Improving Mobility: A Case Report on the Rehabilitation of a Gait Anomaly in an Asian Elephant at a Thai Elephant Conservation Center
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
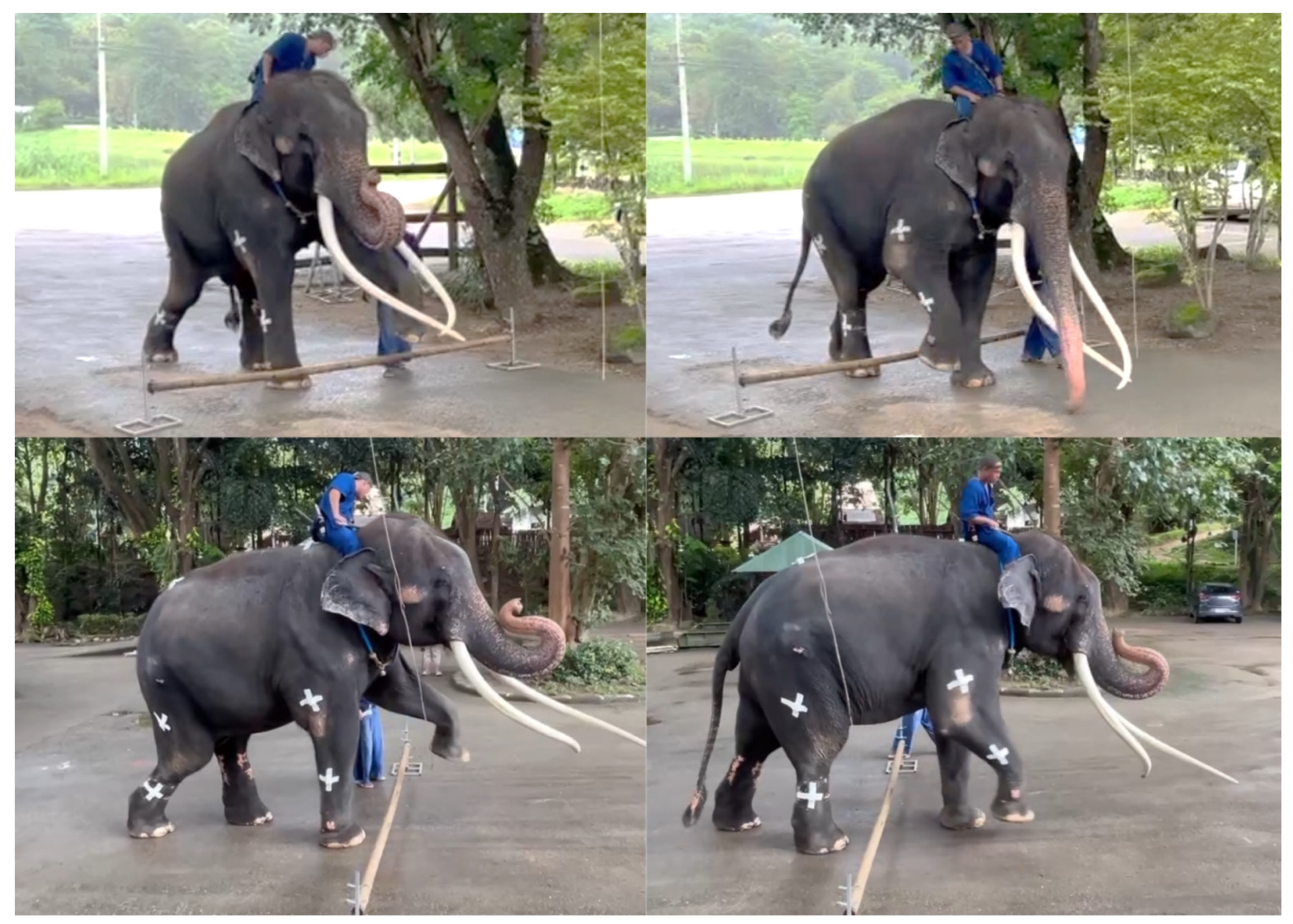
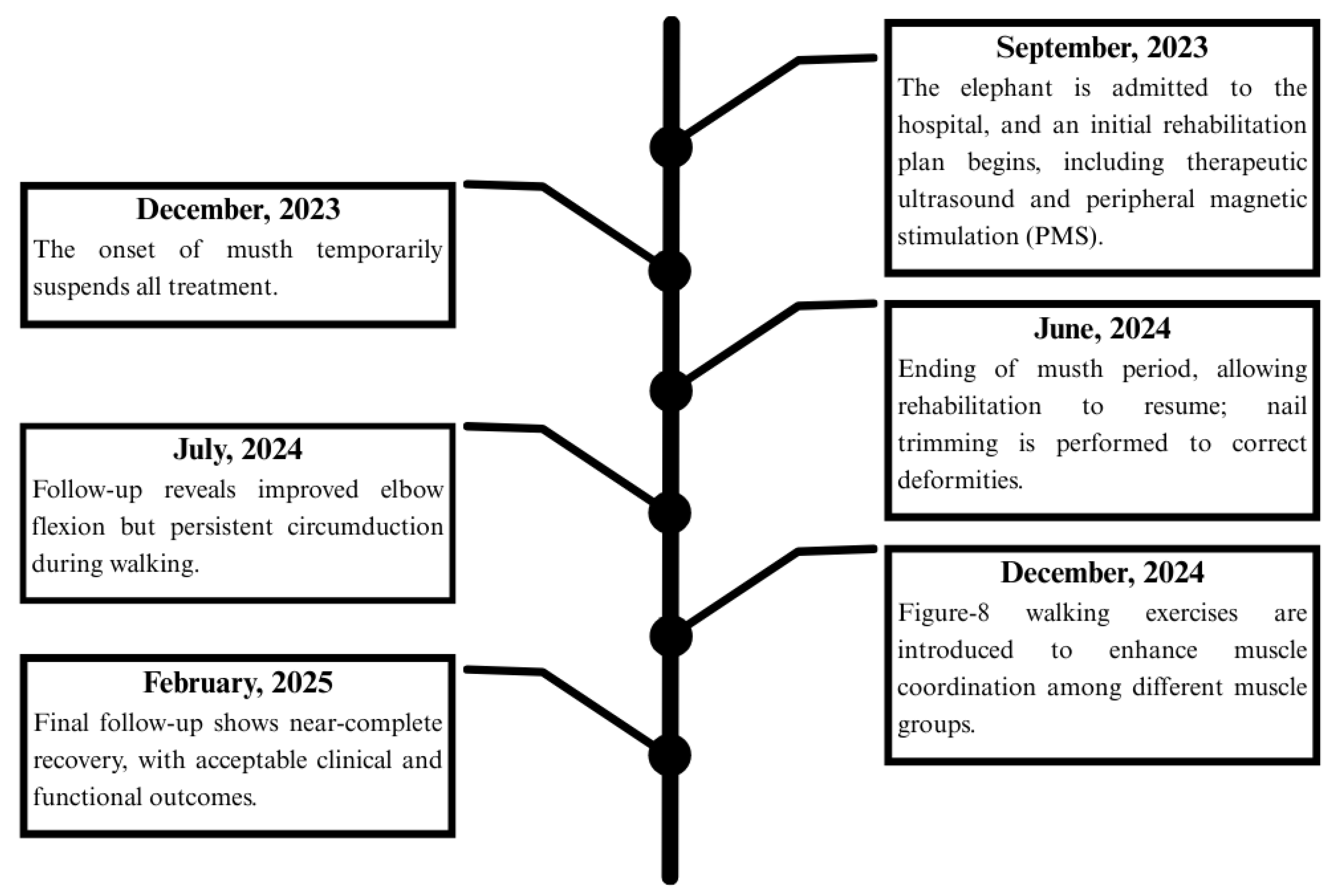
2. Detailed Case Description
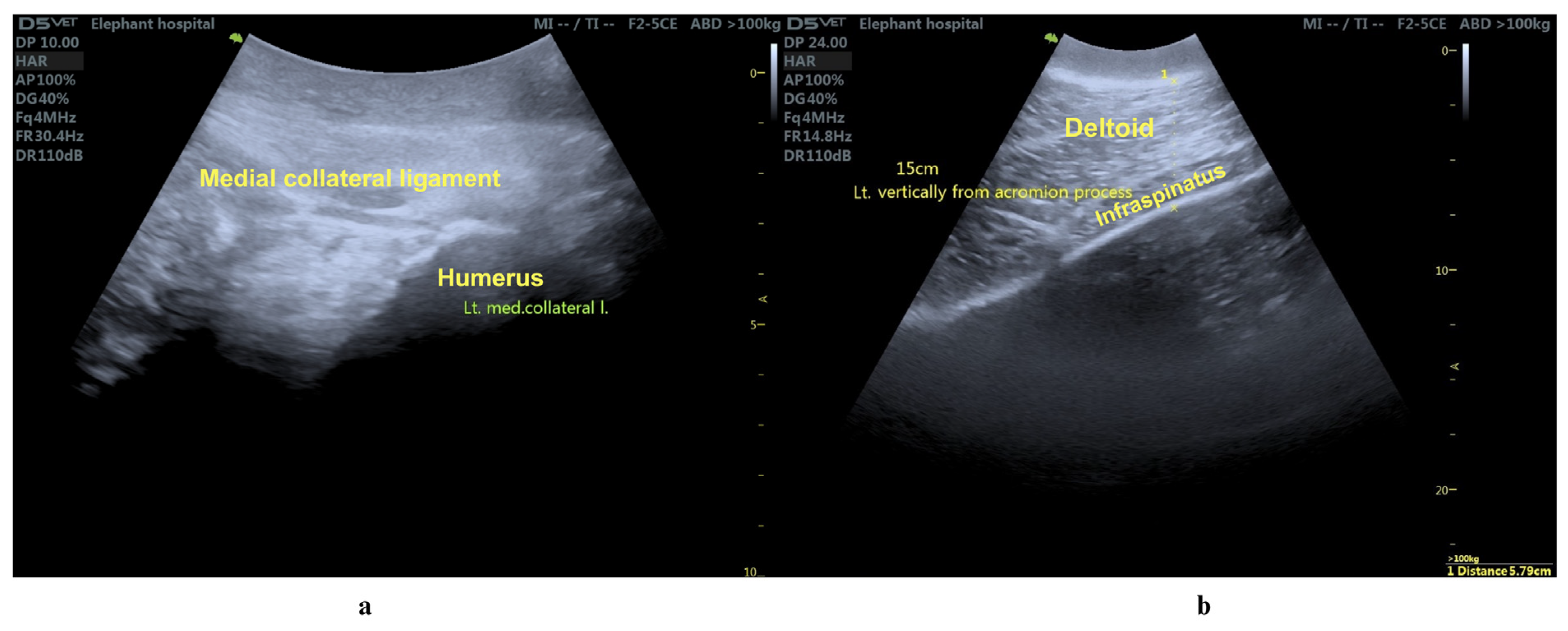
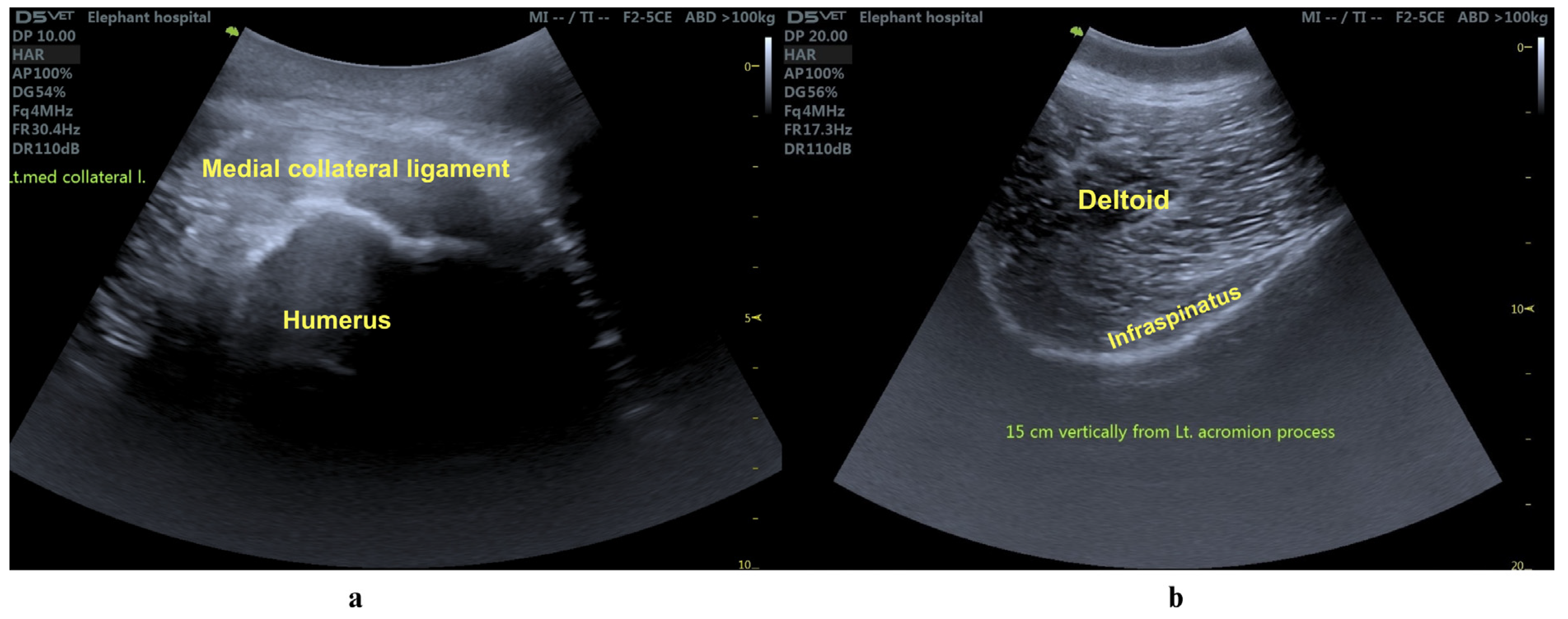
Rehabilitation Regimens
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Evaluation
3.2. Biomechanical Gait Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchinson, J.R.; Schwerda, D.; Famini, D.J.; Dale, R.H.; Fischer, M.S.; Kram, R. The locomotor kinematics of Asian and African elephants: Changes with speed and size. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 3812–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Hutchinson, J.R. The three-dimensional locomotor dynamics of African (Loxodonta africana) and Asian (Elephas maximus) elephants reveal a smooth gait transition at moderate speed. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, J.; Delmer, C.; Miller, C.; Hildebrandt, T.; Pitsillides, A.; Boyde, A. From Flat Foot to Fat Foot: Structure, Ontogeny, Function, and Evolution of Elephant “Sixth Toes”. Science 2011, 334, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Hogan, J.N.; Meehan, C.L. Housing and Demographic Risk Factors Impacting Foot and Musculoskeletal Health in African Elephants (Loxodonta africana) and Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus) in North American Zoos. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnault, S.; Dixon, J.J.I.; Warren-Smith, C.; Hutchinson, J.R.; Weller, R. Skeletal pathology and variable anatomy in elephant feet assessed using computed tomography. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, N.; Tanaka, S.; Omiya, T.; Shoji, Y.; Senzaki, M.; Hanzawa, S.; Ando, M.; Osaki, T.; Hatai, H.; Miyoshi, N.; et al. Novel treatment for chronic pododermatitis in an Indian elephant (Elephas maximus indicus) with Mohs’ paste. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1834–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfeld, K.A.; Meehan, C.L.; Hogan, J.N.; Brown, J.L. Assessment of Body Condition in African (Loxodonta africana) and Asian (Elephas maximus) Elephants in North American Zoos and Management Practices Associated with High Body Condition Scores. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLaren, J.A.; McHorse, B.K. Comparative forelimb myology and muscular architecture of a juvenile Malayan tapir (Tapirus indicus). J. Anat. 2020, 236, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquiet, B.; Biau, S.; Trébot, Q.; Debril, J.-F.; Durand, F.; Fradet, L. Detection of Horse Locomotion Modifications Due to Training with Inertial Measurement Units: A Proof-of-Concept. Sensors 2022, 22, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, N.W.; Byrne, D.T.; O’Connor, A.H.; Shalloo, L. Invited review: Cattle lameness detection with accelerometers. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3895–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Kerrigan, D.C.; Thirunarayan, M.A.; Duff-Raffaele, M. The Vertical Displacement of the Center of Mass During Walking: A Comparison of Four Measurement