Dietary Administration of Postbiotics from Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 Enhanced Intestinal Integrity, Microbiota, and Immune Response in Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Extracellular Product (ECPs) Extraction
2.2. Experimental Diets
2.3. Feeding Trial
2.4. Immunological Challenge
2.5. Fish Sampling
2.6. Intestine Histology
2.7. Ultrastructural Study of the Intestinal Mucosa
2.8. Microbiota Analysis from the Fish Gut
2.9. Gene Expression Evaluation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
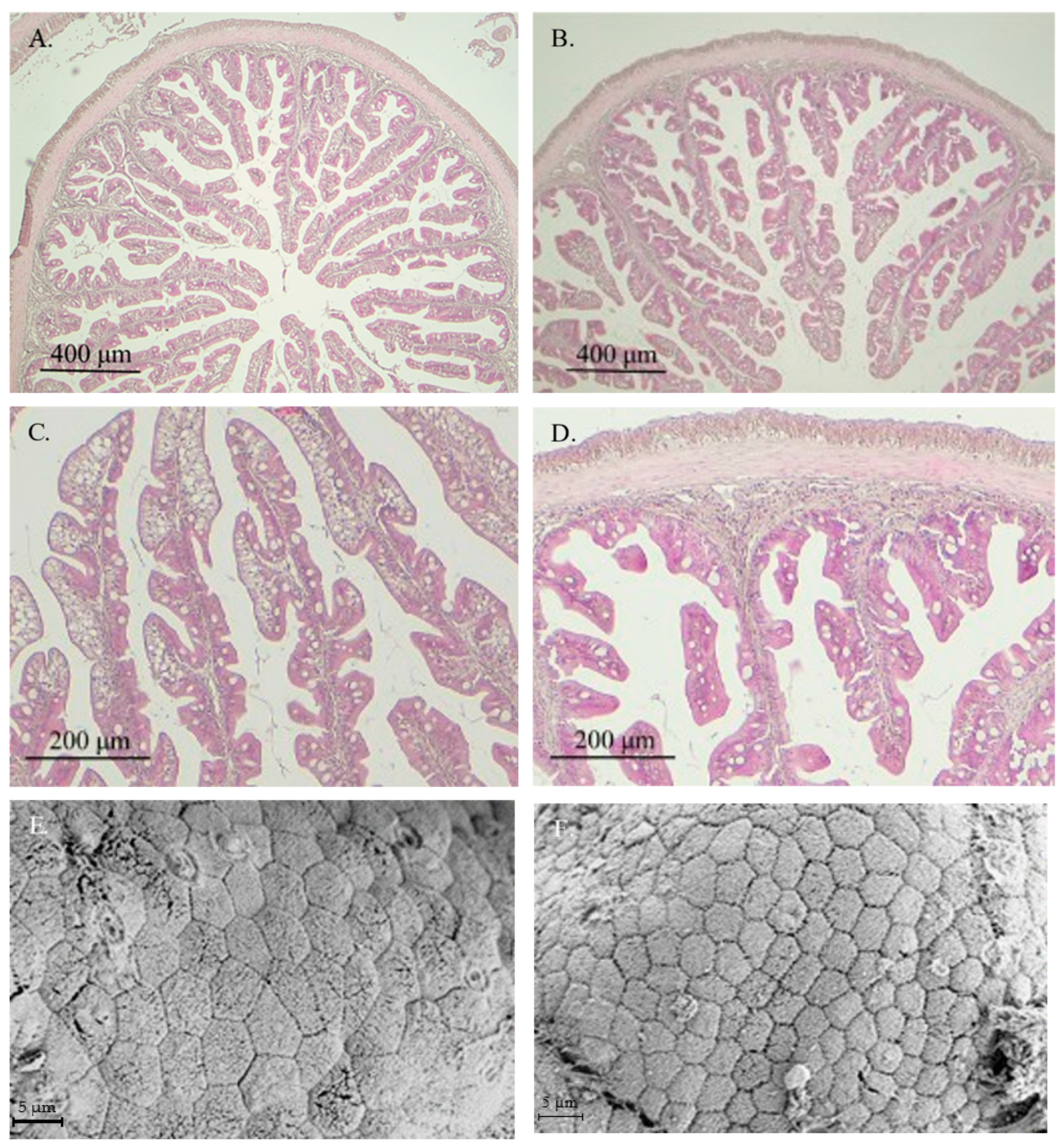
3.1. Effect of ECPs on Intestinal Histology and Ultrastructure
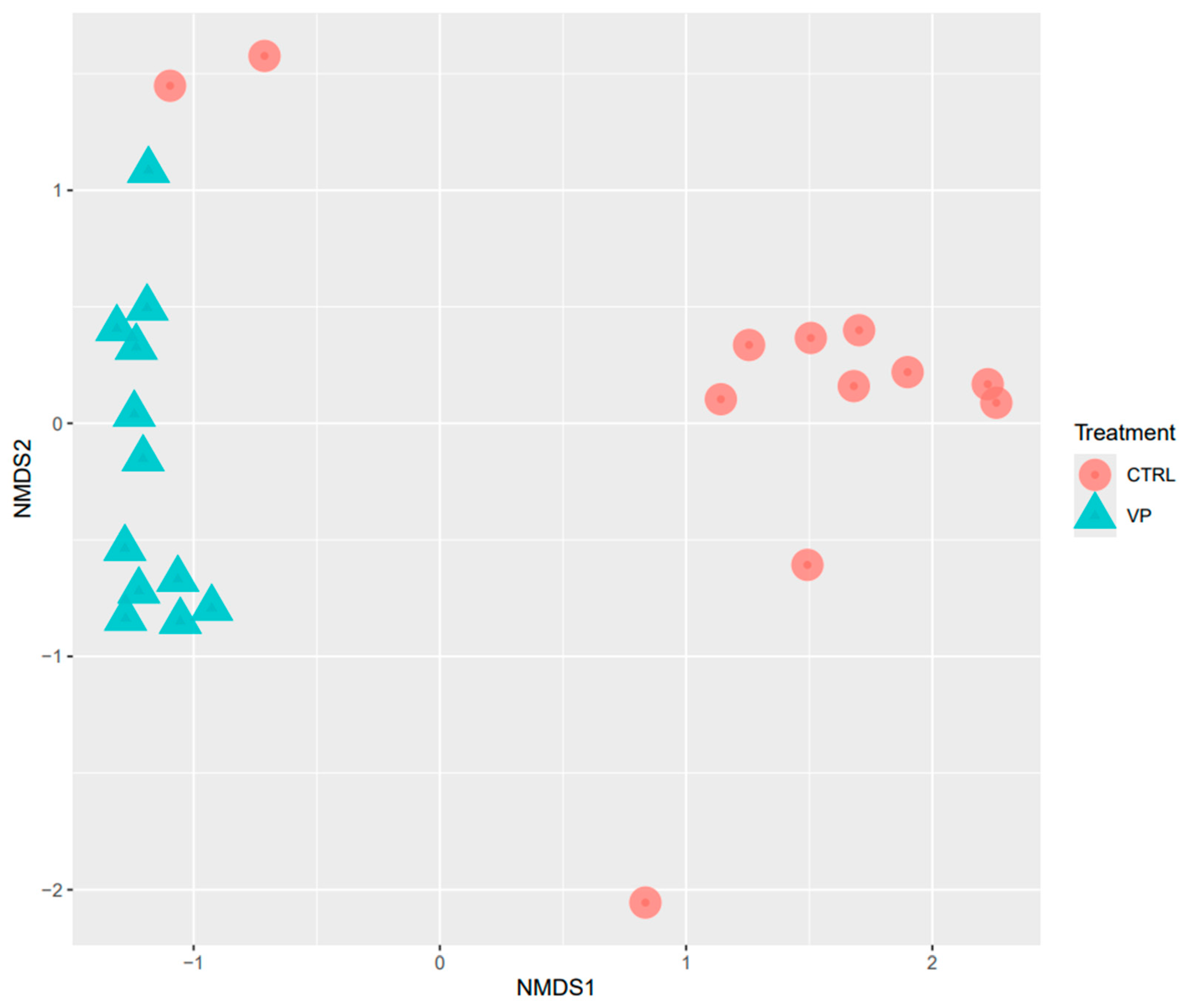
3.2. Effect of ECPs on Intestinal Microbiota
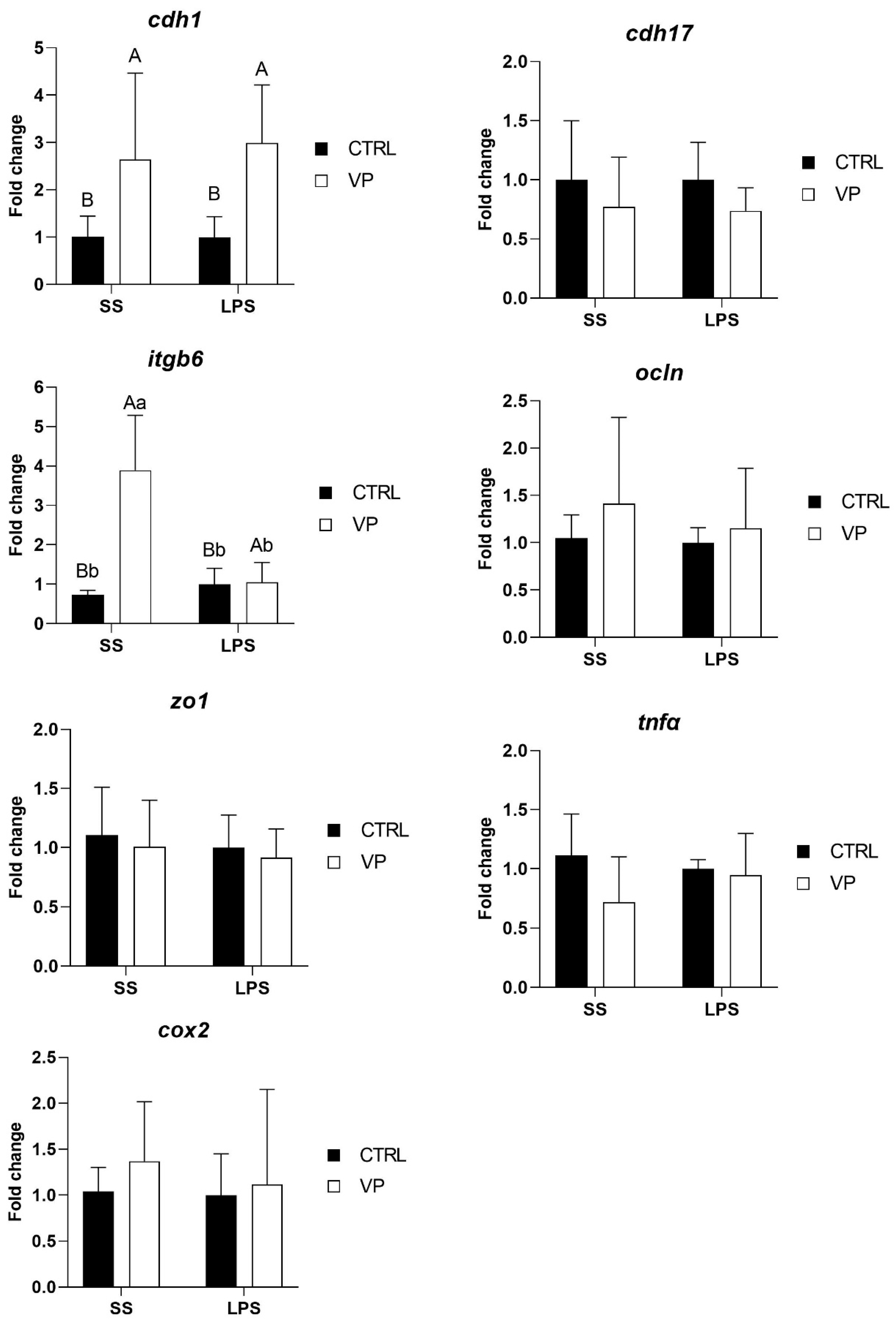
3.3. Influence of ECPs on Intestinal Gene Expression
3.4. Effect of LPS Challenge on Intestinal Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ISAPP | International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics |
| UTHSCSA | University of Texas Health Sciences Center, San Antonio |
| SCI-CM | Servicios Centrales de Investigación en Cultivos Marinos |
| ECPs | Extracellular Product |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| CRTL | Control |
| VP | Vibrio proteolyticus |
| qPCR | Quantitative PCR |
| TSA | Tryptic soy agar |
| TSB | Tryptic soy broth |
| CFU | Colony-Forming Unit |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| EA | Apical area of enterocytes |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| ASVs | Amplicon sequence variants |
| Cq | Quantification Cycle |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| FL | Fold length |
| EH | Enterocyte height |
| LP | Lamina propria |
| ML | Muscular layer |
| SBL | Submucosa layer thickness |
| GC | Goblet cells |
| AE | Enterocyte apical area |
| NMDS plot | Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling plot |
| NA | Not assigned |
References
- Naeem, M.; Salam, A.; Tahir, S.S.; Rauf, N. Assessment of the essential element and toxic heavy metals in hatchery reared Oncorhynchus mykiss. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 935–938. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, M.; Salam, A.; Zuberi, A. Proximate composition of freshwater rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in relation to body size and condition factor from Pakistan. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 53, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Ismat, N.; Ashraf, M.; Naeem, M.; Rehman, M.H.U. Effect of different feed ingredients on growth and level of intestinal enzyme secretions in juvenile Labeo rohita, Catla catla, Cirrhinus mrigala, and Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Int. J. Aquac. 