Integrative QTL Mapping and Transcriptomic Profiling to Identify Growth-Associated QTL and Candidate Genes in Hong Kong Catfish (Clarias fuscus)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Preparation and Phenotyping
2.3. QTL Mapping for Growth Traits
2.4. Screening of Candidate Genes for Growth Traits QTL and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Transcriptome Library Creation and Raw Data Processing
2.6. Screening of DEGs and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.7. QTL and Transcriptome Association Analysis
2.8. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) Validation
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Statistics
3.2. QTL Analysis and Candidate Gene Identification
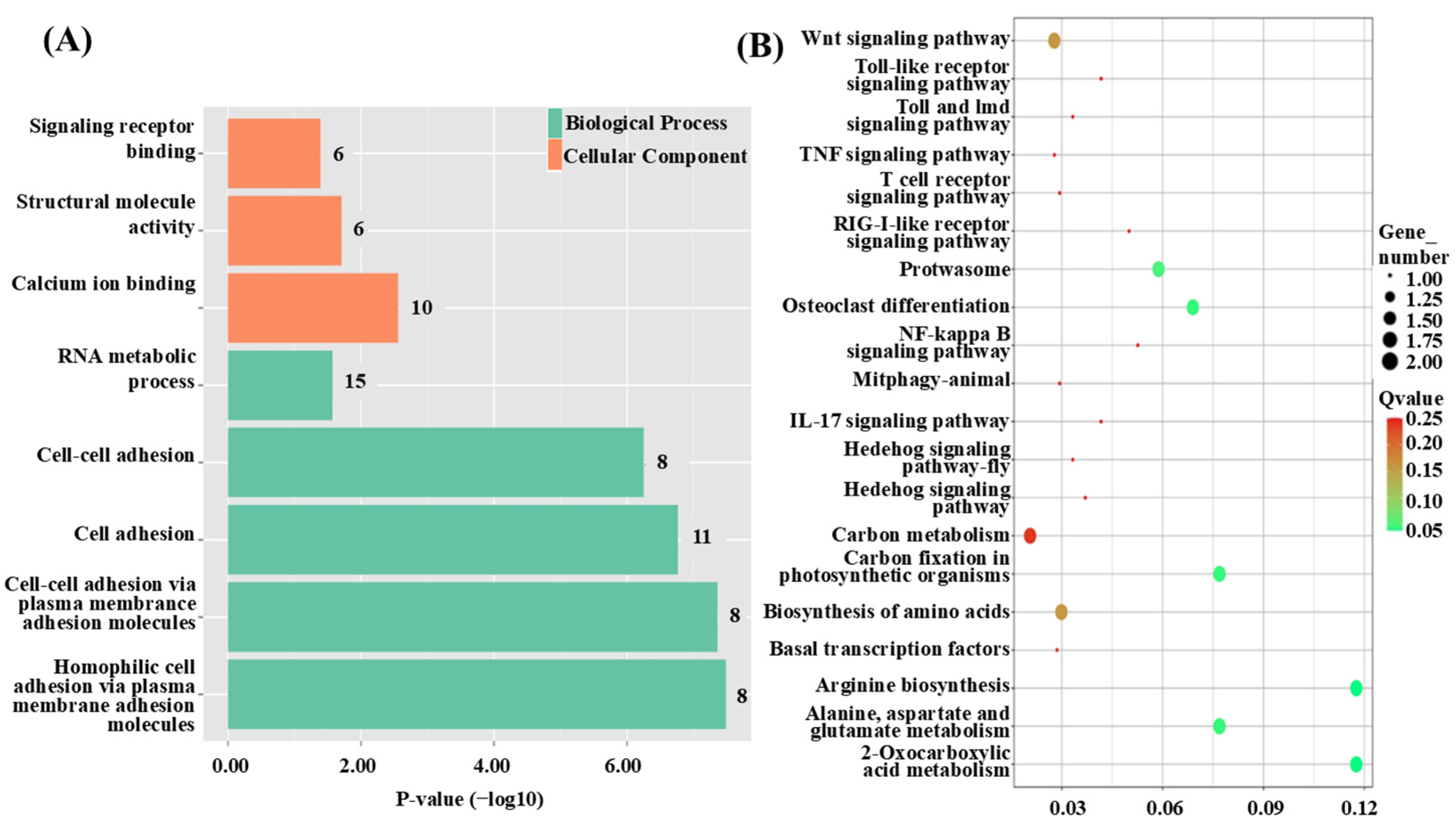
3.3. Functional Annotation of QTL Candidate Genes
3.4. Quality Control of Transcriptome Sequencing Data
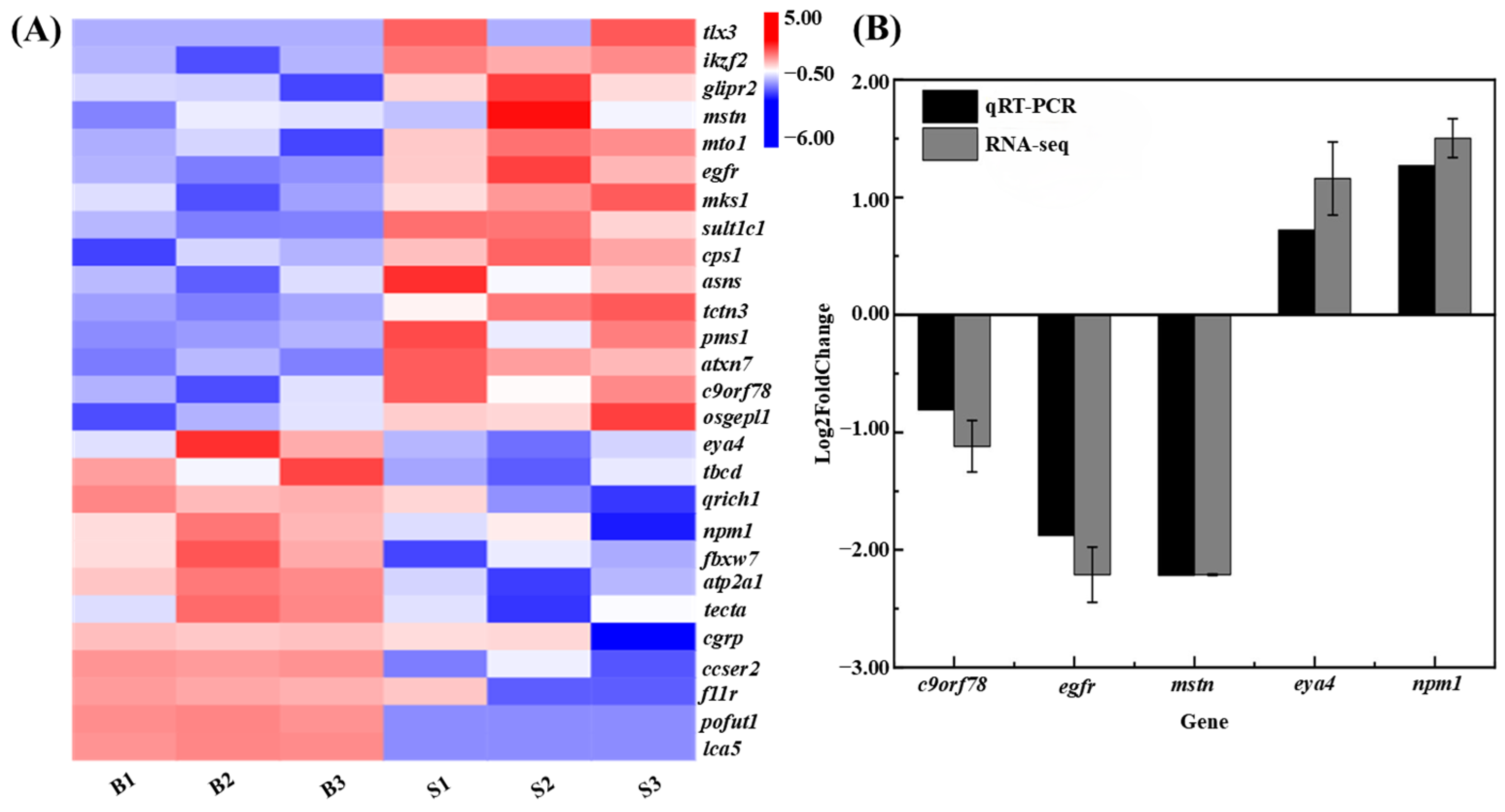
3.5. Differential Gene Expression Analysis Related to Body Size
3.6. Functional Classification of DEGs
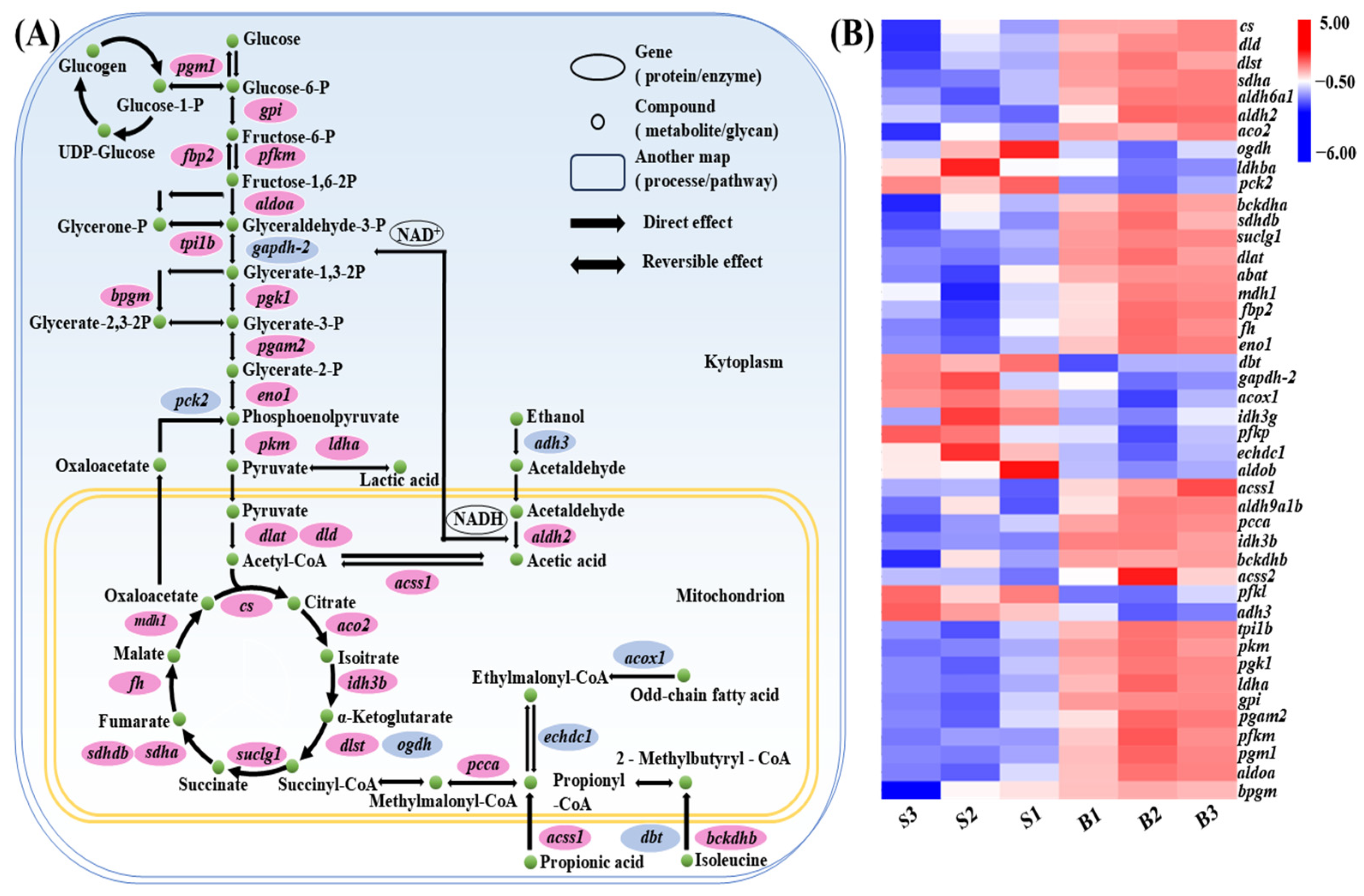
3.7. Carbohydrate Metabolism Pathway Analysis
3.8. Integration of QTL Mapping and Transcriptome Data
4. Discussion
4.1. QTL Mapping of Growth Traits in C. fuscus
4.2. Transcriptome Enrichment Pathways Associated with Body Size in C. fuscus
4.3. Identification and Characterization of Growth-Associated Genes in C. fuscus
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Wang, A.; Mao, S.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Shen, Y. Construction of High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Mapping for Growth Performance in Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus). Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, D.T.; Ritchie, P.A.; Wellenreuther, M. Fifteen Years of Quantitative Trait Loci Studies in Fish: Challenges and Future Directions. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndandala, C.B.; Dai, M.; Mustapha, U.F.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Current Research and Future Perspectives of GH and IGFs Family Genes in Somatic Growth and Reproduction of Teleost Fish. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 26, 101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, J.M.; García-González, E.G.; Brun, C.E.; Rudnicki, M.A. The Myogenic Regulatory Factors, Determinants of Muscle Development, Cell Identity and Regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, B.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Melanocortin Receptor 4 (MC4R) Signaling System in Nile Tilapia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.M.; Bertucci, J.I.; Sánchez-Bretaño, A.; Delgado, M.J.; Valenciano, A.I.; Unniappan, S. Ghrelin Modulates Gene and Protein Expression of Digestive Enzymes in the Intestine and Hepatopancreas of Goldfish (Carassius auratus) via the GHS-R1a: Possible Roles of PLC/PKC and AC/PKA Intracellular Signaling Pathways. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 442, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Sun, X. Genetic and Genomic Analyses for Economically Important Traits and Their Applications in Molecular Breeding of Cultured Fish. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhode, C.; Jackson, T.K.; Le Cordeur, N.S.; Jenkins, S.F.; Sampson, J.E.; Vervalle, J. Performance, Heritability, and Candidate Genes for Growth in Dusky Kob (Argyrosomus japonicus): Implications for Genetic Improvement during Early Phase Domestication. Aquaculture 2023, 577, 739971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W. A High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Mapping for Sex and Growth-Related Traits of Large-Scale Loach (Paramisgurnus dabryanus). Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiokostas, C.; Bekaert, M.; Khan, M.G.; Taggart, J.B.; Gharbi, K.; McAndrew, B.J.; Penman, D.J. A Novel Sex-Determining QTL in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Gu, X.H.; Li, B.J.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, H.R.; Xia, J.H. Genome-Wide QTL Analysis Identified Significant Associations Between Hypoxia Tolerance and Mutations in the GPR132 and ABCG4 Genes in Nile Tilapia. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, C.; Geng, X.; Zhou, T.; Li, N.; Bao, L.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Multiple Across-Strain and within-Strain QTLs Suggest Highly Complex Genetic Architecture for Hypoxia Tolerance in Channel Catfish. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 292, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.J.; Zhu, Z.X.; Gu, X.H.; Lin, H.R.; Xia, J.H. QTL Mapping for Red Blotches in Malaysia Red Tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Quin, C.T.; Drilea, A.C.; Conte, M.A.; Kocher, T.D. Mapping of Pigmentation QTL on an Anchored Genome Assembly of the Cichlid Fish, Metriaclima zebra. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Zheng, X.; Kuang, Y.; Cao, D.; Yan, Y.; Sun, X. QTL Variations for Growth-Related Traits in Eight Distinct Families of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Hu, G.; Li, C.; Lu, C.; Chao, D. QTL Analysis of Body Weight, Body Length, Body Depth and Body Thickness in Mirror Carp Cyprinus Carpio. Chin. J. Fish. 2023, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockman, M.V. The Qtn Program and the Alleles that Matter for Evolution: All That’s Gold Does not Glitter. Evolution 2012, 66, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Yang, P.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, G.; Kong, W.; Xu, Z. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Potential Mechanisms of Growth and Disease Resistance Dimorphism in Male and Female Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 158, 110150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ouyang, X.; Liao, Z.; Huang, T.; Tong, G.; Tan, H.; Zhou, M.; Lu, X.; Wei, X.; Yang, X.; et al. Comprehensive Transcriptomic, Proteomic, and Intestinal Microbiota Analyses of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Intestines Reveal New Insights into Immune Responses to Aeromonas Hydrophila Infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 156, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Vallejo, R.L.; Leeds, T.D.; Palti, Y.; Liu, S.; Sabbagh, A.; Rexroad, C.E.; Yao, J. RNA-Seq Identifies SNP Markers for Growth Traits in Rainbow Trout. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Cao, L.; Cao, Z.; Bing, X. Characterization of the Growth-Related Transcriptome in the Liver and Brain of Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi) through RNA-Seq Analysis. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2024, 52, 2440045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, K.N.; Zuloaga, R.; Valenzuela, C.A.; Bastias-Molina, M.; Meneses, C.; Vizoso, P.; Valdés, J.A.; Molina, A. RNA-Seq Analysis of Compensatory Growth in the Skeletal Muscle of Fine Flounder (Paralichthys adspersus). Aquaculture 2018, 490, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Weng, Z.; Hua, S.; Li, D.; Xia, J.; Liu, X.; Meng, Z. Genome-Wide QTL Mapping and RNA-Seq Reveal the Genetic Variation Influencing Growth Traits in Giant Grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Yu, S.; Chen, G.; Liu, L.; Zhu, J.; et al. Genome-Wide QTL Mapping and RNA-Seq Reveal Genetic Mechanisms behind Discrepant Growth Traits in Pacific Whiteleg Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2025, 599, 742084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Lin, X.