Effects of Feed Additives (Nannochloropsis gaditana and Hermetia illucens) on Growth and Expression of Antioxidant and Cytokine Genes in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Subjected to Air Exposure Stress
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Fish Husbandry
2.2. Ethical Issues
2.3. Feed Preparation
2.4. Chemical Analysis of the Diets
2.5. Sampling and Air Exposure Stress
2.6. Growth Parameters
- Specific Growth Rate (g/day), SGR = 100 × (ln FBW − ln IBW)/t
- FBW = final average weight at the end of the experiment (g)
- IBW = initial average weight at the beginning of the experiment (g)
- t = experimental time in days
- Weight gain (g), WG = FBW − IBW
- Condition factor (g cm−3), CF = 100 × FBW/L3
- L—total body length at the end of the trial
- Feed conversion ratio (g/g), FCR = total amount of feed given (g)/final total body weight − initial total body weight (g)
- Specific Feed Cost (€kg−1 fish) = feed cost × FCR
2.7. Analysis of Gene Expression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
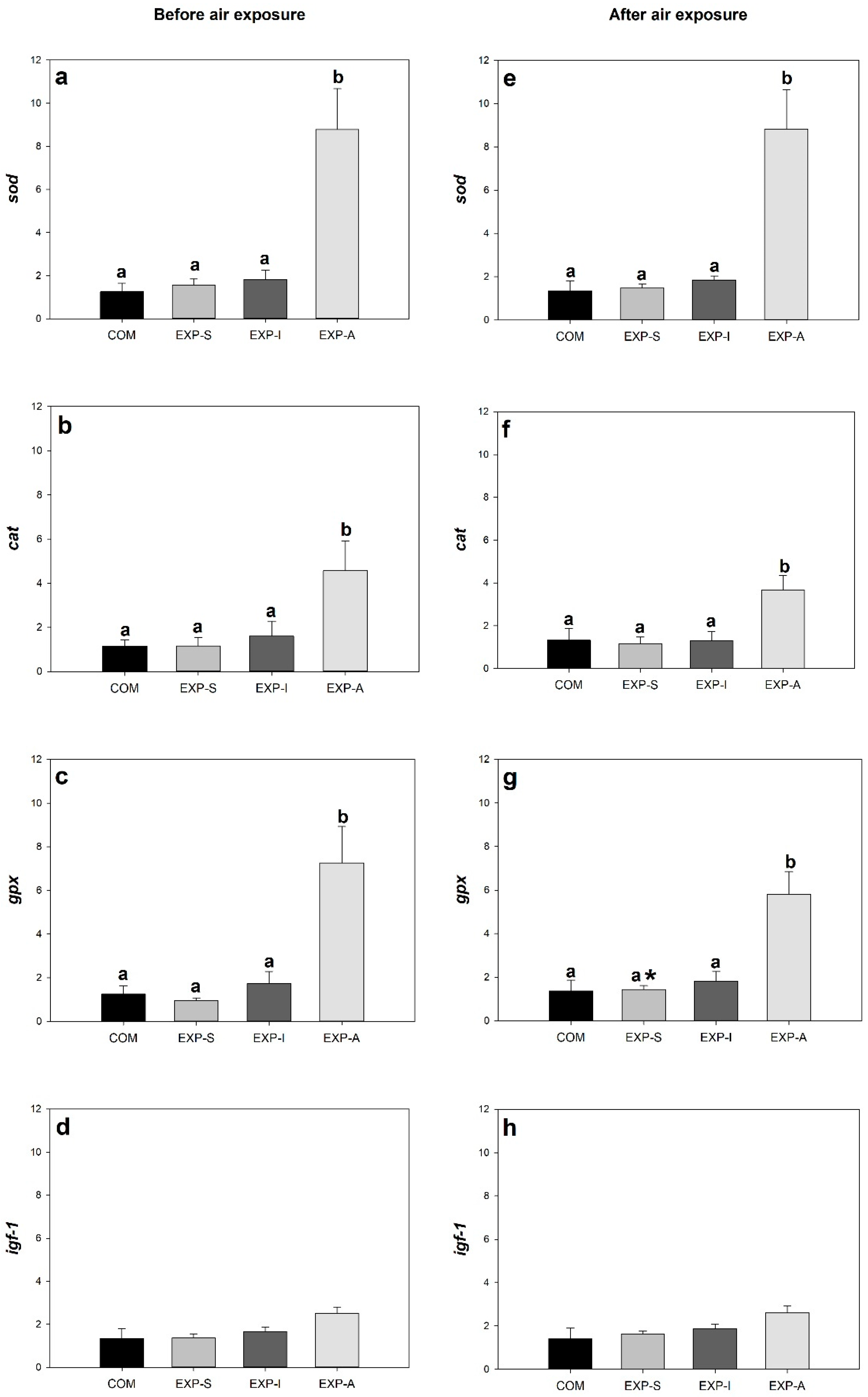
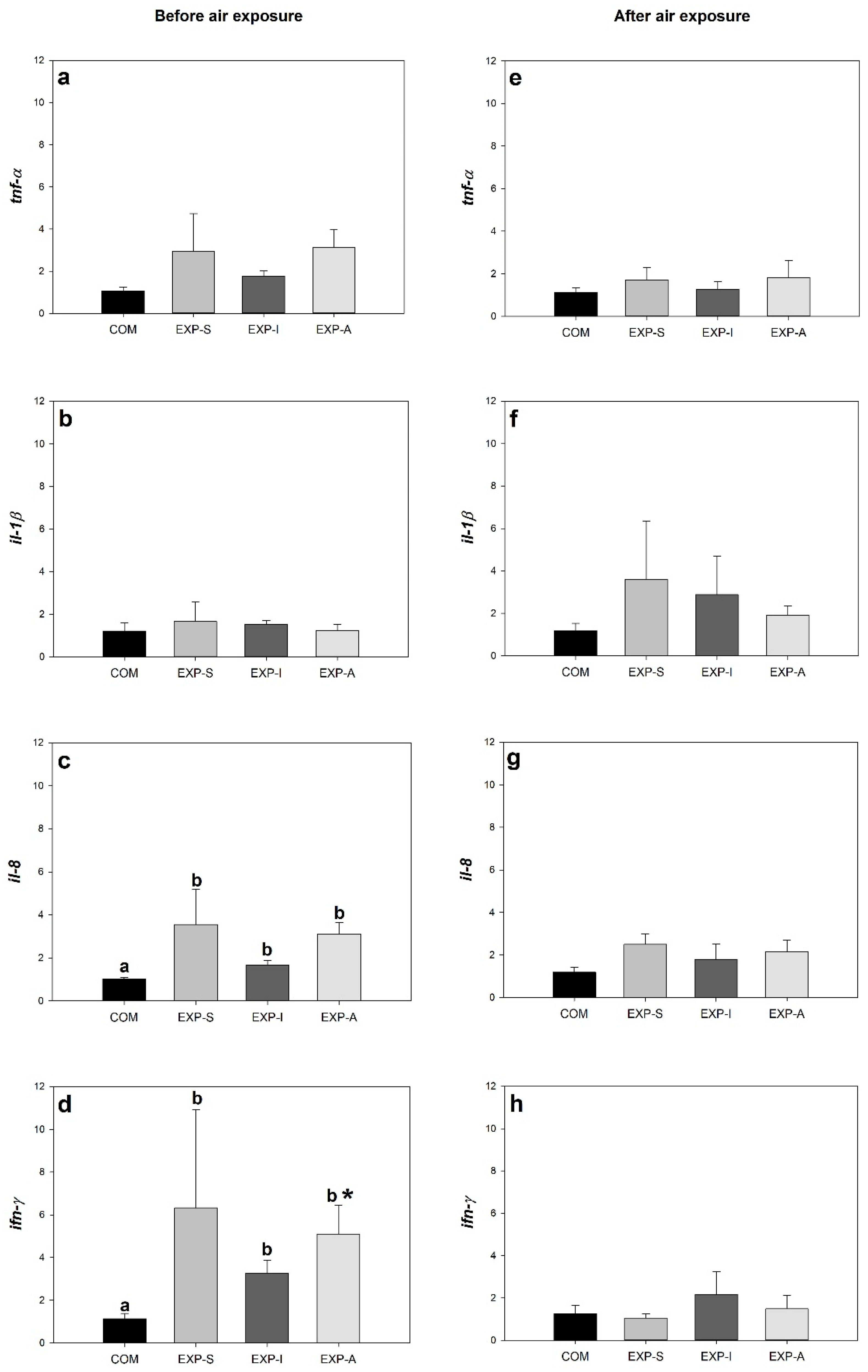
3.2. Expression of Genes Related to Growth, Stress, and Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO FishstatJ. Global Aquaculture Production 1950–2022; FishStatJ: 2024. Available online: www.fao.org/fishery/en/statistics/software/fishstatj (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Kesarcodi-Watson, A.; Kaspar, H.; Lategan, M.J.; Gibson, L. Probiotics in aquaculture: The need, principles and mechanisms of action and screening processes. Aquaculture 2008, 274, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Priyam, M.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Kumar, N.; Mishra, P.K.; Gupta, K.K.; Sarkar, B.; Sharma, T.R.; Pattanayak, A. Immunomodulation by dietary supplements: A preventive health strategy for sustainable aquaculture of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822). Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2364–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, L.; Vianello, F. Microalgae of the genus Nannochloropsis: Chemical composition and functional implications for human nutrition. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, E.T.; Schenk, P.M. A biorefinery for Nannochloropsis: Induction, harvesting, and extraction of EPA-rich oil and high-value protein. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Preez, R.; Majzoub, M.E.; Thomas, T.; Panchal, S.K.; Brown, L. Nannochloropsis oceanica as a microalgal food intervention in diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.; Elbahnaswy, S.; Ibrahim, I.; Khaled, A.A. Nannochloropsis oculata enhances immune response, transcription of stress, and cytokine genes in Nile tilapia subjected to air exposure stress. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, M.F.; El-Sawy, H.B.; Abd El-hameed, S.A.A.; Khames, M.K.