NDUFAB1 as a Novel Regulator of NEFA-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction in Bovine Adipocytes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gathering and Cultivating Cow Primary Adipocytes
2.2. Preparation of the NEFA Storage Solution
2.3. Preparing Sequencing Samples
2.4. Assay for Cell Viability
2.5. Identification of 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuracil (EDU)
2.6. Oil Red O Coloring
2.7. Extracting RNA and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Interference with Synthesis and Transfection
2.9. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.10. Triglyceride Measurement
2.11. RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
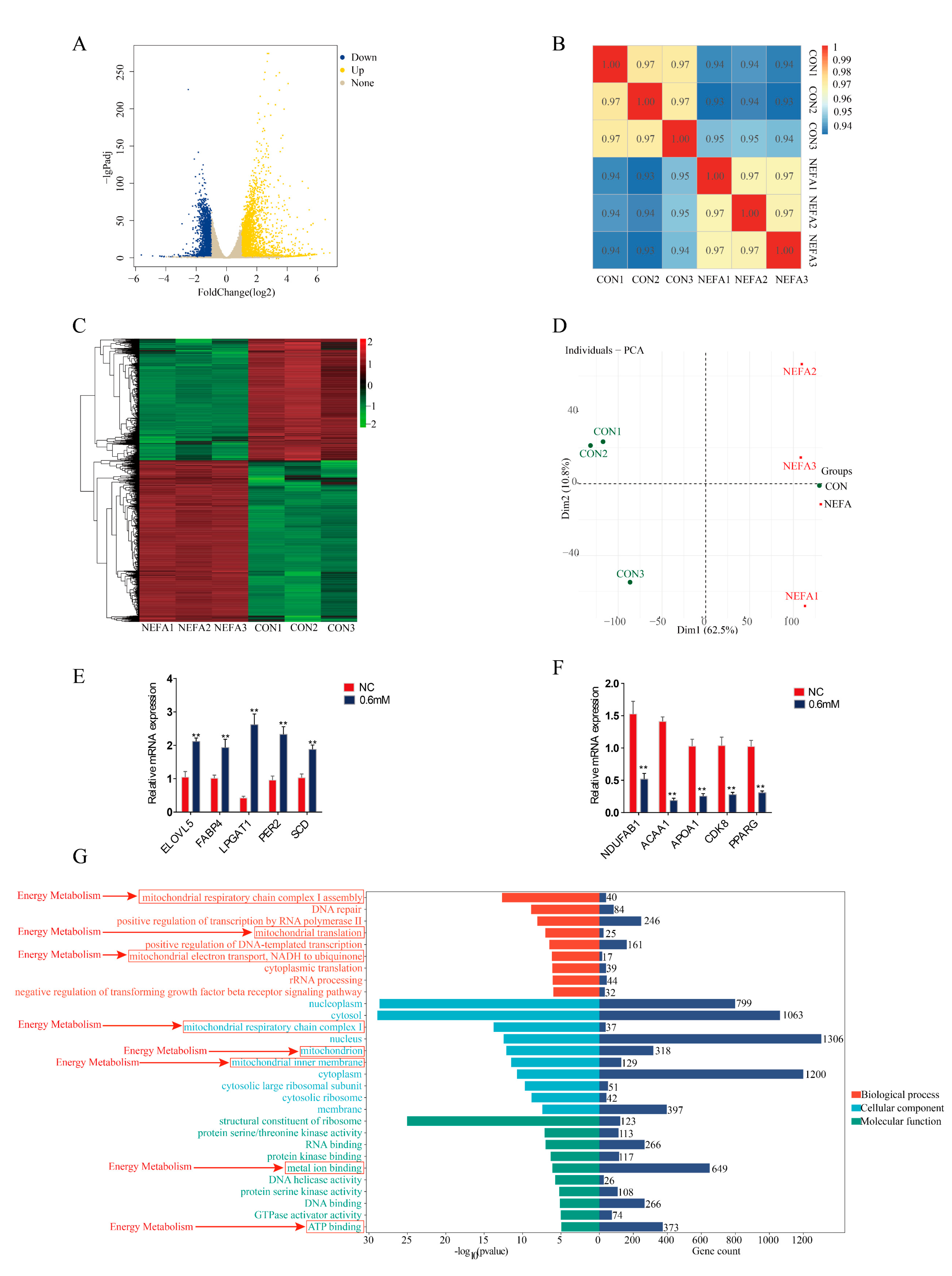
3. Results
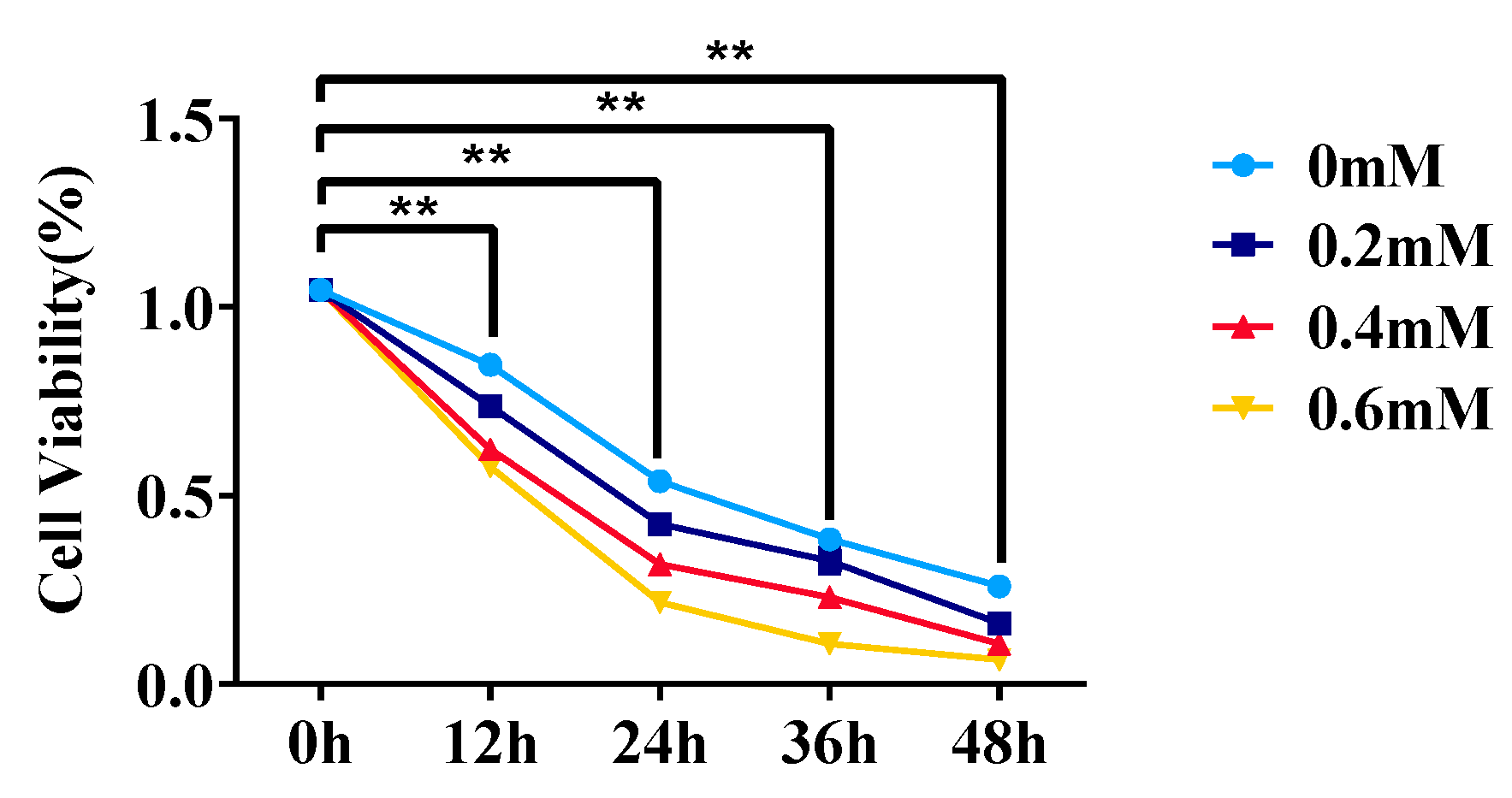
3.1. Effect of Different Treatment Concentrations and Times on Adipocyte Viability
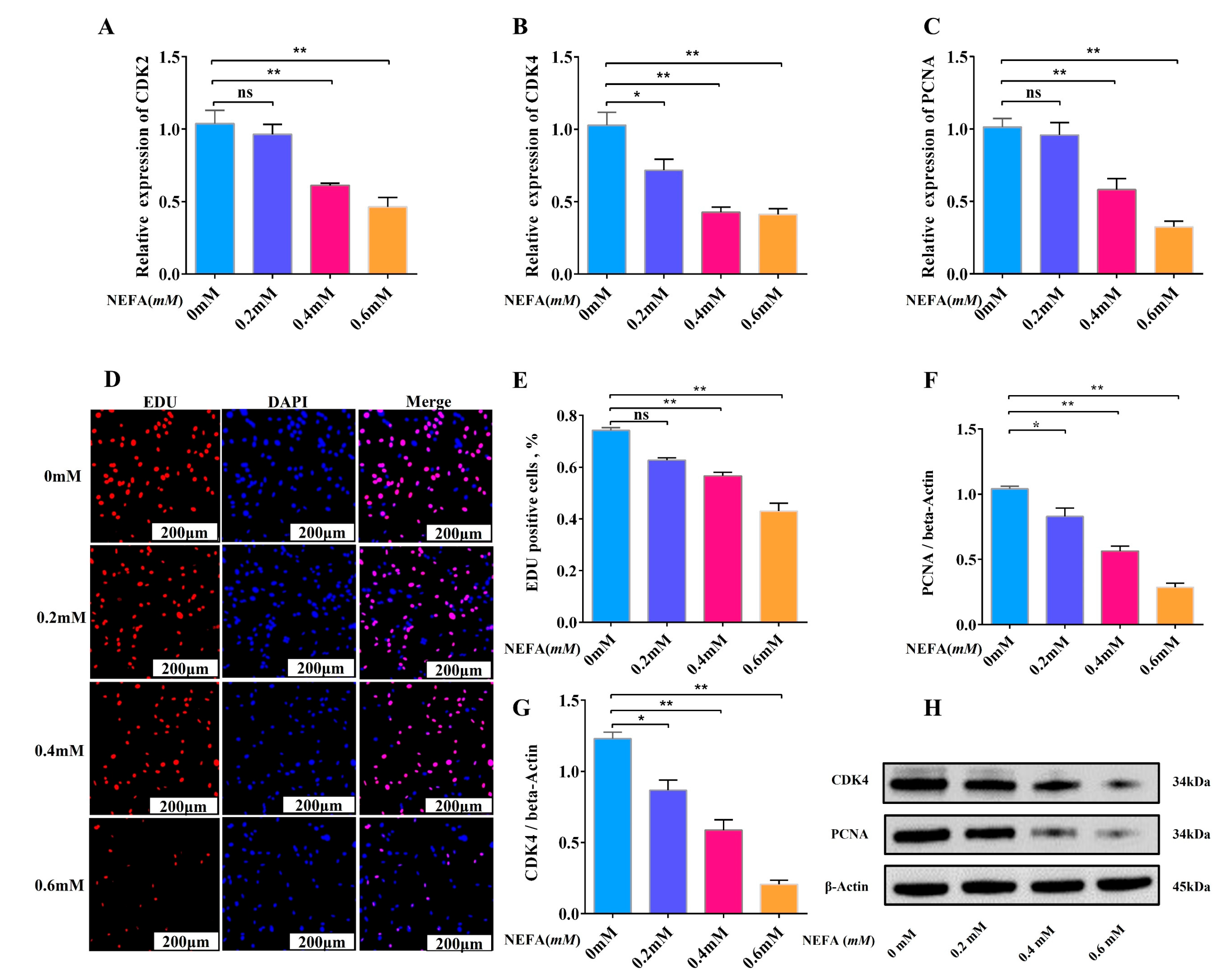
3.2. High Concentration of NEFA Inhibits Adipocyte Proliferation
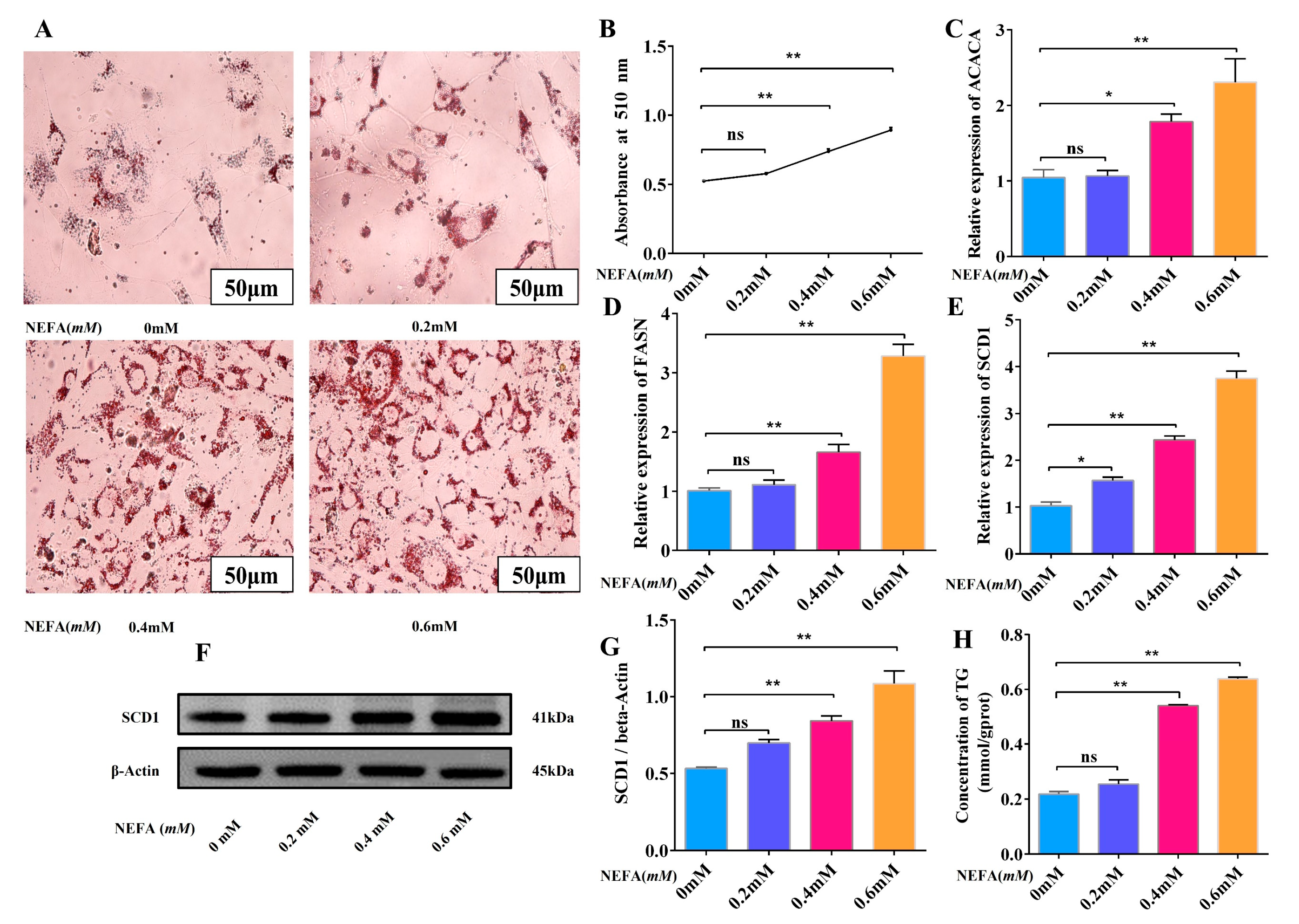
3.3. High Concentration of NEFA Promotes Adipocyte Lipid Deposition
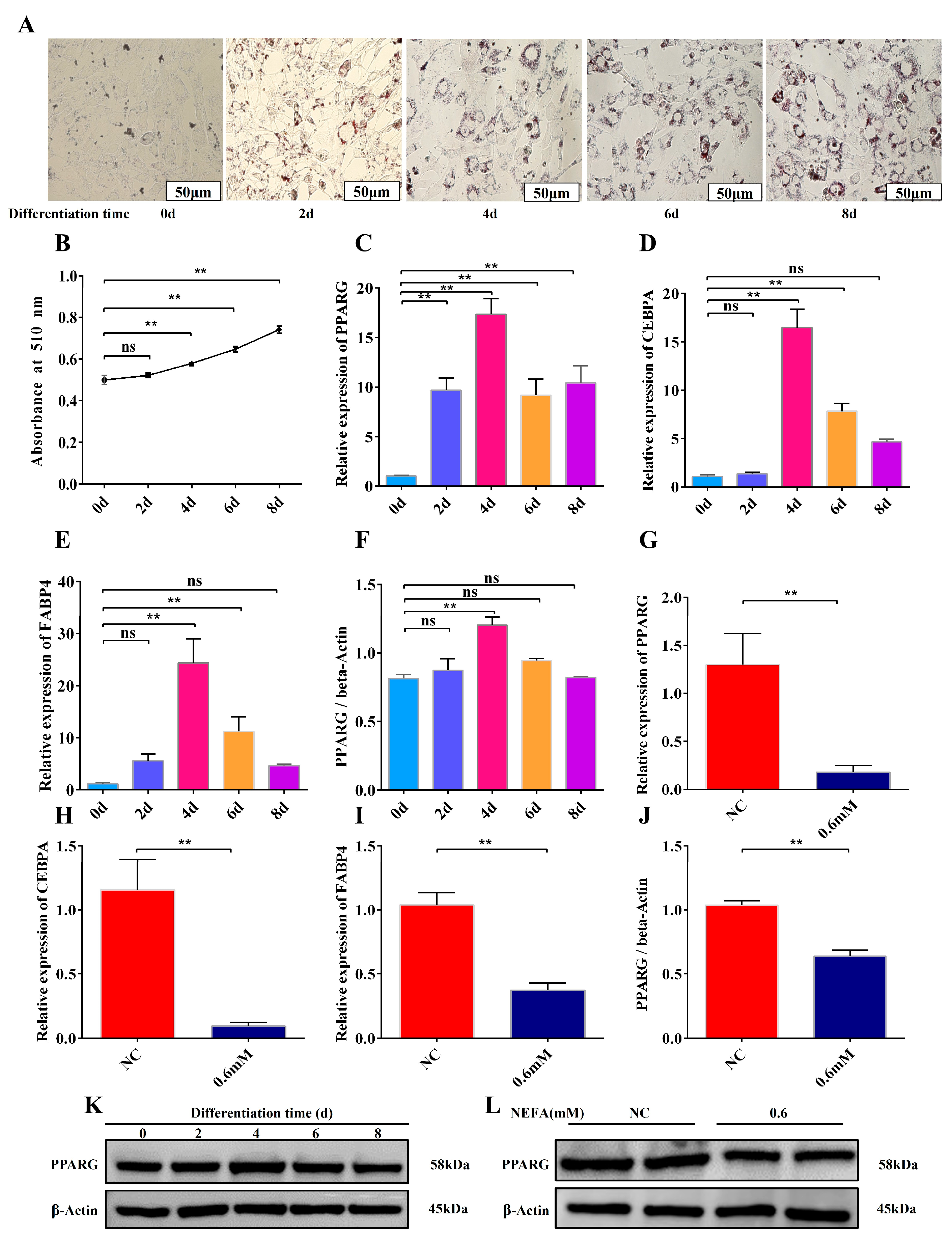
3.4. Construction of a Differentiation Model and Inhibition of Adipocyte Differentiation by the Optimal Concentration of NEFA
3.5. Analysis of Transcriptomics Sequencing Results
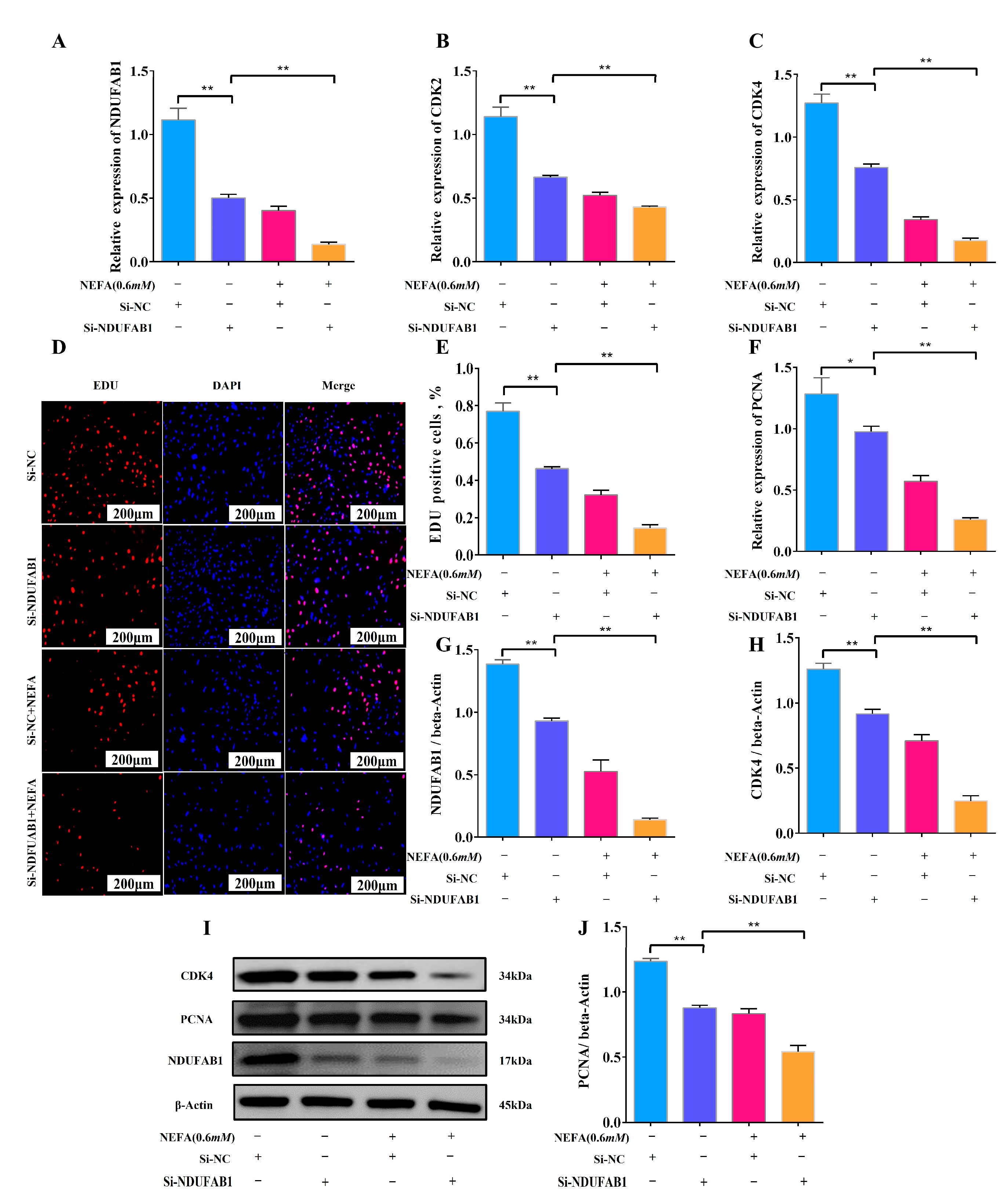
3.6. Interference with NDUFAB1 and NEFA Co-Treatment Inhibits Adipocyte Proliferation
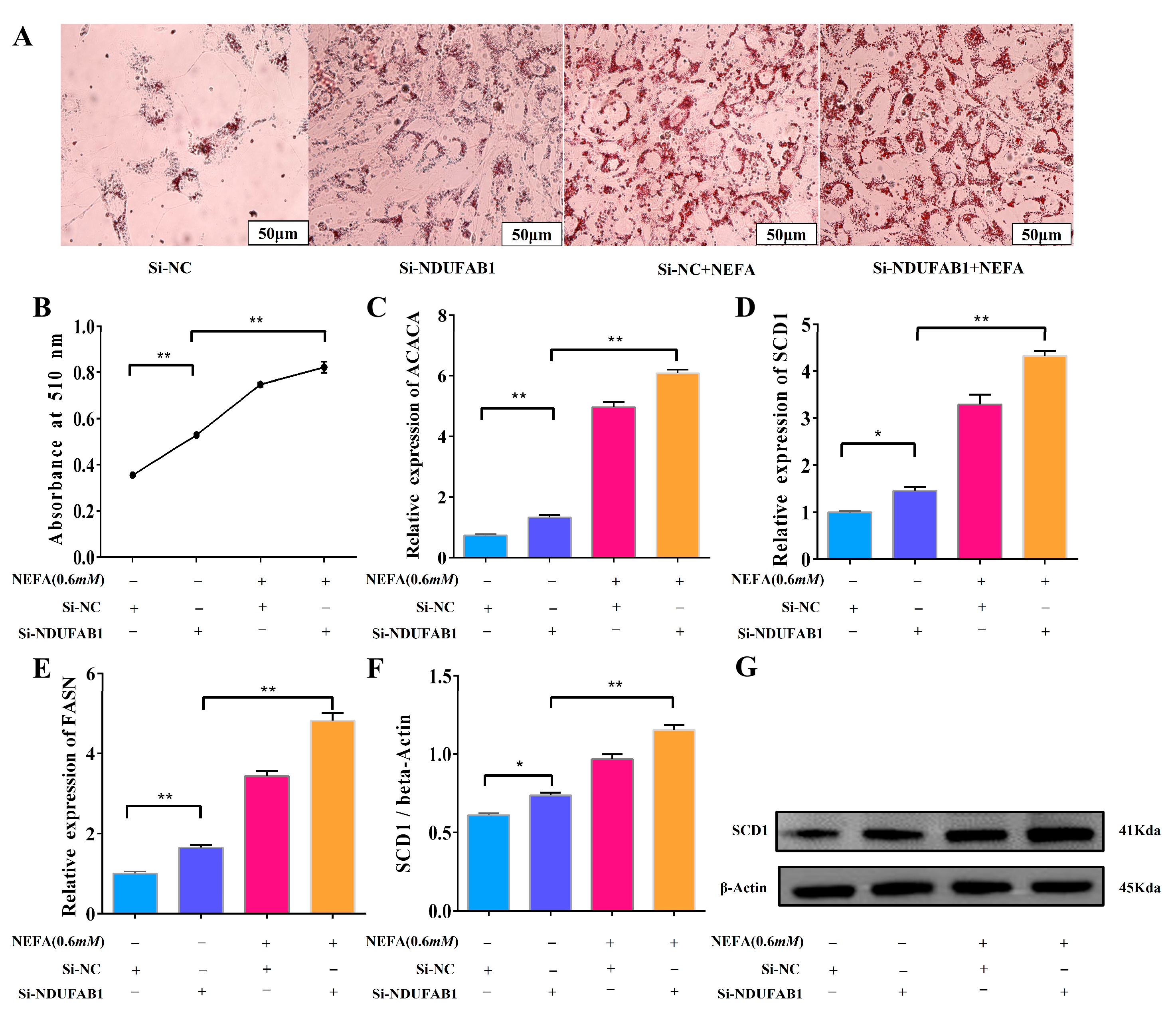
3.7. Interference with NDUFAB1 and NEFA Co-Treatment Promotes Lipid Deposition
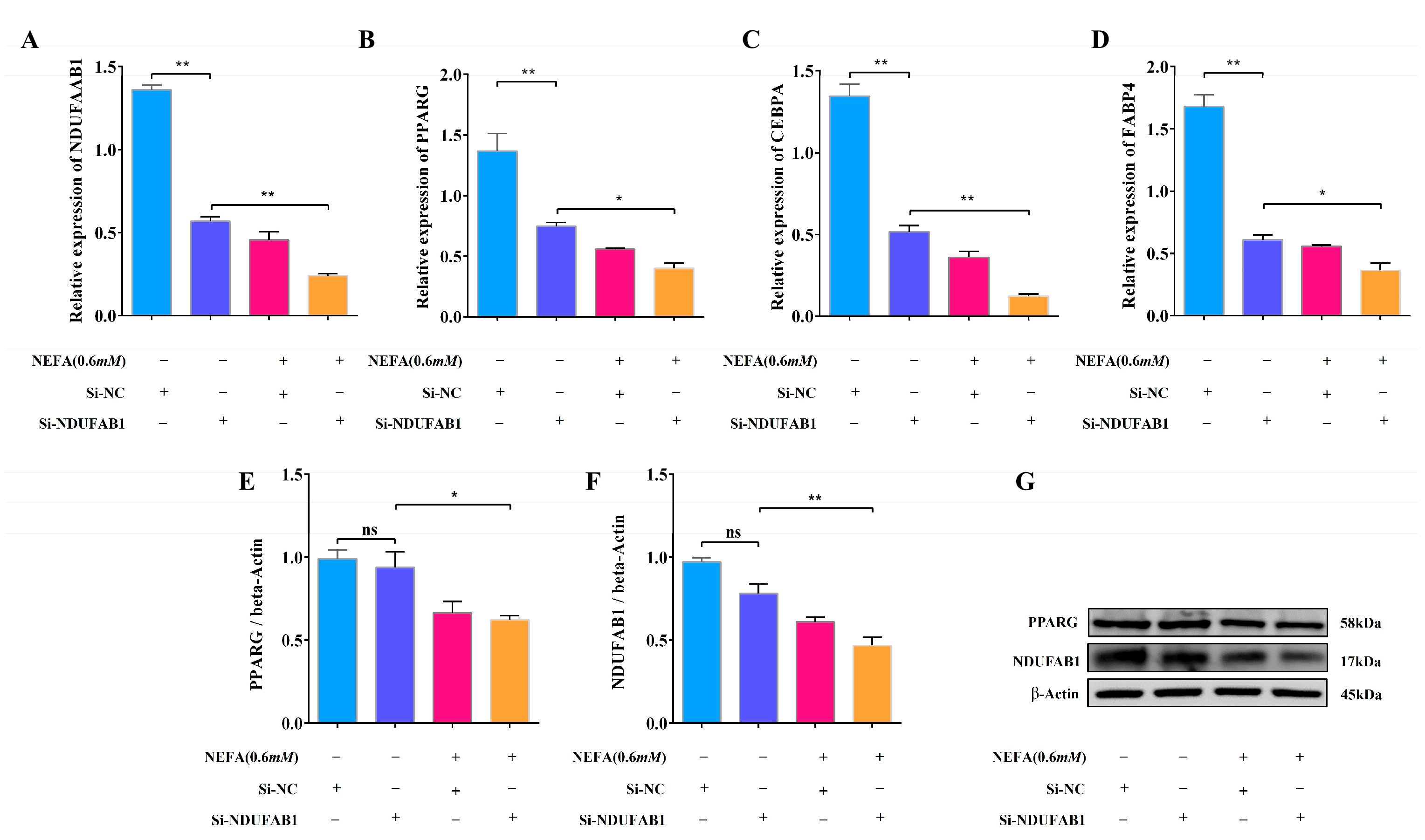
3.8. Interference with NDUFAB1 and NEFA Co-Treatment Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACAA1 | Acetyl-CoA Acyltransferase 1 |
