Simple Summary
Gastric ulcers are a common problem in performance horses and can affect their health, behaviour, and welfare. Ulcers are often linked to feeding practices involving high levels of starch and sugar and not enough fibre. Unfortunately, not all horses respond well to medication, so feed-based approaches to managing gastric ulcers alongside veterinary treatment are highly desirable. We examined how switching from a high- to low-starch diet affected gastric ulcers and the gut microbiome in elite showjumping horses. Over a 12 week period, we observed improvements in stomach health, with fewer and less severe ulcers following the diet change. Although we found no overall changes in gut bacteria communities, the balance between two major groups of bacteria shifted in a manner previously linked to improved gut health. These findings suggest that diet changes alone, without the use of anti-ulcer drugs, may improve gastric ulcer healing in performance horses.
Abstract
Equine gastric disease (EGD) is a common condition in performance horses (Equus caballus), potentially compromising behaviour, performance, and welfare. EGD is often attributed to high-starch, high-sugar feeds and limited forage. Evidence for diet-induced changes on digestive microbiota is lacking. Nine elite showjumping horses were housed at the same performance yard with standardised diet and management throughout the study. Horses were transitioned from a high-sugar and -starch (31%) feed to a low-starch and -sugar (16.5%) concentrate feed. Gastroscopies, blood, and faecal samples were taken pre- and 12 weeks post-diet change. Squamous and glandular ulceration was blindly graded a posteriori using 0–4 scores and faecal microbiota profiled using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Total (t(1,8) = −6.17, p < 0.001; Pre: 4 [0–5], Post: 1 [0–2]), squamous (t(1,8) = −5.32, p < 0.001; Pre: 1 [0–3], Post: 0 [0–1]), and glandular (t(1,8) = −2.53, p = 0.04; Pre: 2.5 [0–4], Post: 0 [0–2]) disease improved following the introduction of a low-starch diet. Diet change did not impact microbiota communities (PERMANOVA: F(1,16) = 1.37, p = 0.15, r2 = 0.08), but Firmicute to Bacteroidota (F/B) ratio reduced (t(1,8) = −3.13, p = 0.01; Pre: 2.07 ± 0.21 vs. Post: 1.29 ± 0.14). Lower F/B ratios were associated with reduced total EGD scores (ChiSq(1,17) = 3.83, p = 0.05). Low-starch diets did not influence faecal microbiota diversity but aided gastric disease healing and reduced F/B ratios in elite showjumpers during a competition season without medication.
1. Introduction
Equine gastric disease (EGD) is a prevalent and debilitating disease, encompassing lesions in the proximal squamous region (equine squamous gastric disease [ESGD]) and the distal glandular region (equine glandular gastric disease [EGGD]) of the stomach. EGD is prevalent in performance horses, affecting up to 100% of racehorses [1], 60% of eventers [2], and 70% of showjumpers [3]. Clinical signs are variable, but competition horses may present with subpar performance, reduced appetite and bodyweight [4]. Competing horses are typically provisioned with high-starch and -sugar feeds, alongside reduced quantities of long-stem forage, both established risk factors for ESGD development [5]. Risk factors for EGGD development are still unclear, but include stress, exercise intensity and frequency, high-starch diets [6], and reduced feeding frequency [7].
As hindgut fermenters, horses rely on a rich and diverse intestinal microbiota for fibre digestion, producing short-chain volatile fatty acids (VFAs) acetate, butyrate, and propionate, which supply up to 65% of the horse’s daily energy requirements [8,9]. In healthy horses, the faecal microbiota is dominated by Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria [10,11,12]. However, disease, diet, and antimicrobial or pharmaceutical use can negatively impact microbiota composition and fermentation capacity. Starch-rich diets and intestinal disease reduce microbiota diversity and richness [13,14] and increase abundance of lactic acid-producing bacteria [15,16,17,18,19], reducing hindgut pH [13] and cellulolytic taxa abundance [20,21]. The Firmicute/Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio has been proposed as a clinical indicator of gut dysbiosis in human patients [22], and high F/B ratios correspond with small and large intestinal colic in horses [23].
The high cost of medication, prescription requirements, and failure of clinical responses in many EGD cases [24] have encouraged investigations into nutritional supplements for preventing, or healing, gastric disease [25,26,27,28]. Altering feeding schedules successfully reduces EGD severity scores in unridden horses [29]; however, ad libitum access to long-stem forage has the greatest gastro-protective effect [30] by buffering gastric pH [31].
Understanding the influence of diet and feeding schedules on gut health in performance horses can contribute to the prevention of EGD and improve management and welfare in these populations. The objectives of the study were to determine if a low-starch feed, designed to protect gut health, would (1) reduce gastric disease severity and influence blood parameters, and (2) induce compositional changes in the digestive microbiota of competing showjumpers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
Nine showjumping Warmbloods, involved in national and FEI (1* to 5*) competitions, stayed at the same yard before and throughout the study. Our inclusion criteria required horses to be between 4–16 years old, in active showjumping training and competition, receiving no medication, and with no overt signs of gastrointestinal disease or compromised health. Horse ages ranged from 4–13 years old, with an average bodyweight 604 ± 4.3 kg at initial assessment, and 605 ± 4.3 kg post-diet change. Their average body condition score (BCS) was 5 ± 0.3 pre- and 5 ± 0.2 post-diet change, measured on a standardised 9-point BCS scale [32]. Horses were housed in individual stables for 18 h per day, bedded on shavings, and allowed access to turnout in separate grass paddocks for four hours per day. In the twelve weeks preceding the study, and throughout the twelve weeks post-diet change period, the horses exercised six times per week and maintained their competition schedules and levels. Full details of individual horse BCS, bodyweight, age, and exercise and competition schedules twelve weeks prior to, and throughout, the study period are detailed in Table S1. Nine weeks after implementing the diet change, Horse 7 received a course of antibiotics for a respiratory tract infection between the two sampling points.
2.2. Diet Change
Dietary requirements were determined based on BCS, total bodyweight (BWT), and exercise level. Initial assessments occurred when the horses were fed a high-starch and -sugar (31%) pelleted concentrate diet (HS feed; Table 1). This had been the maintenance diet for the prior 18 months. Horses were transitioned onto a low-starch and -sugar (16.5%) concentrate feed (Regul Digest, Lambey SAS, Torpes, France; Table 1), for twelve weeks, before subsequent re-assessment. Regul Digest is a complete feed with dry alfalfa chaff and variable particulate sizes, marketed as supporting gastrointestinal health. Horses were gradually transitioned from the HS feed to the low-starch feed over seven days to minimise gastrointestinal disturbance, with the twelve-week assessment period commencing on the first day horses exclusively received the new feed. Pre-diet change, horses were fed the HS feed at three points during the day (09:00, 12:00, 17:00) with Omento Sport fibre blocks (Omento, Switzerland) at 21:00. Post-diet change, horses were fed Regul Digest at four timepoints (09:00, 12:00, 17:00, and 21:00). Horses were provided with hay at 1.6% to 2.4% BWT/day, divided into four meals. All horses received the same quantity of hay, fed at the same timepoints (09:00, 12:00, 17:00, and 21:00), before and throughout the study. Hay was steamed pre-feeding to reduce respirable allergens using a commercial hay steamer (Haygain®, London, UK). We provided water and salt licks ad libitum, and no other supplementary feeding. Concentrate and hay quantities were weighed (kg) prior to feeding. A control visit for weight and BCS assessment was conducted four weeks after study commencement and feed quantities were adjusted if necessary. Horses were not administered any anti-ulcer medication during the study.

Table 1.
Nutrient composition of supplementary and long-stem forage portions of the diet provided throughout the length of the study (per kg feed), the overall nutrient intake per day (per kg feed), and the average ingested nutrients per day (g/kg body weight [BWT]) pre- and post-diet change.
2.3. Blood Collection
Venous blood was collected before and twelve weeks after changing the diet via jugular venipuncture into heparinized, plain, citrate, and EDTA tubes, and submitted for haematology and biochemistry at an external laboratory (Antech, Heppignies, Belgium).
2.4. Gastric Disease Scoring
Veterinarians performed gastroscopies at the initial assessment and twelve weeks post-diet change. Horses had feed withheld for 15–18 h and water for 2–3 h, and were sedated with 0.04 mg/kg romifidine (Sedivet®, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany), and the gastric mucosa was assessed using a flexible 3 m video-endoscope (VO320; Optomed®, Les Ulis, France). Gastric lesions were graded based on the score from Pineau et al. [33]. The total EGD score was calculated by adding the non-glandular and glandular lesion scores, both based on previously published scoring systems [30,34,35,36,37,38], with scores providing a qualitative severity rating from no pathology (NP) to moderately severe lesions (Table 2). After gastric mucosa assessment, we aspirated and collected 50 mL of gastric fluid using a sterile catheter inserted through the biopsy port of the endoscope, and collected rectal faecal samples whilst horses were sedated. We stored gastric aspirates and faecal samples in sample collection tubes (PowerBead Pro Tubes, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and sent them to an external microbiota sequencing company (EquiBiome®, Bangor, UK). Gastric disease was blindly scored by the two attending veterinarians (EVE and VP) a posteriori. Gastric disease scores pre- and post-diet change are shown as median [range].

