The Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici in the Feed of Salmonids: A Strategy to Improve Reproductive Parameters
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Handling and Study Conditions
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Biometric Measures
2.4. Blood Biochemistry Analysis
2.5. Semen Collection and Analysis
2.6. Gonadosomatic Index (GSI)
2.7. Sperm Quality Analysis
2.8. Fertilization Assay and Embryo Viability Assessment
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reproductive Parameters
3.2. Blood Biochemical Parameters
3.3. Semen Quality Analysis
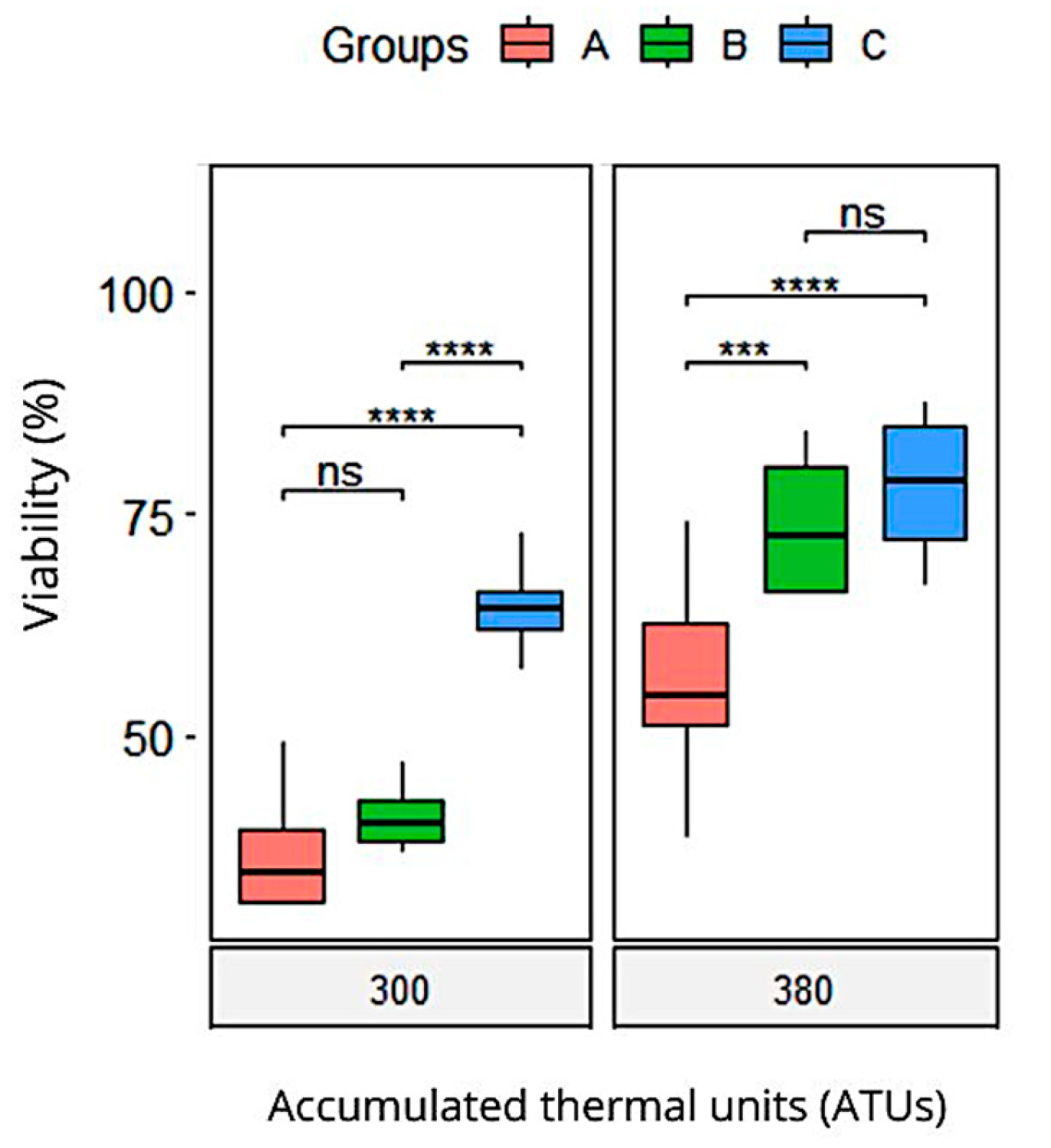
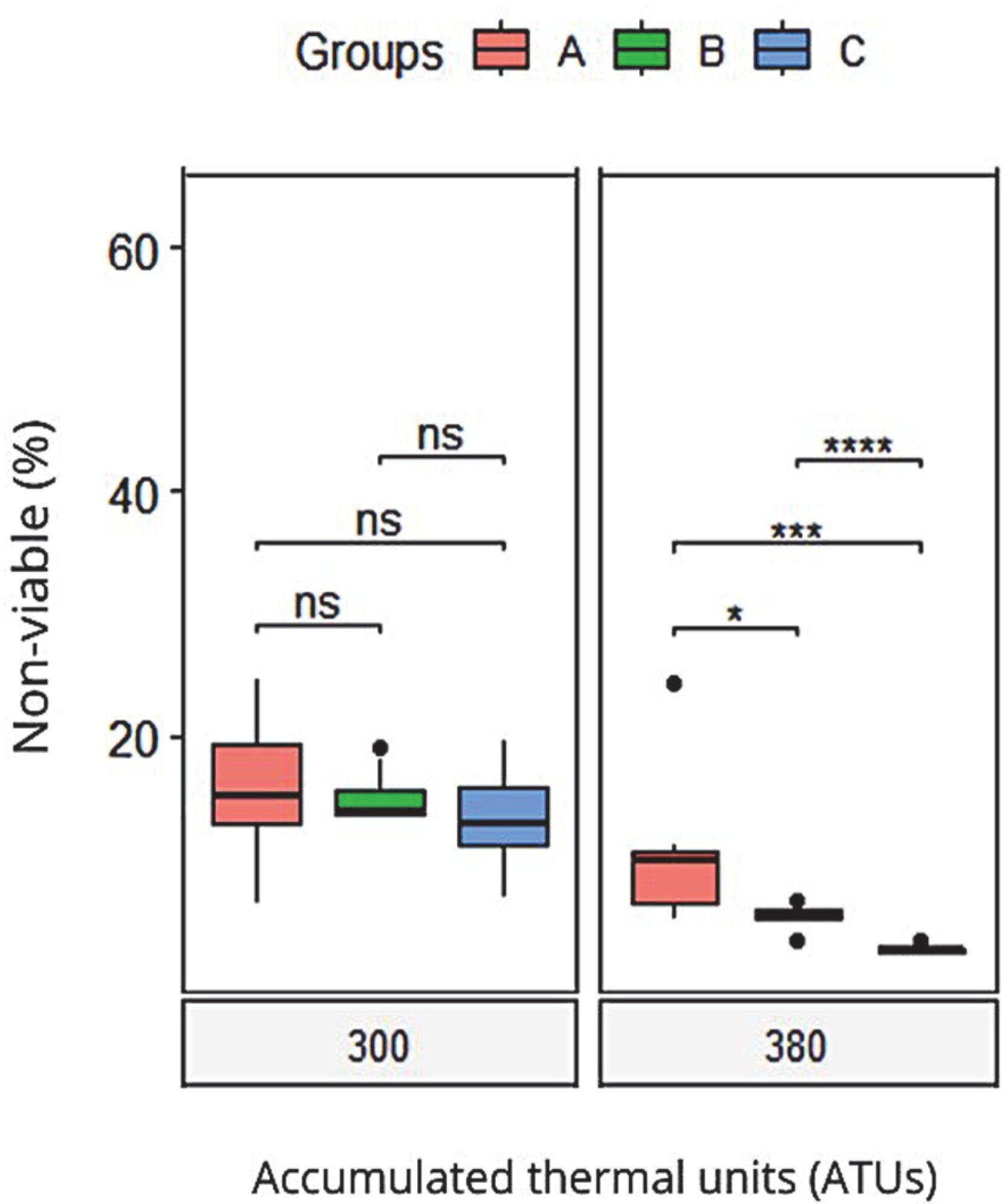
