Effects of Goji Berry Supplementation on Immune-Related and Antioxidant Gene Expression in the Male Rabbit Reproductive Tract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Diets, and Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction from Rabbit Reproductive Tissues, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time PCR
2.3. Statistical Analysis
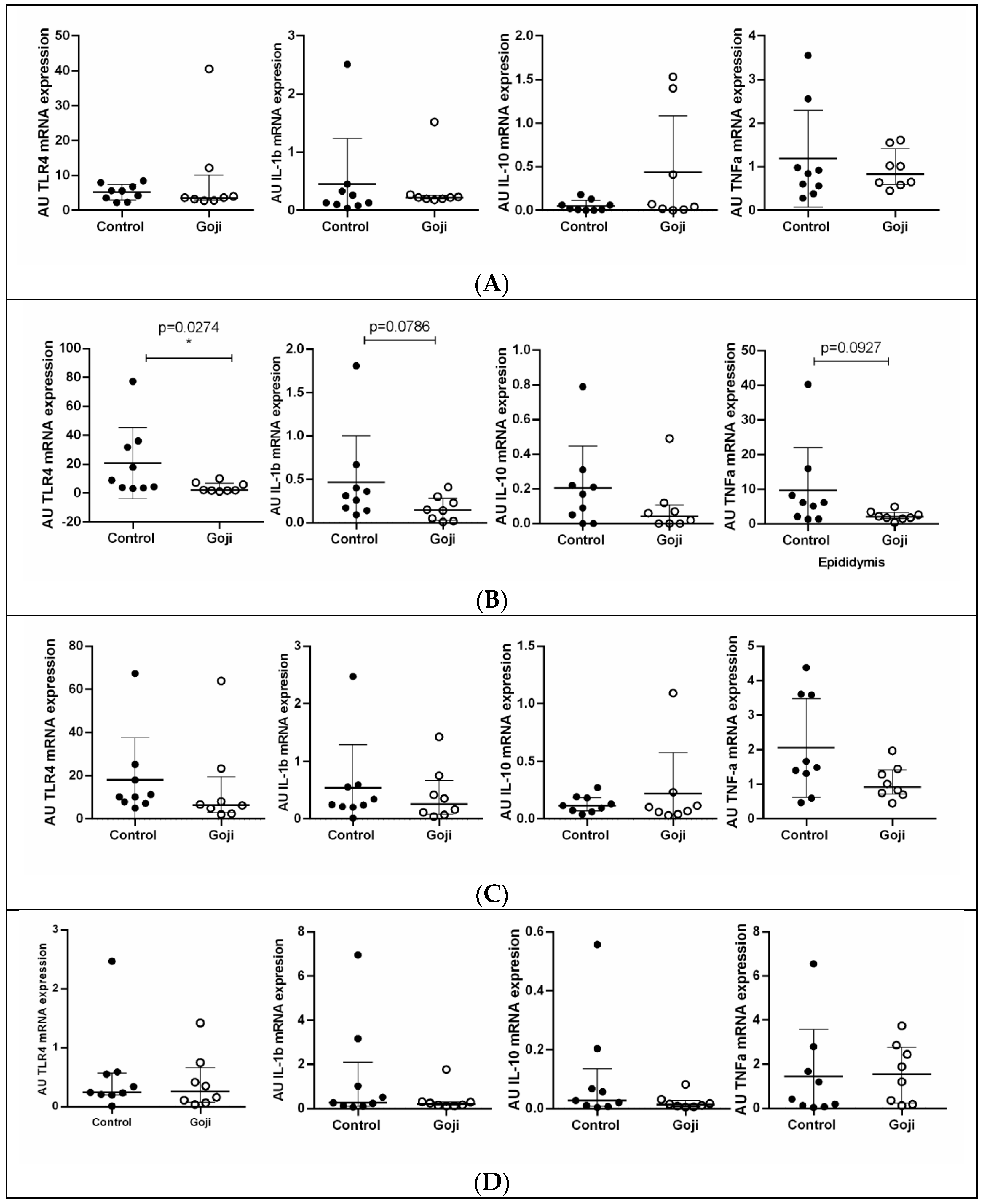
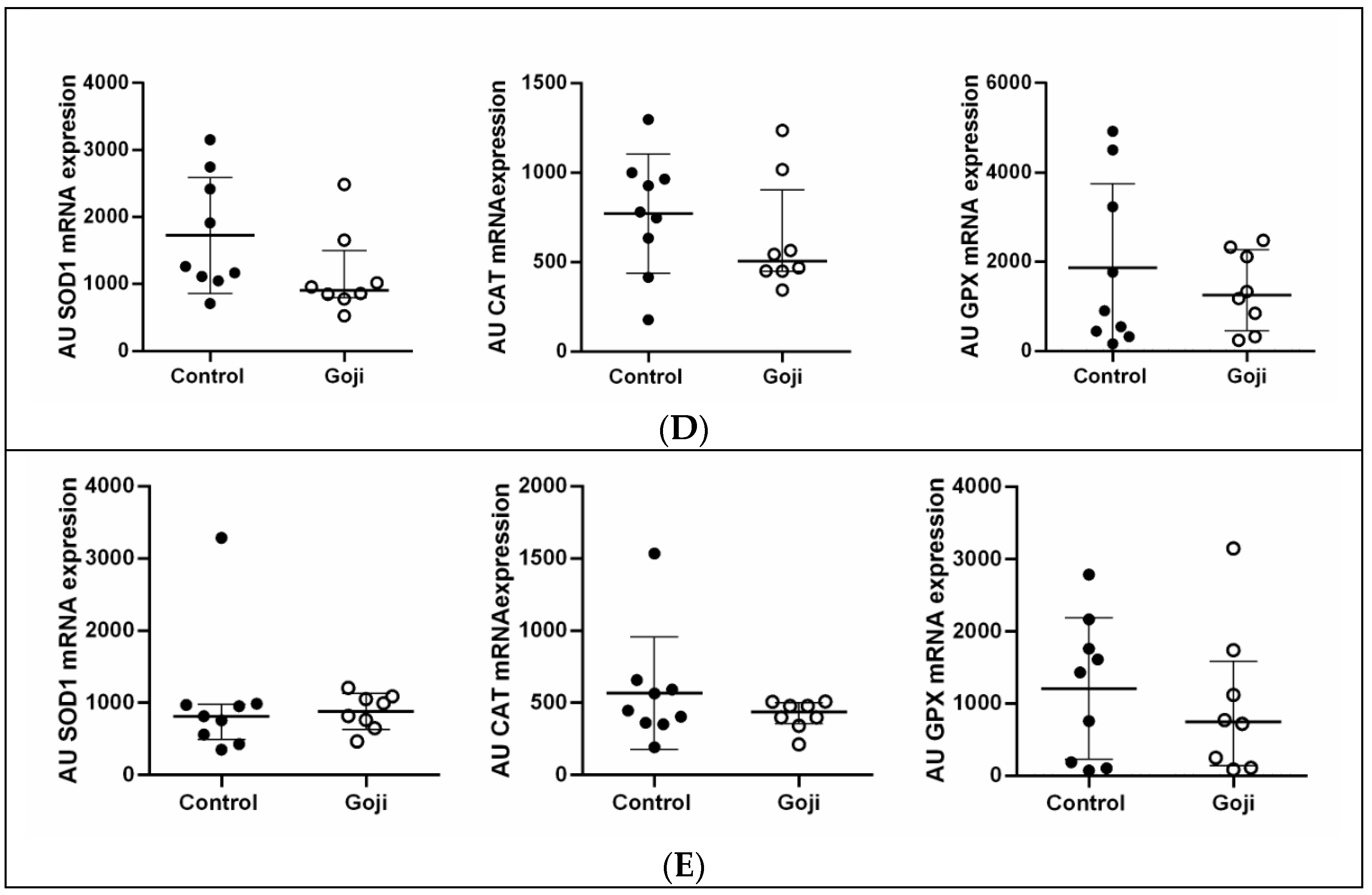
3. Results
3.1. Goji Berry Supplementation Modulates Immune-Related Gene Expression in the Epididymis
3.2. Goji Berry Supplementation Modulates Antioxidant-Related Gene Expression Only in the Epididymis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTB | Actin beta |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase 1 |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GPX | Glutathione peroxidase |
References
- Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Chen, S.; Yuan, F.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Superfruits in China: Bioactive Phytochemicals and Their Potential Health Benefits—A Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6892–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Gong, H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, S.; Yang, T.; Ai, P.; Pan, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y. Identification of Fruit Size Associated Quantitative Trait Loci Featuring SLAF Based High-Density Linkage Map of Goji Berry (Lycium Spp.). BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.F.; Zhang, H.; Teh, S.S.; Wang, C.W.; Zhang, Y.; Hayford, F.; Wang, L.; Ma, T.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Goji Berries as a Potential Natural Antioxidant Medicine: An Insight into Their Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2437397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Tian, J.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, W.; Yang, W. Traditional Goji Berry-Based Functional Food in Chinese History. In Phytochemicals in Goji Berries, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Liu, X.M.; Dong, Q. A study of lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP) extraction technology and its anti-aging effect. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nardi, G.M.; De Farias Januário, A.G.; Freire, C.G.; Megiolaro, F.; Schneider, K.; Perazzoli, M.R.A.; Do Nascimento, S.R.; Gon, A.C.; Mariano, L.N.B.; Wagner, G.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Berry Fruits in Mice Model of Inflammation Is Based on Oxidative Stress Modulation. Pharmacogn. Res. 2016, 8, S42–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.C.; Wu, J.M.; Chang, Y.H.; Dubey, N.K.; Chiu, A.W.; Yeh, C.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Yeh, K.Y. Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity Mediates Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides-Enhanced Sexual Performance without Stimulating Noncontact Erection in Rats. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Luo, S.; Luo, X.; Hu, M.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Huang, R. Fraction From Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides Reduces Immunotoxicity and Enhances Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin in Mice. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, Y.; Wong, F.S.Y.; So, K.F.; Chan, H.H.L. Potential Role of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides in Glaucoma Management: Evidence from Preclinical in Vivo Studies. Neural Regen. Res 2023, 18, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ah Kang, K.; Piao, M.J.