Genetic Parameters, Linear Associations, and Genome-Wide Association Study for Endotoxin-Induced Cortisol Response in Holstein heifers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and LPS Challenge
2.2. Cortisol Analysis and Phenotyping
2.3. Linear Association Analysis
2.4. Variance Components and Heritability Estimation
2.5. Single-Step Genome-Wide Association Studies (ssGWAS)
Gene and QTL Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Variance Components and Heritability
3.2. Linear Associations
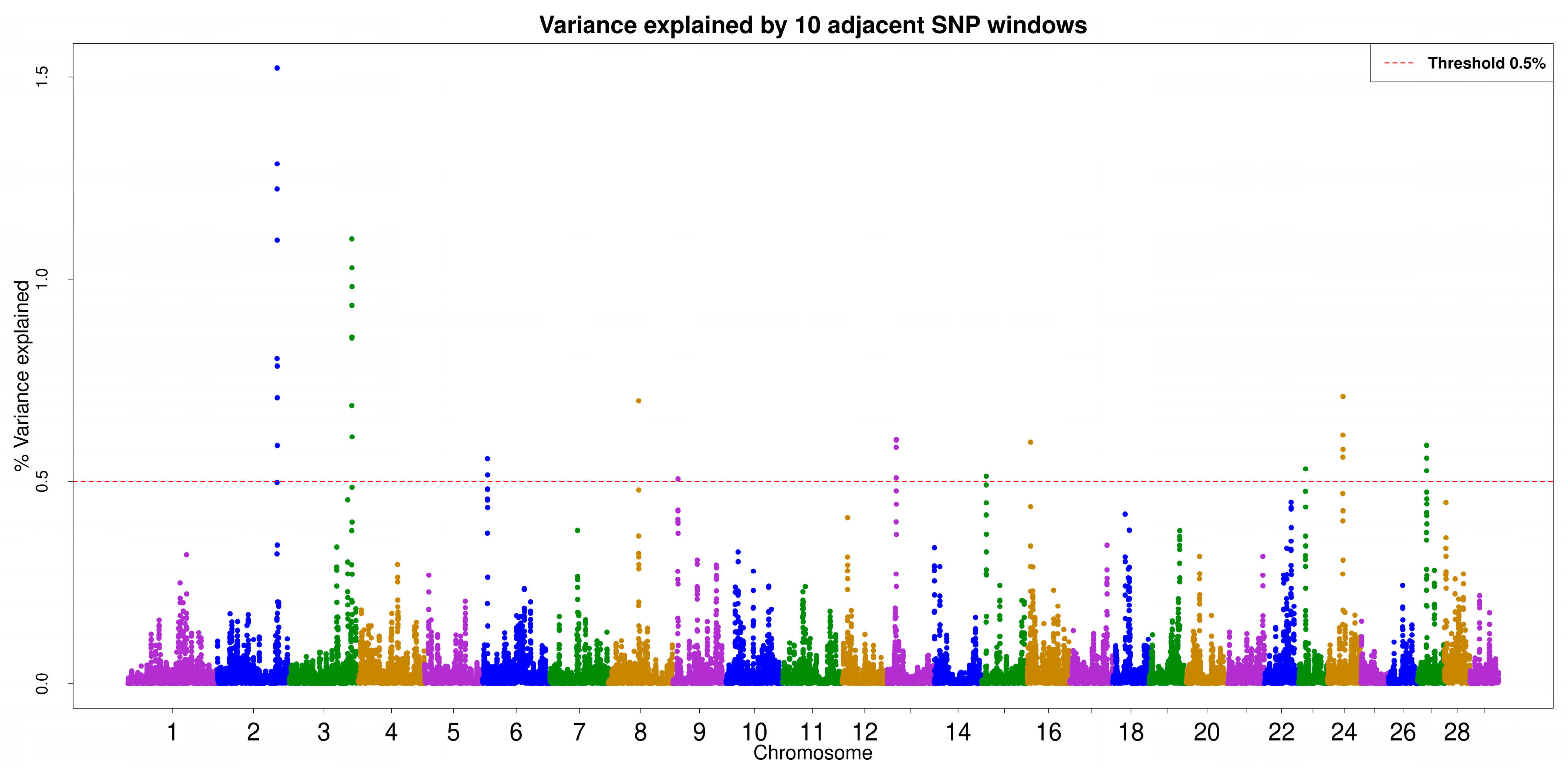
3.3. ssGWAS
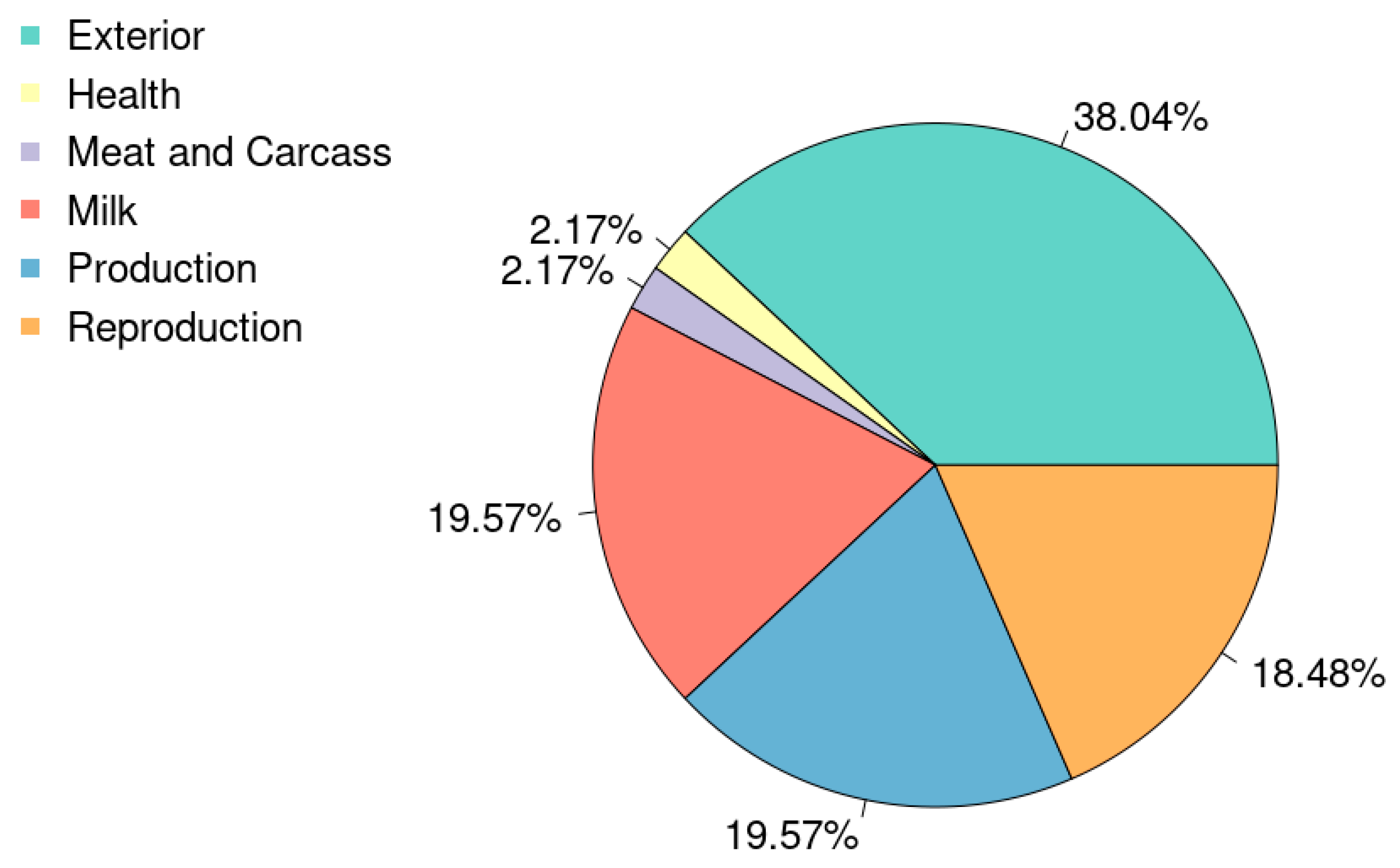
3.4. Gene and QTL Annotation
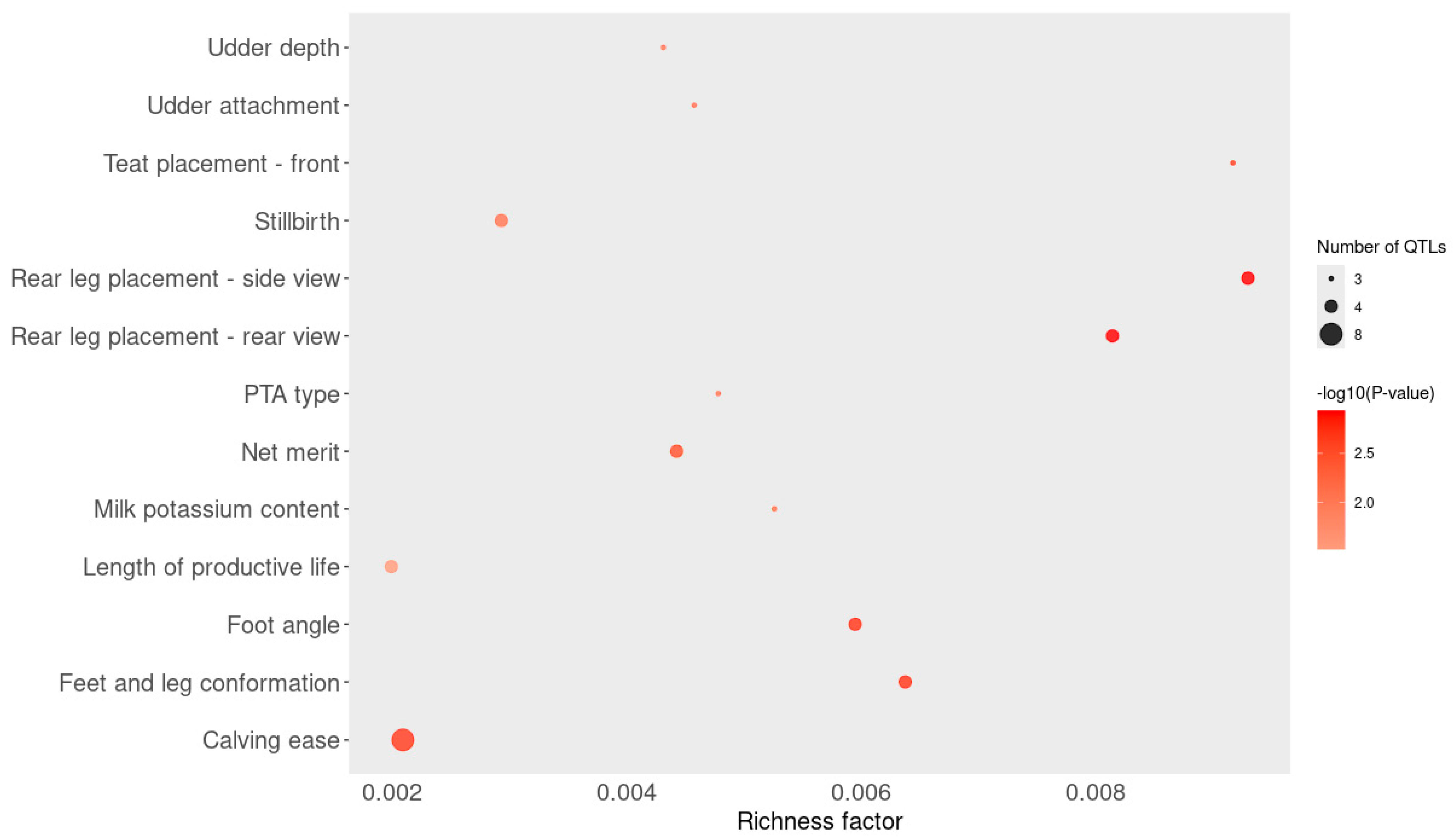
3.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Linear Association Between Cortisol Response and Important Genetically Evaluated Traits
4.2. Candidate Genes and Enriched Terms
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Möstl, E.; Palme, R. Hormones as Indicators of Stress. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2002, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, H.; Routly, J.E.; Smith, R.F. Understanding the Trade-off between the Environment and Fertility in Cows and Ewes. Anim. Reprod. 2020, 17, e20200017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnzon, C.-F.; Dahlberg, J.; Gustafson, A.-M.; Waern, I.; Moazzami, A.A.; Östensson, K.; Pejler, G. The Effect of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Experimental Bovine Mastitis on Clinical Parameters, Inflammatory Markers, and the Metabolome: A Kinetic Approach. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, H.F.; Faciola, A.P. Ruminal Acidosis, Bacterial Changes, and Lipopolysaccharides. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinok Yipel, F.; Yipel, M. LPS Ile Indüklenen Septisemik Koyunlarda Bazı Eser Element Konsantrasyonlarının İncelenmesi. Kocatepe Vet. J. 2022, 15, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.; Sharma, A.; Lamers, K.; White, C.; Mallard, B.A.; Cánovas, A.; Karrow, N.A. Dynamic Changes in Holstein Heifer Circulatory Stress Biomarkers in Response to Lipopolysaccharide Immune Challenge. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2022, 248, 110426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckersall, P.D.; Bell, R. Acute Phase Proteins: Biomarkers of Infection and Inflammation in Veterinary Medicine. Vet. J. 2010, 185, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, H.D.; Carroll, J.A.; Burdick Sanchez, N.C.; Richeson, J.T. Natural Variations in the Stress and Acute Phase Responses of Cattle. Innate Immun. 2014, 20, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, D.; Sharma, A.; Li, Z.; Monteith, G.; Mallard, B.A.; Bergeron, R.; Baes, C.; Karrow, N.A. Endotoxin-Induced Cytokine, Chemokine and White Blood Cell Profiles of Variable Stress-Responding Sheep. Stress 2021, 24, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartin, J.L.; Whitlock, B.K.; Daniel, J.A. Triennial Growth Symposium: Neural Regulation of Feed Intake: Modification by Hormones, Fasting, and Disease1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1991–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larzul, C.; Terenina, E.; Foury, A.; Billon, Y.; Louveau, I.; Merlot, E.; Mormede, P. The