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Naiel, M.A.E. Effects of dietary Nannochloropsis oculata on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, immune responses, and resistance against Aeromonas veronii challenge in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 107, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.; Elbahnaswy, S.; Ahmed, F.; Ibrahim, I.; Khaled, A.A.; Eldessouki, E.A. Nutritional and immunological evaluation of Nannochloropsis oculata as a potential Nile tilapia-aquafeed supplement. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, M.D.; Galián, C.; Fernández, V.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; de la Serrana, D.G.; Sáez, M.I.; Díaz, A.G.; Alarcón, F.J.; Martínez, T.F.; Arizcun, M. Influence of low dietary inclusion of the microalga Nannochloropsis gaditana (Lubián 1982) on performance, fish morphology, and muscle growth in juvenile gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Animals 2020, 10, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, M.I.; Galafat, A.; Vizcaíno, A.J.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Ayala, M.D.; Arizcun, M.; Alarcón, F.J.; Suárez, M.D.; Martínez, T.F. Evaluation of Nannochloropsis gaditana raw and hydrolysed biomass at low inclusion level as dietary functional additive for gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. Aquaculture 2022, 556, 738288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, N.F.N.M.; Seok-Kian, A.Y.; Seng, L.L.; Mustafa, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Shapawi, R. Nutritional value of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae processed by different methods. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Wolf, D.; Gutzeit, H.O. The black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens—A promising source for sustainable production of proteins, lipids and bioactive substances. Z. Fur Naturforschung—Sect. C J. Biosci. 2017, 72, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Fawole, F.J.; Romano, N.; Hossain, M.S.; Labh, S.N.; Overturf, K.; Small, B.C. Insect (black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens) meal supplementation prevents the soybean meal-induced intestinal enteritis in rainbow trout and health benefits of using insect oil. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 109, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Khalil, R.H.; Metwally, A.A.; Shakweer, M.S.; Ghetas, H.A.; Khallaf, M.A. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal in diets of European seabass: Effects on antioxidative capacity, non-specific immunity, transcriptomic responses, and resistance to the challenge with Vibrio alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 111, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Jin, P.; Zheng, L.; Cai, M.; Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal protein as a fishmeal replacement on the growth and immune index of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysal, M.J.; Fotedar, R.; Tay, C.Y.; Gupta, S.K. Dietary supplementation of black soldier fly (Hermetica illucens) meal modulates gut microbiota, innate immune response and health status of marron (Cherax cainii, Austin 2002) fed poultry-by-product and fishmeal based diets. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbohessou, P.S.; Mandiki, S.N.M.; Gougbédji, A.; Megido, R.C.; Hossain, M.S.; De Jaeger, P.; Larondelle, Y.; Francis, F.; Lalèyè, P.A.; Kestemont, P. Total replacement of fish meal by enriched-fatty acid Hermetia illucens meal did not substantially affect growth parameters or innate immune status and improved whole body biochemical quality of Nile tilapia juveniles. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 880–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbohessou, P.S.; Mandiki, S.N.M.; Mbondo Biyong, S.R.; Cornet, V.; Nguyen, T.M.; Lambert, J.; Jauniaux, T.; Lalèyè, P.A.; Kestemont, P. Intestinal histopathology and immune responses following Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide challenge in Nile tilapia fed enriched black soldier fly larval (BSF) meal supplemented with chitinase. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 128, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippayadara, N.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Krutmuang, P.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Doan, H.; Van Paolucci, M. Replacement of fish meal by black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal: Effects on growth, haematology, and skin mucus immunity of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Animals 2021, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSZ EN ISO 16634-1:2009; Hungarian Standard. Determination of Total Nitrogen Content by Combustion According to the Dumas Principle and Calculation of Crude Protein Content—Part 1: Oilseeds and Feedingstuffs. Hungarian Standards Institute: Budapest, Hungary, 2009.
- Guan, L.; Zhao, M.; Liu, T.; Fan, X.; Chen, D. Cooling combined with hyperoxic CO2 anesthesia is effective in improving the air exposure duration of tilapia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhao, M.; Guan, W.; Liu, T.; Chen, D. Carbon dioxide anesthesia: A potential application to improve the air exposure duration of tilapia. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2022, 21, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E. Effects of dietary anthocyanin on innate immune parameters, gene expression responses and ammonia resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; El Asely, A.; Abd El-Naby, A.S.; Samir, F.; El-Ashram, A.; Sudhakaran, R.; Dawood, M.A.O. Growth performance, intestinal histomorphology and growth-related gene expression in response to dietary Ziziphus mauritiana in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Harikrishnan, R.; Khamlor, T.; Punyatong, M.; Tapingkae, W.; Yousefi, M.; Palma, J.; El-Haroun, E. Impacts of pineapple peel powder on growth performance, innate immunity, disease resistance, and relative immune gene expression of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 114, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Elbadawy, M.; Aleya, L.; Alkahtani, S. Spirulina platensis reduced oxidative damage