Table 2.
The equine gastric disease quantitative grading method utilized [33] adapted from previously published scoring systems [30,34,35,36,37,38], with a maximum severity score of 8.
2.5. Microbiota Sequencing
The commercial equine microbiota sequencing company EquiBiome® performed faecal DNA extraction and rRNA gene sequencing. Faecal bacterial communities were profiled by 2 × 250 bp Illumina® (San Diego, CA, USA) next-generation Miseq amplicon sequencing of the V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene. We downloaded demultiplexed paired-end sequences, with non-biological nucleotides removed, from the EquiBiome® Illumina® BaseSpace Sequence Hub in FASTQ format for microbiota community analyses.
2.6. Microbiota Analyses
We performed all microbiota analyses on RStudio (v.4.3.1), using the dada2 package [39] (v.1.26) for initial filtering, trimming, and merging, sequence table construction, and chimera removal stages. We assigned taxonomy to amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) using the native Bayesian classifier database, Silva [40] (v.132). We used the DECIPHER package [41] (v.2.28.0) to align sequences for phylogenetic analyses, before using the phangorn [42] (v.2.11.1), and FastTree [43] (v.2.1.11) packages to construct maximum likelihood trees. All graphs were plotted using the ggplot2 package [44] (v.3.4.2).
We identified the core microbiota communities at the Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) level by determining OTUs shared across all horses pre- and post-diet change at ≥0.1% relative abundance, as previously described [45]. We determined the most abundant taxa at the phylum and family level from mean abundance measures before and after diet change. Proportion percentage changes of individual taxa pre- and post-diet change were calculated using the phylosmith [46] (v.1.0.7) and corncob [47] (v.0.3.2) packages.
Faecal microbiota alpha and beta diversity were computed using the phyloseq package [48] (v.1.44.0). We determined changes in alpha diversity metrics for richness (Shannon and Simpson’s diversity indices) using pairwise t-tests with Bonferroni correction. For beta diversity, we determined variation in individual microbiota phyla, families and class abundance, and faecal Firmicute to Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio changes, between pre- and post-diet change using pairwise t-tests with Bonferroni correction. We additionally selected bacterial families reported to have nutritional amylolytic or cellulolytic functions [45], or involvement in lactic acid production [49], from previous reviews. Variation in relative abundance of amylolytic or cellulolytic groups between the two sampling timepoints was determined using pairwise t-tests with Bonferroni correction.
The packages microbiomeMarker [50] (v.1.6.0) and microbial (v.0.0.20) were used to plot Linear Discriminate Analysis (LDA) Effect Size (LeFSe) bacterial taxa changes in response to diet change. All data was log10 transformed, normalized using counts per million (CPM), with a Kruskal–Wallis cut-off of 0.05 and an LDA cut-off value of 4. Due to the small sample size of nine horses, we removed multiple comparisons from LeFSe analysis. We assessed changes in gut-specific functional groups in response to diet modification using the prokaryote database NJC19 [51] in the microeco package [52] (v.1.0.0), using a differential abundance test of traits percentage and random forest model, reporting MeanDecreaseGini scores, with multiple comparisons removed due to the small sample size.
2.7. Associations Between Microbiota Structure and Gut Health
We used Shapiro–Wilk tests to assess data normality. We determined the influence of diet change on total EGD, glandular, and squamous disease scores using pairwise t-tests with Bonferroni correction. We determined relationships between faecal F/B ratio and total EGD, glandular, and squamous scores using linear mixed models with Type III Wald tests, with gastric disease score as the response variable, F/B ratio as the explanatory variable, and horse as the random variable. Linear mixed models with Type III Wald tests assessed the relationship between F/B ratio and selected blood markers, with blood marker as the response variable, F/B ratio as the explanatory variable, and horse as the random variable. We built linear mixed models using the lme4 package [53] (v.1.1-27.1) with Type III Wald tests using the car package [54] (v.3.1-2).
2.8. Blood Parameter Responses to Diet Change
Blood biochemistry and haematology parameters were used to broadly screen the health status of the population pre- and post-diet change. As all horses were competitive showjumpers, we retained biochemistry markers of liver and muscle functioning gamma glutamyl-transferase (GGT), aspartate amino-transferase (AST), and creatinine kinase (CK) and the antioxidant marker vitamin E as variables of interest. We assessed changes in selected blood parameter concentrations at the two assessment timepoints using pairwise t-tests with Bonferroni correction. Mean blood marker concentrations (±standard error of the mean [SEM]) were calculated using the plotrix [55] (v.3.8-2) package. Vitamin E values post-diet change were not available for Horse 4; therefore, we excluded this horse from pre/post analysis for this marker.
2.9. Microbiota Community Composition and Gastric Disease Score
To determine the variation in beta dispersion within faecal microbiota in response to diet change, we calculated microbiota beta dispersion (PERMDISP) using the microeco package [52]. Intra-individual variation in faecal microbiota community structure was calculated using permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA), with 10,000 permutations, using the microeco package [52] and adonis2() in the vegan package [56] (v.2.5.7). Associations between faecal microbiota community structure and total EGD, glandular, and non-glandular scores were determined using PERMANOVA. We determined relationships between faecal microbiota communities and individual variables, including body condition score, sex, age, and the influence of the individual horse, using PERMANOVA.
We calculated principal component analyses (PCAs) using covariance matrices and associated eigenvalues and eigenvectors, produced using the maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree and centred log ratio (clr) transformed values, and constructed using the microeco [52], microViz [57] (v.0.11.0), GUniFrac [58] (v.1.8), caret [59] (v.6.0-94), and ggplot2 [44] packages. PERMANOVA tests using adonis2() in the vegan package [56] were used to assess total dissimilarity of the faecal microbiota across diet change and EGD qualitative rating. We used taxa annotations on the PCA at phylum level to show sample clustering and similarity pre- and post-diet change in faecal microbiota, and associations between faecal microbiota community structure and total EGD rating.
3. Results
3.1. Blood Parameter Responses to Diet Change
Haematology parameters remained within normal limits pre- and post-diet change.
GGT (U/L), AST (UI/L), and CK (U/L) activity significantly decreased after diet change (Table 3). Antioxidant vitamin E (mg/L) concentration significantly increased after diet change, with two horses increasing from below the normal reference range prior to diet change. Additionally, GGT and AST activity, and vitamin E concentrations were associated with total EGD (Table 4), EGGD, and ESGD scores, and CK activity with EGD and ESGD scores in linear mixed models (Table 4).

Table 3.
Pairwise t-tests indicated blood liver and muscle enzyme markers reduced after transitioning to a low-starch diet, whereas circulating vitamin E concentrations increased after diet change.

Table 4.
Linear mixed models were used to determine relationships between total (EGD), squamous (ESGD), and glandular (EGGD) gastric disease scores and liver and muscle enzyme markers and circulating vitamin E concentrations.
3.2. Influence of Diet Change on Gastric Disease
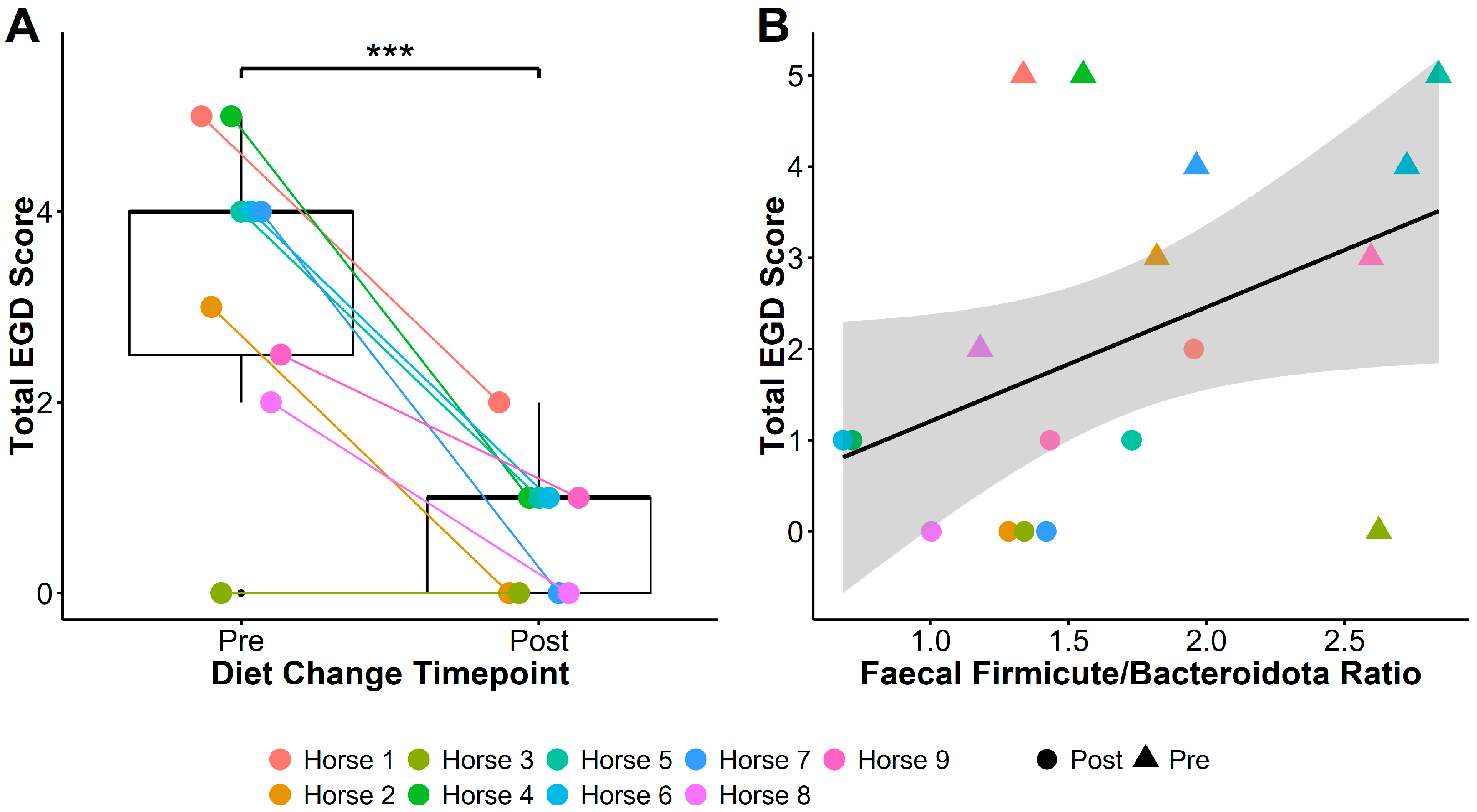
Glandular, squamous, and total gastric disease scores of all nine horses reduced between the two sampling time points. Total EGD score reduced from 4 [0–5] to 1 [0–2] (Pairwise t(1,8) = −6.17, p = 0.0002; Figure 1A), EGGD score from 2 [0–4] to 0 [0–2] (t(1,8) = −2.53, p = 0.04), and ESGD score from 1 [0–3] to 0 [0–1] (t(1,8) = −5.32, p = 0.0007).
