Integrated mRNA and miRNA Analysis Reveals Layer-Specific Mechanisms of Antler Yield Variation in Sika Deer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Sample Preparation
2.2. RNA-Seq Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. miRNA-Seq Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
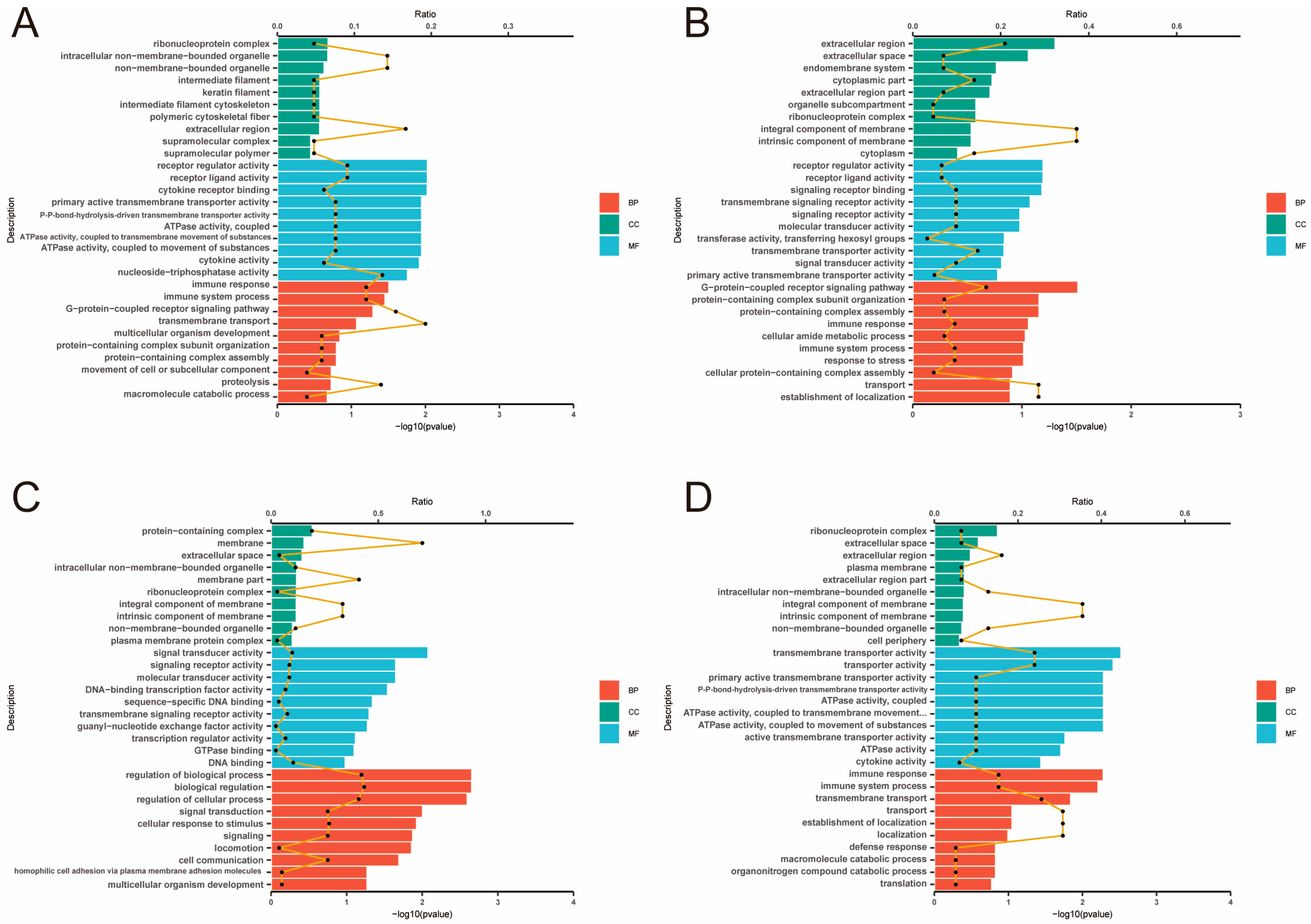
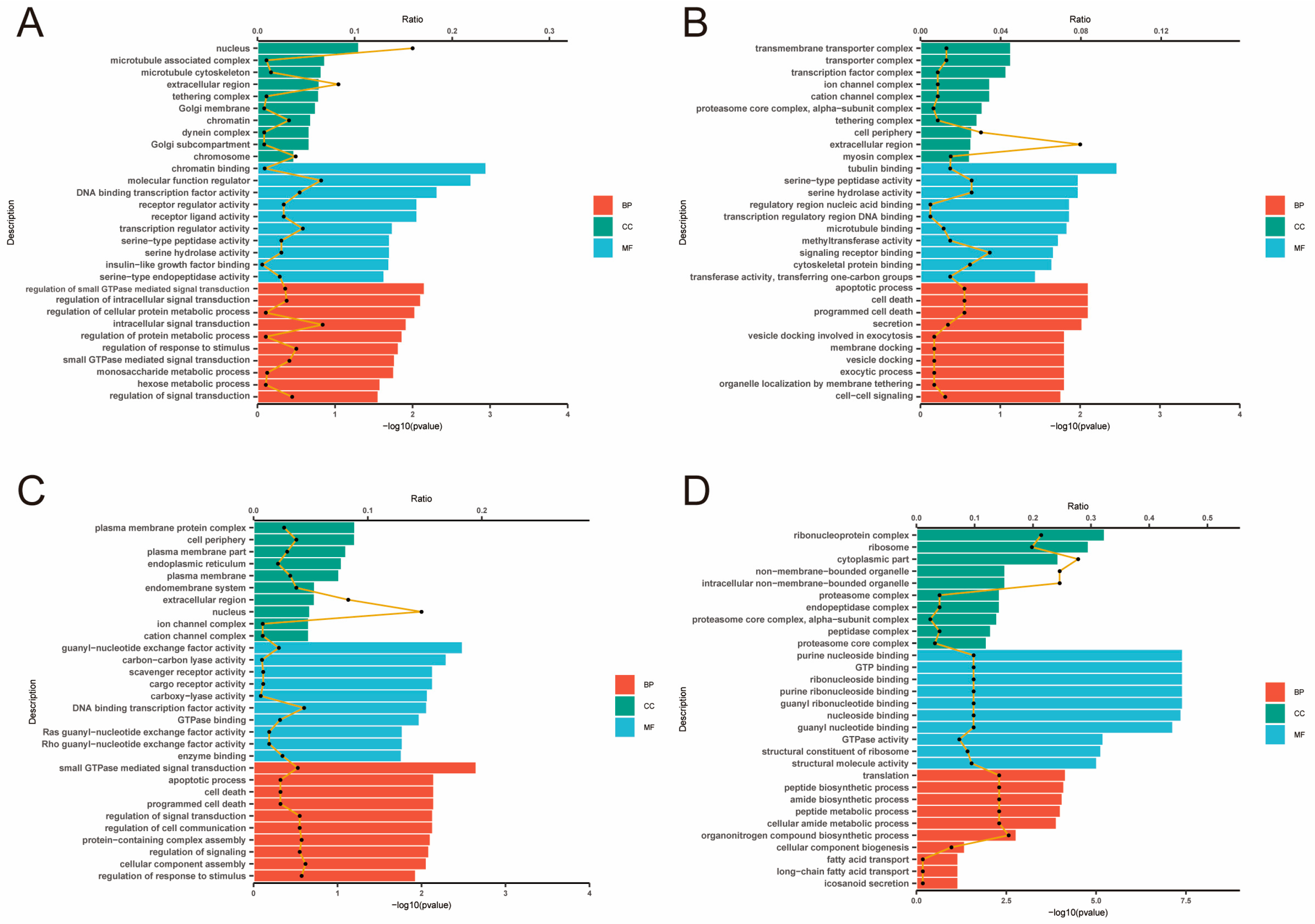
2.4. Analysis of GO and KEGG Pathway
2.5. Construction of miRNA-Target Gene Co-Expression Network
2.6. Validation of DEGs by qRT-PCR
3. Results
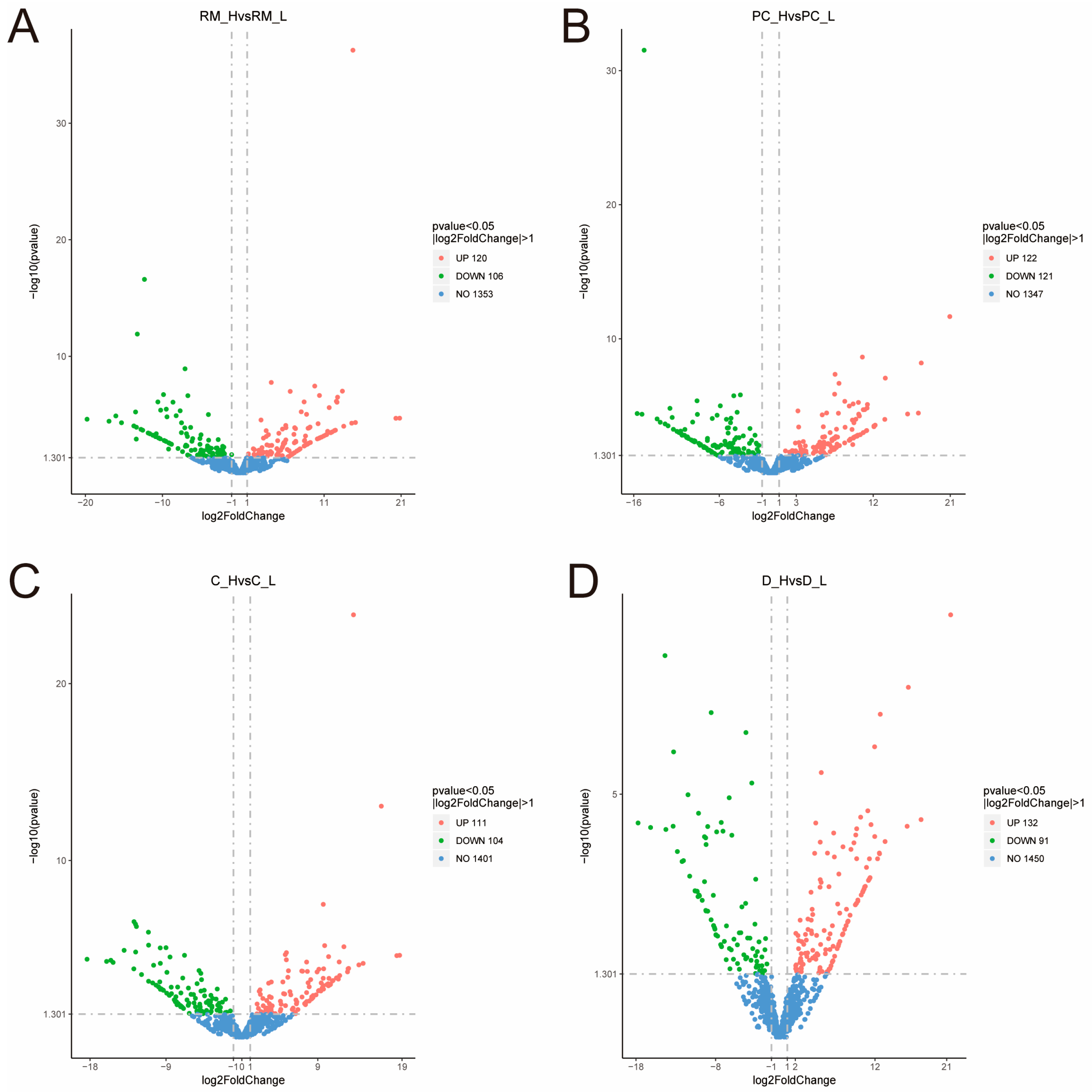
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of mRNA Expression Analysis
3.2. Descriptive Statistics of miRNA Expression Analysis
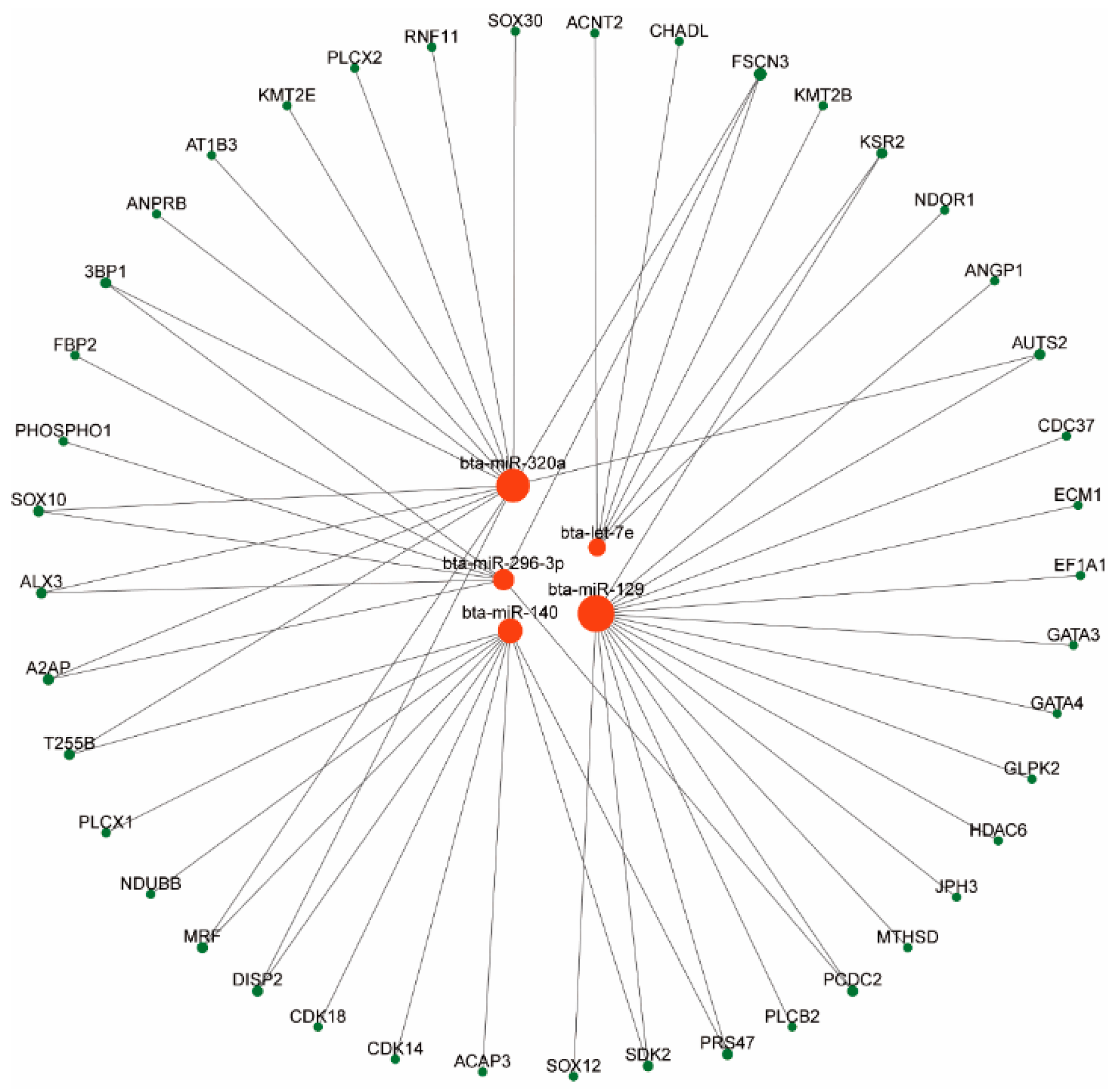
3.3. Results of Network Analysis of miRNA-mRNA
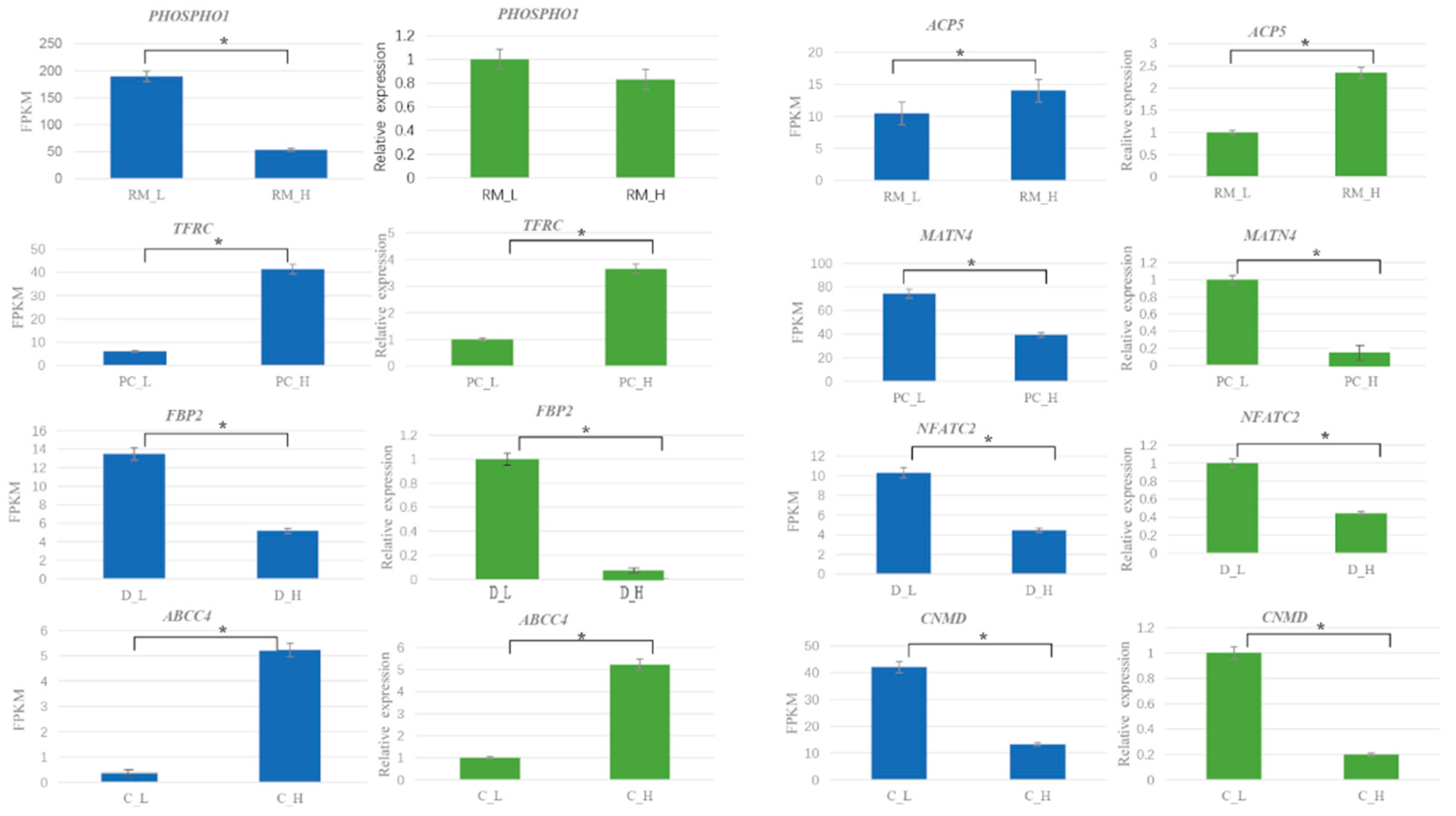
3.4. qRT-PCR Verification of DEGs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feleke, M.; Bennett, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Williams, D.; Xu, J. New physiological insights into the phenomena of deer antler: A unique model for skeletal tissue regeneration. J. Orthop. Transl. 2021, 27, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chu, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, C. Deer antler: A unique model for studying mammalian organ morphogenesis. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016, 56, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Fu, C.; Jiang, C.; Yue, X.; Ma, S. Water extract of pilose antler can inhibit breast cancer progression of the mouse through modulating its immune system. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Long, H.; Yang, C.; Cai, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, W. Anti-inflammatory Role of Pilose Antler Peptide in LPS-Induced Lung Injury. Inflammation 2017, 40, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y. Investigation of Anti-Fatigue Effect and Simultaneous Determination of Eight Nucleosides in Different Parts of Velvet Antler in Red Deer and Sika Deer. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyowati, R.; Suciati, S.; Haryadi, D.M.; Chang, H.; Suryawan, I.N.; Tarigan, N. The effect of deer antler from East Kalimantan to increase trabecular bone density and calcium levels in serum on osteoporotic mice. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 32, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, W.; Lei, H.; Zuo, J.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, Y. Velvet antler polypeptide is able to induce differentiation of neural stem cells towards neurons in vitro. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 37, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Fan, M.; Choi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yao, G.; Deng, Y.; Moon, S.; Kim, E. Sika deer (Cervus nippon) velvet antler extract attenuates prostate cancer in xenograft model. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, M.; Leem, K. Comparison of the Effect of Velvet Antler from Different Sections on Longitudinal Bone Growth of Adolescent Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1927534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbey, A.; Perezgonzalez, J.D. Health benefits of deer and elk velvet antler supplements: A systematic review of randomised controlled studies. N. Z. Med. J. 2012, 125, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; McMahon, C. Deer antler—A novel model for studying organ regeneration in mammals. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 56, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, M.; Si, H.; Wei, G.; Gao, X.; et al. A population of stem cells with strong regenerative potential discovered in deer antlers. Science 2023, 379, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Clark, D.E.; Lord, E.A.; Stanton, J.L.; Suttie, J.M. Sampling technique to discriminate the different tissue layers of growing antler tips for gene discovery. Anat. Rec. 2002, 268, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Suttie, J.M.; Clark, D.E. Histological examination of antler regeneration in red deer (Cervus elaphus). Anat. Rec. Part A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2005, 282A, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, J.G.; Muzylak, M.; Allen, S.; Althnaian, T.; McGonnell, I.M.; Price, J.S. Evidence that the canonical Wnt signalling pathway regulates deer antler regeneration. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.; Angelini, C.; De Feis, I.; Ciccodicola, A. Uncovering the Complexity of Transcriptomes with RNA-Seq. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 853916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Wang, D.; Yau, T.O.; Shang, Y.; Li, C. Transcriptomic analysis of different tissue layers in antler growth Center in Sika Deer (Cervus nippon). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Heller, R.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Han, J.; Pan, X.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Genetic basis of ruminant headgear and rapid antler regeneration. Science 2019, 364, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, M.; Gao, H.; Lu, B.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y. Global analysis of tissue-differential gene expression patterns and functional regulation of rapid antler growth. Mammal Res. 2019, 64, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Li, J. De novo characterization of the antler tip of Chinese Sika deer transcriptome and analysis of gene expression related to rapid growth. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 364, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, W. Comparative analysis of differentially expressed genes in Sika deer antler at different stages. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, C. RNA sequencing-based identification of microRNAs in the antler cartilage of Gansu red deer (Cervus elaphus kansuensis). Peerj 2022, 10, e13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.-F.; Xu, J.