Integrated Microbiome–Metabolome Analysis Reveals Intestine–Liver Metabolic Associations in the Moustache Toad
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
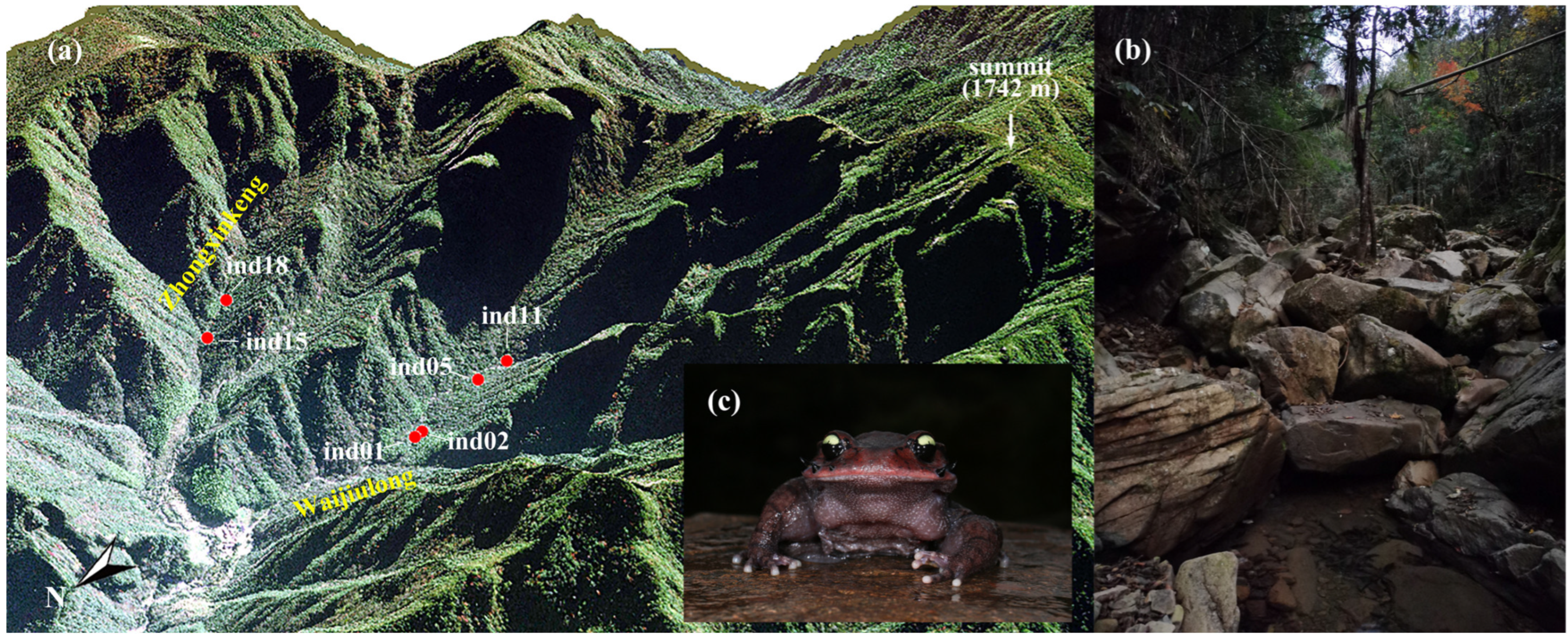
2.1. Intestinal Content and Liver Tissue Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.3. Analysis of the Intestinal Microbial Data
2.4. Hepatic Metabolite Extraction and Quality Control (QC)
2.5. Identification and Analysis of Hepatic Metabolites
2.6. Microbiota–Metabolome Correlation Analysis
2.7. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Data
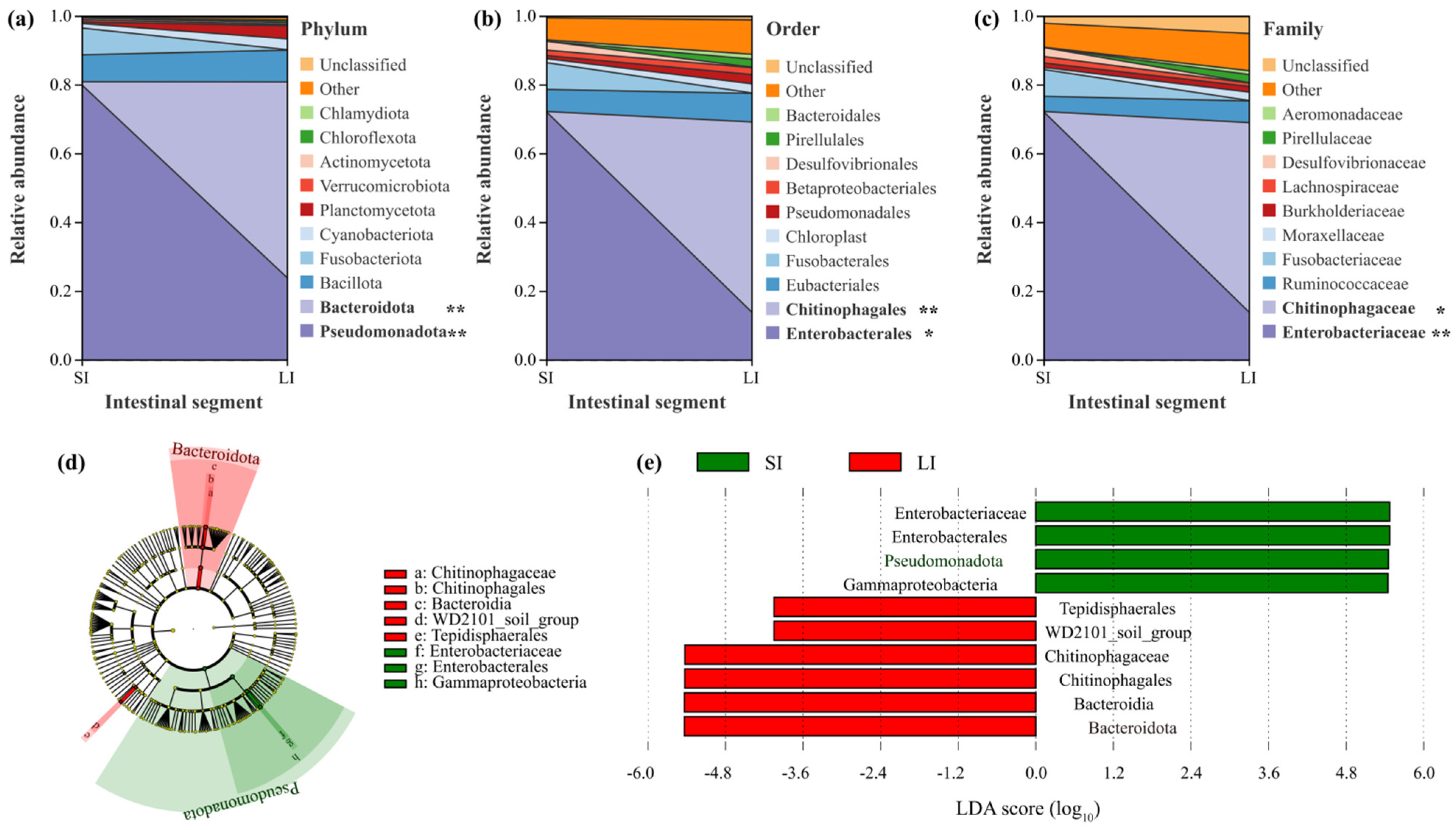
3.2. Microbial Composition Between the Two Intestinal Compartments
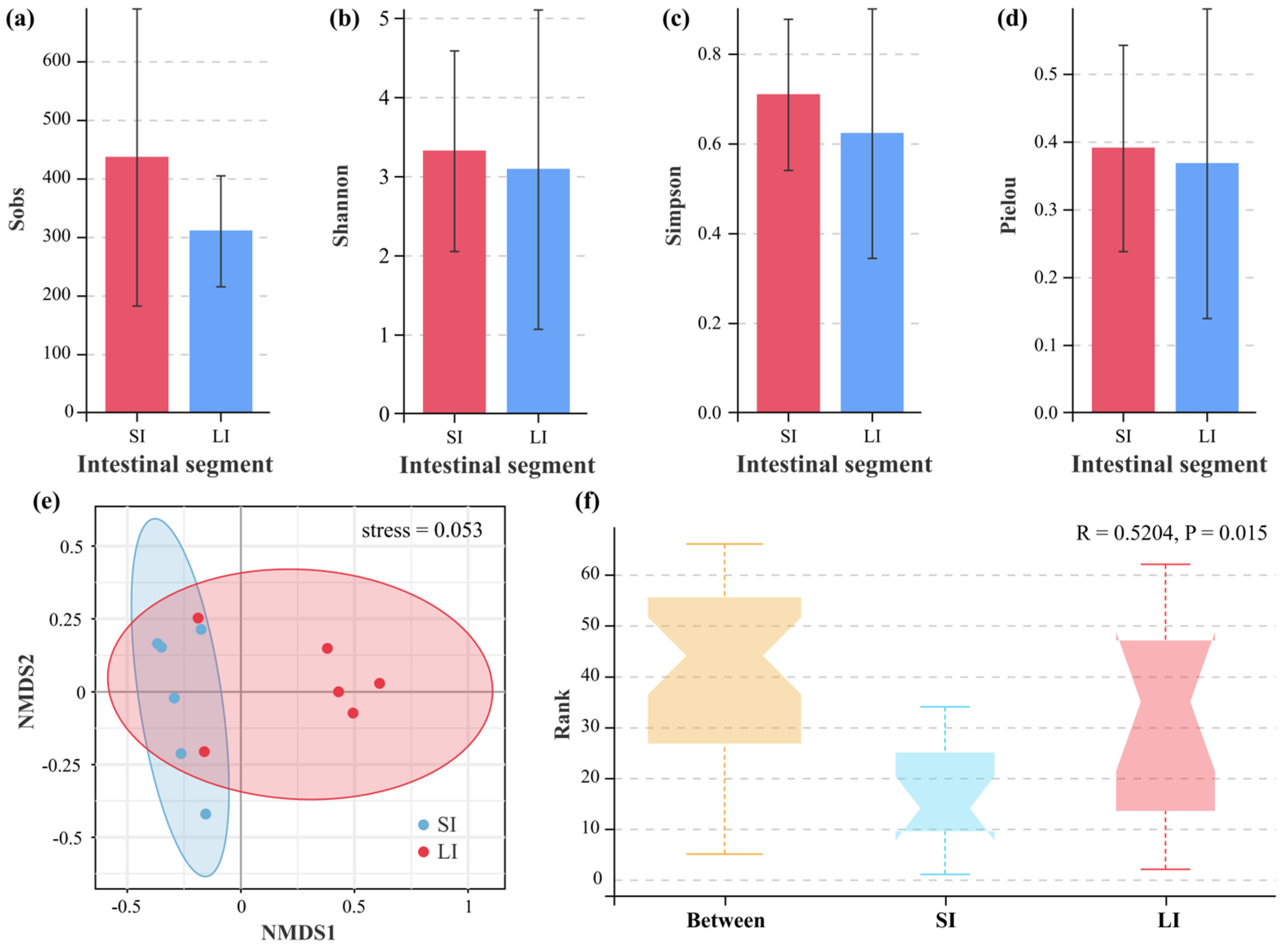
3.3. Microbial Diversity Between the Two Intestinal Compartments
3.4. QC Assessment for Metabolomic Analysis
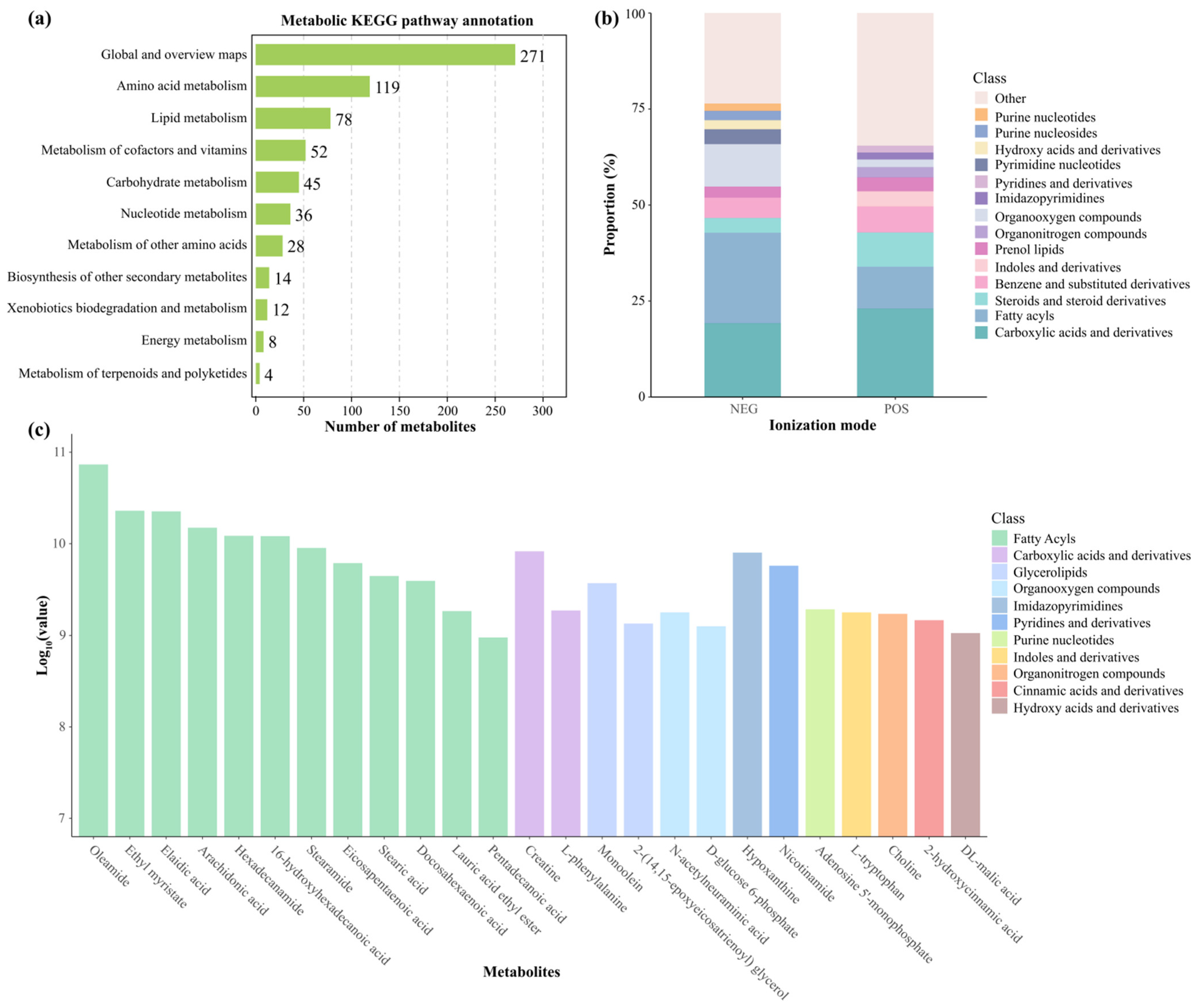
3.5. Hepatic Metabolome Characterization and Quantification
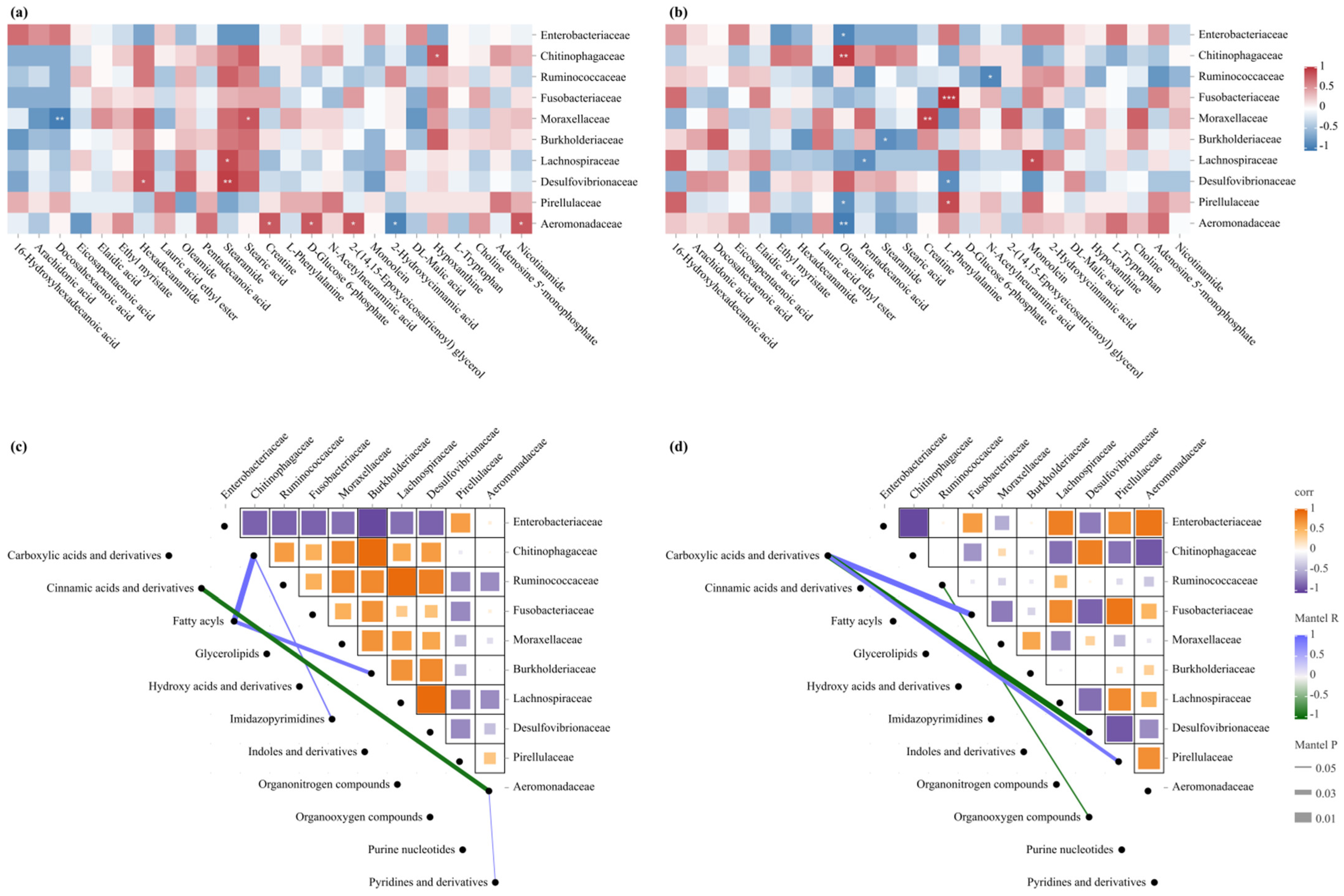
3.6. Integrated Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota and Hepatic Metabolome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Revel-Muroz, A.; Akulinin, M.; Shilova, P.; Tyakht, A.; Klimenko, N. Stability of human gut microbiome: Comparison of ecological modelling and observational approaches. Comput. Struct. Biotec. 2023, 21, 4456–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jian, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.N.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.T.; Sun, H.H.; Liu, M.D.; Zhou, H.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Xu, Z.X. Short-chain fatty acids in diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.J.; Zheng, L.; Campbell, E.L.; Saeedi, B.; Scholz, C.C.; Bayless, A.J.; Wilson, K.E.; Glover, L.E.; Kominsky, D.J.; Magnuson, A. Crosstalk between microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and intestinal epithelial HIF augments tissue barrier function. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Pérez, O.; Cruz-Ramón, V.; Chinchilla-López, P.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. The role of the gut microbiota in bile acid metabolism. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Lee, S.M.; Song, J.W.; Choi, J.W. Gut microbiota metabolite messengers in brain function and pathology at a view of cell type-based receptor and enzyme reaction. Biomol. Ther. 2024, 32, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festi, D.; Schiumerini, R.; Eusebi, L.H.; Marasco, G.; Taddia, M.; Colecchia, A. Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. World J. Gastroentero. 2014, 20, 16079–16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Ishimoto, T.; Fu, L.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y. The gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Mi. 2022, 12, 733992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.K.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.S.; Liu, Q.; Cai, L. The gut microbiota and its interactions with cardiovascular disease. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Whitley, C.S.; Haribabu, B.; Jala, V.R. Regulation of intestinal barrier function by microbial metabolites. Cell. Mol. Gastroenter. 2021, 11, 1463–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, T.; Cortese, M.; Rouphael, N.; Boudreau, C.; Linde, C.; Maddur, M.S.; Das, J.; Wang, H.; Guthmiller, J.; Zheng, N. Antibiotics-driven gut microbiome perturbation alters immunity to vaccines in humans. Cell 2019, 178, 1313–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, C.; Ruhn, K.A.; Behrendt, C.L.; Olson, E.N.; Hooper, L.V. The intestinal microbiota programs diurnal rhythms in host metabolism through histone deacetylase 