Simple Summary
The aim of this research was to characterize the structure, expression and function of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m, which was generated by alternative splicing of the Nr5a2 gene. The expression profile suggested that Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m had different expression profiles in the gonads of females and males. Nr5a2f expressed significantly high in the ovary, while Nr5a2f in the testis. Furthermore, when Nr5a2f expression was inhibited, we observed that female-based gene expression was decreased, while male-based gene expression was increased.
Abstract
Nr5a2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group a, member 2) is involved in gonad development and sex hormone synthesis. In this study, the full length of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m were obtained by Nr5a2 variable splicing from Andrias davidianus, and the tissue distribution was detected. We identified Nr5a2f of 2455 bp and Nr5a2m of 2150 bp length, encoding 479 and 325 amino, respectively. We first characterized Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m gene expression in developing gonads. Results showed that Nr5a2f had significantly high expression in the ovary and little expression in other tissues, during the sex differentiation and sex reversal, Nr5a2f expression was gradually decreased in the ovary and the expression in the testis was significantly lower than in the ovary from 1 year to 6 year old. Significantly high expression was observed in the ovary and reversal ovary, while low expression was in the testis and reversal testis. While Nr5a2m expression exhibited the opposite profile, high expression was observed in the brain and testis. During sex differentiation and sex reversal, high expression was shown in the testis and low expression in the ovary from one year to six years old and significantly higher expression emerged in testis and reversal testis than in ovary and reversal ovary. In situ hybridization, results showed that Nr5a2f began to express in female undifferentiated gonads and the expression level increased from 48 dpf to 91, while Nr5a2m was expressed in male undifferentiated gonads. Three RNA interference sites were designed and we detected that site 293 exhibited a significant inhibitory effect in ovary cells. After Nr5a2f expression was inhibited by site 293, we observed that female-based gene Nr5a2f, foxl2 and cyp19 expression were decreased, while the male-based gene dmrt1 and cyp17 expression was increased. These results suggested that Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m exhibited different expression patterns in the process of sex differentiation, which provided a foundation for further functional characterizations.
1. Introduction
Nr5a2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group a, member 2, known as LRH-1 as fetoprotein transcription factor (FTF), which belongs to the NR5A subfamily of nuclear receptors, is an orphan nuclear receptor and a transcriptional factor requires ligand activation. Nr5a2 plays an important role in regulating the development, maturation and ovulation of mammals, and is a key regulator of female fertility [1,2,3]. Nr5a2 is related to somatic cell reprogramming, embryonic development, steroid hormone production and some cancers [4]. The Nr5a2 gene was originally identified in fruit flies. The Fushi Tarazu fragment in fruit fly was a founding member of NR5A [5]. Subsequently, the homologous gene has been found in mice, chickens, horses, humans and zebra fish [6]. Nr5a2 is essential in early embryonic development, especially in maintaining the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells and endoderm formation [7]. In eutherian mammals, Nr5a2 is mainly expressed in endoderm tissues, likely expressed in the liver, intestine and ovary [8], and high expression in the ovary [9,10]. In addition, studies found that the Nr5a2 gene is expressed at higher levels in the ovary than in the liver or other tissues, the expression of Nr5a2 is limited to granulosa cells and luteal cells [11]. Later studies found that Nr5a2−/− mouse embryos died and the fertility of Nr5a2+/− female mice decreased, which identified that Nr5a2 plays an important regulatory role in female reproductive ability [12]. In addition, further studies have shown that Nr5a2 up-regulates the expression of STAR, Cyp11 and Cyp19a1 genes, which promote E2 synthesis and secretion [13,14].
The Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianua is the largest-tailed amphibian in the world and one of the animal resources in China [15]. However, due to its habitat destruction, overfishing and climate change, the wild resource of the giant salamander has declined dramatically and it was classified as an endangered species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Nature Resources in 1988 [16]. The Chinese giant salamander is believed to be a living fossil that existed before the Middle Jurassic [17]. Because the sex chromosomes of most amphibians are difficult to identify, the genes involved in the sex determination of amphibians are largely unknown. On the one hand, this is because there are multiple sex-matching types in amphibians; on the other hand, it is because the sex genes of homologous chromosomes are more likely to be converted compared to heterologous chromosomes. Amphibians have various types of genetic sex determination systems. Female (ZW) heterozygous in birds and male (XY) heterozygous in mammals can both be found in amphibians [18]. Even systems with multiple chromosomes or female OO/WO heterozygous have been reported in amphibians [19]. It can link aquatic and terrestrial organisms together and has a complex sex determination and differentiation mechanism. Therefore, it is considered to be a valuable species for studying.
