Effects of Dietary Protein Levels on the Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Indices of Juvenile Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material and Diets
2.2. Experimental Design and Feeding Management
2.3. Sample Collection and Fish Performance
2.4. Index Measurement
2.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT–PCR)
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Basic Nutrients
3.3. Serum Biochemical Indices
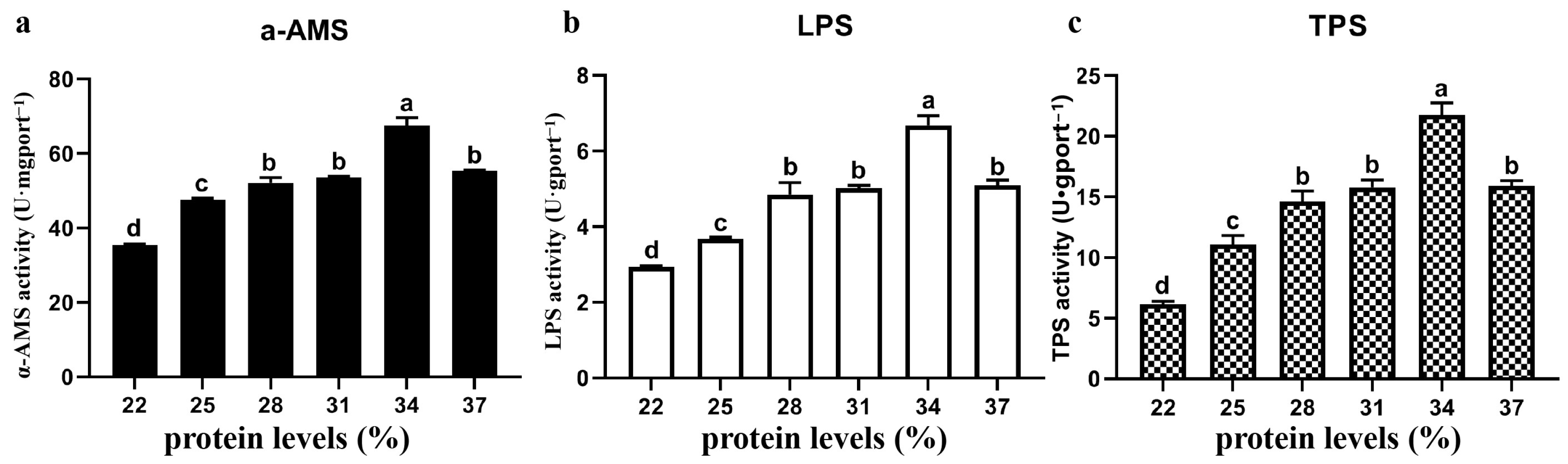
3.4. Digestive Enzyme Activity
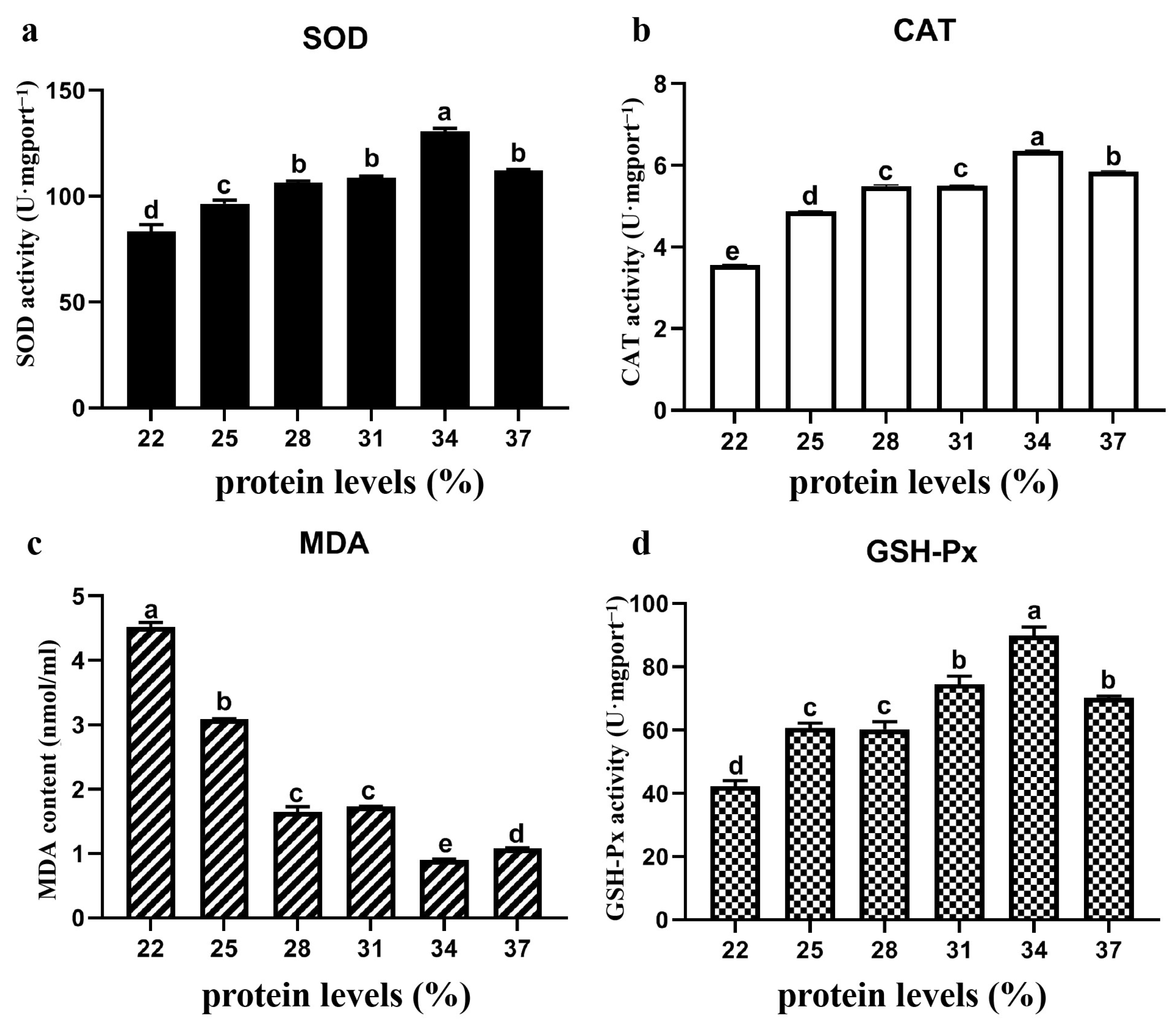
3.5. Antioxidant Oxidase Content
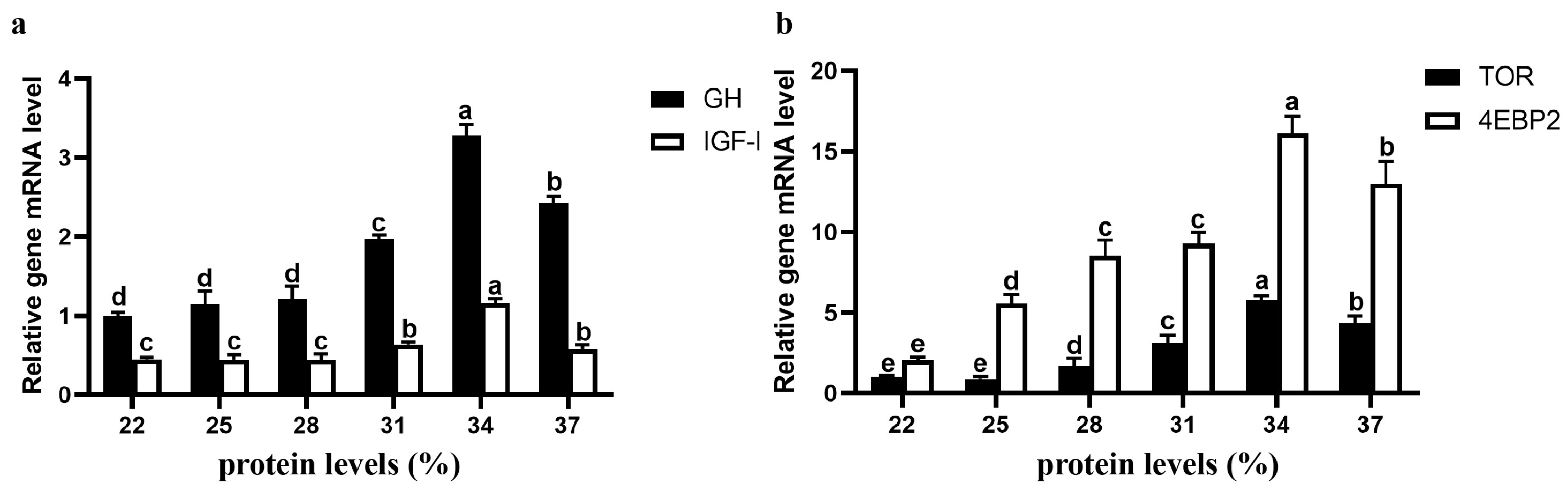
3.6. Expression of Genes Related to Growth and Protein Synthesis
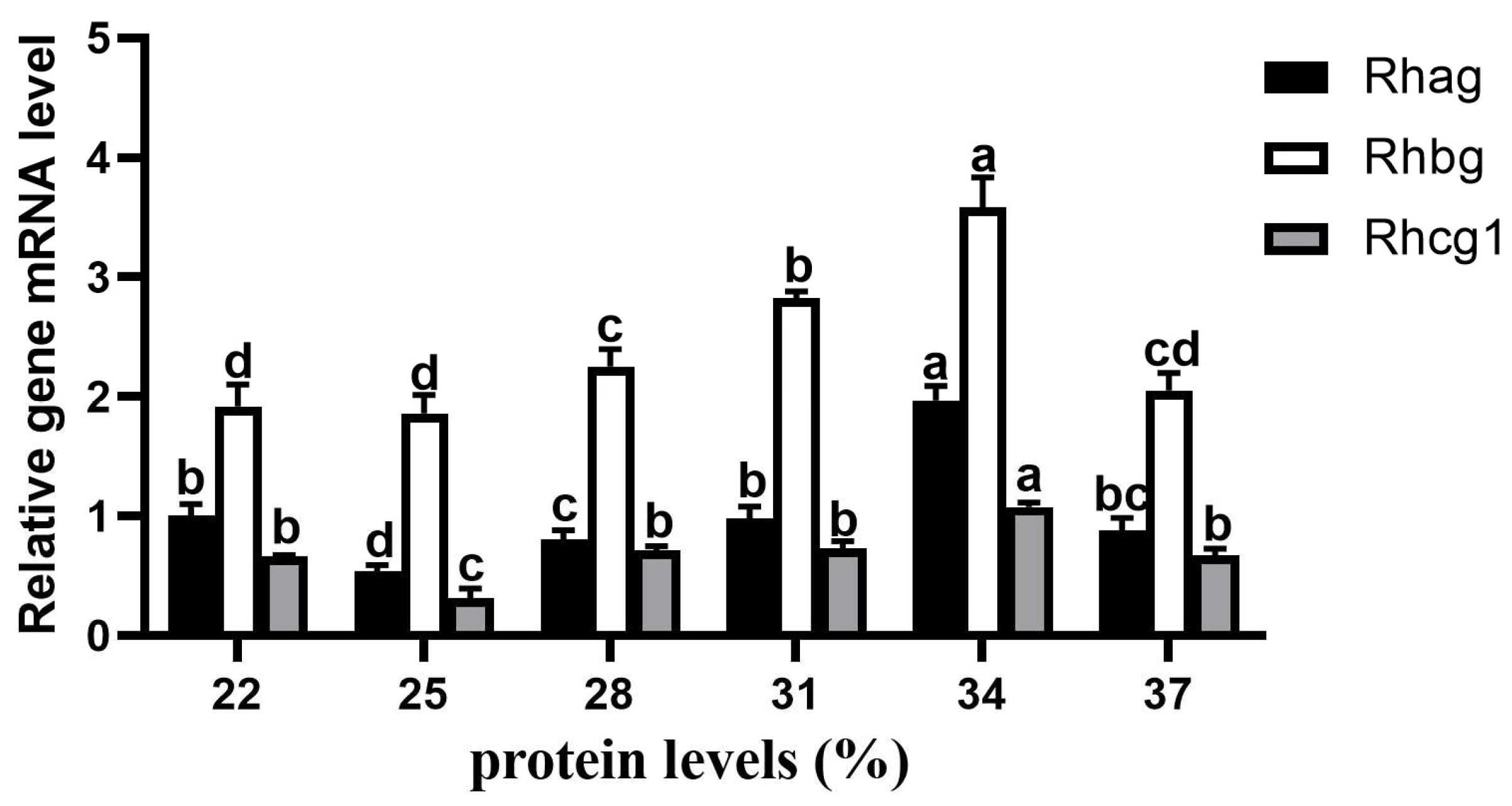
3.7. Expression of Genes Related to Metabolism
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth
4.2. Muscle Quality
4.3. Biochemical Indicators
4.4. Physiological Indicators
4.5. Gene Expression
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SR | Survival rate |
| WGR | Weight gain rate |
| SGR | Specific growth rate |
| FCR | Feed conversion ratio |
| PER | Protein efficiency ratio |
| TP | Total protein |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase enzyme |
| CAT | Catalase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| TBA | Thiobarbituric acid |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| α-AMS | α-amylase |
| LPS | Lipase |
| TPS | Trypsin |
| ALP | Phosphatase |
| UA | Uric acid |
| β-actin | Beta-actin |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| IGF-I | Insulin-like growth factor I |
| TOR | Rapamycin target protein |
| 4EBP2 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4e binding protein 2 |
| Rhag | Rhesus-associated glycoprotein |
| Rhbg | Rhesus type B glycoprotein |
| Rhcg1 | Rh family C glycoprotein 1 |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| FCE | Feed cost estimate |
| AF | Absolute feed of each fish |
| PI | Protein intake of each fish |
| FER | Feed efficiency ratio |
| FBW | Final body weight |
| IBW | Initial body weight |
| CP | Crude protein |
| CL | Crude lipid |
| Asp | Aspargine |
| Thr | Threonine |
| Ser | Serine |
| Glu | Glutamine |
| Gly | Glycine |
| Ala | Alanine |
| Cys | Cystine |
| Val | Valine |
| Met | Methionine |
| Ile | Isoleucine |
| Leu | Leucine |
| Tyr | Tyrosine |
| Phe | Phenylalanine |
| Lys | Lysine |
| His | Histidine |
| Arg | Arginine |
| Pro | Proline |
| EAA | Essential amino acid |
| HEAA | Half essential amino acids |
| FAA | Flavor amino acid |
| NEAA | Non-essential amino acids |
| TAA | Total amino acids |
| SFA | Saturated fatty acid |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated fatty acid |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| TFA | Total fatty acid |
References
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Ahmad, M.H.; Khattab, Y.A.; Shalaby, A.M. Effect of dietary protein level, initial body weight, and their interaction on the growth, feed utilization, and physiological alterations of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquaculture 2010, 298, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.D.; Lim, C. Introduction to Fish Nutrition. Nutrient Requirements and Feeding of Finfish for Aquaculture; CABI Publishing: Wallingford Oxon, UK, 2002; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Chen, H.; Huang, L. Growth, faecal