Changes of CB1 Receptor Expression in Tissues of Cocaine-Exposed Eels
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.5. Semiquantitative Analysis of the Immunoreactivity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
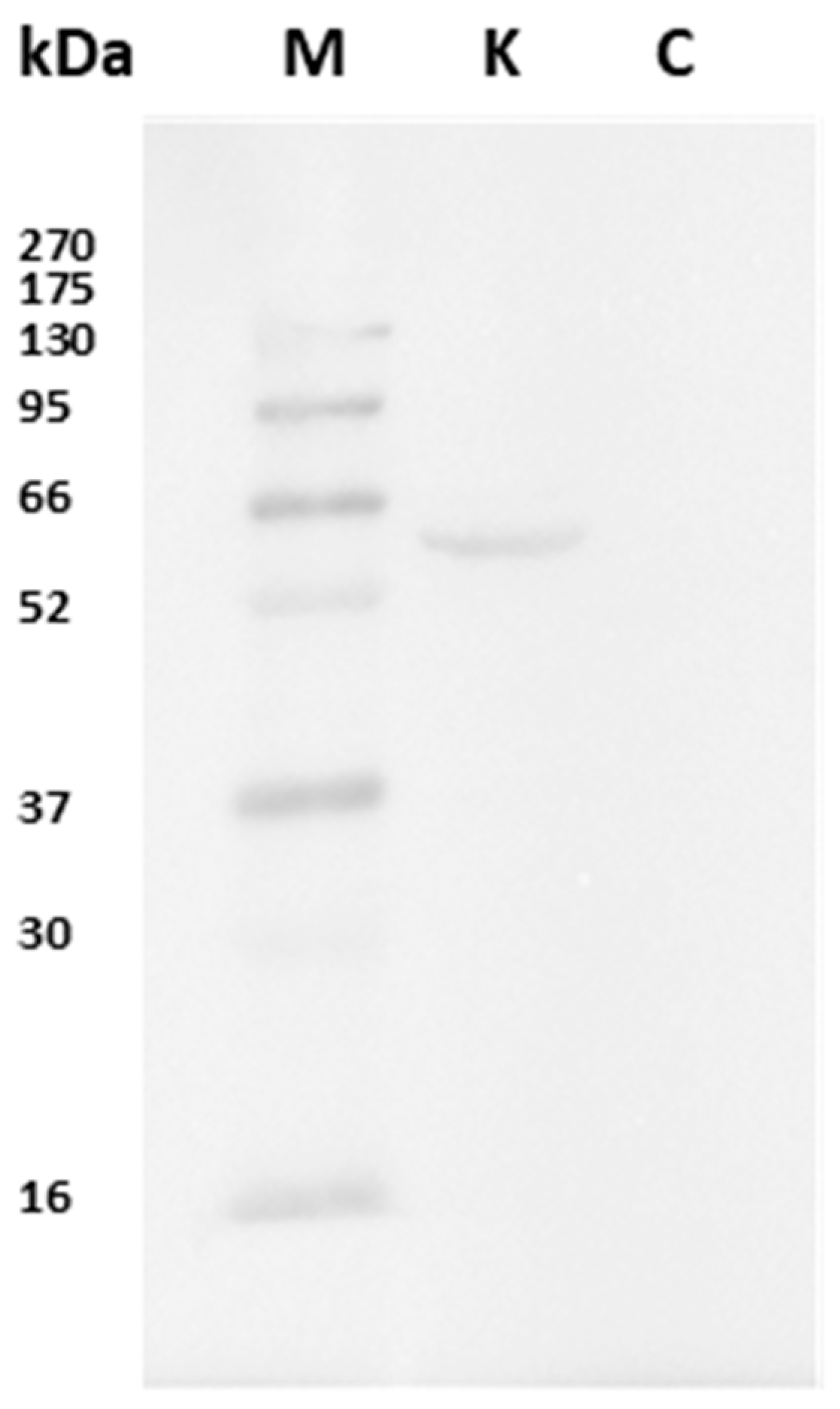
3.1. Western Blot
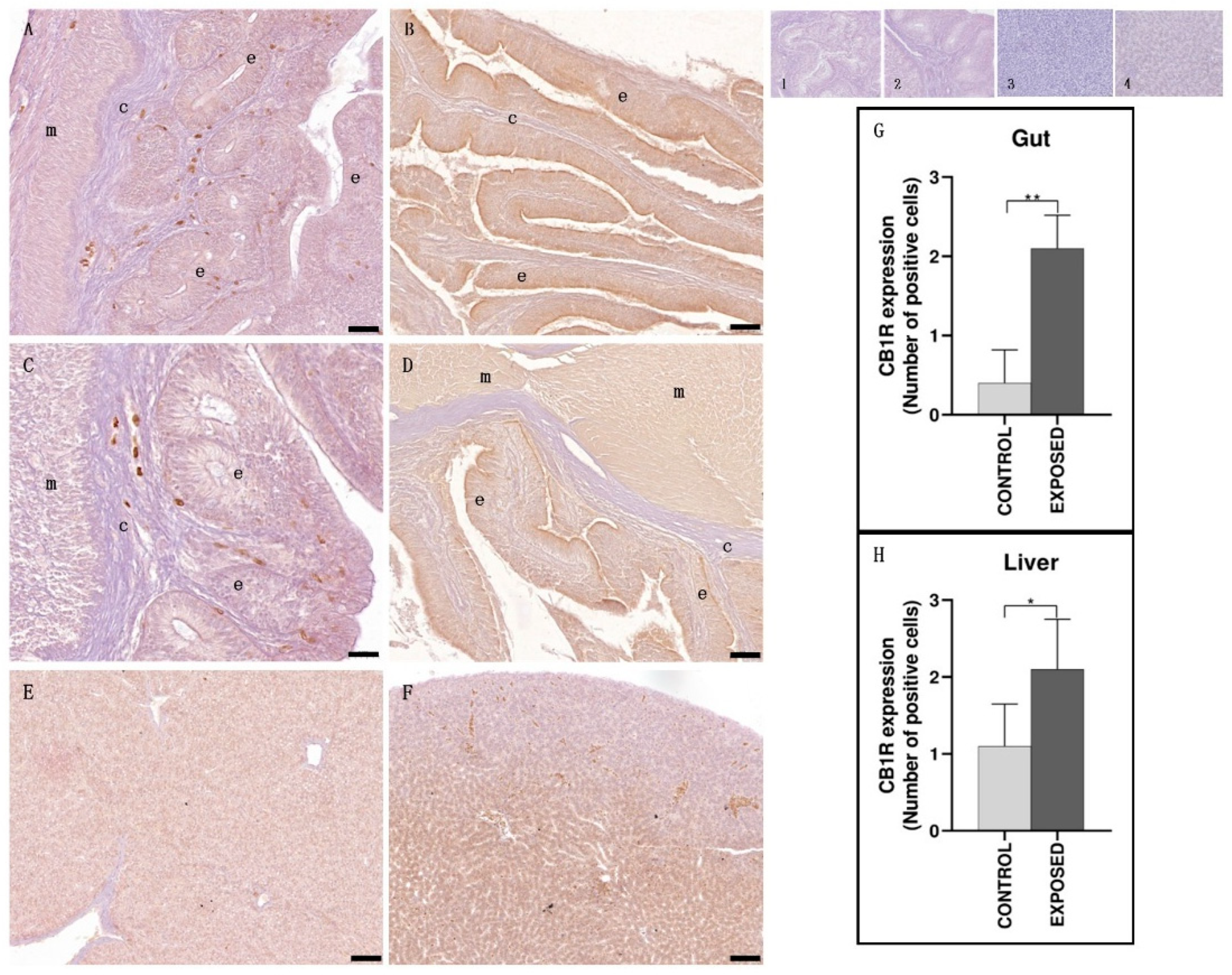
3.2. Gut and Liver Immunohistochemistry
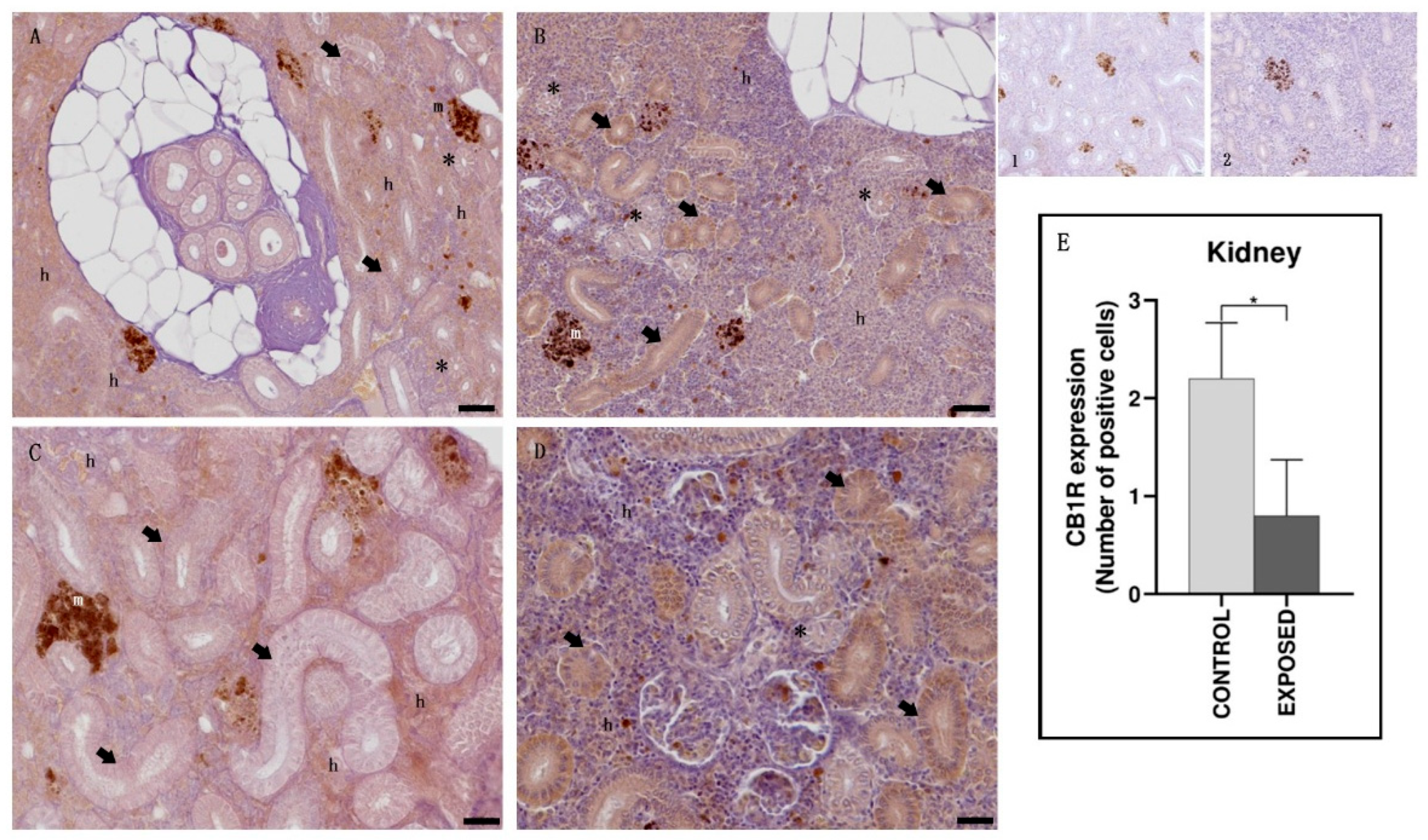
3.3. Kidney Immunohistochemistry
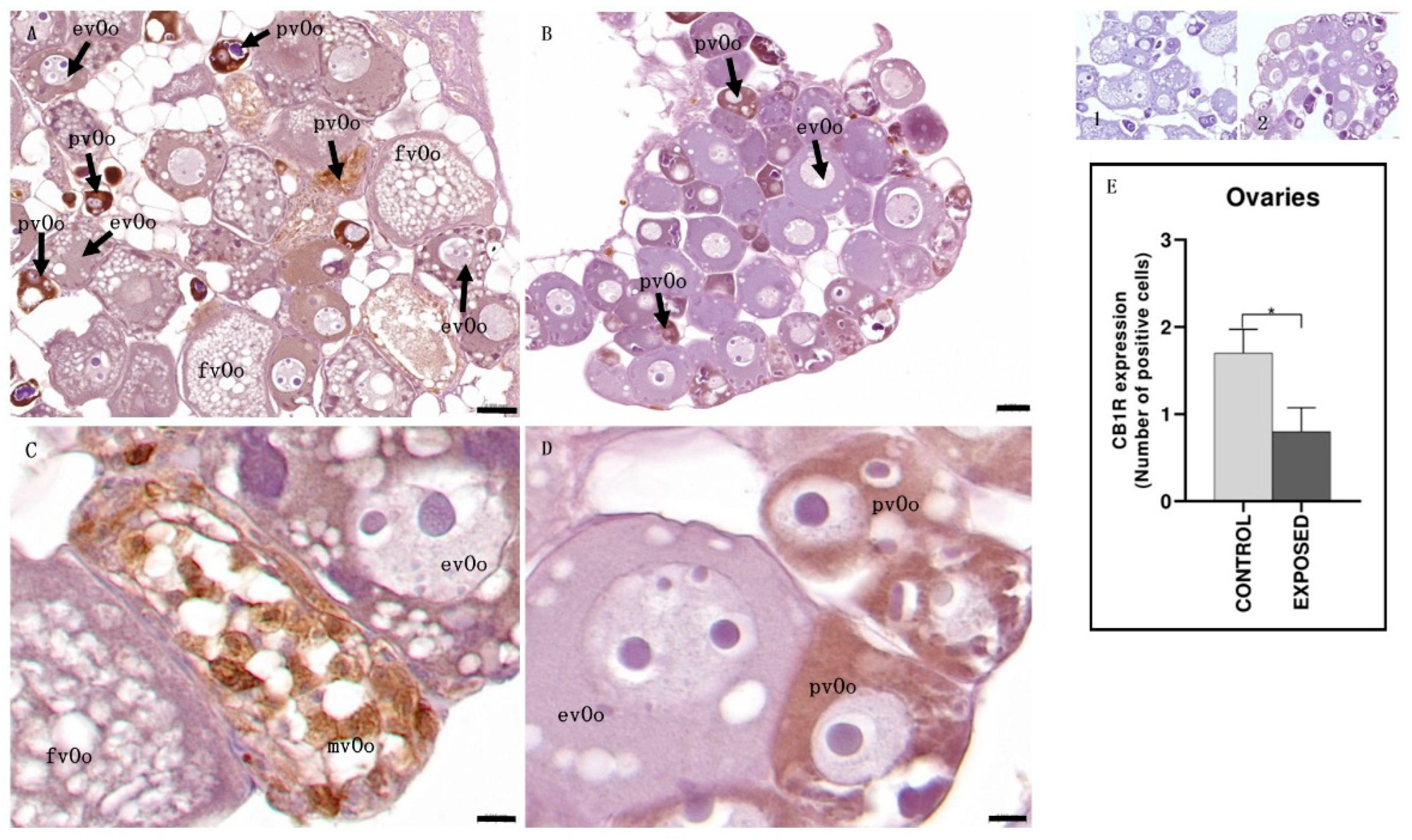
3.4. Ovary Immunohistochemistry
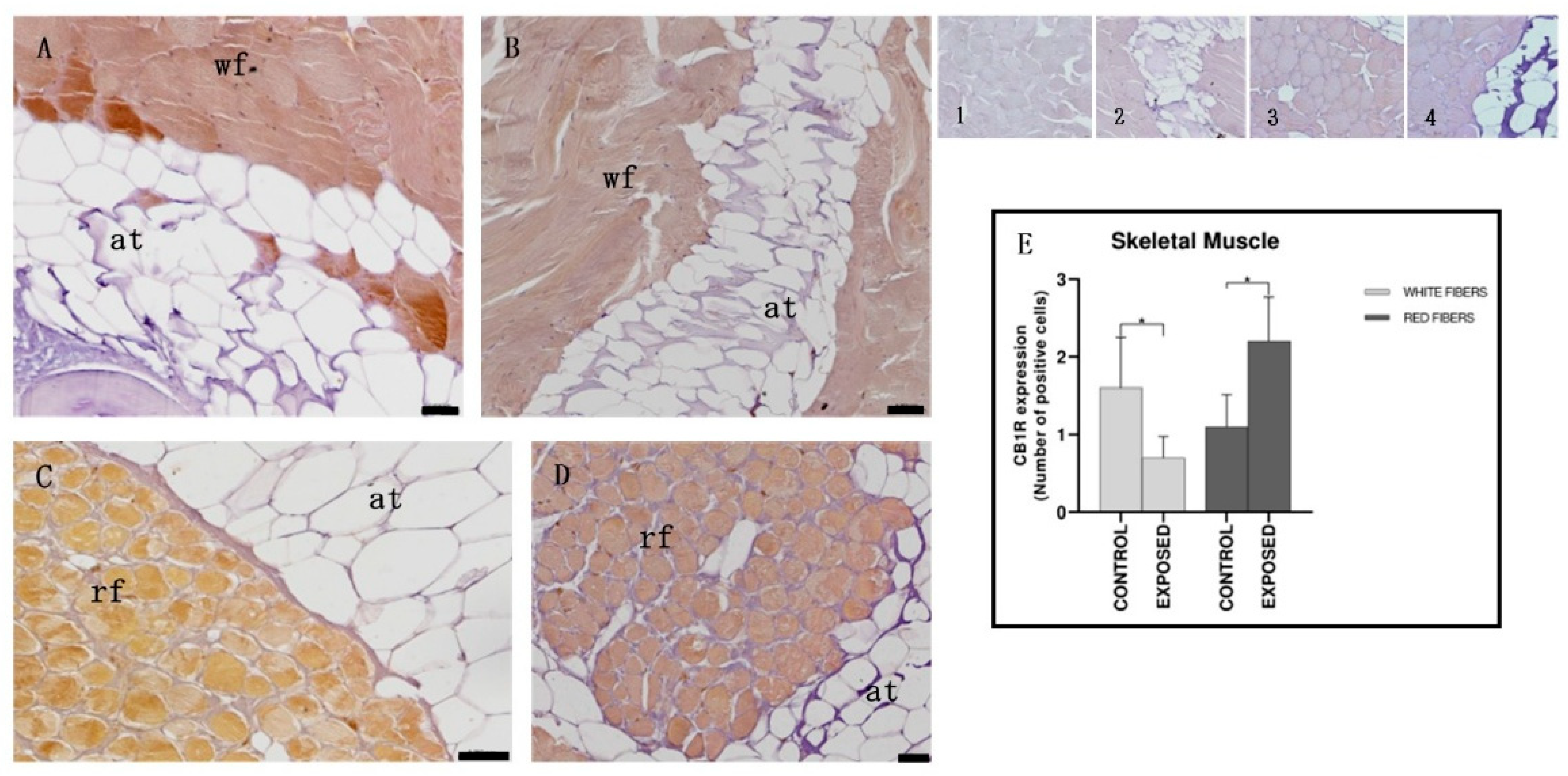
3.5. Skeletal Muscle Immunohistochemistry
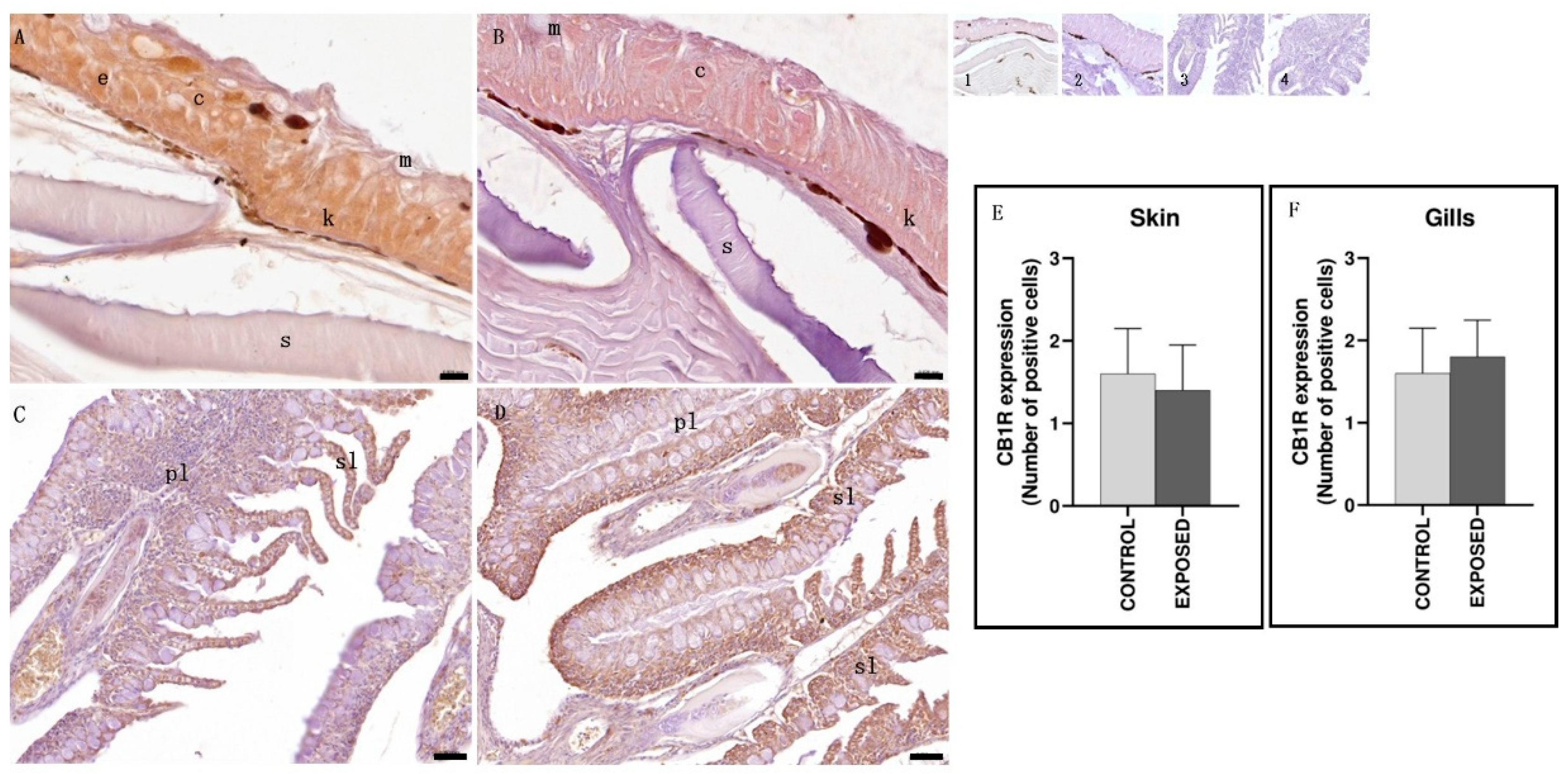
3.6. Skin and Gills Immunohistochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, R.; Megharaj, M.; Kirkbride, K.P.; Naidu, R. Illicit drugs and the environment—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Snow, D.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Paspalof, A.; Tank, J.L. A review of ecological effects and environmental fate of illicit drugs in aquatic ecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aligizakis, N.A.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Borova, V.L.; Pavlidou, A.; Hatzianestis, I.; Thomaidis, N.S. Occurrence and spatial distribution of 158 pharmaceuticals, drugs of abuse and related metabolites in offshore seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra-Pereira, C.D.; Maranho, L.A.; Cortez, F.S.; Pusceddu, F.H.; Santos, A.R.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Cesar, A.; Guimarães, L.L. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and cocaine in a Brazilian coastal zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.K.; Maranho, L.; Pereira, C.D.S. Review on the occurrence and biological effects of illicit drugs in aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30998–31034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñiz-Bustamante, L.; Caballero-Casero, N.; Rubio, S. Drugs of abuse in tap water from eight European countries: Determination by use of supramolecular solvents and tentative evaluation of risks to human health. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNODC, World Drug Report 2024 (United Nations Publication 2024). Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/data-and-analysis/WDR_2024/WDR24_Key_findings_and_conclusions.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Res. 2009, 43, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Yin, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Xu, J. Occurrence and removal of illicit drugs in different wastewater treatment plants with different treatment techniques. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, C.J.E.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Pratorius, A.; ter Laak, T.L.; van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence, hazard, and risk of psychopharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in European surface waters. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Pedriali, A.; Riva, C.; Parolini, M. Illicit drugs as new environmental pollutants: Cyto-genotoxic effects of cocaine on the biological model Dreissena polymorpha. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, C.; Sun, Z.; Xu, J. Occurrence, bioaccumulation and toxicological effect of drugs of abuse in aquatic ecosystem: A review. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.K.; Dourado, P.L.R.; de Campos, B.G.; Maranho, L.A.; de Almeida, E.A.; de Souza Abessa, D.M.; Pereira, C.D.S. Environmentally realistic concentrations of cocaine in seawater disturbed neuroendocrine parameters and energy status in the marine mussel Perna perna. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 251, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, L.; Caputo, I.; Lionetti, L.; Fontes, M.K.; Seabra Pereira, C.D.; Capaldo, A. Side effects of human drug use: An overview of the consequences of eels’ exposure to cocaine. Fishes 2023, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, A.; Mordec, M.; Caban, M.; Øverjordet, I.B.; Wielogorska, E.; Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Balazy, P.; Chełchowski, M.; Lepoint, G. Bioaccumulation of pharmaceuticals and stimulants in macrobenthic food web in the European Arctic as determined using stable isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Farias Araujo, G.; de Oliveira, L.V.A.; Hoff, R.B.; Wosnick, N.; Vianna, M.; Verruck, S.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Saggioro, E.M. “Cocaine Shark”: First report on cocaine and benzoylecgonine detection in sharks. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, M.R. The evolution and comparative neurobiology of endocannabinoid signalling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2012, 367, 3201–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltrabella, F.; Melgoza, A.; Nguyen, B.; Guo, S. Role of the endocannabinoid system in vertebrates: Emphasis on the zebrafish model. Dev. Growth Differ. 