Previous studies of A. davidianus mostly focused on the immune system [20,21,22], with little research on sex determination and sex differentiation [23,24,25]. Therefore, to study the mechanism of sex differentiation in A. davidianus, it is of great importance to enrich the mechanism of sex differentiation of amphibians. In this study, Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m were produced by Nr5a2 variable splicing, which was used to produce two spliceosomes with differential expression in the gonads of males and females. This study obtained the full-length sequence of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m from A. davidianus. We characterized Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m expression in different tissues, different developmental gonads and gonads from normal and sex-reversal giant salamanders by using qRT-PCR. Then, we determined their expression in undifferentiated and differentiated gonads by in situ hybridization. Furthermore, RNA interference technology was used to study the function of Nr5a2f. This work provides the basis for understanding the molecular mechanism of gonadal differentiation of A. davidianus and enriches the biological information of the Nr5a2 gene in amphibians to further understand the mechanism of sex differentiation in amphibians.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
The A. davidianus were collected from Zhangjiajie Giant Salamander Breeding Base (Zhangjiajie, Hunan Province, China). This experiment followed the guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (YSFRI-2025017). The salamanders were killed after anesthesia by MS222, samples of heart, liver, spleen, kidney, stomach, intestine, skin, muscle, lung, brain, ovary and testis tissues were collected from three species of salamanders. Gonads from male and female salamanders at the ages of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 years old (6 years old) were collected from three individuals in each group, frozen in liquid nitrogen and then transferred to a refrigerator at −80 °C for storage until RNA extraction. The sex-reversal salamanders were prepared according to the previous reports [26]. At least three ovaries and testes from the salamander and sex-reversal salamander were collected and stored at -80 °C for RNA extraction. The developing stage gonads of 48 dpf (days post fertilization) and 98 dpf giant salamanders in the normal group were collected and then preserved in 4% paraformaldehyde (pH 7.5) to prepare tissue sections.
2.2. Sequence Analysis
According to the giant salamander transcriptome database from our laboratory, the sequences of the Nr5a2 gene were obtained. By utilizing alternative promoter splicing, the giant salamander Nr5a2 generates two splice variants, Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m. The sequence was searched in the GeneBank database using BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 20 April 2025). The amino acid sequence was predicted by the software DNAman 9.0. The tertiary structure of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m was predicted using the software SWISS-MODEL [27].
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
The expression of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m genes in various tissues and developing gonads in A. davidianus were detected and analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Following the manufacturer’s instructions, total RNA was extracted from the tissue samples using TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA, 15596018). EF-1α was selected as the internal reference gene [28], and cDNA was used as a template. The primers were designed according to the gene sequences (Table 1). qRT-PCR samples from three individual tissues were used for three replicates. qRT-PCR was performed on a QuantStudio 5 real-time PCR system (APPLIED Biosystems, Foxboro, MA, USA). qRT-PCR was performed as follows: 30 s at 95 °C; forty cycles of 95 °C for 5 s, 60 °C for 30 s and 72 °C for 30 s; and then 72 °C for 5 min. Relative expression was calculated by the selected 2−∆∆CT method [29]. Differences in expression were evaluated using SPSS 22.0 (IBM, New York, NY, USA). One-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple comparison tests was performed to analyze differences in Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m, and values of p < 0.05 were considered significant.

Table 1.
Sequence of the primers used in this study.