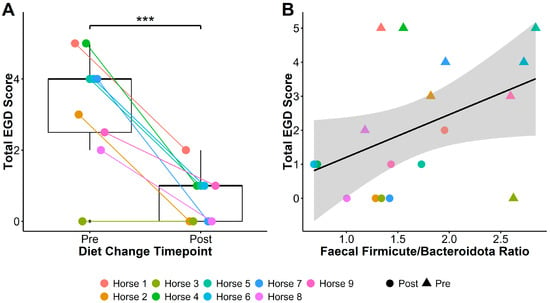
Figure 1.
Total EGD score (A) significantly reduced after transitioning horses to a low-starch diet, and faecal Firmicute to Bacteroidota (F/B) ratio (B) was associated with reductions in total EGD score post-diet change. Boxplots in (A) show total EGD scores pre- and post-diet change: middle lines represent the median; the top and bottom of the box represent the 3rd and 1st quartiles, respectively; box height indicates the interquartile range (IQR); and whiskers extend to the furthest values within 1.5 × IQR. Plot (B) shows the relationship between F/B ratios and total EGD score, with triangles indicating pre-diet change, and circles indicating post-diet change samples. The solid line represents the fitted linear regression, and the shaded area shows the standard error around the regression line. *** = p < 0.001.
3.3. Gastric and Faecal Microbiota Phylogenetic Sequencing
After chimeras were removed, 1,311,714 paired-end sequences were retained as high-quality sequences from 18 samples. Faecal samples had an average read number of 16,226 ± 712.3 and sequence reads were similar pre- and post-diet change. A total of 27,162 ASVs were identified across all samples. Across faecal samples, 99.5% of reads were classified at phylum, 72.6% at family, and 45% at genus level. Gastric fluid samples collected during gastroscopy were additionally sent for sequencing; however, due to poor sequence quality, these were excluded from final analyses.
3.4. Core Microbiota
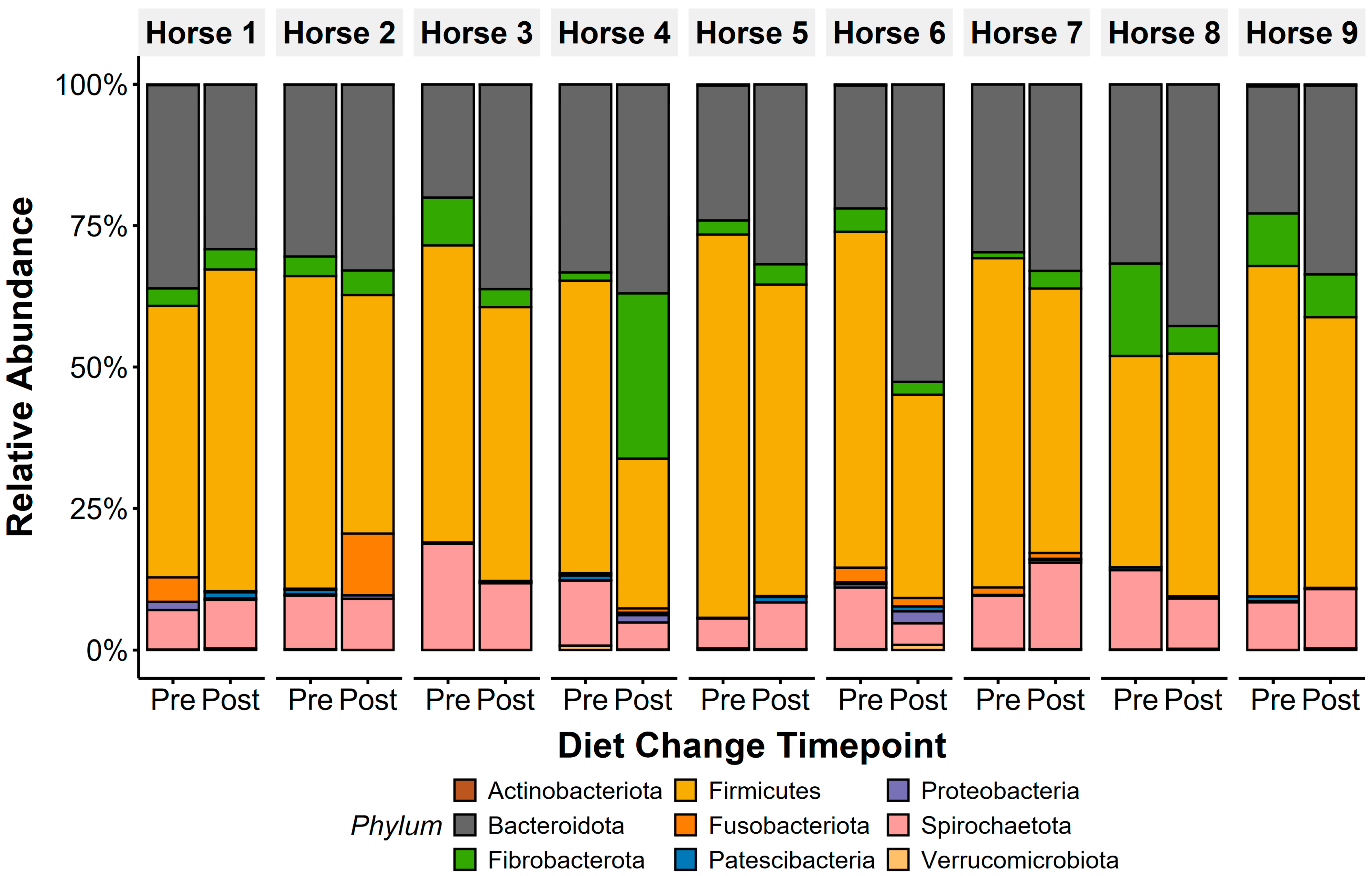
The core microbiota community at the Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) level was determined by identifying OTUs shared across all horses in the study at ≥0.1% relative abundance, as previously described [45]. Faecal microbiota were heavily dominated by the phylum Firmicutes (pre: 54.2 ± 2.8%, post: 44.6 ± 3.1%; Figure 2), with Bacteroidota as the second most abundant phylum (pre: 27.6 ± 1.9%, post: 36.4 ± 2.4%). Families from the phyla Firmicutes (Lachnospiraceae; pre: 20.2 ± 2.5%, post: 10.2 ± 1.4%; Erysipelatoclostridiaceae: pre: 7.6 ± 1.6%, post: 8.7 ± 1.2%), Spirochaetota (Spirochaetaceae: pre: 10.5 ± 1.3%, post: 8.9 ± 1.2%), Bacteroidota (Rikenellaceae: pre: 8.5 ± 1.2%, post: 10.1 ± 1.1%), and Fibrobacterota (Fibrobacteraceae: pre: 5.5 ± 1.7%, post: 6.8 ± 2.9%) were highly abundant in faecal microbiota.