production, nitrogenous excretion and energy budget of juvenile yellow grouper (Epinephelus awoara) relative to ration level. Aquaculture 2007, 264, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liang, H.; Kabwe Hamunjo, C.M.; Ge, X.; Ji, K.; Yu, H.; Huang, D.; Xu, H.; Ren, M. Culture salinity alters dietary protein requirement, whole body composition and nutrients metabolism related genes expression in juvenile Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (GIFT) (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.; El-Sayed, A.; Soltanb, M.; Iraqib, M.; Godaa, A.; Daviesc, S.; El-Haround, E.; Ramadanb, H. Partial dietary fish meal replacement with cotton seed meal and supplementation with exogenous protease alters growth, feed performance, hematological indices and associated gene expression markers (GH, IGF-I) for Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L. Dietary protein requirement for large-size Songpu mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio Songpu). Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World-Organisation-for-Animal-Health. OIE-Listed Diseases Infections and Infestations in Force in 2019. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/home/ (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Song, D.; Yun, Y.; He, Z.; Mi, J.; Wang, L.; Jin, M.; Zhou, Q.; Nie, G. Fillet texture, physicochemical indexes, muscle cellularity and molecular expression in muscle of Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus) in response to dietary hydroxyproline supplementation. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Tian, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, C.; Ge, Y.; Hu, X.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Jia, Z. Effects of Different Dietary Protein Levels on the Growth Performance, Physicochemical Indexes, Quality, and Molecular Expression of Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Animals 2023, 13, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Song, D.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Nie, G. Effects of methionine supplementation in plant protein based diet on growth performance and fillet quality of juveniles Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 36782-2018; Formula Feed for Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1–6.
- Jiang, X.; Song, Z.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Ge, Y. Effects of Dietary Lipid Levels on the Growth, Muscle Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Composition, Antioxidant Capacity, and Lipid Deposition in Mirror Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Animals 2024, 14, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.5; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Protein in Food. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.6; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Fat in Food. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.124; Determination of Amino Acids in Food Safety National Standards. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, C.; Ge, Y.; Hu, X.