Cortisol Response to ACTH in Pigs, Heritability and Influence of Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin. Animal 2015, 9, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Q.; Karrow, N.A.; Cao, H.; Rodriguez, A.; Mallard, B.A.; Boermans, H.J. Variation in the Ovine Cortisol Response to Systemic Bacterial Endotoxin Challenge Is Predominantly Determined by Signalling within the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 230, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanas, I.; Chouzouris, T.-M.; Dadouli, K.; Dovolou, E.; Stamperna, K.; Barbagianni, M.; Valasi, I.; Tsiaras, A.; Amiridis, G.S. A Study on Stress Response and Fertility Parameters in Phenotypically Thermotolerant and Thermosensitive Dairy Cows during Summer Heat Stress. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2020, 55, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, D.; Tsuruta, S.; Aguilar, I.; Masuda, Y.; Bermann, M.; Legarra, A.; Misztal, I. 366. Recent Updates in the BLUPF90 Software Suite. Proceedings of 12th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production (WCGALP), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 3–8 July 2022; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1530–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Misztal, I.; Tsuruta, S.; Strabel, T.; Auvray, B.; Druet, T.; Lee, D.H. BLUPF90 and related programs (BGF90). In Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Montpellier, France, 19–23 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- VanRaden, P.M. Efficient Methods to Compute Genomic Predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, S.G.; Liang, K.-Y. Asymptotic Properties of Maximum Likelihood Estimators and Likelihood Ratio Tests under Nonstandard Conditions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Houle, D. Sampling Based Approximation of Confidence Intervals for Functions of Genetic Covariance Matrices. Proc. Assoc. Adv. Anim. Breed. 2013, 20, 523–526. [Google Scholar]
- Legarra, A.; Aguilar, I.; Misztal, I. A Relationship Matrix Including Full Pedigree and Genomic Information. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4656–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmanova, J.; Sargolzaei, M.; Schenkel, F.S. Characteristics of Linkage Disequilibrium in North American Holsteins. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, P.A.S.; Suárez-Vega, A.; Marras, G.; Cánovas, Á. GALLO: An R Package for Genomic Annotation and Integration of Multiple Data Sources in Livestock for Positional Candidate Loci. GigaScience 2020, 9, giaa149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Adler, P.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. G:Profiler—Interoperable Web Service for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Gene Identifier Mapping (2023 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W207–W212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Viteri, G.; Marin-Garcia, P.; Ping, P.; Stein, L.; D’Eustachio, P.; Hermjakob, H. Reactome Diagram Viewer: Data Structures and Strategies to Boost Performance. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.R.; Alejandro, M.; Romero, G.; Moya, F.; Peris, C. Variation in Milk Cortisol during Lactation in Murciano-Granadina Goats. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, W.; Heimbürge, S.; Tuchscherer, A.; Kanitz, E. Hair Cortisol Concentration in Postpartum Dairy Cows and Its Association with Parameters of Milk Production. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2023, 84–85, 106792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkerk, G.A.; Phipps, A.M.; Carragher, J.F.; Matthews, L.R.; Stelwagen, K. Characterization of Milk Cortisol Concentrations as a Measure of Short-Term Stress Responses in Lactating Dairy Cows. Anim. Welf. 1998, 7, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, K.B.; Ljungvall, Ö.A.; Jones, B.V. Low Cortisol Levels in Blood from Dairy Cows with Ketosis: A Field Study. Acta Vet. Scand. 2010, 52, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Kumar, S.; Jaiswal, M. Biochemical Markers of Ketosis in Dairy Cows at Post-Parturient Period. Biol. Rhythm Res. 2021, 52, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolakoğlu, H.E.; Küplülü, S.; Polat, I.M.; Pekcan, M.; Özenç, E.; Baklacı, C.; Seyrek-İntaş, K.; Gümen, A.; Vural, M.R. Association among Lipopolysaccharide, the Transforming Growth Factor–Beta Superfamily, Follicular Growth, and Transcription Factors in Spontaneous Bovine Ovarian Cysts. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2020, 70, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonari, A.; Martino, N.A.; Burgio, M.; Cicirelli, V.; Frattina, L.; Dell’Aquila, M.E.; Rizzo, A. New Insights in Bovine Follicular Cysts. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2025, 60, e70048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoković, H.; Capak, D.; Stojević, Z.; Pirkić, B.; Vnuk, D.; Babić, T. The influence of functional hoof correction on cortisol concentrations in bovine blood serum. Vet. Stanica 2014, 45, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ghoul, W.; Hofmann, W. Influence of claw diseases of varying degrees on measurable stress reactions with special consideration of cortisol and lactate in bovine blood serum. Prakt. Tierarzt 2002, 83, 354+361. [Google Scholar]
- Manica, E.; Silva, P.D.S.; Merighe, G.K.F.; de Oliveira, S.A.; Bomfim, G.F.; Negrão, J.A. Effect of Experimental Stress and Cortisol Release Induced by ACTH Administration on Expression of Key Genes Related to Milk Synthesis and Apoptosis during Mammary Involution of Saanen Goats. J. Dairy Res. 2022, 89, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terenina, E.; Iannuccelli, N.; Billon, Y.; Fève, K.; Gress, L.; Bazovkina, D.; Mormede, P.; Larzul, C. Genetic Determinism of Cortisol Levels in Pig. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1461385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormede, E.; Mormede, P. Genetic Variation of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Activity in Farm Animals and Beyond. Neuroendocrinology 2024, 115, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, D.; Swart, P.; Cloete, J.J.E.; Cloete, S. Searching for SNPs That Affect Sheep Robustness: CYP17 SNP Affects Behavioural Responses to Psychological Stress. In Proceedings of the 20th Association for the Advancement of Animal Breeding and Genetics Conference, Napier, New Zealand, 20–23 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Scheimann, J.; Myers, B. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Stress Response. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assémat, E.; Bazellières, E.; Pallesi-Pocachard, E.; Le Bivic, A.; Massey-Harroche, D. Polarity Complex Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himes, A.D.; Fiddler, R.M.; Raetzman, L.T. N-Cadherin Loss in POMC-Expressing Cells Leads to Pituitary Disorganization. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chambers, T.J.G.; Giles, A.; Brabant, G.; Davis, J.R.E. Wnt Signalling in Pituitary Development and Tumorigenesis. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R101–R111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himes, A.D.; Raetzman, L.T. Premature Differentiation and Aberrant Movement of Pituitary Cells Lacking Both Hes1 and Prop1. Dev. Biol. 2009, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt-P15116-CADH2_MOUSE. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P15116/entry (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Ferreira, N.G.B.P.; Madeira, J.L.O.; Gergics, P.; Kertsz, R.; Marques, J.M.; Trigueiro, N.S.S.; Benedetti, A.F.F.; Azevedo, B.V.; Fernandes, B.H.V.; Bissegatto, D.D.; et al. Homozygous CDH2 Variant May Be Associated with Hypopituitarism without Neurological Disorders. Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e220473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, A.C.; Buckley, C.E.; Williams, C.A.; Clarke, J.D.W. Coordinated Assembly and Release of Adhesions Builds Apical Junctional Belts during de Novo Polarisation of an Epithelial Tube. Development 2020, 147, dev191494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zou, J.; Wen, Y.; Fang, W.; Stolz, D.B.; Sun, M.; Wei, X. Apical Cell-Cell Adhesions Reconcile Symmetry and Asymmetry in Zebrafish Neurulation. iScience 2018, 3, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem B3GAT2-Beta-1,3-Glucuronyltransferase 2 (Human). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/B3GAT2/human (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- QuickGO::Term GO:0015018. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO/GTerm?id=GO:0015018#term=history (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Błąd, J.; Weitz, E. Glycosaminoglycan Synthesis in Fibroblasts; WikiPathways: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, J.; Reinhardt, D.P. Chapter 3—Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Molecules. In Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Engineering in Dental Sciences; Vishwakarma, A., Sharpe, P., Shi, S., Ramalingam, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 25–45. ISBN 978-0-12-397157-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Xing, T.; Yang, Z.; Dudek, R.; Lu, Q.; Chen, Y.-H. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Embryonic Development, Tissue Repair and Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A Key System for Immune Surveillance and Homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, D.M.; Elliott, G.S.; Chute, H.; Horan, T.; Pfenninger, K.H.; Sanford, S.D.; Foster, S.; Scully, S.; Welcher, A.A.; Holers, V.M. CSMD1 Is a Novel Multiple Domain Complement-Regulatory Protein Highly Expressed in the Central Nervous System and Epithelial Tissues1. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4419–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besedovsky, H.O.; del Rey, A. Immune-Neuro-Endocrine Interactions: Facts and Hypotheses. Endocr. Rev. 1996, 17, 64–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and Physiological Roles of Inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, A.; Hebecker, M.; Svobodová, E.; Józsi, M. Factor H: A Complement Regulator in Health and Disease, and a Mediator of Cellular Interactions. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 46–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MedlinePlus Genetics: CFH Gene. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/gene/cfh/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Chen, H.-J.C.; Spiers, J.G.; Lerskiatiphanich, T.; Parker, S.E.; Lavidis, N.A.; Fung, J.N.; Woodruff, T.M.; Lee, J.D. Complement C5a Receptor Signaling Alters Stress Responsiveness and Modulates Microglia Following Chronic Stress Exposure. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2024, 4, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, J.D.; Mayor, R. Complement in Animal Development: Unexpected Roles of a Highly Conserved Pathway. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Föcking, M.; Sabherwal, S.; Cates, H.M.; Scaife, C.; Dicker, P.; Hryniewiecka, M.; Wynne, K.; Rutten, B.P.F.; Lewis, G.; Cannon, M.; et al. Complement Pathway Changes at Age 12 Are Associated with Psychotic Experiences at Age 18 in a Longitudinal Population-Based Study: Evidence for a Role of Stress. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaus, F.; Guetter, K.; Schlegel, R.; Spiller, T.R.; Seifritz, E.; Cathomas, F.; Kaiser, S. Common and Disorder-Specific Upregulation of the Inflammatory Markers TRAIL and CCL20 in Depression and Schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.S.; Körner, H. The CCR6-CCL20 Axis in Humoral Immunity and T-B Cell Immunobiology. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hong, X.; Du, H. Association Between Serum Chemokine Ligand 20 Levels and Disease Activity and Th1/Th2/Th17-Related Cytokine Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023, 43, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.Y.; Zhang, M.J.; Liu, P.F.; Xiao, G.; Lyu, X.M. Correlation between serum CCL20 level and disease severity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021, 55, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affò, S.; Morales-Ibanez, O.; Rodrigo-Torres, D.; Altamirano, J.; Blaya, D.; Dapito, D.H.; Millán, C.; Coll, M.; Caviglia, J.M.; Arroyo, V.; et al. CCL20 Mediates Lipopolysaccharide Induced Liver Injury and Is a Potential Driver of Inflammation and Fibrosis in Alcoholic Hepatitis. Gut 2014, 63, 1782–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, K.S.; Filor, V.; Bäumer, W. Early Inflammatory Events of Mastitis—A Pilot Study with the Isolated Perfused Bovine Udder. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Zhan, K.; Zhao, G. Quercetin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses via Regulation of the TLR4-NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Bovine Rumen Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2023, 15, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchio, A.; Salmon, E.D. The Spindle-Assembly Checkpoint in Space and Time. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Chen, T. A Matter of Life and Death: Self-renewal in Stem Cells. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; He, Y. HMGB Family Proteins: Potential Biomarkers and Mechanistic Factors in Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Yang, W.; Duan, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Biological Functions and Theranostic Potential of HMGB Family Members in Human Cancers. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920970850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert-Kuss, L.M.; Krenz, H.; Tekath, T.; Wöste, M.; Persio, S.D.; Terwort, N.; Wyrwoll, M.J.; Cremers, J.-F.; Wistuba, J.; Dugas, M.; et al. Transcriptome Analyses in Infertile Men Reveal Germ Cell–Specific Expression and Splicing Patterns. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202201633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; He, Z. High Mobility Group Proteins in Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 911152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Iwamoto, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Horimasu, Y.; Masuda, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Nakashima, T.; Ohshimo, S.; Fujitaka, K.; Hamada, H.; et al. Serum High-Mobility Group Box 1 Is Associated with the Onset and Severity of Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respirology 2020, 25, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, B.-M.; Cai, S.; Liu, P.-L. The Role of Serum High Mobility Group Box 1 and Interleukin-6 Levels in Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentino, A.R.R.; Fraga-Junior, V.d.S.; Palazzo, M.; Tasmo, N.R.A.; Rodrigues, D.A.S.; Barroso, S.P.C.; Ferreira, S.N.; Neves-Borges, A.C.; Allonso, D.; Fantappié, M.R.; et al. High Mobility Group Box 1, ATP, Lipid Mediators, and Tissue Factor Are Elevated in COVID-19 Patients: HMGB1 as a Biomarker of Worst Prognosis. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 16, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Itoh, M. Multifunctional Strands in Tight Junctions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Ohno, S. The PAR-aPKC System: Lessons in Polarity. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchiando, A.M.; Graham, W.V.; Turner, J.R. Epithelial Barriers in Homeostasis and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2010, 5, 119–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefont, C.M.D.; Rainard, P.; Cunha, P.; Gilbert, F.B.; Toufeer, M.; Aurel, M.-R.; Rupp, R.; Foucras, G. Genetic Susceptibility to S. Aureus Mastitis in Sheep: Differential Expression of Mammary Epithelial Cells in Response to Live Bacteria or Supernatant. Physiol. Genom. 2012, 44, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, A.G.; Komesu, M.C.; Duarte, G.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Mussi-Pinhata, M.M.; Yamamoto, A.Y. High Levels of Chemokine C-C Motif Ligand 20 in Human Milk and Its Production by Oral Keratinocytes. Breastfeed Med. 2017, 12, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Corvo, M.; Bongiorni, S.; Stefanon, B.; Sgorlon, S.; Valentini, A.; Ajmone Marsan, P.; Chillemi, G. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Profiles in Cows Subjected to Different Stress Level as Assessed by Cortisol in Milk. Genes 2020, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnhardt-San, A.L.; Baker, E.C.; Cilkiz, K.Z.; Cardoso, R.C.; Ghaffari, N.; Long, C.R.; Riggs, P.K.; Randel, R.D.; Riley, D.G.; Welsh, T.H. Evaluation of Prenatal Transportation Stress on DNA Methylation (DNAm) and Gene Expression in the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) Axis Tissues of Mature Brahman Cows. Genes 2025, 16, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trait | Model F-Value | Model p_Value | ρ | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | 0.391 | 5.967 | 1.72 × 10−14 | −11.185 | −0.178 | 0.010 |
| BMR | 0.390 | 5.931 | 2.17 × 10−14 | 14.461 | 0.173 | 0.014 |
| LP | 0.386 | 5.830 | 4.19 × 10−14 | 12.262 | 0.145 | 0.033 |
| MILK | 0.385 | 5.810 | 4.79 × 10−14 | 0.067 | 0.144 | 0.040 |
| PROT | 0.384 | 5.789 | 5.46 × 10−14 | 2.217 | 0.137 | 0.048 |
| UT | 0.382 | 5.743 | 7.38 × 10−14 | −12.124 | −0.125 | 0.073 |
| CK | 0.380 | 5.692 | 1.03 × 10−13 | 12.733 | 0.113 | 0.119 |
| HHE | 0.380 | 5.677 | 1.13 × 10−13 | 7.400 | 0.103 | 0.139 |
| MSP | 0.379 | 5.671 | 1.18 × 10−13 | −7.239 | −0.100 | 0.148 |
| SNP | rsID | chr | Start_Pos | End_Pos | Gene_id | Gene_Name | Gene_Biotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-43721 | rs108974471 | 2 | 115948258 | 115951955 | ENSBTAG00000021326 | CCL20 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-43721 | rs108974471 | 2 | 115992779 | 116028253 | ENSBTAG00000021327 | DAW1 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-107330 | rs109766798 | 2 | 115992779 | 116028253 | ENSBTAG00000021327 | DAW1 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-25298 | rs109868537 | 3 | 111603940 | 112289188 | ENSBTAG00000005784 | CSMD2 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-85333 | rs110742206 | 3 | 111603940 | 112289188 | ENSBTAG00000005784 | CSMD2 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-110683 | rs110606737 | 3 | 111603940 | 112289188 | ENSBTAG00000005784 | CSMD2 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-85333 | rs110742206 | 3 | 111927003 | 111927727 | ENSBTAG00000000335 | HMGB4 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-57285 | rs109872657 | 9 | 9970661 | 10070666 | ENSBTAG00000020817 | B3GAT2 | protein_coding |
| BTA-25900-no-rs | rs41575397 | 13 | 18449975 | 18466359 | ENSBTAG00000052242 | NA | lncRNA |
| BTA-25900-no-rs | rs41575397 | 13 | 18484975 | 19062784 | ENSBTAG00000014991 | PARD3 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-13518 | rs110188001 | 13 | 18484975 | 19062784 | ENSBTAG00000014991 | PARD3 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-109707 | rs109869165 | 13 | 18484975 | 19062784 | ENSBTAG00000014991 | PARD3 | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-13518 | rs110188001 | 13 | 18847324 | 18847381 | ENSBTAG00000054243 | bta-mir-2285aw | miRNA |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-109707 | rs109869165 | 13 | 18847324 | 18847381 | ENSBTAG00000054243 | bta-mir-2285aw | miRNA |