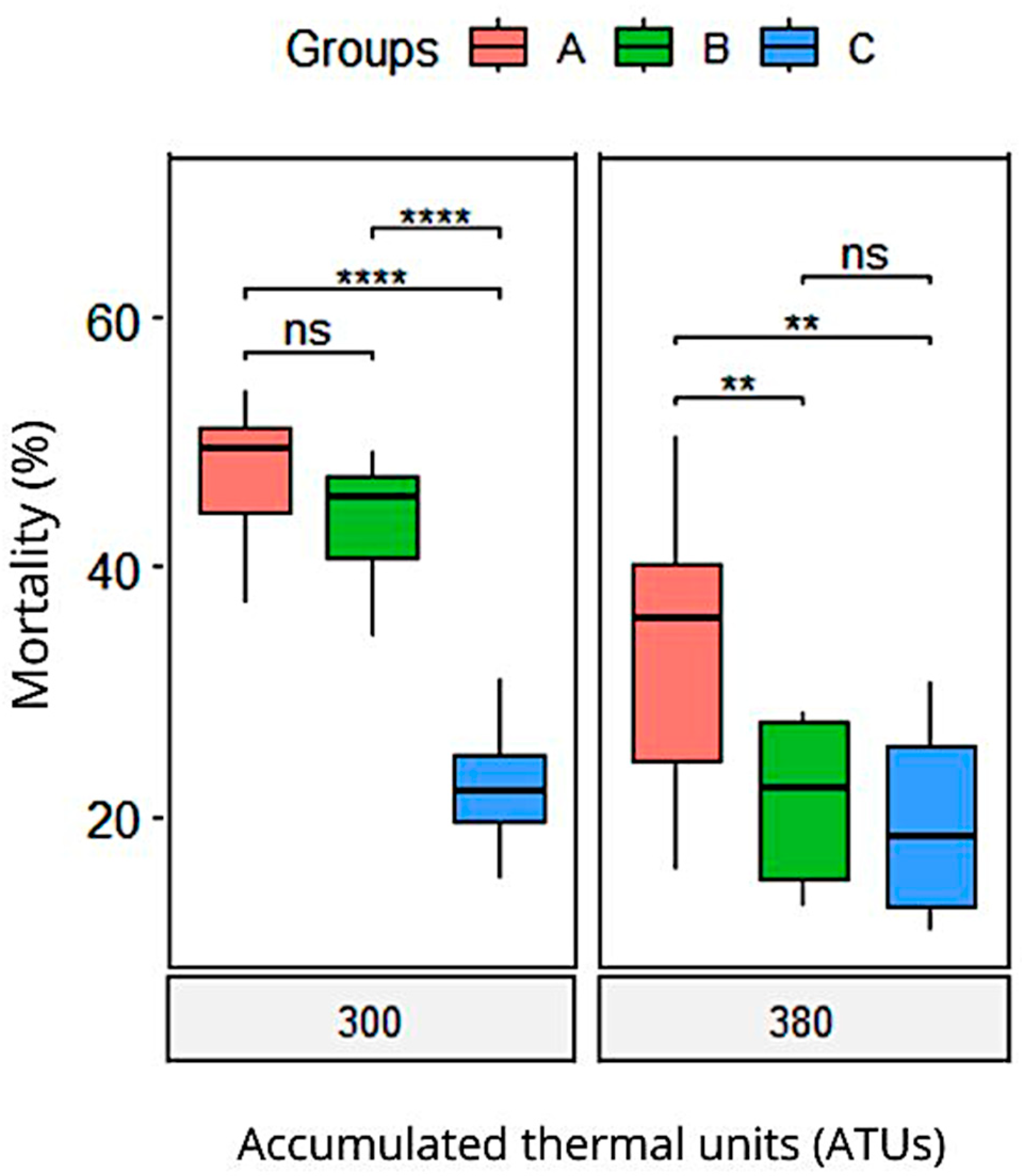
3.4. Fertilization and Embryo Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sumon, M.A.A.; Molla, M.H.R.; Hakeem, I.J.; Ahammad, F.; Amran, R.H.; Jamal, M.T.; Gabr, M.H.; Islam, M.S.; Alam, M.T.; Brown, C.L.; et al. Epigenetics and Probiotics Application toward the Modulation of Fish Reproductive Performance. Fishes 2022, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torfadottir, J.E.; Ulven, S.M. Fish-A Scoping Review for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023. Food Nutr. Res. 2024, 68, 10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, P.; Swapnil, N.; Sheikh, S.; Tekam, I.; Bhalchandra, N.; Madhav, G.; Munilkumar, S. Nutritional Significance of Fish in Combating Malnutrition. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, I.C.; Chao, N.H. Aquaculture and food crisis: Opportunities and constraints. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 18, 564–569. [Google Scholar]
- Hixson, S.M. Fish nutrition and current issues in aquaculture: The balance in providing safe and nutritious seafood, in an environmentally sustainable manner. J. Aquacult. Res. Dev. 2014, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2016. Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/20e618b3-93a1-488a-9697-798f6b6c6b35/content (accessed on 21 December 2024).