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Shi, L.; Jia, Z. Nutritional Components, Biochemical Characteristics, Enzyme Activities, and Growth Differences of Five Freshwater Fish Species? Fishes 2022, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ren, W.; Tian, L.; Ge, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Shi, L.; Jia, Z. IRF9 inhibits CyHV-3 replication by regulating the PI3K-AKT signalling pathway in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) epithelial cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 148, 104905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiau, S.; Lan, C. Optimum dietary protein level and protein to energy ratio for growth of grouper (Epinephelus malabaricus). Aquaculture 1996, 145, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, J.; Dong, X.; Tan, B.; Yang, Y. Optimum protein requirement of juvenile orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.; Rawal, Y. Evaluation of optimum dietary protein requirement for maximum growth of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fingerlings. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5915–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Qi, C. Effect of dietary protein level on growth performance, plasma biochemical indices and flesh quality of grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus × E. fuscoguttatus) at two growth stages. South China Fish. Sci. 2017, 13, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fan, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Qiao, X.; Bai, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhai, S. Effects of reducing dietary protein level on growth performance and muscle nutrient composition of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). China Feed 2016, 17, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Study on Feeding Rhythm and Respiratory Metabolism of Conmon Carp at Different Temperature. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y. Effects of Low-nitrogen Feed with Different Protein Levels on the Growth, Physiological and Biochemical Indicators, and Intestinal Flora of Cyprinus carpio. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin Agricultural University, Tianjin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, Z.; Bai, D.; Qiao, X. Effect of dietary protein level on hapatic function and antioxidant capacity of the juvenile common carps (Cyprinus carpio). South. Fish. Sci. 2017, 13, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Amenyogbe, E.; Chen, G.; Huang, J. Effects of feed fat level on growth performance, body composition and serum biochemical indices of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × Epinephelus polyphekadion). Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Desai, A.; Chavan, S.; Khandagale, P. Effect of water temperature on dietary protein requirement, growth and body composition of Asian catfish, Clarias batrachus fry. J. Therm. Biol. 2009, 34, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habte-Tsion, H. Effects of Dietary Protein Level on Growth Performance, Muscle Composition, Blood Composition, and Digestive Enzyme Activity of Wuchang Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) Fry. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2013, 65, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.; Shin, K.; Kim, S. Muscle Protein Hydrolysates and Amino Acid Composition in Fish. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; He, T.; Li, H.; Tang, H.; Xia, E. The Structure-Activity Relationship of the Antioxidant Peptides from Natural Proteins. Molecules 2015, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, C.; Yang, J.