Methods. J. Biomech. Eng. 1998, 120, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gard, S.A.; Childress, D.S. What Determines the Vertical Displacement of the Body During Normal Walking? J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2001, 13, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khammesri, S.; Wantanajittikul, K.; Namwongprom, K.; Kittisirikul, N.; Ueangpaibool, P.; Thitaram, C.; Brown, J.L.; Kongsawasdi, S. Evaluating Gait Abnormalities in Asian Elephants Using Inertial Measurement Unit-Based Vertical Movement Symmetry Analysis: A Pilot Study. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchner, H.H.; Savelberg, H.H.; Schamhardt, H.C.; Barneveld, A. Head and trunk movement adaptations in horses with experimentally induced fore- or hindlimb lameness. Equine Vet. J. 1996, 28, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodin, M.; Persson-Sjodin, E.; Egenvall, A.; Serra Bragança, F.M.; Pfau, T.; Roepstorff, L.; Weishaupt, M.A.; Thomsen, M.H.; van Weeren, P.R.; Hernlund, E. Vertical movement symmetry of the withers in horses with induced forelimb and hindlimb lameness at trot. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaaod, M.; Luternauer, M.; Hausegger, T.; Kredel, R.; Steiner, A. The cow pedogram—Analysis of gait cycle variables allows the detection of lameness and foot pathologies. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Acosta, L.; Ortiz-Prado, A.; Jacobo-Armendáriz, V.H.; González-Carbonell, R.A. Analysis and characterization of the normal gait phases of walking Warmblood horses as a tool for the diagnosis of lameness. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, H.M.; Hobbs, S.J. A Review of Biomechanical Gait Classification with Reference to Collected Trot, Passage and Piaffe in Dressage Horses. Animals 2019, 9, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, O.; Pataky, T.C.; Day, M.; Hensman, M.C.; Hensman, S.; Hutchinson, J.R.; Clemente, C.J. Foot pressure distributions during walking in African elephants (Loxodonta africana). R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsawasdi, S.; Mahasawangkul, S.; Pongsopawijit, P.; Boonprasert, K.; Chuatrakoon, B.; Thonglorm, N.; Kanta-In, R.; Tajarernmuang, T.; Nganvongpanit, K. Biomechanical Parameters of Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus) Walking Gait. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2017, 23, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesooriya, P.N.; Abeykoon, A.H.S.; Udawatta, L.; Punchihewa, A.; Nanayakkara, T. Gait pattern analysis of an Asian elephant. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 6th International Conference on Information and Automation for Sustainability, Beijing, China, 27–29 September 2012; pp. 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Miller, C.E.; Lair, R.; Hutchinson, J.R. Integration of biomechanical compliance, leverage, and power in elephant limbs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7078–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weishaupt, M.A.; Wiestner, T.; Hogg, H.P.; Jordan, P.; Auer, J.A. Compensatory load redistribution of horses with induced weight-bearing forelimb lameness trotting on a treadmill. Vet. J. 2006, 171, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, H.L.; Bishop, P.J.; Hocking, D.P.; Adams, J.W.; Evans, A.R. Low elbow mobility indicates unique forelimb posture and function in a giant extinct marsupial. J. Anat. 2021, 238, 1425–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Cho, H.; Park, Y.; Jang, J.; Kim, J.W.; Ryu, J.S. Biomechanical influences of gait patterns on knee joint: Kinematic & EMG analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsov, D.; Kaurkin, S.; Prizov, A.; Altukhova, A.; Troitskiy, A.; Lazko, F. Biomechanical Changes in Gait Patterns of Patients with Grade II Medial Gonarthritis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-Y.; Wu, W.-T.; Han, D.-S.; Mezian, K.; Ricci, V.; Özçakar, L.; Hsu, P.-C.; Chang, K.-V. Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Life 2023, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, L.D.; Schneider, C. Repetitive peripheral magnetic stimulation to reduce pain or improve sensorimotor impairments: A literature review on parameters of application and afferents recruitment. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2015, 45, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, M.S. Magnetic Field Therapy: A Review. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2007, 26, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olney, R.K.; So, Y.T.; Goodin, D.S.; Aminoff, M.J. A comparison of magnetic and electrical stimulation of peripheral nerves. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayona, N.A.; Bitensky, J.; Salter, K.; Teasell, R. The role of task-specific training in rehabilitation therapies. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2005, 12, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drum, M.G.; Marcellin-Little, D.J.; Davis, M.S. Principles and Applications of Therapeutic Exercises for Small Animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 45, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Jang, S.-H. Effects of Task-Specific Training after Cognitive Sensorimotor Exercise on Proprioception, Spasticity, and Gait Speed in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study. Medicina 2021, 57, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.C.; Aguiar, L.T.; Nadeau, S.; Scianni, A.A.; Teixeira-Salmela, L.F.; Faria, C. Efficacy of Task-Specific Training on Physical Activity Levels of People with Stroke: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. 2017, 97, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, C.M.; Chisholm, A.E.; Lam, T.; Eng, J.J. A systematic review of the effectiveness of task-specific rehabilitation interventions for improving independent sitting and standing function in spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2018, 41, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



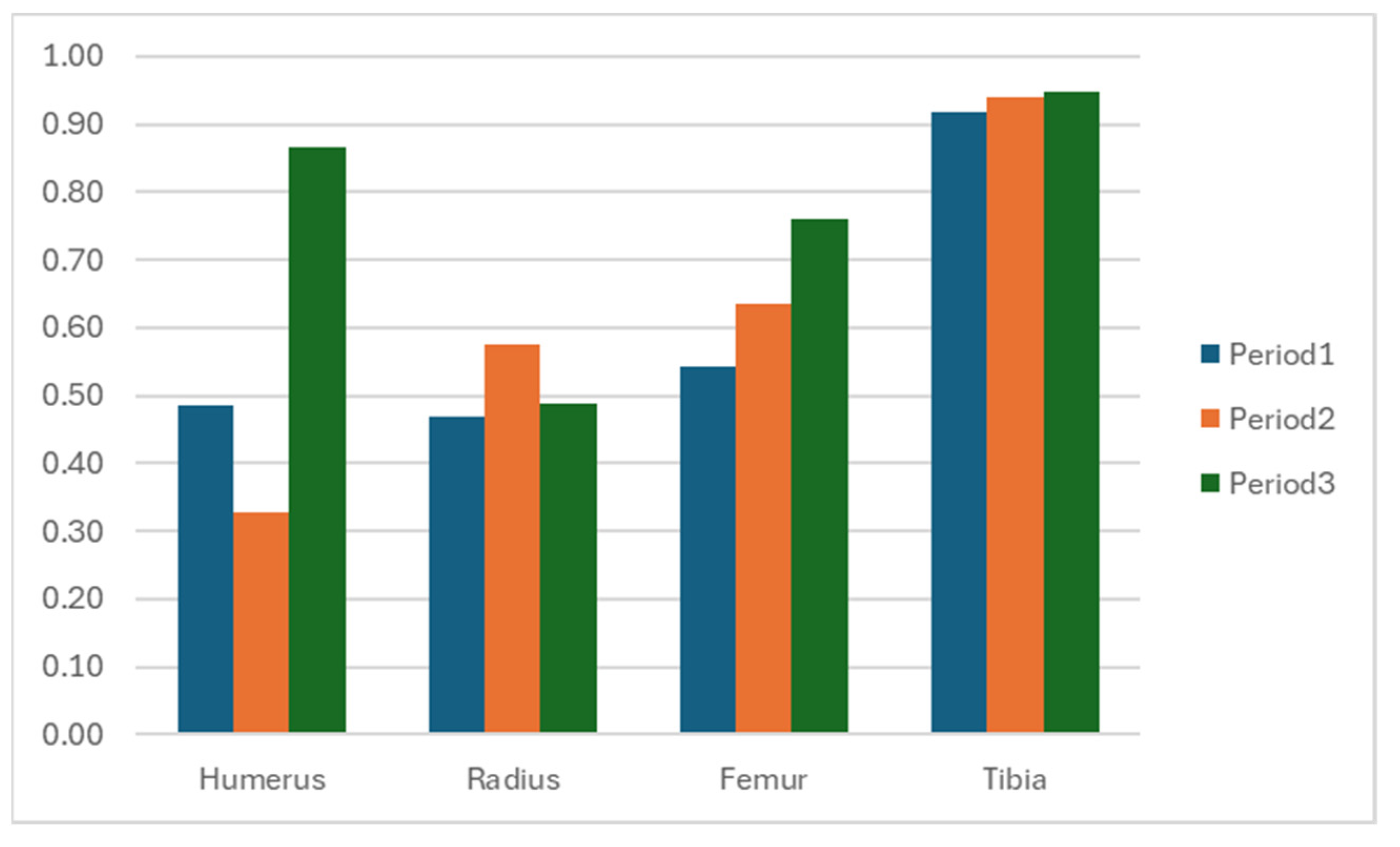

| Segment | Period 1 Mean (sd) | Period 2 Mean (sd) | Period 3 Mean (sd) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forelimb; Humerus | 0.49 (0.01) | 0.33 (0.07) | 0.87 (0.03) |
| Forelimb; Radius | 0.47 (0.01) | 0.58 (0.00) | 0.49 (0.11) |
| Hindlimb; Femur | 0.54 (0.01) | 0.64 (0.01) | 0.76 (0.04) |
