged Horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Equine Pract. 2016, 32, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, H.M.; Green, M.J.; Freeman, S.L. Short Communications: Prevalence of Obesity in a Population of Horses in the UK. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantulà, M.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Arismendi, E.; Picado, C. Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Zhang, S.; Willett, W.C.; Speizer, F.E. Prospective Study of Body Mass Index, Weight Change, and Risk of Adult- Onset Asthma in Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2582–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.O.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Montgomery, S.M.; Azima, H. Birth Weight, Body Mass Index and Asthma in Young Adults. Thorax 1999, 54, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, W.S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Xinhua, Y.U.; Iribarren, C.; Dale Williams, O. Asthma Is Associated with Weight Gain in Females but Not Males, Independent of Physical Activity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dales, R.; Tang, M.; Krewski, D. Obesity May Increase the Incidence of Asthma in Women but Not in Men: Longitudinal Observations from the Canadian National Population Health Surveys. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Pekkanen, J.; Laitinen, J.; Järvelin, M.R. Body Build from Birth to Adulthood and Risk of Asthma. Eur. J. Public Health 2002, 12, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.; Sherrill, D.L.; Bobadilla, A.; Martinez, F.D.; Barbee, R.A. The Relation of Body Mass Index to Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema. Chest 2002, 122, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huovinen, E.; Kaprio, J.; Koskenvuo, M. Factors Associated to Lifestyle and Risk of Adult Onset Asthma. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystad, W.; Meyer, H.E.; Nafstad, P.; Tverdal, A.; Engeland, A. Body Mass Index in Relation to Adult Asthma among 135,000 Norwegian Men and Women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, E.S. The Epidemiology of Obesity and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronander, U.N.; Falkenberg, M.; Olle, Z. Prevalence and Incidence of Asthma Related to Waist Circumference and BMI in a Swedish Community Sample. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Behren, J.; Lipsett, M.; Horn-Ross, P.L.; Delfino, R.J.; Gilliland, F.; McConnell, R.; Bernstein, L.; Clarke, C.A.; Reynolds, P. Obesity, Waist Size and Prevalence of Current Asthma in the California Teachers Study Cohort. Thorax 2009, 64, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, V.; de Courten, M.P.J.; Stojanovska, L.; Blatch, G.L.; Tangalakis, K.; de Courten, B. The Complex Immunological and Inflammatory Network of Adipose Tissue in Obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A. Obesity, Adipokines, and Lung Disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Solis, E.; Zee, T.; Emala, C.W.; Vinson, C.; Wess, J.; Karsenty, G. Inhibition of Leptin Regulation of Parasympathetic Signaling as a Cause of Extreme Body Weight-Associated Asthma. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, H.; Shore, S.A. Obesity and Severe Asthma. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, M.; Hsu, J.W.Y.; Zeiger, R.S.; Chen, W.; Dorenbaum, A.; Chipps, B.E.; Haselkorn, T. Phenotypes Determined by Cluster Analysis in Severe or Difficult-to-Treat Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ather, J.L.; Poynter, M.E.; Dixon, A.E. Immunological Characteristics and Management Considerations in Obese Patients with Asthma. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A. The Treatment of Asthma in Obesity. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2012, 6, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Grace, J.; Wang, B.R.; Lugogo, N. The Effects of Obesity in Asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.J.; de Solis, C.N.; Coleman, M.C. Case-Control Study of Risk Factors for Equine Asthma in Texas. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 103, 103644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, K. Immune Cell Metabolism and Metabolic Reprogramming. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 9783–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, S.H.; Wang, L.; Ho, P.C. Metabolic Programming in Dendritic Cells Tailors Immune Responses and Homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Yan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, J.; Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Y. Metabolic Regulation of Dendritic Cell Activation and Immune Function during Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1140749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettel, P.; Weichhart, T. Not Just Sugar: Metabolic Control of Neutrophil Development and Effector Functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024, 116, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Metabolic Plasticity of Neutrophils: Relevance to Pathogen Responses and Cancer. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yipeng, Z.; Chao, C.; Ranran, L.; Tingting, P.; Hongping, Q. Metabolism: A Potential Regulator of Neutrophil Fate. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1500676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, T.; Watts, E.R.; Sadiku, P.; Walmsley, S.R. The Emerging Role for Metabolism in Fueling Neutrophilic Inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 314, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorek, M.; Konečná, B.; Janko, J.; Janovičová, Ľ.; Podracká, Ľ.; Záhumenský, J.; Šteňová, E.; Dúbrava, M.; Hodosy, J.; Vlková, B.; et al. Mitochondria-Induced Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Is Enhanced in the Elderly via Toll-like Receptor 9. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2023, 114, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Sun, H.; Hu, L.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Z. Roles of Mitochondria in Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, S.E.; Mao, S.; Bhalla, M.; Tchalla, E.Y.I.; Kramer, J.M.; Bou Ghanem, E.N. Mitochondrial ROS Production by Neutrophils Is Required for Host Antimicrobial Function against Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Is Controlled by A2B Adenosine Receptor Signaling. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, G.; Moulding, D.A.; Spiller, D.G.; Moots, R.J.; White, M.R.H.; Edwards, S.W. The Mitochondrial Network of Human Neutrophils: Role in Chemotaxis, Phagocytosis, Respiratory Burst Activation, and Commitment to Apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, J.P.; Bullone, M.; Rodrigues, N.; Germim, P.; Albrecht, B.; von Salis-Soglio, M. Effect of Different Doses of Inhaled Ciclesonide on Lung Function, Clinical Signs Related to Airflow Limitation and Serum Cortisol Levels in Horses with Experimentally Induced Mild to Severe Airway Obstruction. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneke, D.R.; Potter, G.D.; Kreider, J.L.; Yeates, B.F. Relationship between Condition Score, Physical Measurements and Body Fat Percentage in Mares. Equine Vet. J. 1983, 15, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, B.; Henriquez, C.; Sarmiento, J.; Morales, N.; Folch, H.; Galesio, J.S.; Uberti, B.; Morán, G. Tamoxifen as a New Therapeutic Tool for Neutrophilic Lung Inflammation. Respirology 2016, 21, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, P.; Hidalgo, A.I.; Manosalva, C.; Cristi, R.; Teuber, S.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A. Metabolic Disturbances in Synovial Fluid Are Involved in the Onset of Synovitis in Heifers with Acute Ruminal Acidosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albornoz, A.; Alarcon, P.; Morales, N.; Uberti, B.; Henriquez, C.; Manosalva, C.; Burgos, R.A.; Moran, G. Metabolomics Analysis of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Samples in Horses with Naturally-Occurring Asthma and Experimentally-Induced Airway Inflammation. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 133, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlone, C.; Morales, N.; Henriquez, C.; Folch, H.; Olave, C.; Sarmiento, J.; Uberti, B.; Moran, G. In Vitro Effects of Tamoxifen on Equine Neutrophils. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 110, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards More Transparent and Integrative Metabolomics Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caër, C.; Rouault, C.; Le Roy, T.; Poitou, C.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Torcivia, A.; Bichet, J.C.; Clément, K.; Guerre-Millo, M.; André, S. Immune Cell-Derived Cytokines Contribute to Obesity-Related Inflammation, Fibrogenesis and Metabolic Deregulation in Human Adipose Tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carobbio, S.; Pellegrinelli, V.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose Tissue Function and Expandability as Determinants of Lipotoxicity and the Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 161–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, C. Is Interleukin-1 b a Culprit in Macrophage-Adipocyte Crosstalk in Obesity? Adipocyte 2015, 4, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, X.; Ibrahim, M.; Peltzer, N. Cell Death and Inflammation during Obesity: “Know My Methods, WAT(Son)”. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, N.S.; Schulthess, F.T.; Galasso, R.; Castellani, L.W.; Maedler, K. The Antiinflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Protects from High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperglycemia. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2208–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, H.; Love, T.; Harrington, D. Blood Neutrophil Count Is Associated with Body Mass Index in Adolescents with Asthma. JSM Allergy Asthma 2018, 3, 1019. [Google Scholar]