- Mair, G.C.; Halwart, M.; Derun, Y.; Costa-Pierce, B.A. A decadal outlook for global aquaculture. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2023, 54, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørndal, T.; Dey, M.; Tusvik, A. Economic analysis of the contributions of aquaculture to future food security. Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cc0461en (accessed on 21 December 2024).
- Singh, S.K.; Baidya, S.; Das, P.; Biswas, P. Functional role of dietary supplements on reproductive physiology of fishes. In Recent Updates in Molecular Endocrinology and Reproductive Physiology of Fish; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickney, R.R.; Gatlin, D.D. Aquaculture: An Introductory Text, 3rd ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2022; pp. 192–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, D.; Ringø, E. Aquaculture Nutrition: Gut Health, Probiotics and Prebiotics, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, E.; Robles, V.; Herraez, P. Methods in Reproductive Aquaculture: Marine and Freshwater Species; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 1–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, F.; Karmani, M.; Templeman, N.M. Metabolic hormones are integral regulators of female reproductive health and function. Biosci. Rep. 2024, 44, BSR20231916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, B.L.; Chaves, S.N.; Albuquerque, E.; Rodrigues, J.; Coimbra, V.; Miranda, S.; Caldas, A.L.; Leite, M.; dos Santos, M.P.; Caetano, R.A.; et al. Gametogenesis and seminatural reproduction of the Amazon twospot astyanax Astyanax bimaculatus (Linnaeus, 1758) cultivated in an enriched environment. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 267, 107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bruce, T.J.; Jones, E.M.; Cain, K.D. A review of fish vaccine development strategies: Conventional methods and modern biotechnological approaches. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, I.A. Nanotechnology in reproduction, breeding and conservation of fish biodiversity: Current status and future potential. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumon, T.A.; Hussain, H.M.A.; Sumon, M.A.A.; Jang, W.J.; Guardiola, F.A.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Brown, C.L.; Lee, E.W.; Kim, C.H.; Hasan, M.T. Functionality and prophylactic role of probiotics in shellfish aquaculture. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Martyniuk, C.; Tubbs, C.; Bisesi, J. Regulation of endocrine systems by the microbiome: Perspectives from comparative animal models. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 292, 113437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.T.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, B.-J.; Hur, S.W.; Lim, S.G.; Kim, K.W.; Han, H.-S.; Kong, I.-S. Effects of immunostimulants, prebiotics, probiotics, symbiotics, and potentially immunoreactive feed additives in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus): A review. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2019, 27, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.N.; Banerjee, G. Recent studies on probiotics as beneficial mediators in aquaculture: A review. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2020, 81, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.T.; Sumon, A.A.; Pugazhendi, A.; Al Harbi, M.; Hussain, A.; Haque, F. Use of probiotics in the aquaculture of commercially important fish species. Int. J. Probiotics Prebiotics 2020, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, G.; Dalla Valle, L.; Benato, F.; Fimia, G.M.; Nardacci, R.; Ciccosanti, F.; Piacentini, M.; Borini, A.; Carnevali, O. Interplay between autophagy and apoptosis in the development of Danio rerio follicles and the effects of a probiotic. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2013, 25, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, F.; Çehreli, Ş.-Y. Effect of probiotics on reproductive performance of fish. Nat. Eng. Sci. 2019, 4, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department. Top 10 Species Groups in Global Aquaculture 2018. In Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/15bc5f8d-6a9d-4019-aa7c-076b3a3614a3/content#:~:text=Half%20of%20the%20top%2010,and%20brown%20seaweeds%20(%233%3B (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024-Blue Transformation in Action. Rome. Available online: https://doi.org/10.4060/cd0683en (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Su, W.; Jiang, Z.; He, H.; Gong, T.; Lu, Z. Co-fermented yellow wine lees by Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium regulates growth performance and gut microbiota in finishing pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1003498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasiri, A.K.S.; Jaramillo-Torres, A.; Chikwati, E.M.; Forberg, T.; Krogdahl, Å.; Kortner, T.M. Effects of dietary supplementation with prebiotics and Pediococcus acidilactici on gut health, transcriptome, microbiota, and metabolome in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) after seawater transfer. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.T. Probiotics. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Bajagai, A.V.; Klieve, P.J.; Dart, P.J.; Bryden, W.L. Probiotics in animal nutrition—Production, impact and regulation. In FAO Animal Production and Health Paper; Makkar, H.P.S., Ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016; Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/2fda2226-b000-4cee-8186-8cacab86316b/content (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Gupta, S.; Fečkaninová, A.; Lokesh, J.; Koščová, J.; Sørensen, M.; Fernandes, J.; Kiron, V. Lactobacillus dominate in the intestine of Atlantic salmon fed dietary probiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastyk, H.C.; Perelman, D.; Topf, M.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Robinson, J.L.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Gardner, C.D.; Sonnenburg, E.D. Randomized controlled trial demonstrates response to a probiotic intervention for metabolic syndrome that may correspond to diet. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2178794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, E.B.-M.; Ofosu, F.K.; Xiuqin, C.; Chelliah, R.; Oh, D.-H. Probiotic effector compounds: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Kerry, R.; Patra, J.K.; Gouda, S.; Park, Y.; Shin, H.-S.; Das, G. Benefaction of probiotics for human health: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vílchez, M.C.; Santangeli, S.; Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Verdenelli, C.; Gallego, V.; Peñaranda, D.S.; Tveiten, H.; Pérez, L.; Carnevali, O.; et al. Effect of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus on the expression of genes involved in European eel spermatogenesis. Theriogenology 2015, 84, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, F.; Lombardo, F.; Merrifield, D.; Silvi, S.; Cresci, A.; Avella, M.; Carnevali, O. Effects of probiotic on zebrafish reproduction. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, S1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, M.M.; Salati, A.P.; Keyvanshokooh, S.; Safari, O. The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici on mucosal immune responses, growth, and reproductive performance in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinejad, N.; Imanpour, M.R.; Jafari, V. Combined or individual effects of dietary probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici and nucleotide on reproductive performance in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klakegg, Ø.; Salonius, K.; Nilsen, A.; Fülberth, M.; Sørum, H. Enhanced growth and decreased mortality in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) after probiotic bath. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Liu, G.; Chang, W.; Beckers, Y.; Cai, H. Screening and Characterization of Pediococcus acidilactici LC-9-1 toward Selection as a Potential Probiotic for Poultry with Antibacterial and Antioxidative Properties. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; Zheng, R.; Jacobi, S.K. PSIII-2 Pediococcus acidilactici demonstrates probiotic properties and inhibits the growth of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 101 (Suppl. 3), 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Bao, K.; Li, G. Impact of Pediococcus acidilactici GLP06 supplementation on gut microbes and metabolites in adult beagles: A comparative analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1369402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Zheng, R.; Jacobi, S.K. PSV-21 Pediococcus acidilactici survives an in vitro simulated digestion. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102 (Suppl. 2), 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão, J.; Zilli, L.; Vilella, S.; Cabrita, E.; Schiavone, R.; Herráez, M.P. Improving sperm cryopreservation with antifreeze proteins: Effect on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) plasma membrane lipids. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, A.; Sahu, C. Effect of probiotic on reproductive performance in female livebearing ornamental fish. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, R.; Quiñones, J.; Short, S.; Contreras, P.; Ulloa-Rodríguez, P.; Cancino-Baier, D.; Sepúlveda, N.; Valdebenito, I.; Farías, J.G. Effect of exogenous lipids on cryotolerance of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) spermatozoa. Cryobiology 2021, 98, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2024. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Kassambara, A. rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. R Package Version 0.7.2. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rstatix (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Shah, A.A.; Khan, R.U.; Khan, M.S.; Wanapat, M. Emerging trends and applications in health-boosting microorganisms-specific strains for enhancing animal health. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 176, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, N.; Alam, A.M.M.N.; Rahman, M.M.; Ali, M.S.; Hashem, M.A. Probiotics to enhance animal production performance and meat quality: A review. Meat Res. 2024, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, R.; Hossain, M.A.; Islam, M.R.; Iqbal, M.M. Does commercial probiotics improve the growth performance and hematological parameters of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus? Aquat. Res. 2021, 4, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.; Marzouk, M.; Moustafa, M. Use of different Saccharomyces cerevisiae biotic forms as immune-modulator and growth promoter for Oreochromis niloticus challenged with some fish pathogens. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2013, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, T.; Sofi Uddin Mahamud, A.G.M.; Acharjee, T.K.; Hassan, R.; Akter Snigdha, T.; Islam, T.; Alam, R.; Khoiam, M.U.; Akter, F.; Azad, M.R.; et al. Probiotic supplementations improve growth, water quality, hematology, gut microbiota and intestinal morphology of Nile tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Alagawany, M.; Patra, A.K.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Dhama, K.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: An overview. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Joshi, N. Probiotics in aquaculture. In Handbook of Aquatic Microbiology, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, D.D.C.; Furlaneto, F.D.P.B.; Sussel, F.R.; Tachibana, L.; Gonçalves, G.S.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Economic feasibility of probiotic use in the diet of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, during the reproductive period. Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2020, 42, e47960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Nargesi, E.; Falahatkar, B.; Sajjadi, M.M. Dietary supplementation of probiotics and influence on feed efficiency, growth parameters and reproductive performance in female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) broodstock. Aquacult. Nutr. 2020, 26, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Jun, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Han, S.J.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Therapeutic effect of intestinal autochthonous Lactobacillus reuteri P16 against waterborne lead toxicity in Cyprinus carpio. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugwanya, M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Kimera, F.; Sewilam, H. Updating the role of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for tilapia aquaculture as leading candidates for food sustainability: A review. Probiotics Antimicro. Prot. 2022, 14, 130–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, S.; Amoah, K.; Huang, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, B.; Shija, V.M.; Jin, X.; Anokyewaa, M.A.; Jiang, M. Probiotics application in aquaculture: Its potential effects, current status in China and future prospects. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1455905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.M.; Merrifield, D.L.; Harper, G.M.; Rawling, M.D.; Mustafa, S.; Picchietti, S.; Balcàzar, J.L.; Davies, S.J. The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici on the gut microbiota and immune status of on-growing red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shija, V.M.; Amoah, K.; Li, Y.; Yong, Z.; Chen, Z.; Cai, J. Influence of dietary Bacillus amyloliquefaciens AV5 on growth, immune responses, and resistance to Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Rep. 2024, 25, 102391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelal, A.E.; El-Danasoury, A.M.; Mohamed, E.K.; Sharaf, S.M. The effect of dietary probiotic (Bactocill, Pediococcus acidilactici) supplementation on reproductive performance of Oreochromis niloticus. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2021, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Akhter, S.; Mallik, M.K.M.; Rashid, I. Probiotic enriched dietary effect on the reproduction of butter catfish, Ompok pabda (Hamilton, 1872). Int. J. Curr. Res. Life Sci. 2018, 7, 866–873. [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G. Integrated control of fish metabolism, wellbeing and reproduction: The role of probiotic. Aquaculture 2017, 472, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Gordon, J.I. Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 2001, 292, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Midtvedt, T.; Gordon, J.I. How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroglou, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Carnevali, O.; Picchietti, S.; Avella, M.; Daniels, C.; Güroy, D.; Davies, S.J. Microbial manipulations to improve fish health and production—A Mediterranean perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Salinas, I.; Olsen, R.E.; Nyhaug, A.; Myklebust, R.; Mayhew, T.M. Histological changes in intestine of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) following in vitro exposure to pathogenic and probiotic bacterial strains. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 328, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, E.S.H.; Baghdady, E.S.; Gaafar, A.Y.; El-Badawi, A.A.; Bazina, W.K.; Abd Al-Kareem, O.M.; Abd El-Hamed, N.N. Assessing the influence of dietary Pediococcus acidilactici probiotic supplementation in the feed of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) (Linnaeus, 1758) on farm water quality, growth, feed utilization, survival rate, body composition, blood biochemical parameters, and intestinal histology. Aquacult. Nutr. 2022, 1, 5841220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladisa, C.; Ma, Y.; Habibi, H.R. Metabolic changes during growth and reproductive phases in the liver of female goldfish (Carassius auratus). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 834688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcarce, D.G.; Riesco, M.F.; Martínez-Vázquez, J.M.; Robles, V. Diet supplemented with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory probiotics improves sperm quality after only one spermatogenic cycle in zebrafish model. Nutrients 2019, 11, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Gui, J.; Xiao, W. Zebrafish androgen receptor is required for spermatogenesis and maintenance of ovarian function. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24320–24334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulish, S.; Kramer, C.R.; Grier, H.J. Organization of the male gonad in a protogynous fish, Thalassoma bifasciatum (Teleostei: Labridae). J. Morphol. 2002, 254, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, G.; Maradonna, F.; Lombardo, F.; Bizzaro, D.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Increase of fecundity by probiotic administration in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Reproduction 2010, 140, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | A N = 16 | B N = 16 | C N = 16 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total weight (kg) | 7.71 (0.61) | 7.30 (1.07) | 8.33 (0.51) | 0.22 |
| Standard length (cm) | 79.2 (1.9) | 77.6 (2.3) | 81.0 (2.0) | 0.59 |
| Gonad weight (kg) | 0.21 (0.03) a | 0.16 (0.03) a | 0.28 (0.02) b | 0.048 |
| GSI (%) | 2.64 (0.18) ab | 2.15 (0.18) a | 3.21 (0.21) b | 0.028 |
| Fresh semen volume (mL) | 12.0 (2.5) | 20.0 (0.0) | 14.9 (1.8) | 0.21 |
| Sum Sq | Df | F Value | Pr (>F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.00 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.84 |
| Total weight | 0.07 | 1 | 16.32 | 0.00 |
| Group | 0.02 | 2 | 2.47 | 0.11 |
| Residuals | 0.09 | 21 |
| Group | Adj. Mean | CI 95% | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.29 |
| B | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.26 |
| C | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.30 |
| Parameter | A N = 16 | B N = 16 | C N = 16 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilirubin (μmol/L) | 2.00 (0.14) ab | 2.45 (0.09) a | 1.98 (0.10) b | 0.045 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 19.50 (0.65) | 20.00 (1.08) | 20.57 (0.36) | 0.42 |