| Hindlimb; Tibia | 0.92 (0.01) | 0.94 (0.00) | 0.95 (0.01) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kongsawasdi, S.; Wantanajittikul, K.; Jivacate, T.; Langkaphin, W.; Chansitthiwet, S.; Sombutputorn, P.; Namwongprom, K.; Kittisirikul, N.; Khammesri, S.; Angkawanish, T. Improving Mobility: A Case Report on the Rehabilitation of a Gait Anomaly in an Asian Elephant at a Thai Elephant Conservation Center. Animals 2025, 15, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111632
Kongsawasdi S, Wantanajittikul K, Jivacate T, Langkaphin W, Chansitthiwet S, Sombutputorn P, Namwongprom K, Kittisirikul N, Khammesri S, Angkawanish T. Improving Mobility: A Case Report on the Rehabilitation of a Gait Anomaly in an Asian Elephant at a Thai Elephant Conservation Center. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111632
Chicago/Turabian StyleKongsawasdi, Siriphan, Kittichai Wantanajittikul, Therdchai Jivacate, Warangkhana Langkaphin, Saran Chansitthiwet, Petthisak Sombutputorn, Kittikul Namwongprom, Narueporn Kittisirikul, Siripat Khammesri, and Taweepoke Angkawanish. 2025. "Improving Mobility: A Case Report on the Rehabilitation of a Gait Anomaly in an Asian Elephant at a Thai Elephant Conservation Center" Animals 15, no. 11: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111632
APA StyleKongsawasdi, S., Wantanajittikul, K., Jivacate, T., Langkaphin, W., Chansitthiwet, S., Sombutputorn, P., Namwongprom, K., Kittisirikul, N., Khammesri, S., & Angkawanish, T. (2025). Improving Mobility: A Case Report on the Rehabilitation of a Gait Anomaly in an Asian Elephant at a Thai Elephant Conservation Center. Animals, 15(11), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111632