-P.; Ai, C.; Shao, X.-J.; Wang, H.-L.; Dong, Y.-M.; Cui, X.-Z.; Yang, F.; Xing, X. Screening weight related genes of velvet antlers by whole genome re-sequencing. Yi Chuan Hered. 2017, 39, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Jia, B.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Kedem, G.; Li, C. Genome-Wide SNP Discovery and Analysis of Genetic Diversity in Farmed Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) in Northeast China Using Double-Digest Restriction Site-Associated DNA Sequencing. G3-Genes Genom. Genet. 2017, 7, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Dong, Y.; Xing, X. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of sika deer antler using PacBio and Illumina sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Qin, T.; Ma, J.; Feng, Z.; Yue, H.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, B.; Han, G.; et al. High-quality sika deer omics data and integrative analysis reveal genic and cellular regulation of antler regeneration. Genome Res. 2025, 35, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Min, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, G. Comparison of Prediction Accuracy of Genomic Selection for Growth-related Traits in Sika Deer (Cervus Nippon) based on GBLUP and other Models. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2023, 54, 608–616. [Google Scholar]
- Kruuk, E.B.; Slate, J.; Pemberton, J.M.; Brotherstone, S.; Guinness, F.; Clutton-Brock, T. Antler size in red deer: Heritability and selection but no evolution. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 2002, 56, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samakova, A.; Gazova, A.; Sabova, N.; Valaskova, S.; Jurikova, M.; Kyselovic, J. The pi3k/Akt Pathway Is Associated with Angiogenesis, Oxidative Stress and Survival of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Pathophysiologic Condition in Ischemia. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, S131–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lin, C.; Jia, X.; Fang, D.; Gao, Q.; Han, C. HGF/c-Met signaling promotes the migration and proliferation of deer antler MSCs. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzavlaki, K.; Moustakas, A. TGF-β Signaling. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Leng, X.; Yao, B.; Wang, X.; Dong, H. Comparative transcriptome analysis provides insight into the molecular targets and signaling pathways of deer TGF-1 regulating chondrocytes proliferation and differentiation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 3155–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, F.; Molday, R.S. Lipid transport by mammalian ABC proteins. Essays Biochem. 2011, 50, 265–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Tampe, R. Structural and Mechanistic Principles of ABC Transporters. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 605–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.; Allen, S. Exploring the mechanisms regulating regeneration of deer antlers. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2004, 359, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttie, J.M.; Fennessy, P.F.; Lapwood, K.R.; Corson, I.D. Role of steroids in antler growth of red deer stags. J. Exp. Zool. 1995, 271, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttie, J.M.; Gluckman, P.D.; Butler, J.H.; Fennessy, P.F.; Corson, I.D.; Laas, F.J. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) antler-stimulating hormone? Endocrinology 1985, 116, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarin, J.; Laketa, V.; Malz, M.; Roessler, S.; Stein, I.; Horwitz, E.; Singer, S.; Dimou, E.; Cigliano, A.; Bissinger, M.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR-Dependent Stabilization of Oncogenic Far-Upstream Element Binding Proteins in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Hepatology 2016, 63, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Ni, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Yang, L.; He, Z.; Mao, G.; et al. The far-upstream element-binding protein 2 is correlated with proliferation and doxorubicin resistance in human breast cancer cell lines. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 9755–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acunzo, J.; Baylot, V.; So, A.; Rocchi, P. TCTP as therapeutic target in cancers. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.; Labbe, J.C.; Vigneron, S.; Bonneaud, N.; Strub, J.M.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. Chfr interacts and colocalizes with TCTP to the mitotic spindle. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5554–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Chen, S.; Huang, C.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, R. TCTP increases stability of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α by interaction with and degradation of the tumour suppressor VHL. Biol. Cell 2013, 105, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Yao, L.; Ma, G.; Cui, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, W.; Zhao, B.; Li, K. TCTP promotes glioma cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via enhanced β-catenin/TCF-4 transcription. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.M.; Antrobus, R.; Johnson, L.N. Plk1 activation by Ste20-like kinase (Slk) phosphorylation and polo-box phosphopeptide binding assayed with the substrate translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP). Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3688–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenblatt, M.B.; Ritter, S.Y.; Wright, J.; Tsang, K.; Hu, D.; Glimcher, L.H.; Aliprantis, A.O. NFATc1 and NFATc2 repress spontaneous osteoarthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19914–19919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, A.M.; Gerstenfeld, L.C.; Wang, J.; Kon, T.; Bae, H.; Gravallese, E.M.; Glimcher, M.J.; Glimcher, L.H. The nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) transcription factor NFATp (NFATc2) is a repressor of chondrogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Zhang, K.; Liu, K.; Shao, X.; Ding, Z.; Wang, F.