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J. Effects of dietary protein and lipid levels on growth and feed utilization of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). China Feed 2011, 16, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Yue, X.; Liu, J. Changes in serum biochemical parameters of Acipenser sinensis, Gray 1835, caused by decreasing environmental salinity. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2011, 27, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.G.; Hu, S.; Lou, B.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, R.; Liu, F.; Xu, D. Effect of different dietary protein and lipid levels on the growth, body composition, and intestinal digestive enzyme activities of juvenile yellow drum Nibea albiflora (Richardson). J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.; Ali, M.; Amer, A.; Gewaily, M.; Mahmoud, M.; Alkafafy, M.; Assar, D.; Soliman, A.; Van, D. The influence of coconut oil on the growth, immune, and antioxidative responses and the intestinal digestive enzymes and histomorphometry features of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragun, Z.; Mariji, F.; Krasnići, N.; Ramani, S.; Valic, D.; Rebok, K.; Kostov, V.; Jordanova, M.; Erk, M. Malondialdehyde concentrations in the intestine and gills of Vardar chub (Squalius vardarensis Karaman) as indicator of lipid peroxidation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 16917–16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alireza, E.; Reza, A.; Ebrahim, H.; Zahra, G.; Hadi, K. Effects of different protein levels and carbon sources on water quality, antioxidant status and performance of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) juveniles raised in biofloc based system. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ge, X.; Sun, S.; Zhu, J.; Ren, M.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Mi, H. The effect of dietary protein level on the growth, digestive enzymes activities and antioxidant ability of the big head carp (Aristichthys nobilis). J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2019, 42, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Wang, L.; Lou, B.; Tan, P.; Xu, D.; Chen, R. Dietary protein and lipid levels affect the growth performance, intestinal digestive enzyme activities and related genes expression of juvenile small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Huang, X.; Ruan, R.; Ye, H.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Effects of dietary protein levels on the growth, body composition, serum biochemistry and digestive enzyme activity in Chinese rice field eel (Monopterus albus) fingerlings. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Requeni, P.; Mingarro, M.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Medale, F.; Martin, S.A.M. Protein growth performance, amino acid utilisation and somatotropic axis responsiveness to fish meal replacement by plant protein sources in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2004, 232, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllopoulos, K.; Cartas, D.; Miliou, H. Factors influencing GH and IGF-I gene expression on growth in teleost fish: How can aquaculture industry benefit? Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1637–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Mandal, S.; Patel, A.; Maurya, P. Evaluation of dietary protein requirement for the growth performance of minor carp, Cirrhinus reba (Hamilton, 1822) fingerlings. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3343–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, S.; Wu, M.; Yao, W.; Jin, Z.; Wu, X. Effects of dietary protein levels on growth, feed utilization and expression of growth related genes of juvenile giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus). Aquaculture 2019, 504, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch, D.; Wilkie, M.; Walsh, P. Ammonia and urea transporters in gills of fish and aquatic crustaceans. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 1716–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Zhao, J.; Huang, S.; Hao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, X. Ammonia transporter expression of Rh protein gen in gills of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus under stress of alkali. Chin. J. Fish. 2019, 38, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, L.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; Yang, H.; Yue, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, J.; Liang, G. Effect of dietary protein reduction with lysine and methionine supplementation on growth performance, body composition and total ammonia nitrogen excretion of juvenile grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Q. Cloning and expression of Rhesus glycoprotein genes in tissues in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Chin. J. Fish. 2013, 26, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nakada, T.; Westhoff, C.; Kato, A.; Hirose, S. Research Communication Ammonia secretion from fish gill depends on a set of Rh glycoproteins. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.H.; Steele, S.L.; Perry, S.F. The responses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) to high external ammonia and urea transporter inhibition: Nitrogen excretion and expression of rhesus glycoproteins and urea transporter proteins. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212 Pt 23, 3846–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porteus, C.; Kumai, Y.; Abdallah, S.; Hong, M.; Perry, S. Respiratory responses to external ammonia in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2021, 251, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredient | Dietary Protein Levels (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 25 | 28 | 31 | 34 | 37 | |
| Fish meal % | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 |
| Casein % | 4.50 | 9.30 | 14.00 | 19.00 | 23.70 | 28.50 |
| Fish oil % | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Soybean oil % | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Wheat meal % | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 |
| Cornstarch % | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 |
| 1 Vitamin premix % | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| 2 Mineral premix % | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Choline chloride % | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 % | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Cellulose % | 23.70 | 19.60 | 15.50 | 11.30 | 7.30 | 3.20 |
| DL-Met % | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| L-Thr % | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.00 |
| L-Lys % | 1.90 | 1.50 | 1.20 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.00 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 3 Nutrient level % | ||||||