| BTB-01975868 | rs43082091 | 16 | 6199772 | 6333310 | ENSBTAG00000023177 | CFH | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-118806 | rs42048457 | 24 | 28655047 | 28904115 | ENSBTAG00000021190 | CDH2 | protein_coding |
| BTB-00952622 | rs42110734 | 27 | 16673409 | 16675767 | ENSBTAG00000050498 | NA | protein_coding |
| ARS-BFGL-NGS-58358 | rs109507088 | 27 | 16673409 | 16675767 | ENSBTAG00000050498 | NA | protein_coding |
| Source | Term Name | Term Id | p-Value * | Intersections | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:MF | galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase activity | GO:0015018 | 0.042 | B3GAT2 | |
| GO:MF | gamma-catenin binding | GO:0045295 | 0.048 | CDH2 | |
| GO:MF | complement component C3b binding | GO:0001851 | 0.048 | CFH | |
| GO:MF | complement binding | GO:0001848 | 0.048 | CFH | |
| GO:MF | alpha-catenin binding | GO:0045294 | 0.048 | CDH2 | |
| GO:MF | opsonin binding | GO:0001846 | 0.048 | CFH | |
| GO:CC | adherens junction | GO:0005912 | 0.048 | PARD3 | CDH2 |
| GO:CC | PAR polarity complex | GO:0120157 | 0.048 | PARD3 | |
| REAC | cell–cell junction organization | REAC: R-BTA-421270 | 0.005 | PARD3 | CDH2 |
| REAC | cell junction organization | REAC: R-BTA-446728 | 0.006 | PARD3 | CDH2 |
| REAC | cell–Cell communication | REAC: R-BTA-1500931 | 0.006 | PARD3 | CDH2 |
| REAC | tight junction interactions | REAC: R-BTA-420029 | 0.020 | PARD3 | |
| REAC | TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) | REAC: R-BTA-2173791 | 0.039 | PARD3 | |
| REAC | myogenesis | REAC: R-BTA-525793 | 0.048 | CDH2 | |
| WP | EBV LMP1 signaling | WP:WP984 | 0.032 | CCL20 | |
| WP | complement and coagulation cascades | WP:WP1056 | 0.038 | CFH | |
| HP | interhypothalamic adhesion | HP:0033105 | 0.045 | CDH2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galindo, B.A.; Shandilya, U.K.; Sharma, A.; Schenkel, F.S.; Canovas, A.; Mallard, B.A.; Karrow, N.A. Genetic Parameters, Linear Associations, and Genome-Wide Association Study for Endotoxin-Induced Cortisol Response in Holstein heifers. Animals 2025, 15, 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131890
Galindo BA, Shandilya UK, Sharma A, Schenkel FS, Canovas A, Mallard BA, Karrow NA. Genetic Parameters, Linear Associations, and Genome-Wide Association Study for Endotoxin-Induced Cortisol Response in Holstein heifers. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131890
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalindo, Bruno A., Umesh K. Shandilya, Ankita Sharma, Flavio S. Schenkel, Angela Canovas, Bonnie A. Mallard, and Niel A. Karrow. 2025. "Genetic Parameters, Linear Associations, and Genome-Wide Association Study for Endotoxin-Induced Cortisol Response in Holstein heifers" Animals 15, no. 13: 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131890
APA StyleGalindo, B. A., Shandilya, U. K., Sharma, A., Schenkel, F. S., Canovas, A., Mallard, B. A., & Karrow, N. A. (2025). Genetic Parameters, Linear Associations, and Genome-Wide Association Study for Endotoxin-Induced Cortisol Response in Holstein heifers. Animals, 15(13), 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131890