2013, 3, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Madhulika, M.M.; Deepti, M.; Ngasotter, S.; Gupta, S.S.; Varghese, T. Functional Feed Additives in Aquaculture to Improve Food Security. In Food Security, Nutrition and Sustainability Through Aquaculture Technologies; Sundaray, J.K., Rather, M.A., Ahmad, I., Amin, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 375–396. ISBN 978-3-031-75830-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, S.; Ishtiaq, A.; Ghaffar, A.; Ishtiaq, T.; Naeem, M. Impact of in-feed Multispecies Probiotic Mixtures on Growth Patterns and Length-weight Relationships of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. TSF J. Biol. 2025, 3, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Van Doan, H. Probiotic application for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Taufek, N.M.; Thiran, J.P.; Rahman, J.F.P.; Yerima, G.; Subramaniam, K.; Rowan, N. Investigations on the use of exopolysaccharide derived from mycelial extract of Ganoderma lucidum as functional feed ingredient for aquaculture-farmed red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis sp.). Future Foods 2021, 3, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Arijo, S. Selection of putative probiotics based on antigen-antibody cross-reaction with Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida and Vibrio harveyi for use in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; García-Márquez, J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Arijo, S. Effect of the potential probiotic Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 on the immune system of Solea senegalensis and protection against Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida and Vibrio harveyi. Fishes 2023, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucko, J.; Starcevic, A.; Diminic, J.; Oros, D.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Putnik, P. Probiotic—Friend or foe? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Molaei, R.; Guimarães, J.T. A review on preparation and chemical analysis of postbiotics from lactic acid bacteria. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2021, 143, 109722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Espinosa-Ruíz, C.; Esteban, M.Á.; Alarcón, F.J.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.Á. An ex vivo approach in European seabass leucocytes supports the in vitro regulation by postbiotics of Aip56 gene expression of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, H.; Divsalar, E.; Rezaei, Z.; Liu, S.Q.; Moradi, M. The potential of postbiotics as a novel approach in food packaging and biopreservation: A systematic review of the latest developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 12524–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Duan, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. The effect of Lactobacillus plantarum administration on the intestinal microbiota of whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Sun, Y.Z.; Hu, X.; Ye, J.-D.; Lu, K.L.; Hu, L.H.; Zhang, J.J. Bacillus pumilus SE5 originated PG and LTA tuned the intestinal TLRs/MyD88 signaling and microbiota in grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Márquez, J.; Díaz, A.G.; Molina-Roque, L.