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, A.D.; Chae, S.; Park, J.S.; Youn, U.J.; Hyun, J.W. Cytoprotective Effect of the Fruits of Lycium Chinense Miller against Oxidative Stress-Induced Hepatotoxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; McLean, R.J.C.; Chu, W. Prebiotic, Immuno-Stimulating and Gut Microbiota-Modulating Effects of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharide. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Du, M.; Kang, Y.; Zhu, M.J. Prebiotic Effects of Goji Berry in Protection against Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5206–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.M.; Huang, L.J.; Qi, C.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Tian, G.Y. Studies on Chemistry and Immuno- Modulating Mechanism of a Glycoconjugate from Lycium Barbarum L.†. J. Chem. 2001, 19, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Sheng, X.; Gambino, P.E.; Costello, B.; Bojanowski, K. Protective Effect of Fructus Lycii Polysaccharides against Time and Hyperthermia-Induced Damage in Cultured Seminiferous Epithelium. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 82, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Zhang, S.H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, H.B. A Polysaccharide-Protein Complex from Lycium Barbarum Upregulates Cytokine Expression in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 471, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Stanisz, E.; Waśkiewicz, A. Potential Health Benefits and Quality of Dried Fruits: Goji Fruits, Cranberries and Raisins. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Cai, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, M.; Corke, H. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects and Antioxidant Activity of Fruit Extracts from Lycium Barbarum. Life Sci. 2004, 76, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.; Silva, A.M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. Lycium barbarum Berries (Solanaceae) as Source of Bioactive Compounds for Healthy Purposes: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, A.C.; Sánchez-Mata, M.C.; Pérez-Rodríguez, M.L.; Cámara, M.; López-Colón, J.L.; Bach, F.; Bellettini, M.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. Qualitative and Nutritional Comparison of Goji Berry Fruits Produced in Organic and Conventional Systems. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoni, E.; Curone, G.; Agradi, S.; Barbato, O.; Menchetti, L.; Vigo, D.; Zelli, R.; Cotozzolo, E.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Faustini, M.; et al. Effect of Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum) Supplementation on Reproductive Performance of Rabbit Does. Animals 2021, 11, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Biological Functions of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides: A Review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczyński, B.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum): Composition and Health Effects—A Review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 66, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidović, B.B.; Milinčić, D.D.; Marčetić, M.D.; Djuriš, J.D.; Ilić, T.D.; Kostić, A.; Pešić, M.B. Health Benefits and Applications of Goji Berries in Functional Food Products Development: A Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skenderidis, P.; Leontopoulos, S.; Lampakis, D. Goji Berry: Health Promoting Properties. Nutraceuticals 2022, 2, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, F.; Borgmann, H.; Struck, J.P.; Salem, J.; Kuru, T.H. Antioxidant Supplementation on MaleAntioxidant Supplementation on Male Fertility—A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Cai, Y.Z. Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides: Protective Effects against Heat-Induced Damage of Rat Testes and H2O2-Induced DNA Damage in Mouse Testicular Cells and Beneficial Effect on Sexual Behavior and Reproductive Function of Hemicastrated Rats. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Cui, X.; Yan, J.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y. Antagonistic Effects of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides on the Impaired Reproductive System of Male Rats Induced by Local Subchronic Exposure to 60Co-γ Irradiation. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, B.W.M.; Lee, J.C.D.; Li, Y.; Fung, S.M.Y.; Sang, Y.H.; Shen, J.; Chang, R.C.C.; So, K.F. Polysaccharides from Wolfberry Prevents Corticosterone-Induced Inhibition of Sexual Behavior and Increases Neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, B.W.M.; Yau, S.Y.; Lee, T.M.C.; Ching, Y.P.; Tang, S.W.; So, K.F. Effect of Corticosterone and Paroxetine on Masculine Mating Behavior: Possible Involvement of Neurogenesis. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.N.; Kang, B.J.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, J.S. Effects of Dietary Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activities, Antioxidant Status, and Immunity of Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Long, L.; Jiang, Q.; Kang, B.; Li, Y.; Yin, J. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides on Growth Performance, Immune Status, Antioxidant Capacity and Selected Microbial Populations of Weaned Piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Luo, Y.; Du, M.; Yin, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, G. Integrated Metabolomics and Transcriptome Revealed the Effect of Fermented Lycium Barbarum Residue Promoting Ovis Aries Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 16648714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L. Modulation of Cytokine Level and Sperm Quality of Mice by Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brecchia, G.; Muça, G.; Munga, A.; Menchetti, L.; Galosi, L.; Rossi, G.; Barbato, O.; Pastorelli, G.; Agradi, S.; Serra, V.; et al. Goji Berry in the Diet of the Rabbit Buck: Effects on Semen Quality, Oxidative Status and Histological Features of the Reproductive Tract. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecchia, G.; Sulce, M.; Curone, G.; Barbato, O.; Canali, C.; Troisi, A.; Munga, A.; Polisca, A.; Agradi, S.; Ceccarini, M.R.; et al. Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum) Supplementation during Pregnancy Influences Insulin Sensitivity in Rabbit Does but Not in Their Offspring. Animals 2022, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agradi, S.; Cremonesi, P.; Menchetti, L.; Balzaretti, C.; Severgnini, M.; Riva, F.; Castiglioni, B.; Draghi, S.; Di Giancamillo, A.; Castrica, M.; et al. Bovine Colostrum Supplementation Modulates the Intestinal Microbial Community in Rabbits. Animals 2023, 13, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, L.; Moermans, R.; De Groote, G. Prediction of the Apparent Digestible Energy Content of Commercial Pelleted Feeds for Rabbits. J. Appl. Rabbit. Res. 1988, 11, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative CT Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agradi, S.; Draghi, S.; Cotozzolo, E.; Barbato, O.; Castrica, M.; Quattrone, A.; Sulce, M.; Vigo, D.; Menchetti, L.; Ceccarini, M.R.; et al. Goji Berries Supplementation in the Diet of Rabbits and Other Livestock Animals: A Mini-Review of the Current Knowledge. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 823589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Eun, S.; Chae, S.; Lee, S. Prebiotic Potential of Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum) in Improving Intestinal Integrity and Inflammatory Profiles via Modification of the Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. J. Med. Food 2024, 27, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.N.; Trindade, F.M.R.; Penteado, J.O.; Janke, F.; Schneider, J.P.; Uecker, J.N.; Rincón, J.A.A.; de Barros, C.C.; Andreazza, R.; Pieniz, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Goji Berry Extract (Lycium Barbarum) in Rats Subjected to Inflammation by Lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, 20180612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinčić, D.D.; Kostić, A.; Lević, S.; Gašić, U.M.; Božić, D.D.; Suručić, R.; Ilić, T.D.; Nedović, V.A.; Vidović, B.B.; Pešić, M.B. Goat’s Milk Powder Enriched with Red (Lycium Barbarum L.) and Black (Lycium Ruthenicum Murray) Goji Berry Extracts: Chemical Characterization, Antioxidant Properties, and Prebiotic Activity. Foods 2024, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barıt, M.; Duru, A.A. The Effects of Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum L.) Leaves on Performance, Meat Lipid Oxidation, Digestive Tract Parts, and Some Blood Parameters of Broiler Chickens. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2023, 74, 5676–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, R.; Han, D. Innate Immune Defense in the Male Reproductive System and Male Fertility. In Innate Immunity in Health and Disease; Saxena, S.K., Prakash, H., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, C.; He, C.; Mei, C.; Liao, A.; Huang, D. The Immune Characteristics of the Epididymis and the Immune Pathway of the Epididymitis Caused by Different Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Légaré, C.; Sullivan, R. Differential Gene Expression Profiles of Human Efferent Ducts and Proximal Epididymis. Andrology 2020, 8, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchetti, L.; Barbato, O.; Sforna, M.; Vigo, D.; Mattioli, S.; Curone, G.; Tecilla, M.; Riva, F.; Brecchia, G. Effects of Diets Enriched in Linseed and Fish Oil on the Expression Pattern of Toll-Like Receptors 4 and Proinflammatory Cytokines on Gonadal Axis and Reproductive Organs in Rabbit Buck. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 4327470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The Nuclear Factor NF-KappaB Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.C. The Non-Canonical NF-ΚB Pathway in Immunity and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwangbo, C. Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4): New Insight Immune and Aging. Immun. Ageing 2023, 20, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Yu, K.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 4 Promotes NO Synthesis by Upregulating GCHI Expression under Oxidative Stress Conditions in Sheep Monocytes/Macrophages. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 359315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.A.; Smith, M.F.; Sanders, M.K.; Ernst, P.B. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species Differentially Regulate Toll-Like Receptor 4-Mediated Activation of NF-ΚB and Interleukin-8 Expression. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, M.K.; Schlatt, S.; Gerdprasert, O.; Phillips, D.J.; De Kretser, D.M.; Hedger, M.P. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in the Rat Testis: Evidence for Potential Roles in Both Normal Function and Inflammation-Mediated Infertility. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 63, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidl, G.; Allam, J.P.; Schuppe, H.C. Chronic Epididymitis: Impact on Semen Parameters and Therapeutic Options. Andrologia 2008, 40, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, M.A.M.; Hussein, M.T.; Mustafa, F.E.Z.A.; Abdelhefeez, E.; Hussein, A.M.A.; Abdelfattah, M.G. Attenuation of Chronic Oxidative Stress-Induced Testicular and Epididymal Dysfunction by Oral Intake of Lepidium Meyenii in New Zealand Rabbits. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 109, 682–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedger, M.P. Immunophysiology and Pathology of Inflammation in the Testis and Epididymis. J. Androl. 2011, 32, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, A.; Saez, F.; Drevet, J.; Guiton, R. The Epididymal Immune Balance: A Key to Preserving Male Fertility. Asian. J. Androl. 2019, 21, 531–539. [Google Scholar]
- Quattrone, A.; Fehri, N.E.; Agradi, S.; Menchetti, L.; Barbato, O.; Castrica, M.; Sulçe, M.; Castellini, C.; Muça, G.; Mattioli, S.; et al. In Vitro Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on Rabbit Sperm: Toll-like Receptor 4 Expression, Motility, and Oxidative Status. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaure, C.; Liu, Y. A Comparative Review of Toll-like Receptor 4 Expression and Functionality in Different Animal Species. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, T.; Lilly, M.; Jiang, W. The Pathologic Role of Toll-like Receptor 4 in Prostate Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudney, J.; Anderson, D.J. Expression of Toll-like Receptors in Genital Tract Tissues from Normal and HIV-Infected Men. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 65, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Yu, W.W.; Zhou, H.C.; Lan, Z.C.; Wu, T.; Xiong, S.M.; Yan, L.; Liu, H. Bin Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides Ameliorate LPS-Induced Inflammation of RAW264.7 Cells and Modify the Behavioral Score of Peritonitis Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhou, Z.W.; Sheng, H.P.; He, L.J.; Fan, X.W.; He, Z.X.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.J.; Gu, L.; et al. An Evidence-Based Update on the Pharmacological Activities and Possible Molecular Targets of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 33–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olivera, A.; Moore, T.W.; Hu, F.; Brown, A.P.; Sun, A.; Liotta, D.C.; Snyder, J.P.; Yoon, Y.; Shim, H.; Marcus, A.I.; et al. Inhibition of the NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway by the Curcumin Analog, 3,5-Bis(2-Pyridinylmethylidene)-4-Piperidone (EF31): Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Properties. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liu, R.; Lu, X.; Wu, X.; Heneberg, P.; Mao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Loor, J.; Yang, Z. Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides Alleviate LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through PPARγ/MAPK/NF-ΚB Pathway in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skab345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, L. Advances in the Study of Bioactive Compounds and Nutraceutical Properties of Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum L.). Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, V.; Silva, A.R.; Silva, B.; Zhang, X.; Dias, A.C.P. Comparative Studies on the Anti-Neuroinflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of Black and Red Goji Berries. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 92, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Yu, X.; Badwal, T.S.; Xu, B. Comparative Studies on Phenolic Profiles, Antioxidant Capacities and Carotenoid Contents of Red Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum) and Black Goji Berry (Lycium Ruthenicum). Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilić, T.; Dodevska, M.; Marčetić, M.; Božić, D.; Kodranov, I.; Vidović, B. Chemical Characterization, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Goji Berries Cultivated in Serbia. Foods 2020, 9, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagase, H.; Sun, B.; Borek, C. Lycium Barbarum (Goji) Juice Improves in Vivo Antioxidant Biomarkers in Serum of Healthy Adults. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan Karakaş, F.; Coşkun, H.; Soytürk, H.; Bozat, B.G. Anxiolytic, Antioxidant, and Neuroprotective Effects of Goji Berry Polysaccharides in Ovariectomized Rats: Experimental Evidence from Behavioral, Biochemical, and Immunohistochemical Analyses. Turk. J. Biol. 2020, 44, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabory, E.; Damon, C.; Lenoir, A.; Kauselmann, G.; Kern, H.; Zevnik, B.; Garrel, C.; Saez, F.; Cadet, R.; Henry-Berger, J.; et al. Epididymis Seleno-Independent Glutathione Peroxidase 5 Maintains Sperm DNA Integrity in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2074–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Fan, X.; Zhang, T.; Song, H.; Bian, X.; Nai, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Expression of Selenium-Independent Glutathione Peroxidase 5 (GPx5) in the Epididymis of Small Tail Han Sheep. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, R.J. Gpx5 Protects the Family Jewels. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agradi, S.; Sulce, M.; Menchetti, L.; Vigo, D.; Castrica, M.; Barbato, O.; Andoni, E.; Quattrone, A.; Munga, A.; Marongiu, M.L.; et al. Dietary Supplementation with N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Effects on Reproductive and Productive Performance and Meat Quality in Rabbit Breeding. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 14, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, C.; Mattioli, S.; Signorini, C.; Cotozzolo, E.; Noto, D.; Moretti, E.; Brecchia, G.; Dal Bosco, A.; Belmonte, G.; Durand, T.; et al. Effect of Dietary N-3 Source on Rabbit Male Reproduction. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3279670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A. The Role of the Natural Antioxidant Mechanism in Sperm Cells. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevet, J.R. The Antioxidant Glutathione Peroxidase Family and Spermatozoa: A Complex Story. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 250, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabory, E.; Damon, C.; Lenoir, A.; Henry-Berger, J.; Vernet, P.; Cadet, R.; Saez, F.; Drevet, J.R. Mammalian Glutathione Peroxidases Control Acquisition and Maintenance of Spermatozoa Integrity. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblanc, A.; Kocer, A.; Chabory, E.; Vernet, P.; Saez, F.; Cadet, R.; Conrad, M.; Drevet, J.R. Glutathione Peroxidases at Work on Epididymal Spermatozoa: An Example of the Dual Effect of Reactive Oxygen Species on Mammalian Male Fertilizing Ability. J. Androl. 2011, 32, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelatty, A.M.; Badr, O.A.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Khattab, M.S.; Dessouki, S.H.M.; Farid, O.A.A.; Elolimy, A.A.; Sakr, O.G.; Elhady, M.A.; Mehaisen, G.M.K.; et al. Erratum: Long Term Conjugated Linoleic Acid Supplementation Modestly Improved Growth Performance but Induced Testicular Tissue Apoptosis and Reduced Sperm Quality in Male Rabbit. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, T. Function and Inhibition of P38 MAP Kinase Signaling: Targeting Multiple Inflammation Diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 220, 115973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredients | Diets | |