| AST (U/L) | 228 (17) | 234 (11) | 229 (8) | 0.82 |
| ALT (U/L) | 24 (5) a | 17 (1) ab | 12 (1) b | 0.017 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 972 (196) | 900 (110) | 992 (67) | 0.93 |
| Protein (g/L) | 55.8 (2.3) | 58.0 (1.3) | 57.8 (1.5) | 0.74 |
| GGT | 0.75 (0.48) | 1.25 (0.75) | 1.36 (0.32) | 0.68 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 1.00 (0.14) | 1.08 (0.05) | 1.01 (0.03) | 0.52 |
| Phosphorus (mmol/L) | 5.35 (0.07) | 5.33 (0.14) | 5.41 (0.05) | 0.74 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 3.14 (0.06) | 3.24 (0.08) | 3.20 (0.05) | 0.65 |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 13.7 (2.6) | 14.1 (0.7) | 16.2 (1.7) | 0.47 |
| Globulins (g/L) | 36.3 (1.9) | 38.0 (0.7) | 37.2 (1.3) | 0.69 |
| Characteristic | A N = 16 | B N = 16 | C N = 16 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sperm concentration (sperm/mL) | 8.76 × 109 (1.51 × 109) a | 10.47 × 109 (0.87 × 109) a | 20.13 × 109 (1.77 × 109) b | <0.001 |
| Membrane integrity (%) | 97.83 (0.39) | 97.83 (0.24) | 98.06 (0.31) | 0.76 |
| Membrane mitochondrial potential (%) | 62 (6) | 64 (4) | 63 (5) | 0.89 |
| Anion superoxide negative (%) | 95.75 (0.62) | 95.96 (0.60) | 96.38 (0.24) | 0.90 |
| Total motility (%) | 79 (3) | 85 (3) | 84 (3) | 0.28 |
| Stage | Characteristic | A N = 8 | B N = 8 | C N = 8 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertility (%) | |||||
| 180 ATUs | Fertilized eggs | 51.2 (3) ab | 50.0 (1) a | 59.1 (3) b | 0.039 |
| Non-fertilized eggs | 28.5 (2.4) a | 24.2 (0.6) ab | 20.1 (1.1) b | 0.004 | |
| Mortality | 20.3 (2.1) | 25.8 (1.0) | 20.8 (2.2) | 0.14 | |
| Embryo viability (%) | |||||
| 300 ATUs | Viability | 36.7 (2) a | 41.1 (1) a | 64.4 (2) b | <0.001 |
| Non-viable | 15.0 (2.2) | 14.2 (0.8) | 12.4 (1.5) | 0.47 | |
| Mortality | 48.3 (2) a | 44.7 (2) a | 23.2 (2) b | <0.001 | |
| 380 ATUs | Viability | 56.5 (4) a | 73.6 (3) b | 78.1 (3) b | 0.003 |
| Non-viable | 34.1 (4) a | 22.1 (2) b | 20.5 (3) b | 0.035 | |
| Mortality | 9.4 (2.2) a | 4.3 (0.38) b | 1.4 (0.14) b | <0.001 | |
| Characteristic | Contrast | Estimate | Std. Error | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 40 | 91.76 | −140, 220 | 0.67 | |
| Group | 0.002 | ||||
| A × (B + C) | 1.3 | 0.82 | −0.36, 2.9 | 0.13 | |
| B × C | 4.5 | 1.39 | 1.7, 7.2 | 0.003 | |
| ATUs | <0.001 | ||||
| 300 | −6.0 | 1.39 | −8.7, −3.3 | <0.001 | |
| 380 | 16 | 1.39 | 13, 19 | <0.001 | |
| Mem | 0.21 | 1 | −1.8, 2.2 | 0.84 | |
| Mito | 0.01 | 0.06 | −0.10, 0.13 | 0.83 | |
| Anion | 0.00 | 0.49 | −0.97, 0.98 | >0.99 | |
| Motility | −0.10 | 0.11 | −0.32, 0.13 | 0.40 | |
| Group × ATUs | <0.001 | ||||
| ATUs 300 | A × (B + C) | 4.2 | 0.97 | 2.3, 6.2 | <0.001 |
| ATUs 300 | B × C | 7.1 | 1.69 | 3.8, 10 | <0.001 |
| ATUs 380 | A × (B + C) | 5.3 | 0.97 | 3.4, 7.3 | <0.001 |
| ATUs 380 | B × C | −2.3 | 1.69 | −5.6, 1.0 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz, R.; Carrasco, D.; Quiñones, J.; Martínez, A.; Sepúlveda, G.; Pérez-Núñez, I.; Huaiquipán, R.; Cancino-Baier, D.; Beltrán, J.F.; Farías, J.G.; et al. The Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici in the Feed of Salmonids: A Strategy to Improve Reproductive Parameters. Animals 2025, 15, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111659
Díaz R, Carrasco D, Quiñones J, Martínez A, Sepúlveda G, Pérez-Núñez I, Huaiquipán R, Cancino-Baier D, Beltrán JF, Farías JG, et al. The Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici in the Feed of Salmonids: A Strategy to Improve Reproductive Parameters. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111659
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz, Rommy, Doris Carrasco, John Quiñones, Ailín Martínez, Gastón Sepúlveda, Isabela Pérez-Núñez, Rodrigo Huaiquipán, David Cancino-Baier, Jorge F. Beltrán, Jorge G. Farías, and et al. 2025. "The Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici in the Feed of Salmonids: A Strategy to Improve Reproductive Parameters" Animals 15, no. 11: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111659
APA StyleDíaz, R., Carrasco, D., Quiñones, J., Martínez, A., Sepúlveda, G., Pérez-Núñez, I., Huaiquipán, R., Cancino-Baier, D., Beltrán, J. F., Farías, J. G., Paz, E. A., & Sepúlveda, N. (2025). The Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici in the Feed of Salmonids: A Strategy to Improve Reproductive Parameters. Animals, 15(11), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111659