| Crude protein % | 22.63 | 25.32 | 28.15 | 31.43 | 34.18 | 37.27 |
| Crude lipid % | 7.00 | 7.10 | 6.80 | 7.10 | 7.00 | 7.20 |
| Lys % | 2.27 | 2.74 | 2.77 | 2.68 | 2.67 | 2.64 |
| Met % | 0.81 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.90 |
| Thr % | 1.53 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.51 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| Phosphorus % | 1.13 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 1.15 | 0.98 |
| Growth Index | Dietary Protein Levels (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 25 | 28 | 31 | 34 | 37 | |
| FCE(¥/kg) | 33.71 | 44.97 | 56.20 | 67.73 | 78.71 | 90.22 |
| IBW (g) | 51.98 ± 0.47 | 51.04 ± 0.47 | 51.32 ± 0.19 | 51.50 ± 0.75 | 51.90 ± 0.85 | 51.16 ± 0.08 |
| FBW (g) | 148.54 ± 0.49 e | 162.30 ± 1.15 d | 171.45 ± 1.14 cd | 181.87 ± 0.75 c | 205.13 ± 2.13 a | 178.36 ± 1.16 b |
| WGR (%) | 185.82 ± 2.07 e | 218.03 ± 0.82 d | 234.08 ± 1.73 c | 253.31 ± 5.38 b | 295.34 ± 2.94 a | 248.65 ± 2.15 b |
| SGR (%/d) | 1.88 ± 0.01 d | 2.07 ± 0.00 c | 2.15 ± 0.01 c | 2.25 ± 0.03 b | 2.45 ± 0.01 a | 2.23 ± 0.01 b |
| AGR (g/d) | 1.74 ± 0.14 c | 1.87 ± 0.09 c | 2.13 ± 0.10 bc | 2.06 ± 0.27 bc | 2.42 ± 0.40 ab | 2.84 ± 0.31 a |
| AF (g/d) | 0.29 ± 0.02 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | 0.35 ± 0.01 a | 0.36 ± 0.01 a |
| PI (g/d%) | 0.06 ± 0.01 f | 0.09 ± 0.00 e | 0.09 ± 0.00 d | 0.10 ± 0.00 c | 0.12 ± 0.00 b | 0.13 ± 0.00 a |
| FER | 0.49 ± 0.04 c | 0.58 ± 0.03 b | 0.60 ± 0.03 b | 0.62 ± 0.02 ab | 0.67 ± 0.02 a | 0.60 ± 0.02 b |
| PER (%) | 1.71 ± 0.01 e | 1.76 ± 0.00 d | 1.86 ± 0.02 d | 1.89 ± 0.02 b | 2.00 ± 0.01 a | 1.89 ± 0.03 c |
| FCR | 2.05 ± 0.02 a | 1.96 ± 0.01 b | 1.77 ± 0.02 c | 1.70 ± 0.02 d | 1.54 ± 0.01 e | 1.70 ± 0.01 d |
| SR (%) | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Amino Acid | Dietary Protein Levels (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 25 | 28 | 31 | 34 | 37 | |
| Asp * | 1.52 ± 0.01 | 1.52 ± 0.01 | 1.51 ± 0.01 | 1.52 ± 0.01 | 1.51 ± 0.01 | 1.48 ± 0.00 |
| Thr # | 0.65 ± 0.01 c | 0.66 ± 0.01 bc | 0.67 ± 0.01 ab | 0.68 ± 0.01 a | 0.69 ± 0.01 a | 0.67 ± 0.01 ab |
| Ser ● | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.01 |
| Glu * | 2.06 ± 0.01 c | 2.07 ± 0.01 c | 2.10 ± 0.00 b | 2.12 ± 0.01 b | 2.15 ± 0.01 a | 2.17 ± 0.01 a |
| Gly * | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.72 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.70 ± 0.00 |
| Ala * | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.91 ± 0.00 |
| Cys ● | 0.13 ± 0.01 c | 0.14 ± 0.01 bc | 0.14 ± 0.01 abc | 0.15 ± 0.01 abc | 0.16 ± 0.01 ab | 0.16 ± 0.01 a |
| Val # | 0.72 ± 0.01 c | 0.75 ± 0.01 b | 0.77 ± 0.01 b | 0.77 ± 0.01 b | 0.80 ± 0.01 a | 0.77 ± 0.00 ab |
| Met # | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.01 |
| Ile # | 0.65 ± 0.00 c | 0.66 ± 0.00 c | 0.67 ± 0.01 bc | 0.69 ± 0.01 ab | 0.70 ± 0.00 a | 0.69 ± 0.01 ab |
| Leu # | 1.22 ± 0.01 | 1.23 ± 0.00 | 1.22 ± 0.00 | 1.23 ± 0.00 | 1.24 ± 0.01 | 1.23 ± 0.00 |
| Tyr ● | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 |
| Phe # | 0.61 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.00 | 0.61 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.01 |
| Lys # | 1.48 ± 0.01 d | 1.48 ± 0.01 d | 1.50 ± 0.00 c | 1.55 ± 0.01 b | 1.57 ± 0.01 a | 1.54 ± 0.00 b |
| His ※ | 0.59 ± 0.01 | 0.59 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.59 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.57 ± 0.00 |