2.4. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
To detect whether Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m expression before gonadal differentiation, a fluorescence in situ hybridization probe was synthesized in the region of difference between the two spliceosome cDNA sequences of Nr5a2. The probe of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m were modified with FITC and Cy3 on oligo-RNA at the 5′ end, respectively. Gonad tissues at 48 dpf and 91 dpf were collected and embedded by paraffin. The tissue paraffin blocks were treated as follows: tissue paraffin blocks were sliced by a slicer with a thickness of 4 μm, fished by a spreading machine and baked at 62 °C for 2 h. We sequentially put the slices into 2 changes of BioDewax and Clear solution, for 15 min each and then dehydrated them in 2 changes in pure ethanol for 5 min each, then put them into 85% alcohol and 75% alcohol for 5 min each and soaked them in DEPC water. Then, in situ hybridization was performed as follows: after natural cooling, the stroke circle was assembled. Protease K (20 μg/mL) was added dropwise for 40 °C digestion. The digestion time is 10 min. After washing with pure water, we performed PBS washes 3 times, for 5 min each time. We added a pre-hybridization solution and incubated it at 40 °C for 1 h. We poured out that pre-hybridization solution, added the hybridization solution containing probes and let it hybridize overnight in a constant temperature box. We washed off the hybridization solution as follows: 2 × SSC, washed at 40 °C for 10 min; 1 × SSC, washed at 40 °C for 2 × 5 min; and 0.5 × SSC was washed at room temperature for 10 min. If there are more nonspecific hybrids, formamide washing can be increased. We gently spin-dried the slice, dropped the preheated branch probe hybridization solution (60 μL) and horizontally put it in a wet box for hybridization at 40 °C for 45 min. In this process, 50 mL 2 × SSC was added to the bottom of the wet box to prevent drying. We poured off the hybridization solution and rinsed the slices with 2 × SSC, 1× SSC, 0.5× SSC and 0.1× SSC preheated at 40 °C in turn for 5 min. If there are many nonspecific hybrids, you can increase the washing time and times and adjust the concentration of formamide in the hybrid solution at this step. We added the hybridization solution containing the signal probe, and incubated it at 40 °C for 3 h at the dilution ratio of 1:400. After that, they were washed by the following SSC in turn: 2 × SSC at 40 °C for 10 min, 1 × SSC at 40 °C for 2 × 5 min and 0.5× SSC at 40 °C for 10 min. DAPI solution was dripped into the slice and incubated at room temperature for 8 min in the dark, then washed with running water and the coverslip with an anti-fade mounting medium. We used microscopy detection and collected images using Olympus-BX53 (Tokyo, Japan).
2.5. RNA Interference
According to the Nr5a2f sequence, three siRNA at different sites, nr5a2-1F-42, nr5a2-1F-139 and nr5a2-1F-293, were designed in the region of difference between Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m (Table 1). Three siRNA was modified with FAM.
According to the previous description [30], primordial ovary cells were prepared and the siRNA was transfected into the ovarian primary cell using Lipofectamine TM3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The cells were then incubated in opti-MEM medium (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 37 °C for 6 h, after which the opti-MEM medium was removed and 2 mL of DMEM including 10%PBS and P/S was added and incubated at 28 °C for 48 h. The signal of green fluorescence was detected by Olympus IX93. The RNA was extracted according to the TRIzol method for qRT-PCR to further examine sex-related gene expression.
2.6. Identification of Phenotypic Sex and Genetic Sex
In order to obtain the individuals with sex reversal in the previous study [26], the larvae at 55 dpf were treated with 17β-estradiol or exposed to temperatures of 28 °C until eight months after fertilization. The genetic sex of the giant salamander used was identified using the female-specific marker adf431 developed in our laboratory, and tissue sections and microscopes were used to identify the biological sex of the giant salamander samples. The reaction mixture consists of 100 ng genomic DNA, 12.5 μL 2× Master Mix (Tsingke, Nanjing, China), 0.5 μL of each primer (10 μm) and double-distilled water, with a final volume of 25 μL. The reaction conditions were 95 °C for 5 min, 33 cycles of 15 s at 94 °C, 15 s at 60 °C, 72 °C for 30 s and 5 min at 72 °C. If the phenotypic sex and genetic sex are consistent, there will be no sex reversal. If the phenotypic sex and genetic sex are different, the genetic sex is male and the phenotypic sex is female, then this individual is regarded as a sex-reversed male (RM) individual. If the sex is female and the genotype is male, then this individual is regarded as a sex-reversed female (RF) individual.
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m
By alternative splicing, the giant salamander Nr5a2 generates two splice variants, Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m. The full length of Nr5a2f was 2455 bp, and the full length of Nr5a2m was 2150 bp (Figure 1A). Nr5a2f encodes 479 amino acids, and Nr5a2m encodes 325 amino acids (Figure 1B). Nr5a2f encodes the full-length transcript, whereas Nr5a2m loses the first exon due to alternative promoter usage and initiates transcription at the first intron (Figure 1C). The online prediction software predicted the tertiary structure of proteins encoded by Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m, as shown in the figure (Figure 1D).
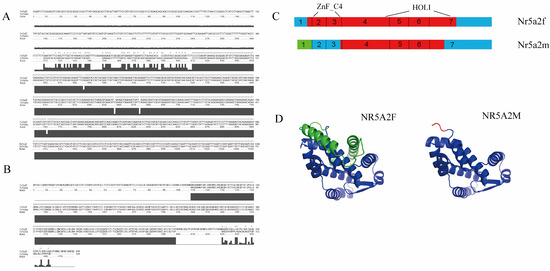
Figure 1.