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Ye, M.; Duan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Deng, S.; et al. A Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of Hong Kong Catfish (Clarias fuscus) Uncovers a Sex-Determining Region. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Tian, C. A Time-Course Transcriptome Analysis of Gonads from HongKong Catfish (Clarias fuscus) Reveals Genes and Pathways Associated with Gonadal Development. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 37, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Fast, A.W. Temperature and Feed Rate Effects on Chinese Catfish, Clarias Fuscus (Lacepède), Growth. Aquac. Res. 1991, 22, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Tan, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, D.; Li, G.; Tian, C. A High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Mapping for Sex in Clarias Fuscus. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, O. MapQTL6, Software for the Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci in Experimental Population of Diploid Species; Kyazma B.V.: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhomchuk, D.; Borodina, T.; Amstislavskiy, V.; Banaru, M.; Hallen, L.; Krobitsch, S.; Lehrach, H.; Soldatov, A. Transcriptome Analysis by Strand-Specific Sequencing of Complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, M.; Guo, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Liu, P.; Lian, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yan, J.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Profiling of Human Preimplantation Embryos and Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and Quantifying Mammalian Transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie Enables Improved Reconstruction of a Transcriptome from RNA-Seq Reads. Nat. Biotechnol 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, L.M.P.; Moutou, K.A.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Engrola, S.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Johnston, I.A. What Determines Growth Potential and Juvenile Quality of Farmed Fish Species? Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, S168–S193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Meng, Q.; Chen, S.; Sun, R.; Xu, D.; Zhu, F.; Gao, B.; Zhao, J.; Shen, H. Construction of the First High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Mapping for Growth Traits in Black Seabream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii). Aquaculture 2025, 595, 741588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, D.; Fernández, C.; Hermida, M.; Sciara, A.; Álvarez-Dios, J.; Cabaleiro, S.; Caamaño, R.; Martínez, P.; Bouza, C. Integrative Transcriptome, Genome and Quantitative Trait Loci Resources Identify Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Candidate Genes for Growth Traits in Turbot. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, M.Y.; Lashari, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Identification of Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) in Aquaculture Species. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2014, 22, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, T.F.C. The Genetic Architecture of Quantitative Traits. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2001, 35, 303–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, B.; Pang, M.; Feng, X.; Yu, X.; Tong, J. A High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Fine Mapping for Body Weight in Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus) Using 2b-RAD Sequencing. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2017, 7, 2473–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, H.; Pan, Z.; Chang, G.; Wang, H.; Wu, N.; Ding, H.; Yu, X. Construction of a High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Mapping for Growth Traits in Pseudobagrus ussuriensis. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.K.; Rhode, C. A High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Identification for Growth Traits in Dusky Kob (Argyrosomus japonicus). Aquaculture 2024, 586, 740786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-L.; Wang, Z.-W.; Guo, X.-F.; Wu, J.-J.; Lu, W.-J.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.-F. Construction of a High-Density Genetic Linkage Map and Fine Mapping of QTLs for Growth and Sex-Related Traits in Red-Tail Catfish (Hemibagrus wyckioides). Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N.H.; Keightley, P.D. Understanding Quantitative Genetic Variation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnier, F.; Solberg, M.F.; Harvey, A.C.; Carvalho, G.R.; Bekkevold, D.; Taylor, M.I.; Creer, S.; Nielsen, E.E.; Skaala, Ø.; Ayllon, F.; et al. Epistatic Regulation of Growth in Atlantic Salmon Revealed: A QTL Study Performed on the Domesticated-Wild Interface. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadmor-Levi, R.; Hulata, G.; David, L. Multiple Interacting QTLs Affect Disease Challenge Survival in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Heredity 2019, 123, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, C.; Teng, T.; Shen, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Ling, Q. Construction of the First High-Density Genetic Linkage Map of Pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) Using Specific Length Amplified Fragment (SLAF) Sequencing and QTL Analysis of Growth-Related Traits. Aquaculture 2018, 497, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Qian, X.; Gui, J. Transcriptome Analysis of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) between Fast- and Slow-Growing Fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 35, 100688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Solberg, M.F.; Chen, Z.; Wei, M.; Zhu, F.; Jia, C.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Mixed Tissues of Black Porgy (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) with Differing Growth Rates. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 5800–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Han, C.; Shu, H. Multiple Tissues Transcriptome of Zig-Zag Eel (Mastacembelus armatus) with Different Growth Rates. Animals 2024, 14, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Sachdeva, U.M.; Bui, T.V.; Cross, J.R.; Thompson, C.B. ATP-Citrate Lyase Links Cellular Metabolism to Histone Acetylation. Science 2009, 324, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiber, M. Body Size and Metabolic Rate. Physiol. Rev. 1947, 27, 511–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocher, D.R. Metabolism and Functions of Lipids and Fatty Acids in Teleost Fish. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2003, 11, 107–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, U.; Chu, R.; Chu, S.; Espinosa, R.; LeBeau, M.M.; Reddy, J.K. Isolation of the Human Peroxisomal Acyl-CoA Oxidase Gene: Organization, Promoter Analysis, and Chromosomal Localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3107–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.S.; Roche, T.E. Molecular Biology and Biochemistry of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complexes. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 3224–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linster, C.L.; Noël, G.; Stroobant, V.; Vertommen, D.; Vincent, M.-F.; Bommer, G.T.; Veiga-da-Cunha, M.; Van Schaftingen, E. Ethylmalonyl-CoA Decarboxylase, a New Enzyme Involved in Metabolite Proofreading. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42992–43003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panov, A.V.; Mayorov, V.I.; Dikalov, S.I. Role of Fatty Acids β-Oxidation in the Metabolic Interactions Between Organs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trefely, S.; Lovell, C.D.; Snyder, N.W.; Wellen, K.E. Compartmentalised Acyl-CoA Metabolism and Roles in Chromatin Regulation. Mol. Metab. 2020, 38, 100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrell, M.S.; Baker, C.V.H. Evolution of Electrosensory Ampullary Organs: Conservation of Eya4 Expression during Lateral Line Development in Jawed Vertebrates. Evol. Dev. 2012, 14, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sewell, W.F.; Kim, S.D.; Shin, J.T.; MacRae, C.A.; Zon, L.I.; Seidman, J.G.; Seidman, C.E. Eya4 Regulation of Na+/K+-ATPase Is Required for Sensory System Development in Zebrafish. Development 2008, 135, 3425–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.B.; Rogers, S.; Roychoudhury, K.; Tan, Y.S.; Atkinson, C.J.; Sobinoff, A.P.; Tomlinson, C.G.; Hsu, A.; Lu, R.; Dray, E.; et al. The Eyes Absent Family Members EYA4 and EYA1 Promote PLK1 Activation and Successful Mitosis through Tyrosine Dephosphorylation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammers, A.N.; Susser, S.E.; Hamm, N.C.; Hlynsky, M.W.; Kimber, D.E.; Kehler, D.S.; Duhamel, T.A. The Regulation of Sarco (Endo)Plasmic Reticulum Calcium-ATPases (SERCA). Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Razek, O.; Marzouk, A.; MacKinnon, M.; Guy, E.T.; Pohar, S.A.; Zhushma, E.; Liu, J.; Sia, I.; Gokey, J.J.; Tay, H.G.; et al. Calcium Signaling Mediates Proliferation of the Precursor Cells That Give Rise to the Ciliated Left-Right Organizer in the Zebrafish Embryo. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1292076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Hamada, H. Left-Right Patterning: Conserved and Divergent Mechanisms. Development 2012, 139, 3257–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebnet, K. Junctional Adhesion Molecules (JAMs): Cell Adhesion Receptors with Pleiotropic Functions in Cell Physiology and Development. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1529–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Li, C.; Gui, J. Molecular Characterization and Functional Commonality of Nucleophosmin/Nucleoplasmin in Two Cyprinid Fish. Biochem. Genet. 2009, 47, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stooke-Vaughan, G.A.; Obholzer, N.D.; Baxendale, S.; Megason, S.G.; Whitfield, T.T. Otolith Tethering in the Zebrafish Otic Vesicle Requires Otogelin and α-Tectorin. Development 2015, 142, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.N.; Valdés, J.A.; Molina, A.; Björnsson, B.T. Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Growth in Fish by the Growth Hormone—Insulin-like Growth Factor System. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joulia, D.; Bernardi, H.; Garandel, V.; Rabenoelina, F.; Vernus, B.; Cabello, G. Mechanisms Involved in the Inhibition of Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation by Myostatin. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 286, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Langley, B.; Berry, C.; Sharma, M.; Kirk, S.; Bass, J.; Kambadur, R. Myostatin, a Negative Regulator of Muscle Growth, Functions by Inhibiting Myoblast Proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40235–40243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coogan, M.; Alston, V.; Su, B.; Khalil, K.; Elaswad, A.; Khan, M.; Simora, R.M.C.; Johnson, A.; Xing, D.; Li, S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas-9 Induced Knockout of Myostatin Gene Improves Growth and Disease Resistance in Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2022, 557, 738290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Niu, P.; Wang, M.; Huang, G.; Xu, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Hou, Y.; Sun, X.; Yan, Y.; et al. Targeted Disruption of Sp7 and Myostatin with CRISPR-Cas9 Results in Severe Bone Defects and More Muscular Cells in Common Carp. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomsma, R.A.; Scott, H.; Walters, K. Immunocytochemical Localization of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Early Embryos of the Japanese Medaka Fish (Oryzias latipes). Histochem. J. 2001, 33, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Tang, Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, L. Insulin-like Growth Factor I Promotes Oocyte Maturation through Increasing the Expression and Phosphorylation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in the Zebrafish Ovary. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 419, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; He, X.; Yao, S.; Lin, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Chen, C.; Yang, Q.; Li, F.; Zhu, Y.-M.; et al. Ablation of Mto1 in Zebrafish Exhibited Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Manifested by Mitochondrion RNA Maturation Deficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 4689–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Lu, D. The Ikaros Family of Zinc-Finger Proteins. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherbee, S.D.; Niswander, L.A.; Anderson, K.V. A Mouse Model for Meckel Syndrome Reveals Mks1 Is Required for Ciliogenesis and Hedgehog Signaling. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4565–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, J.; Konarzewski, M.; Czarnoleski, M. Coevolution of Body Size and Metabolic Rate in Vertebrates: A Life-history Perspective. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1393–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, F. Marker-Assisted Selection in Fish: A Review. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2019, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
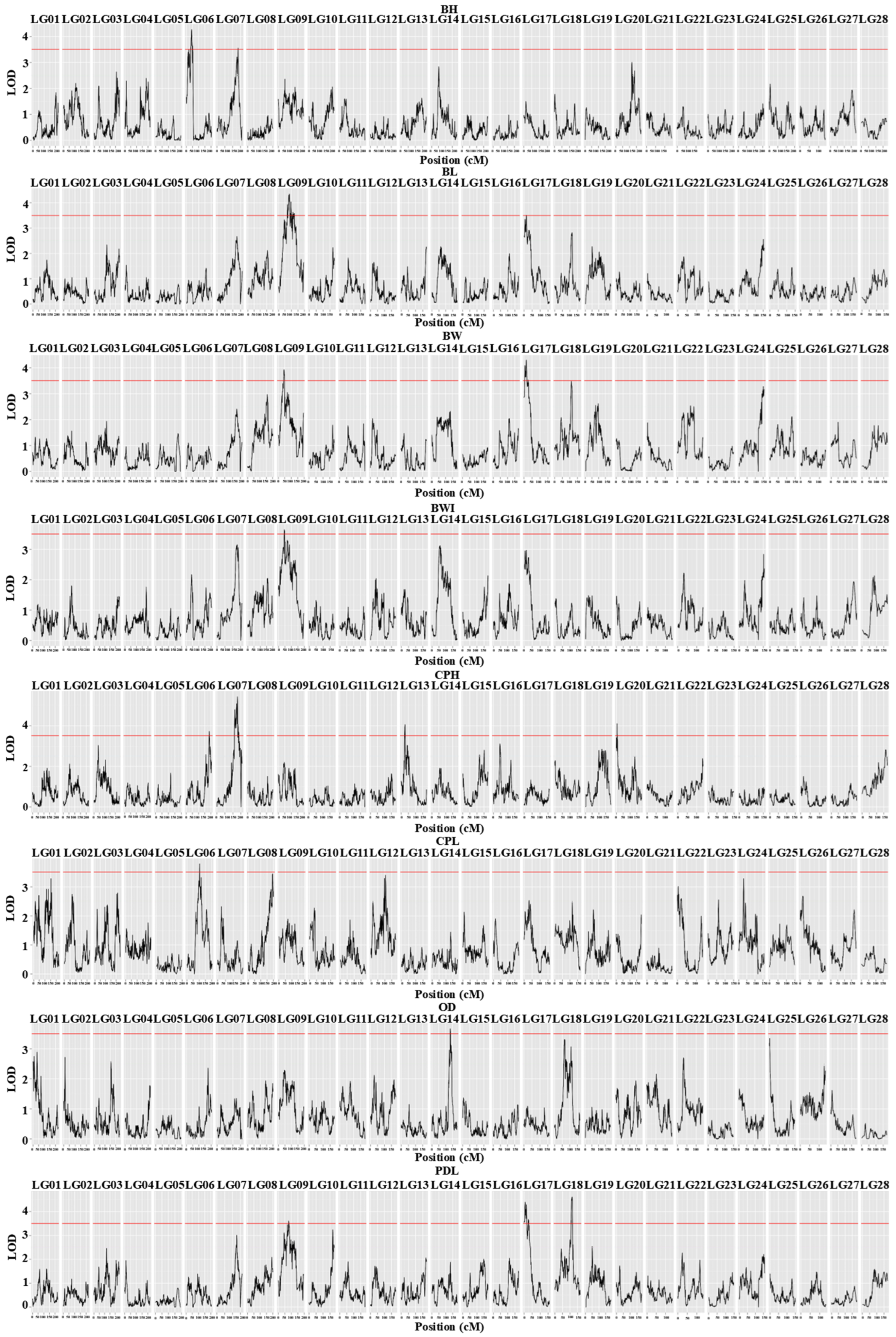

| Trait | QTL | Linkage Group | Marking Interval (cM) | Peak Marker (cM) | LOD | PVE (%) | LOD Peak (cM) | Corresponding Markers for LOD Peaks | Candidate Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW | qBW-1 | LG09 | 41.931–45.835 | np27 | 3.910 | 8.70 | 44.543 | LG9 6545823 | |
| qBW-2 | LG17 | 13.52–17.098 | np1240 | 4.280 | 9.50 | 14.832 | LG17 28458728 | slc4a1 | |