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, M.; Li, H.; Li, H. Transferrin receptor facilitates TGF-β and BMP signaling activation to control craniofacial morphogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y. TFRC Ablation Induces Insufficient Cartilage Development Through Mitochondrial p53 Translocation-Mediated Ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcos, M.W.; Al-Jallad, H.; Li, J.; Farquharson, C.; Milian, J.L.; Hamdy, R.C.; Murshed, M. PHOSPHO1 is essential for normal bone fracture healing. Orthop. Proc. 2018, 7, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.C.; Simao, A.M.S.; Narisawa, S.; Huesa, C.; McKee, M.D.; Farquharson, C.; Millan, J.L. Loss of Skeletal Mineralization by the Simultaneous Ablation of PHOSPHO1 and Alkaline Phosphatase Function: A Unified Model of the Mechanisms of Initiation of Skeletal Calcification. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Lv, W.; Xu, Y.; Gong, M.; Chen, X.; Jiang, N.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Di, L.; Lu, T.; et al. Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Zou, M.; Zhu, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Huang, X. Pro-angiogenic role of ZEB1 in skin wound healing by upregulating VEGFA via microRNA-206 suppression. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaki, S.; Sato, T.; Inoue, A.; Otsuki, S.; Ito, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Kato, Y.; Takemoto, F.; Nakasa, T.; Yamashita, S.; et al. MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and homeostasis. Gene Dev. 2010, 24, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, C.; Yang, F.; Du, R.; Ba, H. Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA transcriptomic reveals antler growth regulatory network. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2021, 296, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvedova, M.; Kobayashi, T. MicroRNAs in cartilage development and dysplasia. Bone 2020, 140, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Du, G.; Fu, H. miR-296-3p promotes the proliferation of glioblastoma cells by targeting ICAT. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