Nr5a2 spliceosome sequence and structure model diagram. (A) Nucleotide sequence analysis; (B) amino sequence analysis of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m; (C) Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m structure. Blue color indicates untranslated region in cDNA. Red color indicates exon. Blue color indicates non-translated region. The green color indicates 5′ end untranslated region in Nr5a2m, which was different from Nr5a2f; (D) tertiary structure diagrams of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m proteins. * indicated same amino acid.
3.2. Expression of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m in Different Developing Gonads and Sex Reversal
Expression levels of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m in different tissues, developing gonads and sex-reversal gonads, were detected using qRT-PCR and RT-PCR. Results of qRT-PCR and RT-PCR have high consistency. Nr5a2f was expressed high in the ovary, low in the intestine, liver and kidney, and little expression in other tissues (Figure 2A). During gonadal development, Nr5a2f expression was significantly higher in the ovary than in the testis, with expression levels gradually decreasing from 1 to 6 years (Figure 2B). The expression level of Nr5a2f in the sex-reversal ovary is significantly higher than in the testis and similar to that in the normal ovary (p < 0.05; Figure 2C). Expression of Nr5a2m was observed in various tissues and significantly higher expression levels were detected in the testis than that in the ovary (p < 0.05; Figure 2D). Expression of Nr5a2m in the testis was significantly higher than in the ovary from one year to three years, while, from four years to six years, no significant difference was observed between the ovary and testis (Figure 2E). The expression of Nr5a2m in sex-reversal testis was significantly higher than that in normal testis and ovary (p < 0.05; Figure 2F).
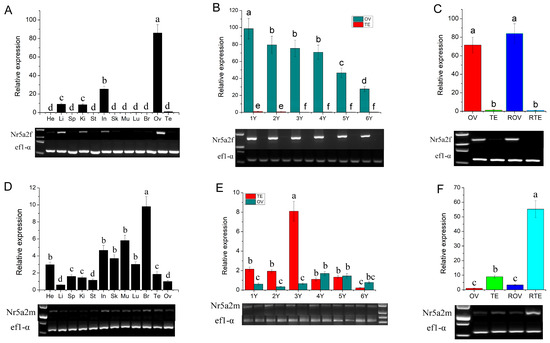
Figure 2.
Expression of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m in different stages of developmental and sex reversal gonads. (A) Expression analysis of Nr5a2f in various tissues; (B) expression analysis of Nr5a2f in developing gonads; (C) expression analysis of Nr5a2f in sex reversal gonads of A. davidianus; (D) expression analysis of Nr5a2m in various tissues; (E) expression analysis of Nr5a2m in developing gonads; (F) expression analysis of Nr5a2m in sex reversal gonads of A. davidianus. ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple comparison tests. Different letters differed with statistical significance (p < 0.05). He, heart; Li, liver; Sp, spleen; Ki, kidney; St, stomach; In, intestine; Sk, skin; Mu, muscle; Lu, lung; Br, brain; Ov, ovary; Te, testis; ROV, sex reversal ovary; RTE, ex reversal testis.
3.3. Expression of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m Identified by In Situ Hybridization
To detect whether Nr5a2f or Nr5a2m expressed before gonad differentiation, in situ hybridization was conducted to identify the expression of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m. In a previous study, we determined that the gonad of A. davidianus began to differentiate about 98 days post fertilization, and the female-specific marker was explored to determine the genetic sex of A. davidianus. In situ hybridization results showed that Nr5a2f began to express before gonadal differentiation in female A. davidianus, with its signal strength increased from 48 dpf to 91 dpf (Figure 3A). In contrast, Nr5a2m starts to express before gonadal differentiation in male A. davidianus (Figure 3B).
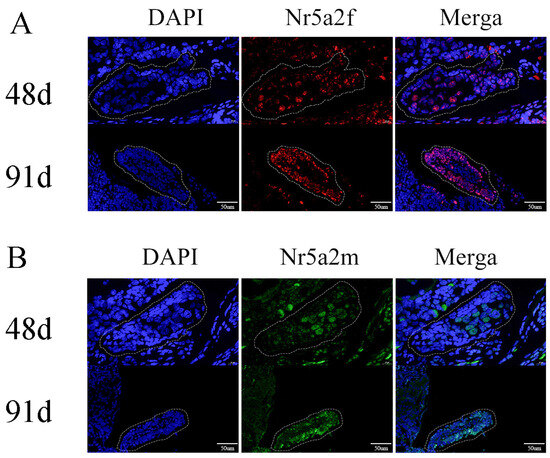
Figure 3.
Expression of Nr5a2 (A) and Nr5a2m (B) in gonads detected by in situ hybridization. (A) Expression of Nr5a2f in undifferentiated gonads on 48 d and 91 d; (B) expression of Nr5a2m in undifferentiated gonads on 48 d and 91 d. The dashed box shows the early gonads.