| BL | qBL-3 | LG09 | 82.998–85.093 | lm55 | 4.350 | 9.80 | 83.615 | LG9 13097329 | |
| qBL-4 | LG17 | 11.779–14.832 | lm1144 | 3.510 | 8.00 | 13.520 | LG17 28458720 | slc4a1 | |
| CPH | qCPH-5 | LG06 | 184.207–186.967 | lm3244 | 3.730 | 8.30 | 186.516 | LG6 4577776 | pgap1 |
| qCPH-6 | LG07 | 128.571–129.622 | lm3434 | 5.440 | 11.90 | 128.590 | LG7 8175232 | ||
| qCPH-7 | LG13 | 24.138–31.262 | np671 | 4.060 | 9.00 | 26.118 | LG13 30699773 | ltk | |
| qCPH-8 | LG20 | 5.037–6.976 | lm1639 | 4.110 | 9.10 | 5.619 | LG20 1586316 | ||
| CPL | qCPL-9 | LG06 | 102.507–103.569 | np3359 | 3.790 | 9.50 | 102.644 | LG6 22085749 | pdk1 |
| OD | qOD-10 | LG14 | 132.742–134.846 | hk257 | 3.580 | 8.00 | 134.365 | LG14 25875874 | qrich1 |
| PDL | qPDL-11 | LG09 | 77.872–80.447 | lm52 | 3.610 | 8.10 | 79.160 | LG9 12492904 | pp2a |
| qPDL-12 | LG17 | 2.533–6.695 | np1243 | 4.400 | 9.80 | 5.627 | LG17 29429338 | mto1 | |
| qPDL-13 | LG18 | 112.055–115.500 | lm1230 | 4.580 | 10.20 | 112.554 | LG18 25096181 | ||
| BWI | qBWI-14 | LG09 | 44.543–46.478 | np28 | 3.630 | 8.10 | 45.835 | LG9 6720412 | |
| BH | qBH-15 | LG06 | 21.046–22.095 | np3410 | 3.500 | 8.00 | 21.431 | LG6 36044360 | cps |
| qBH-16 | LG06 | 41.649–44.768 | np3396 | 4.220 | 9.60 | 41.702 | LG6 34731920 | ||
| qBH-17 | LG07 | 134.41–134.773 | lm3428 | 3.550 | 8.10 | 134.410 | LG7 7360877 |
| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Read Rate (%) | Total Map | Total Map Rate (%) | Q20 | Q30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 49,640,720 | 47,460,188 | 95.61 | 41,564,096 | 87.58 | 98.16 | 95.10 |
| S2 | 46,547,234 | 44,737,262 | 96.11 | 35,866,634 | 80.17 | 98.12 | 95.23 |
| S3 | 42,787,644 | 40,724,206 | 95.18 | 33,787,631 | 82.97 | 98.01 | 94.76 |
| B1 | 51,865,132 | 50,973,770 | 98.38 | 46,109,511 | 90.46 | 98.61 | 95.99 |
| B2 | 50,052,990 | 49,099,298 | 98.09 | 43,891,232 | 89.39 | 98.76 | 96.40 |
| B3 | 52,370,048 | 51,467,180 | 98.28 | 47,125,928 | 91.57 | 98.71 | 96.22 |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Gene Annotation | log2 (FC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| cfu_9G0006470 | trim32 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM32 | 9.534 |
| cfu_15G0008560 | bloc-1 | Biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1 | 9.487 |
| cfu_16G0005300 | wwtr1 | WW domain-containing transcription regulator protein 1 | 8.941 |
| cfu_26G0005640 | scfd2 | Sec1 family domain-containing protein 2 | 8.833 |
| cfu_1G0009900 | nipsnap3a | Protein NipSnap homolog 3A | 8.720 |
| cfu_27G0004410 | camlg | Guided entry of tail-anchored protein factor | 8.636 |
| cfu_10G0006000 | slc16a4 | Monocarboxylate transporter 5 | 8.621 |
| cfu_26G0004610 | atraid | All-trans retinoic acid-induced differentiation factor | 8.559 |
| cfu_27G0003260 | efemp2 | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 2 | 8.472 |
| cfu_5G0009050 | aadac | Arylacetamide deacetylase | 8.306 |
| cfu_3G0006820 | rims4 | Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis protein 4 | −6.820 |
| cfu_9G0008290 | shc3 | SHC-transforming protein 3 | −6.933 |
| cfu_6G0004030 | lpa1 | High-affinity lysophosphatidic acid receptor | −6.988 |
| cfu_15G0007480 | nos2 | Nitric oxide synthase | −7.002 |
| cfu_3G0009150 | tcf23 | Transcription factor 23 | −7.015 |
| cfu_14G0005780 | hrh1 | Histamine H1 receptor | −7.032 |
| cfu_4G0003010 | apoc-1 | Apolipoprotein C-I | −7.104 |
| cfu_14G0006580 | chia | Acidic mammalian chitinase | −7.329 |
| cfu_11G0001850 | fgfbp2 | Fibroblast growth factor-binding protein 2 | −7.474 |