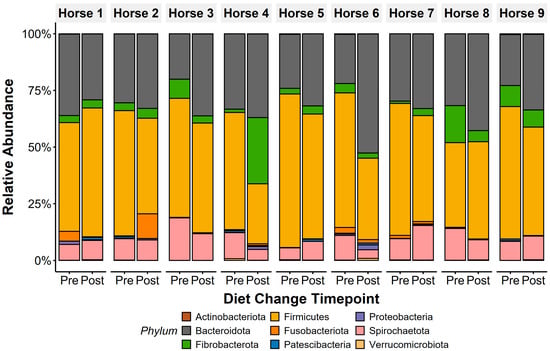
Figure 2.
Faecal microbiota composition of all horses was dominated by anaerobic bacterial phyla, with Firmicutes and Bacteroidota presenting the highest abundance in both sample types. Other anaerobic taxa, including Fibrobacterota, Spirochaetota, and Fusobacteriota, were additionally identified pre- and post-diet changes. Only phyla with >0.1% mean relative abundance are displayed.
3.5. Alpha Diversity Measures
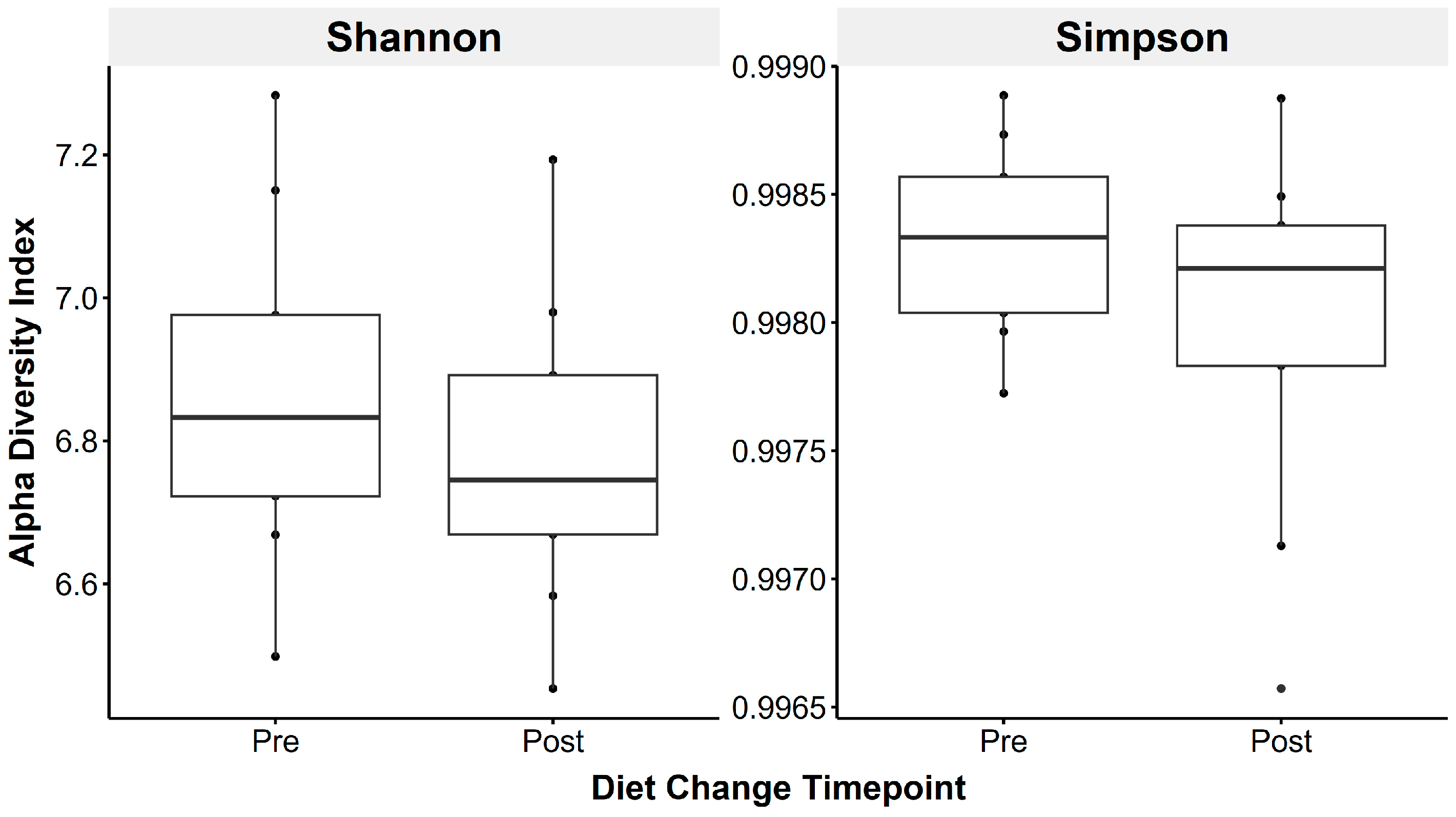
Faecal microbiota species richness did not change following the introduction of a low-starch diet (Shannon: t(1,8) = 0.83, p = 0.43; Simpson: t(1,8) = 1.49, p = 0.18; Figure 3).
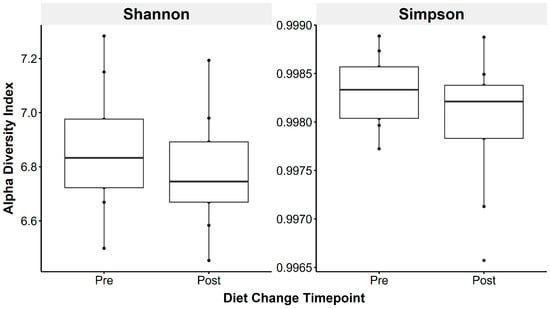
Figure 3.
Faecal microbiota alpha diversity metrics were not significantly altered by transitioning horses to a low-starch diet, using the Shannon (left) and Simpson (right) indices, reflecting species richness and evenness.
3.6. Beta Diversity Measures
3.6.1. Changes in Microbiota Composition
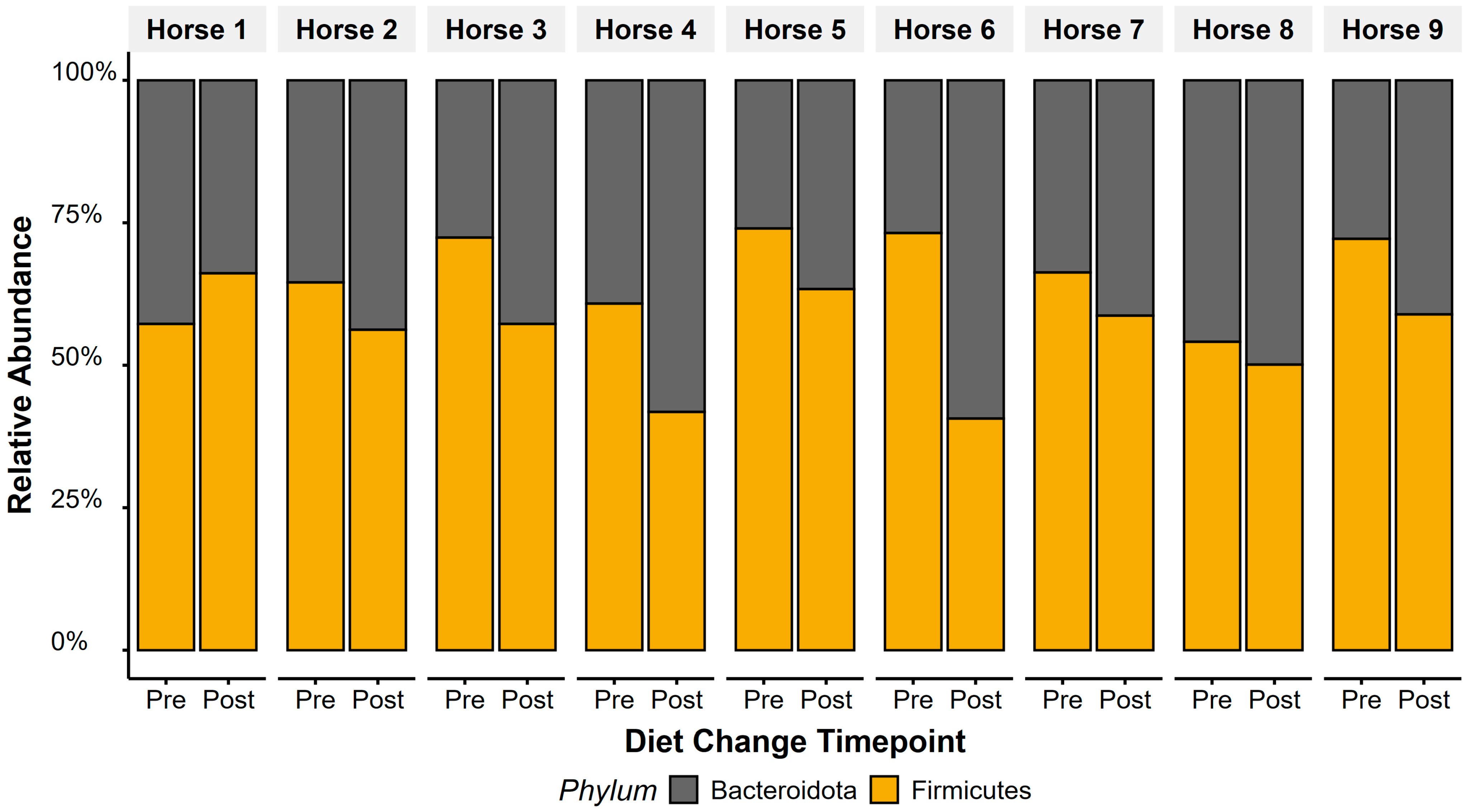
Bacteroidota relative abundance increased (t(1,8) = 2.5, p = 0.04) and Firmicutes decreased (t(1,8) = −2.5, p = 0.037) in faecal microbiota after diet change (Figure 4). Overall, this led to a decrease in F/B ratios following the diet change (t(1,8) = −3.13, p = 0.01), with faecal F/B ratio dropping from a ratio of 2.07 (±0.21) to 1.29 (±0.14). Horse 1 showed opposing patterns to Horses 2–9, showing an increase in F/B ratios after diet change.