2017, 59, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, R.J. The endocannabinoid system of animals. Animals 2019, 9, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailone, R.L.; Fukushima, H.C.S.; Kluwe de Agular Borra, R.C. The endocannabinoid system in zebrafish and its potential to study the effects of Cannabis in humans. Lab. Anim. Res. 2022, 38, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Batkai, S.; Kunos, G. The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 389–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, F.; Grandi, V.; Banerjee, A.; Trant, J. Cannabinoids and Cannabinoid Receptors: The Story so Far. iScience 2020, 23, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.A.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoids and the gut: New developments and emerging concepts. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; de Petrocellis, L. Why do cannabinoid receptors have more than one endogenous ligand? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2012, 367, 3216–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Shim, J.Y.; Assi, A.A.; Norford, D.; Howlett, A.C. CB1 cannabinoid receptor-g protein association: A possible mechanism for differential signaling. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2002, 121, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciola, G.; Chianese, R.; Chioccarelli, T.; Ciaramella, V.; Fasano, S.; Pierantoni, R.; Meccariello, R.; Cobellis, G. Cannabinoids and Reproduction: A Lasting and Intriguing History. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 3275–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliarini, B.; Carnevali, O. Anandamide modulates growth and lipid metabolism in the zebrafish Danio rerio. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 286S, S12–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattore, L.; Martellotta, C.; Cossu, G.; Mascia, M.S.; Fratta, W. CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55, 212–2 decreases intravenous cocaine self-administration in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 104, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzàlez, S.; Fernàndez-Ruiz, J.; Sparpaglione, V.; Parolaro, D.; Ramos, J. Chronic exposure to morphine, cocaine or ethanol in rats produced different effects in brain cannabinoid CB1 receptor binding and mRNA levels. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2002, 66, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centonze, D.; Battista, N.; Rossi, S.; Mercuri, N.B.; Finazzi-Agro, A.; Bernardi, G.; Calabresi, P.; Maccarrone, M. A critical interaction between Dopamine D2 receptors and endocannabinoids mediates the effects of cocaine on striatal GABAergic transmission. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, G.; Mendizabal, V.; Tourin, C.; Robledo, P.; Ledent, C.; Parmentier, M.; Maldonado, R.; Valverde, O. Lack of CB1 cannabinoid receptor impairs cocaine self-administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanda, G. Modulation of the endo-cannabinoid system: Therapeutic potential against cocaine dependence. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 56, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey-Girard, E.; Giassi, A.C.C.; Ellis, W.; Maler, L. Expression of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in the Gymnotiform fish brain and its implications for the organization of the teleost pallium. J. Comp. Neurol.-Res. Syst. Neurosci. 2013, 521, 949–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, C.; Jong-Raadsen, S.A.; Dufour, S.; Weltzien, F.-A.; Palstra, A.P.; Pelster, B.; Spaink, H.P.; Van Den Thillart, G.E.; Jansen, H.; Zahm, M.; et al. A Chromosome-Scale Assembly of European Eel, Anguilla anguilla. UniProt: A0A9D3MIM1_ANGAN; Submitted to MBL/GenBank/DDBJ. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/citations/CI-4V42E84B85DHN (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Gheorghe, A.; van Nuijs, A.; Pecceu, B.; Bervoets, L.; Jorens, P.G.; Blust, R.; Neels, R.; Covaci, A. Analysis of cocaine and its principal metabolites in waste and surface water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, T.; Trinchese, G.; Leandri, R.; De Falco, M.; Mollica, M.P.; Scudiero, R.; Rosati, L. Glyphosate Exposure Induces Cytotoxicity, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Activation of ERα and ERβ Estrogen Receptors in Human Prostate PNT1A Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Aquino, I.; Piegari, G.; Miletti, G.; Sannino, E.; Costanza, D.; Meomartino, L.; Fico, R.; Riccio, L.; Vaccaro, E.; De Biase, D.; et al. Morphometrical and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Kidney as an Indirect Parameter to Estimate Age in Puppies in Veterinary Forensic Pathology. Animals 2023, 13, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spampinato, M.; Siciliano, A.; Travaglione, A.; Chianese, T.; Mileo, A.; Libralato, G.; Guida, M.; Trifuoggi, M.; De Gregorio, V.; Rosati, L. Unravelling the ecotoxicological impacts of gadolinium (Gd) on Mytilus galloprovincialis embryos and sperm in seawater: A preliminary study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.J.; Walker, F.R. Strategies to improve quantitative assessment of immunohistochemical and immunofluorescent labelling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.M.; Yin, J.X.; Castillo, L.; Young, A.I.; Piggin, C.; Rogers, S.; Caldon, C.E.; Burgess, A.; Millar, E.K.A.; O’Toole, S.A.; et al. Andy’s Algorithms: New automated digital image analysis pipelines for FIJI. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, B. Molecular biology of cannabinoid receptors. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2002, 66, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, F.; Macrae, A.D.; Brenner, S. Molecular cloning of two cannabinoid type 1-like receptor genes from the puffer fish Fugu rubripes. Genomics 1996, 35, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elphick, M.R. Evolution of cannabinoid receptors in vertebrates: Identification of a CB2 gene in the puffer fish Fugu rubripes. Biol. Bull. 2002, 202, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, J.; Szopa, A.; Ignatiuk, K.; Swiader, K.; Serefko, A. Zebrafish as an animal model in cannabinoid research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, M.A.; Porcella, A.; Ruiu, S.; Saba, P.; Marchese, G.; Carai, M.A.M.; Reali, R.; Gessa, G.L.; Pani, L. Differential distribution of functional cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the mouse gastroenteric tract. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 459, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, S.W. The Eel; Blackwell Science, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Matias, I. Endocannabinoid control of food intake and energy balance. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Patrizio, N. Endocannabinoids in the Gut. Cannabis Cann. Res. 2016, 1, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, F.; Ferrandino, I.; Monaco, A.; Cerulo, M.; Capasso, G.; Capaldo, A. Histological and hormonal changes in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla) after exposure to environmental cocaine concentration. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.; Alrafas, H.R.; Busbee, P.B.; Walla, M.D.; Wilson, K.; Miranda, K.; Cai, G.; Putluri, V.; Putluri, N.; Nagarkatti, M.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptor Activation on Haematopoietic Cells and Enterocytes Protects against Colitis. J. Chrohn’s Colitis 2021, 15, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinç, E.; Bozcaarmutlu, A. Catalyzation of Cocaine N-Demethylation by Cytochromes P4502B, P4503A, and P4502D in Fish Liver. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2003, 17, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.; Liu, J.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Cinar, R.; Godlewski, G.; Kunos, G. Endocannabinoids in Liver Disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazwinsky-Wutschke, I.; Zipprich, A.; Dehghani, F. Endocannabinoid System in Hepatic Glucose Metabolism, Fatty Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E. CB1 & CB2 Receptor Pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagotto, U.; Pasquali, R. Endocannabinoids and energy metabolism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Caputo, I.; Lionetti, L.; Paolella, G.; Di Gregorio, I.; Martucciello, S.