| ACACA | Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Alpha |
| APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A1 |
| CDK2 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 2 |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 |
| C/EBPα | CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein Alpha |
| ELOV5 | ELOVL Fatty Acid Elongase 5 |
| FABP4 | Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 |
| FASN | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| LPGAT1 | Lysophosphatidylglycerol Acyltransferase 1 |
| NEFA | Non-Esterified Fatty Acids |
| NDUFAB1 | NADH: Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Subunit AB1 |
| PCNA | Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen |
| PER2 | Period Circadian Regulator 2 |
| PPARG | Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma |
| SCD | Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| β-actin | Beta-Actin |
References
- Melendez, P.; Serrano, M.V. Update on ketosis in dairy cattle with major emphasis on subclinical ketosis and abdominal adiposity. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, G.; Du, X.; Shi, Z.; Jin, M.; Sha, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Expression patterns of hepatic genes involved in lipid metabolism in cows with subclinical or clinical ketosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanacker, N.; Blouin, R.; Ster, C.; Lacasse, P. Effect of different fatty acids on the proliferation and cytokine production of dairy cow peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 3508–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.; Pan, B.; Xu, A.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effect of high NEFA concentration on lipid metabolism disorders in hepatocytes based on lipidomics. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1372296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathmaperuma, A.N.; Mana, P.; Cheung, S.N.; Kugathas, K.; Josiah, A.; Koina, M.E.; Broomfield, A.; Delghingaro-Augusto, V.; Ellwood, D.A.; Dahlstrom, J.E.; et al. Fatty acids alter glycerolipid metabolism and induce lipid droplet formation, syncytialisation and cytokine production in human trophoblasts with minimal glucose effect or interaction. Placenta 2010, 31, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L.; Gong, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, B.; Wang, Q.; et al. ANXA1-FPR2 axis mitigates the susceptibility to atrial fibrillation in obesity via rescuing AMPK activity in response to lipid overload. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, C.; Dixit, G.; Li, Z. Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinases Prevents Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, B.; Li, X.; Qin, X.; Zheng, Q. Enhancing Fatty Acids Oxidation via L-Carnitine Attenuates Obesity-Related Atrial Fibrillation and Structural Remodeling by Activating AMPK Signaling and Alleviating Cardiac Lipotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 771940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Luan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Z. Berberine Ameliorates High-fat-induced Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells by Modulating PPARs Signaling Pathway. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, Y.; Xu, L.; Dong, B. Evaluation of the Regulatory Effect of the Pan-PPAR Agonist Chiglitazar on the Dawn Phenomenon. Diabetes Ther. Res. Treat. Educ. Diabetes Relat. Disord. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Jin, C.; Cui, J.; Diao, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, R.; Yao, Z.; Li, X. Integrating Single-Cell RNA-Seq and Bulk RNA-Seq Data to Explore the Key Role of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Hou, T.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X. NDUFAB1 protects against obesity and insulin resistance by enhancing mitochondrial metabolism. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 13310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zheng, M.; Cui, H.; Chen, Z. RNA sequencing identifies key genes involved in intramuscular fat deposition in chickens at different developmental stages. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Xing, P. Identification of a novel lipid metabolism-related gene signature within the tumour immune microenvironment for breast cancer. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F.D.; Muiño, R.; Pereira, V.; Campos, R.; Benedito, J.L. Relationship among blood indicators of lipomobilization and hepatic function during early lactation in high-yielding dairy cows. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 12, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F. Hepatic steatosis: A role for de novo lipogenesis and the transcription factor SREBP-1c. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12 (Suppl. 2), 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Ren, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Jia, X.; Lai, S.; Gan, X.; et al. L-Histidine attenuates NEFA-induced inflammatory responses by suppressing Gab2 expression. Life Sci. 2024, 350, 122672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, X. The effects of non-esterified fatty acids and β-hydroxybutyrate on the hepatic CYP2E1 in cows with clinical ketosis. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, J.; Huan, C.; Li, L.; Li, C. Non-Esterified Fatty Acid Induces ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis via ROS/MAPK Signaling Pathway in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Metabolites 2022, 12, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza, G.H.; Lanzon, L.F.; Rabaglino, M.B.; Walker, W.L.; Vahmani, P.; Denicol, A.C. Exposure to non-esterified fatty acids in vitro results in changes in the ovarian and follicular environment in cattle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 238, 106937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Li, L. Non-Esterified Fatty Acid-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Mediated Granulosa Cells Apoptosis Is Regulated by Nrf2/p53 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Ali, I.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, L. Non-Esterified Fatty Acid-Induced Apoptosis in Bovine Granulosa Cells via ROS-Activated PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, X. Non-Esterified Fatty Acids Over-Activate the TLR2/4-NF-Κb Signaling Pathway to Increase Inflammatory Cytokine Synthesis in Neutrophils from Ketotic Cows. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 48, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Kong, Y.; Tan, P.