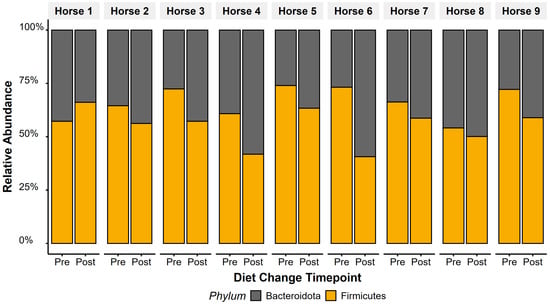
Figure 4.
Twelve weeks after transitioning to a low-starch diet, relative abundance of Firmicutes decreased and Bacteroidetes increased, reflecting significant responses in faecal F/B ratios to diet change. Average faecal F/B ratios dropped from 2.07 (±0.21) to 1.29 (±0.14).
3.6.2. Changes in Functional Groups
The relative abundance of Lachnospiraceae (t(1,8) = −4.73, p = 0.002), but not Lactobacillaceae (t(1,8) = −2.13, p = 0.07), reduced after diet change. Grouped lactic acid-producing families, including Lactobacillaceae, Streptococcaceae, Spirochaetaceae, and Rikenellaceae decreased in abundance after diet change (t(1,80) = −4.32, p = 0.0004). Grouped amylolytic families, including Streptococcaceae, Succinivibrionaceae, Lactobacillus, and Enterococcaceae, similarly reduced in abundance post-diet change (t(1,35) = −2.07, p = 0.05). Diet change did not influence the relative abundance of grouped cellulolytic families, including Ruminococcaceae, Fibrobacteraceae, Lachnospiraceae, Prevotellaceae, Eubacteriaceae, Clostridiaceae, and Acidaminococcaceae (t(1,62) = 1.01, p = 0.32) and the mucin-producing phyla Verrucomicrobiota did not respond to diet change (t(1,8) = 0.38, p = 0.71). Linear Discriminate Analysis (LDA) Effect Size (LEfSe) (Figure S1) shows decreases in Firmicutes phyla (LDA: 5.03, p = 0.02), and enrichment in Bacteroidota phyla (LDA: 4.97, p = 0.01), in faecal microbiota from pre- to post-diet changes. Decreases in abundance of other taxa in response to diet change include Lachnospiraceae (LDA: 5.7, p = 0.004) and Oscillospiraceae (LDA: 4.97, p = 0.04). Taxa abundance enrichment below the phylum level post-diet change were all below the LDA cut-off value.
Functional potential of faecal microbiota community gut taxa pathways was predicted using the prokaryote database NJC19 [51]. There was no significant enrichment in digestion pathways after diet change; however, non-significant decreases in H2O2 production were identified in faeces post-diet change (MeanDecreaseGini: 0.25; p = 0.09).
3.6.3. Associations Between Microbiota Structure and Gut Health
Irrespective of timing, lower Firmicute to Bacteriodota ratios (F/B ratios) were associated with lower total EGD (linear mixed models [LMM]: ChiSq(1,17) = 3.83, p = 0.05; Figure 1B) and EGGD (ChiSq(1,17) = 6.38, p = 0.01) scores, but not ESGD scores (ChiSq(1,17) = 0.8, p = 0.4). Faecal F/B ratio was additionally associated with elevated vitamin E concentration (LMM: ChiSq(1,17) = 6.88, p = 0.009), and reduced GGT activity (ChiSq(1,17) = 6.68, p = 0.01) and CK (ChiSq(1,17) = 7.31, p = 0.007).
3.6.4. Microbiota Community Composition and Gastric Ulceration Score
Diet change did not lead to significant changes in intra-individual (PERMANOVA; F(1,16) = 1.37, p = 0.2, r2 = 0.08; Figure S2A) faecal microbiota community structure, despite observed variations between individual horses. Microbiota beta dispersion did not vary within faecal microbiota communities in response to diet change (PERMDISP; F(1,16) = 0.02, p = 0.8). Gastric disease severity scoring categories pre- and post-diet change were not associated with intra-individual (PERMANOVA; F(6,11) = 1.06, p = 0.4, r2 = 0.06) differences in faecal microbiota community structure (Figure S2B).
Faecal microbiota communities were not associated with total EGD score (PERMANOVA; F(6,11) = 0.9, p = 0.6, r2 = 0.05), EGGD (F(5,12) = 0.94, p = 0.5, r2 = 0.06), or ESGD (F(5,12) = 0.74, p = 0.7, r2 = 0.04) scores. Faecal microbiota composition was not associated with other variables, including individual horse (F(8,9) = 0.77, p = 0.9, r2 = 0.41), body condition score (F(5,10) = 0.87, p = 0.6, r2 = 0.05), sex (F(2,13) = 0.85, p = 0.7, r2 = 0.10), and age (F(4,11) = 0.84, p = 0.8, r2 = 0.21).
4. Discussion
Within our population of high-level showjumpers, switching from a high-starch (29%) to a low-starch (11%) concentrate feed supported gastric disease healing during a competitive season without medication. Although overall microbiota diversity or composition remained unchanged, faecal Firmicute to Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratios reduced, aligning closely with ratios previously reported in healthy horses [23].
Gastric disease is prevalent in high-level performance horses, with risk factors including breed [60], competition schedules [3], and transportation stress [61]. In our cohort, 89% of horses presented with gastric lesions ≥ Grade 2 severity at study onset, higher than previously reported in showjumpers [3], yet lower than racehorses in training [1]. Although pharmaceuticals are the primary treatment for gastric ulceration, spontaneous healing without treatment is not well documented [62], and dietary supplement efficacy remains inconsistent [25,26,27,28]. Dietary management, particularly providing low-starch diets, has shown efficacy at preventing ESGD [63] and EGGD recurrence [35].
As performance level, exercise intensity and pasture turnout were unchanged in the twelve weeks before and after diet change (Table S1), high dietary starch likely contributed to initial gastric disease development. Although the low-starch feed contained a marginally higher sugar content (Table 1), simple sugars can promote Lactobacillus colonisation in the equine glandular stomach [35], a mechanism that aids ulcer healing in rats [64]. Variable particulate sizes and short-stem alfalfa in the tested feed may have reduced mechanical mucosal injury during peristalsis [65]. Alfalfa’s high calcium and protein content also buffer gastric pH [66], reducing EGGD severity and incidence [35]. While we cannot definitively isolate which feed component, whether particulate size, macronutrient (starch, fat, sugar), or micronutrient composition was most beneficial, gastric ulcer scores improved after twelve weeks of feeding, and the same horses showed no change in exercise performance [33]. These findings warrant further targeted investigations into how specific macronutrients, micronutrients, and physical feed characteristics exert gastroprotective [35,65,66] or gastro-injurious [67,68,69,70] effects in equid gastric disease.
Although regular grazing is considered protective against gastric disease, our horse cohort had four hours of grass paddock access, plus daily roughage at 1.6–2.4% of bodyweight in the twelve weeks preceding, and throughout the study. Indeed, broodmares at pasture still develop gastric lesions [71], whereas management changes alongside ad libitum roughage feeding assist lesion healing, even without omeprazole [72]. Despite the time at grass remaining standardised before and after diet change, we did not quantify seasonal fluctuations in grass nutrient content; however, we saw no microbiota shifts typically associated with seasonal grazing changes [73]. Future studies should integrate longitudinal microbiota sequencing, repeated gastroscopies, and analysis of grass non-structural and water-soluble carbohydrate levels to clarify how seasonal pasture variation affects equid gastric health.
Faecal microbiota were dominated by Firmicutes (pre: 54%, post: 45%) and Bacteroidota (pre: 28%, post: 36%), mirroring profiles in Thoroughbred racehorses [74,75] and Arabian endurance horses [76]. In contrast, non-performance horses exhibit higher Bacteroidota abundance [10], indicating performance horses may exhibit distinct faecal microbiota compared to convalescing, retired, or leisure horses. Despite differences in gastric physiology, reduced Bacteroidetes abundance is associated with gastric disease in humans [77], similar to our observation of lower Bacteroidota pre-diet change when lesion scores were highest. Faecal microbiota communities, however, are unlikely to reflect proximal intestine or gastric conditions, and our observed F/B shifts likely reflect dietary alterations more than EGD severity. Nevertheless, these parallels suggest, as in human athletes [78,79,80,81], exercise capacity and diet may shape distinct microbiota signatures in performance horses.