induced by chlorpyrifos toxicity in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals 2020, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawling, M.; Dimitroglou, A.; Leclercq, E.; Castex, M.; Barkas, D.; Merrifield, D. Effects of a yeast-based functional additive on the skin and intestinal mucosal surfaces of juvenile gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). In Proceedings of the Aquaculture Europe 2017, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 17–20 October 2017; pp. 958–959. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury SSaikia, S.K. Oxidative Stress in Fish: A Review. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 12, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.; Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; Al-Zaban, M.I.; Elhady, M.; El-Azzouny, M.M.; Elfeky, T.M.; Al Sadik, G.M.; Samy, O.M.; Hamed, T.A.; Albalwe, F.M.; et al. Impacts of fortifying Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diet with different strains of microalgae on its performance, fillet quality and disease resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila considering the interplay between antioxidant and inflammatory response. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, D.A.; El-Garhy, H.A.S.; Refaat, M.H.; Hassaan, M.S. Protecting deleterious effects of high stocking density of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus using dietary microalgae Golenkinia longispicula: Growth, immune-oxidative markers and associated gene expression. Aquaculture 2024, 581, 740430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, M.; Gueguen, V.; Pavon-Djavid, G.; Letourneur, D. Carotenoids from microalgae to block oxidative stress. BioImpacts 2017, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaulmann, A.; Bohn, T. Carotenoids, inflammation and oxidative stress—implications of cellular signaling pathways and relation to chronic disease prevention. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 907–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, T. Carotenoids and markers of oxidative stress in human observational studies and intervention trials: Implications of chronic diseases. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ji, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H. Defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal in diets for juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian): Growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activities, digestive enzyme activities, intestine and hepatopancreas histological structure. Aquaculture 2017, 477, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Le Bail, P.Y. Growth hormone axis as marker of nutritional status and growth performance in fish. Aquaculture 1999, 177, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.N.; Valdés, J.A.; Molina, A.; Björnsson, B.T. Regulation of skeletal muscle growth in fish by the growth hormone—Insulin-like growth factor system. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The function of fish cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, C.; Folch, H.; Enriquez, R.; Moran, G. Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: A review. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, H.; Wang, H.P.; Shaheen, A.; Matter, A. Nano spirulina dietary supplementation augments growth, antioxidative and immunological reactions, digestion, and protection of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, against Aeromonas veronii and some physical stressors. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 2143–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Mohammady, E.Y.; Soaudy, M.R.; Sabae, S.A.; Mahmoud, A.M.A.; El-Haroun, E.R. Comparative study on the effect of dietary β-carotene and phycocyanin extracted from Spirulina platensis on immune-oxidative stress biomarkers, genes expression and intestinal enzymes, serum biochemical in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 108, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Abdo, S.E.; Gewaily, M.S.; Moustafa, E.M.; SaadAllah, M.S.; AbdEl-kader, M.F.; Hamouda, A.H.; Omar, A.A.; Alwakeel, R.A. The influence of dietary β-glucan on immune, transcriptomic, inflammatory and histopathology disorders caused by deltamethrin toxicity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Metwally, A.E.S.; El-Sharawy, M.E.; Atta, A.M.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Paray, B.A. The role of β-glucan in the growth, intestinal morphometry, and immune-related gene and heat shock protein expressions of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under different stocking densities. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Weeks | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. |
| feeding rate % | 3 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Ingredients | COM | EXP-S | EXP-I | EXP-A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish meal-60 (Thailand) | 40 | 53.5 | 50.8 | 53 |
| Soybean meal-46 (Thailand) | 36 | 18 | 18 | 16 |
| Casava leaf (Laos) | 8 | 12.4 | 12 | 12 |
| Corn (Laos) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6.5 |
| Rice brain (Laos) | 6 | 5.7 | 5.7 | 6 |
| Premix (Hungary) 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Alga meal (Norway) 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.5 |
| Black soldier fly meal (Laos) | 0 | 0 | 3.5 | 0 |
| Bioactive compound (Austria and France) 3 | 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 |
| Proximate composition of the diets (%, as is) | ||||
| Water content | 9.5 | 6.7 | 6.8 | 6.5 |
| Crude protein | 37.0 | 36.8 | 36.1 | 37.5 |
| Crude fat | 3.19 | 3.05 | 2.66 | 3.02 |
| Ca | 3.06 | 3.21 | 3.21 | 3.21 |
| P | 1.73 | 1.65 | 1.62 | 1.72 |
| Target Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sod | GACGTGACAACACAGGTTGC | TACAGCCACCGTAACAGCAG | 2.02 | [25] |
| cat | TCAGCACAGAAGACACAGACA | GACCATTCCTCCACTCCAGAT | 2.00 | [25] |
| gpx | CCAAGAGAACTGCAAGAACGA | CAGGACACGTCATTCCTACAC | 2.03 | [25] |
| igf-1 | GTTTGTCTGTGGAGAGCGAGG | GAAGCAGCACTCGTCCAGG | 2.02 | [26] |