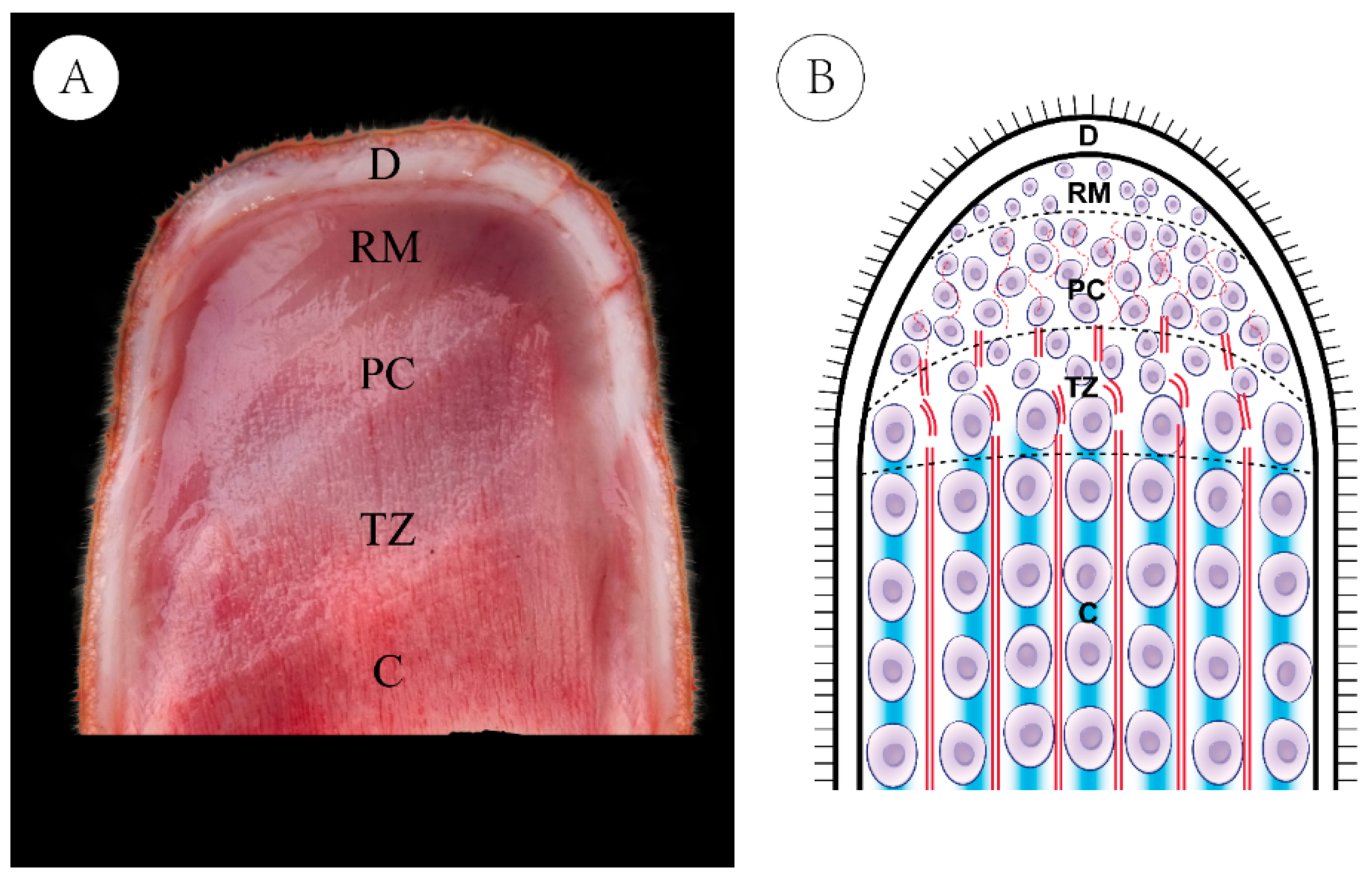



| Items | High-Yield Group (H) | Low-Yield Group (L) |
|---|---|---|
| deer antler weights | 2.738 ± 0.278 | 0.782 ± 0.098 |
| Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| PHOSPHO1 | CATCTCAGACGCCAACACCT | GAAGGGTTGCTGAAGATGCG |
| ACP5 | GAGCCGGAAGTCACTGTCTC | GAGGCAATCAAGTTCCCCGA |
| TFRC | GCTGCTTTCCCTTTCCTTGC | TCTCCGCCCAGTGTCTCATA |
| MATN4 | CAGTGTGTGAGTGAGGGCTT | TCAACGAGCAGAACCAGGTC |
| FBP2 | GGACATGCTTACCCTGACCC | TGGAGTTGAGTAGCTGCGTG |
| NFATC2 | TGGGCAGCAAATTTGGGAGA | TCCGAATGTGCTTGTTCCGA |
| ABCC4 | AGTGAAGGACAGAAAGCCCG | GTTCGAACAAGTGCCTGCTG |
| CNMD | AGCATGACATTCGACCCCAG | CCAGGGGCTCACAGATCTTC |
| β-actin | GCGTGACATCAAGGAGAAGC | GGAAGGACGGCTGGAAGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, H. Integrated mRNA and miRNA Analysis Reveals Layer-Specific Mechanisms of Antler Yield Variation in Sika Deer. Animals 2025, 15, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131964
Zhao D, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Li H. Integrated mRNA and miRNA Analysis Reveals Layer-Specific Mechanisms of Antler Yield Variation in Sika Deer. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131964
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Derui, Zhen Zhang, Qianghui Wang, and Heping Li. 2025. "Integrated mRNA and miRNA Analysis Reveals Layer-Specific Mechanisms of Antler Yield Variation in Sika Deer" Animals 15, no. 13: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131964
APA StyleZhao, D., Zhang, Z., Wang, Q., & Li, H. (2025). Integrated mRNA and miRNA Analysis Reveals Layer-Specific Mechanisms of Antler Yield Variation in Sika Deer. Animals, 15(13), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131964