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J. Elucidation of the mechanism of NEFA-induced PERK-eIF2α signaling pathway regulation of lipid metabolism in bovine hepatocytes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 211, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Li, D.; Deng, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, G.; Yuan, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; et al. NEFAs activate the oxidative stress-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway to induce inflammatory response in calf hepatocytes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Zhang, R.; Jian, C.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.; Ling, S.; Ma, Q.; Hu, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X. NDUFAB1 confers cardio-protection by enhancing mitochondrial bioenergetics through coordination of respiratory complex and supercomplex assembly. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triepels, R.; Smeitink, J.; Loeffen, J.L.C.M.; Smeets, R.; Buskens, C.; Trijbels, F.; van den Heuvel, L.P.W.J. The human nuclear-encoded acyl carrier subunit (NDUFAB1) of the mitochondrial complex I in human pathology. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1999, 22, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, K.W.; Fung, T.S.; Baker, D.C.; Saoi, M.; Park, J.; Febres-Aldana, C.A.; Aly, R.G.; Cui, R.; Sharma, A.; Fu, Y.; et al. Cellular ATP demand creates metabolically distinct subpopulations of mitochondria. Nature 2024, 635, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, C.; Yan, C.; Liswaniso, S.; Xu, R.; Qin, N. Transcriptome comparative analysis of ovarian follicles reveals the key genes and signaling pathways implicated in hen egg production. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, R.A.; Schepers, H.; Yu, Y.; van der Zwaag, M.; Autio, K.J.; Vieira-Lara, M.A.; Bakker, B.M.; Tijssen, M.A.; Hayflick, S.J.; Grzeschik, N.A.; et al. CoA-dependent activation of mitochondrial acyl carrier protein links four neurodegenerative diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| CDK2-F | AAGCCAGAAACAAGTTGACGG |
| CDK2-R | TTGATGAGGGGAAGAGGAATG |
| CDK4-F | CTTTGACCTGATTGGACTGCC |
| CDK4-R | CACTCTGCGTCACCTTCTGC |
| PCNA-F | CTTGAAGAAAGTGCTGGAGGC |
| PCNA-R | TTGGACATGCTGGTGAGGTT |
| PPARG-F | AGCATTTCCACTCCGCACTA |
| PPARG-R | GGGATACAGGCTCCACTTTGAT |
| C/EBPA-F | CGGCAACGACTTTGACTACC |
| C/EBPA-R | TGCTTCGCTTCGTCCTCCTC |
| FABP4-F | TTTGAATGGGGGTGTGGTCA |
| FABP4-R | ACGATGCTCTTGACTTTCCTGT |
| SCD1-F | ACCTGGCTGGTGAATAGTGC |
| SCD1-R | TCATAAGCCAGACCGATGGC |
| ACACA-F | CTGGCTGGACAGACTGATAGCA |
| ACACA-R | CAACTCCCAGCATGGTGTCA |
| FASN-F | CGAGTCCCCTGACCACTATCTG |
| FASN-R | AGGCGTGTGCTCCATGTTCT |
| β-Actin-F | GCCCATCTATGAGGGGTACGC |
| β-Actin-R | CTCCTTGATGTCACGGACGATTTC |
| ELOVL5-F | CGTCCCCACTTTGGTCTGTT |
| ELOVL5-R | CCTTCCCATACTCCCGTCAC |
| LPGAT1-F | GGCTTCTTGGGGATGGTATG |
| LPGAT1-R | TCTCCTGTTGCCTGATGGTTC |
| PER2-F | ATGTCCGCCTACATTACCGAG |
| PER2-R | TTTCCAACCTGTGACCCTTCT |
| NDUFAB1-F | GTGCCTGGAACAGTCACACA |
| NDUFAB1-R | ACTCGGTCCTTGATTCCGTC |
| ACAA1-F | ACGACAAGGGCACAGAGCA |
| ACAA1-R | GAGTTTCCAGCCGTGGTAGAG |
| APOA1-F | ACCTTGGCTGTGCTCTTCCT |
| APOA1-R | CACGGTGGCAAAATCCTTC |
| Name | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|
| Si-NDUFAB1-F | CAGGUUCCAGGCAGAGUUA |