Alpha-diversity and β-diversity metrics remained stable between sampling timepoints. As all horses were deemed clinically healthy throughout, pronounced microbiota dysbiosis was not expected, and the lack of diversity shifts post-diet change was anticipated. However, the F/B ratio decreased after diet change (pre: 2.07 ± 0.21, post: 1.29 ± 0.14), approaching values reported in healthy horses [23]. Elevated Firmicutes and F/B ratios have been linked to gastrointestinal disease [23], doxycycline treatment [82], and obesity [83,84] in humans and horses. Although no standardised healthy F/B threshold exists in equids [84,85,86,87], our findings indicate faecal F/B ratios show potential as a non-invasive microbiota marker of gastrointestinal health.
While nearly all exhibited reduced Firmicutes abundance and F/B ratios after diet change, Horse 1 showed the opposite pattern. Horse 7 received doxycycline for a respiratory infection at week 9, and showed no microbiota community changes. However, by the final sampling timepoint, the faecal microbiome may have stabilized [86], masking any doxycycline-associated impact. The cause of Horse 1’s divergent response remains unclear. Future studies with larger cohorts and more frequent sampling points are necessary to elucidate intra-individual microbiota variability across time.
Before diet change, lactic acid-producing taxa (Lachnospiraceae, Lactobacillaceae, and Lachnospiraceae) and amylolytic taxa (Streptococcaceae, Lactobacillus, and Enterococcus) were more abundant. Overgrowth of these families lowers intestinal pH [8], disrupts microbiota balance [88], and can precipitate hindgut acidosis, laminitis, and colic [23]. Oscillospiraceae was also elevated pre-diet change, but its function in the equine gut remains unclear, despite links to obesity and metabolic disorders in humans [89]. These compositional shifts likely reflect decreased starch fermentation; however, further investigations (e.g., faecal pH, metabolite profiling) are required to determine the roles of lactic acid-producing, amylolytic, and cellulolytic taxa in equid digestive health.
We monitored liver and muscle enzymes (CK, GGT, AST) and antioxidant status (vitamin E) due to their potential performance benefits. All blood enzymes and vitamin E remained within normal limits at both timepoints (Table 3), but CK, AST, and GGT activity decreased, whereas vitamin E concentrations increased after diet change. In our horses, higher EGD, ESGD, and EGGD scores associated with higher CK, AST, and GGT, yet lower vitamin E. These patterns align with equid reports linking gastric disease to high systemic CK [90] and GGT [91] and high salivary GGT, CK [92], and AST [93], alongside rat studies showing lower blood GGT [94] during ulcer healing. Additionally, lower GGT has been linked to improved feed digestibility [95,96] and improved training adaptations [97]. However, given our sample size constraints, we cannot discern whether these blood enzyme and antioxidant changes stem from gastric healing or dietary provision.
This study has some limitations: the EGD quantitative grading system, unmeasured grass nutrients, lack of control group, small sample size, and two-timepoint sampling may have restricted some inferences. We implemented an ordinal EGD scoring method [33], combining glandular and squamous scores [30,34,35,36,37,38], to capture lesion extent and distribution, and expected mucosal healing responses of erythematous, haemorrhagic, fibrinosuppurative lesions (Table 2), while preserving resolution and inter-observer reliability [30,37,98]. Although this approach may introduce measurement error, we minimised this by using two blinded, experienced veterinarians for lesion scoring. Secondly, we attempted gastric fluid microbiota sequencing, but low read counts necessitated exclusion from analysis. Recent successful sequencing (e.g., [17]) indicates tissue and gastric juice sampling may be required. Thirdly, we did not quantify seasonal variation in grass nutrients, which may have contributed to gastric healing. Fourthly, our small sample size, with only two sampling timepoints, limits some conclusions due to the potential for sampling bias and low statistical power. Finally, although our longitudinal, within-individual design controls for individual variability, the lack of an additional control group limits our ability to account for time-related confounders or broader population-level changes that may have influenced outcomes independently of the diet change.
5. Conclusions
We show a commercial low-starch concentrate feed assisted in reducing gastric disease scores and improving faecal F/B ratios in competing performance horses without conventional anti-ulcer medication. Although initial lesion severity was mild, reflecting naturally occurring ulcers in this population, these same horses exhibited fewer ridden pain-associated behaviours after diet change [33]. While causal inference is limited by our small cohort, these results underscore the critical role of dietary composition in equine gastric functionality and lesion healing. Moreover, they highlight the need for deeper investigations into gut microbiota dynamics during exercise and competition in high-level performance horses.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani15131908/s1, Table S1: Competition level, number of competitions, and ridden exercise frequency and level remained standardised in the twelve weeks preceding the diet change, and in the twelve weeks after diet change; Figure S1. LEfSe analysis was used to identify changes in microbiota taxa across phylum, family, order, and genus levels after transitioning horses to a low-starch diet; Figure S2. Principal component analysis (PCA) produced at the phylum level, representing impacts of transitioning horses to a low-starch diet. Reference [32] is cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.I., V.P., S.S., F.t.W. and E.v.E.-W.; methodology, J.I., V.P., S.S., F.t.W. and E.v.E.-W.; software, J.I. and S.S.; validation, J.I., V.P., S.S. and E.v.E.-W.; formal analysis, J.I. and S.S.; investigation, V.P., F.t.W. and E.v.E.-W.; resources, J.I., V.P., S.S., F.t.W. and E.v.E.-W.; data curation, J.I., V.P., S.S., F.t.W. and E.v.E.-W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.I., V.P., S.S. and E.v.E.-W.; writing—review and editing, J.I., V.P., S.S., F.t.W. and E.v.E.-W.; visualization, J.I., V.P., S.S. and E.v.E.-W.; supervision, S.S. and E.v.E.-W.; project administration, J.I., V.P., S.S. and E.v.E.-W.; funding acquisition, V.P., S.S., F.t.W., F.J., S.L. and E.v.E.-W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Lambey SAS funded the study. J. Irving’s PhD studentship is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) Doctoral Training Partnership (Project reference 2625299).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived as this study reports clinical findings from routine veterinary assessment of client-owned performance horses. All examples of gastric ulceration in horses were naturally occurring, and this did not influence animal inclusion (i.e., animals were included opportunistically based on the owner’s suggestions). All procedures horses received (gastroscopy and blood sampling) are standardised, routine veterinary clinical practices conducted by the private equine veterinary practice (Equine Sports Medicine Practice) and were sanctioned by the owner of the horses. We obtained the consent of owners and attending registered veterinarians (VP and EVE, Equine Sports Medicine Practice) for publication of all findings. All horses were maintained in their usual housing, with the main staff and schedule throughout the length of the study. High standards of veterinary care and Good Clinical Practices were adhered to throughout.
Informed Consent Statement
Owners of all horses provided informed consent for participation and for the use of clinical data.