- Gállego-Suárez, C.; Bulan, A.; Hirschfeld, E.; Wachowiak, P.; Abrishami, S.; Griffin, C.; Sturza, J.; Tzau, A.; Hayes, T.; Woolford, S.J.; et al. Enhanced Myeloid Leukocytes in Obese Children and Adolescents at Risk for Metabolic Impairment. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thind, M.K.; Uhlig, H.H.; Glogauer, M.; Palaniyar, N.; Bourdon, C.; Gwela, A.; Lancioni, C.L.; Berkley, J.A.; Bandsma, R.H.J.; Farooqui, A. A Metabolic Perspective of the Neutrophil Life Cycle: New Avenues in Immunometabolism. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1334205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, I.R.; Zhang, S.; Ward, L.E.; Karakelides, H.; Raftery, D.; Sreekumaran Nair, K. Quantitative Metabolomics by 1H-NMR and LC-MS/MS Confirms Altered Metabolic Pathways in Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhre, K.; Meisinger, C.; Döring, A.; Altmaier, E.; Belcredi, P.; Gieger, C.; Chang, D.; Milburn, M.V.; Gall, W.E.; Weinberger, K.M.; et al. Metabolic Footprint of Diabetes: A Multiplatform Metabolomics Study in an Epidemiological Setting. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite Profiles and the Risk of Developing Diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, N. Metabolomics in Diabetes Research. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 215, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature That Differentiates Obese and Lean Humans and Contributes to Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newgard, C.B. Interplay between Lipids and Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Development of Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, K.M.; Shah, S.H.; Stevens, R.D.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.; Slentz, C.A.; Tanner, C.J.; Kuchibhatla, M.; Houmard, J.A.; Newgard, C.B.; et al. Relationships between Circulating Metabolic Intermediates and Insulin Action in Overweight to Obese, Inactive Men and Women. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, W.; Gillman, M.W.; Fleisch, A.F.; Michalek, R.D.; Watkins, S.M.; Isganaitis, E.; Patti, M.E.; Oken, E. Metabolomic Profiles and Childhood Obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, N.D.; Stevens, R.D.; Antinozzi, P.A.; Anderson, A.; Bergman, R.N.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Newgard, C.B.; Bowden, D.W. Metabolomic Profile Associated with Insulin Resistance and Conversion to Diabetes in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E463–E468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walford, G.A.; Ma, Y.; Clish, C.; Florez, J.C.; Wang, T.J.; Gerszten, R.E. Metabolite Profiles of Diabetes Incidence and Intervention Response in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtz, P.; Soininen, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Rönnemaa, T.; Lehtimäki, T.; Kähönen, M.; Viikari, J.S.; Raitakari, O.T.; Ala-Korpela, M. Branched-Chain and Aromatic Amino Acidsare Predictors of Insulinresistance in Young Adults. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanweert, F.; Schrauwen, P.; Phielix, E. Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in the Pathogenesis of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes-Related Metabolic Disturbances BCAA Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2022, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; He, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X. Branched Chain Amino Acids: Beyond Nutrition Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, R.L.; Chantranupong, L.; Saxton, R.A.; Shen, K.; Scaria, S.M.; Cantor, J.R.; Sabatini, D.M. Sestrin2 Is a Leucine Sensor for the MTORC1 Pathway. Science 2016, 351, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Immunity. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 288S–293S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Kong, W.; Zeng, T. Itaconate: A Potent Macrophage Immunomodulator. Inflammation 2023, 46, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Artyomov, M.N. Itaconate: The Poster Child of Metabolic Reprogramming in Macrophage Function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peace, C.G.; O’Neill, L.A.J. The Role of Itaconate in Host Defense and Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e148548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Bambouskova, M.; Nair, S.; Vincent, E.E.; Loginicheva, E.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Ma, X.; Huang, S.C.C.; Griss, T.; et al. Itaconate Links Inhibition of Succinate Dehydrogenase with Macrophage Metabolic Remodeling and Regulation of Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate Is an Anti-Inflammatory Metabolite That Activates Nrf2 via Alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambouskova, M.; Gorvel, L.; Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Loginicheva, E.; Johnson, K.; Korenfeld, D.; Mathyer, M.E.; Kim, H.; Huang, L.H.; et al. Electrophilic Properties of Itaconate and Derivatives Regulate the IκBζ-ATF3 Inflammatory Axis. Nature 2018, 556, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooftman, A.; Angiari, S.; Hester, S.; Corcoran, S.E.; Runtsch, M.C.; Ling, C.; Ruzek, M.C.; Slivka, P.F.; McGettrick, A.F.; Banahan, K.; et al. The Immunomodulatory Metabolite Itaconate Modifies NLRP3 and Inhibits Inflammasome Activation. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 468–478.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, K.L.; Riquelme, S.A.; Baskota, S.U.; Drikic, M.; Monk, I.R.; Stinear, T.P.; Lewis, I.A.; Prince, A.S. Staphylococcus aureus Stimulates Neutrophil Itaconate Production That Suppresses the Oxidative Burst. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wen, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, H.; Ding, N.; et al. Suppressing Neutrophil Itaconate Production Attenuates Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossley, J.L.; Ostashevskaya-Gohstand, S.; Comazzetto, S.; Hook, J.S.; Guo, L.; Vishlaghi, N.; Juan, C.; Xu, L.; Horswill, A.R.; Hoxhaj, G.; et al. Itaconate-Producing Neutrophils Regulate Local and Systemic Inflammation Following Trauma. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e169208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohnert, B.I.; Jacobs, D.R.; Steinberger, J.; Moran, A.; Steffen, L.M.; Sinaiko, A.R. Relation between Serum Free Fatty Acids and Adiposity, Insulin Resistance, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors from Adolescence to Adulthood. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, P.; Manosalva, C.; Quiroga, J.; Belmar, I.; Álvarez, K.; Díaz, G.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Carretta, M.D.; Burgos, R.A.; et al. Oleic and Linoleic Acids Induce the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps via Pannexin 1-Dependent ATP Release and P2X1 Receptor Activation. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Pace-Asciak, C.; Al-Hassan, J.M.; Afzal, M.; Liu, Y.F.; Oommen, S.; Paul, B.M.; Nair, D.; Palaniyar, N. Furanoid F-Acid F6 Uniquely Induces NETosis Compared to C16 and C18 Fatty Acids in Human Neutrophils. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.G.; Vinolo, M.A.R.; Magdalon, J.; Fujiwara, H.; Cavalcanti, D.M.H.; Farsky, S.H.P.; Calder, P.C.; Hatanaka, E.; Curi, R. Dietary Free Oleic and Linoleic Acid Enhances Neutrophil Function and Modulates the Inflammatory Response in Rats. Lipids 2010, 45, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanten, G.J.A.; Janssen, F.P.; Naber, A.H.J. Saturated Triglycerides and Fatty Acids Activate Neutrophils Depending on Carbon Chain-Length. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, E.; Entrup, G.P.; Islam, M.; Mohan, R.; Lerner, A.; Mancuso, P.; Moore, B.B.; Singer, K. High Fat Diet Feeding Impairs Neutrophil Phagocytosis, Bacterial Killing, and Neutrophil-Induced Hematopoietic Regeneration. J. Immunol. 2025, 214, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotfain, E.; Hadad, N.; Shapira, Y.; Avinoah, E.; Zlotnik, A.; Raichel, L.; Levy, R. Neutrophil Functions in Morbidly Obese Subjects. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-pino, M.D.; Richardson, W.S.; Zabaleta, J.; Puttalingaiah, T.; Chapple, A.G.; Liu, J.; Kim, Y.; Ponder, M.; Dearmitt, R.; Baiamonte, B.; et al. Articles Increased in Fl Ammatory Low-Density Neutrophils in Severe Obesity and Effect of Bariatric Surgery: Results from Case-Control and Prospective Cohort Studies. eBioMedicine 2022, 77, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Querol, E.; Rosales, C. Neutrophils Actively Contribute to Obesity-Associated Inflammation and Pathological Complications. Cells 2022, 11, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albornoz, A.; Morales, B.; Fernandez, V.B.; Henriquez, C.; Quiroga, J.; Alarcón, P.; Moran, G.; Burgos, R.A. Obesity-Associated Metabolomic and Functional Reprogramming in Neutrophils from Horses with Asthma. Animals 2025, 15, 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131992
Albornoz A, Morales B, Fernandez VB, Henriquez C, Quiroga J, Alarcón P, Moran G, Burgos RA. Obesity-Associated Metabolomic and Functional Reprogramming in Neutrophils from Horses with Asthma. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131992
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbornoz, Alejandro, Beatriz Morales, Valentina Bernal Fernandez, Claudio Henriquez, John Quiroga, Pablo Alarcón, Gabriel Moran, and Rafael A. Burgos. 2025. "Obesity-Associated Metabolomic and Functional Reprogramming in Neutrophils from Horses with Asthma" Animals 15, no. 13: 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131992
APA StyleAlbornoz, A., Morales, B., Fernandez, V. B., Henriquez, C., Quiroga, J., Alarcón, P., Moran, G., & Burgos, R. A. (2025). Obesity-Associated Metabolomic and Functional Reprogramming in Neutrophils from Horses with Asthma. Animals, 15(13), 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131992