| Si-NDUFAB1-R | UAACUCUGCCUGGAACCUG |
| Antibody | Company | Accession Number | Dilution Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| anti-CDK4 | Zenbio (Chengdu, China) | R23886 | 1:3000 |
| anti-PCNA | Zenbio (Chengdu, China) | R25293 | 1:3000 |
| anti-SCD1 | GenuIN Biotech (Pingdingshan, China) | #51311 | 1:1000 |
| anti-PPARG | Nature Biosciences (Shanghai, China) | A72166 | 1:1000 |
| anti-NDUFAB1 | ABclonal (Wuhan, China) | A2114 | 1:500 |
| anti-β-Actin | GenuIN (Hefei, China) | #2885 | 1:5000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Tang, T.; Sun, W.; Jia, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Lai, S. NDUFAB1 as a Novel Regulator of NEFA-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction in Bovine Adipocytes. Animals 2025, 15, 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111618
Zhou J, Tang T, Sun W, Jia X, Wang J, Yu H, Lai S. NDUFAB1 as a Novel Regulator of NEFA-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction in Bovine Adipocytes. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111618
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jing, Tao Tang, Wenqiang Sun, Xianbo Jia, Jie Wang, Hengwei Yu, and Songjia Lai. 2025. "NDUFAB1 as a Novel Regulator of NEFA-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction in Bovine Adipocytes" Animals 15, no. 11: 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111618
APA StyleZhou, J., Tang, T., Sun, W., Jia, X., Wang, J., Yu, H., & Lai, S. (2025). NDUFAB1 as a Novel Regulator of NEFA-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction in Bovine Adipocytes. Animals, 15(11), 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111618





