Recombinant Bacillus subtilis Improves Growth and Protein Utilization and Regulates PI3K/AKT/TOR Pathway-Related Genes in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Methods
2.2. Management of Crab
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Sample Collection
2.3.2. Proximate Composition Analysis
2.3.3. Assay of Digestive Enzyme Activity
2.3.4. Hemolymphatic Protein Level
2.3.5. Analysis of ROS Levels
2.3.6. Transcriptional Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
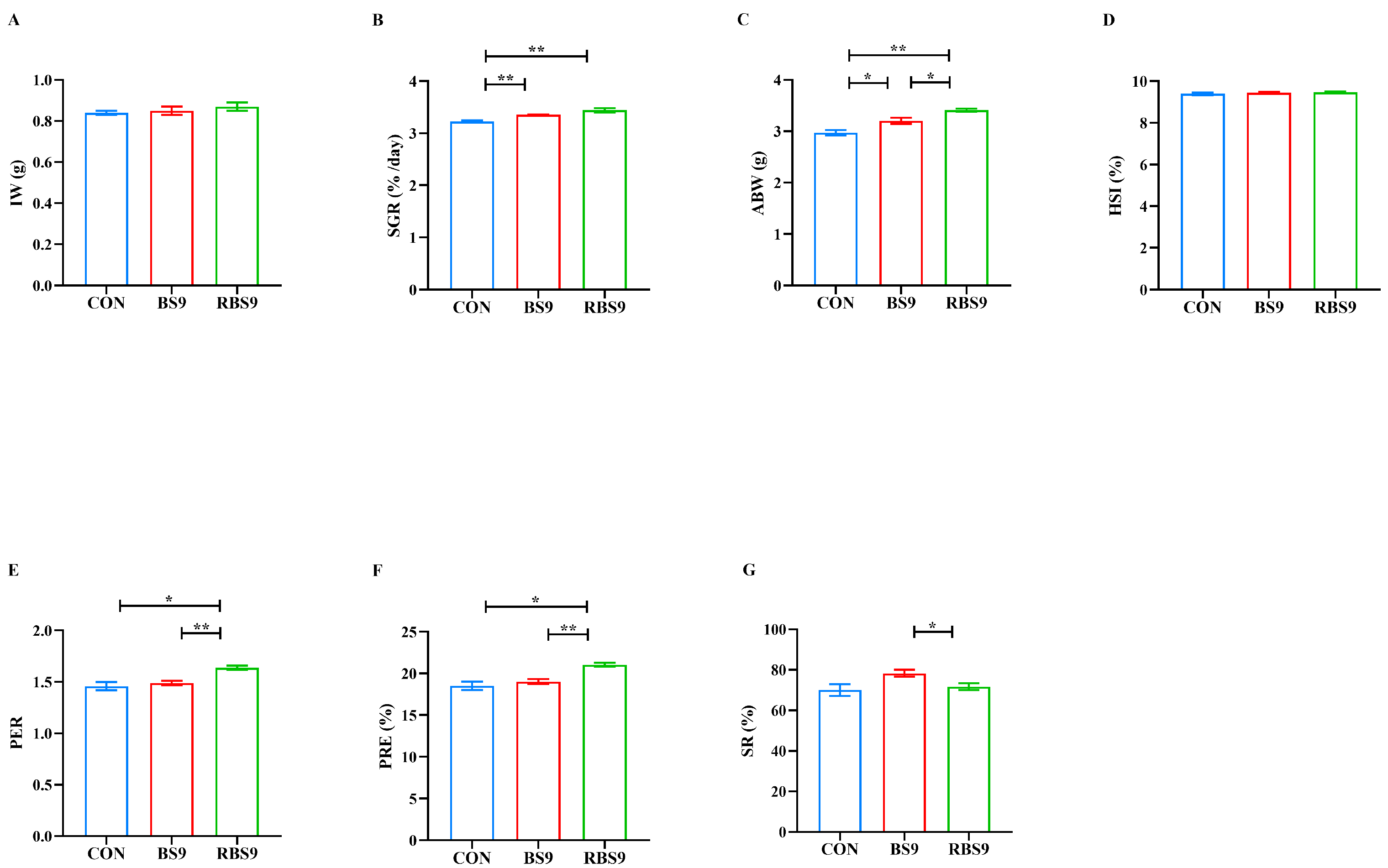
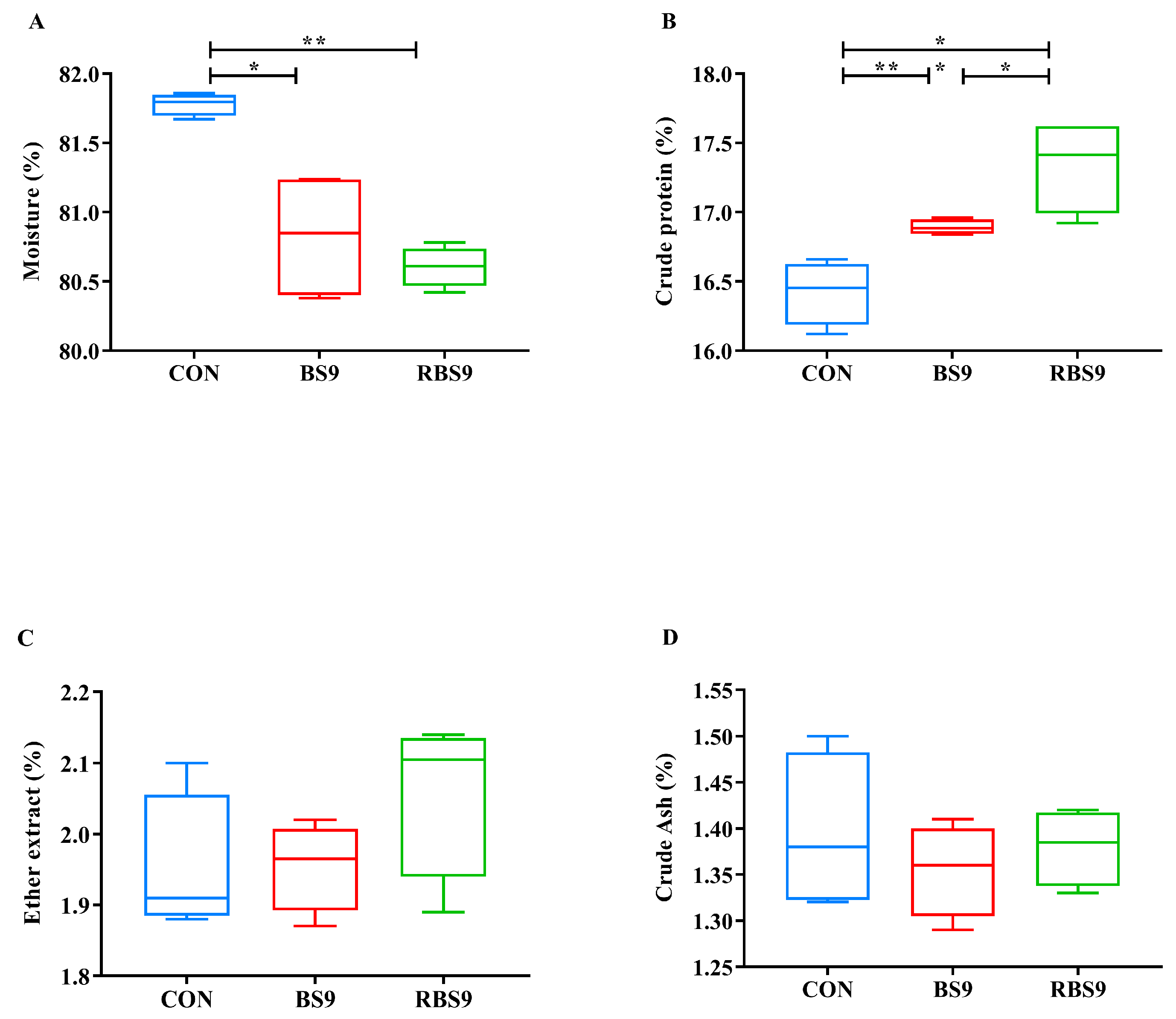
3.1. Growth Performance and Muscle Composition
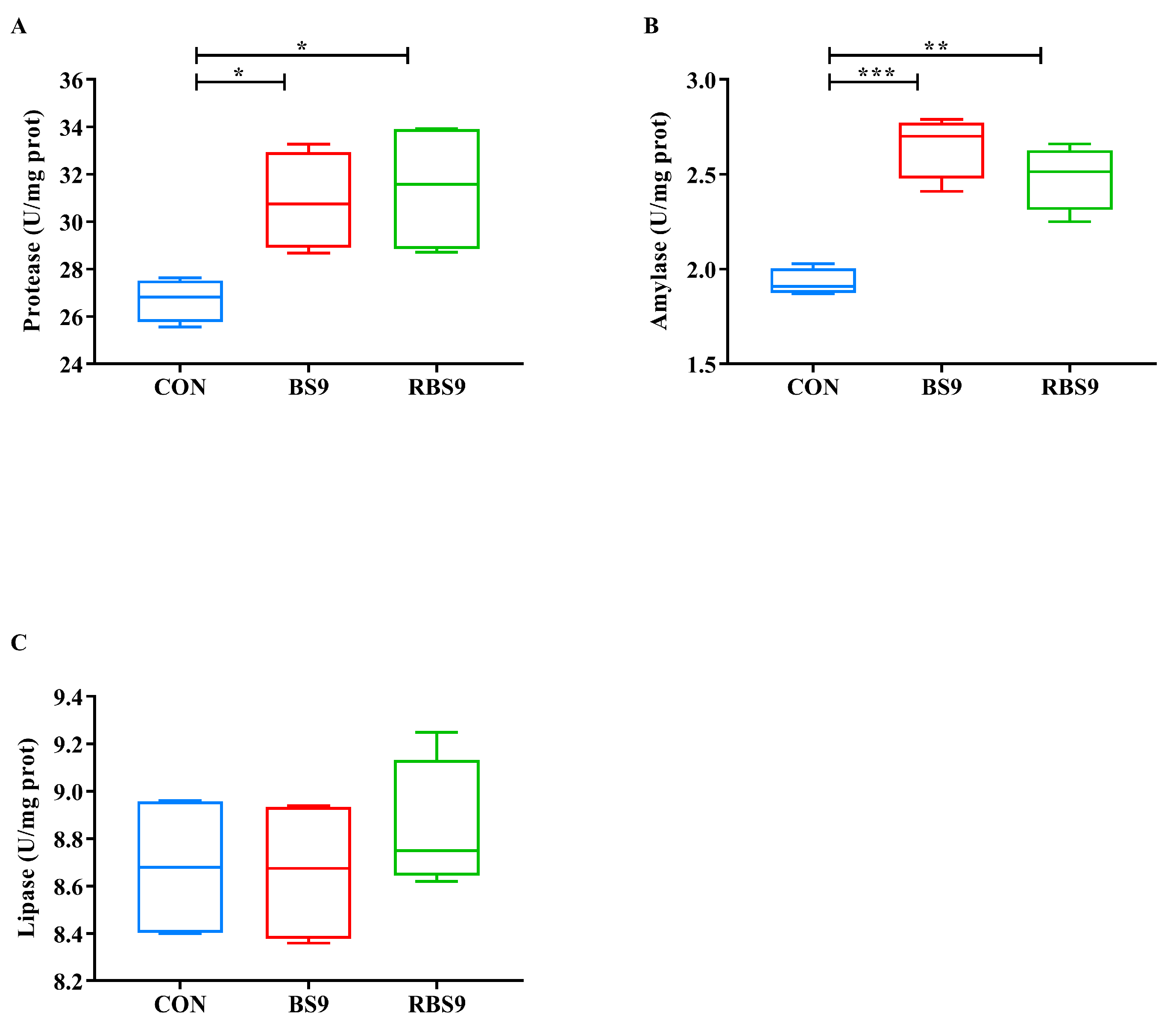
3.2. Activities of Digestion-Related Enzymes
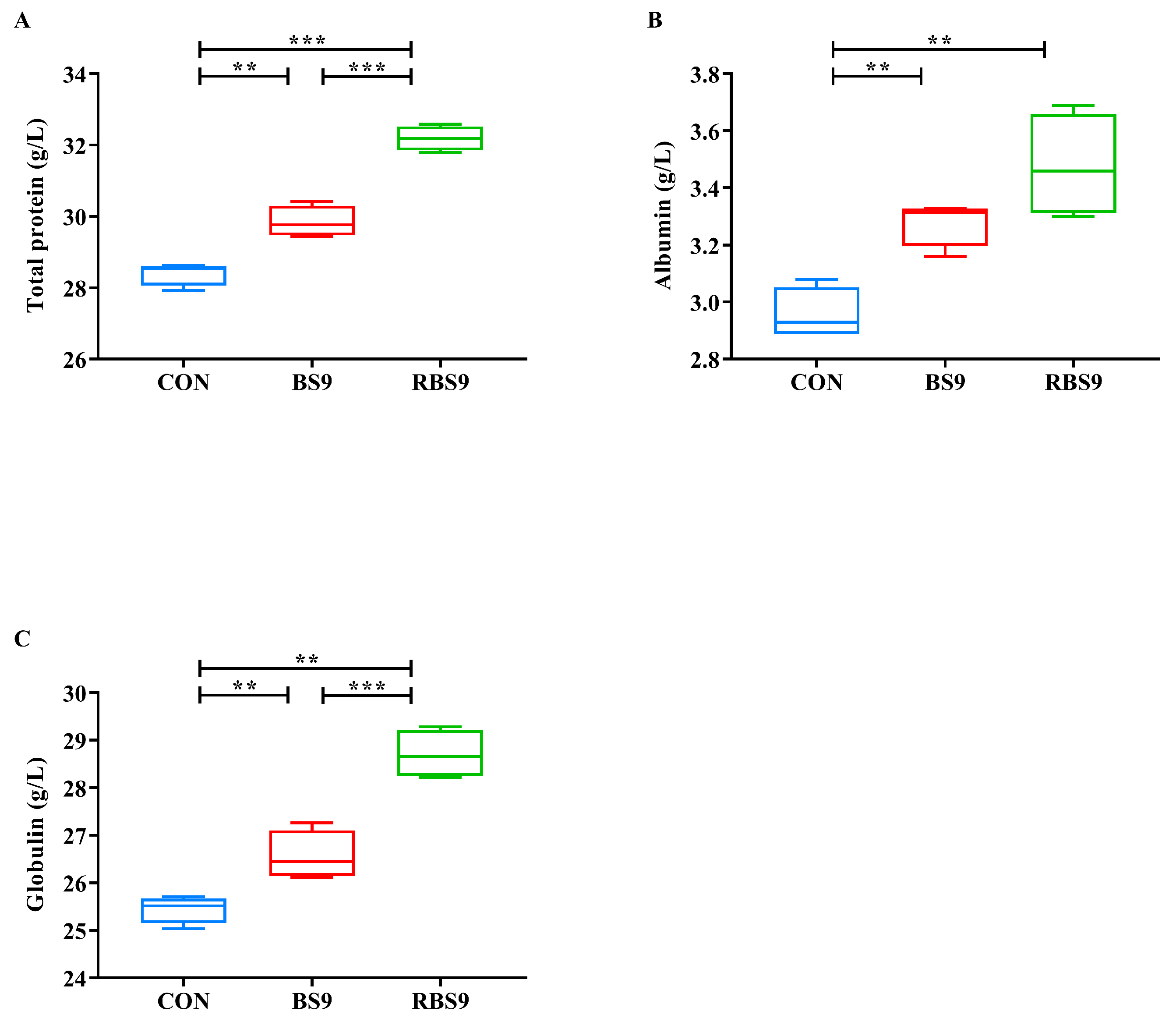
3.3. Levels of Hemolymphatic Protein
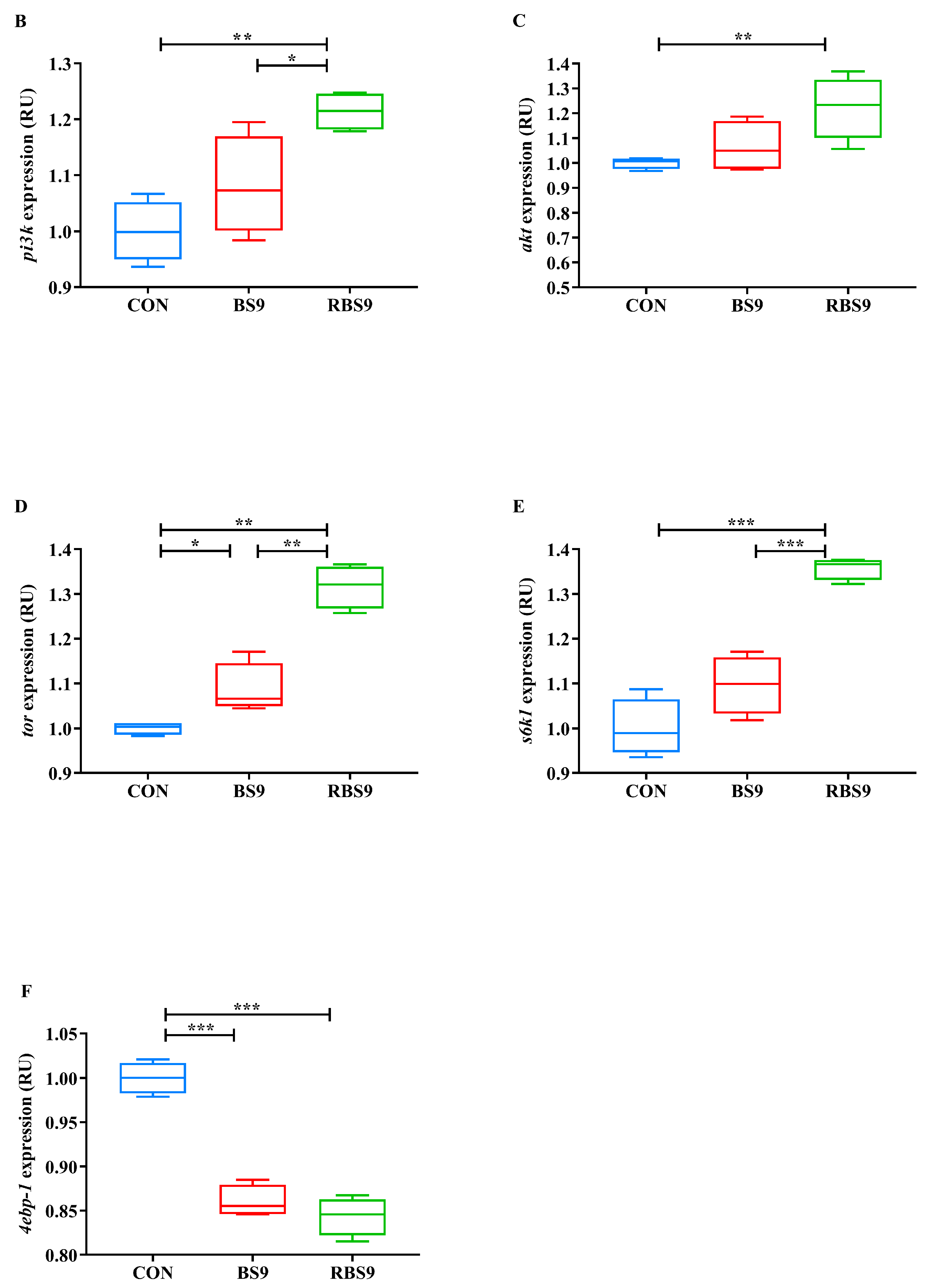
3.4. ROS Levels and Relative Expression of PI3K/AKT/TOR Pathway-Related Genes in the Hepatopancreas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Wu, F.X. Chinese Fishery Statistical Yearbook; Fisheries Agency of China Agriculture Ministry, China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2023. Available online: https://www.shujuku.org/china-fishery-statistical-yearbook-2023.html (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Cheng, H.; Liu, M.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Jiang, G. Cottonseed meal protein hydrolysate stimulates feed intake and appetite in Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 25, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Qian, X.; Li, X. Utilization of Cottonseed Meal Protein Hydrolysate by Crustaceans: Insights on Growth Performance, Protein Turnover, and Metabolism in Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis. Animals 2023, 13, 3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Cottonseed Meal