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; de las Heras, V.; Simó-Mirabet, P.; Vizcaíno, A.J.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Alarcón-López, F.J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; et al. Microalgal and Cyanobacterial Biomasses Modified the Activity of Extracellular Products from Bacillus pumilus: An In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, G.; Sanders, M.E.; Cunningham, M.; Hill, C. Frequently Asked Questions about the ISAPP Postbiotic Definition. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1324565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O. Nutritional Immunity of Fish Intestines: Important Insights for Sustainable Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.V. Survey of Hemolysin Production among Species of Pseudomonads. J. Bacteriol. 1957, 74, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; 1st revision; Association of Official Analytical Communities: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escaffre, A.M.; Kaushik, S.; Mambrini, M. Morphometric Evaluation of Changes in the Digestive Tract of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Due to Fish Meal Replacement with Soy Protein Concentrate. Aquaculture 2007, 273, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaíno, A.J.; López, G.; Sáez, M.I.; Jiménez, J.A.; Barros, A.; Hidalgo, L.; Camacho-Rodríguez, J.; Martínez, T.F.; Cerón-García, M.C.; Alarcón, F.J. Effects of the Microalga Scenedesmus almeriensis as Fishmeal Alternative in Diets for Gilthead Sea Bream, Sparus aurata, Juveniles. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, G.; Shaw, E.M.; Carrillo, M.; Zanuy, S. Protein Salting-out Method Applied to Genomic DNA Isolation from Fish Whole Blood. Biotechniques 1998, 24, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Chabrillón, M.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; de la Banda, I.G.; Lobo, C.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A. Intestinal Microbiota Diversity of the Flat Fish Solea senegalensis (Kaup, 1858) Following Probiotic Administration. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC—A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Babraham Bioinformatics. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.M.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. The Vegan Package. In Community Ecology Package: 190; 2008; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258996522_The_vegan_Package_Community_Ecology_Package_version_113-1 (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Benedito-Palos, L.; Estensoro, I.; Petropoulos, Y.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Browdy, C.L.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Effects of Dietary NEXT ENHANCE®150 on Growth Performance and Expression of Immune and Intestinal Integrity Related Genes in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezuela, R.