| tnf-α | GAGGTCGGCGTGCCAAGA | TGGTTTCCGTCCACAGCGT | 2.10 | [25] |
| il-1β | TGCTGAGCACAGAATTCCAG | GCTGTGGAGAAGAACCAAGC | 1.86 | [25] |
| il-8 | GCACTGCCCGCTGCATTAAG | GCAGTGGGAGTTGGGAAGAA | 2.03 | [25] |
| ifn-γ | TGACCACATCGTTCAGAGCA | GGCGACCTTTAGCCTTTGT | 2.01 | [25] |
| 18S | GTGCATGGCCGTTCTTAGTT | CTCAATCTCGTGTGGCTGAA | 1.98 | [27] |
| Treatments | COM | EXP-S | EXP-I | EXP-A | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBW (g) | 147.8 ± 2.1 | 144.0 ± 1.4 | 140.2 ± 15.8 | 142.5 ± 2.1 | 0.863 |
| FBW (g) | 337.5 ± 68.6 | 344.5 ± 21.9 | 344.0 ± 28.3 | 348.0 ± 46.7 | 0.994 |
| SGR (gday−1) | 1.67 ± 0.30 | 1.78 ± 0.11 | 1.84 ± 0.1 | 1.81 ± 0.03 | 0.845 |
| WG (g) | 190.0 ± 59.4 | 200.5 ± 20.5 | 204 ± 12.7 | 205.5 ± 48.8 | 0.489 |
| FCR (gg−1) | 1.57 ± 0.54 | 1.38 ± 0.04 | 1.29 ± 0.15 | 1.45 ± 0.49 | 0.875 |
| SR (%) | 94.6 ± 0.6 | 96.3 ± 1.8 | 96.3 ± 1.8 | 92.9 ± 0.6 | 0.150 |
| CF (gcm−3) | 3.80 ± 0.32 | 3.87 ± 0.33 | 4.27 ± 0.02 | 3.99 ± 0.32 | 0.435 |
| Feed Cost (€/kg) | 0.77 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.95 | NR |
| Specific Feed Cost (€/kg fish) | 1.21 ± 0.15 | 1.21 ± 0.03 | 1.23 ± 0.07 | 1.26 ± 0.09 | 0.547 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ardó, L.; Sándor, Z.J.; Orbán, M.; Szakáli, J.; Biró, J.; Szűcs, A.A.; Kovács, G.; Lévai, M.; Gregosits, B.; Brlás-Molnár, Z.; et al. Effects of Feed Additives (Nannochloropsis gaditana and Hermetia illucens) on Growth and Expression of Antioxidant and Cytokine Genes in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Subjected to Air Exposure Stress. Animals 2025, 15, 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121776
Ardó L, Sándor ZJ, Orbán M, Szakáli J, Biró J, Szűcs AA, Kovács G, Lévai M, Gregosits B, Brlás-Molnár Z, et al. Effects of Feed Additives (Nannochloropsis gaditana and Hermetia illucens) on Growth and Expression of Antioxidant and Cytokine Genes in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Subjected to Air Exposure Stress. Animals. 2025; 15(12):1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121776
Chicago/Turabian StyleArdó, László, Zsuzsanna J. Sándor, Márton Orbán, János Szakáli, Janka Biró, Anita Annamária Szűcs, Gyula Kovács, Michelle Lévai, Balázs Gregosits, Zsuzsanna Brlás-Molnár, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Feed Additives (Nannochloropsis gaditana and Hermetia illucens) on Growth and Expression of Antioxidant and Cytokine Genes in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Subjected to Air Exposure Stress" Animals 15, no. 12: 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121776
APA StyleArdó, L., Sándor, Z. J., Orbán, M., Szakáli, J., Biró, J., Szűcs, A. A., Kovács, G., Lévai, M., Gregosits, B., Brlás-Molnár, Z., & Békefi, E. (2025). Effects of Feed Additives (Nannochloropsis gaditana and Hermetia illucens) on Growth and Expression of Antioxidant and Cytokine Genes in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Subjected to Air Exposure Stress. Animals, 15(12), 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121776