Data Availability Statement
If the paper is accepted for publication, all associated sequence data will be uploaded to GenBank for data sharing. Further data presented in the study is available on request to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to address their warmest thanks to Nathan Budd for preparing and riding all horses throughout the study. They also thank the owners and staff at the Haras des Rosiers for their active and enthusiastic participation in this study. We additionally wish to thank Emma Caudron and Marie Louvigny for assisting with sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
Félicie Julien and Sandrine Lambey are employees of the company Lambey SAS, which provided the product Regul Digest. The funders had no role in the study design, collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, manuscript writing, or decision to publish the results. Other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AST | Aspartate amino-transferase |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variants |
| BCS | Body condition score |
| BWT | Body weight |
| ChiSq | Chi-squared distribution (χ2) |
| CK | Creatine kinase |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CLR | Centred log ratio |
| CPM | Counts per million |
| DE | Digestible energy |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ECEIM | European College of Equine Internal Medicine |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EGD | Equine Gastric Disease |
| EGGD | Equine Glandular Gastric Disease |
| EGUS | Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome |
| ESGD | Equine Squamous Gastric Disease |
| F/B Ratio | Firmicute to Bacteroidetes Ratio |
| FEI | Fédération Équestre Internationale |
| GGT | Gamma glutamyl-transferase |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| HK | Hyperkeratosis |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LDA | Linear discriminate analysis |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminate analysis effect size |
| LMM | Linear mixed model |
| MJ | Megajoules |
| NP | No pathology |
| NSC | Non-structural carbohydrate |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| rRNA | Ribosomal RNA |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| VFA | Volatile fatty acids |
| WSC | Water-soluble carbohydrate |
References
- Hwang, H.; Dong, H.J.; Han, J.; Cho, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, I. Prevalence and treatment of gastric ulcers in Thoroughbred racehorses of Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidegger, M.D.; Gerber, V.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; van der Kolk, J.H.; Burger, D.; Ramseyer, A. Increased Adrenocortical Response to Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) in Sport Horses with Equine Glandular Gastric Disease (EGGD). Vet. J. 2017, 228, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, S.K.; Cribb, A.E.; Windeyer, M.C.; Read, E.K.; French, D.; Banse, H.E. Risk Factors for Equine Glandular and Squamous Gastric Disease in Show Jumping Warmbloods. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, B.W.; Bowen, M.; Habershon-Butcher, J.L.; Green, M.; Hallowell, G.D. Management Factors and Clinical Implications of Glandular and Squamous Gastric Disease in Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinelli, N.; Wambacq, W.; Broeckx, B.J.G.; Hesta, M. High Intake of Sugars and Starch, Low Number of Meals and Low Roughage Intake Are Associated with Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome in a Belgian Cohort. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 105, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombino, E.; Raspa, F.; Perotti, M.; Bergero, D.; Vervuert, I.; Valle, E.; Capucchio, M.T. Gut Health of Horses: Effects of High Fibre vs High Starch Diet on Histological and Morphometrical Parameters. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, L.; Swain, E.; Santos, H.; Hess, T.; Black, J. Effects of Feeding Frequency Using a Commercial Automated Feeding Device on Gastric Ulceration in Exercised Quarter Horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 64, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, A.S.; Black, S.J.; Blanchard, J.L. An In Vitro Model of the Horse Gut Microbiome Enables Identification of Lactate-Utilizing Bacteria That Differentially Respond to Starch Induction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julliand, V.; Grimm, P. Horse Species Symposium: The Microbiome of the Horse Hindgut: History and Current Knowledge. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 2262–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, H.L.; Pitta, D.; Indugu, N.; Vecchiarelli, B.; Engiles, J.B.; Southwood, L.L. Characterization of the Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 79, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Silva, G.; Ramos, R.V.; Staempfli, H.R.; Arroyo, L.G.; Kim, P.; Weese, J.S. Characterization and Comparison of the Bacterial Microbiota in Different Gastrointestinal Tract Compartments in Horses. Vet. J. 2015, 205, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Kim, P.T.; Sturgeon, A.; Weese, J.S. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Horses and Horses with Colitis by High Throughput Sequencing of the V3–V5 Region of the 16s rRNA Gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, N.C.K.; Avershina, E.; Mydland, L.T.; Næsset, J.A.; Austbø, D.; Moen, B.; Måge, I.; Rudi, K. High Nutrient Availability Reduces the Diversity and Stability of the Equine Caecal Microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, e27216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspa, F.; Chessa, S.; Bergero, D.; Sacchi, P.; Ferrocino, I.; Cocolin, L.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Moretti, R.; Cavallini, D.; Valle, E. Microbiota characterization throughout the digestive tract of horses fed a high-fiber vs. a high-starch diet. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1386135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, P.; Philippeau, C.; Julliand, V. Faecal Parameters as Biomarkers of the Equine Hindgut Microbial Ecosystem under Dietary Change. Animal 2017, 11, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulmer, L.S.; Murray, J.A.; Burns, N.M.; Garber, A.; Wemelsfelder, F.; McEwan, N.R.; Hastie, P.M. High-Starch Diets Alter Equine Faecal Microbiota and Increase Behavioural Reactivity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, L.J.; Ericsson, A.C.; Andrews, F.M.; Keowen, M.L.; Morales Yniguez, F.; Garza, F.; Banse, H.E. Gastric Microbiome in Horses with and without Equine Glandular Gastric Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2458–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erck-Westergren, E.; ter Woort, F. Diet-induced Changes in Gastric and Faecal Microbiota in Horses: Association with Gastric Ulcer Healing. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venable, E.B.; Kerley, M.S.; Raub, R. Assessment of Equine Fecal Microbial Profiles during and after a Colic Episode Using Pyrosequencing. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2013, 33, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, B.; Girard, I.D.; Jacotot, E.; Julliand, V. Effect of a Preparation of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae on Microbial Profiles and Fermentation Patterns in the Large Intestine of Horses Fed a High Fiber or a High Starch Diet. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 2600–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julliand, V.; De Fombelle, A.; Drogoul, C.; Jacotot, E. Feeding and Microbial Disorders in Horses: Part 3—Effects of Three Hay:Grain Ratios on Microbial Profile and Activities. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2001, 21, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.; Cheong, H.; Yoon, J.; Kim, A.; Yun, Y.; Unno, T. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota of Horses with Intestinal Disease and Their Healthy Counterparts. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, B.W.; Sykes, K.M.; Hallowell, G.D. A Comparison between Pre- and Post Exercise Administration of Omeprazole in the Treatment of Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome: A Blinded, Randomised, Clinical Trial. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venner, M.; Lauffs, S.; Deegen, E. Treatment of Gastric Lesions in Horses with Pectin-Lecithin Complex. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 1999, 31, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.J.; Grady, T.C. The Effect of a Pectin-Lecithin Complex on Prevention of Gastric Mucosal Lesions Induced by Feed Deprivation in Ponies. Equine Vet. J. 2002, 34, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, N.K.; Auer, A.D.; Garza, F.; Keowen, M.L.; Kearney, M.T.; McMullin, R.B.; Andrews, F.M. Effect of Sea Buckthorn Berries and Pulp in a Liquid Emulsion on Gastric Ulcer Scores and Gastric Juice PH in Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, M.C.; Huff, N.K.; Garza, F.; Keowen, M.L.; Kearney, M.T.; Andrews, F.M. Effect of Pectin, Lecithin, and Antacid Feed Supplements (Egusin®) on Gastric Ulcer Scores, Gastric Fluid PH and Blood Gas Values in Horses. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowers, N.L.; Waldron, L.A.; Pryor, I.D.; Hill, S.R.; O’Brien, J. The Influence of Two Lucerne-Based Forage Feeds, FiberProtect® and FiberEdge® on Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome in Horses. J. Appl. An. Nut. 2013, 2, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, B.W.; Hewetson, M.; Hepburn, R.J.; Luthersson, N.; Tamzali, Y. European College of Equine Internal Medicine Consensus Statement-Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome in Adult Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.J.; Schusser, G.F. Measurement of 24-h Gastric PH Using an Indwelling PH Electrode in Horses Unfed, Fed and Treated with Ranitidine. Equine Vet. J. 1993, 25, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneke, D.R.; Potter, G.D.; Kreider, J.L.; Yeates, B.F. Relationship between Condition Score, Physical Measurements and Body Fat Percentage in Mares. Equine Vet. J. 1983, 15, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, V.; ter Woort, F.; Julien, F.; Vernant, M.; Lambey, S.; Hébert, C.; Hanne-Poujade, S.; Westergren, V.; van Erck-Westergren, E. Improvement of Gastric Disease and Ridden Horse Pain Ethogram Scores with Diet Adaptation in Sport Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024, 38, 3297–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, B.W.; Jokisalo, J.M. Rethinking Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome: Part 1—Terminology, Clinical Signs and Diagnosis. Equine Vet. Educ. 2014, 26, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julliand, S.; Buttet, M.; Hermange, T.; Hillon, P.; Julliand, V. Effect of Diet Composition on Glandular Gastric Disease in Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J.C.; Wilkes, E.J.A.; Raidal, S.L.; Xie, G.; Crosby, D.E.; Hale, J.N.; Hughes, K.J. Interobserver and Intraobserver Reliability for 2 Grading Systems for Gastric Ulcer Syndrome in Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendle, D.; Bowen, M.; Brazil, T.; Conwell, R.; Hallowell, G.; Hepburn, R.; Hewetson, M.; Sykes, B. Recommendations for the Management of Equine Glandular Gastric Disease. UK-Vet Equine 2018, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshut, F.; Venner, M.; Martinsson, G.; Vervuert, I. The Effects of Feeding Sodium Chloride Pellets on the Gastric Mucosa, Acid-base, and Mineral Status in Exercising Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.S. Using DECIPHER v2.0 to Analyze Big Biological Sequence Data in R. R-Journal 2016, 8, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliep, K.P. Phangorn: Phylogenetic Analysis in R. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. Fasttree: Computing Large Minimum Evolution Trees with Profiles Instead of a Distance Matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2011, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauter, A.; Epping, L.; Semmler, T.; Antao, E.M.; Kannapin, D.; Stoeckle, S.D.; Gehlen, H.