| Arg ※ | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 0.90 ± 0.00 | 0.89 ± 0.00 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.01 |
| Pro ● | 0.51 ± 0.00 | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.01 |
| EAA | 5.69 ± 0.02 e | 5.75 ± 0.02 d | 5.81 ± 0.01 c | 5.89 ± 0.01 b | 5.98 ± 0.01 a | 5.87 ± 0.01 b |
| HEAA | 1.48 ± 0.01 | 1.49 ± 0.00 | 1.48 ± 0.01 | 1.48 ± 0.00 | 1.46 ± 0.01 | 1.45 ± 0.01 |
| FAA | 5.22 ± 0.00 d | 5.23 ± 0.01 cd | 5.24 ± 0.01 bcd | 5.28 ± 0.01 ab | 5.29 ± 0.01 a | 5.26 ± 0.01 abc |
| NEAA | 8.31 ± 0.01 | 8.31 ± 0.02 | 8.33 ± 0.02 | 8.35 ± 0.01 | 8.35 ± 0.00 | 8.31 ± 0.02 |
| TAA | 14.01 ± 0.01 d | 14.07 ± 0.01 d | 14.14 ± 0.02 c | 14.24 ± 0.01 b | 14.33 ± 0.01 a | 14.18 ± 0.03 bc |
| EAA/TAA % | 40.65 ± 0.12 d | 40.85 ± 0.11 cd | 41.10 ± 0.06 bc | 41.39 ± 0.02 b | 41.66 ± 0.09 a | 41.41 ± 0.09 b |
| NEAA/TAA % | 59.35 ± 0.12 a | 59.10 ± 0.11 ab | 58.90 ± 0.06 b | 58.59 ± 0.02 c | 58.27 ± 0.05 d | 58.18 ± 0.03 d |
| HEAA/TAA % | 10.57 ± 0.11 a | 10.59 ± 0.03 a | 10.44 ± 0.08 ab | 10.40 ± 0.01 ab | 10.21 ± 0.07 bc | 10.11 ± 0.03 c |
| FAA/TAA % | 37.24 ± 0.03 a | 37.20 ± 0.10 ab | 37.07 ± 0.07 ab | 37.06 ± 0.04 ab | 36.94 ± 0.10 b | 37.09 ± 0.05 ab |
| Nutrient Composition (%) | ||||||
| Moisture | 76.30 ± 0.05 | 76.20 ± 0.05 | 76.27 ± 0.07 | 76.20 ± 0.05 | 76.13 ± 0.11 | 76.23 ± 0.03 |
| CP | 19.07 ± 0.08 d | 19.20 ± 0.05 d | 19.43 ± 0.03 c | 19.70 ± 0.08 b | 19.96 ± 0.07 a | 19.60 ± 0.05 bc |
| CL | 2.07 ± 0.05 a | 1.97 ± 0.03 ab | 1.97 ± 0.03 ab | 1.93 ± 0.03 ab | 1.87 ± 0.03 b | 1.93 ± 0.03 ab |
| Ash | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 1.07 ± 0.03 | 1.03 ± 0.03 |
| Total sugar | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.00 | 0.55 ± 0.02 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.00 | 0.54 ± 0.00 |
| Fatty Acid | Dietary Protein Levels (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 25 | 28 | 31 | 34 | 37 | |
| C14:0 | 0.032 ± 0.001 b | 0.031 ± 0.001 b | 0.036 ± 0.002 b | 0.033 ± 0.001 b | 0.036 ± 0.002 b | 0.042 ± 0.000 a |
| C15:0 | 0.005 ± 0.000 | 0.005 ± 0.000 | 0.005 ± 0.000 | 0.005 ± 0.000 | 0.006 ± 0.000 | 0.005 ± 0.000 |
| C16:0 | 0.383 ± 0.003 | 0.385 ± 0.004 | 0.373 ± 0.014 | 0.374 ± 0.013 | 0.368 ± 0.008 | 0.400 ± 0.002 |
| C18:0 | 0.112 ± 0.002 ab | 0.107 ± 0.003 b | 0.117 ± 0.003 a | 0.108 ± 0.002 b | 0.107 ± 0.002 b | 0.119 ± 0.002 a |
| SFA | 0.532 ± 0.001 b | 0.528 ± 0.007 b | 0.531 ± 0.012 b | 0.520 ± 0.014 b | 0.516 ± 0.009 b | 0.567 ± 0.004 a |
| C16:1 | 0.067 ± 0.005 | 0.063 ± 0.009 | 0.073 ± 0.006 | 0.075 ± 0.005 | 0.077 ± 0.003 | 0.079 ± 0.004 |
| C18:1n9c | 0.486 ± 0.019 | 0.561 ± 0.043 | 0.543 ± 0.051 | 0.559 ± 0.030 | 0.570 ± 0.045 | 0.587 ± 0.019 |
| C20:1 | 0.038 ± 0.003 | 0.041 ± 0.003 | 0.043 ± 0.004 | 0.049 ± 0.003 | 0.045 ± 0.001 | 0.045 ± 0.001 |
| MUFA | 0.606 ± 0.024 | 0.678 ± 0.050 | 0.675 ± 0.060 | 0.698 ± 0.038 | 0.706 ± 0.048 | 0.726 ± 0.017 |
| C22:1n9 | 0.008 ± 0.000 a | 0.006 ± 0.000 b | 0.007 ± 0.000 a | 0.007 ± 0.000 ab | 0.007 ± 0.001 ab | 0.008 ± 0.000 a |
| C24:1 | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.007 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 |
| C18:2n6c | 0.202 ± 0.006 b | 0.231 ± 0.003 a | 0.224 ± 0.007 ab | 0.232 ± 0.004 a | 0.243 ± 0.002 ab | 0.225 ± 0.009 ab |