|---|---|---|
| Control Group | Goji Group | |
| Wheat bran | 30 | 29.5 |
| Dehydrated alfalfa meal | 42 | 41.5 |
| Barley | 9.6 | 9.6 |
| Sunflower meal | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| Rice bran | 4 | 4 |
| Soybean meal | 4 | 4 |
| Calcium carbonate | 2 | 2 |
| Cane molasses | 2 | 2 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Vitamin–mineral premix 1 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Soybean oil | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Salt | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Goji berries | - | 1 |
| Diet | ||
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Component | Control | Goji |
| Crude protein | 15.74 | 15.64 |
| Ether extract | 2.25 | 2.23 |
| Ash | 9.28 | 9.36 |
| Starch | 16.86 | 17.07 |
| NDF | 38.05 | 38.55 |
| ADF | 19.54 | 19.6 |
| ADL | 4.01 | 4.31 |
| Digestible energy 1 | 2464 | 2463 |
| Gene | Protein | Gene Bank GI Number | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACTB | Actin beta | 100009272 | F: ACATGGAGAAGATCTGGCAC |
| R: GCGTGTTGAACGTCTCGAAC | |||
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor–4 | 100009497 | F: TGCATGTCTCAGAACTGCAC |
| R: GGATAGGGTTTCCTGTCAATATC | |||
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β | 100008990 | F: ACAACAAGAGCTTCC |
| R: GTGTTGCAGAGGACG | |||
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 | 100008701 | F: GCTATGTTGCCTGGTCTTCC |
| R: GCTGTTCAGCTGATCCTTCG | |||
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor | 100009088 | F: GTGGCCCAGATGGTCACC |
| R: CTACTACGTGGGCTAGAGGCTT | |||
| SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase 1 | 100009313 | F: CACTCCGAGCAGAAGGGAAC |
| R: CGTGCCTCTCTTCATCCTTC | |||
| CAT | Catalase | 100340891 | F: GCTGAGATTGAACAGTTGGC |
| R: GGTGAGTATCGGGATAGGAG | |||
| GPX | Glutathione peroxidase 1 | 100009258 | F: CAGTTTGGGCATCAGGAGAAC |
| R: GCATGAAGTTGGGCTCGAAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quattrone, A.; Draghi, S.; Inglesi, A.; Riva, F.; Turmalaj, L.; Filipe, J.; Sulçe, M.; Agradi, S.; Vigo, D.; Muça, G.; et al. Effects of Goji Berry Supplementation on Immune-Related and Antioxidant Gene Expression in the Male Rabbit Reproductive Tract. Animals 2025, 15, 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131921
Quattrone A, Draghi S, Inglesi A, Riva F, Turmalaj L, Filipe J, Sulçe M, Agradi S, Vigo D, Muça G, et al. Effects of Goji Berry Supplementation on Immune-Related and Antioxidant Gene Expression in the Male Rabbit Reproductive Tract. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131921
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuattrone, Alda, Susanna Draghi, Alessia Inglesi, Federica Riva, Luigj Turmalaj, Joel Filipe, Majlind Sulçe, Stella Agradi, Daniele Vigo, Gerald Muça, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Goji Berry Supplementation on Immune-Related and Antioxidant Gene Expression in the Male Rabbit Reproductive Tract" Animals 15, no. 13: 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131921
APA StyleQuattrone, A., Draghi, S., Inglesi, A., Riva, F., Turmalaj, L., Filipe, J., Sulçe, M., Agradi, S., Vigo, D., Muça, G., Menchetti, L., Ozuni, E., Barbato, O., Fehri, N. E., Castrica, M., Brecchia, G., & Curone, G. (2025). Effects of Goji Berry Supplementation on Immune-Related and Antioxidant Gene Expression in the Male Rabbit Reproductive Tract. Animals, 15(13), 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131921