3.4. RNA Interference
To examine the function of the Nr5a2f gene in the gonad, three RNA interference (RNAi) sites were designed based on the differential regions of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m. Liposome 3000 was used to transfect RNAi to primary ovarian cells from one-year-old giant salamanders. The transfection efficiency was exhibited at 50% after 48 h (Figure 4A). The RNAi effects were evaluated using qPCR, which revealed that the RNAi-293 site had the best inhibition effect (Figure 4B). The expression profile of sex differentiation-related genes was detected after Nr5a2f gene expression interfered. The results showed that the expression of Nr5a2f, Foxl2 and Cyp19 genes were significantly down-regulated (Figure 4C; p < 0.05), while the expression of Dmrt1 and Cyp17 genes were remarkly up-regulated (p > 0.05). No significant difference was observed in the expression of sf1 gene (p > 0.05). The results indicate that the Nr5a2f gene regulated the expression of sex differentiation-related genes and participated in the regulation of the sex differentiation process of giant salamanders.
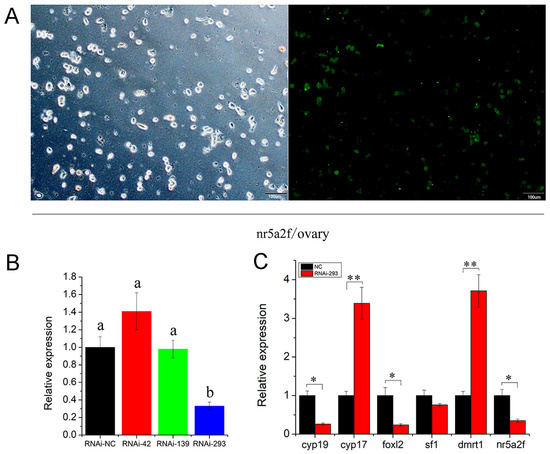
Figure 4.
Inhibited expression of Nr5a2f affected the transcription of sex-related genes in A. davidianus gonad. (A) RNAi of Nr5a2f transfected into ovary primary cells of A. davidianus; (B) expression profile of Nr5a2f after Nr5a2f/siRNA treated at different interference sites; (C) expression profile of sex-related gene after treated with RNAi-293 sites. Data are the mean ± sd. * above columns indicate significant differences among groups. (p < 0.05), ** indicate extremely significant difference (p < 0.01). ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple comparison tests. Different letters differed with statistical significance (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Among different A. davidianus tissues, the highest expression level of Nr5a2f was observed in the ovary, followed by the intestine, and a low level was found in other tissues. Mendelson et al. [31] showed that Nr5a2 was widely expressed in mammalian tissues, with high expression observed in granulosa cells from primordial follicles to preovalatory follicles and in luteal cells. The relative expression of Nr5a2m was evaluated by qRT-PCR. The results showed that the relative expression of Nr5a2m in A. davidianus was the highest in the brain, and the expression level in the testis was significantly higher than that in the ovaries. As gonadal development progressed, Nr5a2m gene expression had no significant difference in male and female gonads from four years to six years. The Nr5a2 gene is an important member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and plays an important role in growth development and cell differentiation. In this study, a higher expression of Nr5a2f was detected in the ovary than in the testis, which indicates that Nr5a2f played an important role in ovarian development. Additionally, we found that the expression of Nr5a2f increased during the process of male-to-female sex reversal, with significantly higher expression levels in the ovary and sex-reversed ovary compared to the testis and sex-reversed testis. The above results indicate that the high expression of Nr5a2f in the ovary confirms the crucial role in ovarian differentiation and development. Similar expression patterns have been observed in other species [32,33,34]. For instance, Boerbom found that the Nr5a2 gene in horses is highly expressed in gonadal tissues, indicating ovary-specific expression [6]. Granulosa cell proliferation in Nr5a2-specific knockout mice was impaired, disrupting the normal processes of E2 synthesis and follicle development, resulting in the mice being unable to ovulate normally [35,36]. Further studies showed that the expression of Nr5a2 is restricted to granulosa cells at various stages of ovarian follicle development, and its downstream target genes were almost all involved in follicular development processes, including genes regulating granulosa cell proliferation, E2 synthesis and ovulation [35,37]. In situ hybridization results determined that Nr5a2f began to express before gonadal differentiation in female A. davidianus, with its expression level increased from 48 dpf to 91 dpf. In contrast, Nr5a2m starts to express before differentiation in male A. davidianus, which indicates that the Nr5a2f gene plays a vital role in the ovary of A. davidianus, but the role in the testis is not obvious.