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Rosati, L.; Laforgia, V. Effects of environmental cocaine concentrations on COX and caspase-3 activity, GRP-78, ALT, CRP and blood glucose levels in the liver and kidney of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumford, S.; Heidel, J.; Smith, C.; Morrison, J.; Mac Connell, B.; Blazer, V. Fish Histology and Histopathology. U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service-National Conservation Training Center. 2007. Available online: https://nctc.fws.gov/resources/course-resources/fish-histology/ (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Watanabe, T.; Takei, Y. Molecular physiology and functional morphology of SO4 2– excretion by the kidney of seawater-adapted eels. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Fu, Y.; Avraham, H.K. Regulation of hematopoietic stem cell trafficking and mobilization by the endocannabinoid system. Transfusion 2011, 51, 65S–71S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottone, E.; Pomatto, V.; Cerri, F.; Campantico, E.; Mackie, K.; Delpero, M.; Guastalla, A.; Dati, C.; Bovolin, P.; Franzoni, M.F. Cannabinoid receptors are widely expressed in goldfish: Molecular cloning of a CB2-like receptor and evaluation of CB1 and CB2 mRNA expression profiles in different organs. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J. The emerging role of the endocannabinoid system in the pathogenesis and treatment of kidney diseases. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 27, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.; Francois, H. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Inhibition in Chronic Kidney Disease: A New Therapeutic Toolbox. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 720734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arceri, L.; Nguyen, T.K.; Gibson, S.; Baker, S.; Wingert, R.A. Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, M.J.; Henrique, R.; Vilas-Boas, V.; Silva, R.; de lourdes Bastos, M.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. Cocaine-induced kidney toxicity: An in vitro study using primary cultured human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchi, F.; Papucci, L.; Schiavone, N.; Lulli, M.; Magnelli, L.; Vinci, M.C.; Messerini, L.; Manera, C.; Ronconi, E.; Romagnani, P.