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. Effects of Dietary Inulin, Bacillus Subtilis and Microalgae on Intestinal Gene Expression in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, G.; Collado, M.C.; Monge-Ortiz, R.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Peñaranda, D.S.; Pérez Martínez, G.; Martínez-Llorens, S. Long-Term Feeding with High Plant Protein Based Diets in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) Leads to Changes in the Inflammatory and Immune Related Gene Expression at Intestinal Level. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerezo-Ortega, I.M.; Di Zeo-Sánchez, D.E.; García-Márquez, J.; Ruiz-Jarabo, I.; Sáez-Casado, M.I.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T. Microbiota Composition and Intestinal Integrity Remain Unaltered after the Inclusion of Hydrolysed Nannochloropsis gaditana in Sparus aurata Diet. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, S.; Saikia, S.K. Absorption of Protein in Teleosts: A Review. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, B.; Deng, J.; Dong, X.; Yang, Q.; Chi, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Xie, S.; Zhang, H. Effects of High Level of Fermented Soybean Meal Substitution for Fish Meal on the Growth, Enzyme Activity, Intestinal Structure Protein and Immune-Related Gene Expression and Intestinal Flora in Juvenile Pearl Gentian Grouper. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 1433–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, G.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M. Histomorphological Changes in Fish Gut in Response to Prebiotics and Probiotics Treatment to Improve Their Health Status: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Castro, L.F.C. Morphological Diversity of the Gastrointestinal Tract in Fishes. Fish Physiol. 2010, 30, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, C. The Relationship between Intestinal Goblet Cells and the Immune Response. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Sánchez, B.; Balcázar, J.L.; Pérez-Sánchez, T. Effect of a Novel Postbiotic Containing Lactic Acid Bacteria on the Intestinal Microbiota and Disease Resistance of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Mora-Sánchez, B.; Vargas, A.; Balcázar, J.L. Changes in Intestinal Microbiota and Disease Resistance Following Dietary Postbiotic Supplementation in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante-Villamil, S.; Huerlimann, R.; Jerry, D.R. Microbiome Diversity and Dysbiosis in Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1077–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukgehnaish, K.; Kumar, P.; Sivachandran, P.; Marimuthu, K.; Arshad, A.; Paray, B.A.; Arockiaraj, J. Gut Microbiota Metagenomics in Aquaculture: Factors Influencing Gut Microbiome and Its Physiological Role in Fish. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1903–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, K.A.; Meziti, A.; Mente, E.; Frentzos, A. Dietary Differences Are Reflected on the Gut Prokaryotic Community Structure of Wild and Commercially Reared Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). MicrobiologyOpen 2014, 3, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikouli, E.; Meziti, A.; Antonopoulou, E.; Mente, E.; Kormas, K.A. Gut Bacterial Communities in Geographically Distant Populations of Farmed Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) and Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Microorganisms 2018, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, B.; Wityk, P.; Gałęcka, M.; Michalik, M. The Many Faces of Enterococcus spp. Commensal, Probiotic and Opportunistic Pathogen. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukułowicz, A.; Steinka, I.; Gardocka, M. Enterococcus spp. in Fish: Analysis of the Presence and Resistance in Samples from Tri-City, Poland. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, M.; Yin, X.; Liang, M.; Lou, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Fan, D.; Shi, L.; et al. The Potential Mechanism of BPF-Induced Neurotoxicity in Adult Zebrafish: Correlation between Untargeted Metabolomics and Gut Microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morya, R.; Salvachúa, D.; Thakur, I.S. Burkholderia: An Untapped but Promising Bacterial Genus for the Conversion of Aromatic Compounds. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.G. Polysaccharide Degradation Systems of the Saprophytic Bacterium Cellvibrio japonicus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Lu, J.; Sun, Z.; Xie, J.; Huang, J.; Su, M.; Wu, N. Characterization of Tissue-Associated Bacterial Community of Two Bathymodiolus Species from the Adjacent Cold Seep and Hydrothermal Vent Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Al-saari, N.; Mohamad, A.; Mursidi, F.A.; Mohd-Aris, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Kasai, H.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T.; Zamri-Saad, M. Vibriosis in Fish: A Review on Disease Development and Prevention. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev, Y.; Davidovich, N.; Berzak, R.; Lau, S.C.K.; Scheinin, A.P.; Tchernov, D.; Morick, D. Molecular Identification and Characterization of Vibrio Species and Mycobacterium Species in Wild and Cultured Marine Fish from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Márquez, J.; Álvarez-Torres, D.; Cerezo, I.M.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Figueroa, F.L.; Alarcón, F.J.; Acién, G.; Martínez-Manzanares, E.; Abdala-Díaz, R.T.; Béjar, J.; et al. Combined Dietary Administration of Chlorella Fusca and Ethanol-Inactivated Vibrio proteolyticus Modulates Intestinal Microbiota and Gene Expression in Chelon Labrosus. Animals 2023, 13, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, F.; Jawahar Abraham, T.; Nagesh, T.S.; Kamilya, D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa FARP72 Offers Protection Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection in Labeo rohita. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielko, K.A.; Jabłoński, S.J.; Milczewska, J.; Sands, D.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Młynarz, P. Metabolomic Studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Jun, J.W.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.W.; Woo, K.J.; Han, S.J.; Oh, W.T.; Kwon, J.; et al. Effects of Dietary Heat-Killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain VSG2 on Immune Functions, Antioxidant Efficacy, and Disease Resistance in Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 2020, 514, 734489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y. Low Fish Meal Diet Supplemented with Probiotics Ameliorates Intestinal Barrier and Immunological Function of Macrobrachium Rosenbergii via the Targeted Modulation of Gut Microbes and Derived Secondary Metabolites. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1074399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zeng, J.; Suo, N.; Ke, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Dynamic Changes in Gut Microbiota and Production Phenotypes Driven by Host Genetic Background in Large Yellow Croaker. Aquaculture 2025, 598, 741948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sham, R.C.; Deng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Leung, K.M.Y. Diversity of Gut Microbiomes in Marine Fishes Is Shaped by Host-Related Factors. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 5019–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galand, P.E.; Pereira, O.; Hochart, C.; Auguet, J.C.; Debroas, D. A Strong Link between Marine Microbial Community Composition and Function Challenges the Idea of Functional Redundancy. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and Functional Redundancy in Microbial Systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartsock, A.; Nelson, W.J. Adherens and Tight Junctions: Structure, Function and Connections to the Actin Cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, C.T.; Powell, D.N.; Kalman, D. Layered Defense: How Mucus and Tight Junctions Seal the Intestinal Barrier. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barany, A.; Fuentes, J.; Martínez-Rodríguez, G.; Mancera, J.M. Aflatoxicosis Dysregulates the Physiological Responses to Crowding Densities in the Marine Teleost Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Animals 2021, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Márquez, J.; Álvarez-Torres, D.; Cerezo, I.M.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Acién, G.; Alarcón-López, F.J.; Figueroa, F.L.; Martínez-Manzanares, E.; Abdala-Díaz, R.T.; Béjar, J.; et al. Effects of Chlorella fusca-Supplemented Diet on Intestinal Microbiota and Gene Expression Related to Metabolism, Stress, and Immune Response in Chelon labrosus. Algal Res. 2024, 77, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, J.R.; Bakhle, Y.S.; Botting, R.M. Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1998, 38, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bonaventura, G.; Pompilio, A.; Zappacosta, R.; Petrucci, F.; Fiscarelli, E.; Rossi, C.; Piccolomini, R. Role of Excessive Inflammatory Response to Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Lung Infection in DBA/2 Mice and Implications for Cystic Fibrosis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 2466–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, R.M.; DeFoor, W.M.; Goller, C.C.; Ott, L.E. Delftia spp. Elicit a Pro-Inflammatory Response in Monocytes. J. Young Investig. 2015, 29, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Sánchez, J.C.; Esteban, M.Á. Review of Inflammation in Fish and Value of the Zebrafish Model. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meecham, A.; Marshall, J.F. The ITGB6 Gene: Its Role in Experimental and Clinical Biology. Gene X 2020, 5, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ingredient (% Dry Basis) | CTRL | VP |
|---|---|---|
| Fishmeal LT94 1 | 20.0 | 20.0 |
| Lysine 2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Methionine 3 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Squid meal 4 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| CPSP90 5 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Krill meal 6 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Wheat gluten 7 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Soybean protein concentrate 8 | 8.5 | 8.5 |
| Soybean meal 9 | 8.5 | 8.5 |
| Pea protein concentrate 10 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| Fish oil 11 | 9.7 | 9.7 |
| Vegetable oil 12 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Soybean lecithin 13 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Wheat meal 14 | 25.0 | 25.0 |
| Monocalcium phosphate 15 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Vitamin and Mineral premix 16 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Vitamin C 17 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| ECPs from V. proteolyticus (mL) 18 | 0 | 1 |
| Crude protein | 48.5 | 49.5 |
| Crude lipid | 17.5 | 17.1 |
| Ash | 7.0 | 7.6 |
| Moisture | 5.8 | 5.7 |
| Product Gene | Code | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Permeability and integrity | ||
| Cadherin 1 | cdh1 | Pérez-Sánchez et al. [33] |
| Cadherin 17 | cdh17 | Pérez-Sánchez et al. [33] |
| Integrin 6-β | itgb6 | Pérez-Sánchez et al. [33] |
| Ocludin | ocln | Pérez-Sánchez et al. [33] |
| Zonula-occludens 1 | tjp1 | Cerezuela et al. [34] |
| Pro-inflammatory | ||
| Tumor necrosis factor α | tnfα | Estruch et al. [35] |
| Cyclooxygenase 2 | cox2 | Estruch et al. [35] |
| Reference genes | ||
| Elongation factor 1α | ef1α | Estruch et al. [35] |
| Ribosomal glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | gadph | Estruch et al. [35] |
| CTRL | VP | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FL (µm) | 805.92 ± 124.96 | 508.61 ± 69.82 * | <0.0001 |
| EH (µm) | 37.67 ± 5.94 | 21.41 ± 3. 53 * | <0.0001 |