Protein Hydrolysate Improves the Growth Performance of Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) by Promoting the Muscle Growth and Molting Performance. Aquac. Nutr. 2023, 2023, 8347921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, D.; Liu, W.; Shao, X.; Xu, W. Effects of different dietary levels of cottonseed meal protein hydrolysate on growth, digestibility, body composition and serum biochemical indices in crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2010, 156, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Long, X. Effects of small peptides, probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on growth performance, digestive enzymes, and oxidative stress in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, juveniles reared in artificial seawater. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2017, 35, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, X.; Guo, X.; Mi, S.; Hua, X.; Li, N.; Yao, J. Enhanced growth performance, muscle quality and liver health of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) were related to dietary small peptides supplementation. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, G. Evaluation of antioxidant capacity and immunomodulatory effects of cottonseed meal protein hydrolysate and its derivative peptides for hepatocytes of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish Immun. 2020, 98, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. The P4’ Peptide-Carrying Bacillus subtilis in Cottonseed Meal Improves the Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis Innate Immunity, Redox Defense, and Growth Performance. Aquac. Nutr. 2024, 2024, 3147505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zou, D.; Mai, K.; Sun, Z.; Ye, C. Leucine promotes protein synthesis of juvenile white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei through TOR signaling pathway. Aquaculture 2023, 564, 739060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, X.Y.; Guo, Z.X.; Wang, S.; Wan, J.W.; Liu, H.J.; Chen, Y.K.; Wang, G.Q.; Wang, Q.J.; Zhang, D.M. The immuneoreaction and antioxidant status of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) involve protein metabolism and the response of mTOR signaling pathway to dietary methionine levels. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Guo, J.; Luo, K.; Zhou, W.; Mai, K.; Zhang, W. Replacement of dietary fish meal with soy protein concentrate on the growth performance, PI3K/AKT/TOR pathway, immunity of abalone Haliotis discus hannai and its resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chi, C.; Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; He, C.; He, C.; Jia, X.; et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with icariin on growth performance, antioxidant capacity and non-specific immunity of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fish Shellfish Immun. 2019, 90, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupp-Enyard, C. Sigma’s Non-specific Protease Activity Assay—Casein as a Substrate. J. Vis. Exp. 2008, 19, e899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.T.; Chopra, R.K. The paradoxical effect of fatty acid on steroid-albumin interaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 427, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clase, C.M.; St Pierre, M.W.; Churchill, D.N. Conversion between bromcresol green- and bromcresol purple-measured albumin in renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Abasubong, K.P.