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Günther, S.; Wieler, L.H.; et al. The Gut Microbiome of Horses: Current Research on Equine Enteral Microbiota and Future Perspectives. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. phylosmith: An R-Package for Reproducible and Efficient Microbiome Analysis with Phyloseq-Objects. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.D.; Witten, D.; Willis, A.D. Modeling Microbial Abundances and Dysbiosis with Beta-Binomial Regression. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2020, 14, 94–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, L.M.T.; Botha, M.; Dicks, E.; Botes, M. The Equine Gastro-Intestinal Tract: An Overview of the Microbiota, Disease and Treatment. Livest. Sci. 2014, 160, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Niu, C. MicrobiomeMarker: An R/Bioconductor Package for Microbiome Marker Identification and Visualization. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 4027–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R.; Cabatbat, J.J.T.; Martin, T.L.P.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Sung, J.; Ghim, C.M.; Kim, P.J. Large-Scale Metabolic Interaction Network of the Mouse and Human Gut Microbiota. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. Microeco: An R Package for Data Mining in Microbial Community Ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lemon, J. Plotrix: A Package in the Red Light District of R; R-News: Rochester, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a Package of R Functions for Community Ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, D.; Arts, I.; Penders, J. MicroViz: An R package for microbiome data visualization and statistics. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Package, T.; Chen, A.J. GUniFrac: Generalized UniFrac Distances, Distance-Based Multivariate Methods and Feature-Based Univariate Methods for Microbiome Data Analysis. CRAN 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/GUniFrac/GUniFrac.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the Caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mönki, J.; Hewetson, M.; Virtala, A.M.K. Risk Factors for Equine Gastric Glandular Disease: A Case-Control Study in a Finnish Referral Hospital Population. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalino, B.; Davis, G.L.; Raidal, S.L. Effects of Transportation on Gastric PH and Gastric Ulceration in Mares. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharbine, K.P.; McConnell, E.J.; Secombe, C.; Byrne, D. The Prevalence and Changes over Time of Equine Glandular Gastric Disease in a Teaching Herd Population. Equine Vet. Educ. 2023, 35, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthersson, N.; Bolger, C.; Fores, P.; Barfoot, C.; Nelson, S.; Parkin, T.D.H.; Harris, P. Effect of changing diet on gastric ulceration in exercising horses and ponies following cessation of omeprazole treatment. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2017, 83, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, S.N.; Buret, A.; McKnight, W.; Miller, M.J.S.; Wallace, J.L. Bacteria rapidly colonize and modulate healing of gastric ulcers in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G425–G432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métayer, N.; Lhǒte, M.; Bahr, A.; Cohen, N.D.; Kim, I.; Roussel, A.J.; Julliand, V. Meal size and starch content affect gastric emptying in horses. Equine Vet. J. 2004, 36, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lybbert, T.; Gibbs, P.; Cohen, N.; Scott, B.; Sigler, D. Feeding alfalfa hay to exercising horses reduces the severity of gastric squamous mucosal ulceration. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–5 December 2007; pp. 525–526. [Google Scholar]
- Fedtke, A.; Pfaff, M.; Volquardsen, J.; Venner, M.; Vervuert, I. Effects of feeding different roughage-based diets on gastric mucosa after weaning in Warmblood foals. Pferdeheilkunde 2015, 31, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vondran, S.; Venner, M.; Vervuert, I. Effects of two alfalfa preparations with different particle sizes on the gastric mucosa in weanlings: Alfalfa chaff versus alfalfa pellets. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappai, M.G.; Picciau, M.; Pinna, W. Ulcerogenic risk assessment of diets for pigs in relation to gastric lesion prevalence. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse Liesner, V.; Taube, V.; Leonhard-Marek, S.; Beineke, A.; Kamphues, J. Integrity of gastric mucosa in reared piglets—Effects of physical form of diets (meal/pellets), pre-processing grinding (coarse/fine) and addition of lignocellulose (0/2.5%). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2009, 93, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Jeune, S.S.; Nieto, J.E.; Dechant, J.E.; Snyder, J.R. Prevalence of gastric ulcers in thoroughbred broodmares in pasture: A preliminary report. Vet. J. 2009, 181, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, L.C.; van der Poel, S.H.; Warmelink, T.S.; van Doorn, D.A.; van den Boom, R. Changes in management lead to improvement and healing of equine squamous gastric disease. Animals 2023, 13, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert-Nelson, J.R.; Biddle, A.S.; Sampath, H.; Williams, C.A. Fecal Microbiota, Forage Nutrients, and Metabolic Responses of Horses Grazing Warm- and Cool-Season Grass Pastures. Animals 2023, 13, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proudman, C.J.; Hunter, J.O.; Darby, A.C.; Escalona, E.E.; Batty, C.; Turner, C. Characterisation of the faecal metabolome and microbiome of Thoroughbred racehorses. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.M.; Harris, H.M.B.; Jeffery, I.B.; Claesson, M.J.; Younge, B.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.P. The core faecal bacterial microbiome of Irish Thoroughbred racehorses. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 57, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, N.; Midoux, C.; Leclercq, S.; Pennarun, S.; Le Moyec, L.; Rué, O.; Robert, C.; Sallé, G.; Barrey, E. Mining the equine gut metagenome: Poorly-characterized taxa associated with cardiovascular fitness in endurance athletes. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, T.B.; Devadas, K.; George, M.; Gandhimathi, A.; Chouhan, D.; Retnakumar, R.J.; Alexander, S.M.; Varghese, J.; Dharmaseelan, S.; Chandrika, S.K.; et al. Low Bifidobacterium Abundance in the Lower Gut Microbiota Is Associated With Helicobacter Pylori-Related Gastric Ulcer and Gastric Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 631140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegierska, A.E.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Potenza, M.A.; Montagnani, M.; Santacroce, L. The Connection Between Physical Exercise and Gut Microbiota: Implications for Competitive Sports Athletes. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mańkowska, K.; Marchelek-Myśliwiec, M.; Kochan, P.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Konopka, T.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Roszkowska, P.; Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Siennicka, A.; Konopka, J.; et al. Microbiota in Sports. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zha, Y.; Yang, K.; Tong, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, Q.; Ning, K. Gut Microbiota and Inflammation Patterns for Specialized Athletes: A Multi-Cohort Study across Different Types of Sports. mSystems 2023, 8, e0025923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.L.; Holscher, H.D. Fueling Gut Microbes: A Review of the Interaction between Diet, Exercise, and the Gut Microbiota in Athletes. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 2190–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, R.J.J.; Becker, A.A.M.J.; Dowling, P.M.; Weese, J.S. Characterisation of faecal microbiota in horses medicated with oral doxycycline hyclate. Equine Vet. J. 2023, 55, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, A.S.; Tomb, J.F.; Fan, Z. Microbiome and Blood Analyte Differences Point to Community and Metabolic Signatures in Lean and Obese Horses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Du, M.; Wu, J.; Bai, D.; Li, B.; Bou, G.; Zhang, X.; et al. Characterization and comparison of the bacterial microbiota in different gastrointestinal tract compartments of Mongolian horses. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, 1085–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Bai, D.; Huang, J.; Shiraigo, W.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, X.; Wu, J.; Bao, W.; et al. Comparison of Fecal Microbiota of Mongolian and Thoroughbred Horses by High-Throughput Sequencing of the V4 Region of the 16S RRNA Gene. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, A.C.; Johnson, P.J.; Lopes, M.A.; Perry, S.C.; Lanter, H.R. A Microbiological Map of the Healthy Equine Gastrointestinal Tract. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milinovich, G.J.; Burrell, P.C.; Pollitt, C.C.; Klieve, A.V.; Blackall, L.L.; Ouwerkerk, D.; Woodland, E.; Trott, D.J. Microbial ecology of the equine hindgut during oligofructose-induced laminitis subject category: Microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions. ISME J. 2008, 2, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakova, I.; Smirnova, Y.; Gryaznova, M.; Syromyatnikov, M.; Chizhkov, P.; Popov, E.; Popov, V. The Effect of Short-Term Consumption of Lactic Acid Bacteria on the Gut Microbiota in Obese People. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Feudo, C.M.; Stucchi, L.; Conturba, B.; Stancari, G.; Zucca, E.; Ferrucci, F. Medical causes of poor performance and their associations with fitness in Standardbred racehorses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1514–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, L.; Martin, M.; Barré, C.; Tanquerel, L. Prevalence of gastric ulcers in horses from the French Republican Guard cavalry regiment and association with plasma gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2025, 149, 105566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Cerón, J.J.; Ayala, I.; Martin-Cuervo, M.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, J.C.; Jacobsen, S.; Kuleš, J.; Beletić, A.; Rubić, I.; et al. Changes in Proteins in Saliva and Serum in Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome Using a Proteomic Approach. Animals 2022, 12, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Escribano, D.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Martín-Cuervo, M.; Lamy, E.; Tecles, F.; Cerón, J.J. Changes in saliva analytes in equine acute abdominal disease: A sialochemistry approach. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnozahi, N.A.; Said, E.A.; Bistawroos, A.E.; Aly, R.G. Effect of sodium butyrate on gastric ulcer aggravation and hepatic injury inflicted by bile duct ligation in rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello-Perez, L.A.; Flores-Silva, P.C.; Agama-Acevedo, E.; Tovar, J. Starch digestibility: Past, present, and future. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 5009–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, F.A.; Montes, J.H.; Philippe, M.G.; Ramos, L.F.P.; Clementino, F.M.M.; Júnior, J.M.d.O.; Moreira, F.; Bianchi, I.; Peripolli, V. Interactive effects between sugar source and pelleting temperature on processing, digestibility and blood metabolites in nursery piglets. Livest. Sci. 2020, 240, 104182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Ramsay, J.D.; Wakshlag, J.J.; Stokol, T.; Reed, S.; Divers, T.J. Investigating the pathogenesis of high-serum gamma-glutamyl transferase activity in Thoroughbred racehorses: A series of case-control studies. Equine Vet. J. 2022, 54, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, S.; Bowen, I.; Hallowell, G.; Shipman, E.; Redpath, A. Assessment of agreement using the equine glandular gastric disease grading system in 84 cases. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).