| cfu_22G0000210 | itln | Intelectin | −7.841 |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Gene Annotation | log2 (FC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| cfu_6G0008310 | calcrla | calcitonin gene-related peptide type 1 receptor isoform X1 | 2.397 |
| cfu_6G0008340 | wdr75 | WD repeat-containing protein 75 | 1.554 |
| cfu_6G0008350 | asnsd1 | asparagine synthetase domain-containing protein 1 | −1.380 |
| cfu_6G0008380 | osgepl1 | probable tRNA N6-adenosine threonylcarbamoyltransferase | −1.102 |
| cfu_6G0008410 | pms1 | PMS1 protein homolog 1 | −1.197 |
| cfu_6G0008420 | mstnb | myostatin | −2.353 |
| cfu_6G0008440 | pofut2 | GDP-fucose protein O-fucosyltransferase 2 | 6.582 |
| cfu_6G0008510 | ikzf2 | IKAROS Family Zinc Finger 2 | −2.744 |
| cfu_6G0008520 | egfr | epidermal growth factor receptor | −2.210 |
| cfu_6G0008530 | cps1 | carbamoyl-phosphate synthase | −1.581 |
| cfu_9G0003920 | c9orf78 | telomere length and silencing protein 1 homolog | −1.118 |
| cfu_9G0003990 | tecta | alpha-tectorin | 2.098 |
| cfu_9G0004000 | tbcel | tubulin-specific chaperone cofactor E-like protein | 1.174 |
| cfu_9G0004050 | f11r | junctional adhesion molecule A | 4.879 |
| cfu_9G0003810 | glipr2 | Golgi-associated plant pathogenesis-related protein 1 | −2.428 |
| cfu_9G0002330 | mks1 | Meckel syndrome type 1 protein | −1.804 |
| cfu_14G0007230 | qrich1 | glutamine-rich protein 1 | 1.404 |
| cfu_17G0007930 | atxn7l3 | ataxin-7protein 3 | −1.171 |
| cfu_17G0008220 | mto1 | protein MTO1 homolog | −2.294 |
| cfu_17G0008240 | tctn3 | tectonic-3 | −1.298 |
| cfu_17G0008260 | sult1c1 | sulfotransferase family cytosolic 1B member 1 | −1.707 |
| cfu_17G0008270 | atp2a1 | sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 1 | 1.895 |
| cfu_17G0008530 | ccser2 | serine-rich coiled-coil domain-containing protein 2 | 2.420 |
| cfu_18G0007570 | lca5 | lebercilin | 7.172 |
| cfu_18G0007610 | eya4 | eyes absent homolog 4 isoform X2 | 1.161 |
| cfu_20G0000670 | tlx3 | T-cell leukemia homeobox protein 3 | −6.172 |
| cfu_20G0000680 | npm1 | nucleophosmin | 1.503 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Shen, Y.; Pan, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, G.; Chen, H.; Tian, C. Integrative QTL Mapping and Transcriptomic Profiling to Identify Growth-Associated QTL and Candidate Genes in Hong Kong Catfish (Clarias fuscus). Animals 2025, 15, 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121707
Zhu Y, Zhou D, Shen Y, Pan C, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Yang B, Li G, Chen H, Tian C. Integrative QTL Mapping and Transcriptomic Profiling to Identify Growth-Associated QTL and Candidate Genes in Hong Kong Catfish (Clarias fuscus). Animals. 2025; 15(12):1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121707
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yian, Dayan Zhou, Yijun Shen, Chuanhao Pan, Yu Chen, Yulei Zhang, Binlan Yang, Guangli Li, Huapu Chen, and Changxu Tian. 2025. "Integrative QTL Mapping and Transcriptomic Profiling to Identify Growth-Associated QTL and Candidate Genes in Hong Kong Catfish (Clarias fuscus)" Animals 15, no. 12: 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121707
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhou, D., Shen, Y., Pan, C., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, B., Li, G., Chen, H., & Tian, C. (2025). Integrative QTL Mapping and Transcriptomic Profiling to Identify Growth-Associated QTL and Candidate Genes in Hong Kong Catfish (Clarias fuscus). Animals, 15(12), 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121707