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Chi, C.; Liu, W. Protective effects of dietary icariin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute oxidative stress and hepatopancreas injury in Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2022, 251, 109192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Yue, W.; Lu, W.; Lu, G.; Wang, C. Selection of appropriate reference genes for qPCR in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis (Decapoda, Varunidae). Crustaceana 2017, 90, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Yao, J.; Zhu, C.; Chi, C. Effects of partial fish meal replacement with two fermented soybean meals on the growth of and protein metabolism in the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 17, 100328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decamp, O.; Moriarty, D.J.W.; Lavens, P. Probiotics for shrimp larviculture: Review of field data from Asia and Latin America. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei-Nejad, S.; Rezaei, M.H.; Takami, G.A.; Lovett, D.L.; Mirvaghefi, A.-R.; Shakouri, M. The effect of Bacillus spp. bacteria used as probiotics on digestive enzyme activity, survival and growth in the Indian white shrimp Fenneropenaeus indicus. Aquaculture 2006, 252, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zokaeifar, H.; Balcázar, J.L.; Saad, C.R.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Sijam, K.; Arshad, A.; Nejat, N. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, digestive enzymes, immune gene expression and disease resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2012, 33, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.X.; Feng, X.; Xie, L.L.; Peng, X.Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, X.X. Effect of probiotic Bacillus subtilis Ch9 for grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes, 1844), on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities and intestinal microflora. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Fumanal, M.; Anguís, V.; Fernández-Díaz, C.; Alarcón, F.J.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Balebona, M.C. Modulation of Intestinal Microbiota in Solea senegalensis Fed Low Dietary Level of Ulva ohnoi. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- League, G.P.; Onuh, O.C.; Hillyer, J.F. Comparative structural and functional analysis of the larval and adult dorsal vessel and its role in hemolymph circulation in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 218, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanemura, A.; Mizuno, S.; Hayasaki, A.; Gyoten, K.; Fujii, T.; Iizawa, Y.; Kato, H.; Murata, Y.; Kuriyama, N.; Kishiwada, M.; et al. Onodera’s prognostic nutritional index is a strong prognostic indicator for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after initial hepatectomy, especially patients with preserved liver function. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.A.; Bodnar, T.S.; Weinberg, J.; Hammond, G.L. Corticosteroid-binding globulin is a biomarker of inflammation onset and severity in female rats. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, I. Effect of dietary protein levels on growth performance, hematological profile and biochemical composition of fingerlings rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss reared in Indian himalayan region. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, B.R.; Kaysen, G. Serum albumin: Relationship to inflammation and nutrition. Semin. Dial. 2004, 17, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Bandura, J.; Zhang, P.; Jin, Y.; Reuter, H.; Edgar, B.A. EGFR-dependent TOR-independent endocycles support Drosophila gut epithelial regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostaid, M.S.; Lee, T.T.; Chana, G.; Sundram, S.; Shannon