3. Science 2019, 365, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.W.; Li, D.Y.; Hazen, S.L. Dietary metabolism, the gut microbiome, and heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Blaser, M.J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Jansson, J.K.; Lynch, S.V.; Knight, R. Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Mohanty, S.; Sharma, S.; Tripathi, P. Possible role of gut microbes and host’s immune response in gut–lung homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 954339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, Z.Z. The role of liver in metabolism: An updated review with physiological emphasis. Int. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 7, 2271–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-liver axis: Pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Xie, R.S.; Xu, L.Y.; Xu, Y.G.; Luo, H.M.; Lan, X.T. The gut-liver axis in fatty liver disease: Role played by natural products. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1365294. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.L.; Schnabl, B. The gut–liver axis and gut microbiota in health and liver disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenazzi, A. State of the world’s amphibians. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2015, 40, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedtke, J.A.; Chanson, J.; Neam, K.; Hobin, L.; Maciel, A.O.; Catenazzi, A.; Borzée, A.; Hamidy, A.; Aowphol, A.; Jean, A. Ongoing declines for the world’s amphibians in the face of emerging threats. Nature 2023, 622, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.; Martins, F.M.; Sabino-Pinto, J.; Licata, F.; Crottini, A. Skin and gut microbiomes of tadpoles vary differently with host and water environment: A short-term experiment using 16S metabarcoding. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chang, L.M.; Shi, S.C.; Lu, N.N.; Du, S.M.; Li, J.T.; Jiang, J.P.; Wang, B. Gut microbiota reflect adaptation of cave-dwelling tadpoles to resource scarcity. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrad009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.W.; Shi, Y.P.; Wang, J.; Niu, Z.Y.; Wei, L.; Tian, H.B.; Yu, F.F.; Gao, L. The intestinal microbiota and metabolic profiles of Strauchbufo raddei underwent adaptive changes during hibernation. Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 612–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bletz, M.C.; Goedbloed, D.J.; Sanchez, E.; Reinhardt, T.; Tebbe, C.C.; Bhuju, S.; Geffers, R.; Jarek, M.; Vences, M.; Steinfartz, S. Amphibian gut microbiota shifts differentially in community structure but converges on habitat-specific predicted functions. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Cui, L.Y.; Hu, Z.F.; Du, X.P.; Abid, H.M.; Wang, H.B. Environmental and host factors shaping the gut microbiota diversity of brown frog Rana dybowskii. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Ye, C.Y. Amphibians of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Gu, Q.H.; Zong, Y. The classification of the Leptobrachium species in Jiulong Mountain, Zhejiang Province is discussed from the perspective of its horny black spines. J. Hangzhou Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 1984, 14, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.H. The Chong’an moustache toad in Jiulong Mountain, Zhejiang Province. Chin. J. Wildl. 1987, 6, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Li, S.Q.; Fu, J.Z. A phylogenetic analysis of the frog genera Vibrissaphora and Leptobrachium, and the correlated evolution of nuptial spine and reversed sexual size dimorphism. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 46, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xiang, H.M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Z.R.; Lan, X.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Jiang, W.S. Two complete mitochondrial genomes of Leptobrachium (Anura: Megophryidae: Leptobrachiinae): Characteristics, population divergences, and phylogenetic implications. Genes 2023, 14, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.H.; Chen, Z.Q.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, W.C.; Ji, X. The advertisement call of the moustache toad Leptobrachium liui Pope, 1947 (Anura: Megophryidae) from eastern China. Zootaxa 2020, 4732, 5588–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.L.; Feng, L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xiang, Z.Y.; Hao, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Ding, G.H. Environmental and morphological determinants of advertisement call variability in a moustache toad. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2025, 16, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Hu, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, G.H. Combined effects of thermal environment and gene regulation on metabolic enzyme activities of major metabolic tissues in a winter-breeding amphibian. J. Therm. Biol. 2024, 125, 104000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, Y.Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.; Ringø, E.; Olsen, R.E.; Clarke, J.L.; Xie, S. The fish microbiota: Research progress and potential applications. Engineering 2023, 29, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.K.; Brown, R.L.; Larkinson, M.L.; Sequeira, R.P.; Edwards, A.M.; Clarke, T.B. Symbiotic Firmicutes establish mutualism with the host via innate tolerance and resistance to control systemic immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 1433–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Huang, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, N.; Ali, Z.; Ding, L.; Hong, M.; Shi, H. Ammonia stress influences intestinal histomorphology, immune status and microbiota of Chinese striped-neck turtle (Mauremys sinensis). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysostomou, D.; Roberts, L.A.; Marchesi, J.R.; Kinross, J.M. Gut microbiota modulation of efficacy and toxicity of cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenes-Soto, A.; Dierenfeld, E.S.; Janssens, G.P. The interplay between voluntary food intake, dietary carbohydrate-lipid ratio and nutrient metabolism in an amphibian, (Xenopus laevis). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e208445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Shao, N.; Qiu, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J. Distribution of gut microbiota across intestinal segments and their impact on human physiological and pathological processes. Cell Biosci. 2025, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Díaz, C.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A.; Mascher, D.; Pavón, N.; Regla, I.; Paredes-Carbajal, M.C. Effects of oleamide on the vasomotor responses in the rat. Cannabis Cannabinoid 2020, 5, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.L.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, S.; Zhang, L.; Cao, C.Y.; Baker, P.N.; Tong, C.; Zheng, P.; Qi, H.B. Altered gut bacterial and metabolic signatures and their interaction in gestational diabetes mellitus. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1840765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, H.; Gheibi, N.; Afshar, D.; Heidarzadeh, S.; Datta, I. Potential role of microRNAs in response to Aeromonas infection in fish. Arch. Razi Inst. 2023, 78, 1668. [Google Scholar]
- Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Goh, K.; Fock, K.M.; Mitchell, H.M.; Kaakoush, N.O. Dysbiosis of the microbiome in gastric carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Ma, Y.N.; Yang, L.Y.; Mao, L.S.; Sun, Q.; Sun, C.Z.; Liu, Z.J.; Mazhar, M.; Yang, S.J.; Ren, W. Uncovering the mechanisms of active components from toad venom against hepatocellular carcinoma using untargeted metabolomics. Molecules 2022, 27, 7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori-Takano, H.; Takano, H.; Ueda, K. Whole-genome sequence of Filimonas lacunae, a bacterium of the family Chitinophagaceae characterized by marked colony growth under a high-CO2 atmosphere. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernheim, A.; Sorek, R. The pan-immune system of bacteria: Antiviral defence as a community resource. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, E.; Brambilla, D.; Ricci, C.; Regazzoni, L.; Taguchi, K.; Ferri, N.; Asai, A.; Sparatore, A. New sulfurated derivatives of cinnamic acids and rosmaricine as inhibitors of STAT3 and NF-κB transcription factors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 1012–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Tao, F.Y.; Cui, T.; Luo, C.; Zhou, Z.G.; Huang, Y.C.; Tan, L.L.; Peng, W.; Wu, C.J. Sources, transformations, syntheses, and bioactivities of monoterpene pyridine alkaloids and cyclopenta [c] pyridine derivatives. Molecules 2022, 27, 7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Gu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, M.; Jiang, W.H.; Chen, J.H.; Rao, W.T.; Luo, S.F.; Chen, Y.Y. Dingxin Recipe IV attenuates atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism through LXR-α/SREBP1 pathway and modulating the gut microbiota in ApoE-/-mice fed with HFD. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, T.; Yuan, J.J.; Xiong, X.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Qiu, Z.M.; Hu, L.L.; Lu, H.; He, Q.; Liu, C. Metabolomics profiling to characterize cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1091616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Pi, X.G.; Zheng, W.X.; Cen, Y.X.; Ni, J.H.; Xu, L.Y.; Wu, K.F.; Liu, W.; Li, L.J. The methanol extract of Polygonatum odoratum ameliorates colitis by improving intestinal short-chain fatty acids and gas production to regulate microbiota dysbiosis in mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 899421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.-S.; Xiang, J.-W.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.-H.; Wang, Y.; Ding, G.-H.; Hu, H.-L. Integrated Microbiome–Metabolome Analysis Reveals Intestine–Liver Metabolic Associations in the Moustache Toad. Animals 2025, 15, 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131973
Yu S-S, Xiang J-W, Zhang L, Guo X-H, Wang Y, Ding G-H, Hu H-L. Integrated Microbiome–Metabolome Analysis Reveals Intestine–Liver Metabolic Associations in the Moustache Toad. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131973
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shui-Sheng, Jing-Wen Xiang, Lin Zhang, Xiao-Hua Guo, Yu Wang, Guo-Hua Ding, and Hua-Li Hu. 2025. "Integrated Microbiome–Metabolome Analysis Reveals Intestine–Liver Metabolic Associations in the Moustache Toad" Animals 15, no. 13: 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131973
APA StyleYu, S.-S., Xiang, J.-W., Zhang, L., Guo, X.-H., Wang, Y., Ding, G.-H., & Hu, H.-L. (2025). Integrated Microbiome–Metabolome Analysis Reveals Intestine–Liver Metabolic Associations in the Moustache Toad. Animals, 15(13), 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131973