| C18:3n3 | 0.018 ± 0.001 | 0.020 ± 0.001 | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.021 ± 0.002 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.021 ± 0.001 |
| C20:2 | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.007 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.007 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 |
| C20:3n6 | 0.017 ± 0.001 b | 0.014 ± 0.000 c | 0.016 ± 0.000 b | 0.014 ± 0.000 c | 0.017 ± 0.000 ab | 0.019 ± 0.000 a |
| C20:4n6 | 0.044 ± 0.002 | 0.045 ± 0.002 | 0.049 ± 0.003 | 0.051 ± 0.001 | 0.045 ± 0.002 | 0.051 ± 0.001 |
| C20:5n3 (EPA) | 0.035 ± 0.002 ab | 0.040 ± 0.001 ab | 0.034 ± 0.001 b | 0.041 ± 0.002 a | 0.041 ± 0.002 a | 0.040 ± 0.001 a |
| C22:6n3 (DHA) | 0.131 ± 0.001 | 0.132 ± 0.004 | 0.140 ± 0.002 | 0.140 ± 0.001 | 0.140 ± 0.001 | 0.137 ± 0.004 |
| PUFA | 0.456 ± 0.007 b | 0.488 ± 0.008 a | 0.487 ± 0.002 a | 0.507 ± 0.006 a | 0.514 ± 0.003 a | 0.500 ± 0.012 a |
| DHA+EPA | 0.1667 ± 0.003 b | 0.172 ± 0.003 ab | 0.174 ± 0.003 ab | 0.181 ± 0.001 a | 0.181 ± 0.001 a | 0.177 ± 0.003 a |
| n-3 PUFA | 0.185 ± 0.003 c | 0.192 ± 0.003 abc | 0.191 ± 0.002 bc | 0.202 ± 0.002 a | 0.202 ± 0.001 a | 0.198 ± 0.003 ab |
| n-6 PUFA | 0.263 ± 0.004 b | 0.289 ± 0.005 a | 0.289 ± 0.005 a | 0.297 ± 0.005 a | 0.304 ± 0.002 a | 0.294 ± 0.009 a |
| n-3 PUFA/n-6 PUFA | 0.703 ± 0.001 | 0.663 ± 0.003 | 0.662 ± 0.020 | 0.679 ± 0.009 | 0.664 ± 0.006 | 0.674 ± 0.009 |
| TFA | 1.594 ± 0.025 | 1.694 ± 0.063 | 1.693 ± 0.051 | 1.725 ± 0.058 | 1.736 ± 0.0057 | 1.794 ± 0.020 |
| Biochemical Index | Dietary Protein Levels (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 25 | 28 | 31 | 34 | 37 | |
| ALP (U·L−1) | 21.10 ± 0.42 d | 27.37 ± 0.28 c | 30.47 ± 0.30 c | 37.77 ± 2.85 b | 43.20 ± 0.99 a | 35.63 ± 0.84 b |
| TP (g·L−1) | 33.73 ± 0.73 | 34.03 ± 0.1 | 32.13 ± 1.8 | 32.53 ± 0.31 | 33.87 ± 0.22 | 32.50 ± 0.71 |
| UA (μmol·L−1) | 20.90 ± 0.08 c | 32.90 ± 1.24 b | 37.57 ± 2.05 ab | 38.57 ± 1.88 a | 41.00 ± 1.97 a | 41.17 ± 0.91 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, X.; Qu, F.; Ge, Y.; Li, C.; Shi, X.; Hu, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, X.; Jia, Z. Effects of Dietary Protein Levels on the Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Indices of Juvenile Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Animals 2025, 15, 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121800
Jiang X, Qu F, Ge Y, Li C, Shi X, Hu X, Cheng L, Zhao X, Jia Z. Effects of Dietary Protein Levels on the Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Indices of Juvenile Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Animals. 2025; 15(12):1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121800
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Xiaona, Feihu Qu, Yanlong Ge, Chitao Li, Xiaodan Shi, Xuesong Hu, Lei Cheng, Xinyu Zhao, and Zhiying Jia. 2025. "Effects of Dietary Protein Levels on the Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Indices of Juvenile Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus)" Animals 15, no. 12: 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121800
APA StyleJiang, X., Qu, F., Ge, Y., Li, C., Shi, X., Hu, X., Cheng, L., Zhao, X., & Jia, Z. (2025). Effects of Dietary Protein Levels on the Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Indices of Juvenile Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Animals, 15(12), 1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121800