Weickert, C.; Pantelis, C.; Everall, I.; Bousman, C. Peripheral Transcription of NRG-ErbB Pathway Genes Are Upregulated in Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibollet-Bahena, O.; Almazan, G. IGF-1-stimulated protein synthesis in oligodendrocyte progenitors requires PI3K/mTOR/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Wu, T.; Peng, Z.; Tan, Q.; Peng, X.; Zhan, Z.; Song, L.; Wei, B. Baicalin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human osteosarcoma cells by increasing ROS to inhibit PI3K/Akt/mTOR, ERK1/2 and β-catenin signaling pathways. J. Bone Oncol. 2022, 33, 100415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui-Xuan, N.H.; Tang, P.M.K.; Wong, C.K.; Fung, K.P. Photo-activated pheophorbide-a, an active component of Scutellaria barbata, enhances apoptosis via the suppression of ERK-mediated autophagy in the estrogen receptor-negative human breast adenocarcinoma cells MDA-MB-231. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Park, K.I.; Kim, S.H.; Yu, S.N.; Park, S.G.; Kim, Y.W.; Seo, Y.K.; Ma, J.Y.; Ahn, S.C. Inhibition of Autophagy Promotes Salinomycin-Induced Apoptosis via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK/p38 MAPK-Dependent Signaling in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, C.; He, Z.; Zhu, F.; Wang, M.; He, R.; Zhao, C.; Shi, X.; Zhou, M.; Pan, S.; et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling via ROS regulation is involved in Rhein-induced apoptosis and enhancement of oxaliplatin sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.F.; Jiang, G.Z.; Liu, W.B. Mitigating LPS-induced stress in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) with P4’peptide-bearing Bacillus subtilis. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2025, 158, 110156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naksuriya, O.; Daowtak, K.; Tima, S.; Okonogi, S.; Mueller, M.; Toegel, S.; Khonkarn, R. Hydrolyzed Flavonoids from Cyrtosperma johnstonii with Superior Antioxidant, Antiproliferative, and Anti-Inflammatory Potential for Cancer Prevention. Molecules 2022, 27, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, C.; Chen, N.; Gu, H.; Yen, A.; Cao, L.; Wang, E.; Wang, L. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33440–33450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Hou, S.; Orr, B.A.; Kuo, B.R.; Youn, Y.H.; Ong, T.; Roth, F.; Eberhart, C.G.; Robinson, G.W.; Solecki, D.J.; et al. mTORC1-mediated inhibition of 4EBP1 is essential for hedgehog signaling-driven translation and medulloblastoma. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Guan, K.L. Amino acid signaling in TOR activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 1001–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wullschleger, S.; Loewith, R.; Hall, M.N. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006, 124, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients (%) | |
|---|---|
| Fish meal | 30.00 |
| Blood meal | 4.00 |
| Soybean meal (defatted) | 10.00 |
| Cotton meal | 4.00 |
| Peanut meal | 18.81 |
| Rapeseed meal | 2.00 |
| α-starch | 20.93 |
| Soybean oil | 3.55 |
| Fish oil | 1.00 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 1.50 |
| Zeolite powder | 0.9 |
| Premix a | 1.00 |
| Mixture b | 2.30 |
| Proximate composition (% dry-matter basis) | |
| Dry matter | 89.46 |
| Crude protein | 39.78 |
| Crude lipid | 7.51 |
| Nitrogen-free extract | 27.09 |
| Metabolizable energy (MJ/kg) | 10.77 |
| Gross energy (MJ/kg) | 17.20 |
| Target Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) | AT (°C) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pi3k | (F) AGCATCATGTTCCCTGCCAA | 59.96 | 56 | JX452100.1 |