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor activation induces apoptosis through tumor necrosis factor α-mediated ceramide de novo synthesis in colon cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7691–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.K.; Rosati, L.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Seabra Pereira, C.D.; Maranho, L.A.; Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A. Aquatic Pollution and Risks to Biodiversity: The Example of Cocaine Effects on the Ovaries of Anguilla anguilla. Animals 2022, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, O.S.; Holloway, A.C.; Raha, S. The role of the endocannabinoid system in female reproductive tissues. J. Ovar. Res. 2019, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, L.; Chianese, T.; Mileo, A.; De Falco, M.; Capaldo, A. Cocaine Effects on Reproductive Behavior and Fertility: An Overview. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Blasio, A.M.; Vignali, M.; Gentilini, D. The endocannabinoid pathway and the female reproductive organs. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 1, R1–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, J.; Madogwe, E.; McCall, A.; Singh, J.; Duggavathi, R. Characterizing the Role of Endocannabinoid Receptor Cnr1 in Mouse Ovarian Granulosa Cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2025, 43, e70070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendizabal-Zublaga, J.M.; Melser Su Bènard, G.; Ramos, A.; Reguero, L.; Arrabal, S.; Elezgaral, I.; Gerrikagoitia, I.; Suarez, J.; De Fonseca, F.R.; Puente, N.; et al. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Are Localized in Striated Muscle Mitochondria and Regulate Mitochondrial Respiration. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavuoto, P.; McAinch, A.J.; Hatzinikolas, G.; Cameron-Smith, G.A.; Wittert, G.A. Effects of cannabinoid receptors on skeletal muscle oxidative pathways. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2007, 267, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavuoto, P.; McAinch, A.J.; Hatzinikolas, G.; Janovskà, A.; Game, P.; Wittert, G.A. The expression of receptors for endocannabinoids in human and rodent skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2007, 364, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle, S.; Schouten, M.; Meeus, G.; Slagmolen, L.; Koppo, K. Molecular networks underlying cannabinoid signaling in skeletal muscle plasticity. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 3517–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Abreu, N.K.; Fabro Feltrin, I.; Russiano Pereira, D.B.; Bezerra, P.P.; Aguiar, A.S., Jr. Impact of CB1 receptor antagonism on skeletal muscle hypertrophy and metabolic health: A systematic review of preclinical studies. Hormones 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, K.I.; Funada, M. Synthetic cannabinoid CP-55,940 induces apoptosis in a human skeletal muscle model via regulation of CB1 receptors and l-type Ca2+ channels. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Lepretti, M.; Paolella, G.; Martucciello, S.; Lionetti, L.; Caputo, I.; Laforgia, V. Effects of environmental cocaine concentrations on the skeletal muscle of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birò, T.; Tòth, B.; Haskò, G.; Paus, R.; Pacher, P. The endocannabinoid system of the skin in health and disease: Novel perspectives and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupczyk, P.; Reich, A.; Szepietowski, J.C. Cannabinoid system in the skin—A possible target for future therapies in dermatology. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 18, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Martin, I.; Herrero-Turrion, M.J.; Marron Fdez de Velasco, E.; Gonzalez-Sarmiento, R.; Rodriguez, R.E. Characterization of two duplicate zebrafish Cb2-like cannabinoid receptors. Gene 2007, 389, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; Laforgia, V. Changes in the gills of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla) after chronic exposure to environmental cocaine concentration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riccio, L.; Chianese, T.; Mileo, A.; Balsamo, S.; Sciarrillo, R.; Gatta, R.; Rosati, L.; De Falco, M.; Capaldo, A. Changes of CB1 Receptor Expression in Tissues of Cocaine-Exposed Eels. Animals 2025, 15, 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121734
Riccio L, Chianese T, Mileo A, Balsamo S, Sciarrillo R, Gatta R, Rosati L, De Falco M, Capaldo A. Changes of CB1 Receptor Expression in Tissues of Cocaine-Exposed Eels. Animals. 2025; 15(12):1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121734
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiccio, Lorenzo, Teresa Chianese, Aldo Mileo, Sabrina Balsamo, Rosaria Sciarrillo, Roberta Gatta, Luigi Rosati, Maria De Falco, and Anna Capaldo. 2025. "Changes of CB1 Receptor Expression in Tissues of Cocaine-Exposed Eels" Animals 15, no. 12: 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121734
APA StyleRiccio, L., Chianese, T., Mileo, A., Balsamo, S., Sciarrillo, R., Gatta, R., Rosati, L., De Falco, M., & Capaldo, A. (2025). Changes of CB1 Receptor Expression in Tissues of Cocaine-Exposed Eels. Animals, 15(12), 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121734