| LP (µm) | 25.71 ± 6.59 | 19.01 ± 4.66 * | <0.0001 |
| ML (µm) | 38.82 ± 10.01 | 25.15 ± 4.69 * | <0.0001 |
| SBL (µm) | 26.69 ± 9.84 | 19.74 ± 4.66 * | <0.0001 |
| GC | 6.99 ± 1.22 | 9.47 ± 1.67 * | <0.0001 |
| AE | 26.94 ± 3.25 | 14.97 ± 2.16 * | <0.0001 |
| CTRL | VP | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | 330.30 ± 116.10 | 277.00 ± 93.14 | 0.2364 |
| Shannon | 2.14 ± 0.51 | 3.30 ± 0.70 * | 0.0183 |
| Simpson | 0.64 ± 0.23 | 0.92 ± 0.02 * | 0.0019 |
| Two-Way ANOVA | Diet | Challenge | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| cdh1 | 0.0009 * | 0.7113 | 0.6878 |
| cdh17 | 0.1247 | 0.9168 | 0.9347 |
| itgb6 | 0.0001 * | 0.0009 * | 0.0002 * |
| ocln | 0.2774 | 0.5258 | 0.6579 |
| zo1 | 0.5172 | 0.4938 | 0.9581 |
| tnfα | 0.0993 | 0.6587 | 0.2032 |
| cox2 | 0.4194 | 0.5972 | 0.7003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Gómez, O.; Rohra-Benítez, S.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Cerezo, I.M.; Galafat, A.; Martínez-Manzanares, E.; Mancera, J.M.; Alarcón-López, F.J.; García-Márquez, J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; et al. Dietary Administration of Postbiotics from Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 Enhanced Intestinal Integrity, Microbiota, and Immune Response in Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Animals 2025, 15, 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131982
Pérez-Gómez O, Rohra-Benítez S, Domínguez-Maqueda M, Cerezo IM, Galafat A, Martínez-Manzanares E, Mancera JM, Alarcón-López FJ, García-Márquez J, Moriñigo MÁ, et al. Dietary Administration of Postbiotics from Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 Enhanced Intestinal Integrity, Microbiota, and Immune Response in Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Animals. 2025; 15(13):1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131982
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Gómez, Olivia, Sonia Rohra-Benítez, Marta Domínguez-Maqueda, Isabel M. Cerezo, Alba Galafat, Eduardo Martínez-Manzanares, Juan Miguel Mancera, Francisco Javier Alarcón-López, Jorge García-Márquez, Miguel Ángel Moriñigo, and et al. 2025. "Dietary Administration of Postbiotics from Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 Enhanced Intestinal Integrity, Microbiota, and Immune Response in Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata)" Animals 15, no. 13: 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131982
APA StylePérez-Gómez, O., Rohra-Benítez, S., Domínguez-Maqueda, M., Cerezo, I. M., Galafat, A., Martínez-Manzanares, E., Mancera, J. M., Alarcón-López, F. J., García-Márquez, J., Moriñigo, M. Á., & Arijo, S. (2025). Dietary Administration of Postbiotics from Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 Enhanced Intestinal Integrity, Microbiota, and Immune Response in Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Animals, 15(13), 1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131982