| (R) GCAGTTTGCGCTCTTGTTCA | 59.97 | |||
| akt | (F) CAAGATCCTGCGCAAAGACG | 59.90 | 56 | KY412800.1 |
| (R) CATGACGAAGCAGAGACGGT | 60.11 | |||
| tor | (F) GCAGCCCCAAGGAGATGAAA | 60.32 | 56 | [2] |
| (R) ACAGTCGAAACGCCCTCATC | 60.39 | |||
| s6k1 | (F) TCAATAGCGTCGTCATCG | 54.70 | 54 | [22] |
| (R) CCCTGCGTGTAGTGGTTG | 58.03 | |||
| 4ebp-1 | (F) GCAACACGCCAACTAAACTC | 57.97 | 54 | [22] |
| (R) GCGACACCACCTAATATCCA | 57.10 | |||
| s27 | (F) GGTCGATGACAATGGCAAGA | 58.26 | 56 | HM177456 |
| (R) CCACAGTACTGGCGGTCAAA | 60.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; He, C. Recombinant Bacillus subtilis Improves Growth and Protein Utilization and Regulates PI3K/AKT/TOR Pathway-Related Genes in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Animals 2025, 15, 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121732
Li Y, Gao S, Liu W, Li X, Jiang G, He C. Recombinant Bacillus subtilis Improves Growth and Protein Utilization and Regulates PI3K/AKT/TOR Pathway-Related Genes in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Animals. 2025; 15(12):1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121732
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yongmin, Shengyu Gao, Wenbin Liu, Xiangfei Li, Guangzhen Jiang, and Chaofan He. 2025. "Recombinant Bacillus subtilis Improves Growth and Protein Utilization and Regulates PI3K/AKT/TOR Pathway-Related Genes in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis)" Animals 15, no. 12: 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121732
APA StyleLi, Y., Gao, S., Liu, W., Li, X., Jiang, G., & He, C. (2025). Recombinant Bacillus subtilis Improves Growth and Protein Utilization and Regulates PI3K/AKT/TOR Pathway-Related Genes in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Animals, 15(12), 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121732