Sex differentiation in amphibians is complex, probably due to their typical two-stage life cycle. Sex differentiation is one of the hot topics in aquatic animal research, Cyp19 and foxl2 are key genes in estrogen synthesis, which play a significant role in the sex differentiation and development of animals, particularly in the differentiation and functional maintenance of ovaries [38]. In the process of sex determination and gonad differentiation, cyp19a, Dmrt1, Foxl2 and Nr5a2 genes interact with each other through a complex regulatory network to control gonad development direction. The genetic studies showed that three developmental genes, Foxl2, cyp19a and Dmrt1, play an indispensable role in the gonad development of the Chinese giant salamander [39,40,41,42]. Dmrt1 plays a key role in male development in mammals, birds, amphibians and bony fish [43,44,45]. Foxl2 is considered to be a highly conserved gene in vertebrates and is involved in almost all stages of ovarian development [46,47,48,49,50,51,52]. Cyp19a plays an important role in vertebrate sex determination and differentiation and is mainly designed to participate in the regulation of estrogen in ovarian differentiation [53,54,55,56]. In this study, when nr5a2f expression was inhibited, female-based gene expression was decreased, while male-based gene expression was increased. The results suggested that nr5a2f regulated the female base genes foxl2 and cyp19a to affect sex differentiation. Above all, we cloned the full-length sequence of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m, which were produced through alternative splicing. Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m were expressed in various tissues, and the expression of Nr5a2f in the ovary was significantly higher than that in the testis, whereas the expression of Nr5a2m in the testis was higher than that in the ovary. Nr5a2f began to express before the gonadal differentiation in female A. davidianus, and Nr5a2m started expressing before the differentiation in males. When RNAi-293 was applied, the expression of Nr5a2f, Foxl2 and Cyp19 genes were significantly down-regulated, and the expression of Dmrt1 and Cyp17 genes were significantly up-regulated. The results indicated that the Nr5a2f gene regulates the expression of genes related to sex differentiation and was involved in the sex differentiation process of A. davidianus. Further study is needed to determine whether it is essential for ovarian development.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we characterized Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m gene expression in various developing gonads and in sex reversal. In situ hybridization was used to detect the expression of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m in undifferentiated gonads. Differential expression of Nr5a2f and Nr5a2m genes were studied and revealed an important role of Nr5a2f in gonad differentiation. Furthermore, when we inhibited the expression of Nr5a2f, we found that the sex-related gene expression significantly changed. Further study in the future should be carried out to unveil the function of Nr5a2 and the mechanism of alternative splicing. A thorough understanding of the sex differentiation mechanism of A. davidianus can not only enhance the understanding of amphibians, but also improve the Chinese giant salamander farming industry.
Author Contributions
Q.H. conceived the project. G.L., G.Z. and J.X. collected and identified the specimens. D.H., W.L. and G.L. performed the experiment. Q.H. and D.H. analyzed the data. Q.H. and D.H. wrote and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (32373131).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study fully complied with research ethics. All animal experiments and methods were performed in accordance with the relevant approved guidelines and regulations, as well as under the approval of the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (YSFRI-2025017).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Guohua Zou was employed by the company Shanghai Jun Ding Fisheries Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Duggavathi, R.; Volle, D.H.; Mataki, C.; Antal, M.C.; Messaddeq, N.; Auwerx, J.; Murphy, B.D.; Schoonjans, K. Liver receptor homolog 1 is essential for ovulation. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinsohn, M.C.; Smith, O.E.; Bertolin, K.; Murphy, B.D. The Orphan Nuclear Receptors Steroidogenic Factor-1 and Liver Receptor Homolog-1: Structure, Regulation, and Essential Roles in Mammalian Reproduction. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1249–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Schmidt, D.R.; Cummins, C.L.; Choi, M.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Goodwin, B.; Hammer, R.E.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kliewer, S.A. Liver receptor homolog-1 regulates bile acid homeostasis but is not essential for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.H.K.; Murphy, B.D. Nuclear receptors: Key regulators of somatic cell functions in the ovulatory process. Mol. Aspects Med. 2021, 78, 100937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J. Effects of FSH-Fox-NR5A2-Mediated Photcycle on Follicle Development in Black-Lined hamsters. Master’s Thesis, Qufu Normal University, Jining, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Boerboom, D.; Pilon, N.; Behdjani, R.; Silversides, D.W.; Sirois, J. Expression and regulation of transcripts encoding two members of the NR5A nuclear receptor subfamily of orphan nuclear receptors, steroidogenic factor-1 and NR5A2, in equine ovarian cells during the ovulatory process. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4647–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Choi, M.; Suino, K.; Kovach, A.; Daugherty, J.; Kliewer, S.A.; Xu, H.E. Structural and biochemical basis for selective repression of the orphan nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog 1 by small heterodimer partner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9505–9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonjans, K.; Dubuquoy, L.; Mebis, J.; Fayard, E.; Wendling, O.; Haby, C.; Geboes, K.; Auwerx, J. Liver receptor homolog 1 contributes to intestinal tumor formation through effects on cell cycle and inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2058–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshelwood, M.M.; Repa, J.J.; Shelton, J.M.; Richardson, J.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Mendelson, C.R. Expression of LRH-1 and SF-1 in the mouse ovary: Localization in different cell types correlates with differing function. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2003, 207, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, B.; Jones, S.A.; Price, R.R.; Watson, M.A.; McKee, D.D.; Moore, L.B.; Galardi, C.; Wilson, J.G.; Lewis, M.C.; Roth, M.E.; et al. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falender, A.E.; Lanz, R.; Malenfant, D.; Belanger, L.; Richards, J.S. Differential expression of steroidogenic factor-1 and FTF/LRH-1 in the rodent ovary. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 3598–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelle-Dumais, C.; Jacob-Wagner, M.; Paré, J.F.; Bélanger, L.; Dufort, D. Nuclear receptor NR5A2 is required for proper primitive streak morphogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaVoie, H.A. Transcriptional control of genes mediating ovarian follicular growth, differentiation, and steroidogenesis in pigs. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Chen, F.; Shi, Z. Suppression of Notch Signaling Stimulates Progesterone Synthesis by Enhancing the Expression of NR5A2 and NR2F2 in Porcine Granulosa Cells. Genes 2020, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Chen, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.F.; Hui, Z.; Qu, L.H. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Chinese giant salamander, Andrias davidianus (Amphibia: Caudata). Gene 2003, 311, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, S. Cloning and characterization of wnt4a gene and evidence for positive selection in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.Q.; Shubin, N.H. Earliest known crown-group salamanders. Nature 2003, 422, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Steinlein, C.; Feichtinger, W. Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XVII. First demonstration of multiple sex chromosomes in amphibians: Eleutherodactylus maussi (Anura, leptodactylidae). Chromosoma 1992, 101, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M. Green. Cytogenetics of the endemic New Zealand frog, Leiopelma hochstetteri: Extraordinary supernumerary chromosome variation and a unique sex-chromosome system. Chromosoma 1988, 97, 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Chang, M.X.; Ma, J.; LaPatra, S.E.; Hu, Y.W.; Huang, L.; Nie, P.; Zeng, L. Transcriptomic analysis of the host response to an iridovirus infection in Chinese giant salamander, Andrias davidianus. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lan, Q.; Liu, R.; Cui, D.; Liu, H.; Xiong, D.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Characterization of galectin-1 from Chinese giant salamanders Andrias davidianus and its involvements during immune response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 70, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, L.; Song, W.; Wang, L. Identification of the first cathelicidin gene from skin of Chinese giant salamanders Andrias davidianus with its potent antimicrobial activity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 77, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Meng, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y.U.; Xiao, H. Sexually Dimorphic Expression of Foxl2 and Ftz-F1 in Chinese Giant Salamander Andrias Davidianus. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2016, 326, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Tian, H.; Meng, Y. Identification and expression of cytochrome P450 genes in the Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus. Theriogenology 2017, 95, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Du, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, L.Q.; Xie, S.S.; Yang, C.M.; Lan, X.Y.; Pan, C.Y.; Dong, W.Z. Comparative microRNAome analysis of the testis and ovary of the Chinese giant salamander. Reproduction 2017, 154, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Tian, H.; Xiao, H. Effects of temperature and sex steroids on sex ratio, growth, and growth-related gene expression in the Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus. Aquat. Biol. 2019, 28, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; de Beer, T.A.P.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Jiang, N.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhong, Q.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y. Characterization of reference genes for qRT-PCR normalization in rice-field eel (Monopterus albus) to assess differences in embryonic developmental stages, the early development of immune organs, and cells infected with rhabdovirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lian, Z.; Tian, H.; Xiao, H.; Hu, Q. Potential antagonistic relationship of fgf9 and rspo1 genes in WNT4 pathway to regulate the sex differentiation in Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 974348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, C.R.; Kamat, A. Mechanisms in the regulation of aromatase in developing ovary and placenta. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 106, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Wei, Z. Localization of LRH-1 expression in HPG axis tissues of Husheep. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 53, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinsohn, M.C.; Hughes, C.H.K.; Estienne, A.; Saatcioglu, H.D.; Pépin, D.; Duggavathi, R.; Murphy, B.D. A role for orphan nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1, NR5A2) in primordial follicle activation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolin, K.; Meinsohn, M.C.; Suzuki, J.; Gossen, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Duggavathi, R.; Murphy, B.D. Ovary-specific depletion of the nuclear receptor Nr5a2 compromises expansion of the cumulus oophorus but not fertilization by intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 96, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolin, K.; Gossen, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Murphy, B.D. The orphan nuclear receptor Nr5a2 is essential for luteinization in the female mouse ovary. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, S.M. The research progress of NR5A2 gene. Anim. Husb. Vet. Heilongjiang 2021, 23, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, N.; Rana, S.; Meena, K. Nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 2 (NR5A2): Role in health and diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 8155–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, Y.; Chakraborty, T.; Paul-Prasanth, B.; Ohta, K.; Nakamura, M. Sex determination, gonadal sex differentiation, and plasticity in vertebrate species. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1237–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.; Uno, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakamura, M. Molecular cloning and gene expression of Foxl2 in the frog Rana rugosa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 159, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Q.; Tian, H.; Meng, Y. Identification and expression of forkhead box genes in the Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus. Reprod Fert Dev. 2018, 30, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Tian, H.; Meng, Y. Characterization and expression of cyp19a gene in the Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 192, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson-Smith, M. The evolution of sex chromosomes and sex determination in vertebrates and the key role of DMRT1. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, K.A.; Schach, U.; Ordaz, A.; Steinfeld, J.S.; Draper, B.W.; Siegfried, K.R. Dmrt1 is necessary for male sexual development in zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2017, 422, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traylor-Knowles, N.G.; Kane, E.G.; Sombatsaphay, V.; Finnerty, J.R.; Reitzel, A.M. Sex-specific and developmental expression of Dmrt genes in the starlet sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis. EvoDevo 2015, 6, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Ito, Y.; Ito, M. Independent evolution for sex determination and differentiation in the DMRT family in animals. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio041962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanger, L.; Pannetier, M.; Gall, L.; Allais-Bonnet, A.; Elzaiat, M.; Le Bourhis, D.; Daniel, N.; Richard, C.; Cotinot, C.; Ghyselinck, N.B.; et al. FOXL2 is a female sex-determining gene in the goat. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocquet, J.; Pailhoux, E.; Jaubert, F.; Servel, N.; Xia, X.; Pannetier, M.; Messiaen, L.; Cotinot, C.; Fellous, M.; Veitia, R.A. Evolution and expression of FOXL2. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 39, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Zhang, G.R.; Wei, K.J.; Ji, W.; Gardner, J.P.; Yang, R.B.; Chen, K.C. Molecular identification and expression of the Foxl2 gene during gonadal sex differentiation in northern snakehead Channa argus. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridevi, P.; Senthilkumaran, B. Cloning and differential expression of FOXL2 during ovarian development and recrudescence of the catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 174, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Ovitt, C.E.; Anlag, K.; Fehsenfeld, S.; Gredsted, L.; Treier, A.C.; Treier, M. The murine winged-helix transcription factor Foxl2 is required for granulosa cell differentiation and ovary maintenance. Development 2004, 131, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Sun, W.; Bao, H.; Liang, X.; Li, P.; Shi, S.; Wang, Z.; Qian, G.; Ge, C. The forkhead factor Foxl2 participates in the ovarian differentiation of Chinese soft-shelled turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Dev. Biol. 2022, 492, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlenhaut, N.H.; Treier, M. Foxl2 function in ovarian development. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2006, 88, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Jiang, S.; Gu, Y.F.; Shi, Z.Y. Molecular characterization and expression of cyp19a gene in Carassius auratus. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oike, A.; Kodama, M.; Yasumasu, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Ito, E.; Nakamura, M. Participation of androgen and its receptor in sex determination of an amphibian species. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nes, S.; Moe, M.; Andersen, Ø. Molecular characterization and expression of two cyp19 (P450 aromatase) genes in embryos, larvae, and adults of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus). Mol. Reprod Dev. 2005, 72, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Lu, H.; Sun, C.; Peng, Y.; Meng, F.; Gan, R.; Cui, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. Nr5a homologues in the ricefield eel Monopterus albus: Alternative splicing, tissue-specific expression, and differential roles on the activation of cyp19a1a promoter in vitro. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 312, 113871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).